Review
History
• 58 y/o female.
• Suffered from head discomfort for ten years and left eyesight diminution for three years.
• Past medical history: HTN for ten years, well-controlled.
• PE: left-inferior vision deficit; normal muscle strength.
• Laboratory test index: RPL 31.6ng/ml↑, SHBG 22.61nmon/L↓,T3 1.04noml/L↓, FT4 22.2pmol/L↑, TSH 0.25mIU/L↓, TSI and other hypophyseal hormone normal.
• Medication: Aspirin and Clopidogrel were prescribed three days before the operation.
• 58岁,女性。
• 头部不适10年伴左侧视力下降3年。
• 既往史:高血压10年,血压控制良好。
• 查体:左下视野缺损;四肢肌力正常。
• 实验室检查:泌乳素31.6ng/ml↑,性激素结合球蛋白22.61nmon/L, T3 1.04noml/L↓, FT4 22.2pmol/L↑, TSH 0.25mIU/L↓,促甲状腺激素受体刺激性抗体和其他垂体激素正常。
• 药物:术前3天予口服阿司匹林及氯吡格雷。

图 1. 高分辨率磁共振提示左侧颈内动脉眼段动脉瘤压迫视交叉、垂体柄和腺垂体。

图 2. TOF-MRA提示左侧颈眼大动脉瘤,瘤内有射流和涡流。

Figure 3 GIF. DSA confirmed a large left ophthalmic aneurysm.
图 3 GIF. DSA 证实左侧颈眼大动脉瘤。
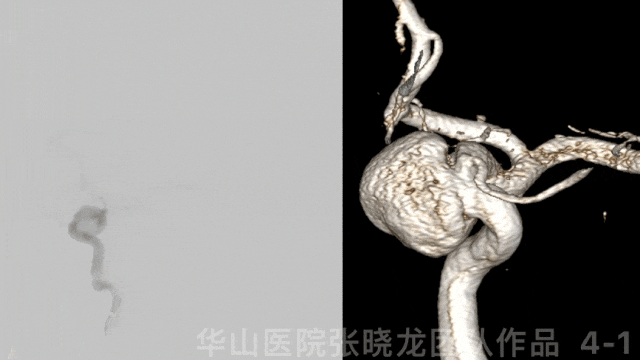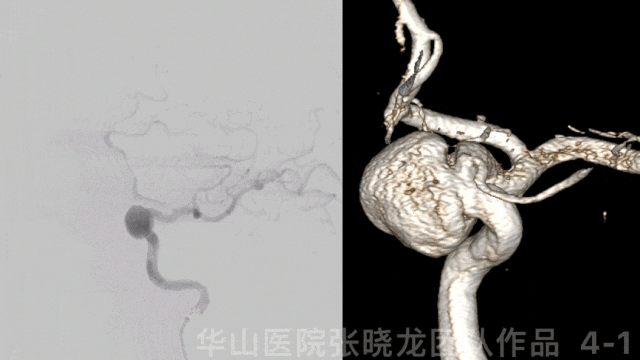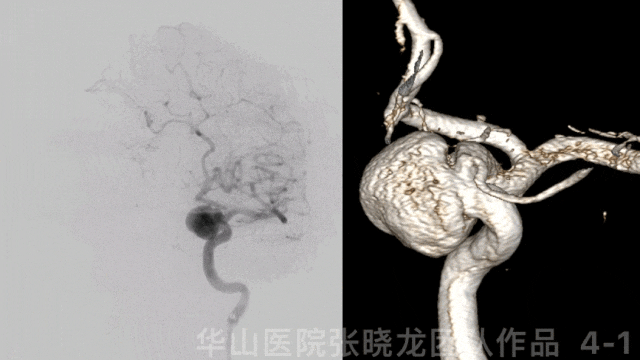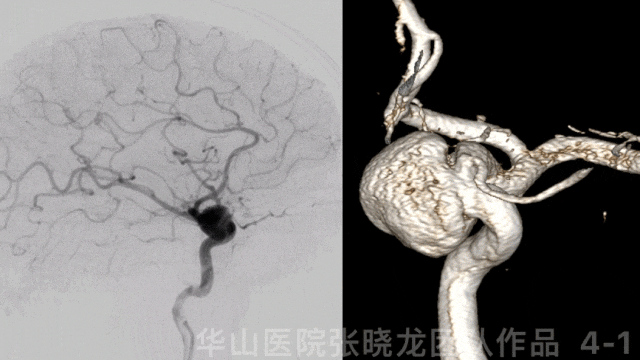

图 4 GIF. 左侧眼动脉发自动脉瘤颈部,动脉瘤内射流明显。
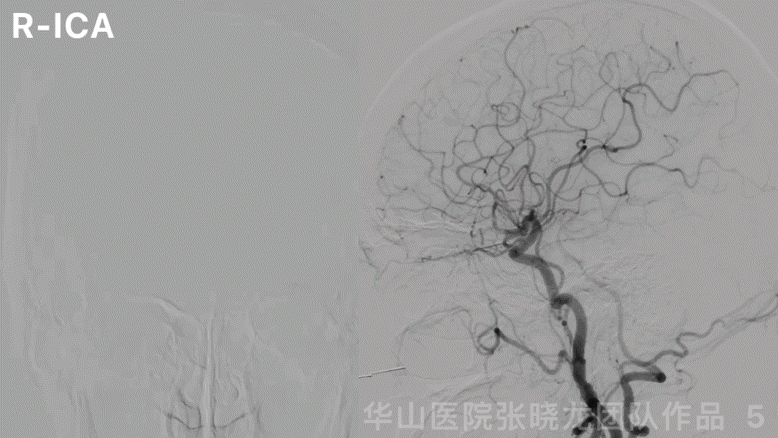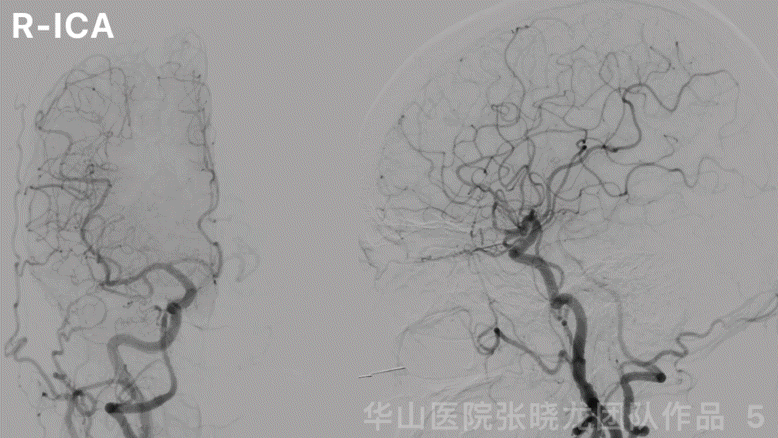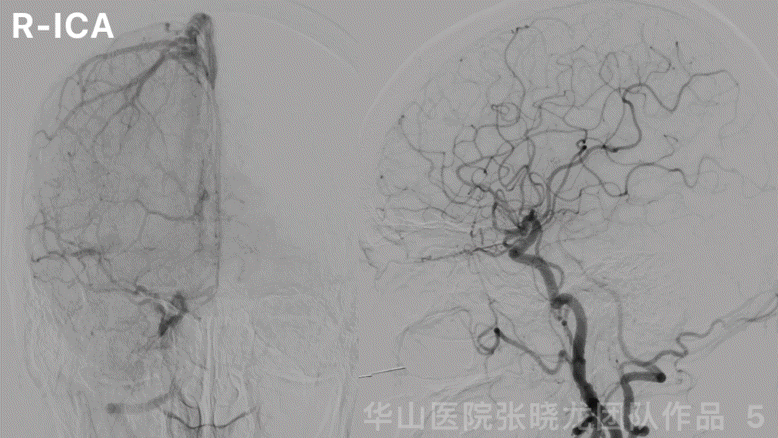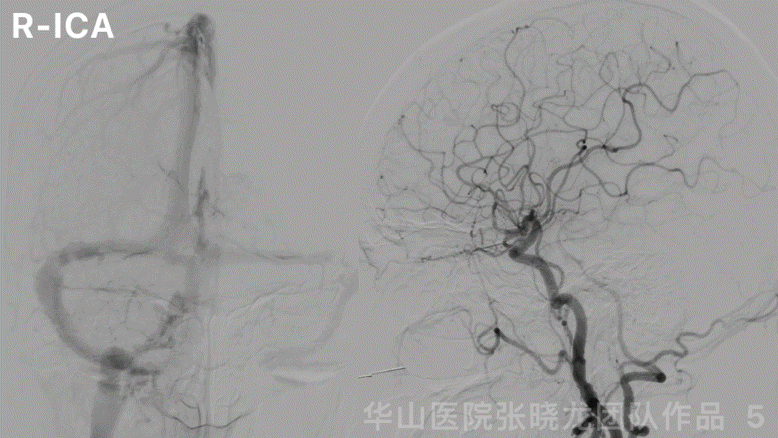
图 5 GIF. 左侧大脑前动脉A1段发育良好,右侧大脑半球无来自左侧大脑前动脉的代偿。
1
Strategy
Indications:
1.The large ophthalmic aneurysm with jet flow and vortex had a high growth and rupture risk.
2.The large ophthalmic aneurysm compressed the optic chiasm, anterior lobe of the hypophysis, and pituitary stalk, causing decreased vision, field deficit, and hypophyseal function abnormality gradually.
Alternatives:
•Conventional stent-assisted coiling possessed a high recurrence rate, which was not preferred.
•Flower divertor was preferred. If a single flower diverter stent was deployed, jet flow still existed. Coils insertion or another flow diverter deployment can be adopted.
•Single pipeline-assisted coiling can accelerate thrombosis formation but harbor a high risk of worsening mass effect.
•Dual-pipeline implantation can effectively decrease jet flow and avoid aggravating mass effects. However, postoperative bleeding and long-term stenosis should be considered.
Two working projections are for navigating and deploying the stent microcatheter.
Difficult points:
•Microcatheter navigation into the distal part of the parent artery.
Dangerous points:
•Caution: The first flower diverter stent herniated into the sac when a second stent microcatheter navigated through the aneurysm neck.
治疗指征:
1.颈内动脉眼段大动脉瘤,瘤内射流和涡流明显,动脉瘤有生长和破裂风险。
2.颈内动脉眼段大动脉瘤压迫视交叉、腺垂体和垂体柄,患者逐渐出现视力下降、视野缺损和垂体功能部分受损。
治疗策略:
治疗策略的选择:
•传统支架辅助弹簧圈栓塞复发风险高,该病例不考虑。
•该病例优先选择密网支架。若单个密网支架置入后动脉瘤仍射流明显,可以选择填入弹簧圈或者再置入另一枚密网支架。
•单pipeline密网支架辅助弹簧圈栓塞可以加快动脉瘤内血栓形成,但可能不能缓解占位效应。
•单纯双pipeline密网支架植入能有效降低瘤内射流,同时避免占位效应加重;但有术后出血和远期血管再狭窄风险。
选择2个工作角度,分别用于支架微导管的超选和支架的释放。
难点:
•微导管超选至动脉瘤远端血管。
危险点:
•选择双密网支架策略时,第2枚支架微导管再次通过瘤颈时谨慎第一枚支架嵌入瘤腔内。
2
Operation


图 6 GIF. 测量:近端载瘤动脉直径4.5mm,远端载瘤动脉直径3.7mm。全身肝素化。将6F Envoy DA置于左侧颈内动脉岩骨段,灌注尼莫地平0.5ml。Phenom-27微导管在Synchro-II微导丝支撑下超选入左侧大脑中动脉M1段。Pipeline 4.75*30mm支架于左侧颈内动脉末端释放。
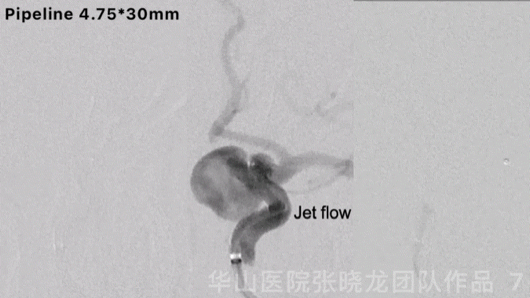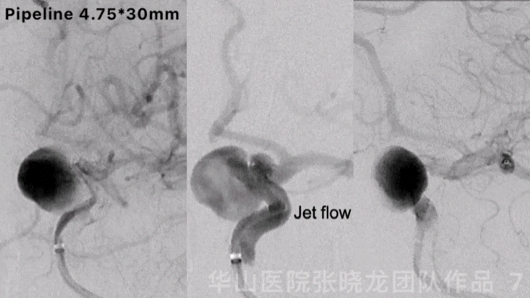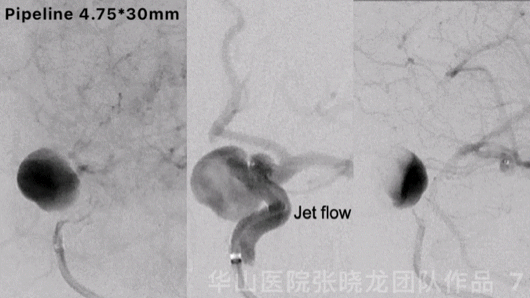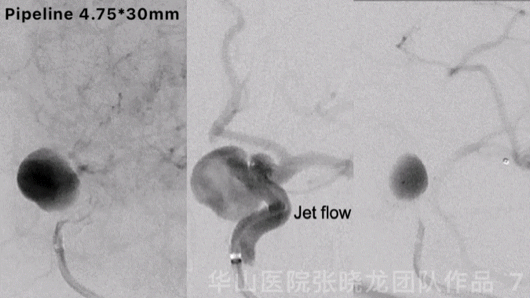
Figure 7 GIF. Contrast medium stagnation was observed. However, jet flow can still be revealed after the first pipeline stenting.
图 7 GIF. 第一枚pipeline支架释放后复查造影动脉瘤内可见造影剂滞留,但瘤内仍有射流。
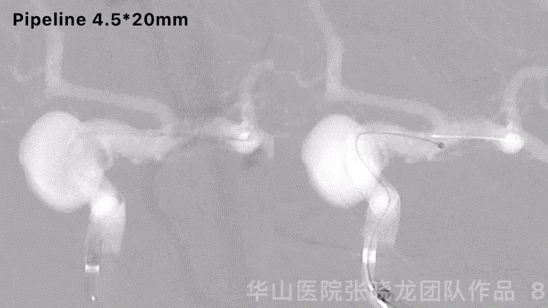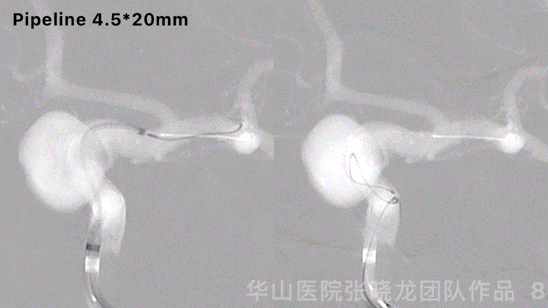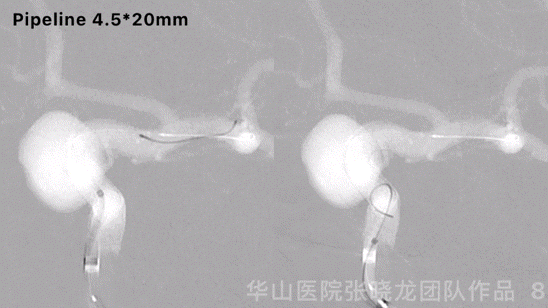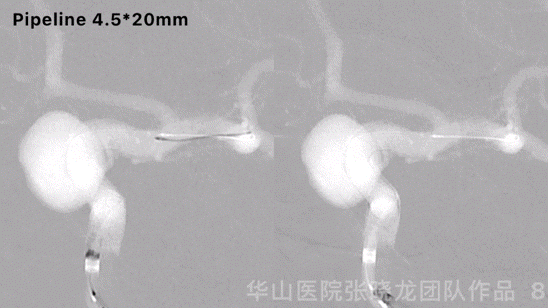
Figure 8 GIF. Another pipeline 4.5*20mm was deployed and massaged stents to make the stents adherent to the vascular wall.
图 8 GIF. 瘤颈部释放pipeline 4.5*20mm,按摩支架使支架贴壁良好。

图 9 GIF. 置入两枚pipeline支架后,瘤内射流明显降低,瘤内造影剂滞留明显。

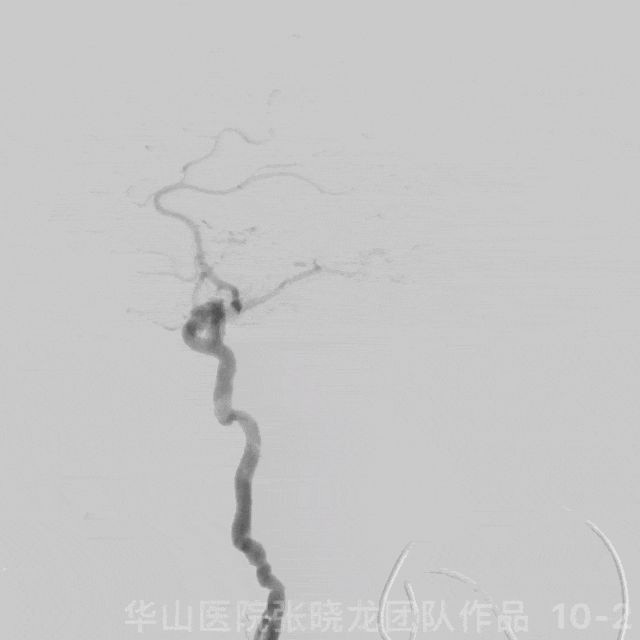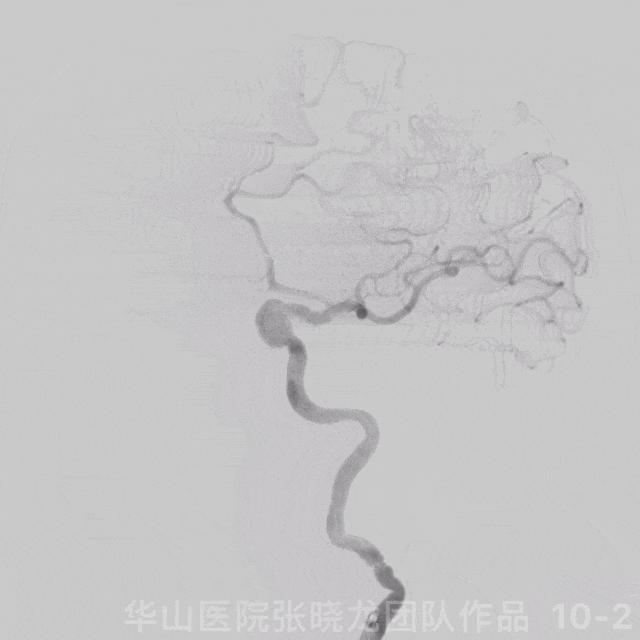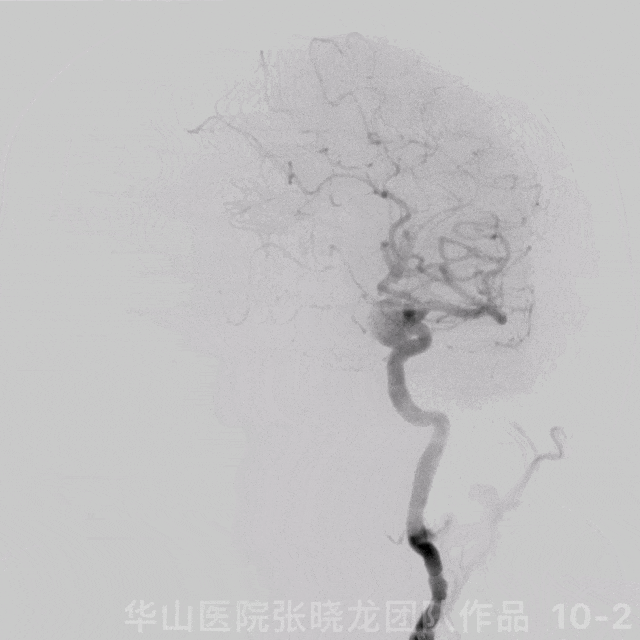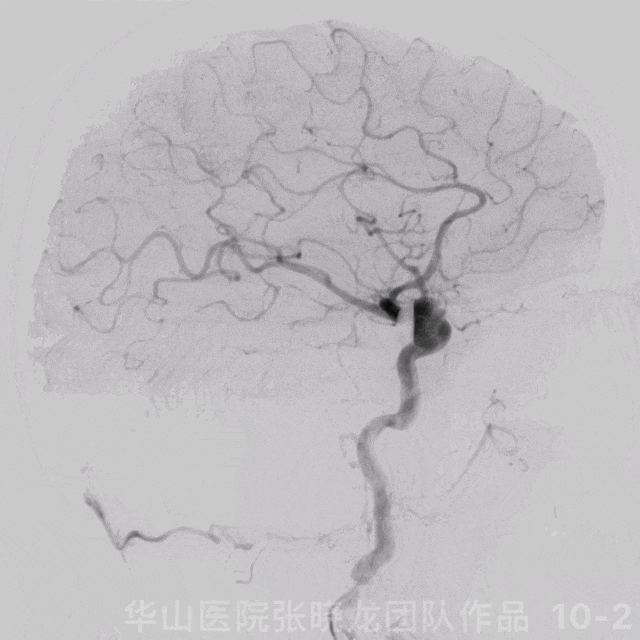
图 10 GIF. 复查造影颅内血管完好,未见血管狭窄。经导引导管予替罗非班5ml。
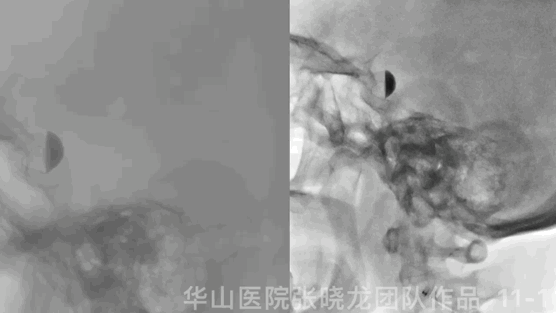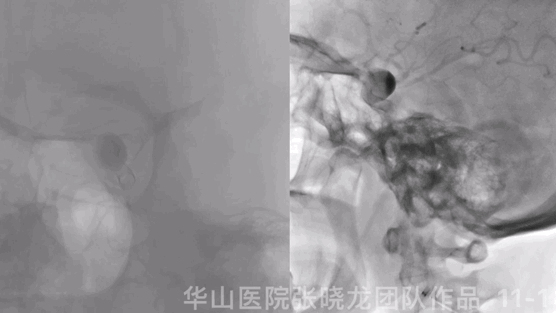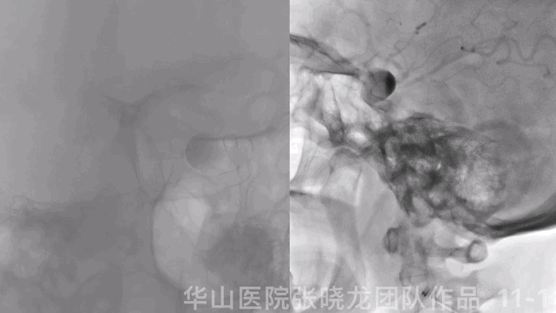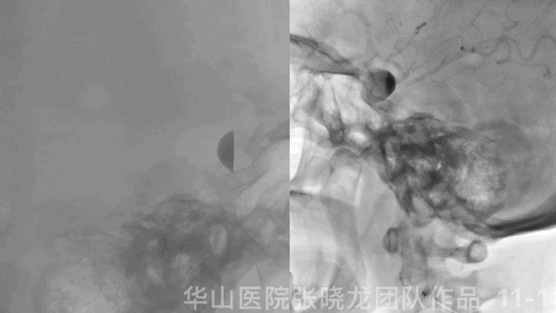
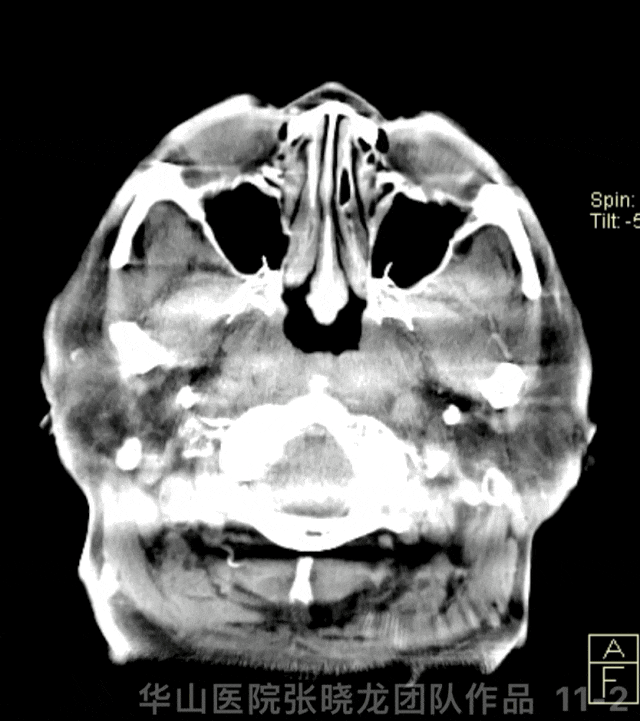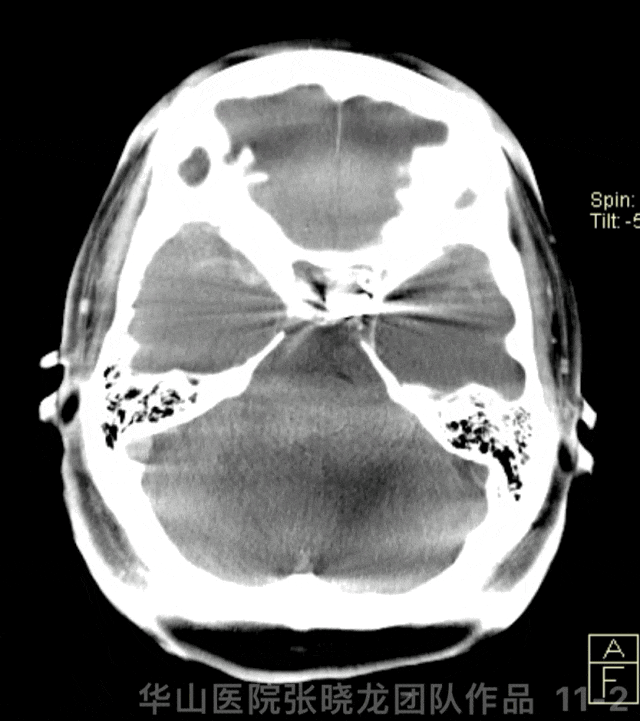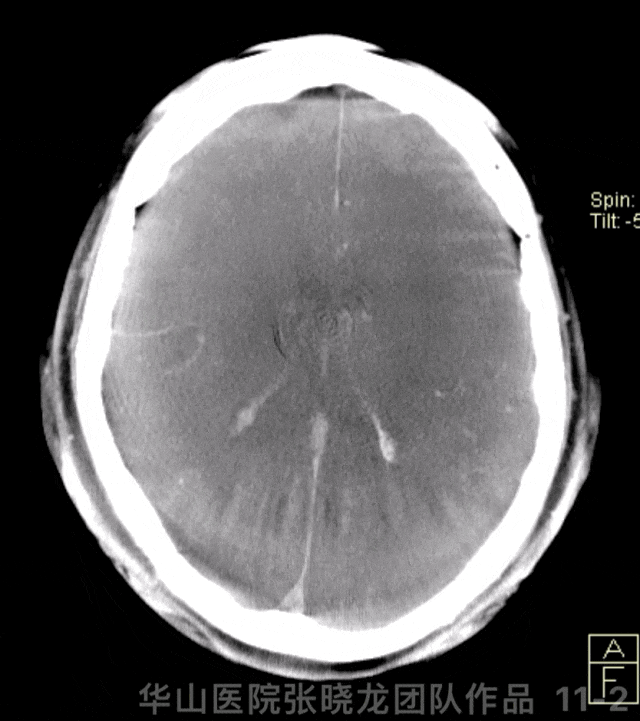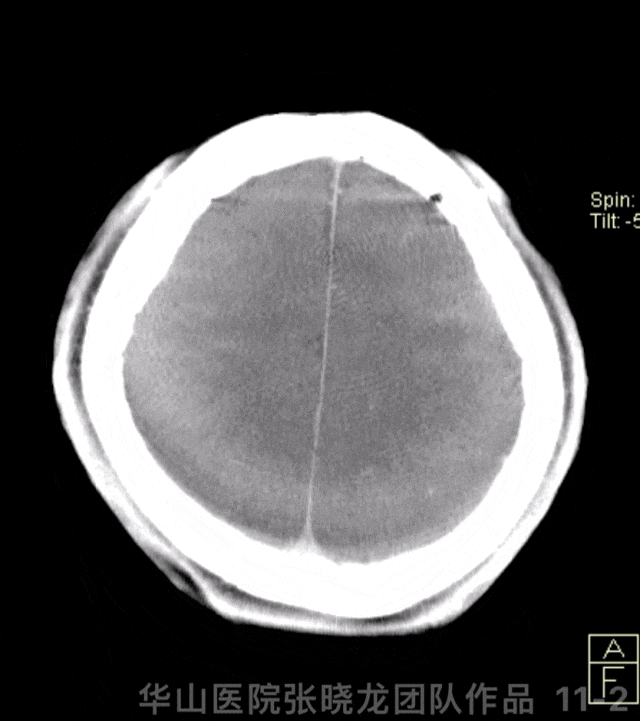
Figure 11 GIF. Stents were deployed well and adherent to the vascular wall satisfactorily. Dyna-CT did not demonstrate any bleeding. Nimodipine 0.5ml was administered.
图 11 GIF. 支架释放及贴壁满意。Dyna-CT未见出血。予尼莫地平0.5ml。
3
Post-Operation
•NE: GCS 15, bilateral pupils movement and light reflux normal, no aggravation of vision deficit nor headache, bilateral muscle strength V, bilateral Babinski negative.
•Medication:
Tirofiban 6ml/h maintained for 24 hours.
Continue Aspirin and Clopidogrel (dual antiplatelets were prescribed 3 days before operation).
TEG: Aspirin 95.8%, ADP 90.4%
ADP gene: NM
•神经查体:GCS 15, 双侧瞳孔运动正常,对光反射灵敏,视野缺损及头痛无加重,双侧肌力正常,双侧Babinski阴性。
•药物:
替罗非班6ml/h维持24h。
继续阿司匹林和氯吡格雷(术前3天已口服双抗)。
血栓弹力图:阿司匹林抑制率95.8%,氯吡格雷抑制率90.4%。
氯吡格雷基因代谢酶活性正常,代谢正常。
4
10M-FU
Video 1. The large aneurysm was not visualized by 10 month follow up. Additionally, Eyesight and vision field recovered.
视频 1. 10个月随访原大动脉瘤不显影。患者视力及视野恢复。
视频 2. 10个月随访颅内血管未见狭窄。


图 12. 4个月高分辨率磁共振随访,动脉瘤腔内血栓形成,动脉瘤仍显影,动脉瘤腔较术前略减小。10个复查头颅MRI动脉瘤完全不显影,原大动脉瘤的占位效应明显减轻,原被压迫的垂体柄及垂体此次显示清晰。
5
Summary
Indications:
1.The large ophthalmic aneurysm with jet flow and vortex had a high growth and rupture risk.
2.The large ophthalmic aneurysm compressed the optic chiasm, anterior lobe of the hypophysis, and pituitary stalk, causing gradually decreased vision, field deficit, and hypophyseal function abnormality.
•The large ophthalmic aneurysm adopted dual pipeline stents. Two working projections are for navigating the stent microcatheter and deploying the stent.
•The aneurysm was not cured by a four-month follow-up. By 10-month follow-up, the large aneurysm was not visualized, and the mass effect was alleviated. What’s more, the eyesight and vision field of the patient recovered. We proposed that middle- and even long-term follow-up was more important for aneurysms cured by flow divertors.
•Dual antiplatelets were recommended for six months, then stopped Clopidogrel and aspirin for one year.
•Long-term follow-up was still needed. Delayed stenosis should be considered for long-term follow-up.
Difficult points:
•Microcatheter navigation into the distal part of the parent artery.
Dangerous points:
•Caution: The first flower diverter stent herniated into the sac when a second stent microcatheter navigated through the aneurysm neck.
治疗指征:
1.颈内动脉眼段大动脉瘤,瘤内射流和涡流明显,动脉瘤有生长和破裂风险。
2.颈内动脉眼段大动脉瘤压迫视交叉、腺垂体和垂体柄,患者逐渐出现视力下降、视野缺损和垂体功能部分受损。
•本例颈眼大动脉瘤采用双pipeline密网支架。术中选择2个工作角度,分为用于支架微导管的超选和支架的释放。
•术后4月随访动脉瘤未消失。10个月随访大动脉瘤未见显影,占位效应明显减轻。患者视力及视野恢复。对于单纯密网支架支架治疗动脉瘤,短期随访动脉瘤可能未完全治愈,需要更时间的随访。
•术后建议口服双抗6月后改单抗,阿司匹林口服一年。
•该病例仍需长期随访,长期随访需警惕延迟血管狭窄事件。
难点:
•微导管超选至动脉瘤远端血管。
危险点:
•选择双密网支架策略时,第2枚支架微导管再次通过瘤颈时谨慎第一枚支架嵌入瘤腔内。
张晓龙
复旦大学附属华山医院
复旦大学附属华山医院放射科主任医师,博士、教授、博士生导师;
斯坦福大学医学院客座临床教授;
主持国家自然科学基金3项,第一作者或通讯作者发表国内外权威期刊文章50余篇;
中华医学会、放射学会、卫生部医政司等组织中担任副主任委员、组长等职务.《中国名医百强榜》神经介入专业中国十强(2012年度、2013年度、2014年度、2015-16年度、2017-18年度);
擅长复杂和疑难脑血管疾病的介入治疗,如复杂脑动脉瘤的栓塞,硬脑膜动静脉瘘栓塞,脑动静脉畸形栓塞,脑梗死的支架,脊髓血管畸形治疗;
自1995年开始从事脑血管疾病介入诊治工作和研究,师从黄祥龙教授、沈天真教授和凌锋教授,是我国最早从事神经介入的专家之一。2010年9月至今连续介入治疗颅内动脉瘤1500余例,无操作致死。
声明:脑医汇旗下神外资讯、神介资讯、脑医咨询、Ai Brain 所发表内容之知识产权为脑医汇及主办方、原作者等相关权利人所有。
投稿邮箱:NAOYIHUI@163.com
未经许可,禁止进行转载、摘编、复制、裁切、录制等。经许可授权使用,亦须注明来源。欢迎转发、分享。
投稿/会议发布,请联系400-888-2526转3。






