Review
History
• Medical history: no HTN or DM.
• Medication: nifedipine delayed-release tablet before operation.
• 反复中度头痛5年,偶有双下肢肌肉抽搐。
• 既往史:否认高血压、糖尿病。
• 药物:术前予硝苯地平缓释片。


图 1. 当地医院头颅MRI提示左侧额顶交接区皮层脑动静脉畸形,深部可疑小血管畸形(红箭),病灶周围未见明显水肿。


Figure 2 GIF. DSA confirmed a left frontal lobe AVM with two nidus, the cortical nidus mainly draining to a cortical vein, while the cortex nidus was in conjunction of a deep minor juvenile nidus draining to deep vein system.
图 2 GIF. DSA证实左侧额叶脑动静脉畸形,有2个部分。皮层畸形团主要经单根皮层静脉引流,同时与一个深部畸形团相连。深部畸形团较幼稚,向深部静脉引流。
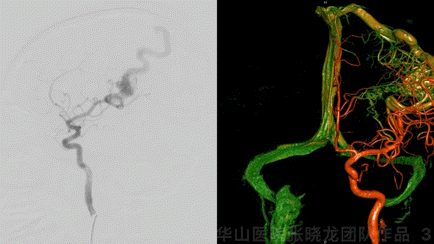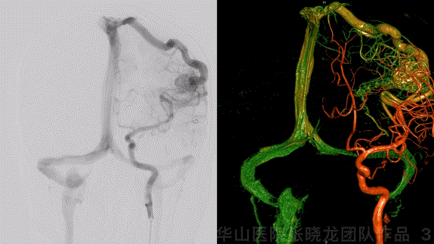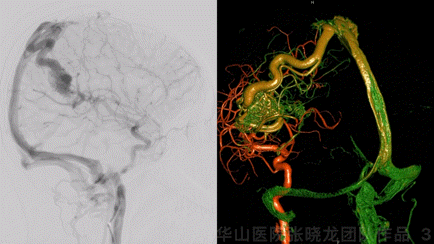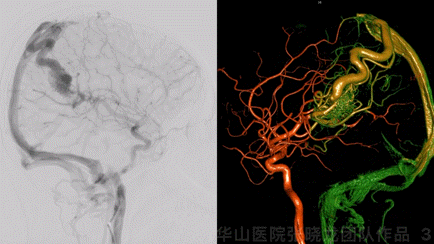
Figure 3 GIF. Minor deep juvenile nidus in conjunction with internal cerebral vein and the larger cortex nidus. The cortex nidus was fed by left middle cerebral artery branches and mainly drained by a single cortex vein. No other feeders from bilateral ECAs, Vas, or right ICA.
图 3 GIF. 选择造影及3D重建示深部幼稚型畸形团向大脑内静脉引流,同时与皮层较大的畸形团相连。皮层畸形团由左侧大脑中动脉分支供血,主要经皮层单根静脉引流。双侧颈外动脉、椎动脉及右侧颈内动脉无供血。
1
Strategy
1.Left frontal-parietal junction AVM can be divided into two units. The nidus in the cortex was fed by left MCA branches and drained to superior sagittal sinus by a cortical vein. While the deep nidus was juvenile drained to the internal cerebral vein.
2.The Spetzler-Martin scale for the cerebral AVM is grade 4:
maximal diameter 3-6cm, 2
function area, 1
deep drainage vein, 1
3.Staged embolization is preferred for the juvenile high-flow AVM.
a.First stage: flow reduction to decrease bleeding risk via arterial route.
b.Second stage: continue flow reduction via arterial route or cure embolization for minor deep nidus (another unit) in conjunction with deep drainage veins and the residual large nidus via venous route.
2.该脑动静脉畸形的SM分级为4:
最大直径3-6cm,2
功能区,1
深静脉引流,1。
3.高流量幼稚型脑动静脉畸形,计划分期栓塞。
a. 一期经动脉减流,降低出血风险。
b. 二期继续经动脉减流或经静脉行根治性栓塞。
4.术中及术后需要严格控制血压,避免出血。
2
Operation

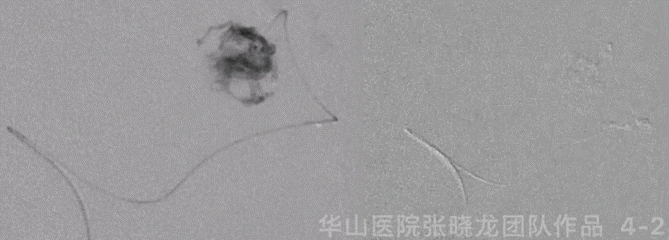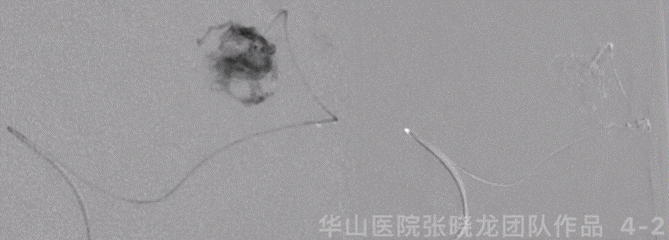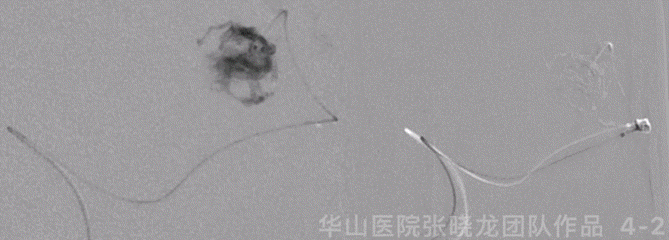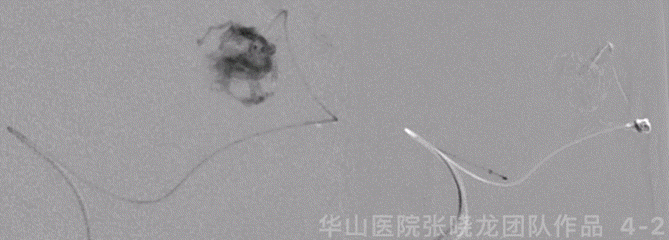
Figure 4 GIF. General anesthesia was performed. 6F guiding catheter was placed at the left ICA ophthalmic segment. Nimodipine 1ml was administered. The systolic BP was controlled below 100 mmHg. Apollo microcatheter was navigated into the distal part of the left MCA superior trunk via the support of Mirage .008 microwire. The microcatheter tip was confirmed into the nidus by hand bolus injection contrast medium. Onyx-18 0.5ml was injected. While the microcatheter was occluded and ruptured at the detachable point. Retrieved the microcatheter.
图 4 GIF. 全麻成功后,将6F导引导管置于左侧颈内动脉眼段。经动脉给予尼莫地平1ml。收缩压控制在100 mmHg以下。选用Apollo微导管在Mirage .008微导丝支撑下超选入左侧大脑中动脉上干远端,手推造影剂证实微导管头端位于畸形团内。注入Onyx-18 0.5ml,微导管堵管后于解脱点外渗。遂撤出微导管。
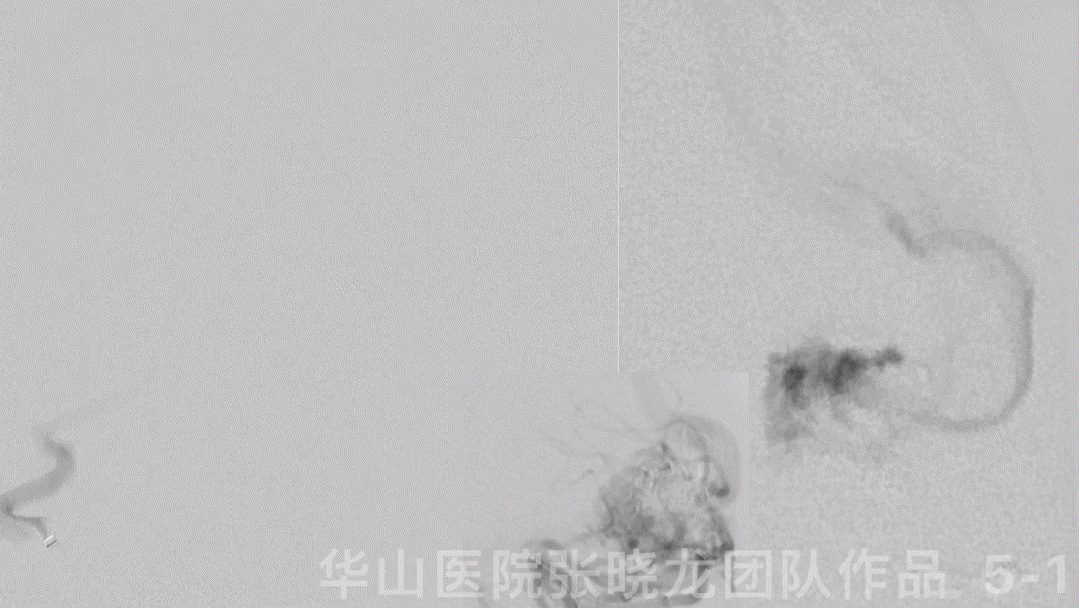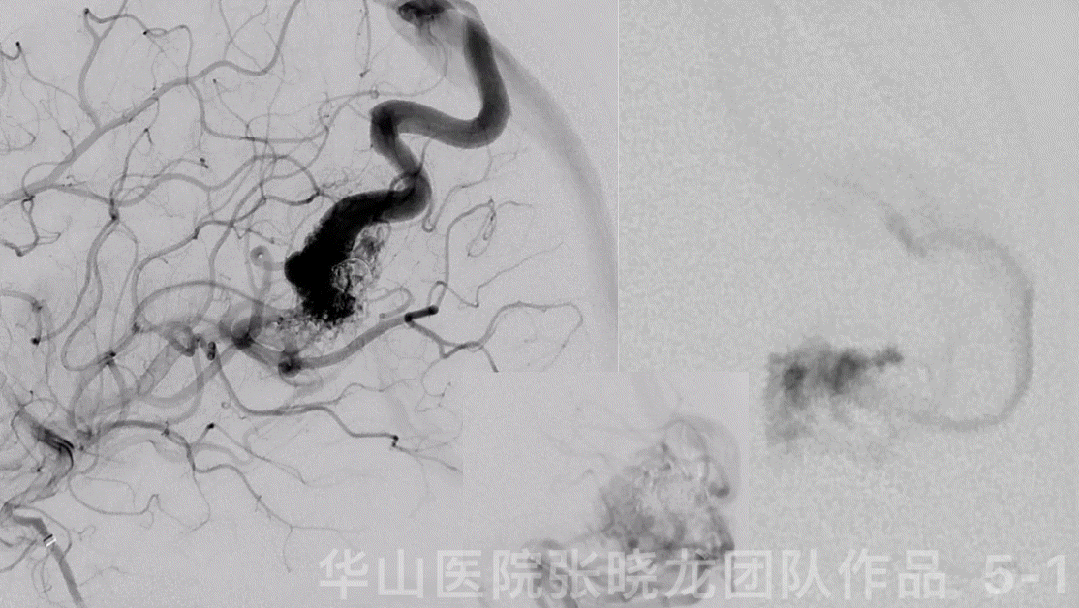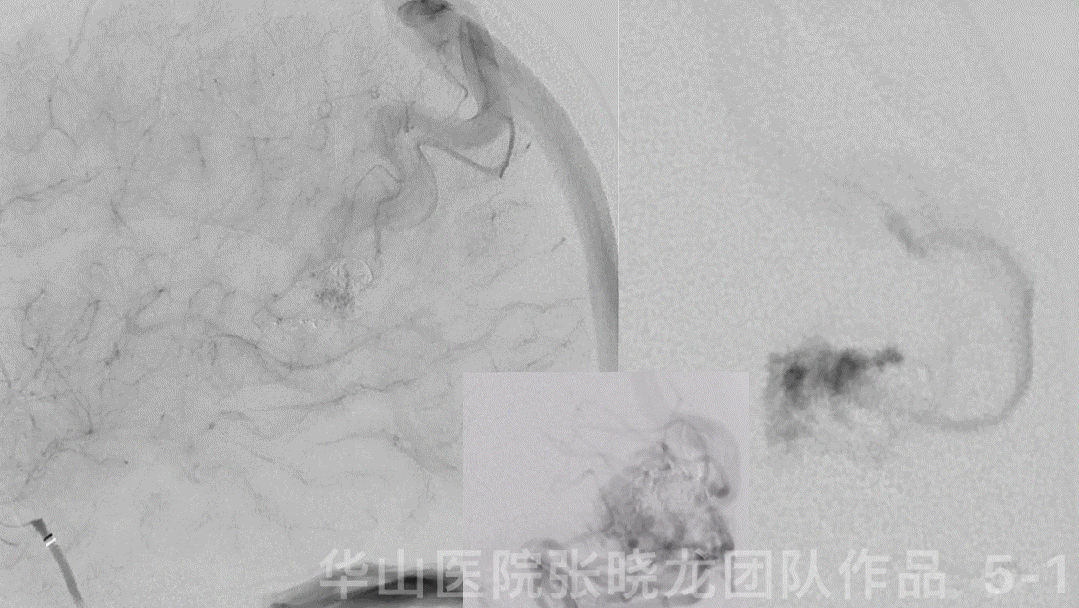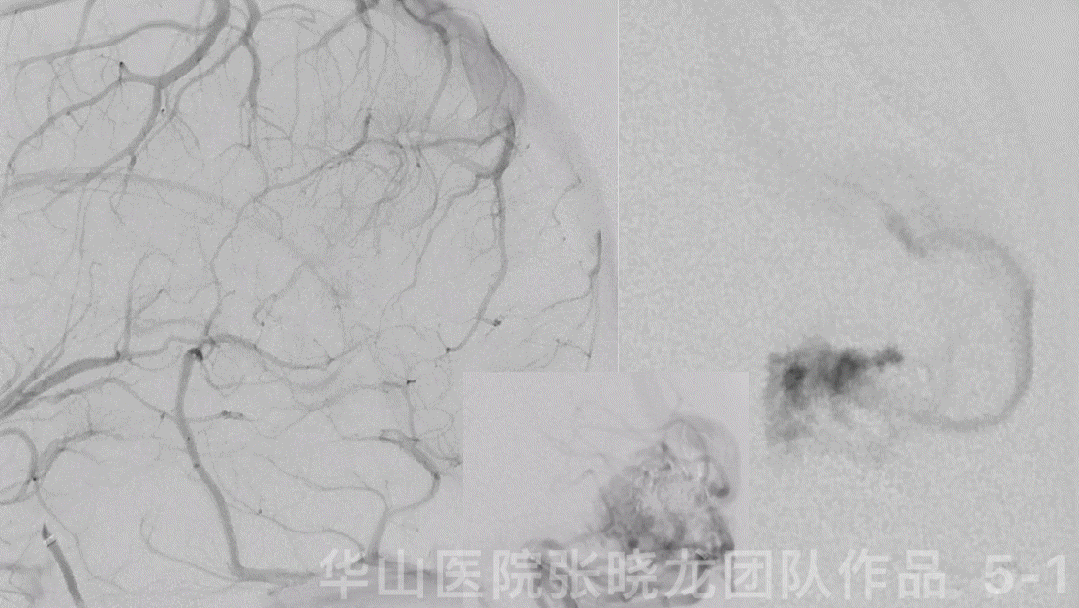

图 5 GIF. 复查造影可见残余畸形团,未见出血。再将一枚Echelon-10 45°微导管超选至畸形团内,注入Onyx-18 4.2ml,液体胶在畸形团及引流静脉起始部部分铸型。

Figure 6 GIF. The flow of the large AVM nidus decreased significantly. The small nidus angioarchitecture was revealed more clearly than pre-operation, which was fed by anterior choroidal artery and drained to the deep vein.
图 6 GIF. 复查造影皮层较大的畸形团流量明显减低。深部残余畸形团结构较前清晰,由左侧脉络膜前动脉供血向深部静脉引流。
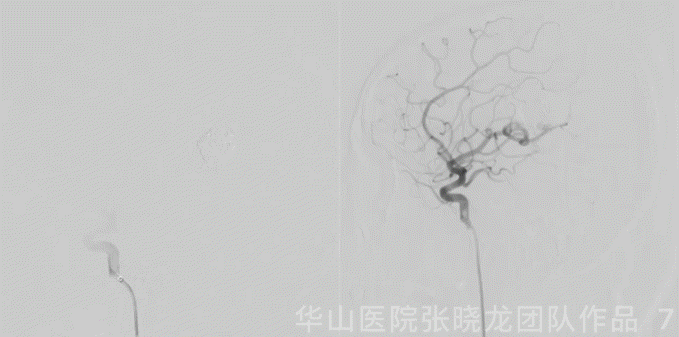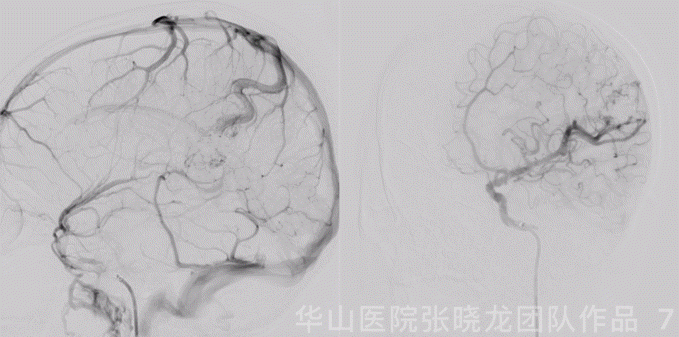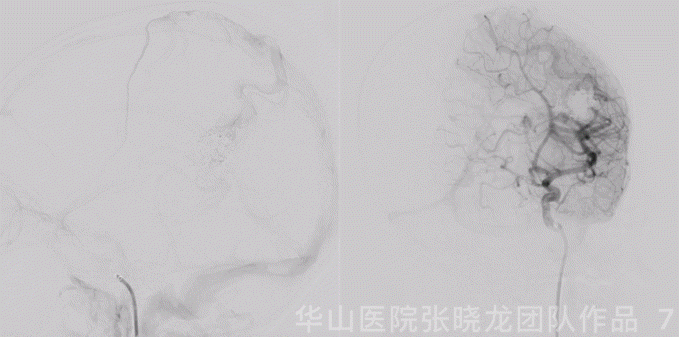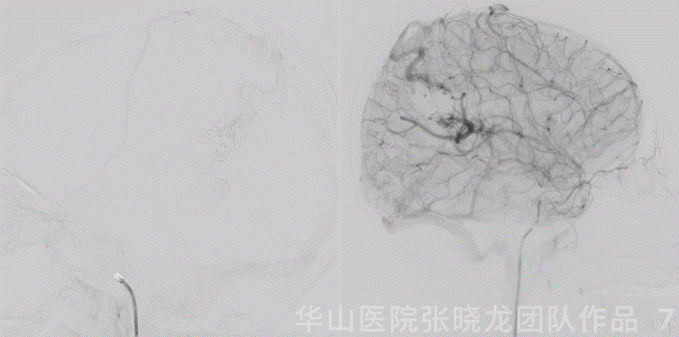
Figure 7 GIF. The cortical drainage vein was patent while the venous velocity decreased due to the decrease of AVM’s blood flow.
图 7 GIF. 复查造影皮层引流静脉通畅,但流量明显降低,静脉流速明显下降,颅内血管未见出血。
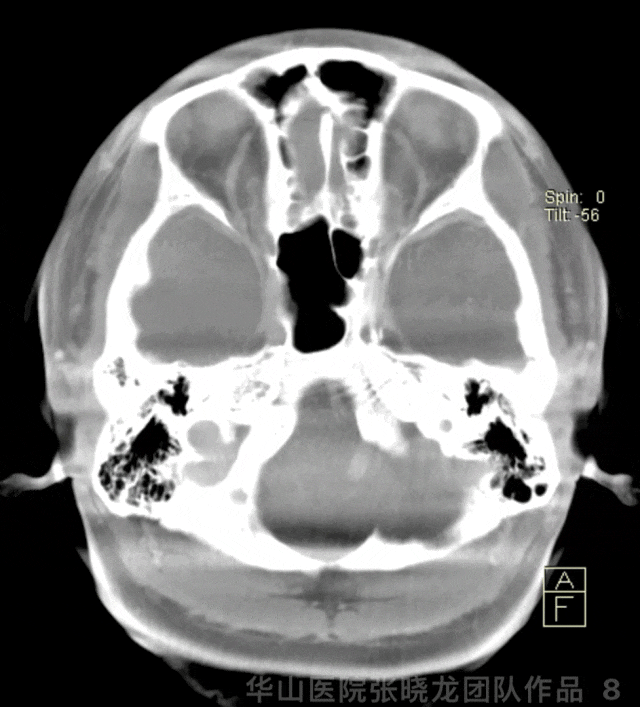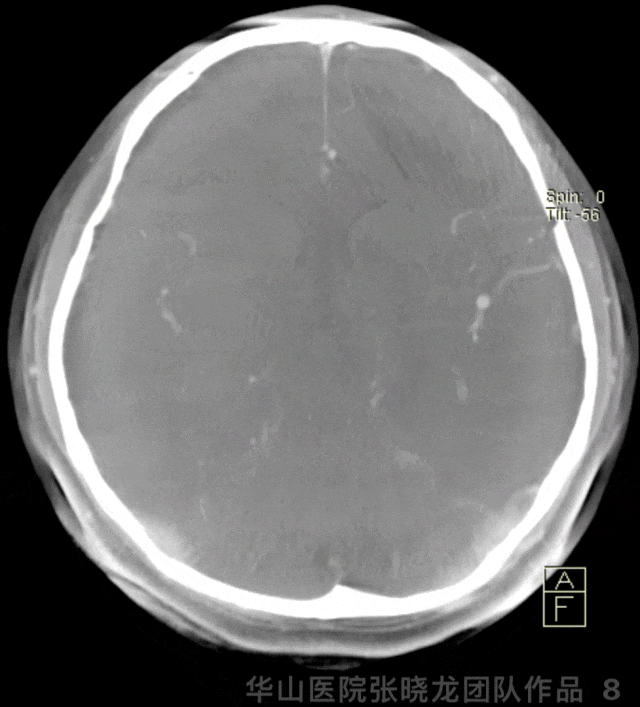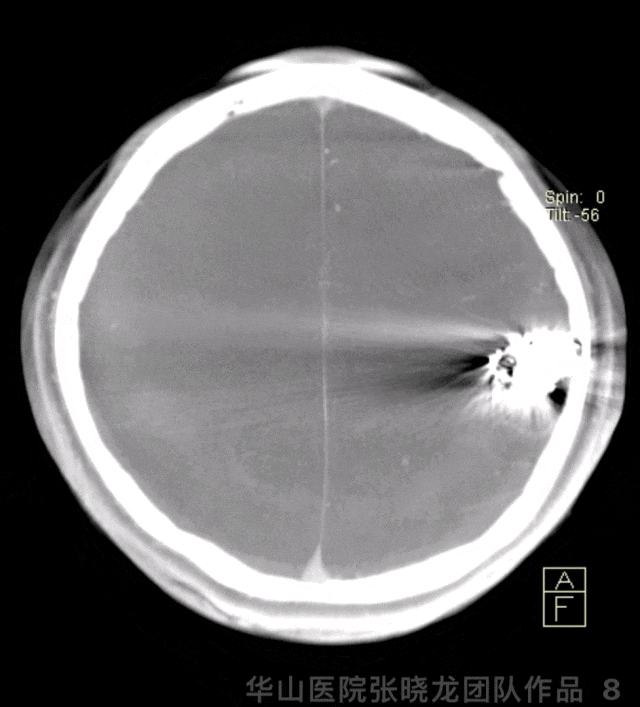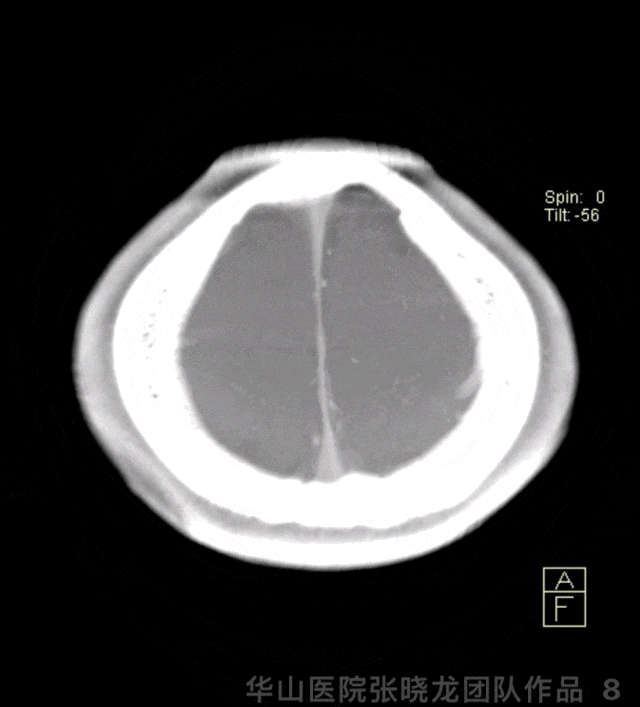
图 8 GIF. 术后即刻Dyna-CT显示无出血。
3
Post-Operation
●The patient suffered from mild headache.
●NE: GCS 15, bilateral pupils normal, light reflux normal, bilateral muscle strength normal, verbal fluency.
●收缩压控制在80-110mmHg。
●患者诉轻度头痛。
●查体:GCS 15,双侧瞳孔等大等圆,对光反射灵敏,四肢肌力正常,言语流利。
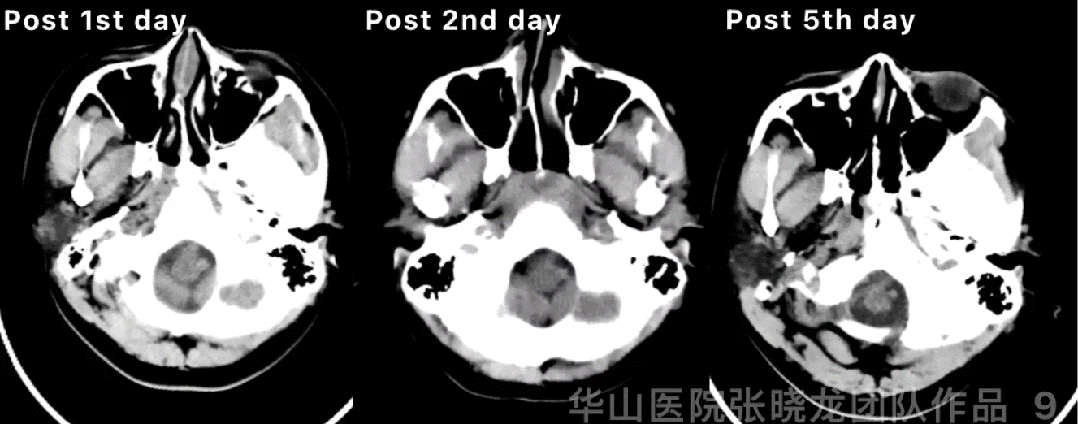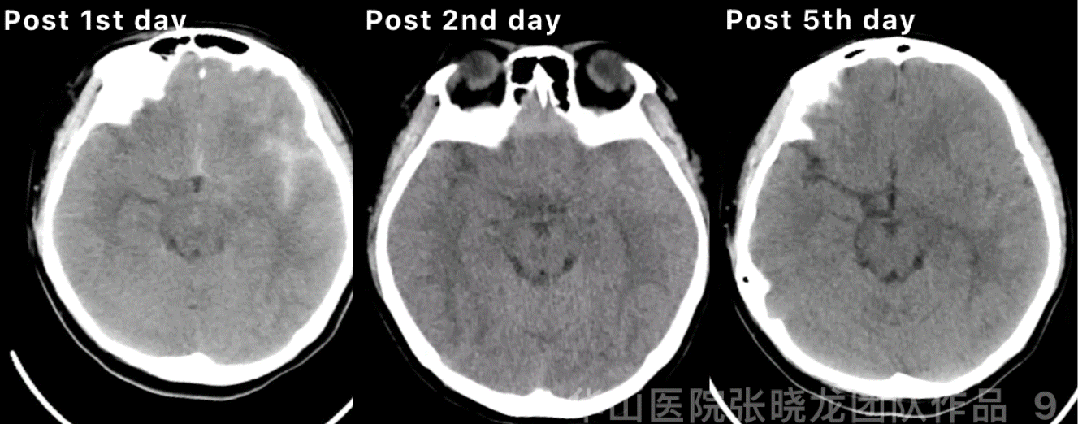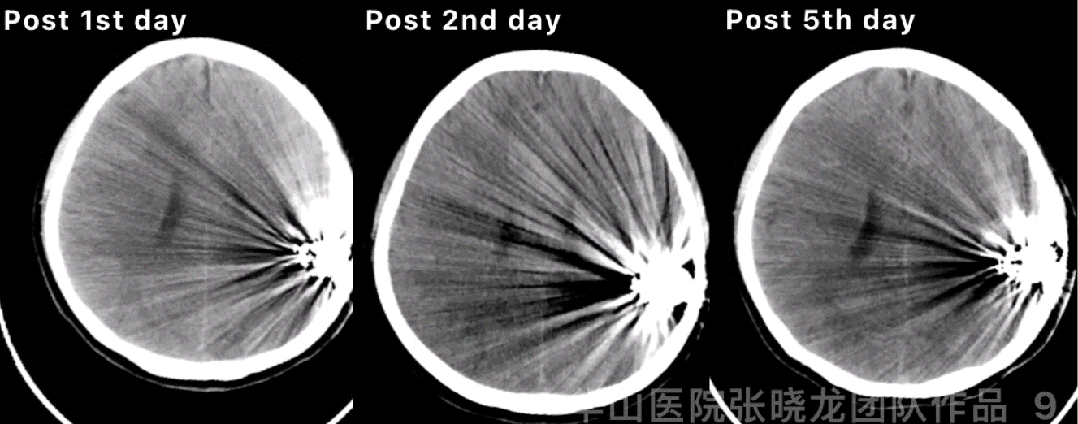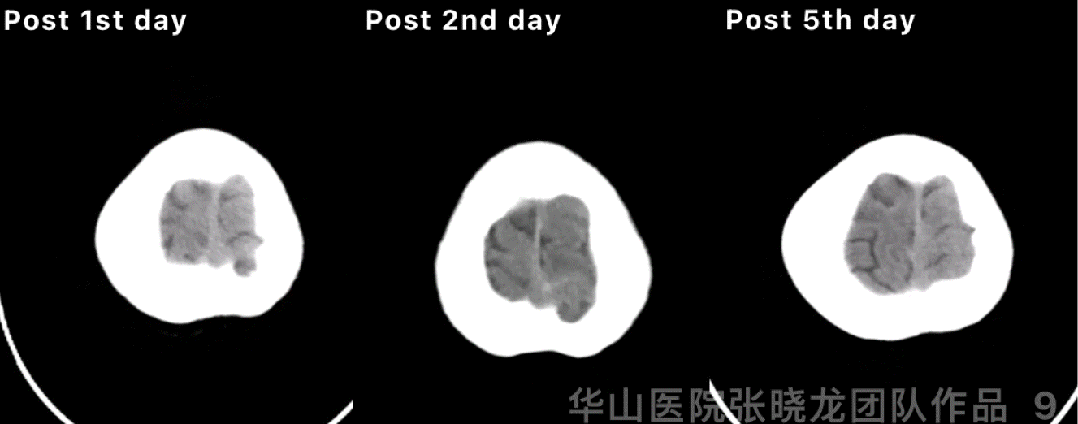
Figure 9 GIF. Post-operative day 1 CT showed hemorrhage. Hemostasis and dehydration were performed. Continue controlling the systolic blood pressure. Post-operative day 2 CT showed the hemorrhage stable while enlargement on post-operative day 5.
图 9 GIF. 术后第一天复查头颅CT提示出血。予止血、脱水、控制收缩压等治疗。术后第2天复查头颅CT血肿稳定,但术后第5天血肿扩大。
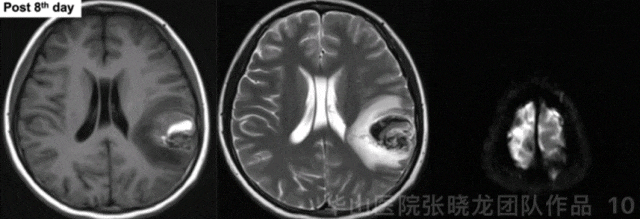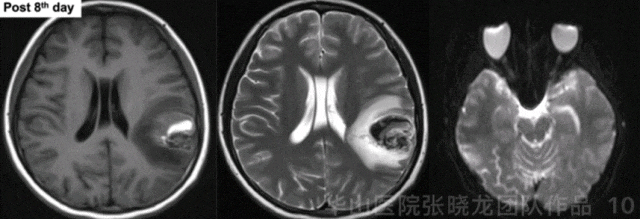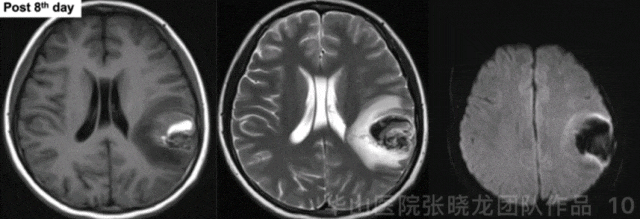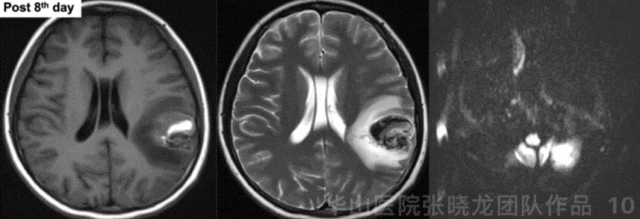
Figure 10 GIF. Hematoma was observed. No acute infarctions were detected from post-operative day 8 MRI.
图 10 GIF. 术后8天复查头颅MRI,可见畸形团内血肿。DWI未见急性脑梗死。


Figure 11. Recheck cranial CT dynamically and the hematoma kept stable. Local hospital CT revealed the hematoma absorption by post 20th day.
图 11. 动态复查头颅CT,血肿稳定。术后20天当地医院复查头颅CT,血肿已基本吸收。
4
1M-FU
Video 1. The residual nidus was mainly in the deep and drained to deep vein system.
视频 1. 残余畸形团主要位于深部,经深静脉引流
Video 2. The diameter of the cortical vein recovered normal by 1 month follow up.
视频 2. 1个月随访原皮层引流静脉管径恢复正常。
Video 3. The cortex nidus shrunk compared with post-operation by 1 month follow up.
视频 3. 1个月随访皮层畸形团较前缩小。
5
Summary
1.Left frontal-parietal junction AVM can be divided into two units. The nidus in the cortex was fed by left MCA branches and drained to superior sagittal sinus by a cortical vein. While the deep nidus was juvenile drained to internal cerebral vein.
2.The Spetzler-Martin scale for the cerebral AVM is grade 4:
maximal diameter 3-6cm, 2
function area, 1
deep drainage vein, 1
3.Target embolization is preferred for the juvenile high-flow AVM to decrease the flow and bleeding risk.
2.该脑动静脉畸形的SM分级为4:
最大直径3-6cm,2
功能区,1
深静脉引流,1。
3.高流量幼稚型脑动静脉畸形行靶向栓塞,通过减流,降低出血风险。
7.1个月随访时残余畸形团主要位于深部,残留皮层畸形团较术后即刻缩小,建议行立体定向放射治疗。
张晓龙
复旦大学附属华山医院
复旦大学附属华山医院放射科主任医师,博士、教授、博士生导师;
斯坦福大学医学院客座临床教授;
主持国家自然科学基金3项,第一作者或通讯作者发表国内外权威期刊文章50余篇;
中华医学会、放射学会、卫生部医政司等组织中担任副主任委员、组长等职务.《中国名医百强榜》神经介入专业中国十强(2012年度、2013年度、2014年度、2015-16年度、2017-18年度);
擅长复杂和疑难脑血管疾病的介入治疗,如复杂脑动脉瘤的栓塞,硬脑膜动静脉瘘栓塞,脑动静脉畸形栓塞,脑梗死的支架,脊髓血管畸形治疗;
自1995年开始从事脑血管疾病介入诊治工作和研究,师从黄祥龙教授、沈天真教授和凌锋教授,是我国最早从事神经介入的专家之一。2010年9月至今连续介入治疗颅内动脉瘤1500余例,无操作致死。
声明:脑医汇旗下神外资讯、神介资讯、脑医咨询、Ai Brain 所发表内容之知识产权为脑医汇及主办方、原作者等相关权利人所有。
投稿邮箱:NAOYIHUI@163.com
未经许可,禁止进行转载、摘编、复制、裁切、录制等。经许可授权使用,亦须注明来源。欢迎转发、分享。
投稿/会议发布,请联系400-888-2526转3。






