Review
History
• 55 y/o male.
• Suffered from sudden left upper limb weakness for twenty days, accompanied with memory impairment and slow reaction.
• Past medical history: HTN for ten years; DM for three years, not well-controlled; smoking for twenty years, quitting for one month.
• Medication: Aspirin, Atorvastatin, Felodipine, Acarbose.
• PE: mild recognitive decline, MoCA 23/30, MMSE 27/30; normal muscle strength.
• 55岁,男性。
• 药物:阿司匹林,阿托伐他汀,非洛地平,阿卡波糖。
1
Pre-operational examination

图 1. 2020年影像学检查提示右侧颈内动脉通畅,左侧丘脑急性脑梗死。该患者当时出现右侧肢体无力。

Figure 2. MRA revealed right ICA occlusion and an irregular basilar artery aneurysm.
图 2. 2023年8月29号头颅MRA提示右侧颈内动脉闭塞,基底动脉不规则动脉瘤。

图 3 GIF. 高分辨率磁共振提示右侧颈内动脉血管壁增厚、强化,右侧颈内动脉可见线样管腔。


图 4. 右侧颈内动脉线样管腔,血管壁增厚强化。左侧颈内动脉床突上段局部狭窄伴斑块,斑块强化。基底动脉瘤瘤壁未见明显强化。
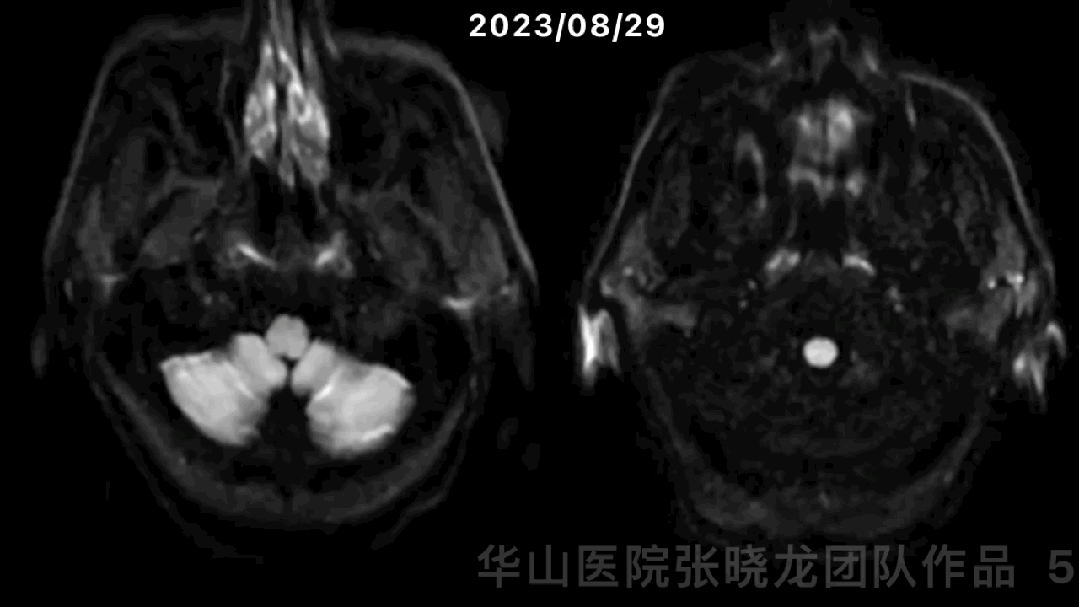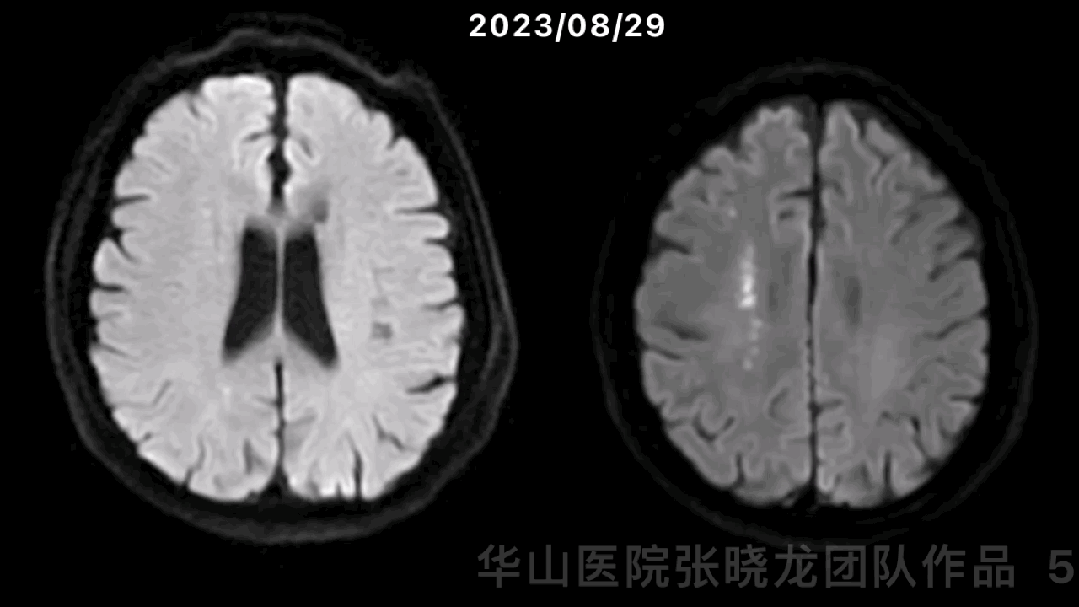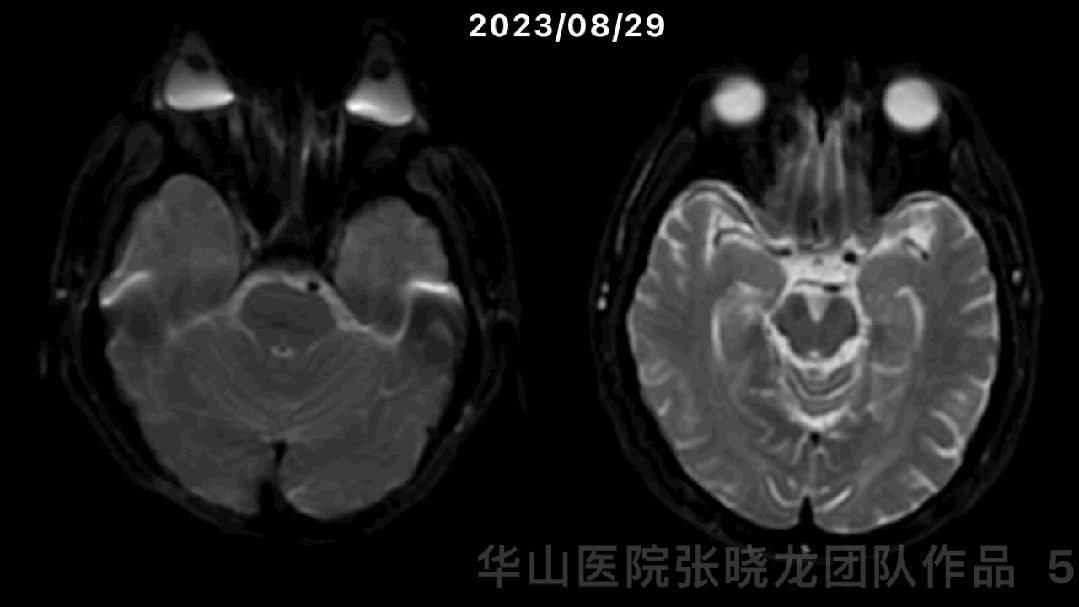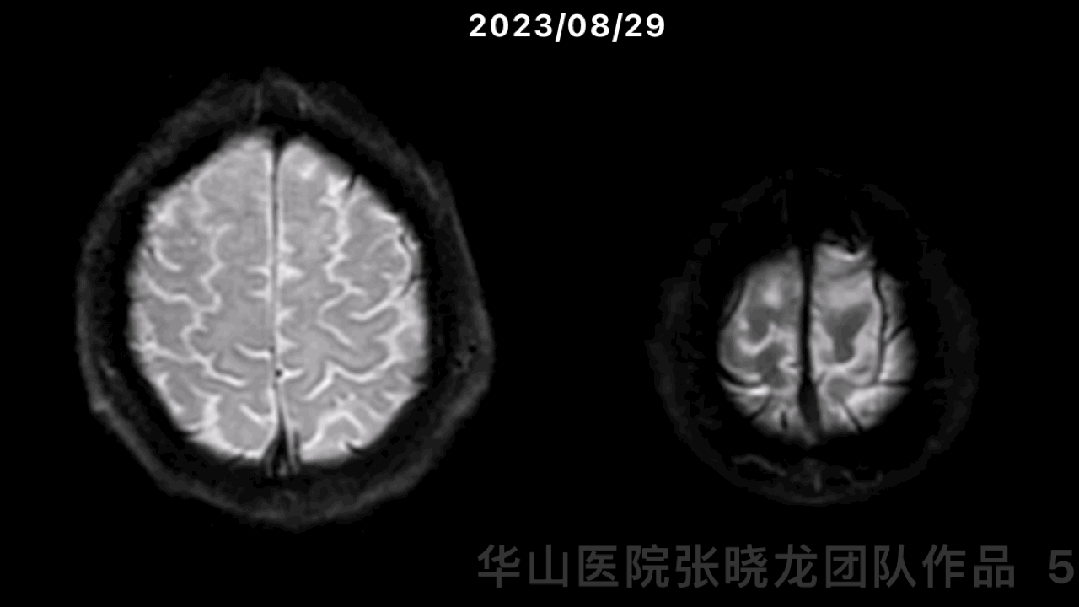
图 5 GIF. 对比磁共振,近1月右侧分水岭区脑梗进展。


图 6. CTP: CBF降低, MTT和TTP时间延长。CT平扫未见明显钙化。
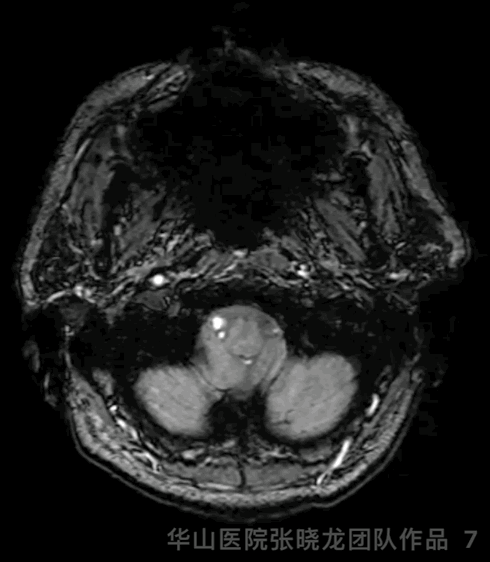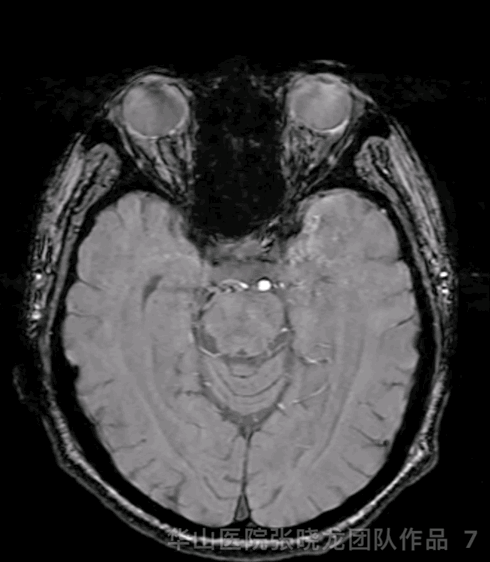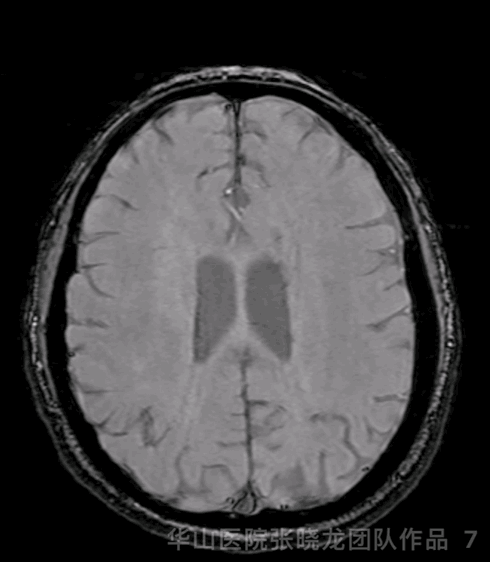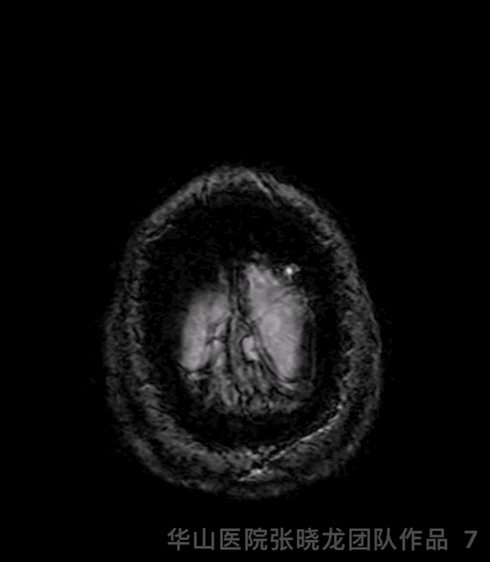
Figure 7 GIF. SWI did not detect significant micro-bleeding lesions.
图 7 GIF. SWI未见明显微出血。

图 8 GIF. DSA造影证实右侧颈内动脉起始部至眼段线样狭窄,超选择造影证实眼段以远闭塞,颈外动脉未见明显代偿。

Figure 9. Left ICA and pial anastomosis from right posterior circulation compensated right anterior circulation. Right A1 segment stenosis.
图 9. 左侧颈内动脉通过前交通动脉及右侧后循环软膜支代偿右侧前循环供血区。右侧大脑前动脉A1段狭窄。
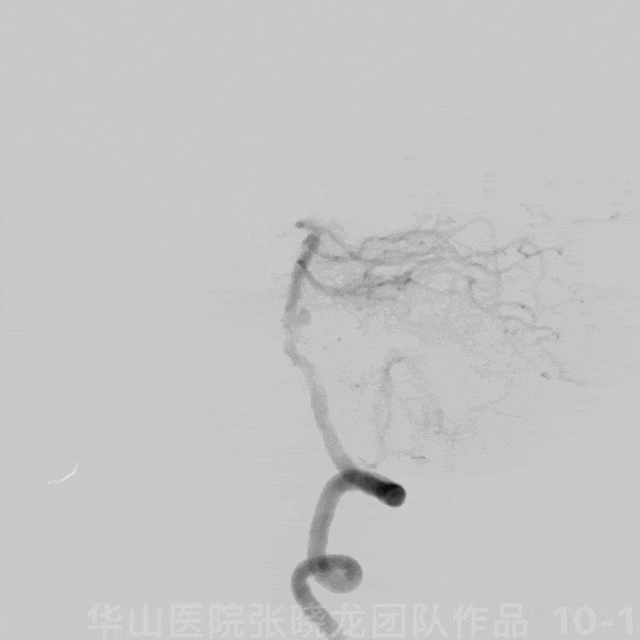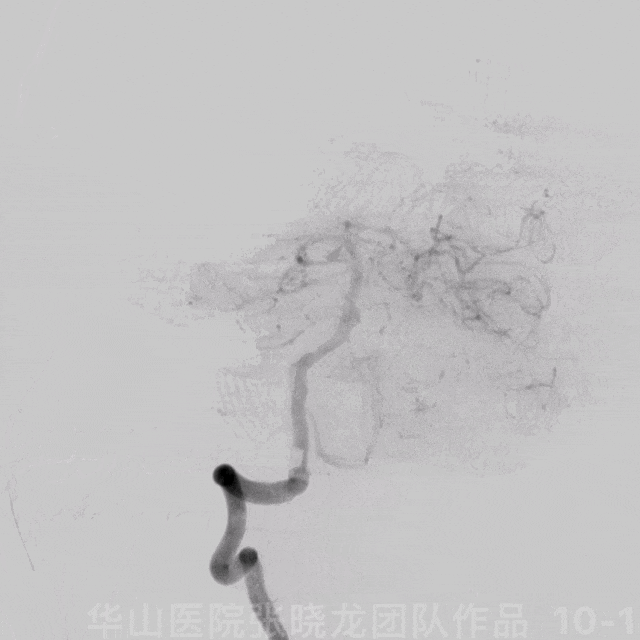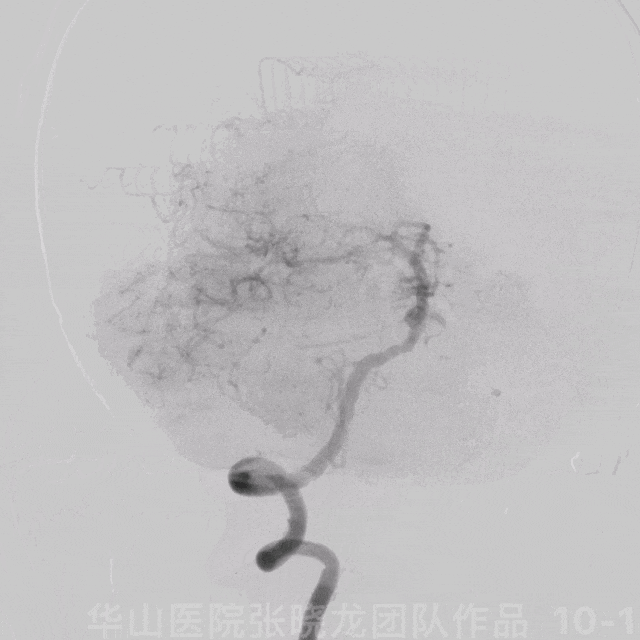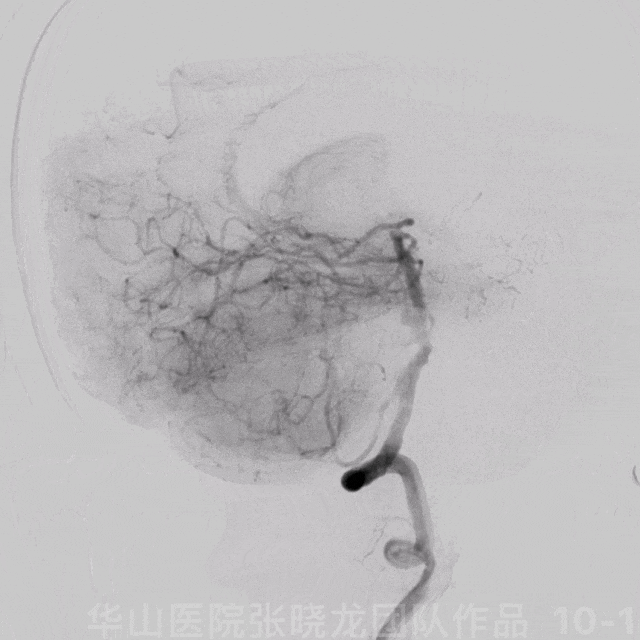

图 10 GIF. 造影证实基底动脉中段动脉瘤,动脉瘤附近发出右侧小脑前下动脉。双侧椎动脉非等势,右侧优势椎动脉。
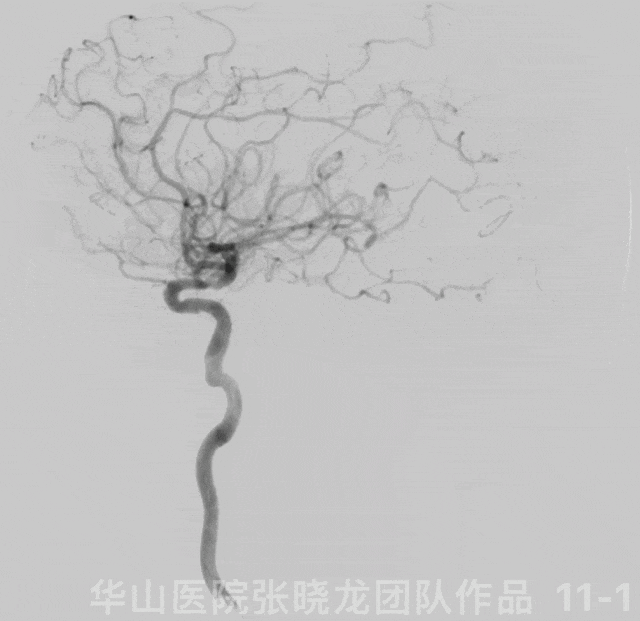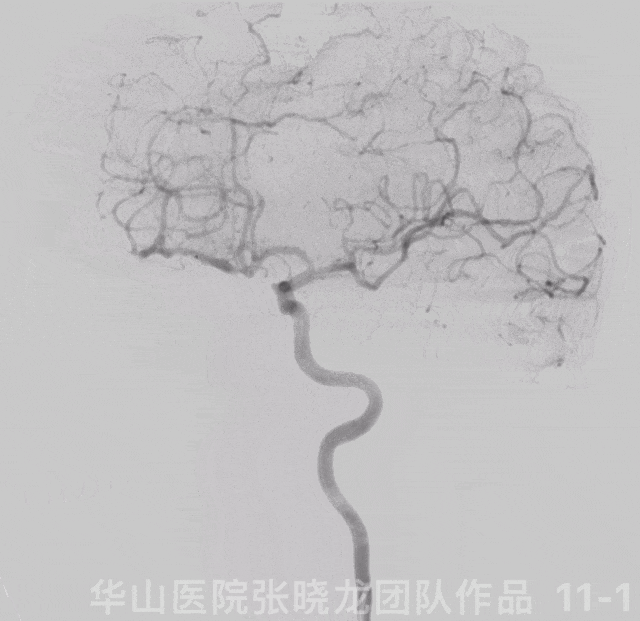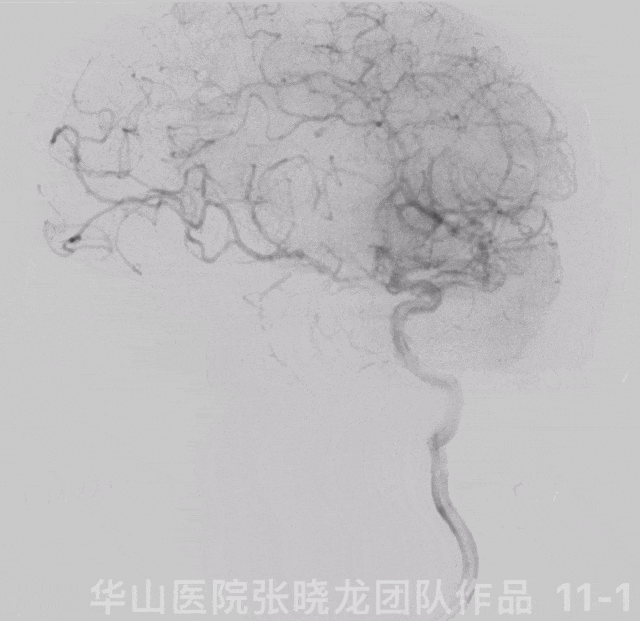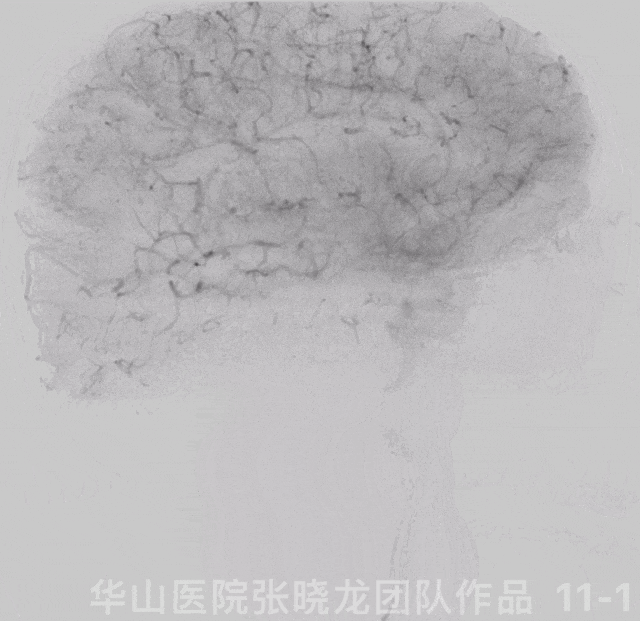

Figure 11 GIF. Angiograms showed left ophthalmic segment local stenosis and distal part of left A2 occlusion.
图 11 GIF. 左侧颈内动脉造影示左侧颈内动脉眼段局部狭窄,左侧大脑前A2段以远闭塞。
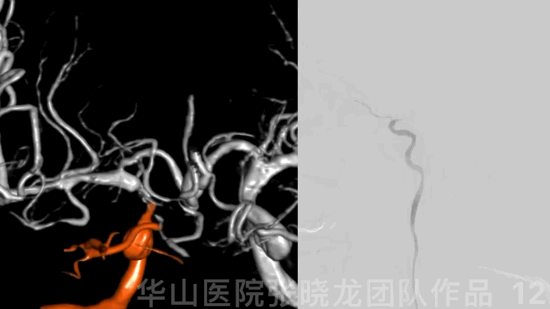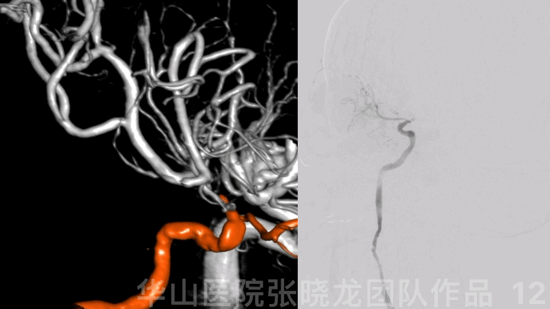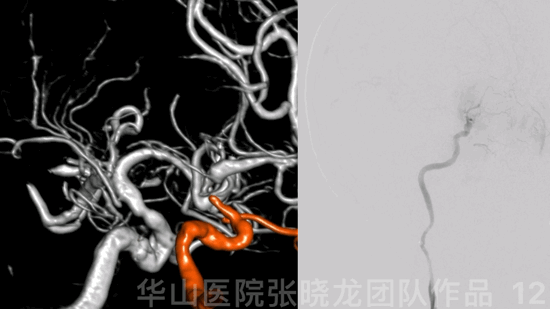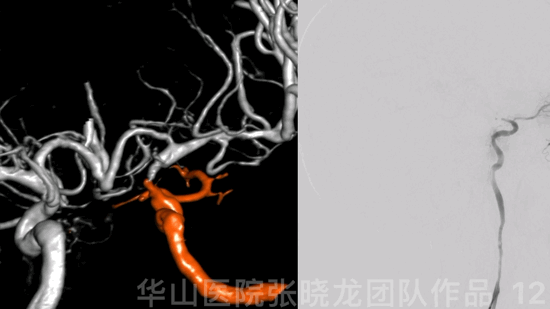
图 12 GIF. 结合造影及3D重建,右侧交通段闭塞,闭塞段较短。
2
Indications and strategies
Distal right ICA occlusion:
Aggravated symptoms under antiplatelet therapy, decreased memory and reaction.
DWI: enlarged infarctions.
CTP: Decreased CBF, increased MTT and TTP; no calcification.
SWI: No significant micro bleeding lesions.
HR-MRI: Linear lumen existed, occluded segment not too long.
Exchange technique: Echelon-10 microcatheter with microwire to cross the occlusion segment and exchanged Gateway balloon.
Balloon angioplasty: The balloon size can be referenced to the contralateral segment.
Three-dimensional fusion navigation of the bilateral ICA.
BA dissecting aneurysm:
BA dissecting aneurysm haboured a high rupture risk.
Stent-assisted coiling was preferred to decrease the recurrence risk.
Recanalization of right ICA occlusion had a higher procedure-related risk, which should be treated first.
右侧颈内动脉闭塞再通:
规范抗板、他汀等药物治疗下,患者仍症状加重,记忆下降、反应进行性减慢。
DWI: 规范药物治疗下,病变责任血管区仍有急性脑梗事件发生。
CTP: 病变侧CBF下降, MTT和TTP延长; 病变血管无钙化。
SWI: 未见明显微出血灶。
HR-MRI: 右侧颈内动脉起始段至眼段仍有线样管腔,交通段闭塞,闭塞段相对不是很长。
交换技术:Echelon-10微导管在微导丝导引下穿过闭塞段,然后交换Gateway球囊。
球囊扩张成形术: 参考对侧血管直径,选择合适大小的球囊。
双侧颈内动脉3D融合路途辅助导航。
基底动脉夹层动脉瘤:
基底动脉夹层动脉瘤破裂风险高,建议治疗。
为降低复发风险,首先支架辅助栓塞。
治疗顺序:先开通风险较高的右侧颈内动脉。
3
Treatment process
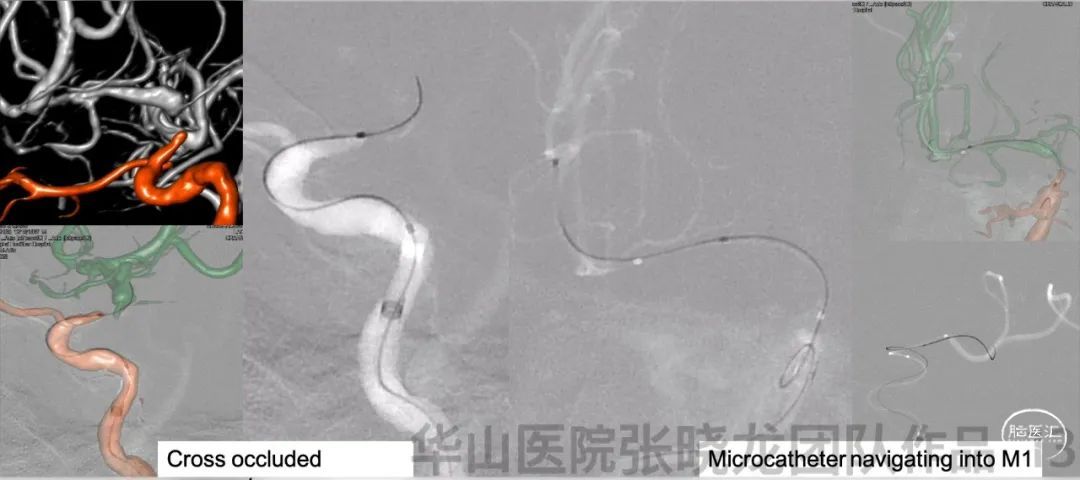
图 13. 6F导引导管置于右侧颈内动脉海绵窦段,经导引导管给予尼莫地平1ml。选用Echelon-10微导管及Synchro-II微导丝,在双侧颈内动脉3D路途辅助导航下,通过闭塞段。然后将微导管位于M1远端真腔内。

图 14. 左侧颈内动脉眼段以远血管直径约2.43mm,遂选用Gateway 2.5*15mm球囊,在闭塞段从远至近扩张,远端4 ATM扩张150s,近端6 ATM扩张120s。球囊扩张过程中患者血压、心率基本稳定,泻除球囊前收缩压控制在130mmHg以下。
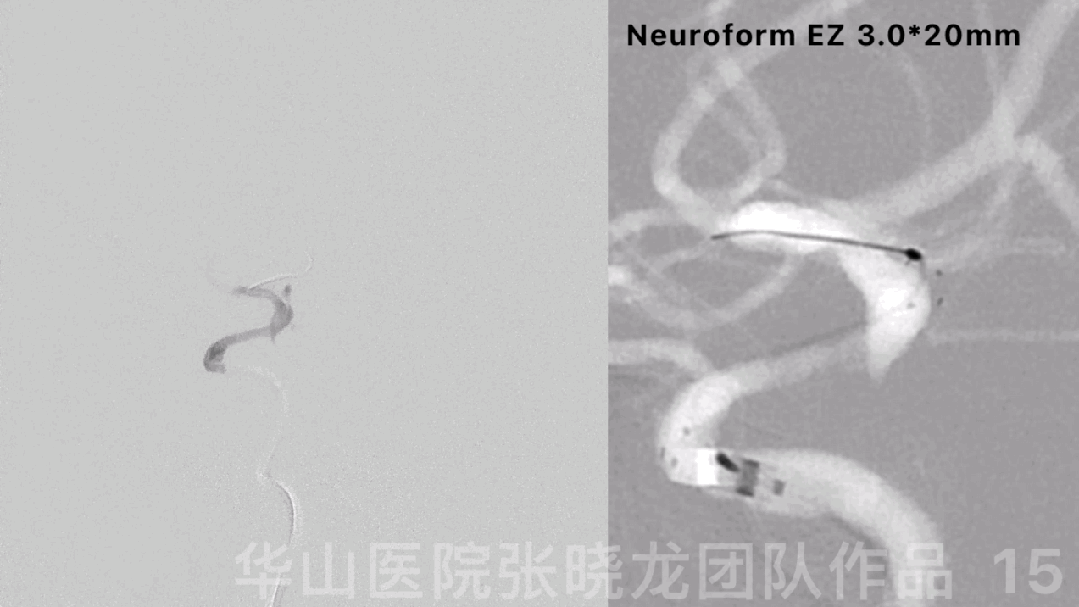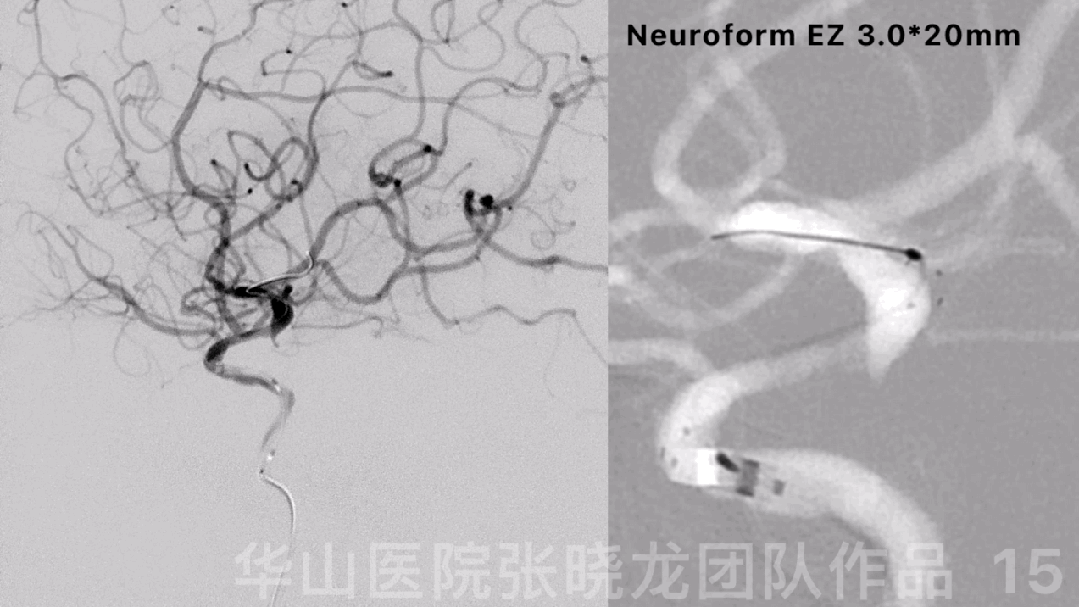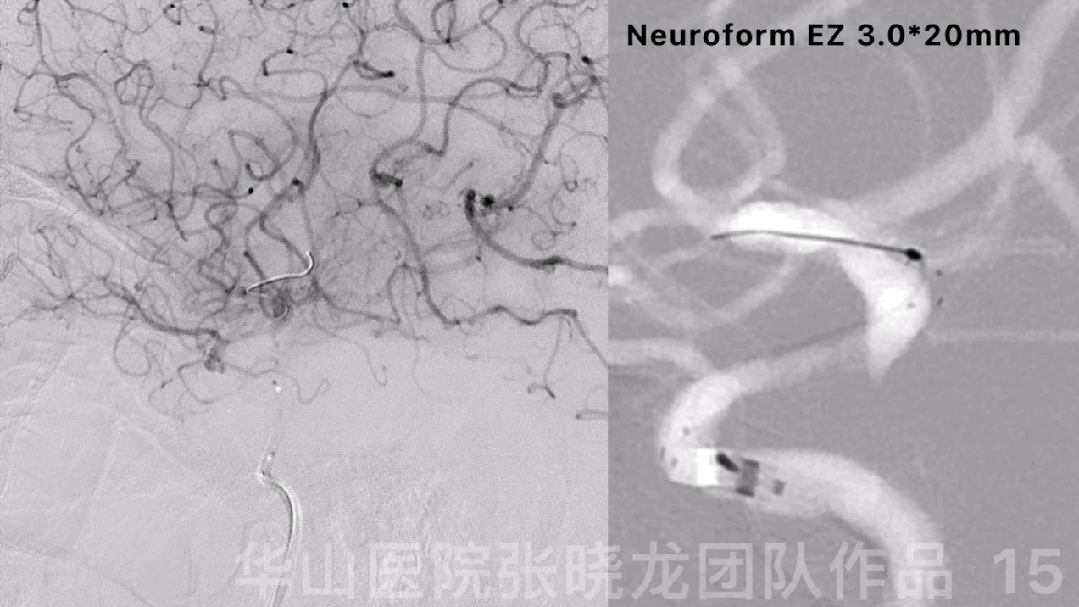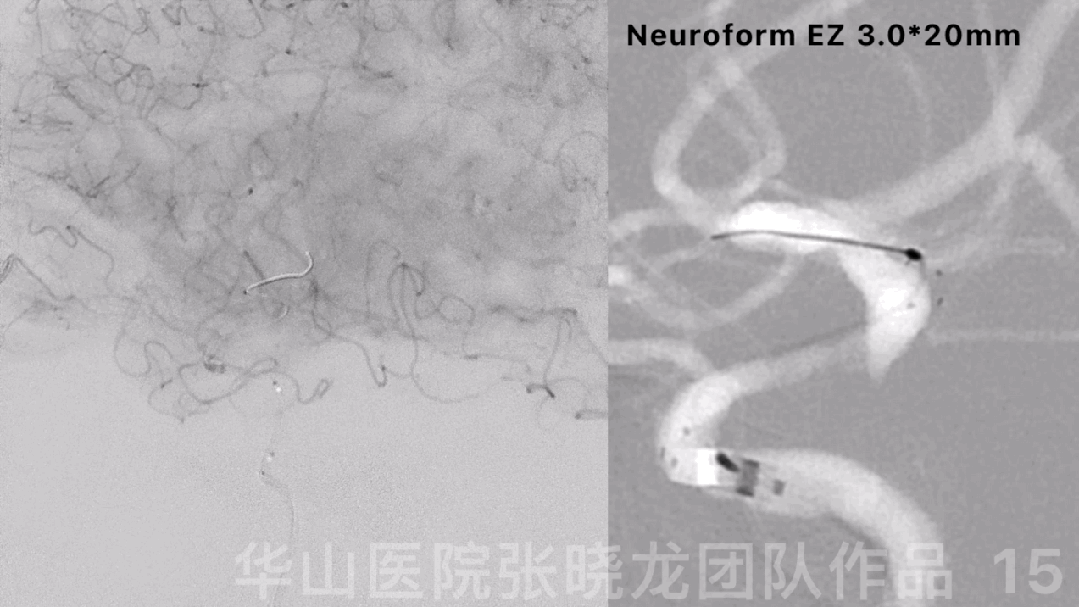
图 15 GIF. 球囊扩张后复查造影,狭窄部位局部回缩,颅内血管未见出血。行全身肝素化。XT-27微导管置于右侧大脑中动脉,狭窄段释放Neuroform EZ 3.0*20mm支架。

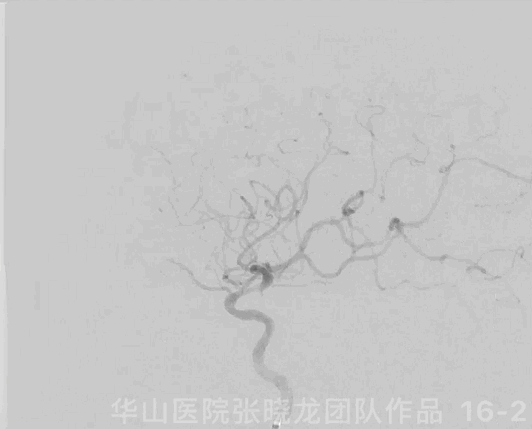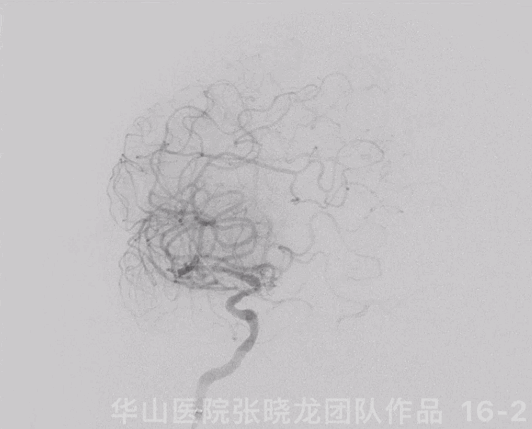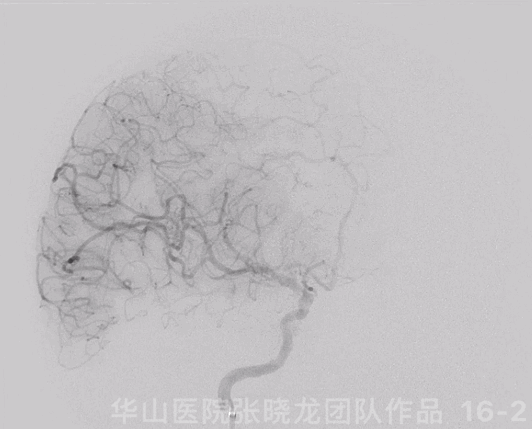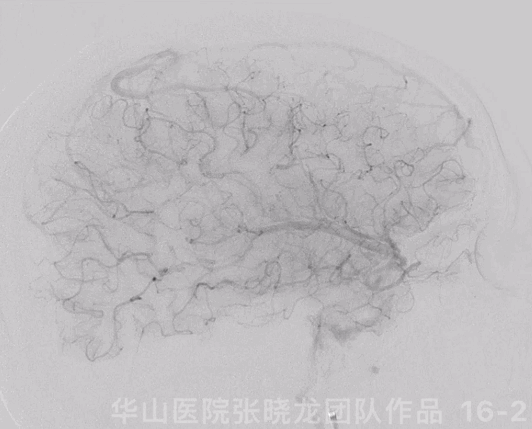
图 16 GIF. 复查造影示原闭塞段扩张满意,右侧大脑半球灌注明显增加,颅内血管未见闭塞或出血。经导引导管给予替罗非班3ml。
Step 2. Basilar artery aneurysm embolization
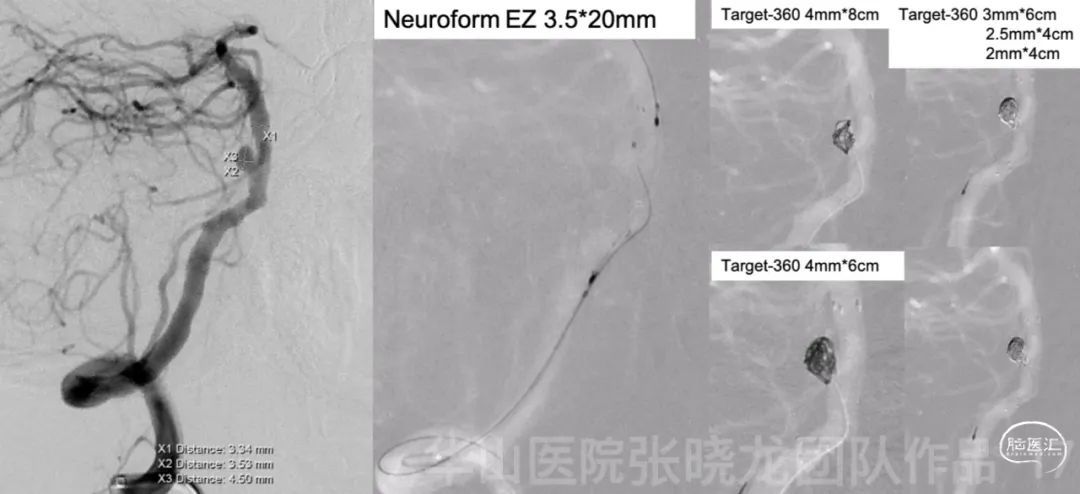
图 17. 基底动脉瘤大小4.5*3.53mm,近端载瘤动脉直径3.4mm,远端载瘤动脉直径3.34mm。6F Envoy DA导引导管置于椎动脉颅底。XT-27微导管在微导丝导引下至于基底动脉远端,Echelon-10微导管置于动脉瘤腔内。瘤颈部释放Neuroform EZ 3.5*20mm。经栓塞微导管依次填入5枚弹簧圈(Target 360 4mm*8cm, 4mm*6cm, 3mm*6cm, 2.5mm*4cm, 2mm*4cm) 。


图 18 GIF. 复查造影动脉瘤不显影,载瘤动脉通畅,颅内血管显影良好。经导管给予替罗非班5ml和尼莫地平1ml。
4
Post-Operation
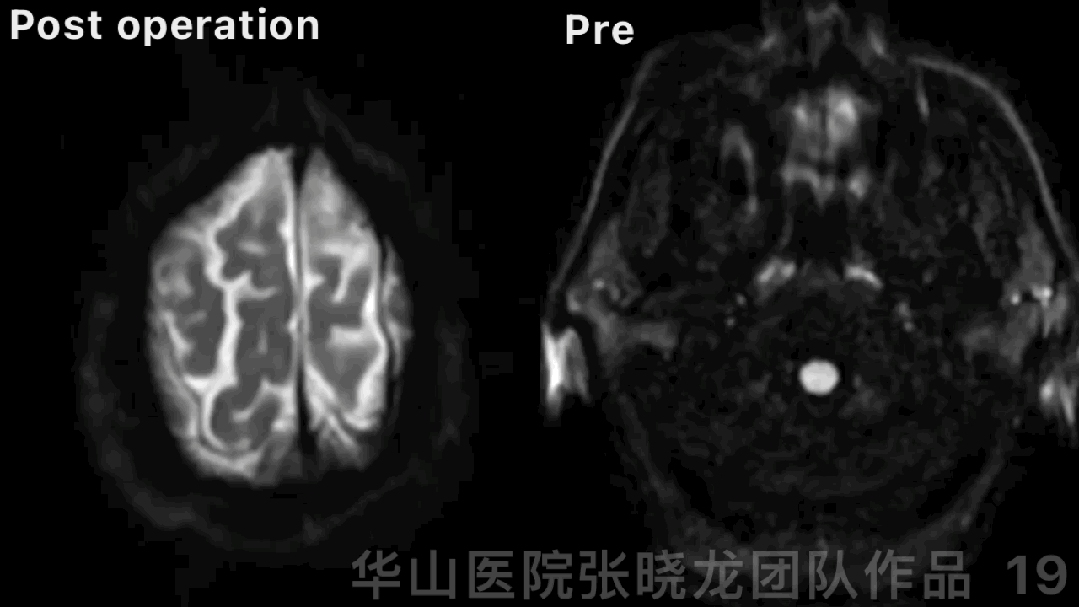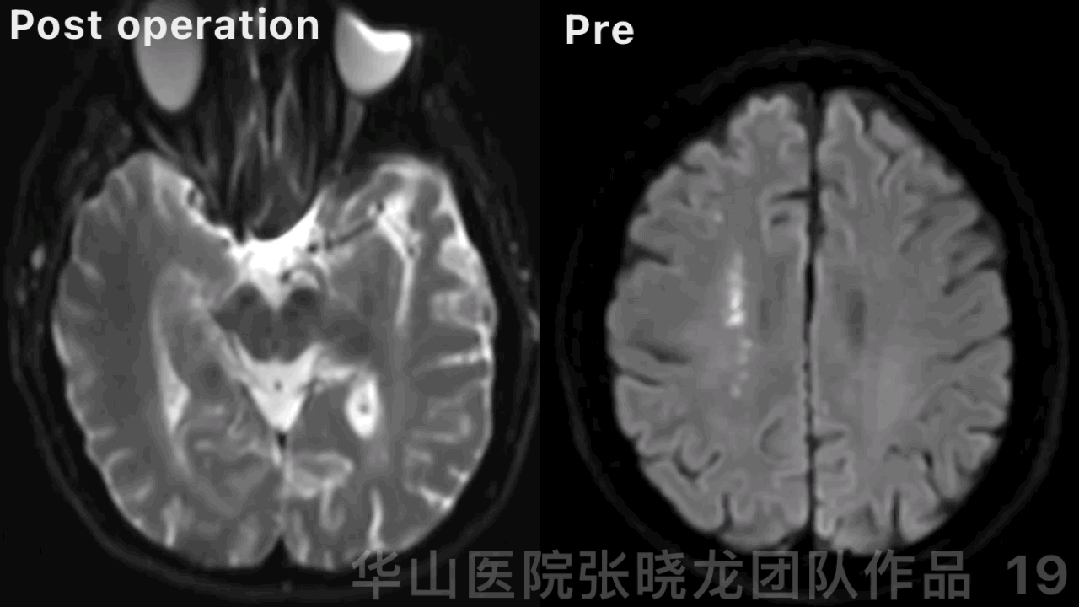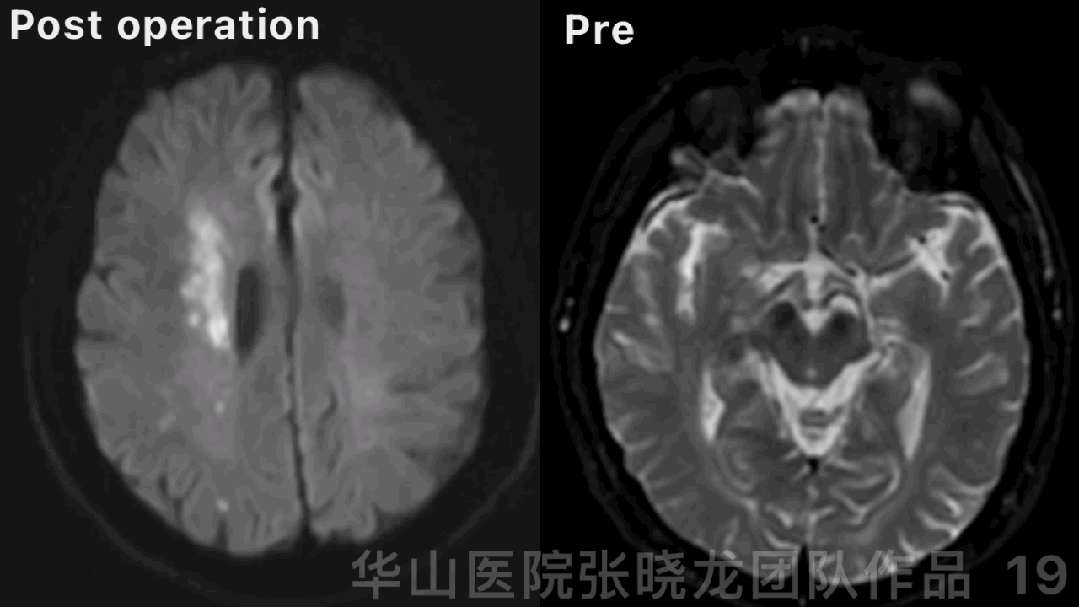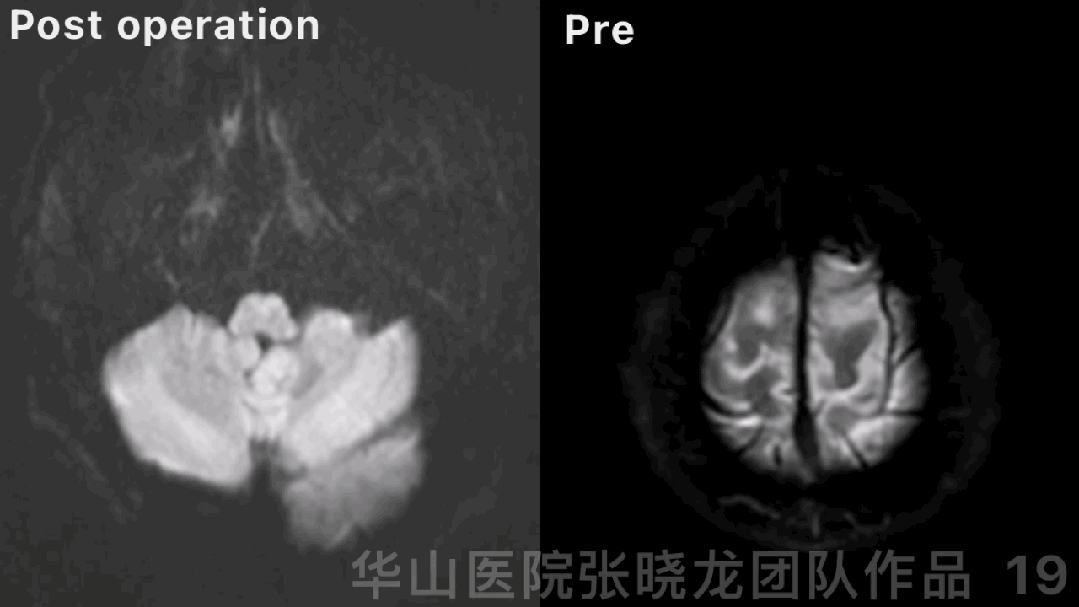
Figure 19 GIF. DWI did not detect obvious new infarctions.
NE: GCS 15, bilateral pupils light reflux normal, normal muscle strength, no new neurologic deficit.
Medication:
Tirofiban 7ml/h maintained for 24h.
Aspirin, Clopidogrel and Atorvastatin were prescribed.
AA 96.1%, ADP 75.4%.
神经查体:GCS 15,双侧瞳孔对光反射灵敏,四肢肌力正常,无新发神经功能缺损。
药物:
替罗非班7ml/h维持24h。
口服阿司匹林,氯吡格雷和阿托伐他汀。
阿司匹林抑制率96.1%,氯吡格雷抑制率75.4%。
5
Summary
Distal right ICA occlusion:
Aggravated symptoms under antiplatelet therapy, decreased memory and reaction.
DWI: enlarged infarctions.
CTP: Decreased CBF, increased MTT and TTP; no calcification.
SWI: No significant micro bleeding lesions.
Exchange technique: Echelon-10 microcatheter with microwire to cross the occlusion segment and exchanged Gateway balloon.
Balloon angioplasty: The balloon size can be referenced to the contralateral segment.
Three-dimensional fusion navigation of the bilateral ICA.
BP was decreased to below 130mmHg before balloon deflation.
BA dissecting aneurysm:
BA dissecting aneurysm haboured a high rupture risk.
The importance of standardized cerebral angiography! Common carotid arteriography showed a "beak sign" in the ICA initial segment, indicating dissection. Super-selective angiograms showed the ICA initial segment was due to supraclinoid occlusion instead of dissection.
Right ICA recanalization has a higher procedure-related risk, which should be treated first.
After the operation, the action was improved. (post: MoCA 26: MMSE:28; Pre 23/27)
右侧颈内动脉闭塞再通:
规范抗板、他汀等药物治疗下,患者仍症状加重,记忆下降、反应进行性减慢。
DWI: 规范药物治疗下,病变责任血管区仍有急性脑梗事件发生。
CTP: 病变侧CBF下降, MTT和TTP延长; 病变血管无钙化。
SWI: 未见明显微出血灶。
交换技术:Echelon-10微导管在微导丝导引下穿过闭塞段,然后交换Gateway球囊。
球囊扩张成形术: 参考对侧血管直径,选择合适大小的球囊。
双侧颈内动脉3D融合路途辅助导航。
泻除球囊前患者收缩压稳定在130mmHg以下。
基底动脉夹层动脉瘤:
基底动脉夹层动脉瘤破裂风险高,建议治疗。
为降低复发风险,首先支架辅助栓塞。
治疗顺序:
先开通风险较高的右侧颈内动脉。
术后患者认知改善。(术后: MoCA 26: MMSE:28; 术前 23/27)
![]()
点击或扫描上方二维码
查看更多“介入”内容






