Review
• 58 y/o, female.
• CC: Suffered from dizziness for 3 months. An anterior-wall ophthalmic aneurysm was detected from MRA in local hospital.
• Medical history: HTN for 10 years well-controlled. Meniere’s disease for 3 months.
• PE: (-)
• 58岁,女性。
• 主诉:头晕3月,当地医院MRA检查发现前壁颈眼动脉瘤。
• 病史:高血压10余年,血压控制良好。诊断美尼尔症3月。
• 体格检查:阴性。
Video 1. DSA shows a right irregular anterior-wall ophthalmic aneurysm with a daughter sac.
视频 1. DSA证实右侧前壁不规则颈眼动脉瘤伴子瘤。
1
Strategy
• Since the irregular anterior-wall ophthalmic aneurysm has a daughter sac, the aneurysm has a high rupture risk due to flow impingement. Stent-assisted coil embolization is preferred for this wide-necked aneurysm.
• For the proximal tortuous route, Navien guiding catheter with a long-sheath is selected. General heparinization should be performed before navigating the guiding catheter.
• The daughter sac should be embolized to decrease the risk of delayed postoperative bleeding.
• 前壁不规则宽颈颈眼动脉瘤伴子瘤,破裂风险高,首选支架辅助栓塞治疗。
• 由于近端血管迂曲,选择Navien导引导管带长鞘。上导引导管前先全身肝素化。
• 为减少术后迟发性出血,应栓塞子瘤。

Figure 1 GIF. General heparinization 90cm long sheath+ 115cm 6F Navien.
1. The long-sheath was in the ICA proximal segment.
2. The guiding wire straightened the tortuous curve. Navien was in position.
3. Retrieve the guide wire and push the Navien guiding catheter complying to the previous ICA shape to prevent vasospasm and thrombosis.
4. Angiography confirmed no contrast medium stagnation.
图 1 GIF. 全身肝素化 90cm长鞘+115cm 6F Navien导引导管。
1. 长鞘置于颈内动脉起始段。
2. 在导引导丝导引下将导引导管置于海绵窦段。
3. 导引导管到位后撤回导引导丝,向前推动导引导管,顺应性良好,从而减少血管痉挛和血栓形成。
4. 造影证实无造影剂滞留。
2
Operation
Video 2. Angiography after guiding shows the thrombosis might have been formed.
视频 2. 造影显示可疑血栓形成。
Video 3. After placing a XT-27 microcatheter in the parent artery, an Echelon-10 45° shaped into an S curve was navigated to the aneurysmal sac. Neuroform 4*15mm was deployed via the XT-27 covering the aneurysmal neck.
视频 3. 将XT-27微导管置于载瘤动脉,Echelon-10 45°塑 “S”型后超选入动脉瘤腔内。于瘤颈部释放Neuroform 4*15mm支架。
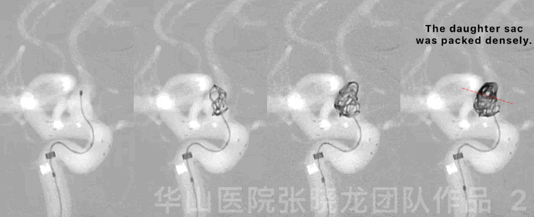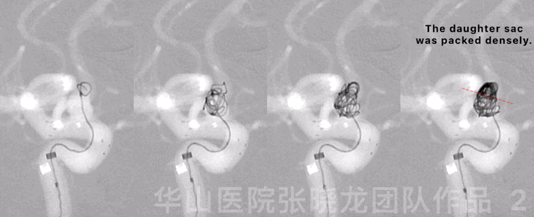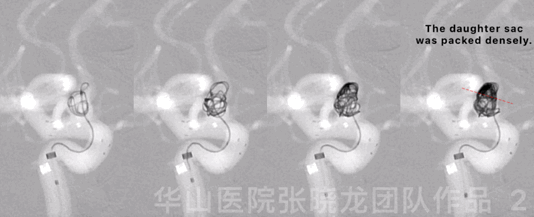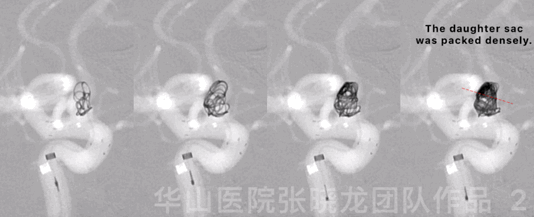
Figure 2 GIF. Four Target-360 4mm*8cm coils were inserted into the aneurysmal sac.
图 2 GIF. 瘤腔内填入4枚Target-360 4mm*8cm弹簧圈。
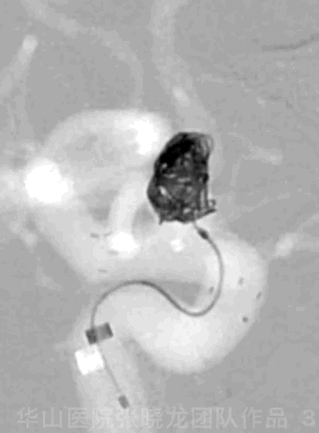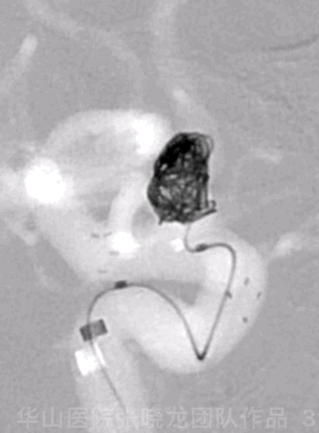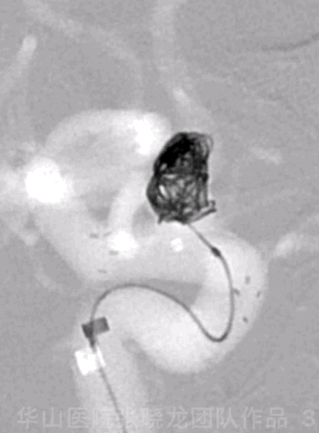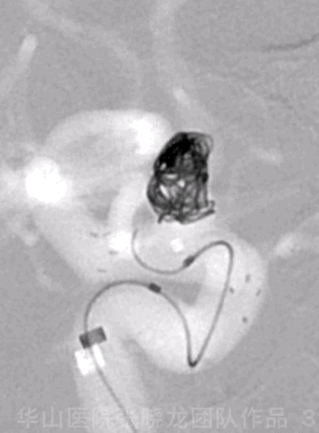
Figure 3 GIF. A Target-helical 4mm*8cm coil was unable to be inserted.
图 3 GIF. 尝试将Target-helical 4mm*8cm弹簧圈填入瘤腔,未能成功。

Figure 4 GIF. Renavigating the microcatheter into the aneurysm sac.
图 4 GIF. 将微导管重新超选入动脉瘤内。

Figure 5 GIF. Another two Target-360 coils were inserted.
图 5 GIF. 继续填入2枚Target-360弹簧圈。

Figure 6 GIF. Thrombosis formed in the proximal MCA segment.
图 6 GIF. 大脑中动脉近端血栓形成。

Figure 7 GIF. The thrombosis was flushed away into the parietal-occipital branch after retrieving the guiding catheter.
图 7 GIF. 导引导管撤回后见右侧大脑中动脉枕顶支闭塞。

Figure 8 GIF. Improved blood flow of the right MCA after using Tirofiban 21ml (12ml+4ml+5ml) in 60 minutes. ACT: 207 sec, heparin 1ml.
图 8 GIF. 60分钟内共间断使用替罗非班21ml(12ml+4ml+5ml),右侧大脑中动脉血流改善。ACT:207秒,追加肝素1ml。

Figure 9. Left VA angiography in the same working projection revealed that the ipsilateral PCA compensated the right parietal-occipital branch territory via the pia anastomosis.
图 9. 相同工作角度的左椎动脉造影提示,右侧从大脑后动脉通后软膜吻合代偿。
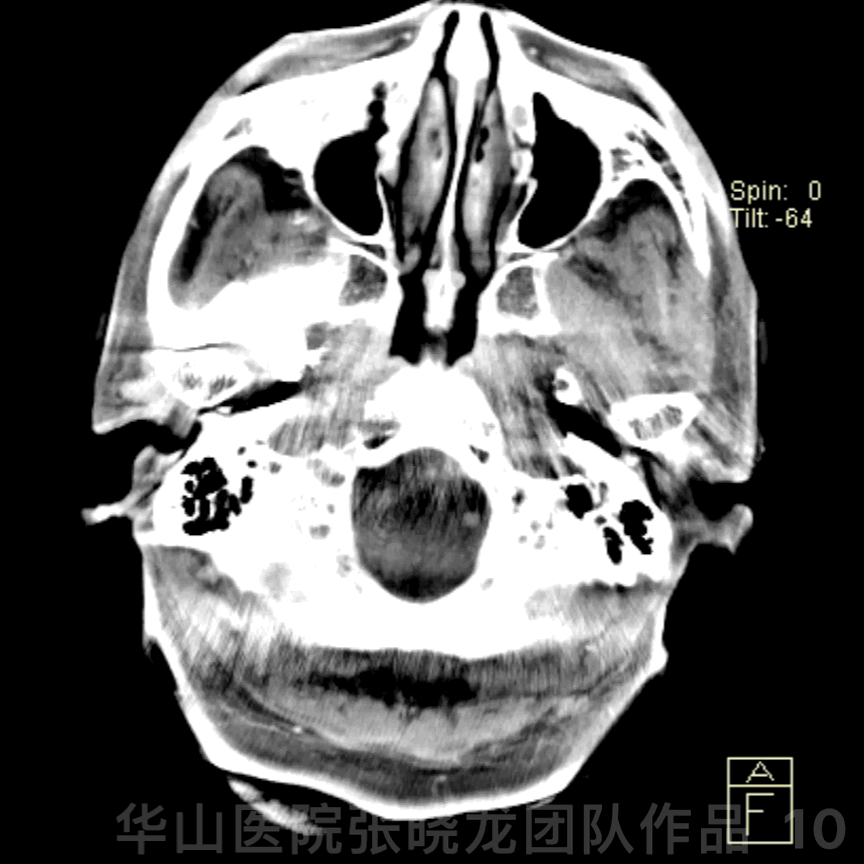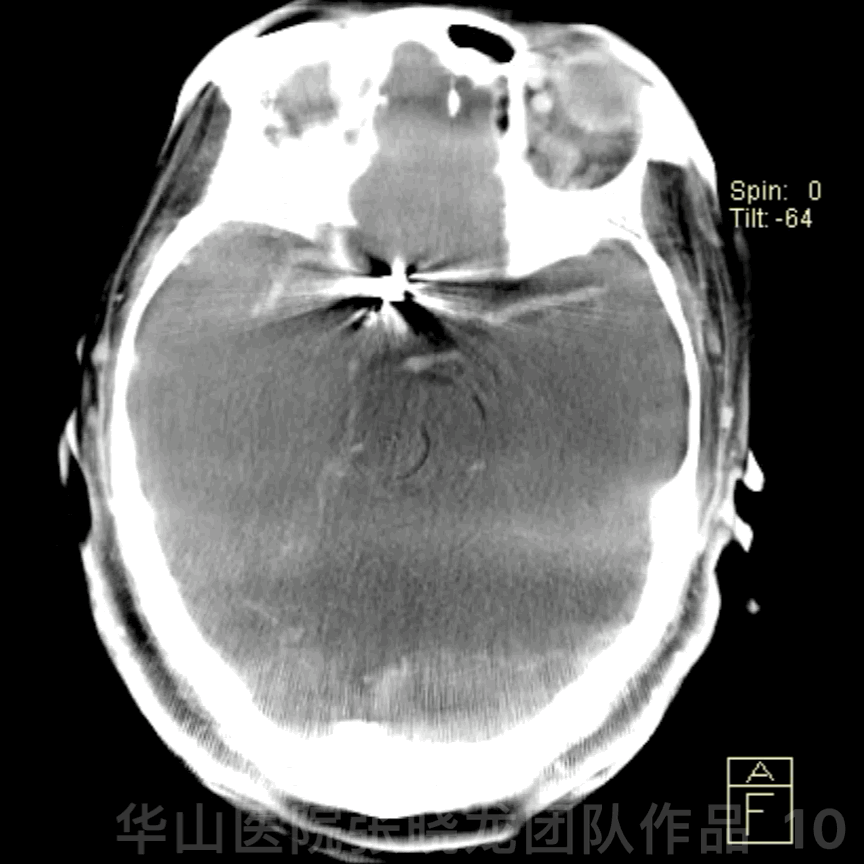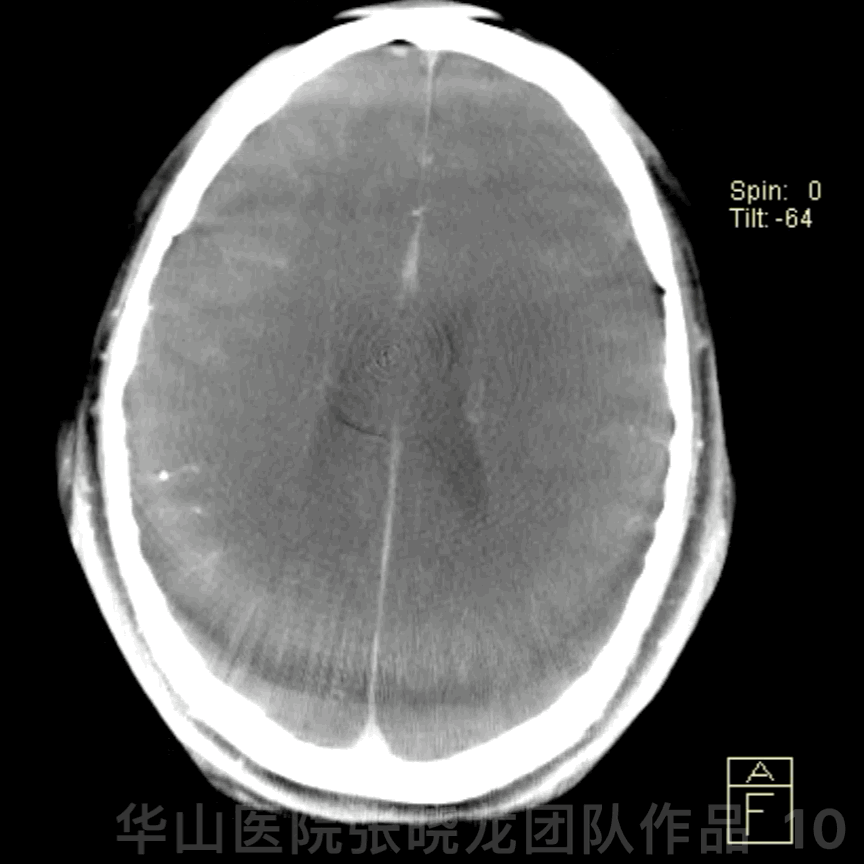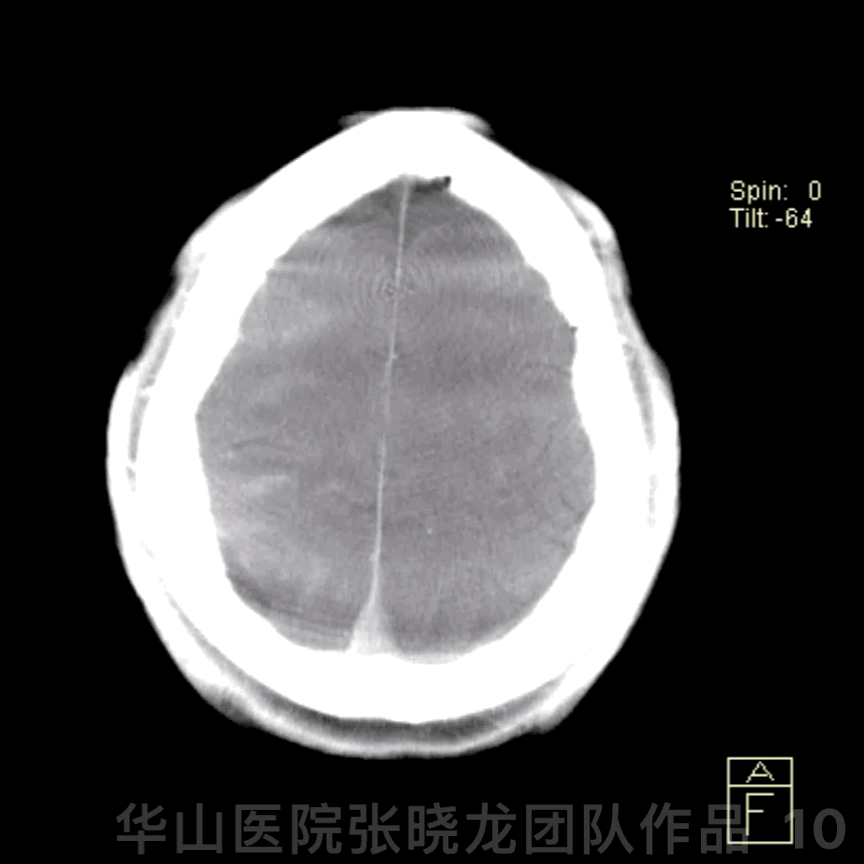
Figure 10 GIF. Post-operative DynaCT (-); PE (-)
图 10 GIF. 术后DynaCT未见出血,神经查体未见异常。

Figure 11. CT 4 hours later: No hemorrhage or infarctions.
图 11. 术后4小时CT:未见出血及梗塞。

Figure 12. MRI DWI 48 hours later: Right temporal and occipital lobe infarction without significant symptoms, especially no visual deficiency.
图 12. 术后48小时头颅MRI DWI序列:右侧颞叶及枕叶皮层无症状性梗死灶。
3
Post Operation
• GCS 15, bilateral strength normal, bilateral pupil movement normal and light reflux normal, Babinskin negative.
• Tirofiban 8ml/h maintained 48 hours.
• ADP 55.7% and AA 93.1%
• At discharge: Clopidogrel for 3 months and Aspirin for long term.
• GCS 15分,四肢肌力正常,双侧眼球运动正常,瞳孔对光反射灵敏,双侧巴氏征阴性。
• 术后替罗非班8ml/h微泵维持48小时。
• 血栓弹力图:氯吡格雷抑制率55.7%,阿司匹林抑制率93.1%。
• 出院:氯吡格雷口服3月,阿司匹林长期口服。
4
Follow-up (9-month)

Figure 13 GIF. 9-month follow up angiography shows the precious occluded artery was patent.
图 13 GIF. 9个月随访造影示术后即刻闭塞的血管再通。

Figure 14 GIF. No relapse of the aneurysm. Stop Aspirin. Next follow up was scheduled in 2-3 years.
图 14 GIF. 动脉瘤无复发及残留。建议停阿司匹林。2-3年后再随访。
Summary
Since the irregular anterior-wall ophthalmic aneurysm has a daughter sac, the aneurysm has a high rupture risk due to flow impingement. Stent-assisted coil embolization is preferred for this wide-necked aneurysm.
For the proximal tortuous route, Navien guiding catheter with long-sheath is selected. General heparinization should be performed before navigating the guiding catheter.
1. The long-sheath was in the ICA proximal segment.
2. The guiding wire straightened the tortuous curve. Navien was in position.
3. Retrieve the guide wire and push the Navien guiding catheter conforming to the previous ICA shape.
4.Angiography confirmed no contrast medium stagnation.
The infusion system must be opened fluently in the long sheath in the ICA.
Large coiling technique was adopted to decrease recurrence risk because of the stable guiding catheter. The daughter sac should be embolized to decrease the delayed postoperative bleeding. When the thrombosis was flushed away into the parietal-occipital branch after retrieving the guiding catheter, Tirofiban was administered via the guiding catheter. Left VA angiography in the same working projection revealed that the ipsilateral PCA compensated the right parietal-occipital branch territory via the pia anastomosis.
前壁不规则宽颈颈眼动脉瘤伴子瘤,破裂风险高,首选支架辅助栓塞治疗。由于近端血管迂曲,选择Navien导引导管带长鞘。上导引导管前先全身肝素化。
1. 长鞘置于颈内动脉起始段。
2. 在导引微导丝导引下将导引导管置于海绵窦段。
3. 导引导管到位后撤回导引导丝,向前推动导引导管,顺应性良好,从而减少血管痉挛和血栓形成。
4. 造影证实无造影剂滞留。
长鞘在颈内动脉时必须打开滴注。
由于导引导管稳定,为降低复发栓塞动脉瘤时选用大圈。为减少术后迟发性出血,须栓塞子瘤。撤回导引导管后枕顶支主干内血栓形成,遂经导引导管给予替罗非班。相同工作角度的左椎造影提示右侧大脑后动脉通后软膜吻合代偿右侧顶枕支供血区。




