Case Review
·50 y/o male.
·Suffering from sudden onset of unconsciousness. Intracranial aneurysms were found 1 month ago.
·NE: (-).
·Past medical history: HTN for 3 years.
·Medication: Diltiazem and valsartan.
·50岁 男性。
·1月前突发一过性意识不清,检查发现颅内多发动脉瘤。
·神经查体:-。
·既往史:高血压3年。
·药物:地尔硫卓和缬沙坦。




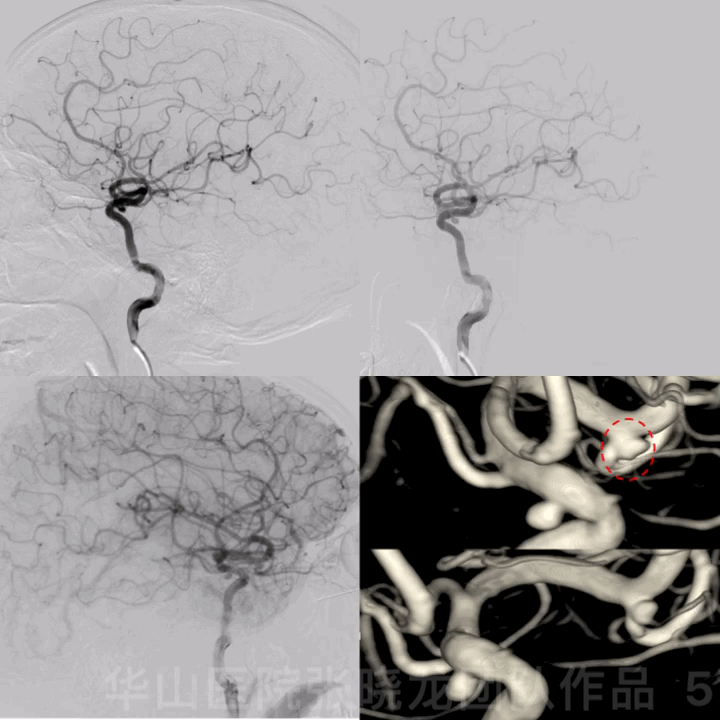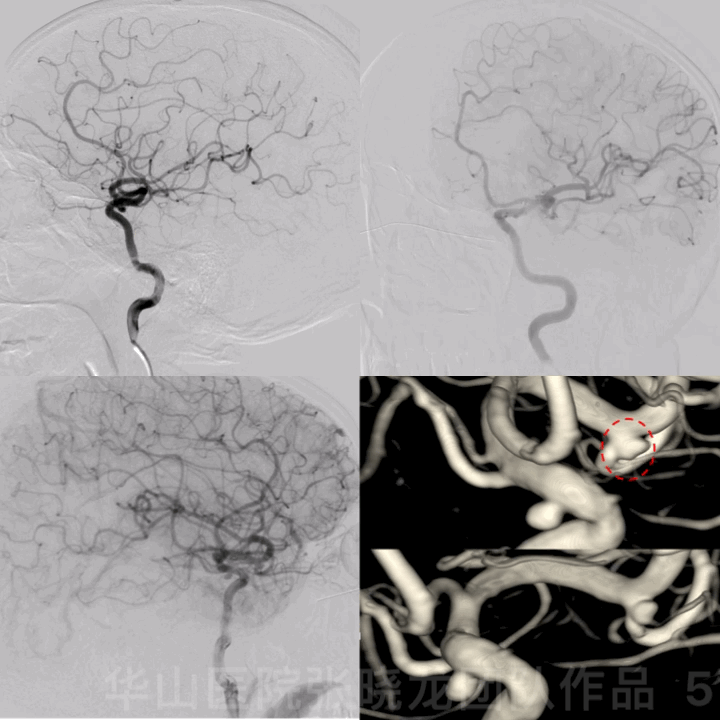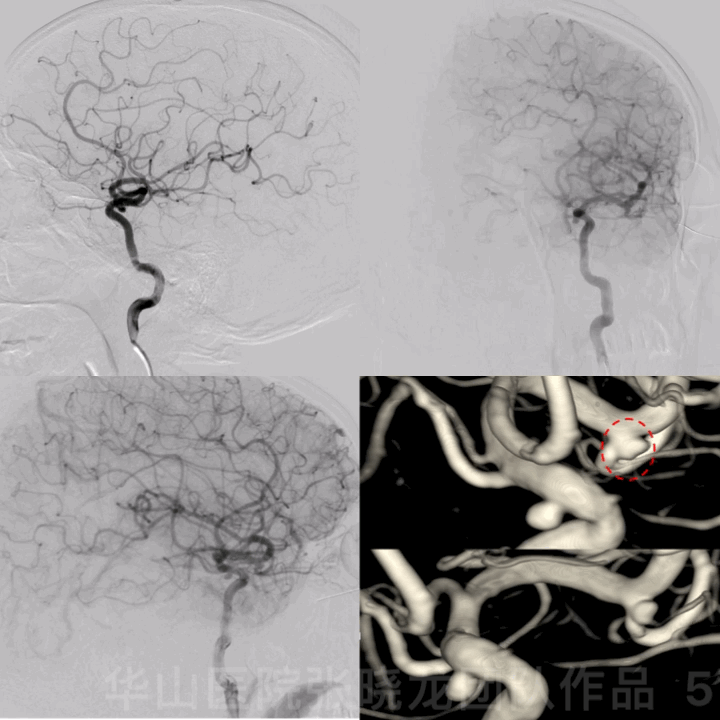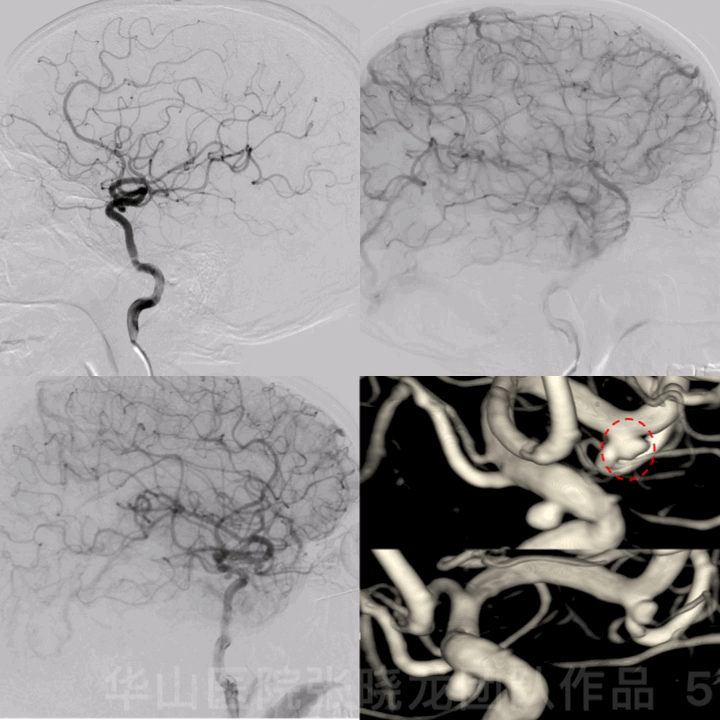
图 5 GIF. 造影证实左侧大脑中动脉瘤,动脉瘤形态不规则,左侧颈眼窄颈动脉瘤。
1
Strategy
·Multiple intracranial aneurysms comprised of bilateral middle cerebral artery aneurysms and a left ophthalmic aneurysm should be treated to lower rupture risk.
·The irregular left middle cerebral artery aneurysm will be treated with stent assisted coiling technique.
·The narrow-necked left ophthalmic aneurysm with a low recurrence and rupture risk could be embolized with simple coiling technique.
·The regular right tiny middle cerebral artery aneurysm, diameter less than 1mm, with a high risk of coiling, could be treated with simple stenting technique.
·多发颅内动脉瘤(双侧大脑中及左侧颈眼动脉瘤),动脉瘤有破裂风险,建议治疗。
·左侧大脑中动脉瘤,形态不规则,计划支架辅助栓塞。
·左侧窄颈颈眼动脉瘤,复发概率低、破裂风险小,采用弹簧圈单纯栓塞技术。
·右侧大脑中小动脉瘤,形体规则,动脉瘤直径小于1mm,填塞弹簧圈破裂风险大,采用单纯支架栓塞。

Figure 6. Measurements. Left middle cerebral artery aneurysm 2.8*2.1mm, AN neck 2.1mm, proximal parent artery diameter 2.9mm, superior branch diameter 2.9mm, inferior branch diameter 1.5mm. Ophthalmic aneurysm 2.4*2.7mm, AN neck 1.8mm, proximal parent artery diameter 4.1mm, distal parent artery diameter 3.6mm.
图 6. 测量。左侧大脑中动脉瘤,大小2.8*2.1mm,动脉瘤瘤颈2.1mm,近段载瘤动脉直径2.9mm,上干直径2.9mm,下干直径1.5mm。颈眼动脉瘤,大小2.4*2.7mm,动脉瘤瘤颈1.8mm,近段载瘤动脉4.1mm,远端载瘤动脉直径3.6mm。
2
Stent assisted coiling for left MCA AN
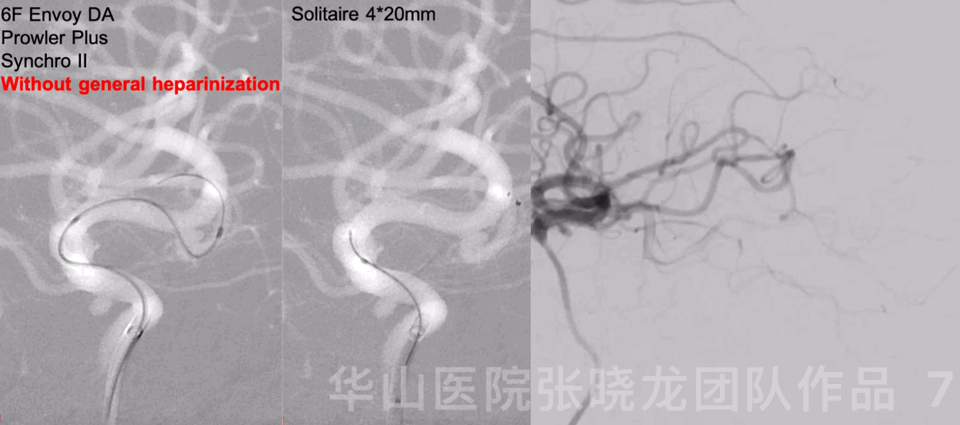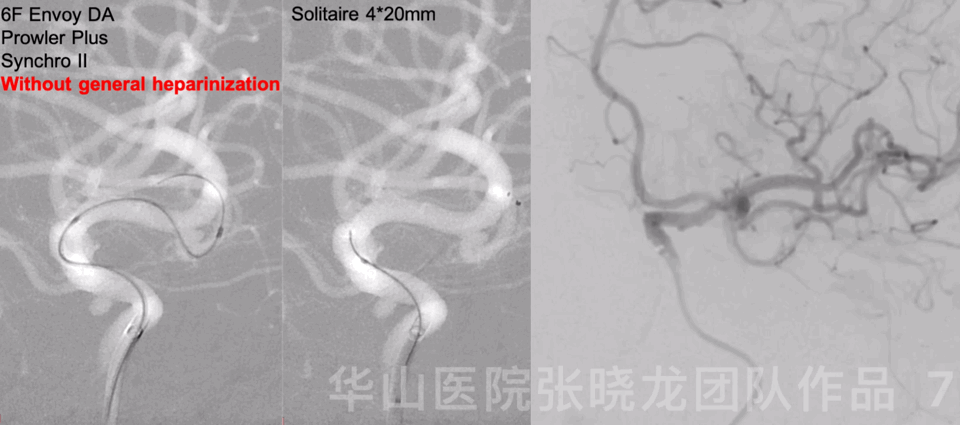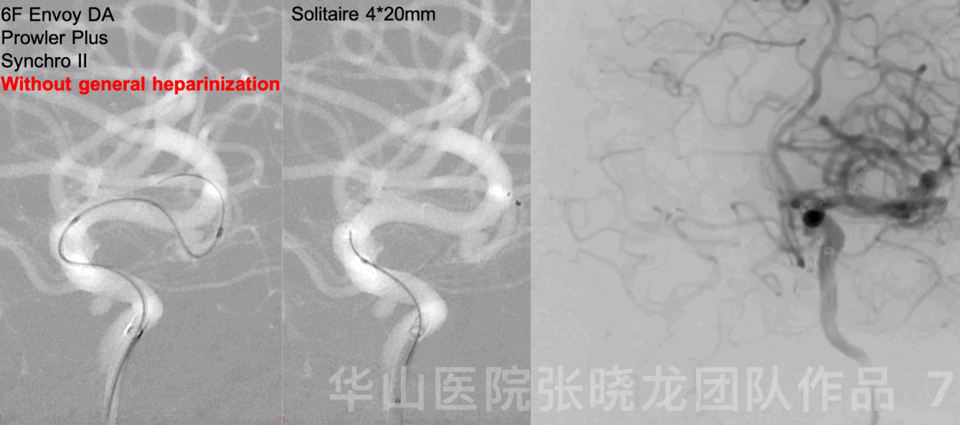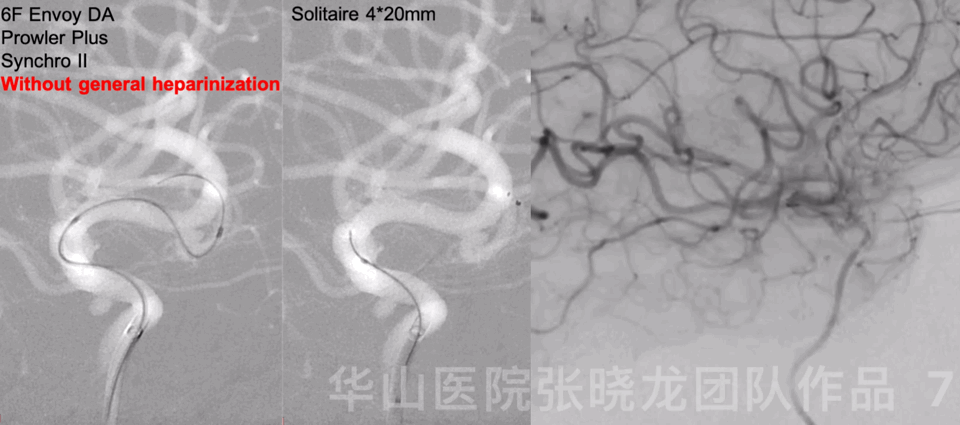
Figure 7 GIF. 6F Envoy DA was placed into the left cavernous sinus segment. C-tipped Prowler Plus was navigated into the left middle cerebral artery inferior branch via a Synchro II microwire. Solitaire 4*20mm was deployed covering the aneurysm neck. Rotational angiography showed the aneurysm sac became smaller.
图 7 GIF. 将6F Envoy DA导引导管至于左侧颈内动脉海绵窦段。Prowler Plus微导管头端塑C形后在Synchro II微导丝导引下置于左侧大脑中动脉M2段下干。瘤颈部释放Solitaire 4*20mm支架。旋转造影示动脉瘤瘤腔缩小。
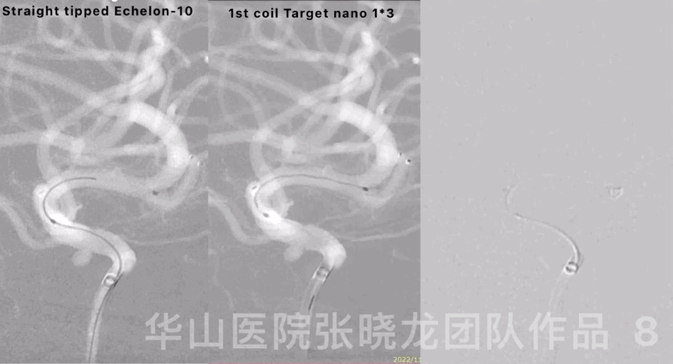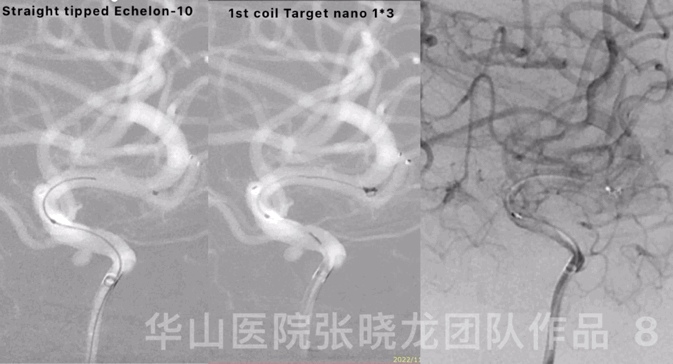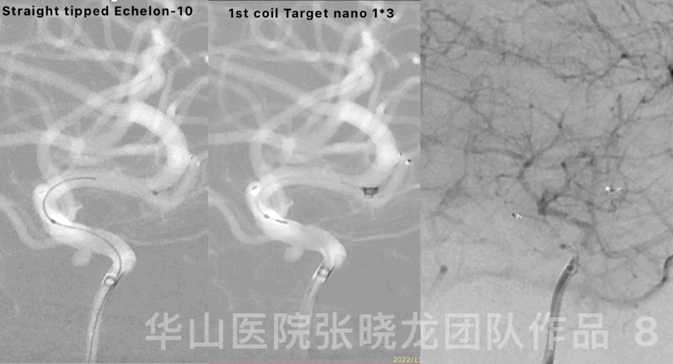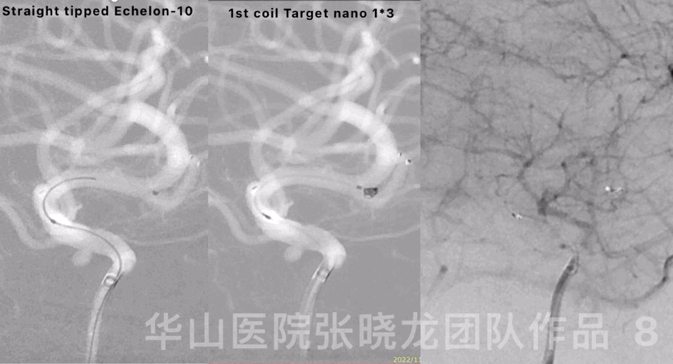
Figure 8 GIF. Reselected a working projection. Straight-tipped Echelon-10 microcatheter was navigated into the sac. Inserted the first coil, a Target nano 1mm*3cm.
图 8 GIF. 重新选择工作角度。将Echelon-10直头微导管置于动脉瘤瘤腔。填入第一枚弹簧圈Target nano 1mm*3cm。
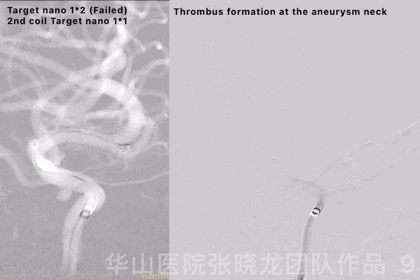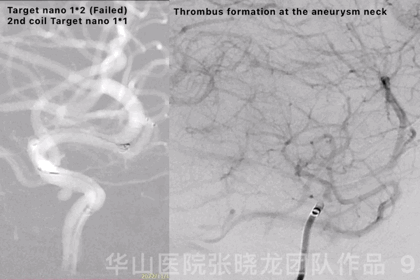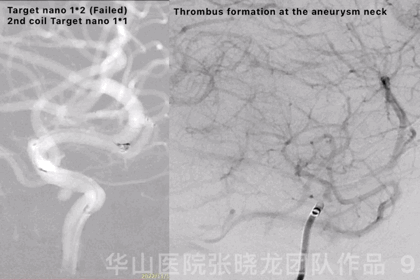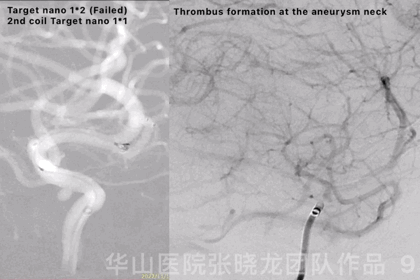
Figure 9 GIF. Failed to insert a Target nano 1mm*2cm. Continued with a smaller coil, a Target nano 1mm*1cm. Angiography revealed thrombus formation at the aneurysm neck and the aneurysm was densely packed. General heparinization was performed and Tirofiban 14ml was administered.
图 9 GIF. 尝试填入Target nano 1mm*2cm弹簧圈未能成功。更换Target nano 1mm*1cm弹簧圈后成功填入。造影提示动脉瘤瘤颈部血栓形成,动脉瘤致密栓塞。行全身肝素化,经导管给予替罗非班14ml。

Figure 10. The parent artery angle straightened significantly.
图 10. 载瘤动脉成交明显拉直。
3
Simple coiling for ophthalmic AN
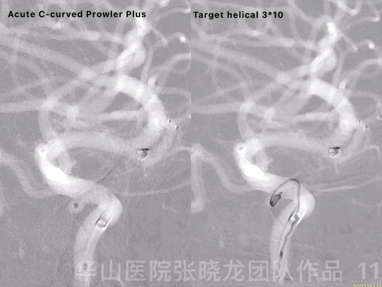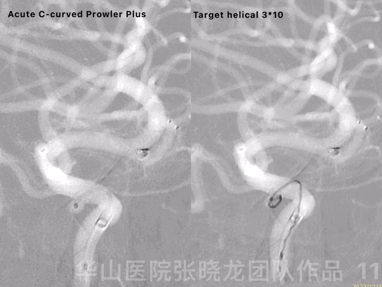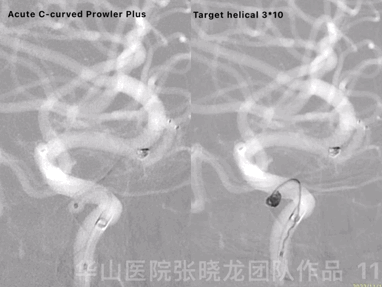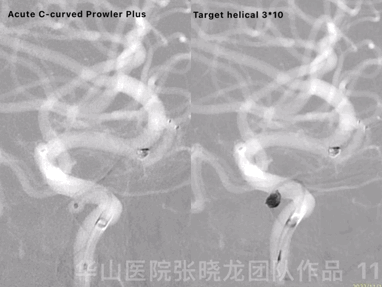
Figure 11 GIF. Prowler Plus with an acute C-curved tip was placed into the ophthalmic aneurysm sac via a Synchro II microwire. Inserted one Target helical 3mm*10cm coil successfully.
图 11 GIF. 将Prowler Plus头端塑急C弯后在Synchro-II微导丝支撑下置于颈眼动脉瘤瘤腔内。成功填入一枚Target helical 3mm*10cm弹簧圈。

Figure 12 GIF. The aneurysm neck thrombus resolved. Rotational DSA showed the two left aneurysms were densely packed.
图 12 GIF. 复查造影动脉瘤颈部血栓消失。旋转造影示左侧2枚动脉瘤均致密栓塞。

Figure 13 GIF. Left intracranial vessels remained intact.
图 13 GIF. 复查左侧颈内动脉造影,颅内血管完好,未见出血或血栓。
4
Simple stenting technique for R-MCA AN

Figure 14 GIF. The regular right tiny middle cerebral artery bifurcation aneurysm, diameter less than 1mm, was detected by angiography.
图 14 GIF. 造影证实右侧大脑中动脉分叉部形态规则的小动脉瘤,直径小于1mm。
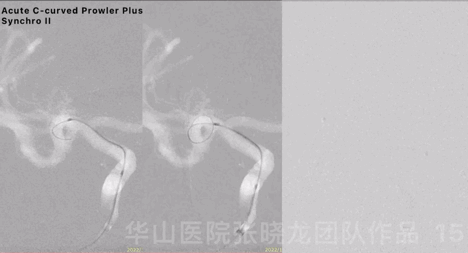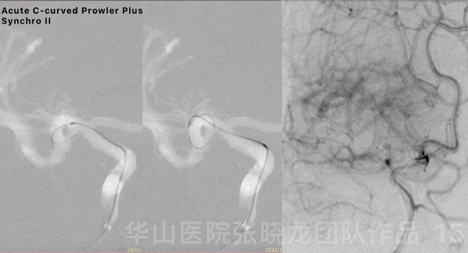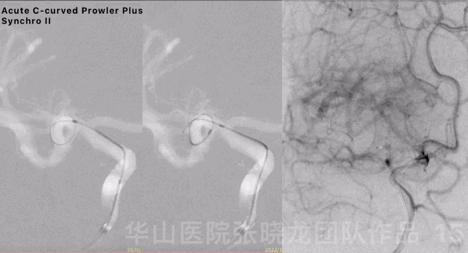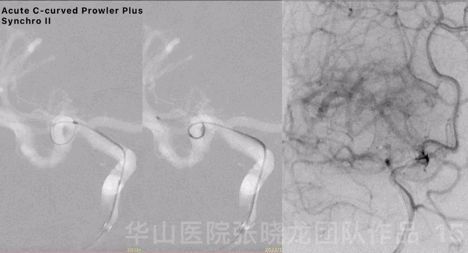
Figure 15 GIF. Acute C-curved Prowler Plus microcatheter was advanced into the right cerebral artery superior branch via Synchro II microwire, after 6F Envoy DA was positioned at the right cavernous sinus segment.
图 15 GIF. 6F Envoy DA导引导管置于右侧海绵窦段,Prowler Plus微导管头端塑急“C”弯后在Synchro-II导引下置于右侧大脑中动脉M2段上干。
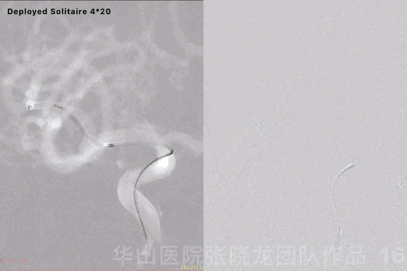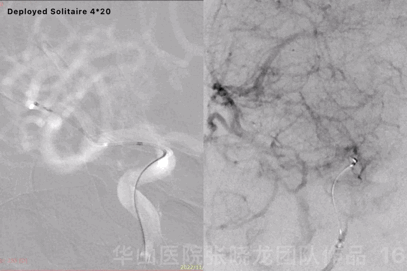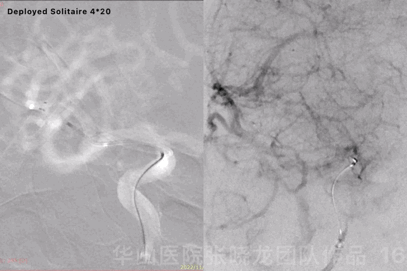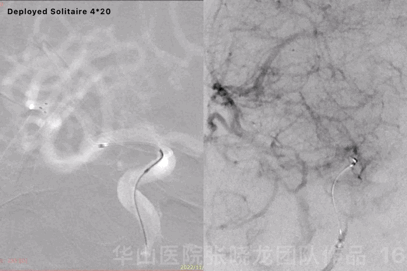
Figure 16 GIF. Solitaire 4*20mm was deployed at the aneurysm neck. Angiography displayed the aneurysm remained while the parent artery straightened.
图 16 GIF. 瘤颈部释放Solitaire 4*20mm支架。复查造影动脉瘤仍有显影,载瘤动脉拉直。

Figure 17 GIF. Right intracranial vessels remained intact.
图 17 GIF. 复查右侧颈内血管造影,颅内血管完好。

Figure 18. The parent artery straightened compared with pre-operation.
图 18. 与术前对比,载瘤动脉拉直。
Video 1. Reperformed a left internal carotid artery angiography, showing no thrombus formation. Dyna-CT demonstrated no hemorrhage.
视频 1. 再次复查左侧颈内动脉造影,证实无血栓形成。行Dyna-CT,未见出血。
5
Post-operation
·Tirofiban 14ml/h maintained for 24 hours then decreased to 7ml/h for another 24 hours.
·AA 74.8%, ADP 22.9%, CYP2C19 PM.
·Dual antiplatelets (Aspirin 100mg qd & Ticagrelor 45mg bid) were prescribed.
·NE: Bilateral normal muscle strength, eye movement normal, bilateral Babinski negative, no new neurological defect.
·替罗非班14ml/h维持24小时后减量至7ml/h,继续维持24小时。
·阿司匹林抑制率74.8%,氯吡格雷抑制率22.9%,氯吡格雷基因慢代谢。
·术后予双抗(阿司匹林100mg qd和替格瑞洛45mg bid)口服。
·查体:双侧肌力正常,眼球各项运动佳,双侧巴氏征阴性,无新发神经功能缺损。
Summary
·Multiple intracranial aneurysms including bilateral middle cerebral artery aneurysms and a left ophthalmic artery aneurysm should be treated to lower rupture risk.
·The irregular-shaped left middle cerebral artery aneurysm was treated with stent assisted coiling technique. As the aneurysm was not difficult to navigate into, a stent was deployed first.
·Jailing technique was not recommended to avoid microcatheter puncturing the tiny aneurysm.
·The narrow-necked left ophthalmic aneurysm with a low recurrence and rupture risk was embolized with simple coiling strategy.
·The narrow-necked left ophthalmic aneurysm was embolized by simple coiling.
·Single coiling technique was considered for the left ophthalmic aneurysm due to an unstable micro-catheter to avoid the first coil kicking out.
·The regular right tiny middle cerebral artery aneurysm, diameter less than 1mm, with a high risk of coiling, was treated with simple stenting technique, but long term follow-up was necessary.
·多发颅内动脉瘤(双侧大脑中及左侧颈眼动脉瘤),动脉瘤有破裂风险,建议治疗。
·左侧大脑中动脉瘤,形态不规则,采用支架辅助栓塞技术。由于栓塞微导管超选至动脉瘤腔难度不大,故先释放支架再填弹簧圈。
·由于动脉瘤较小,为防止微导管刺破该动脉瘤,不建议采用jailing技术。
·左侧窄颈颈眼动脉瘤,复发概率低、破裂风险小,采用弹簧圈单纯栓塞技术。
·左侧颈眼窄颈动脉瘤采用单纯弹簧圈栓塞。
·由于微导管不稳定,同时避免第一枚弹簧圈被踢出,故采用单个弹簧圈栓塞左侧颈眼动脉瘤。
·右侧大脑中小动脉瘤,形体规则,动脉瘤直径小于1mm,填塞弹簧圈破裂风险高,采用单纯支架栓塞;但仍需长期随访。
张晓龙
复旦大学附属华山医院
复旦大学附属华山医院放射科主任医师,博士、教授、博士生导师;
斯坦福大学医学院客座临床教授;
主持国家自然科学基金3项,第一作者或通讯作者发表国内外权威期刊文章50余篇;
中华医学会、放射学会、卫生部医政司等组织中担任副主任委员、组长等职务.《中国名医百强榜》神经介入专业中国十强(2012年度、2013年度、2014年度、2015-16年度、2017-18年度);
擅长复杂和疑难脑血管疾病的介入治疗,如复杂脑动脉瘤的栓塞,硬脑膜动静脉瘘栓塞,脑动静脉畸形栓塞,脑梗死的支架,脊髓血管畸形治疗;
自1995年开始从事脑血管疾病介入诊治工作和研究,师从黄祥龙教授、沈天真教授和凌锋教授,是我国最早从事神经介入的专家之一。2010年9月至今连续介入治疗颅内动脉瘤1500余例,无操作致死。
点击或扫描上方二维码,
前往 张晓龙教授 学术主页
查看更多精彩内容
点击或扫描上方二维码
查看更多“介入”内容







