本文为《Navigating the Ventricles》这一章节的第二部分,主要介绍了颞叶内侧面解剖及其相关入路。共截取266张图片。
《Navigating the Ventricles》第一部分请参见《幕上解剖(1)---Rhoton解剖视频学习笔记系列》

笔者水平所限,错误之处请批评指正!
幕上解剖(2)
Navigating the Ventricles(2)
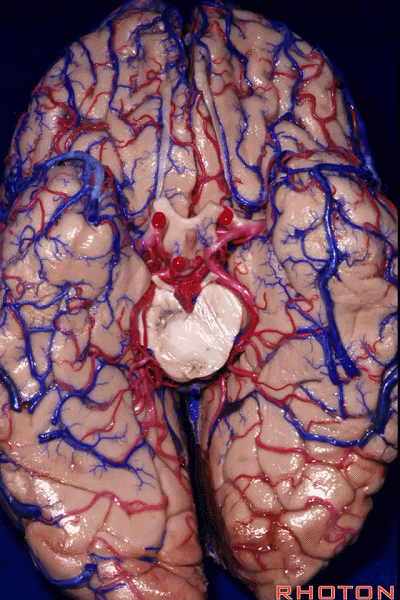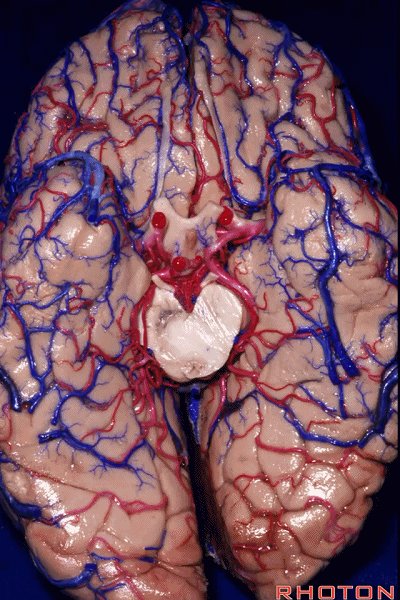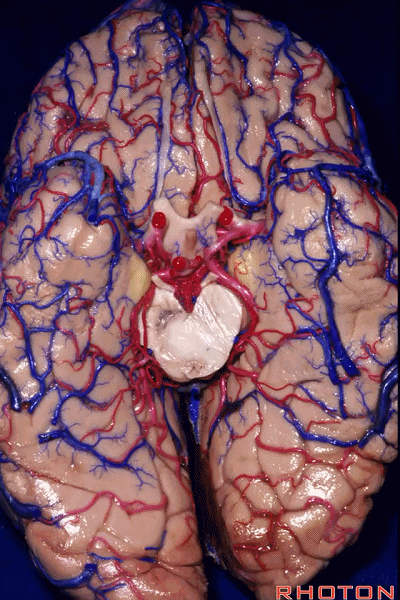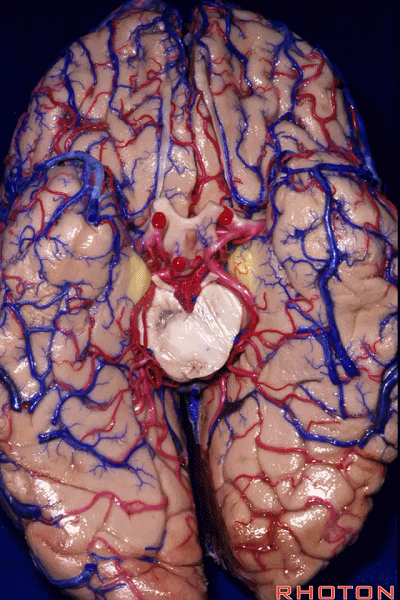
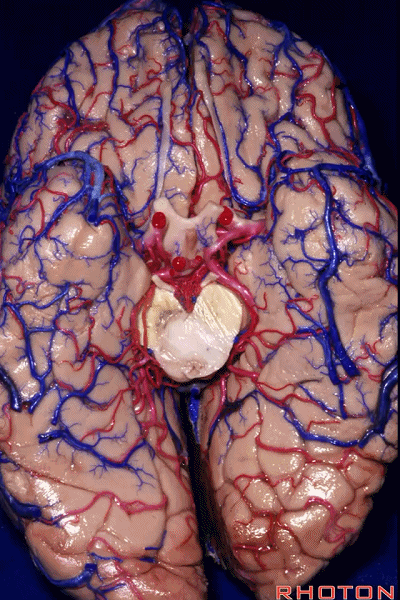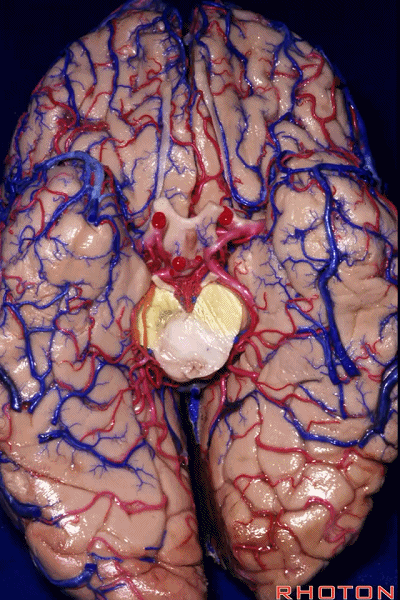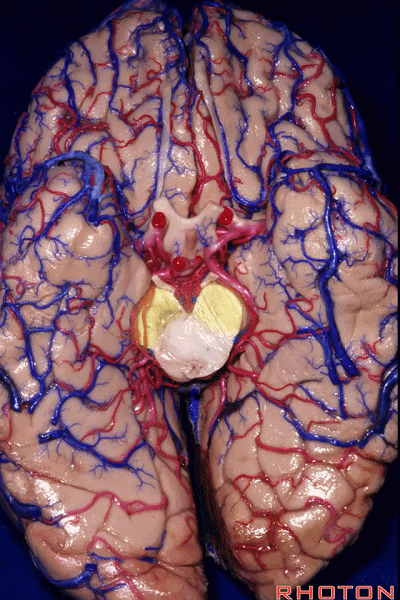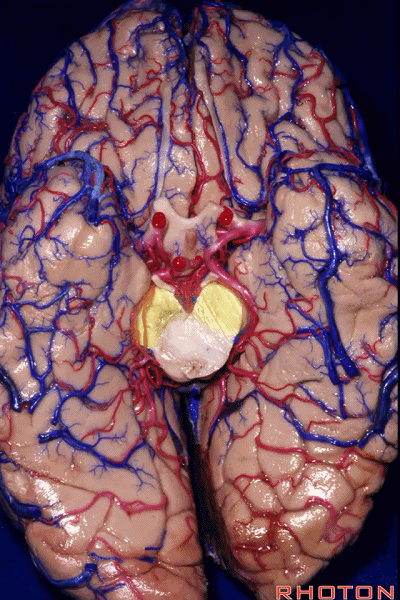
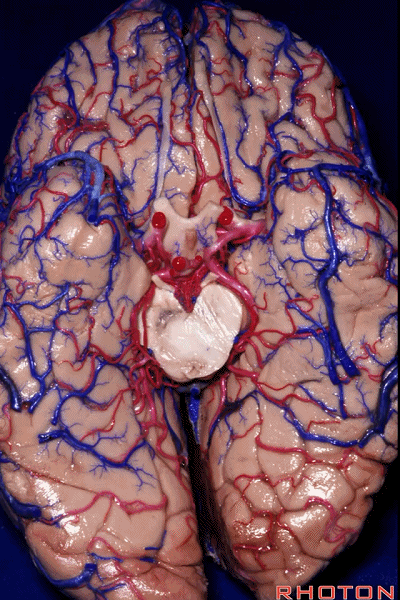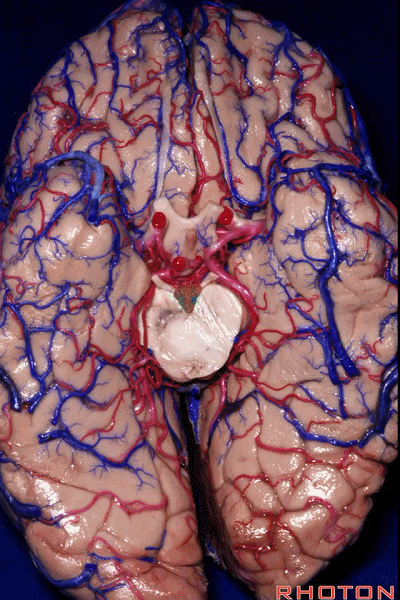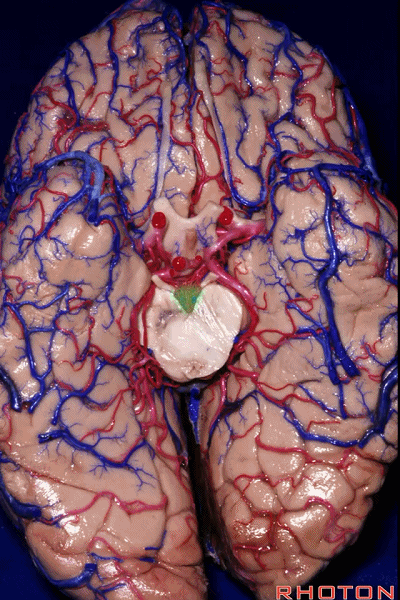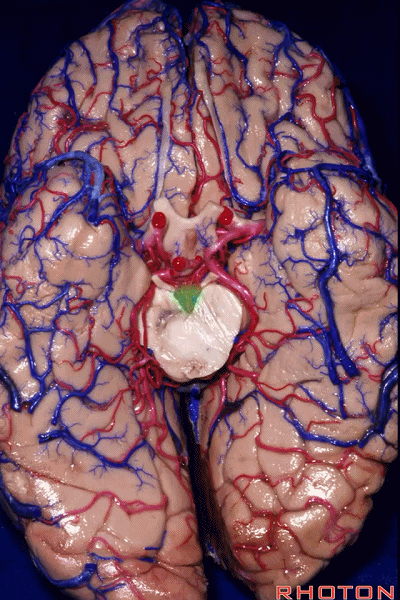
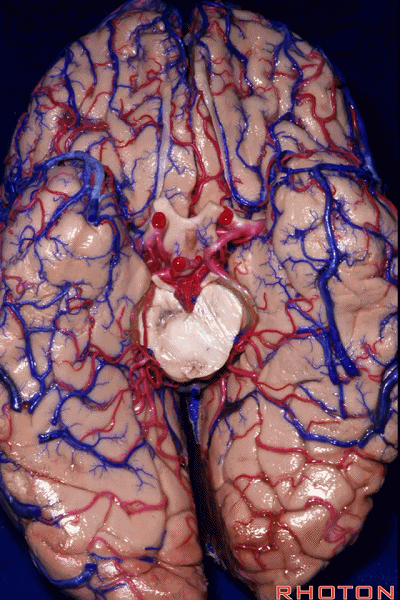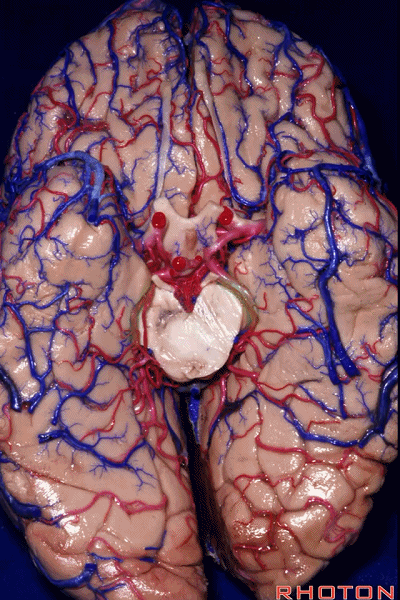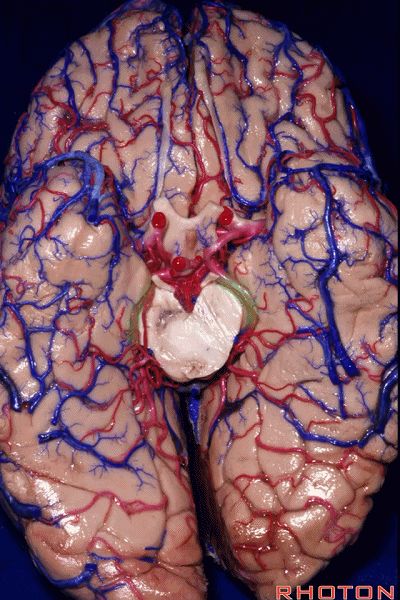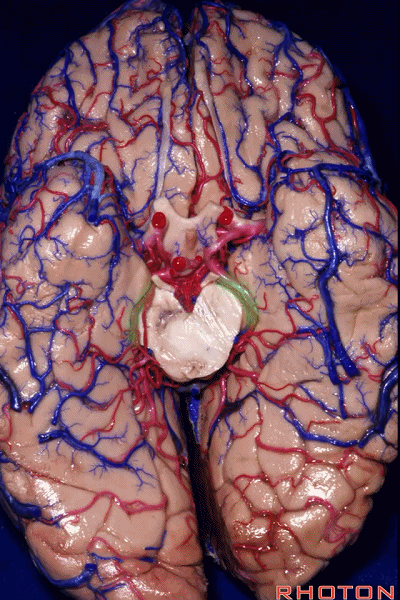
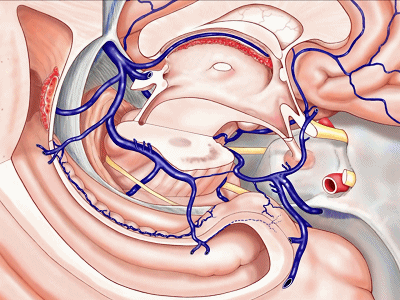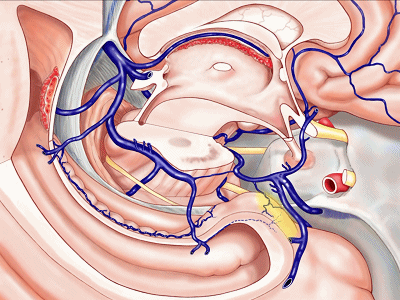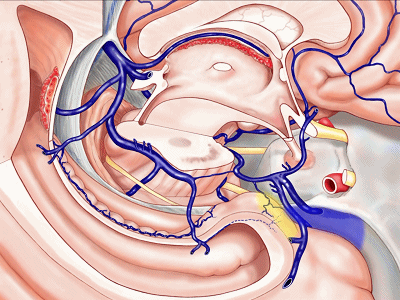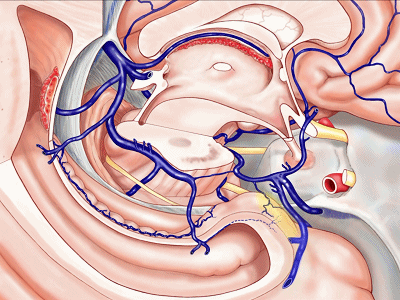
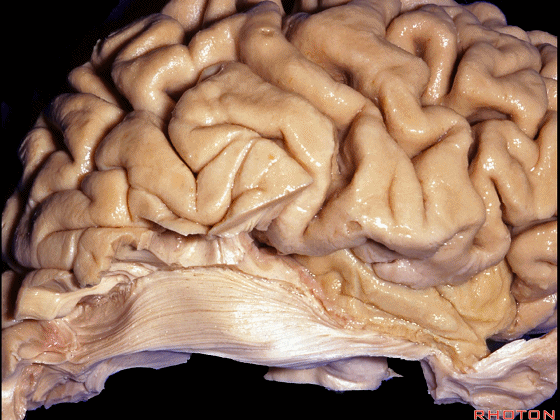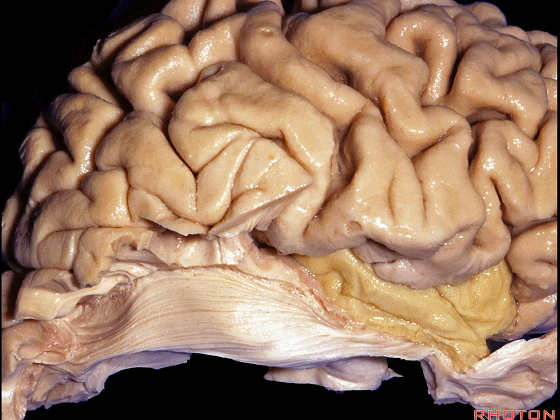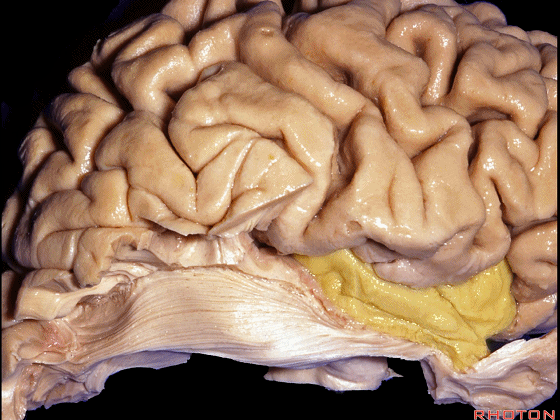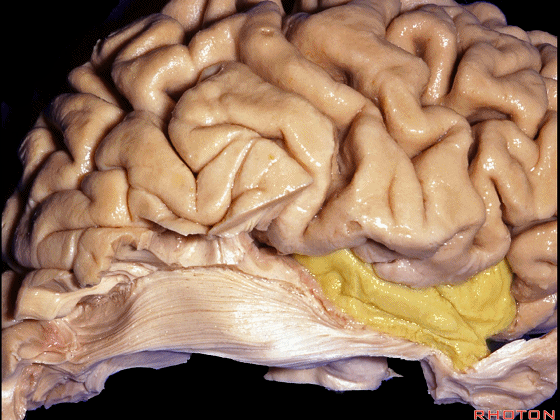
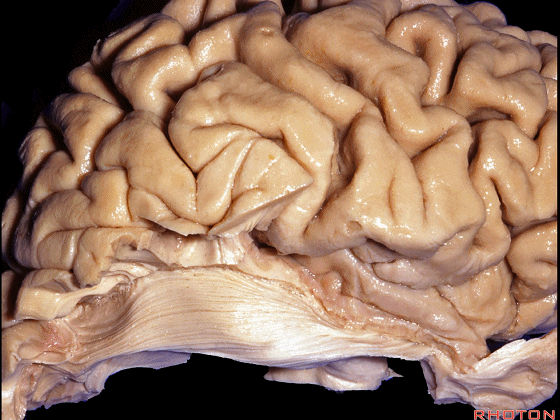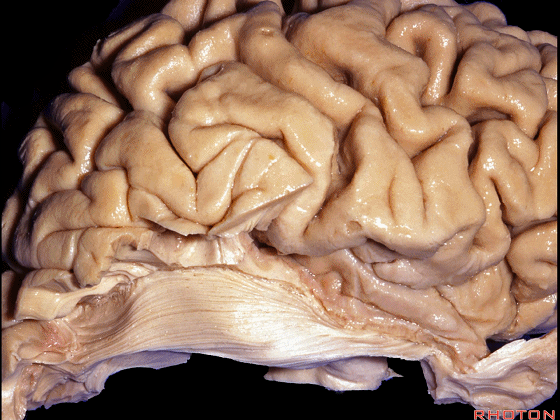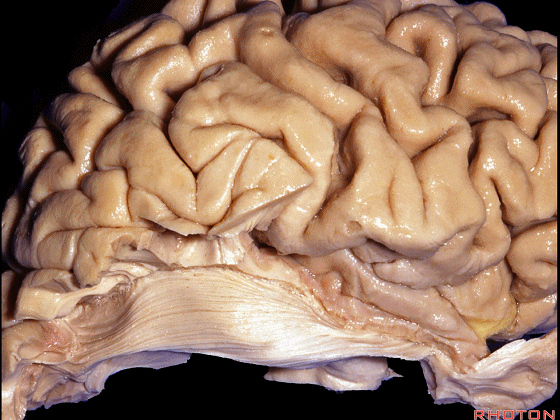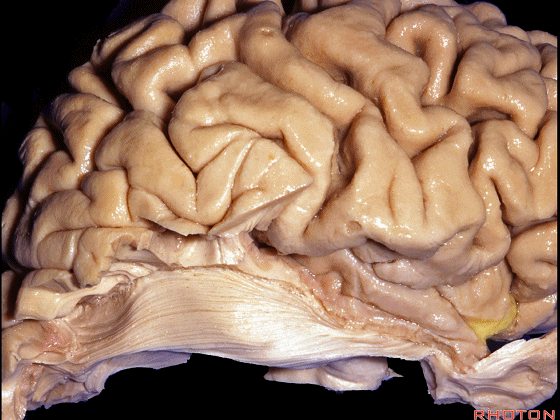
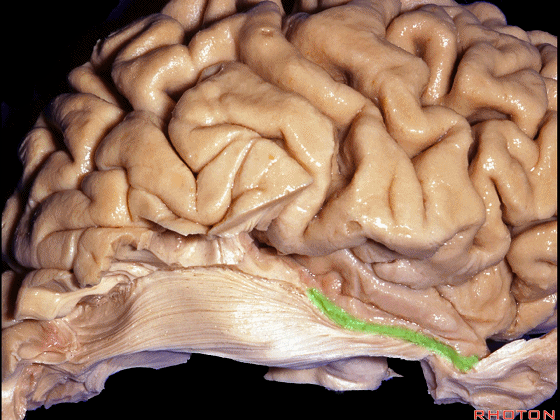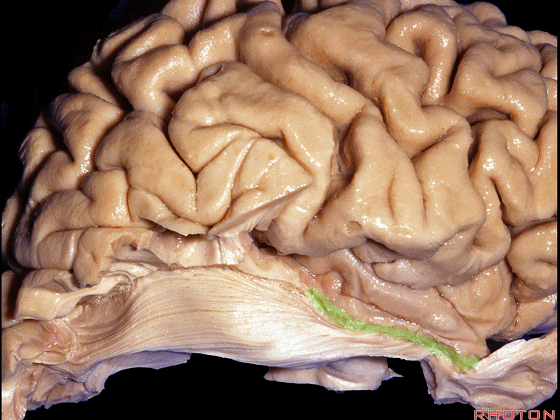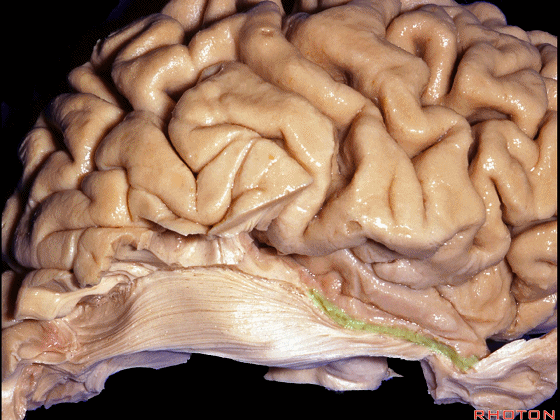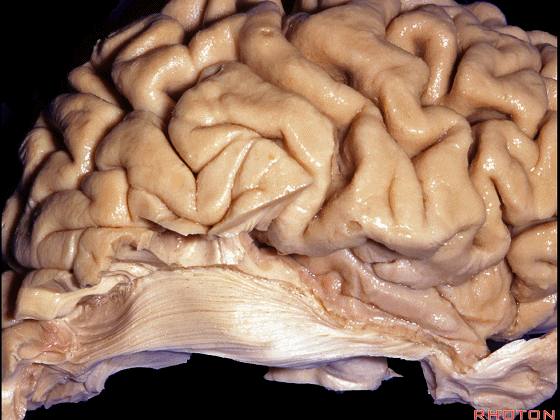
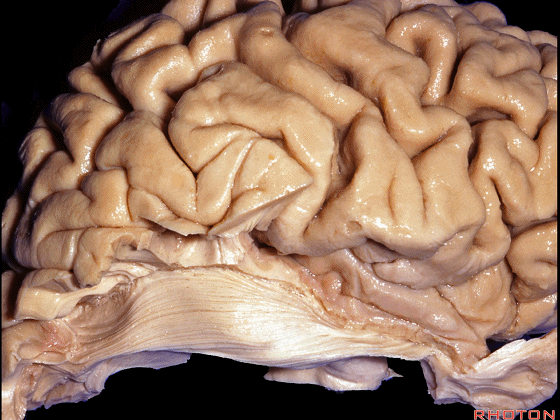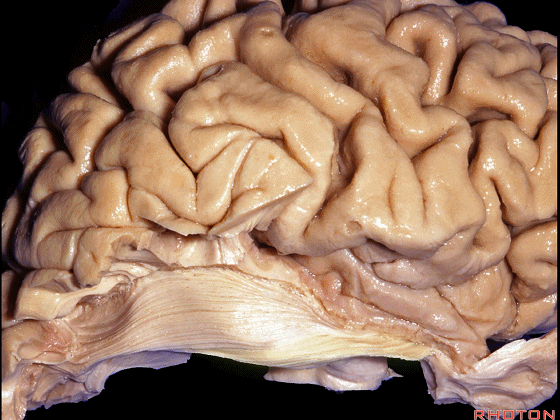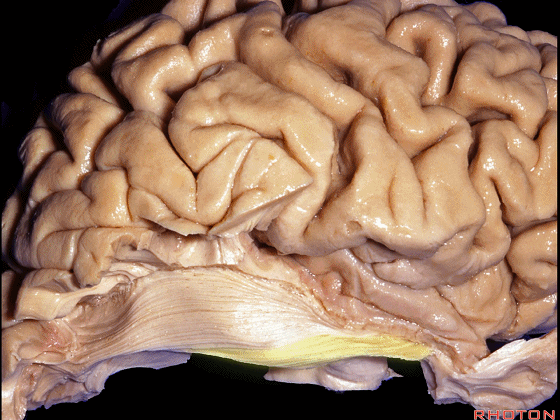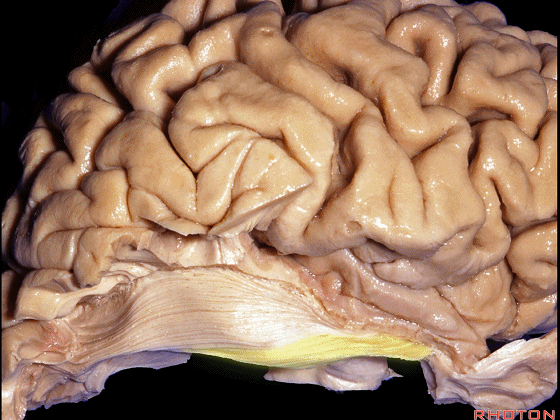
▼今天我们来讲颞叶。
Now we move on around to the temporal lobe,
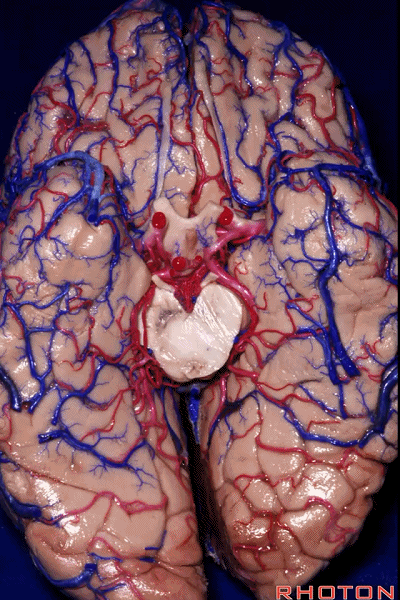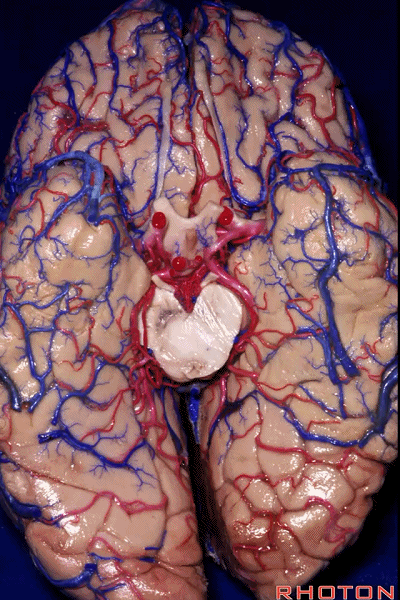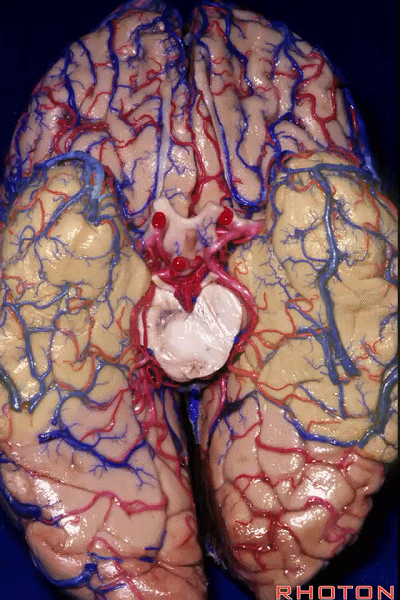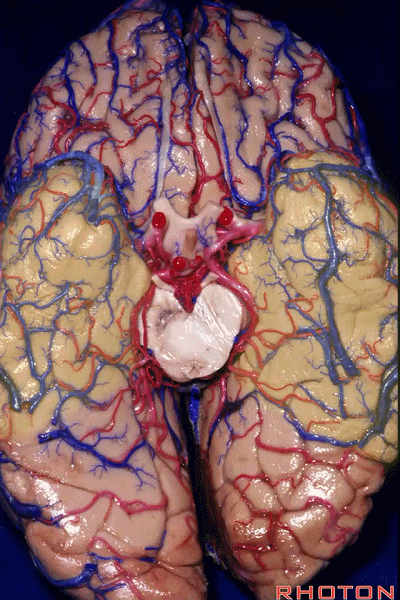
▼颞叶从外向内 向上倾斜。
and notice how the temporal lobe slopes upward as you go from lateral to medial.
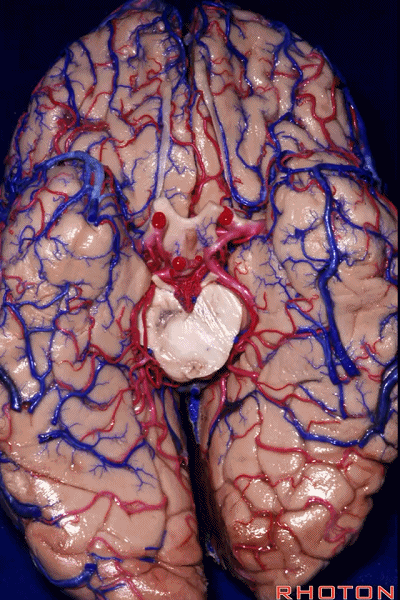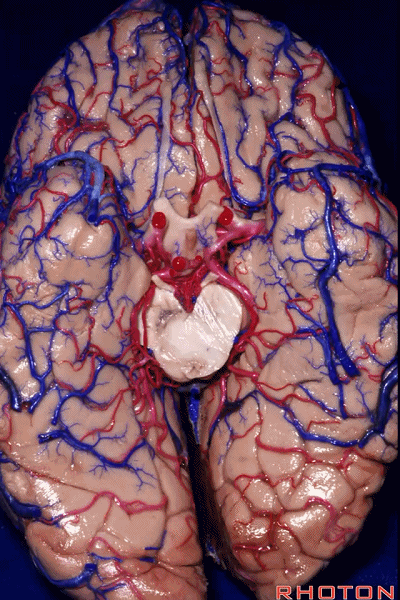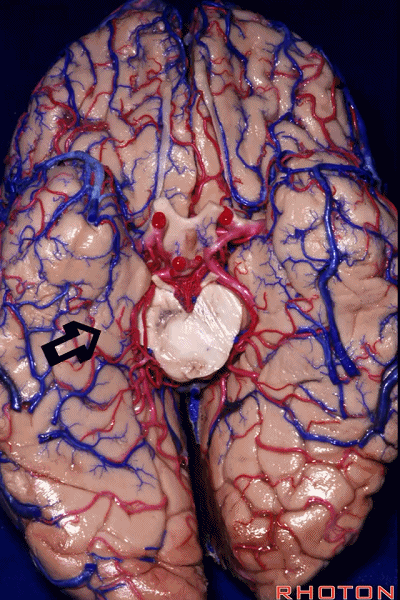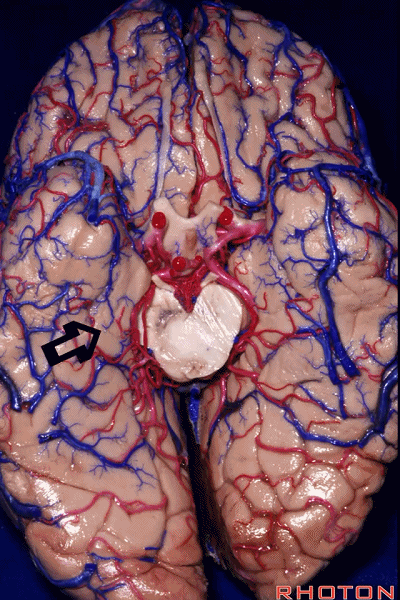
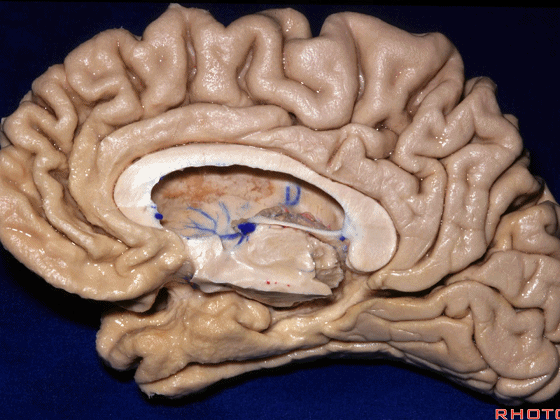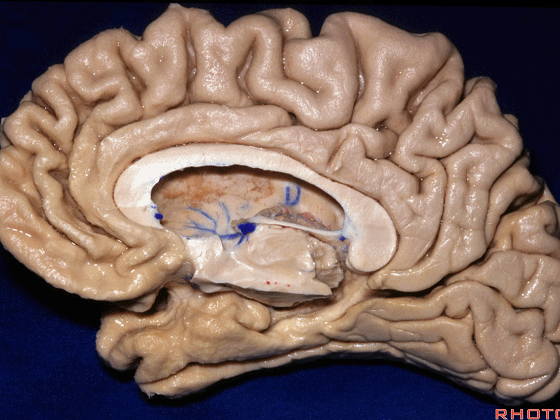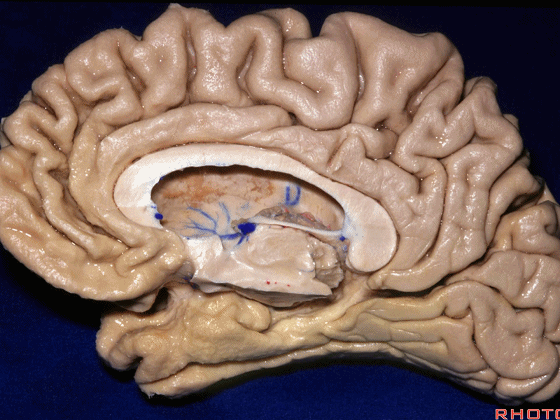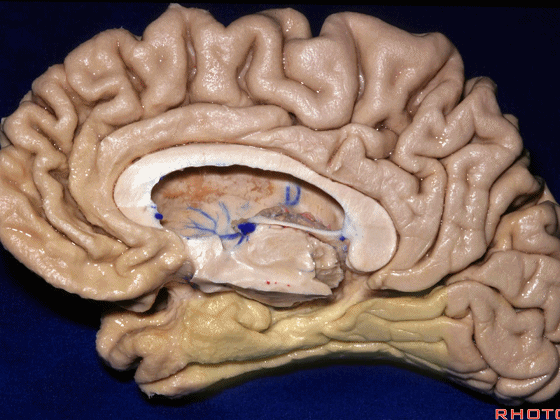
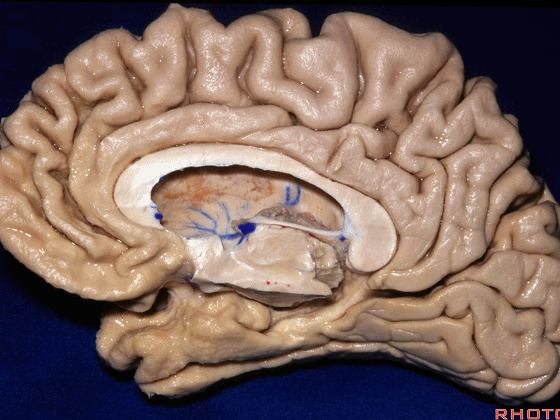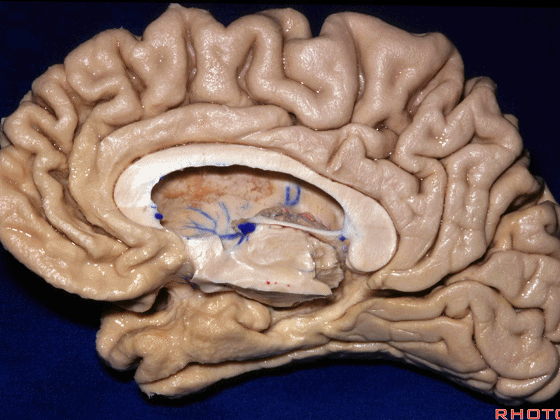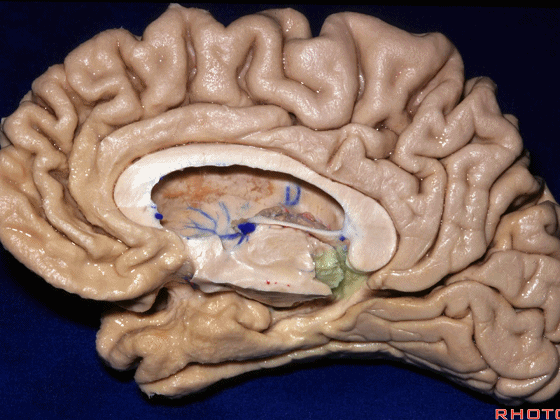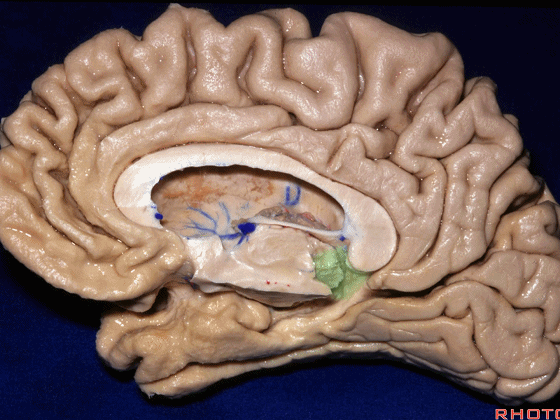
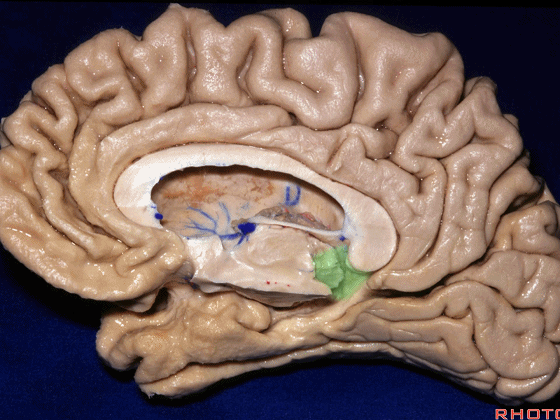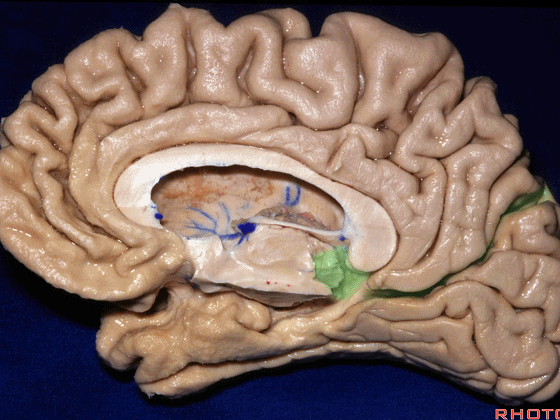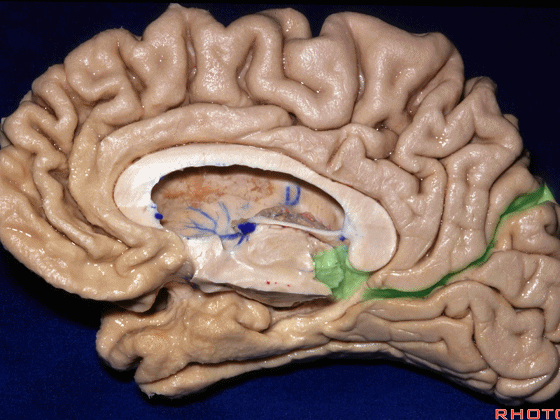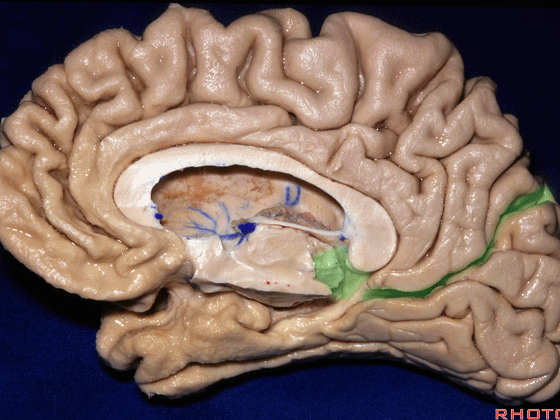
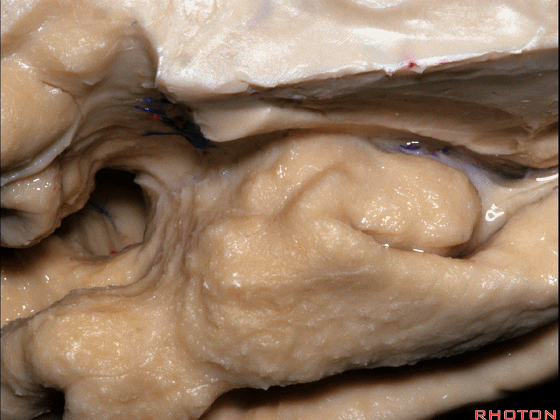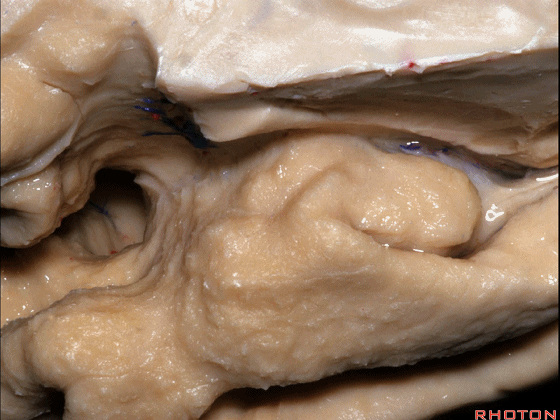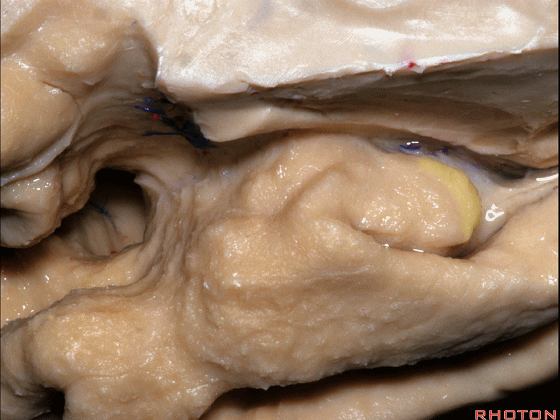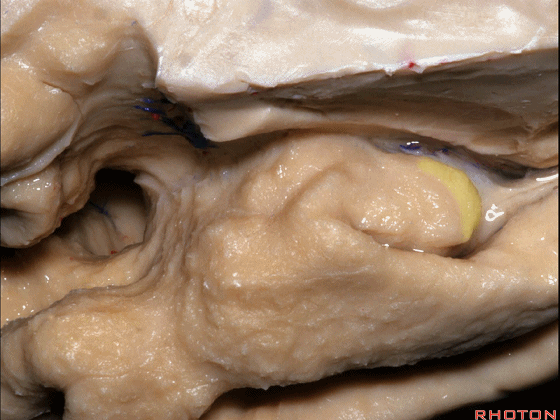
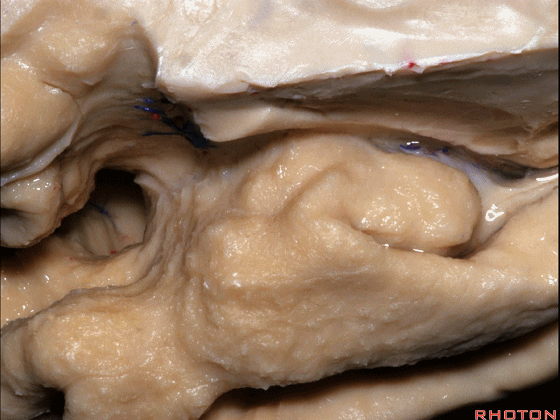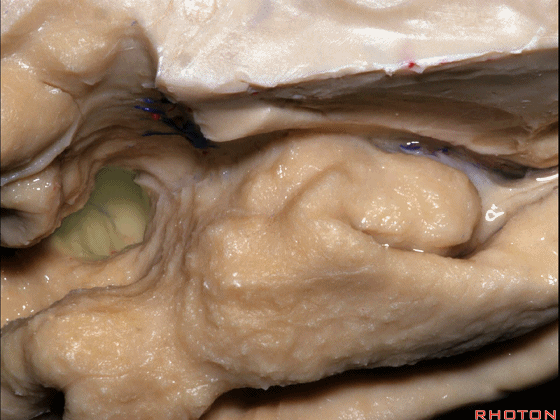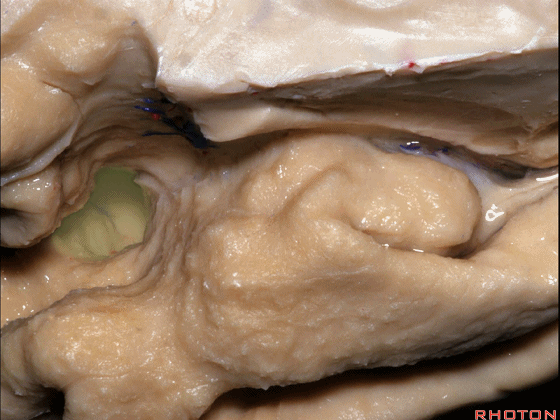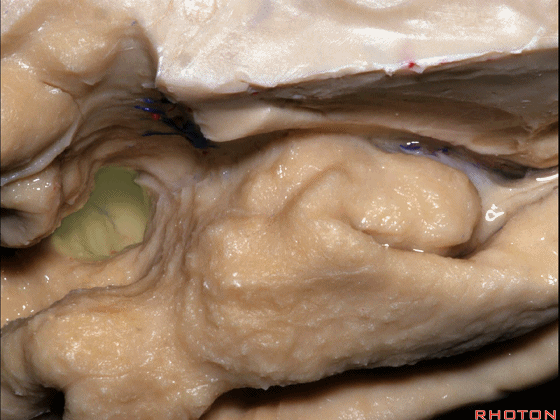
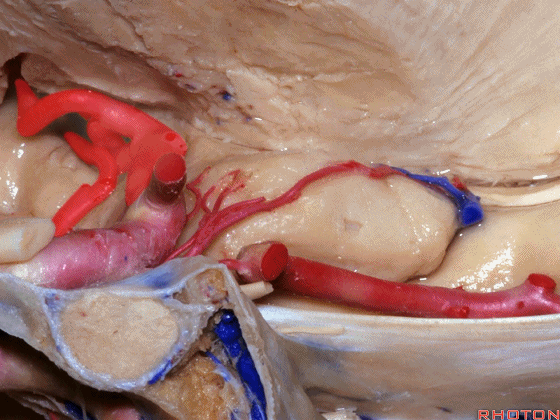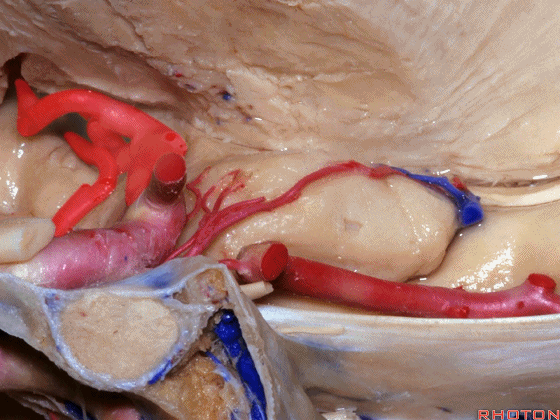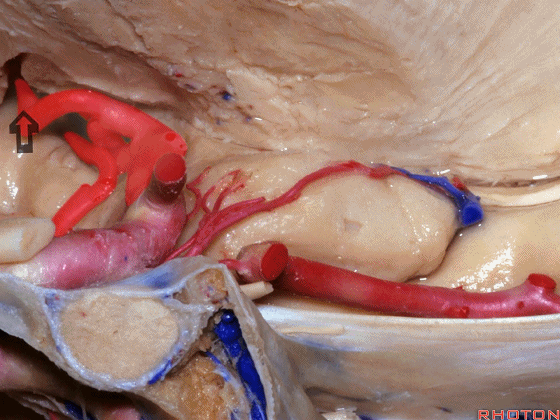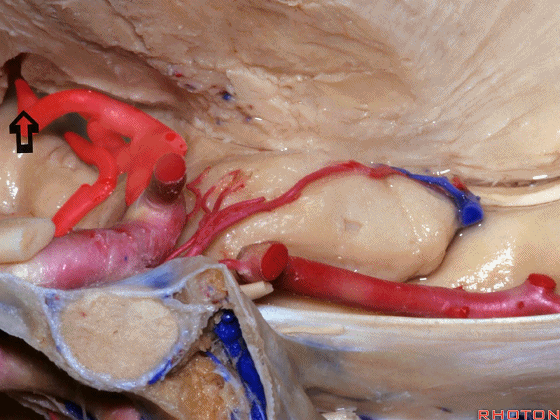
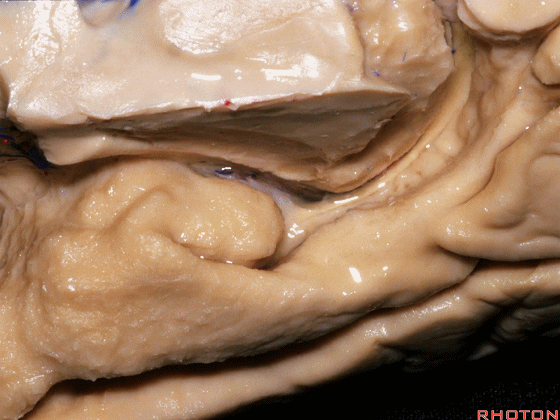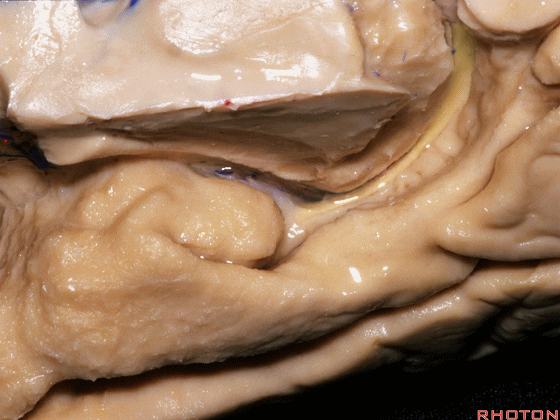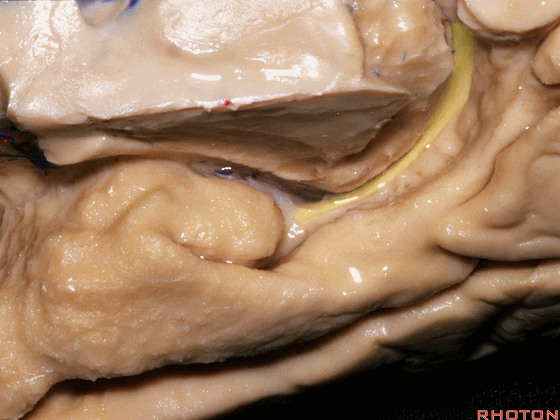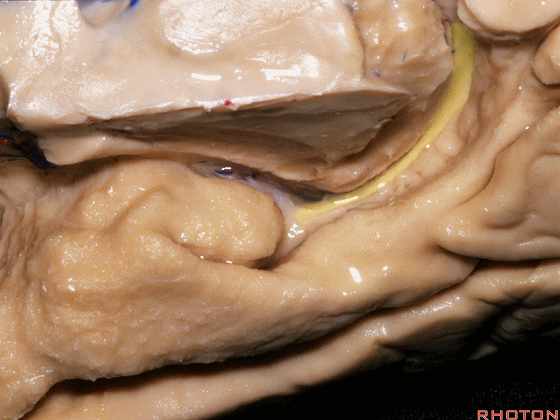
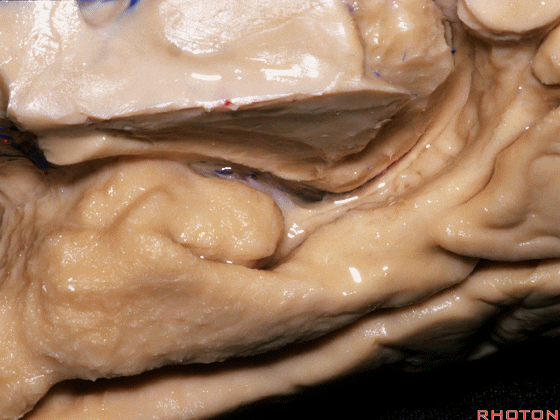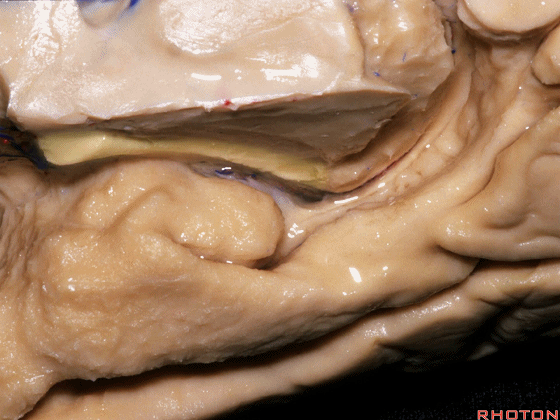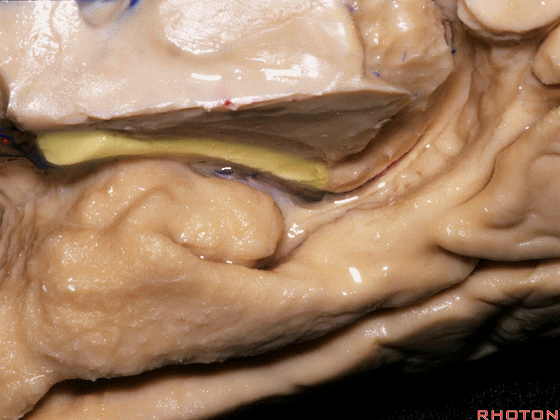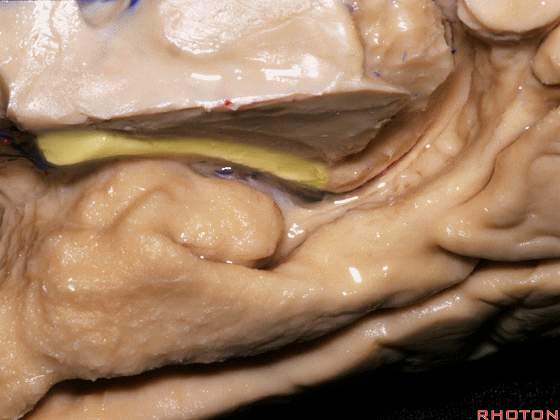
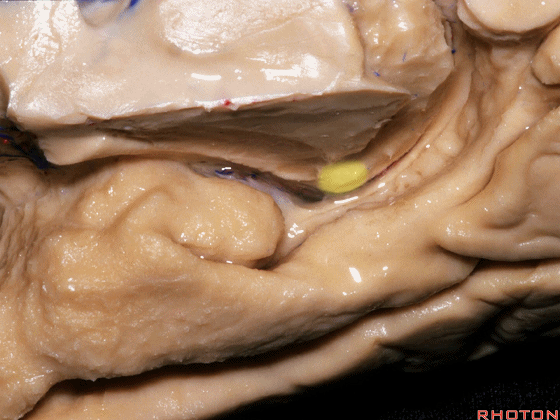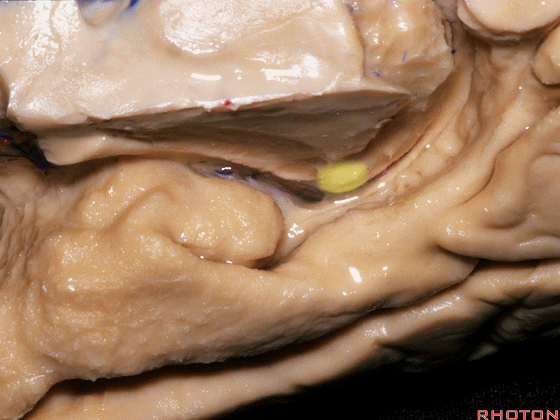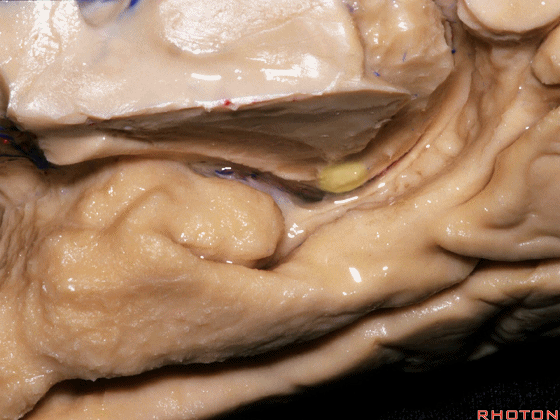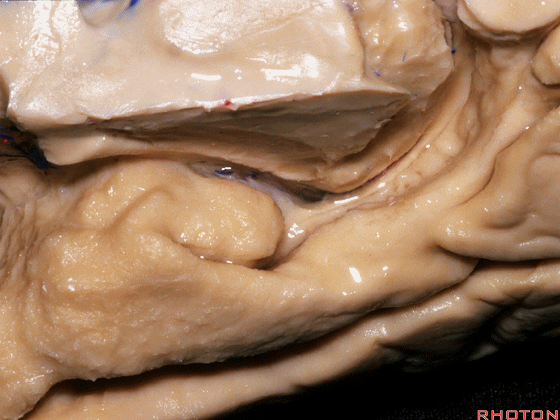
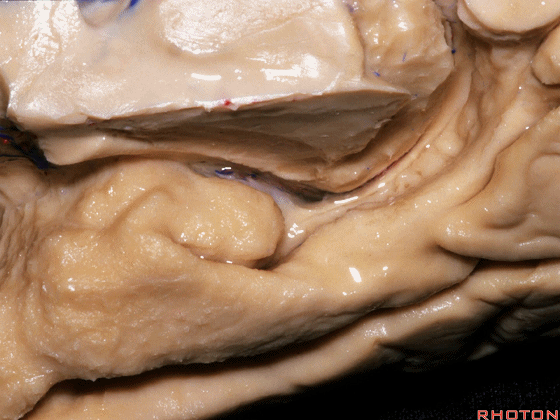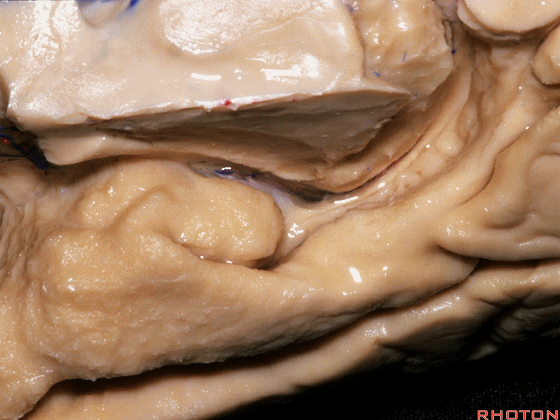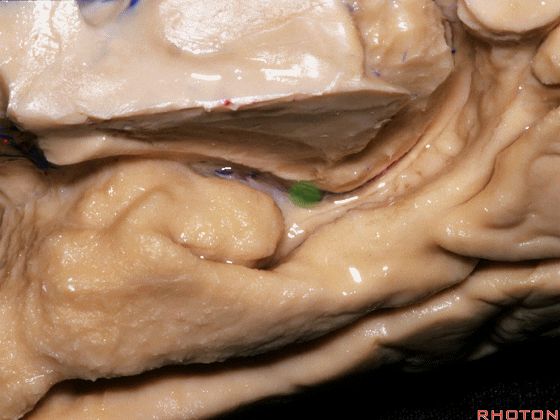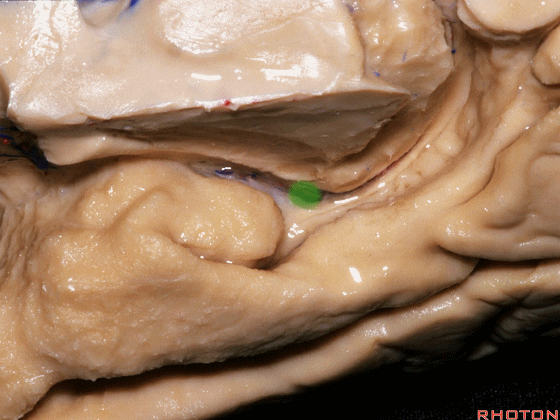
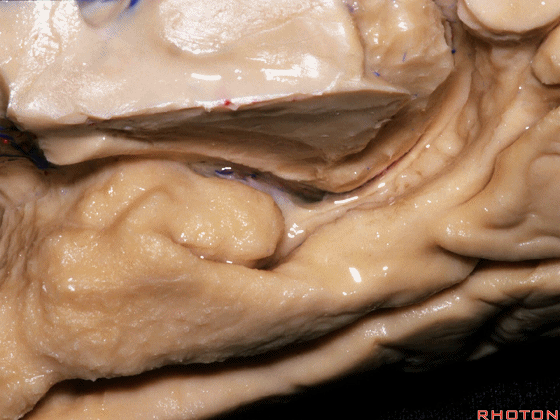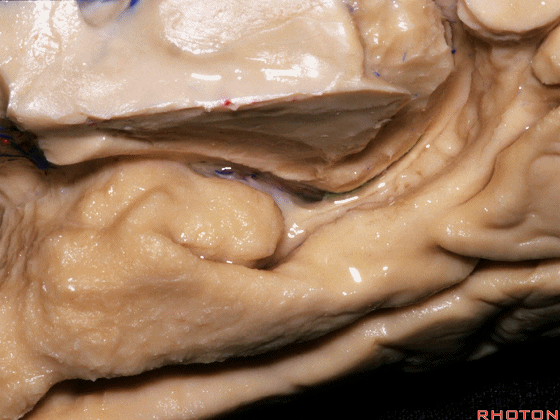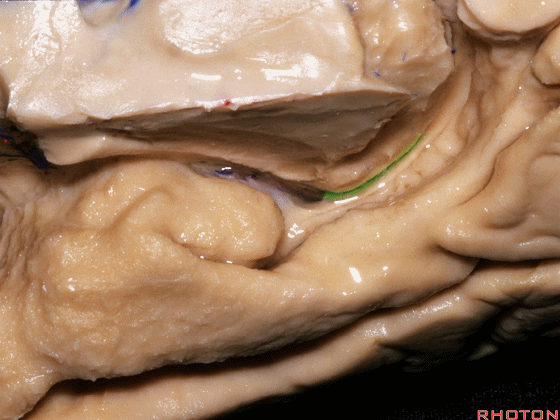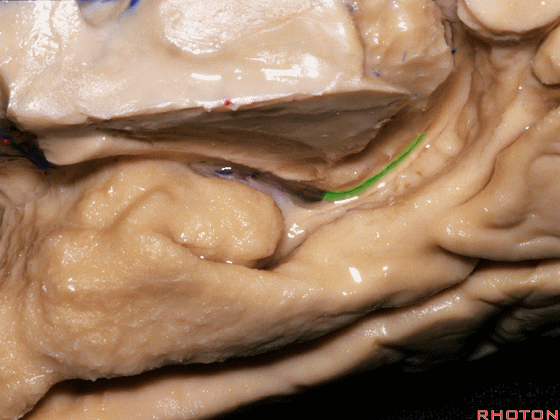
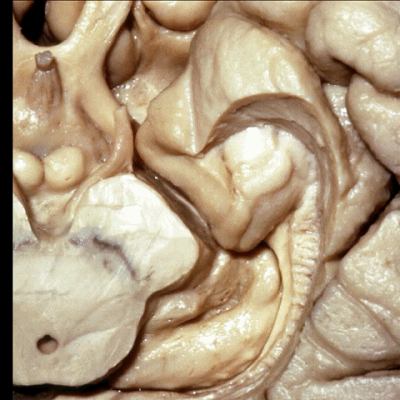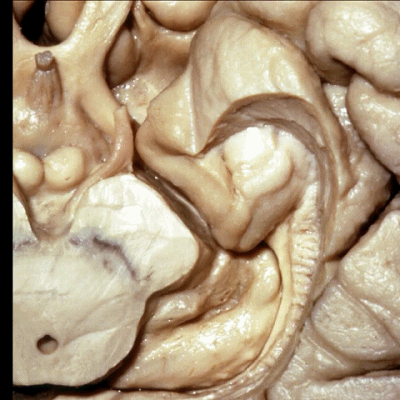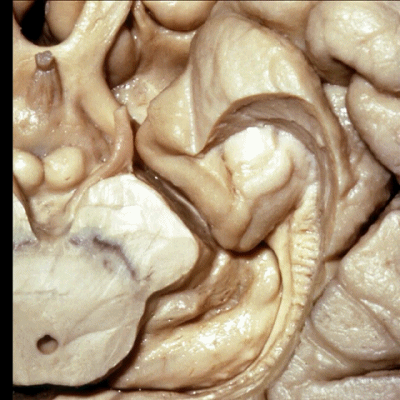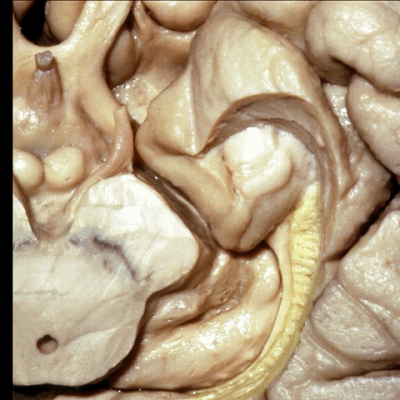
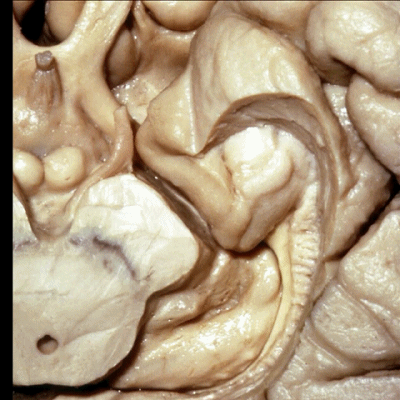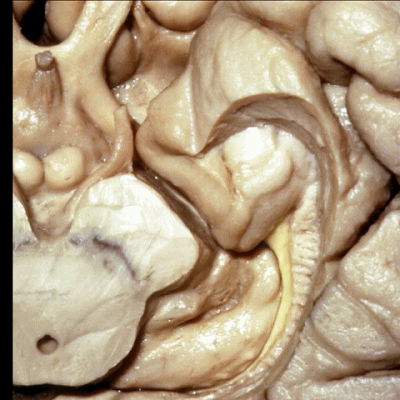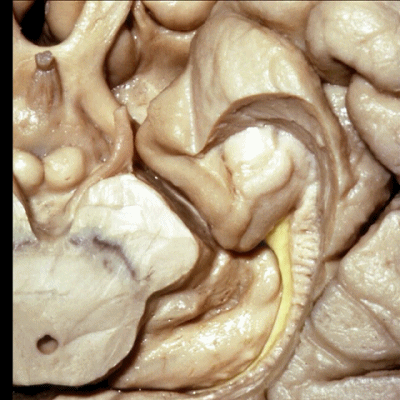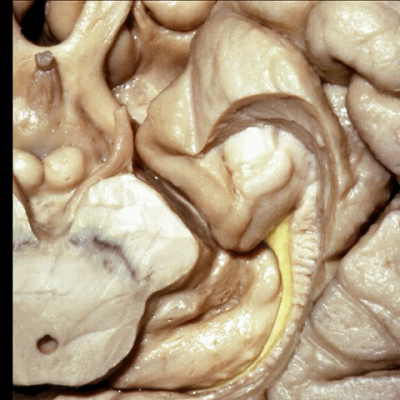
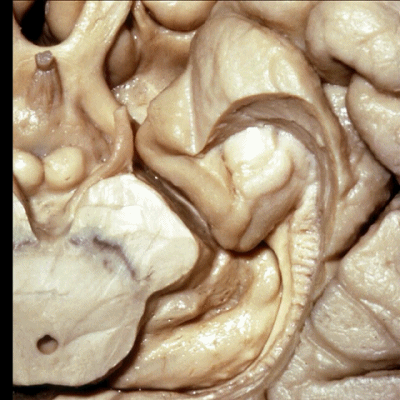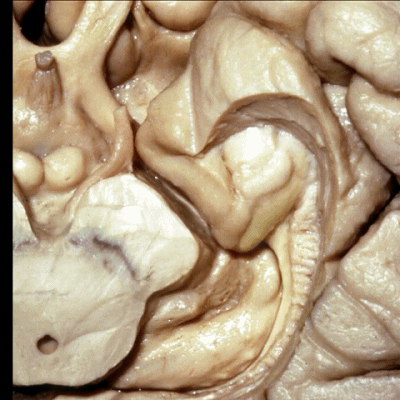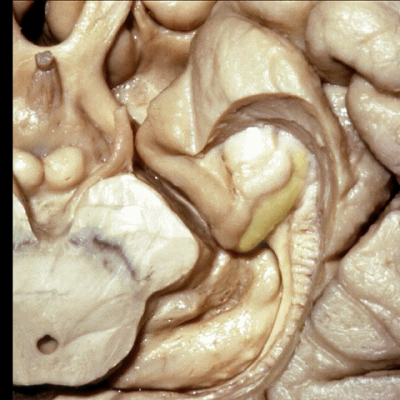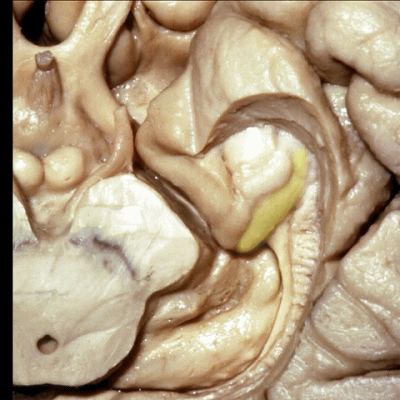
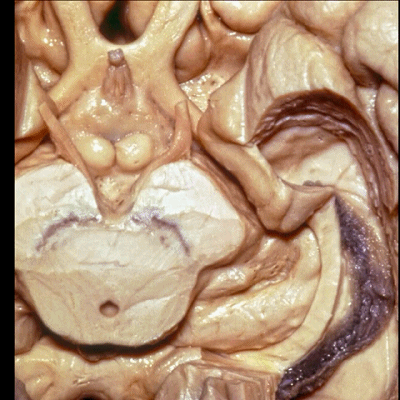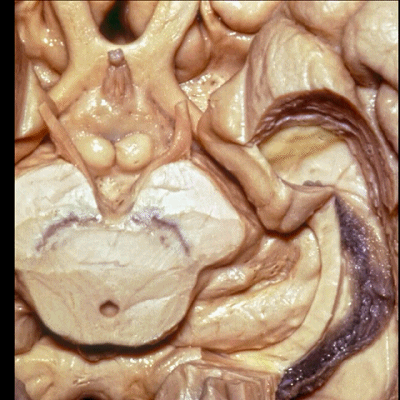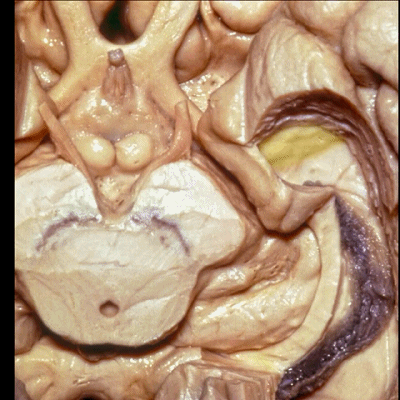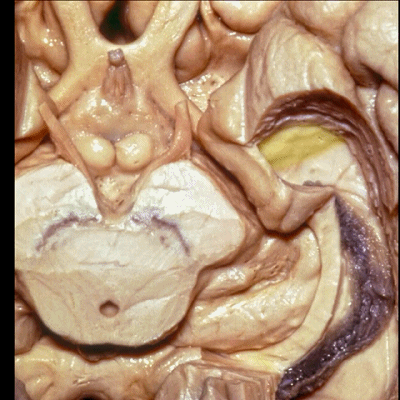
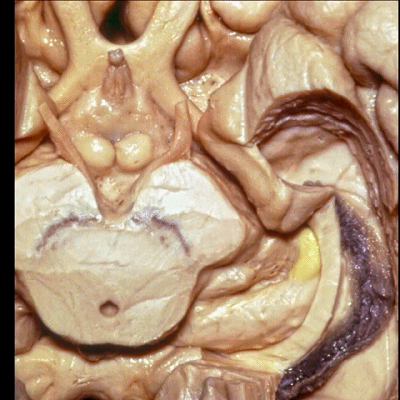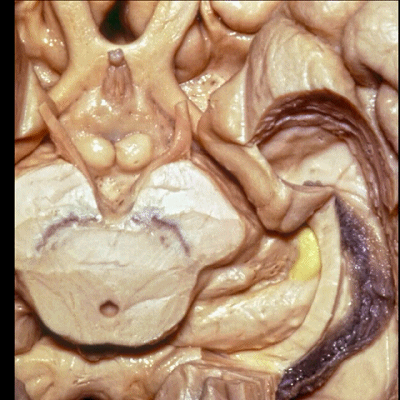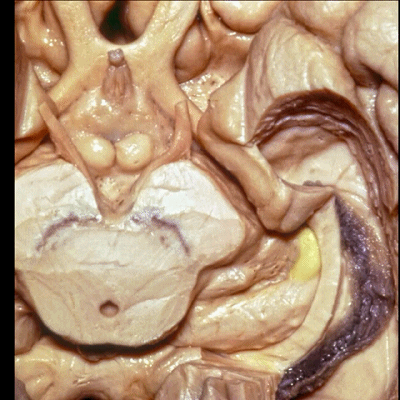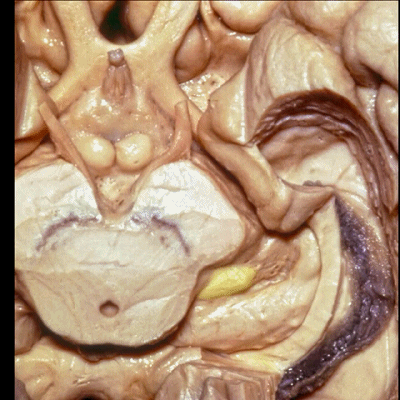
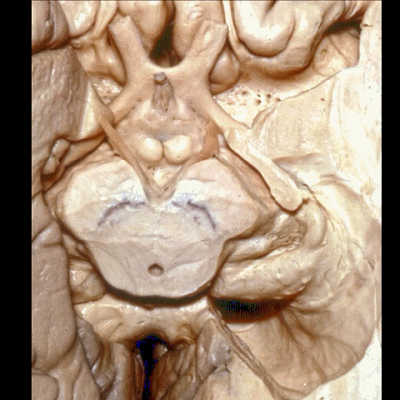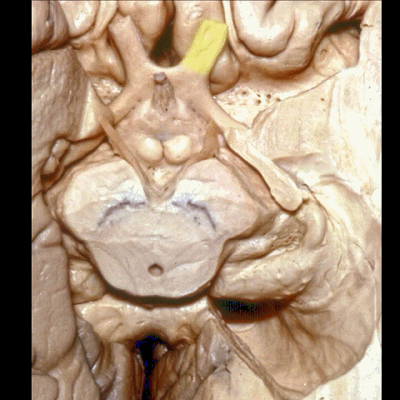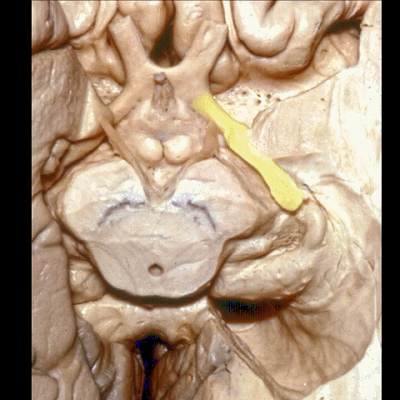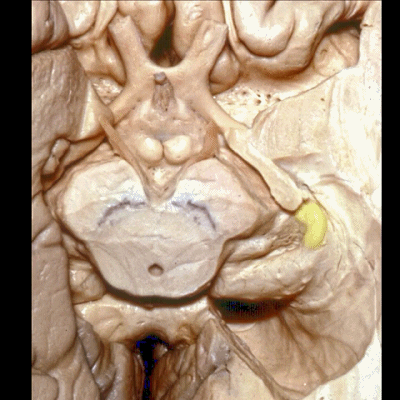
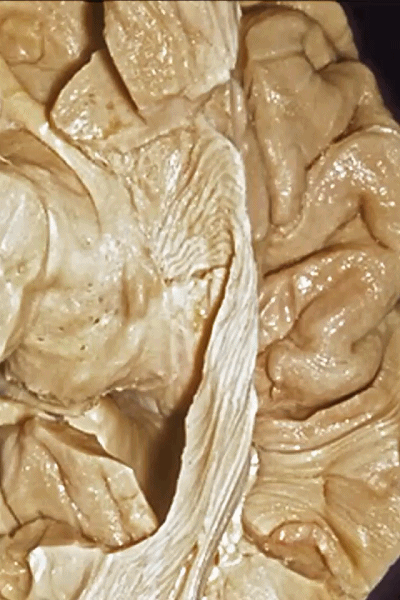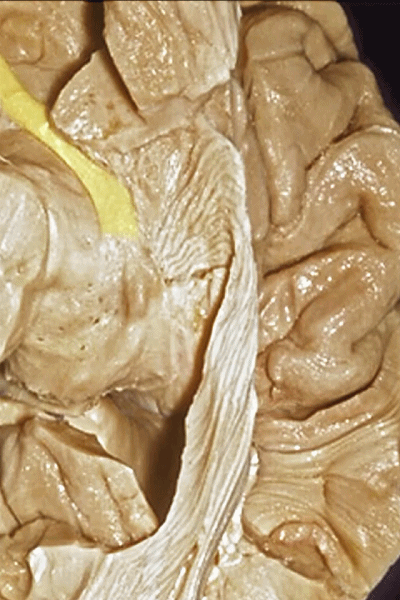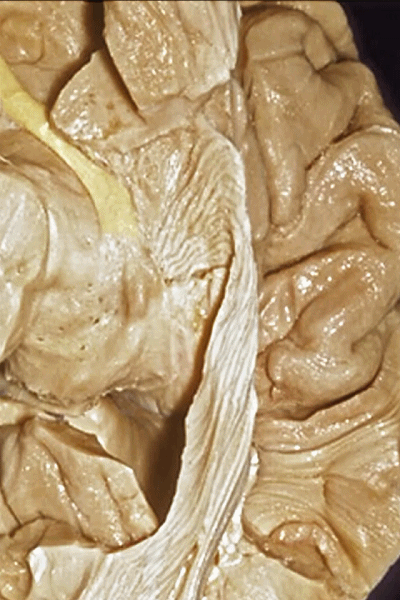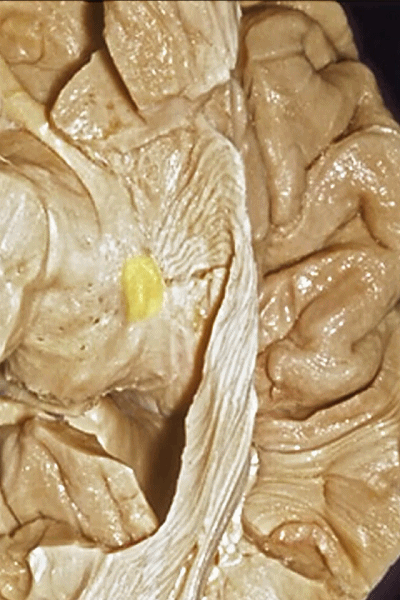
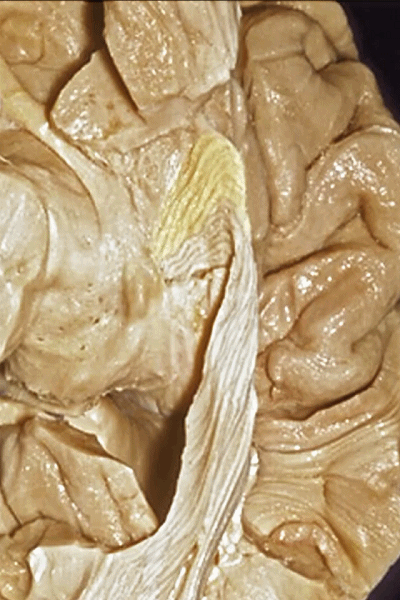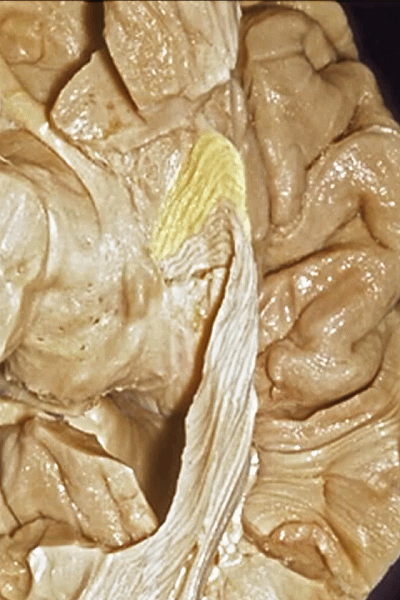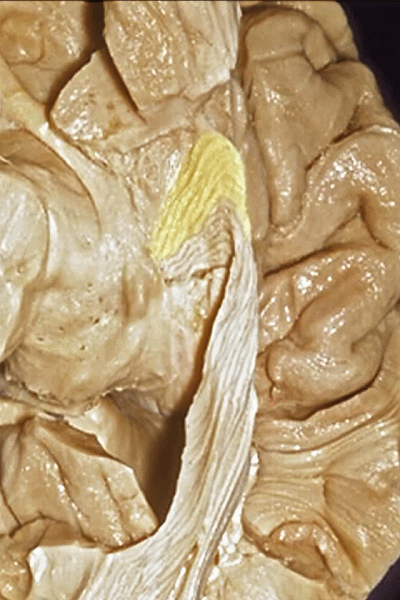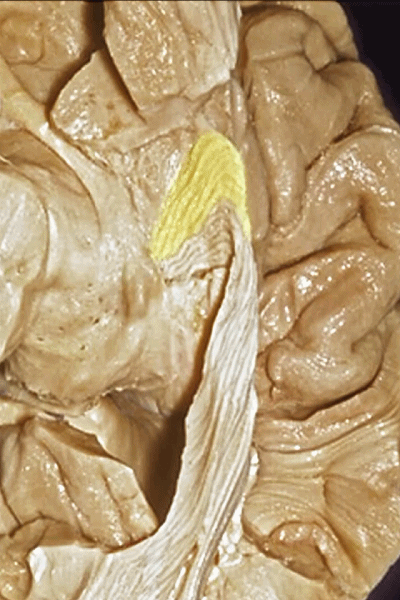
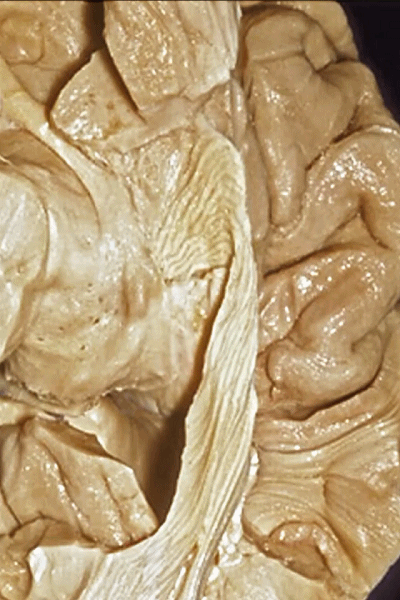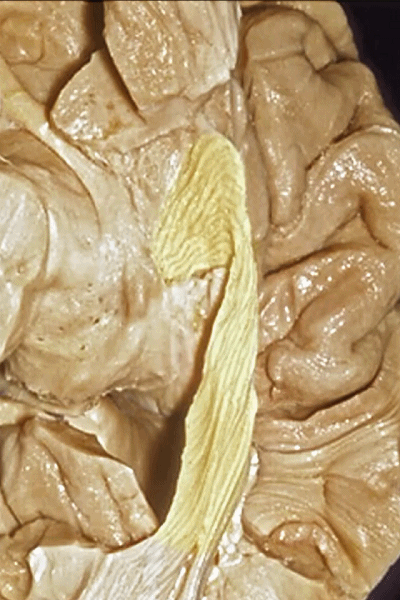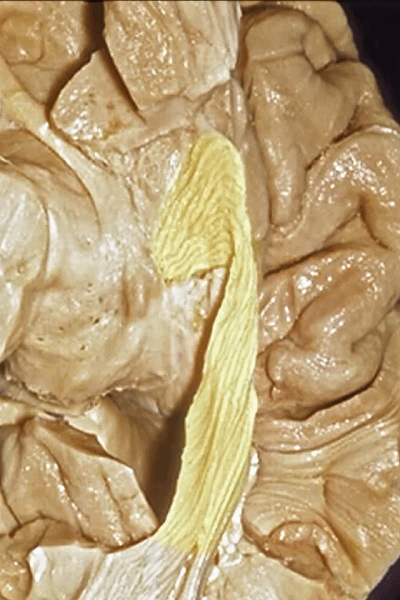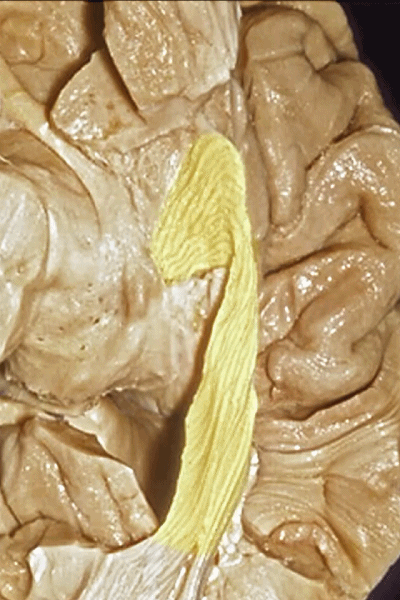
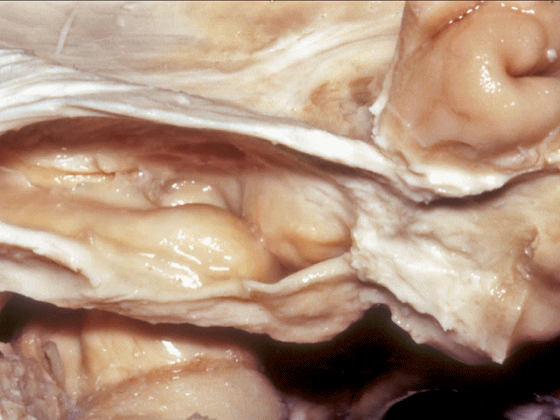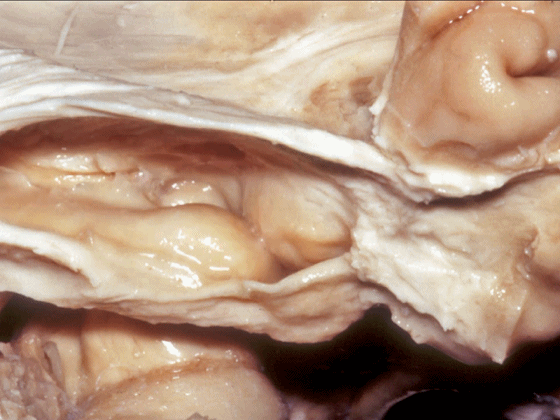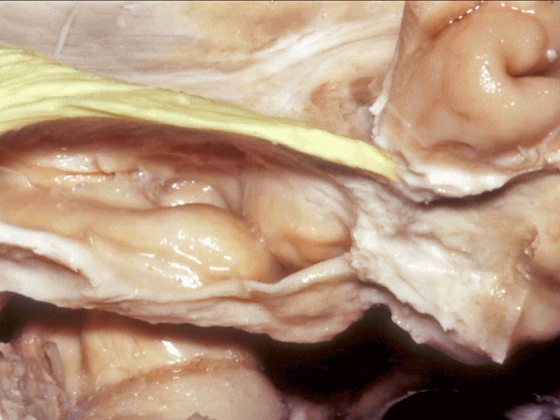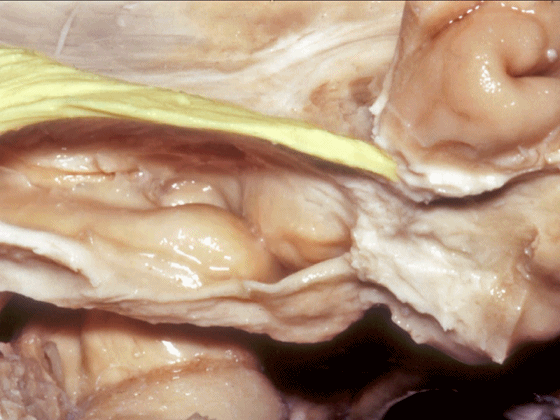
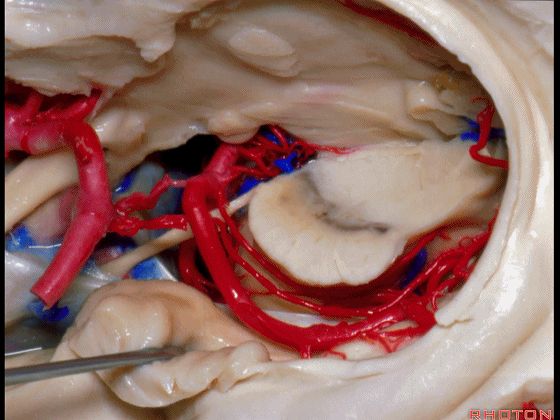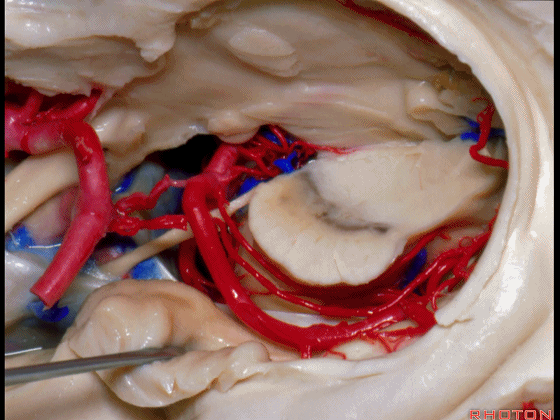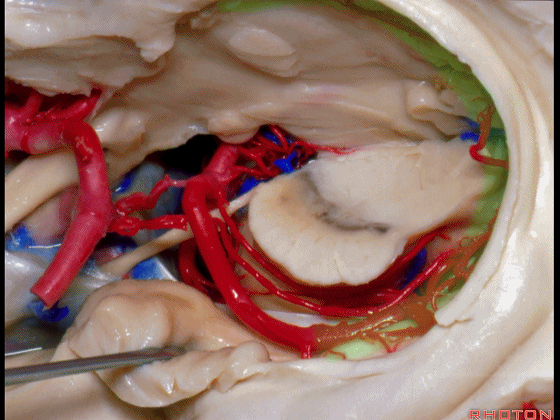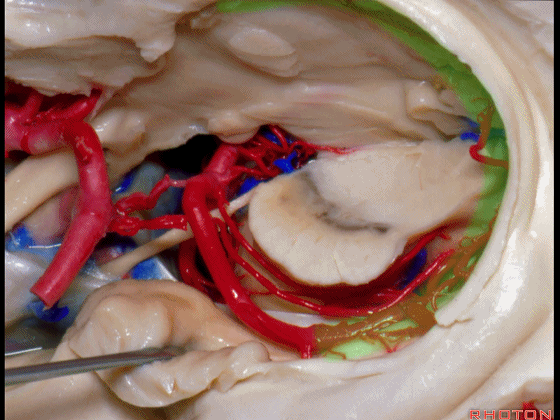
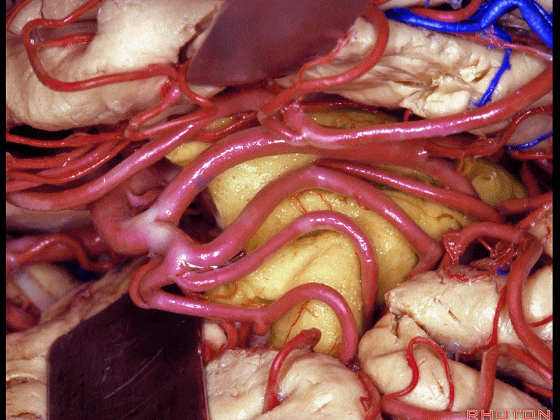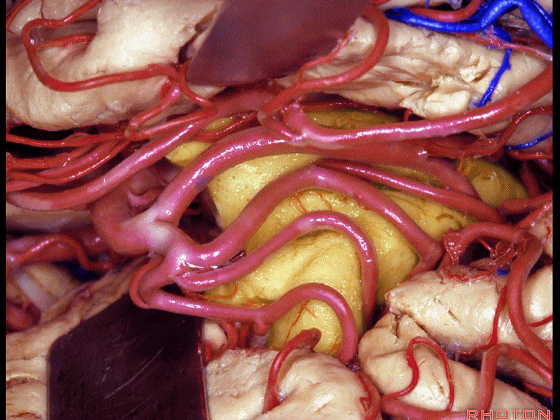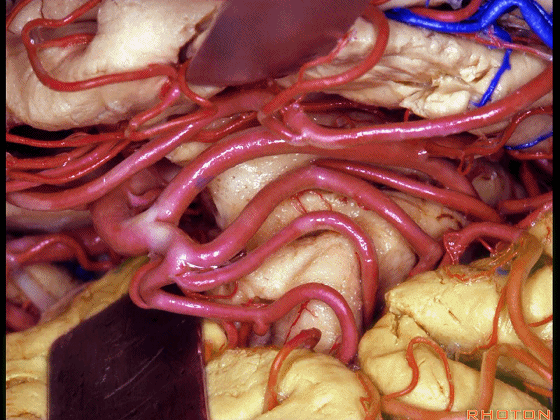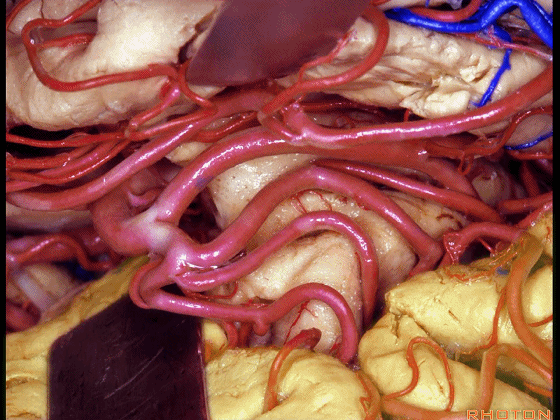
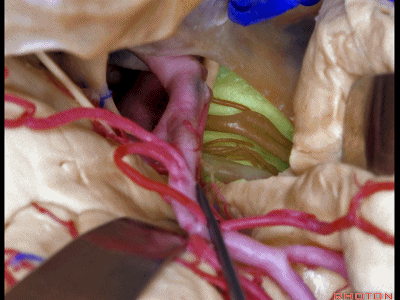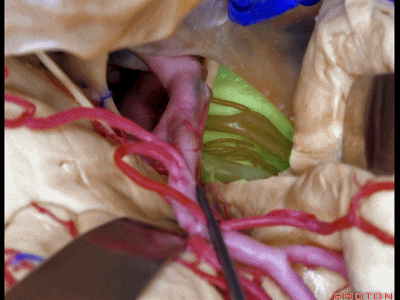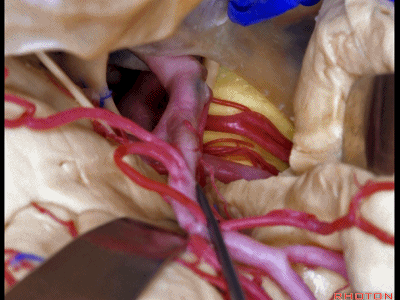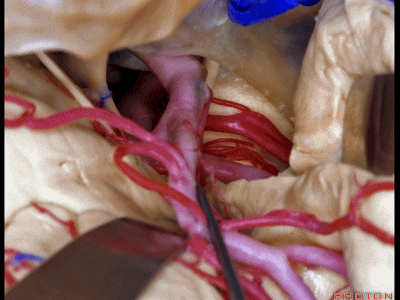
▼这是钩回(下图),其位于大脑脚外侧。
We see the uncus. They are lateral to the cerebral peduncle.
▼这是大脑脚
cerebral peduncle.
▼这是 脚间池
interpeduncular cistern
▼这是大脑脚池
crural cistern
▼这是 环池
ambient cistern
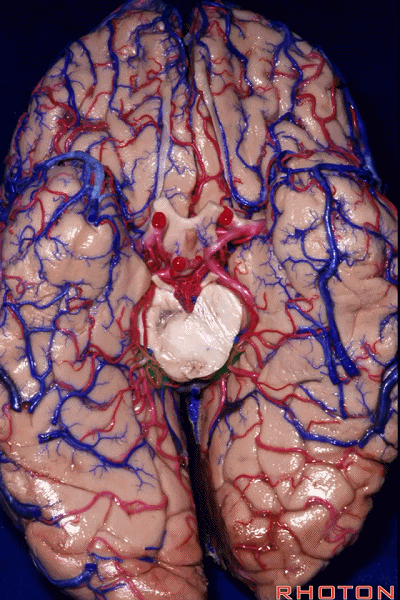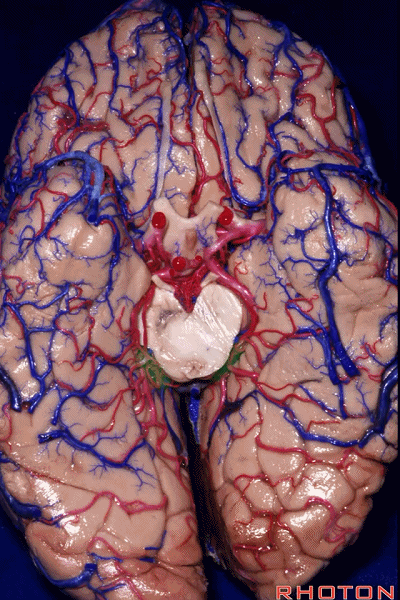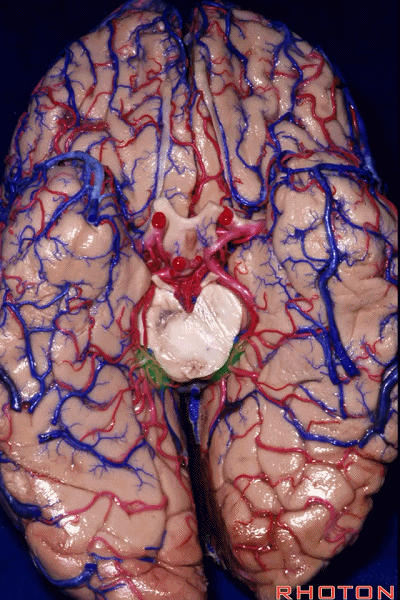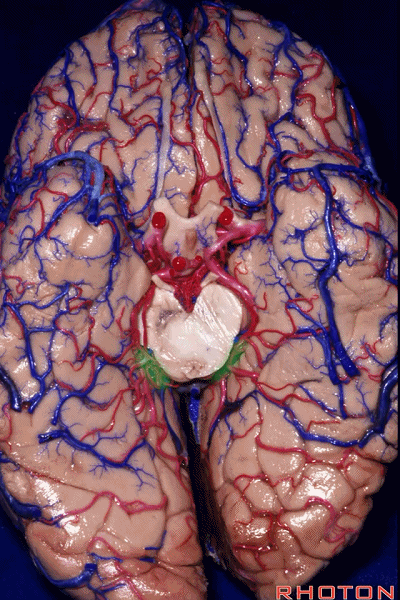
▼这是 四叠体池。均位于颞叶内侧面。
quadrigeminal cistern,on the medial side of the temporal lobe.
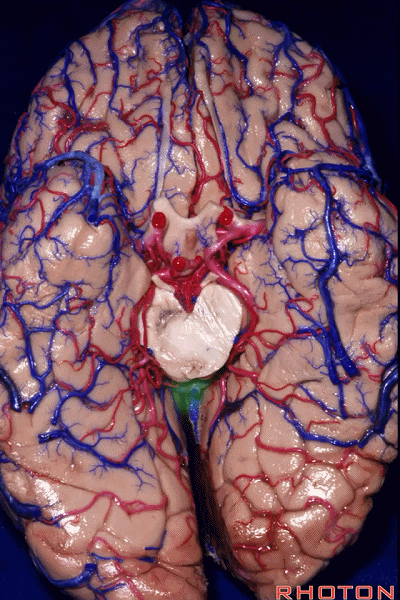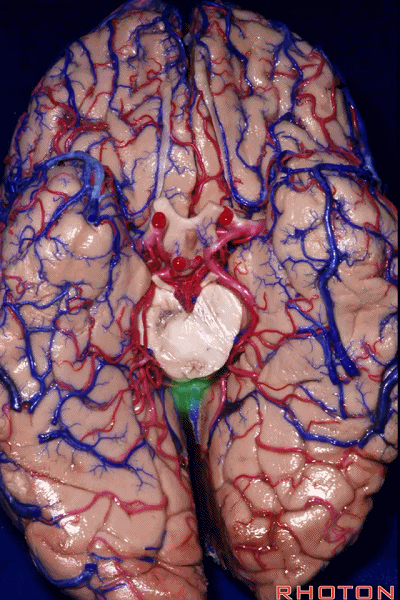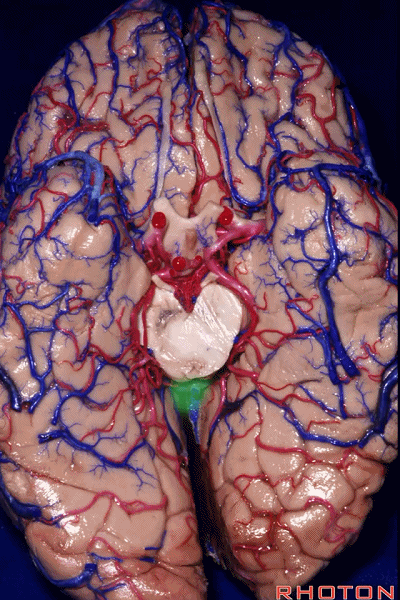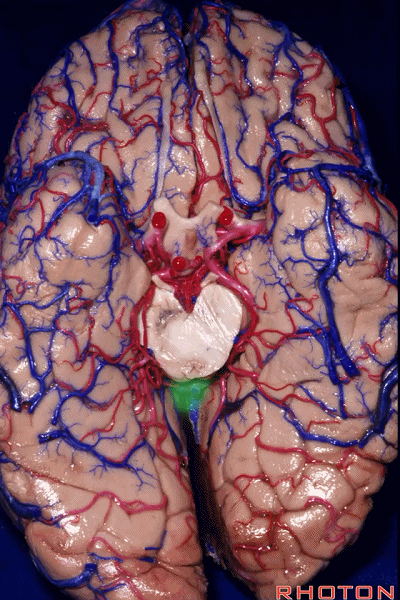
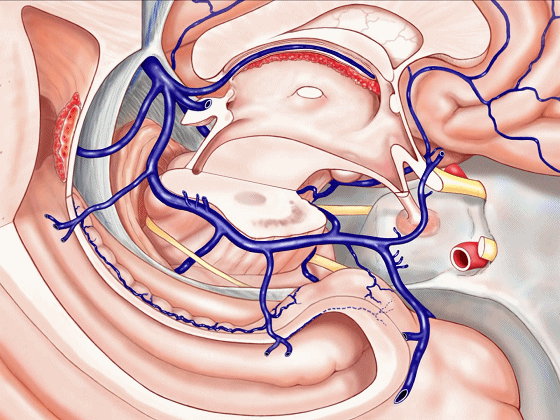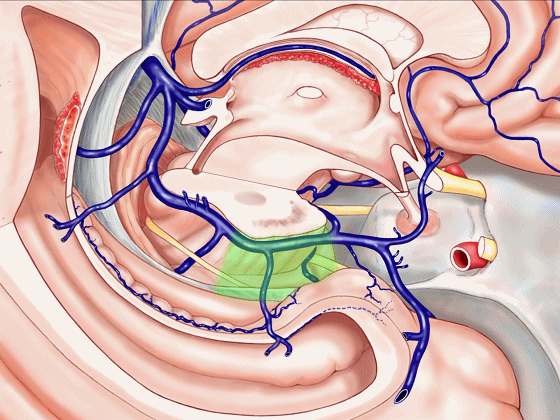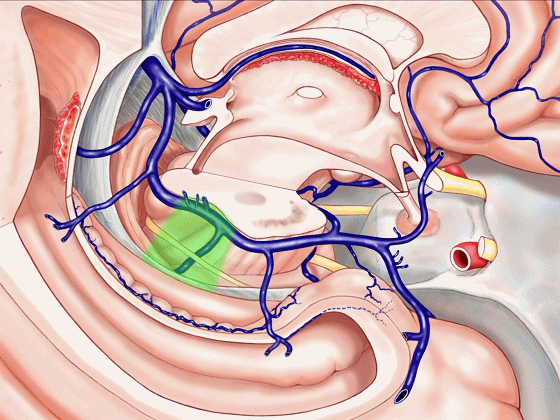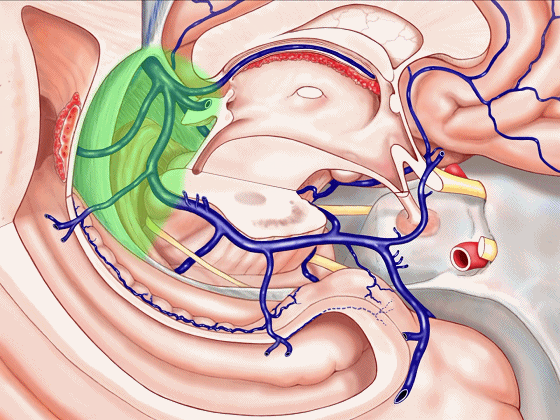
▼因此,关于颞叶,其最复杂的区域就是颞叶内侧面。
So that, as you look at temporal lobe, one of the most complicated areas that we deal with, is medial aspect of temporal lobe.
▼这是 钩回
We have uncus,
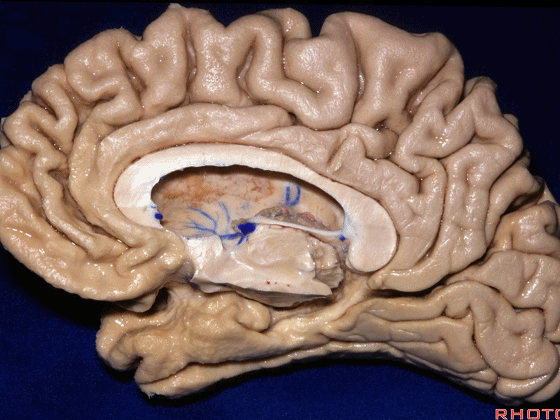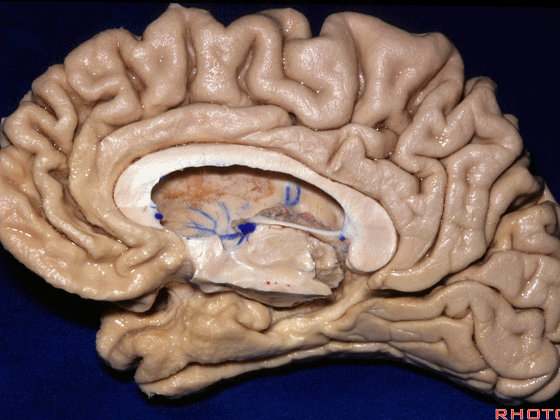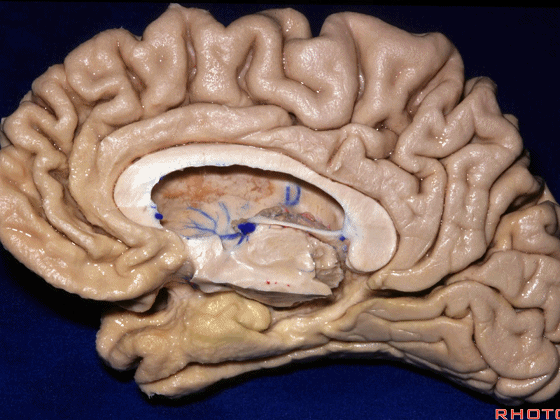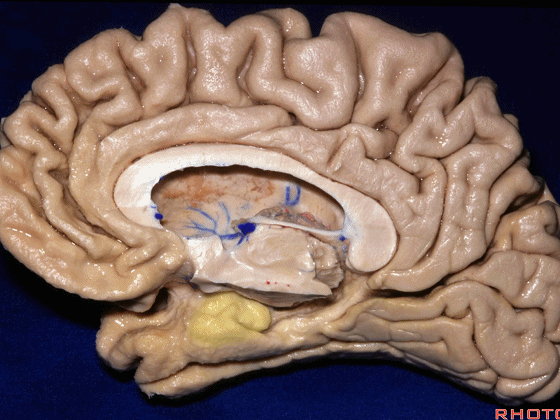
▼这是 环池
and then ambient cistern
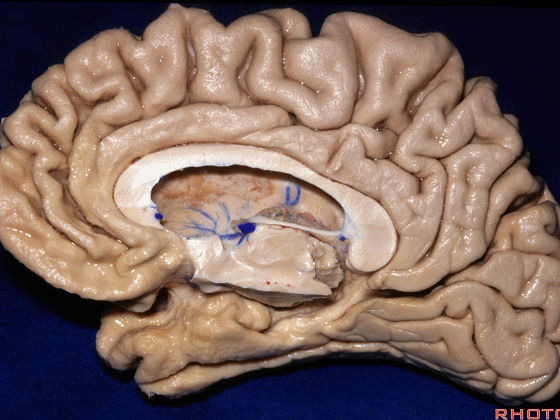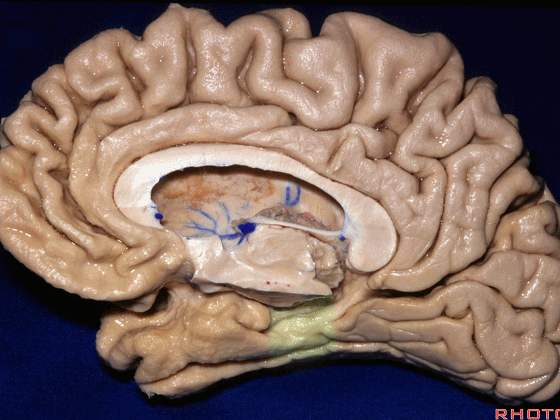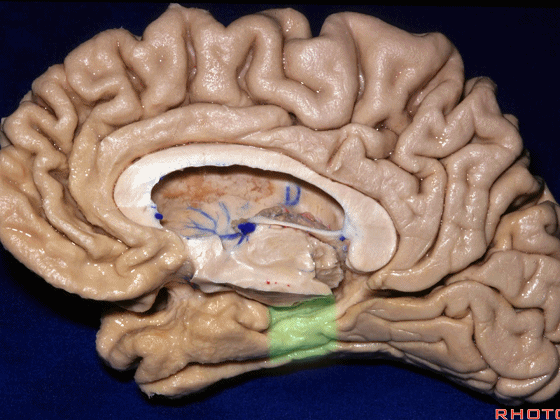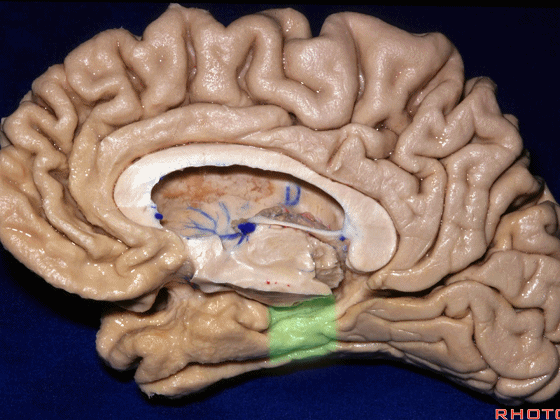
▼这是四叠体池,与颞叶关系密切
quadrigeminal cistern related to temporal lobe,
▼随后,四叠体池 向后延伸至 顶枕沟和距状沟的交界处。下图示顶枕沟
and it extends back to the junction of the parieto-occipital and calcarine sulcus.
▼这是 距状沟
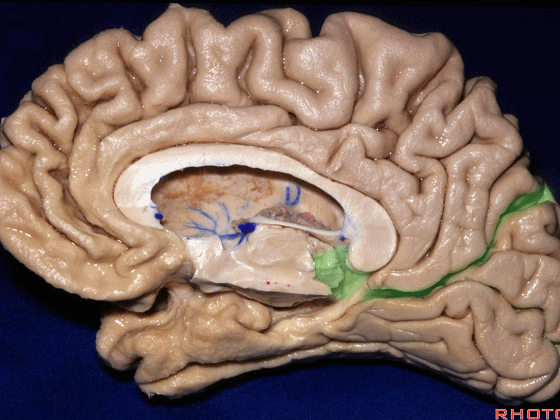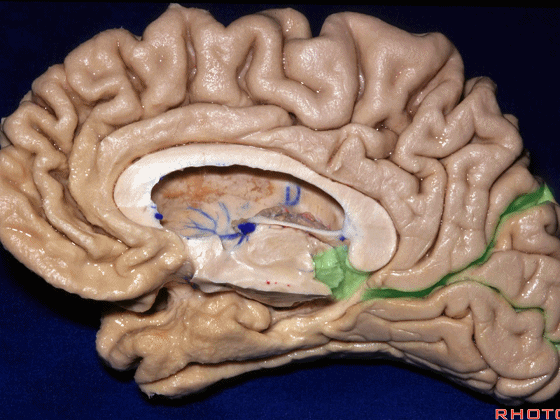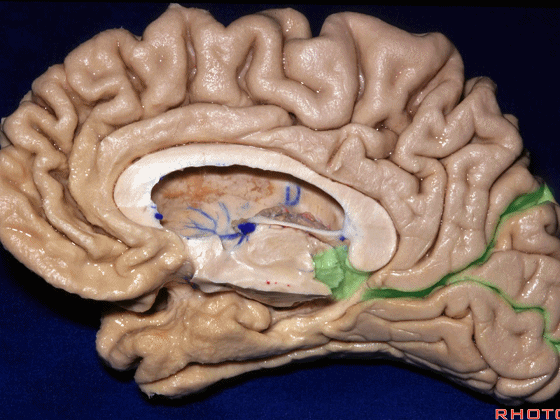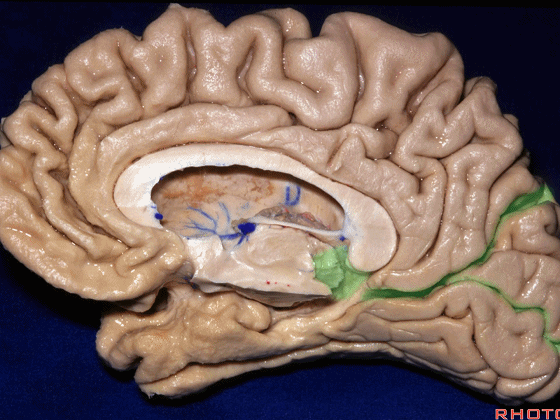
▼我们将颞叶内侧面 分成 前部,中部,后部
So that you can divide medial temporal lobe into an anterior part of medial temporal lobe,a middle part, posterior part
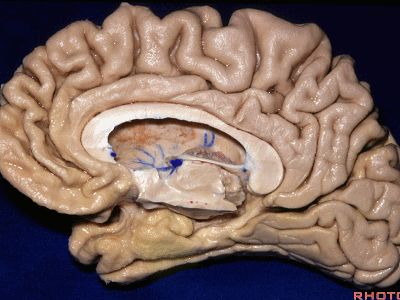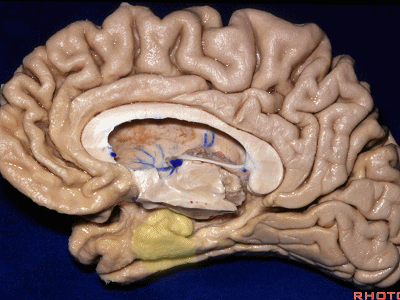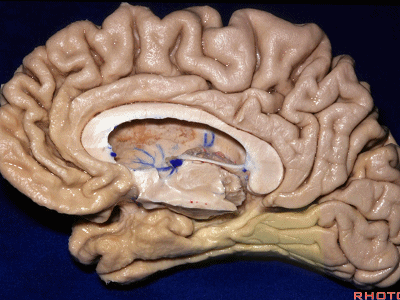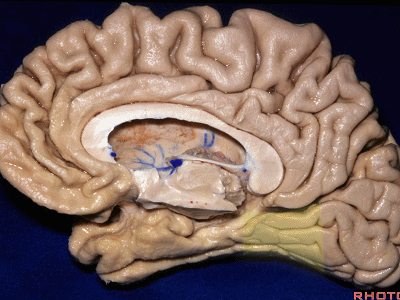
▼这是 前部
an anterior part of medial temporal lobe,
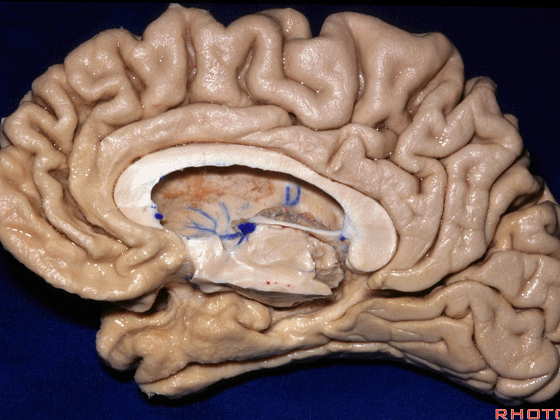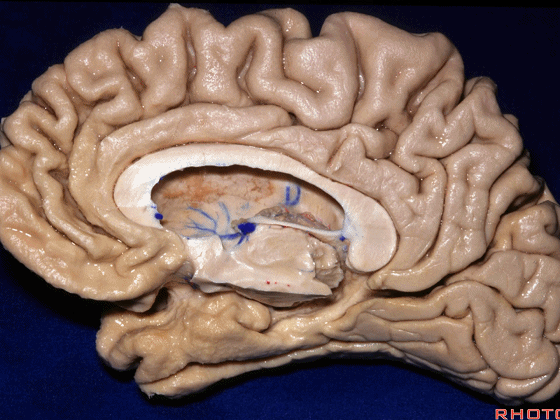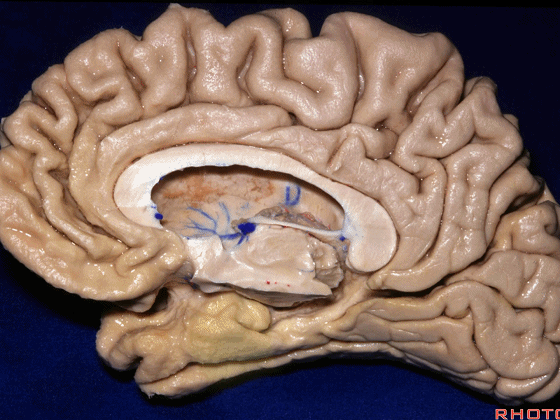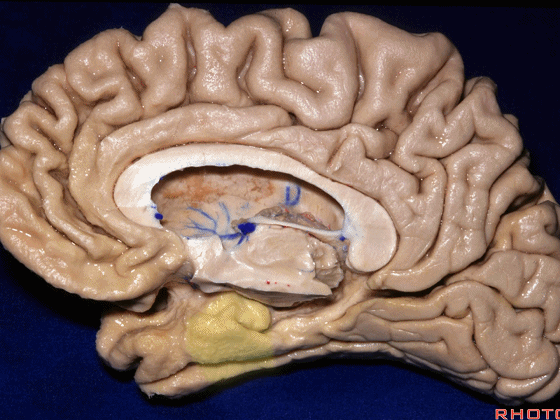
▼这是中部,其范围从钩回后界至四叠体池
a middle part from back edge of uncus to quadrigeminal cistern,
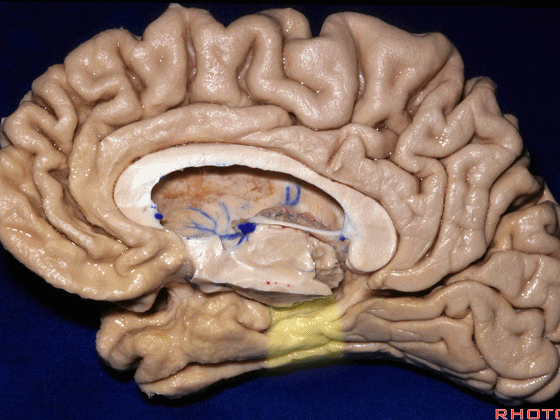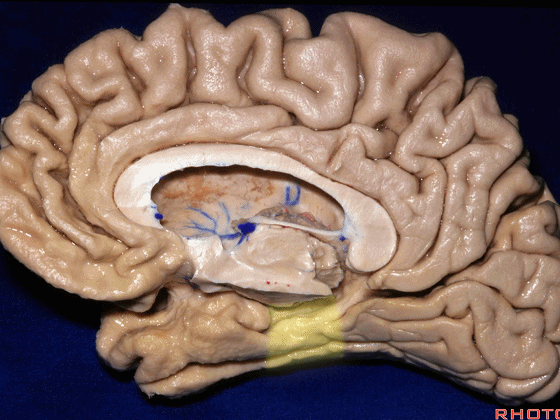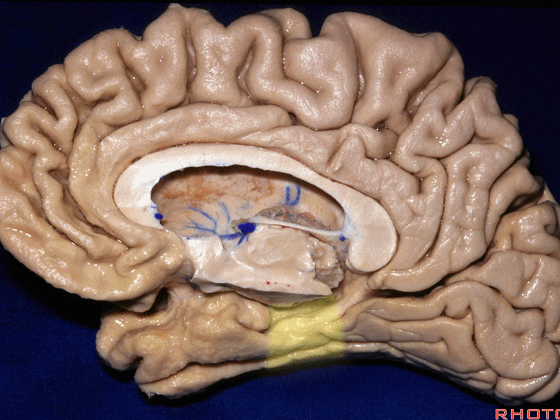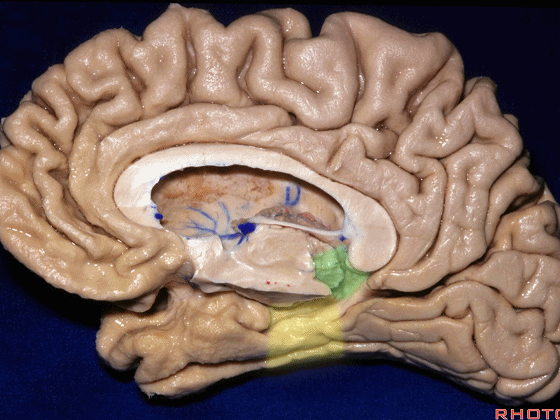
▼这是后部,从四叠体池向后 至 顶枕沟与距状沟的交界
from quadrigeminal cistern back to the junction of the parieto-occipital and calcarine sulcus.
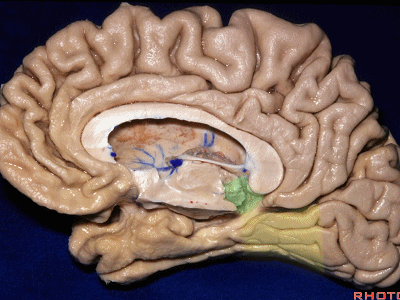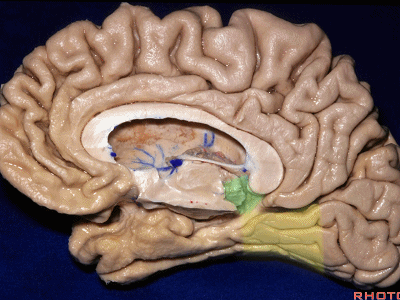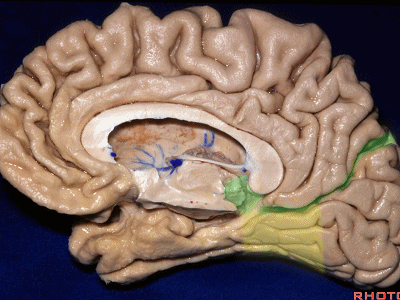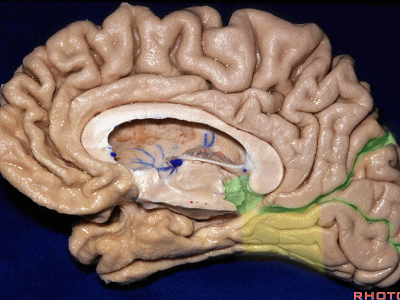
▼对于这些脑回的命名,尤其是颞叶内侧面前部的脑回,是相当有难度的。
这个沿着钩回外侧缘走行的脑沟是 鼻沟(下图)。此脑沟向后延伸至海马旁回的外侧。
and for anyone who can name all these gyri, on the anterior part of the medial temporal lobe,I'll buy a cup of coffee at coffee break. The rest of you don't get any coffee but...what is the sulcus along the lateral side of the uncus?rhinal sulcus. laterally, this extends lateral here... to parahippocampal gyrus...
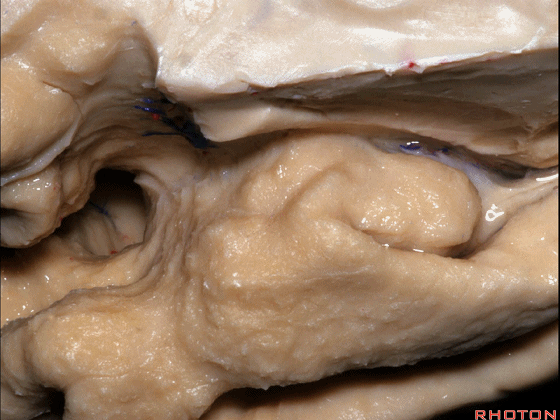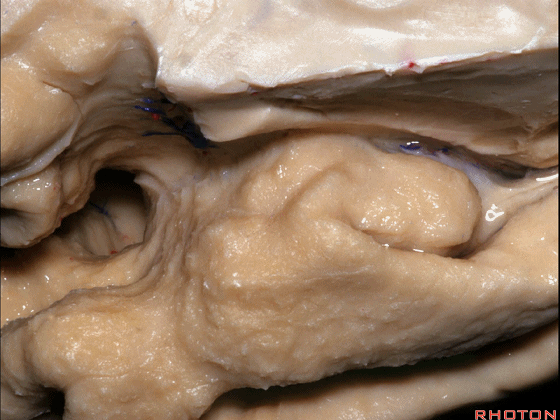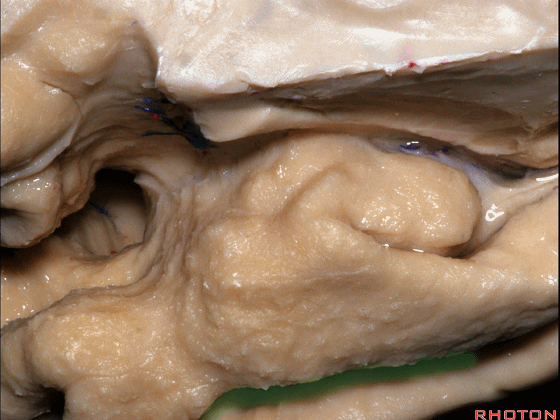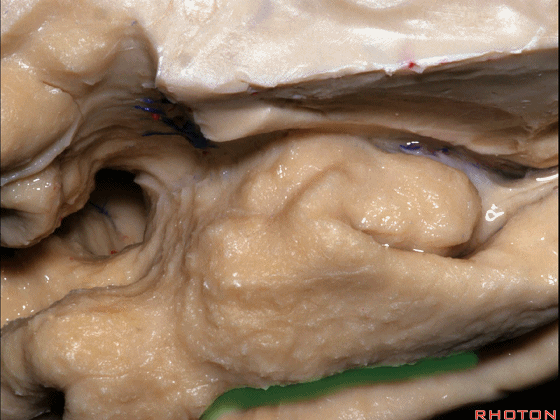
▼海马旁回(下图)向前延伸。
Parahippocampal gyrus extends forward
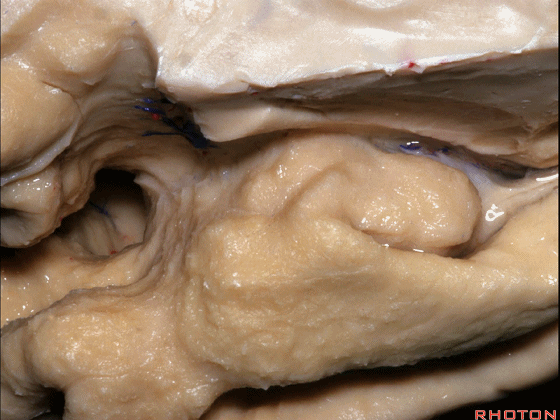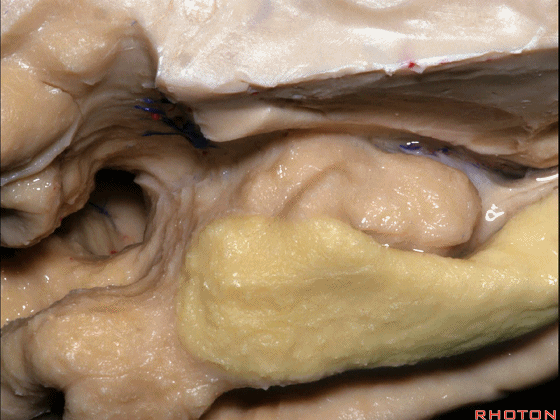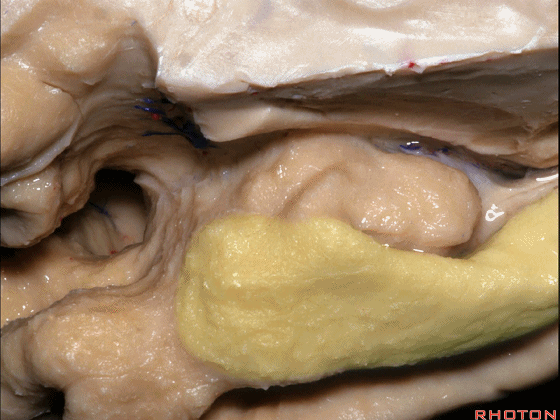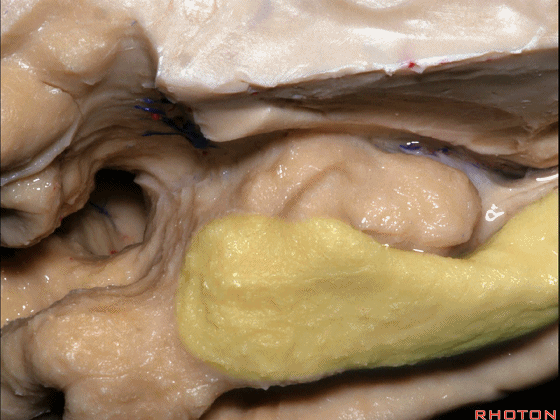
▼来看颞叶内侧面前部的上表面,这是 半月回
Now on this upper surface of the anterior third of medial temporal lobe, we have what gyrus in this area, anyone?semilunar, and..
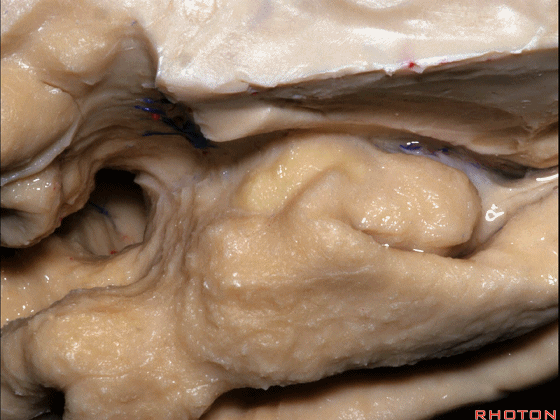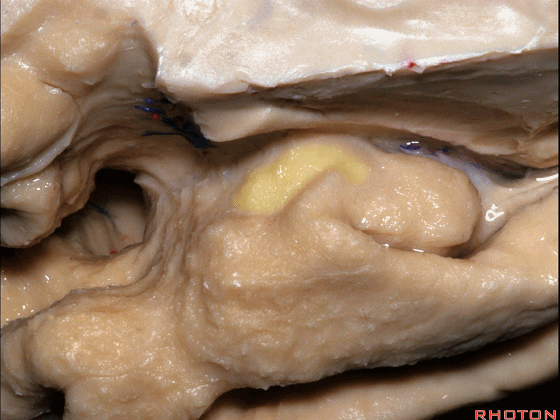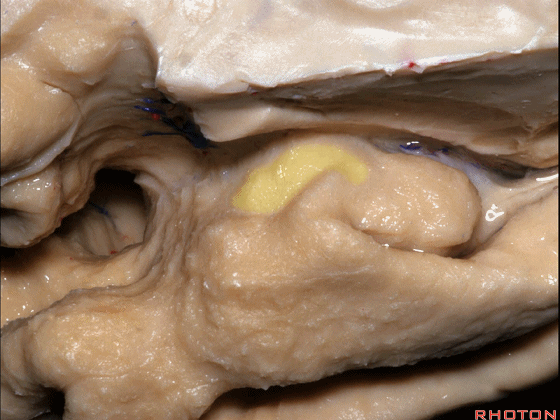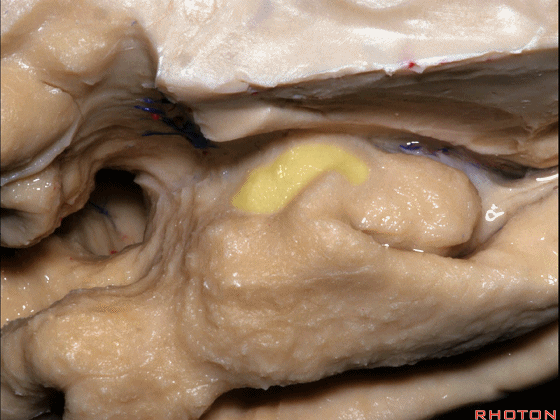
▼这是 半月沟
what is this sulcus? semiannular,
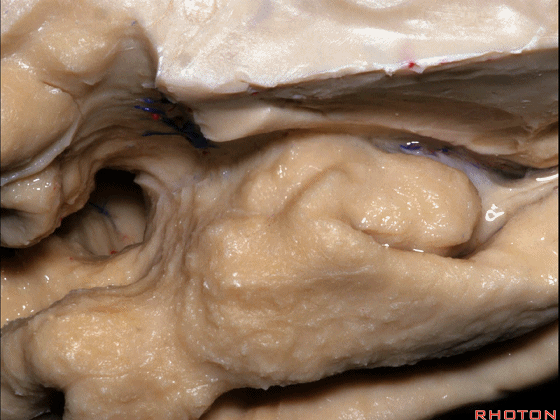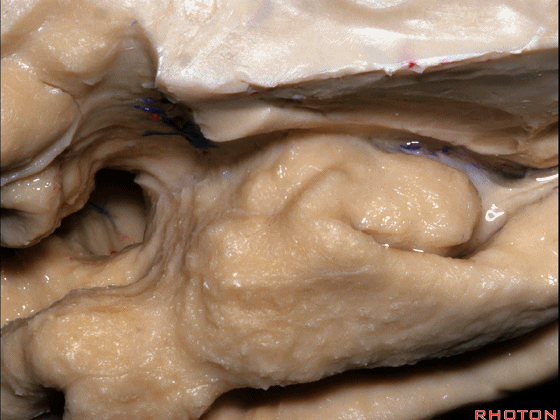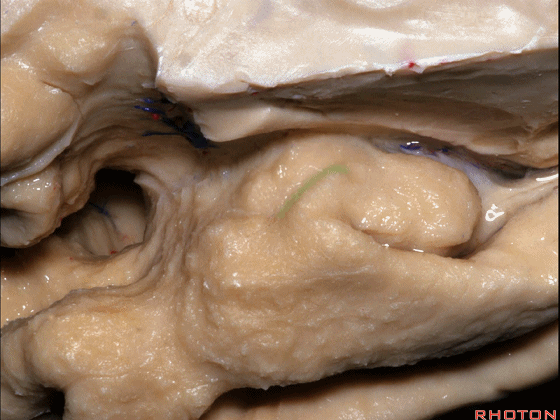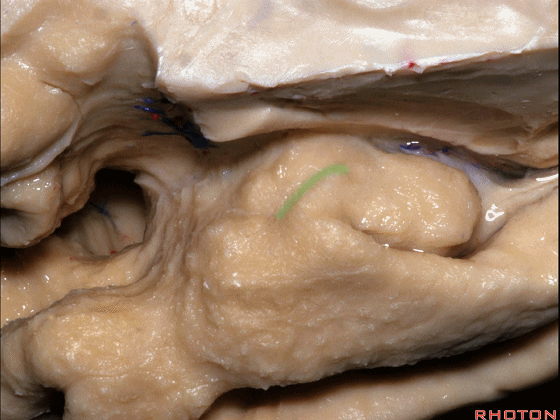
▼这是 环回
and then we have ambient,
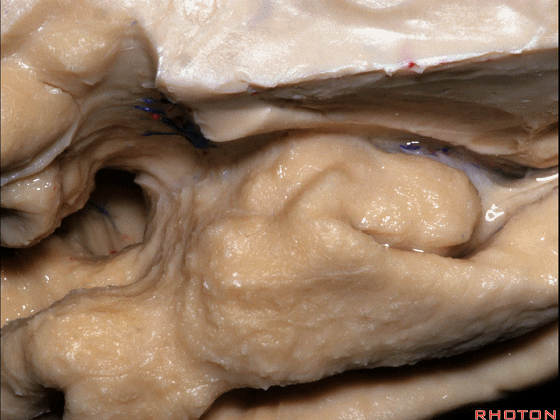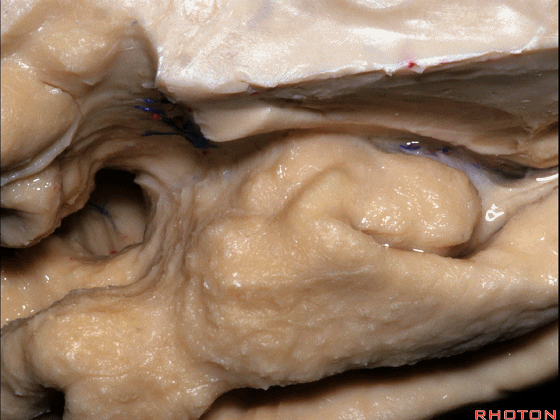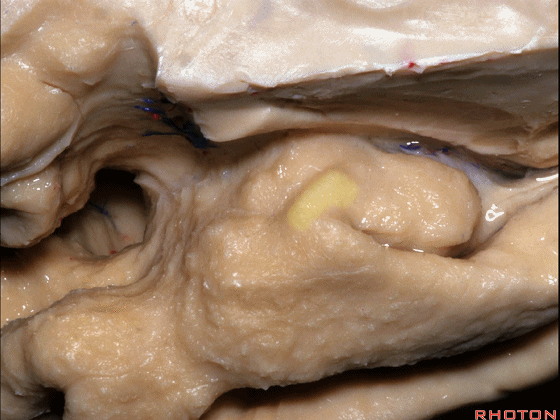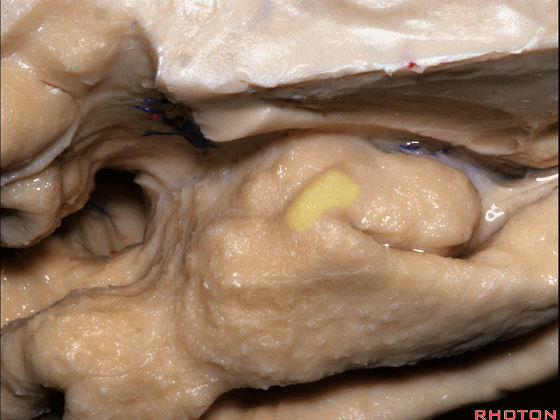
▼这是 钩状回
uncinate gyrus.
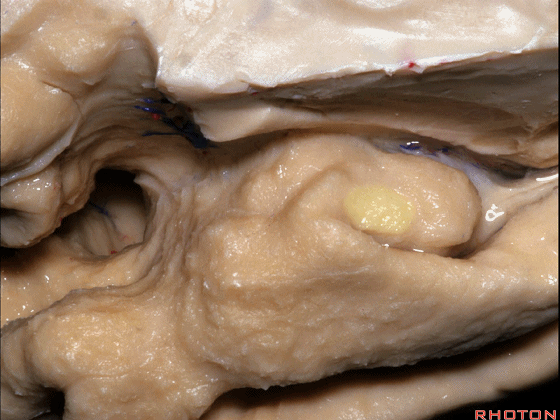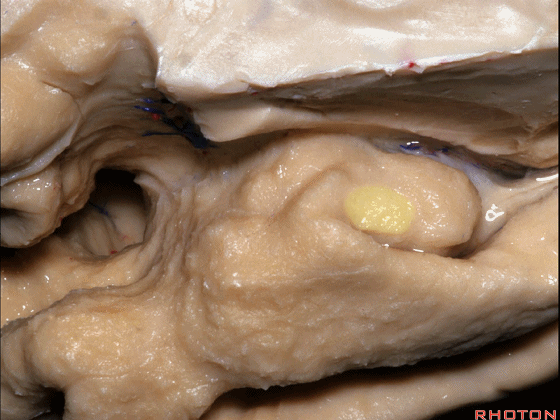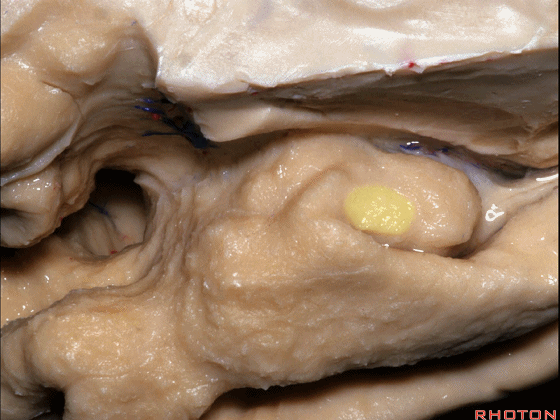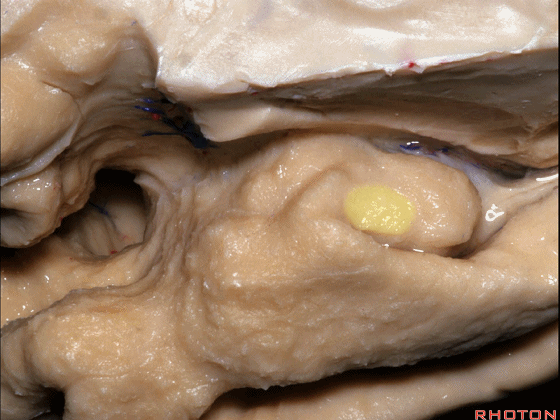
▼颞叶内侧面上方的这一部分(下图)与 内翻的海马头关系密切。
And this upper part of medial temporal lobe is really related to enfolded head of hippocampus.
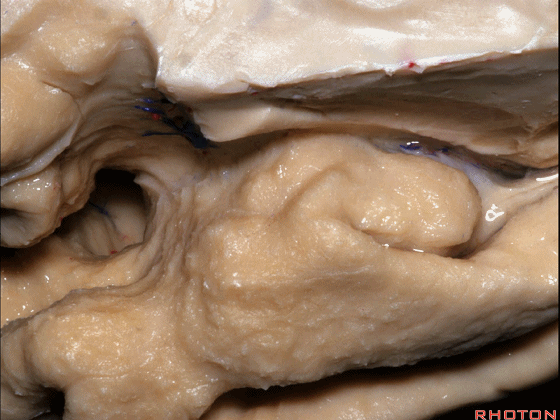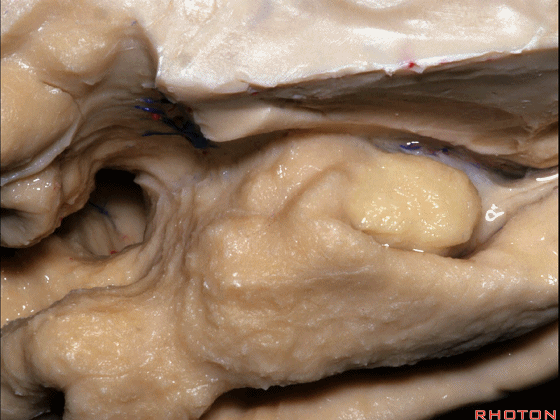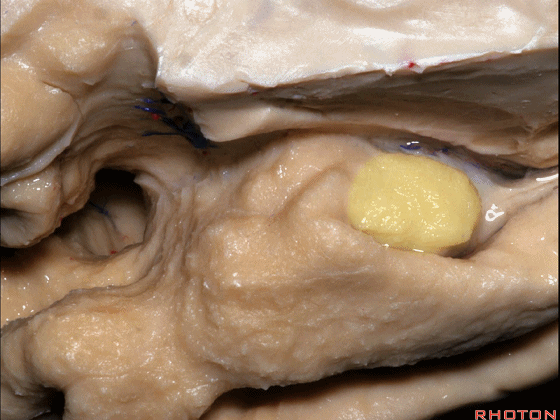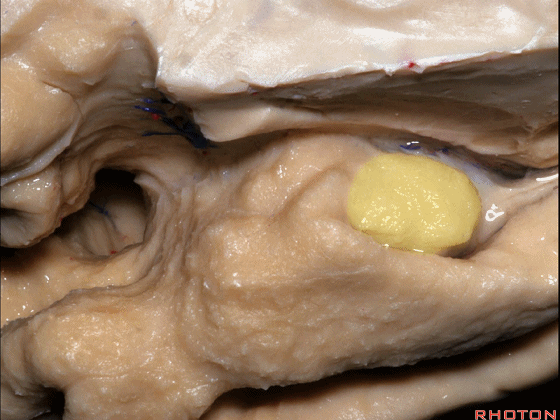
▼下方的区域是海马旁回的前部,位于钩回切迹以下
The lower part here below this uncal notch is the anterior part of parahippocampal gyrus.
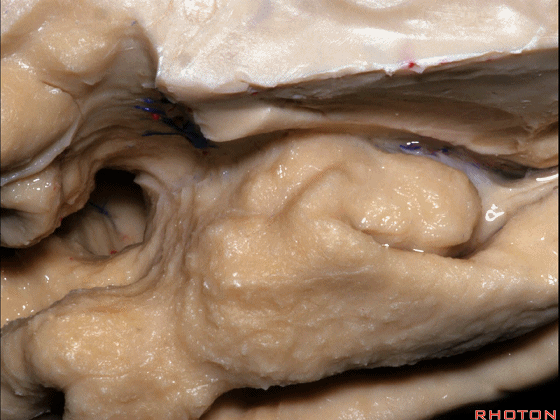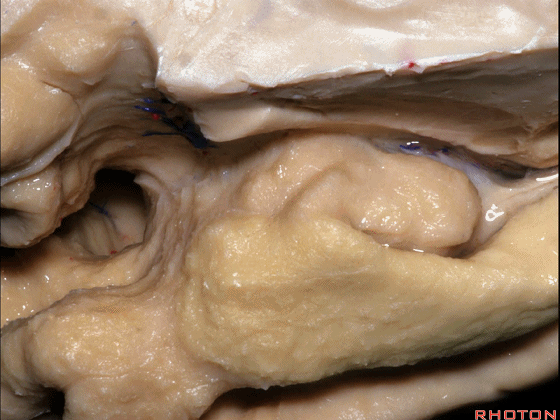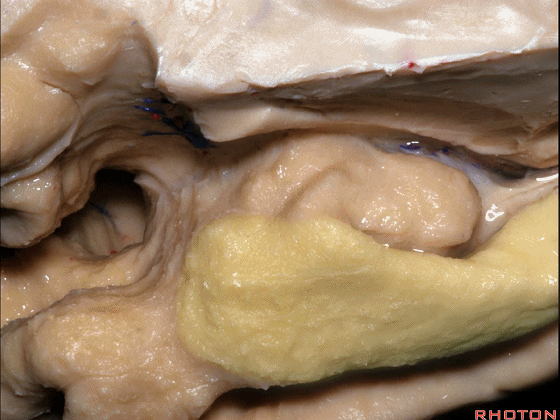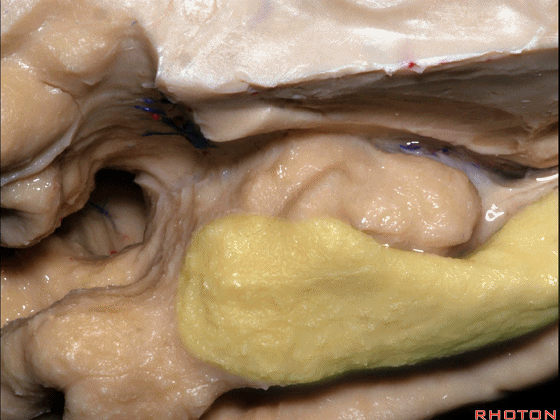
▼这是钩回切迹
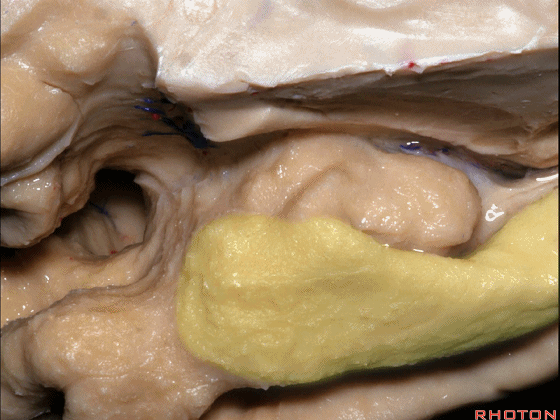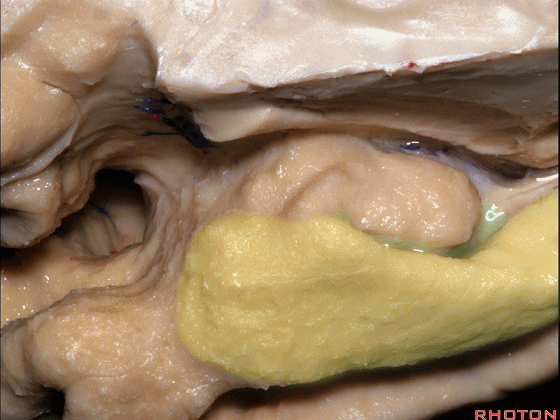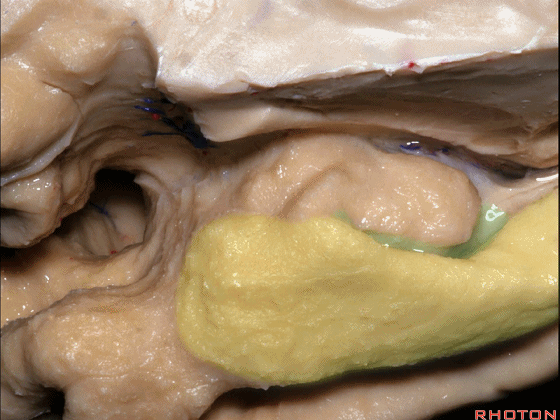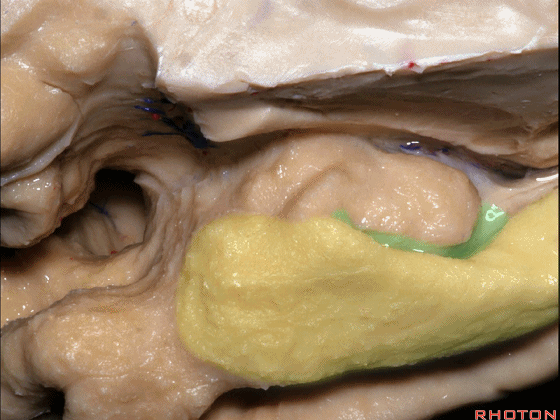
▼该区域有三个脑回,这是 边内回
there's three sort of gyri in this area, intralimbic in this area.
▼这是 Giacomini带(海马齿状回前带)
Band of Giacomini
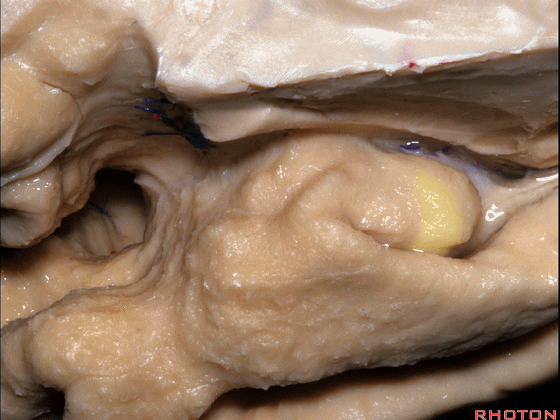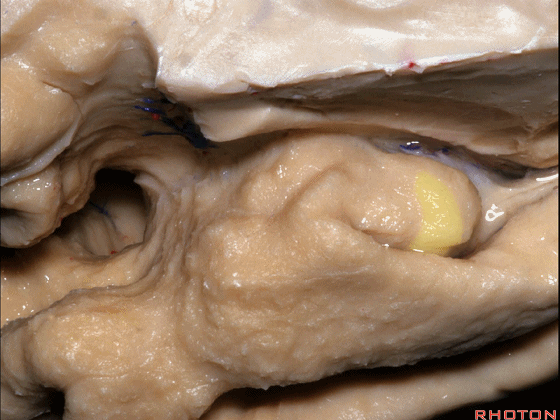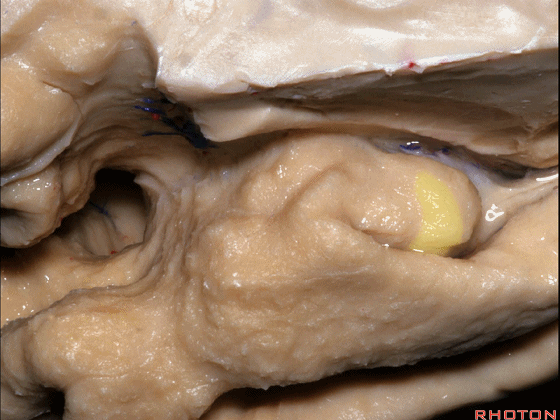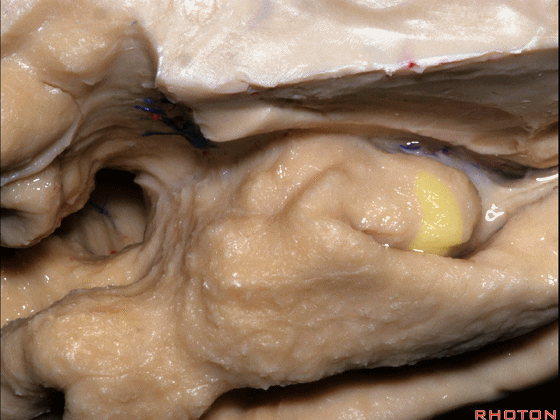
▼这是 钩状回
uncinate gyri
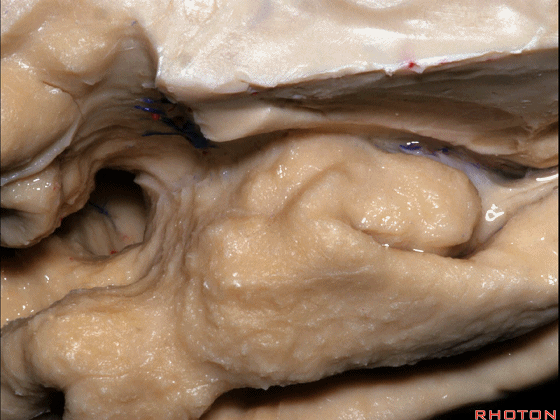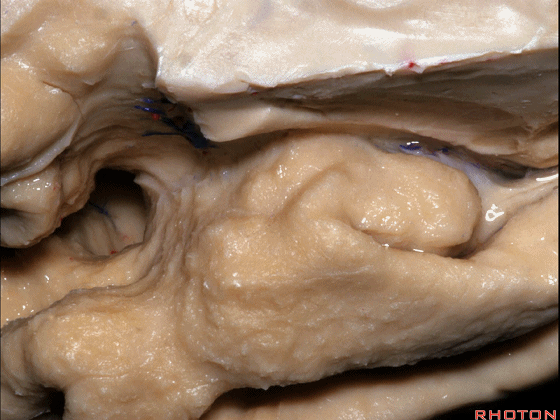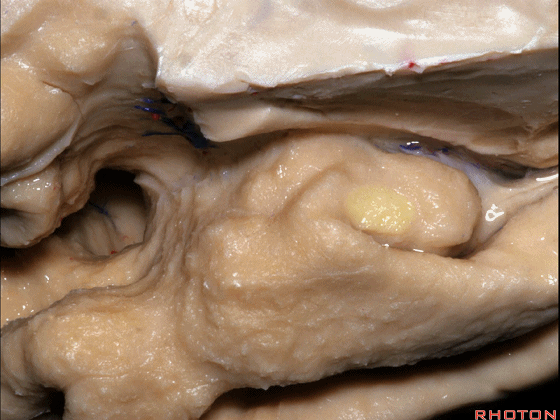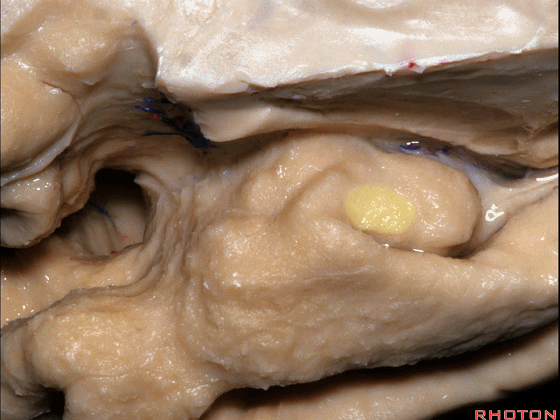
▼该区域的三个脑回其实是位于海马旁回上方的齿状回的延续,该锯齿样的脑回叫做齿状回(下图)。
These are really just continuation of this gyrus above the parahippocampal gyrus, this beady gyrus that is known as the dentate gyrus.
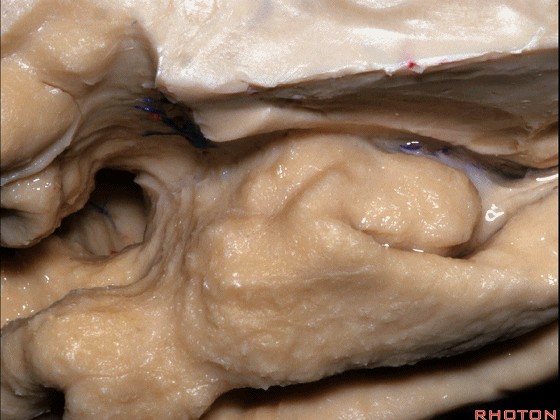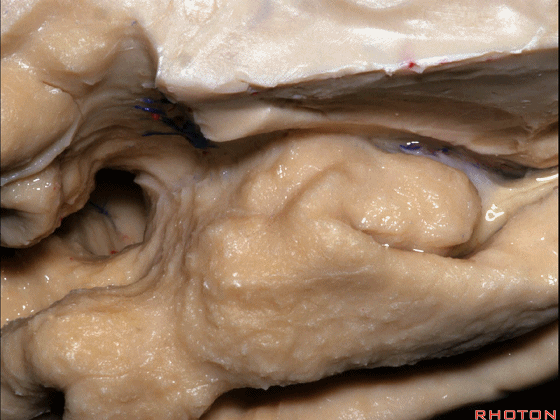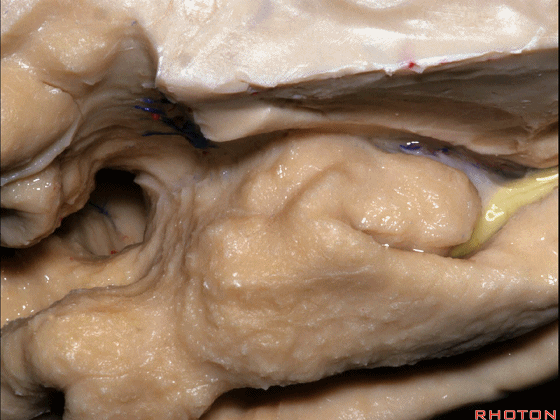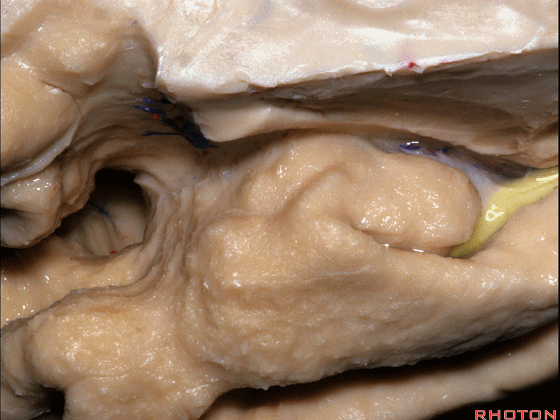
▼因此颞叶内侧面前部的这片区域主要是内翻的海马头(下图)。
So this part of the anterior part of medial temporal lobe is mainly enfolded head of hippocampus.
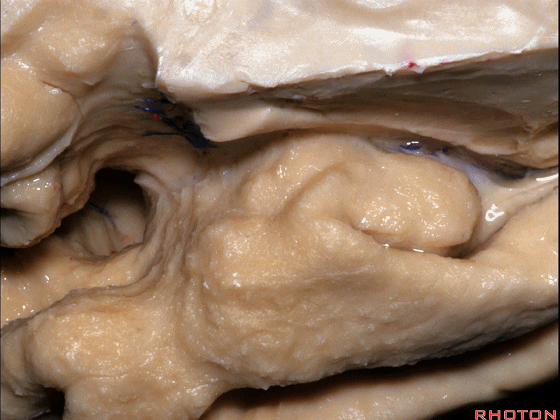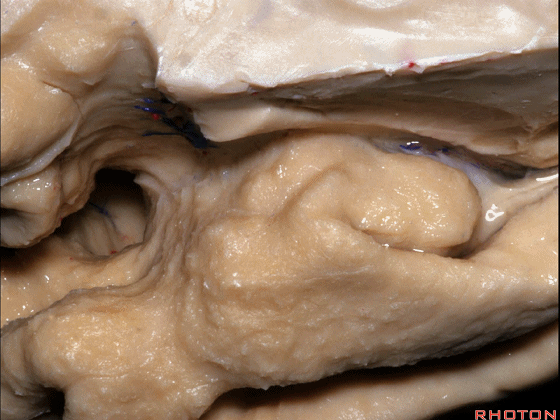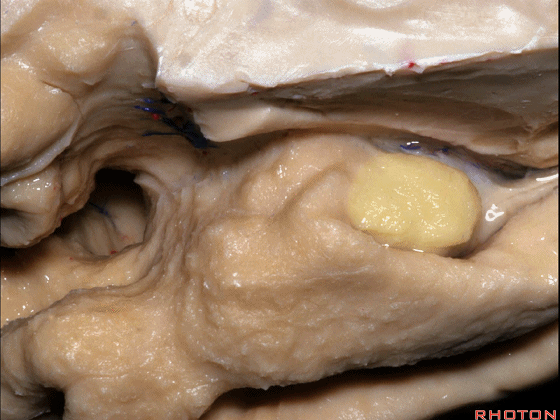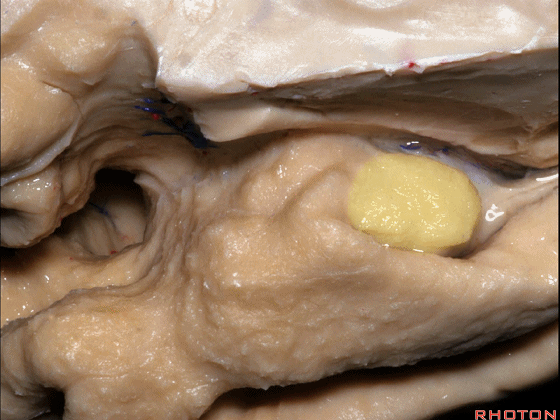
▼这是外侧裂谷。大脑中动脉由此转向侧后方。
And here this is the Sylvian vallecula. The middle cerebral artery runs laterally through this area.
▼这是脉络膜前动脉
So, here we see anterior choroidal artery
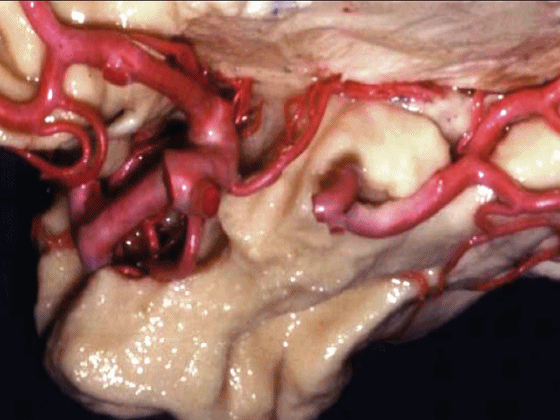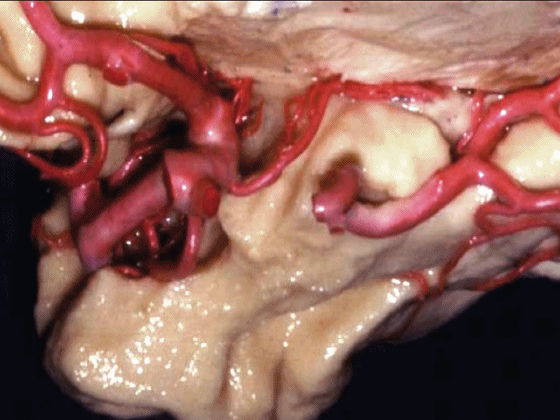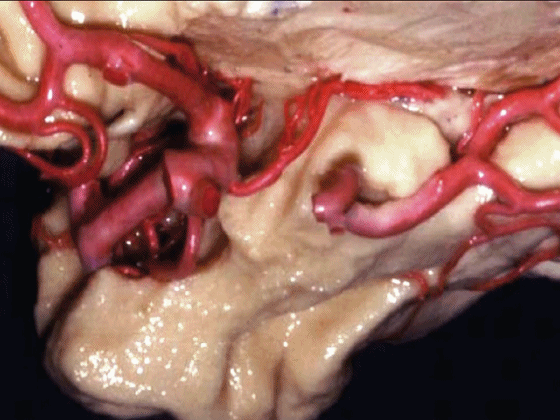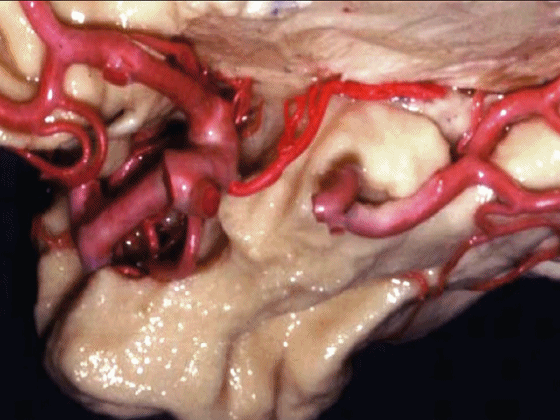
▼脉络膜前动脉 起自 半月回内侧(下图)
anterior choroidal artery arise here medial to semianuler gyrus
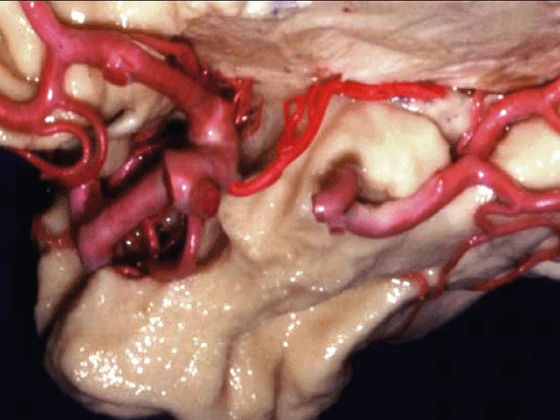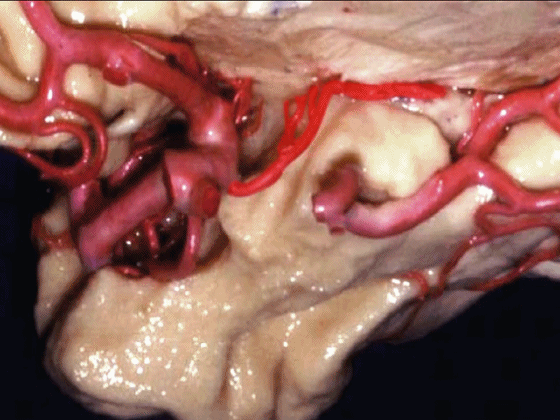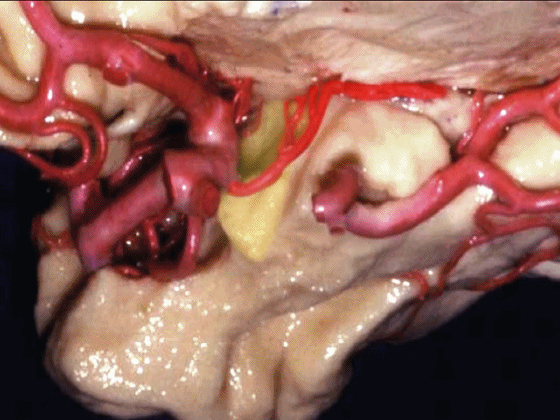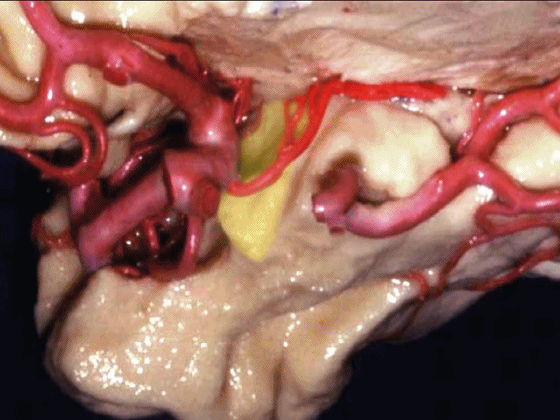
▼脉络膜前动脉沿着 半月沟 (下图)走行
where along this semiannular sulcus,
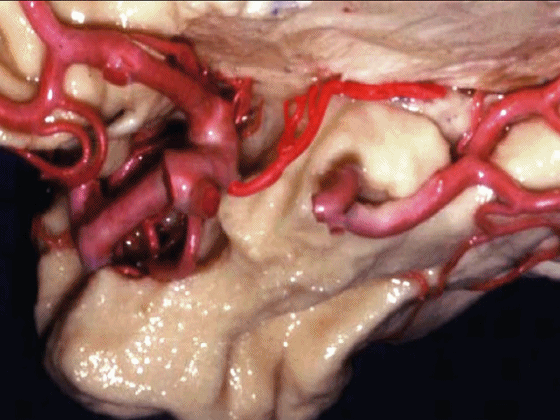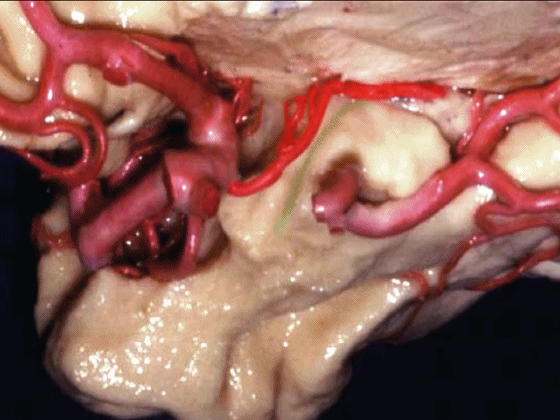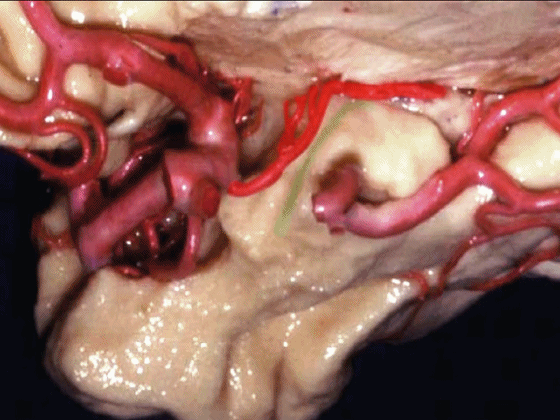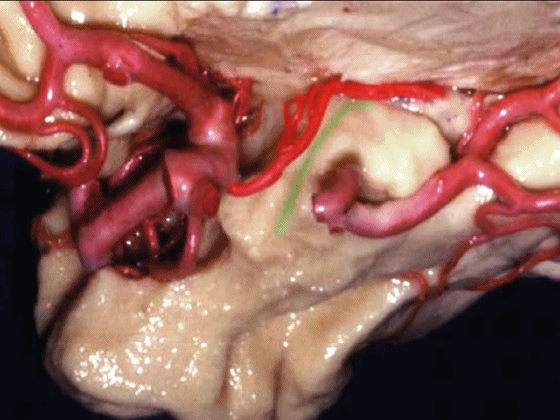
▼脉络膜前动脉 在下脉络点(下图)进入颞角。
and enter the temporal horn at the inferior choroidal point.
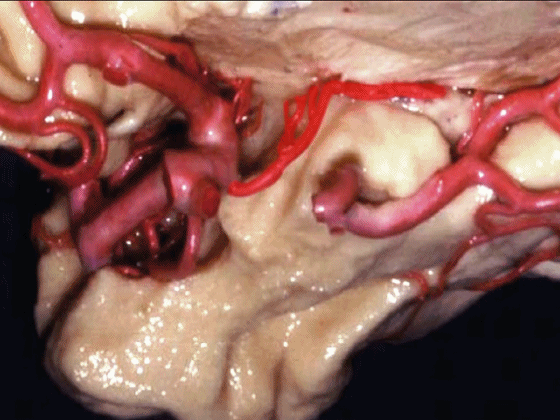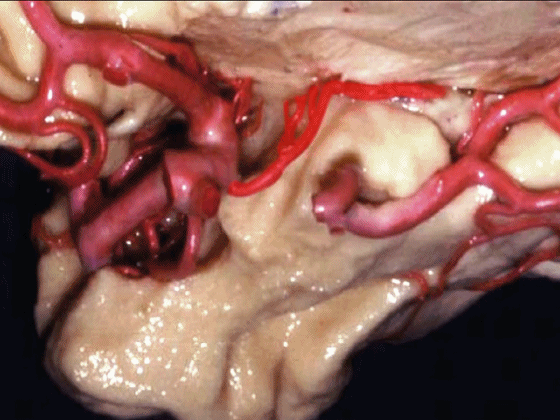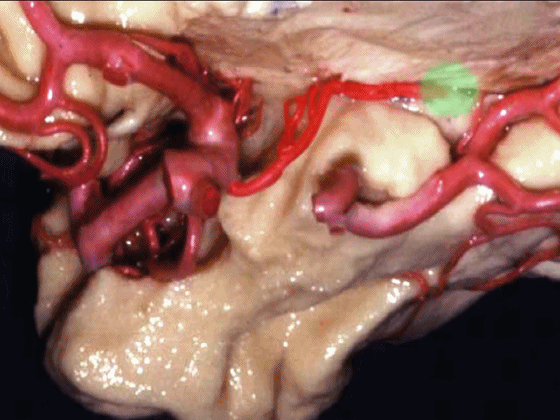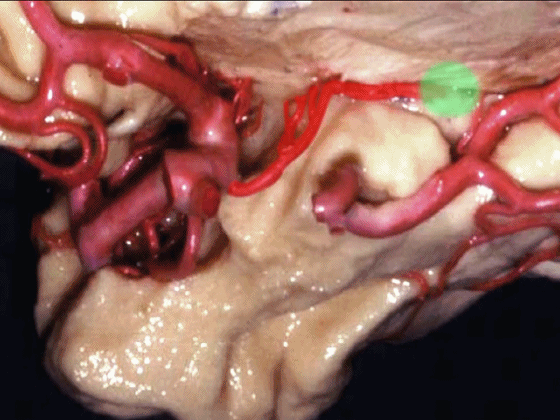
▼沿着钩回后段(下图)走行的是大脑后动脉P2段。
And then running along this posterior segment of the uncus, we have the P2 segment of posterior cerebral artery.
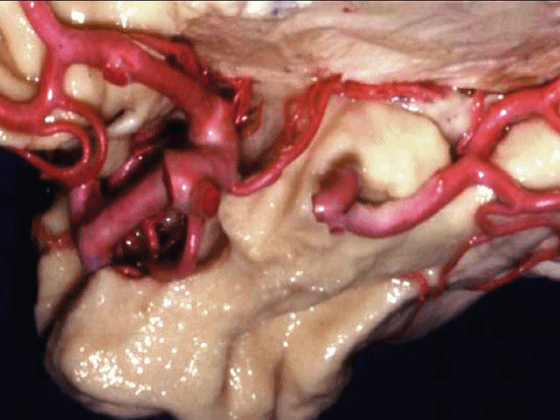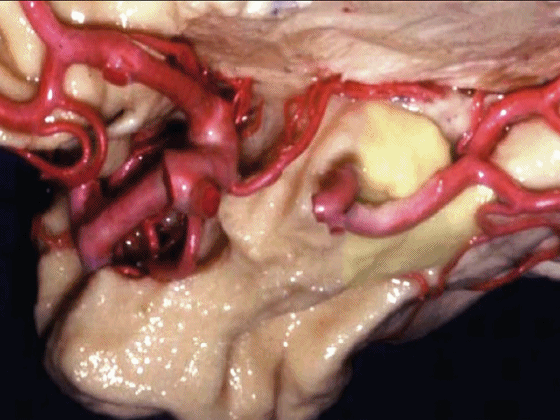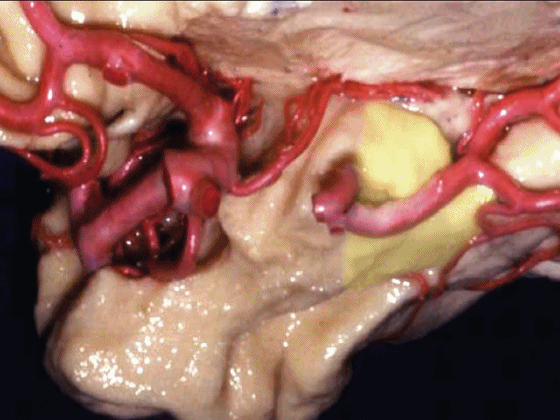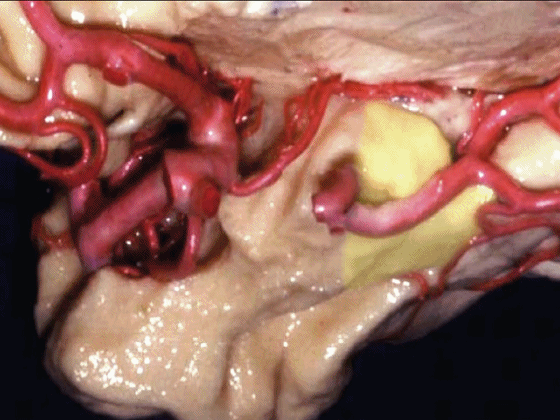
▼这是 大脑后动脉P2段
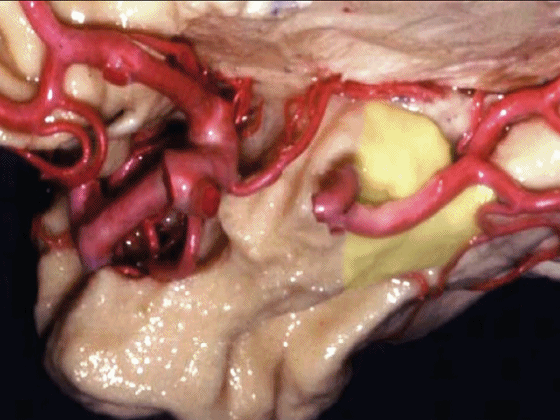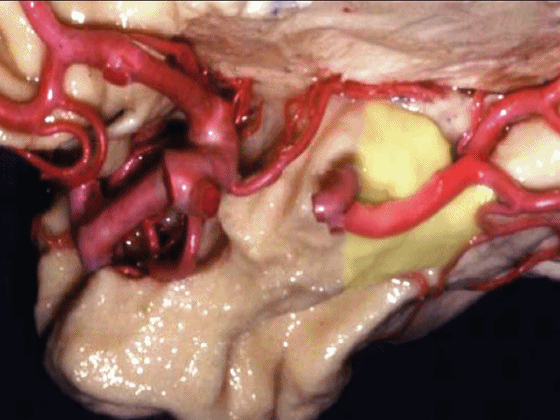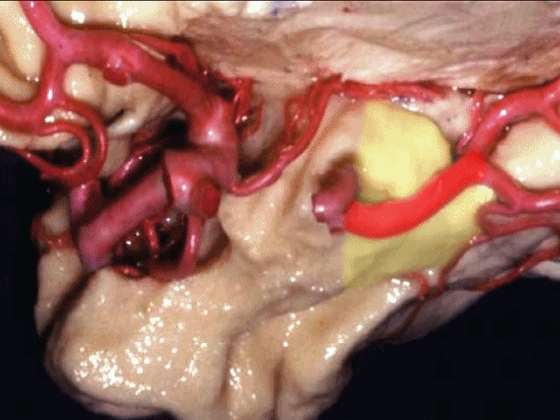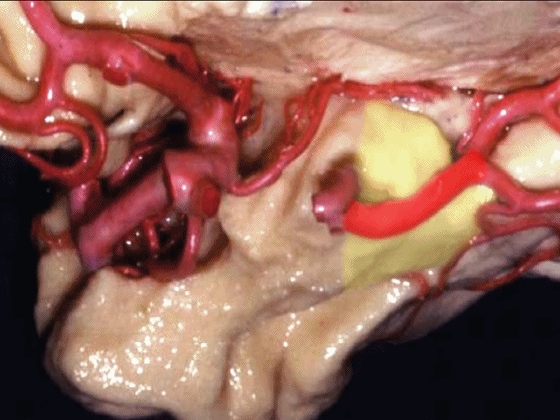
▼这是另一个钩回内侧面,下图示天幕游离缘,脑疝中可出现钩回经天幕游离缘疝出。
Another view of this area of uncus from medially, we see tent edge,and in herniations this uncus can herniate through the tentorial edge here.
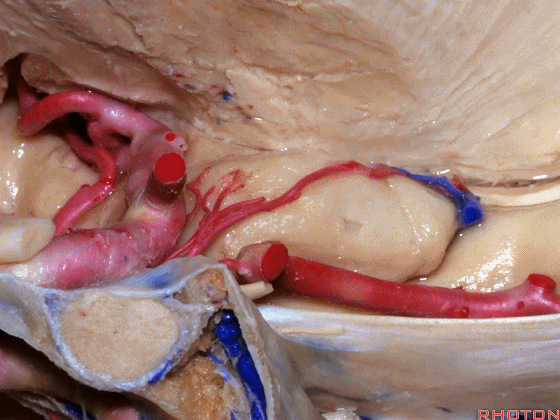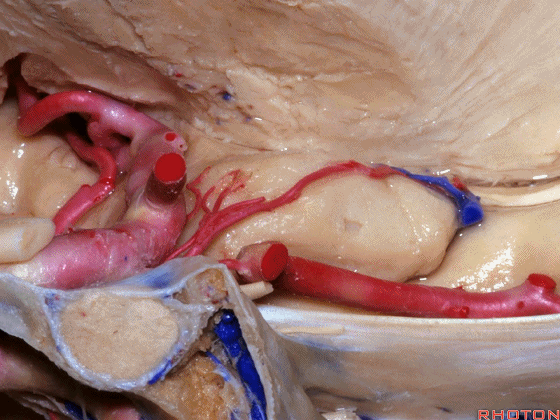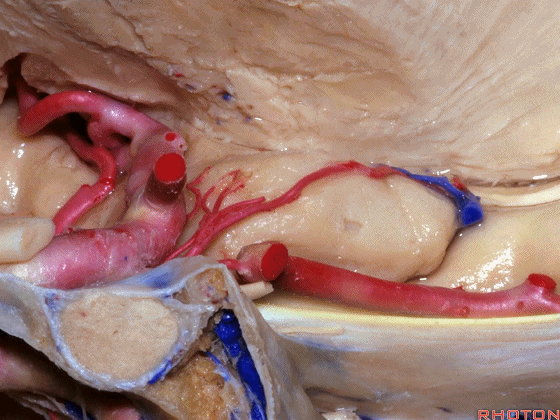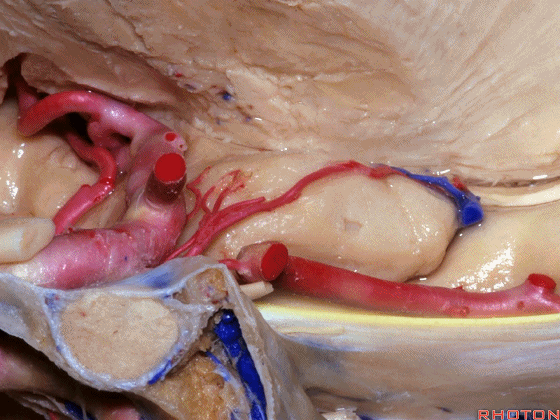
▼大脑后动脉(下图)在钩回切迹内侧走行。
We see posterior cerebral running medial to this uncal notch.
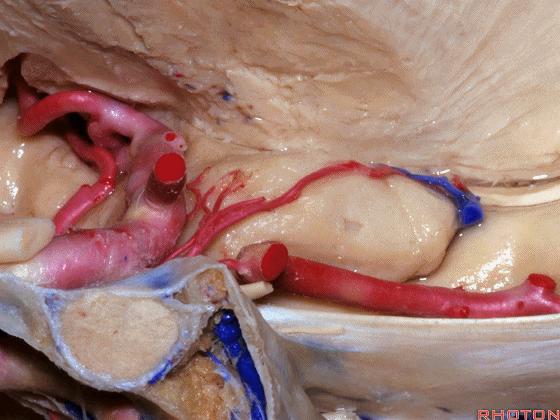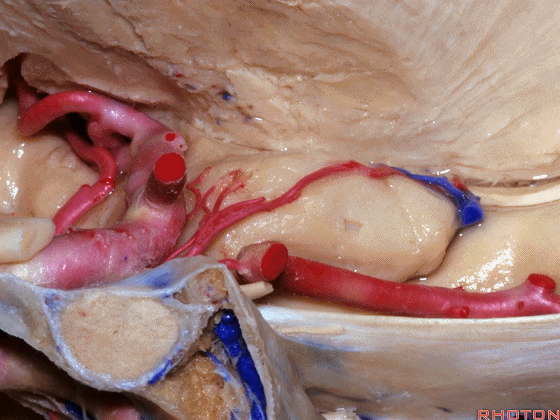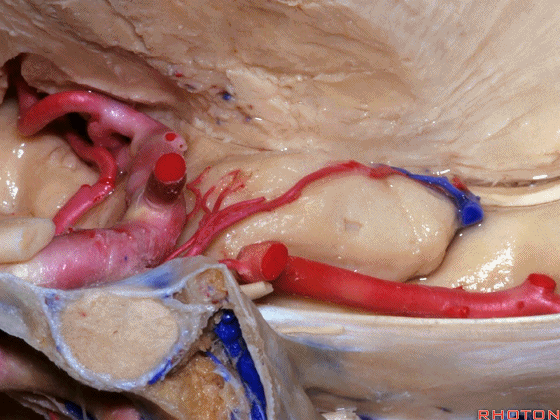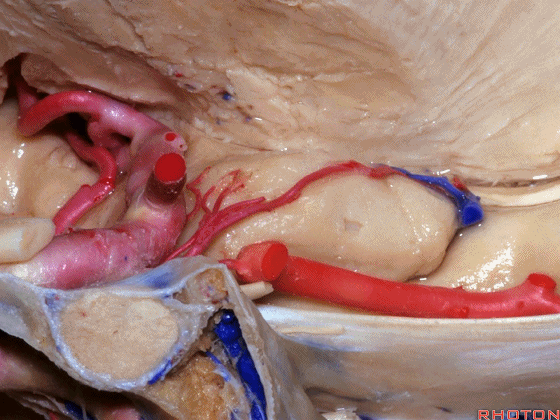
▼这是 钩回切迹
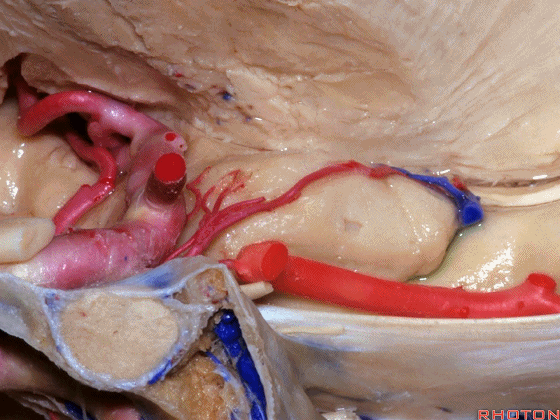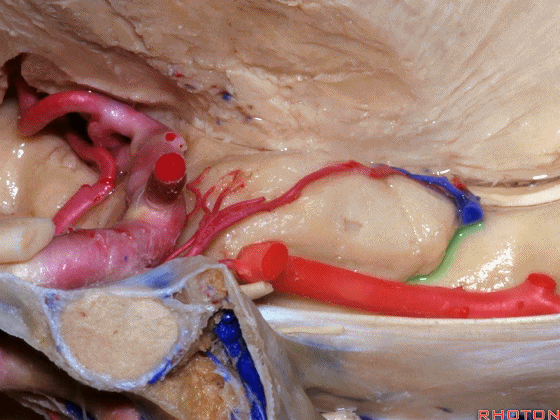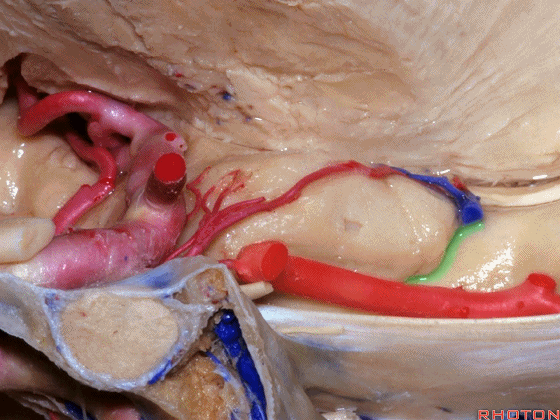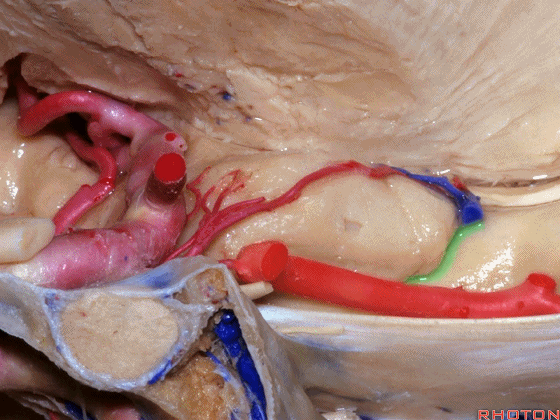
▼脉络膜前动脉(下图)沿着半月沟走行,并于下脉络点进入颞角。
And we see the anterior choroidal artery running along this semiannular sulcus and entering the temporal horn at the inferior choroidal point.
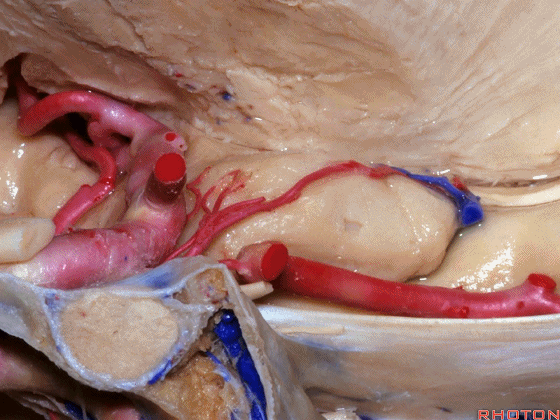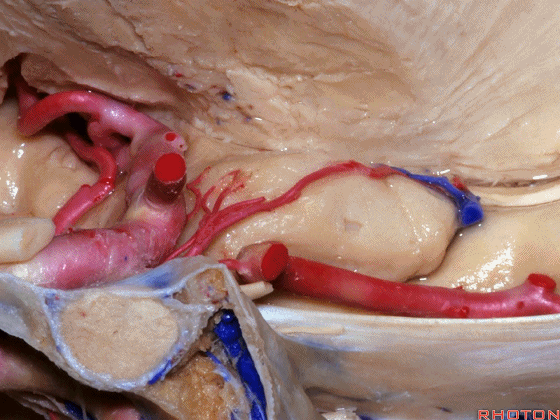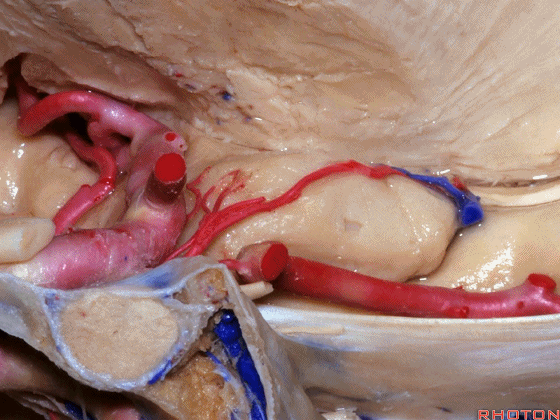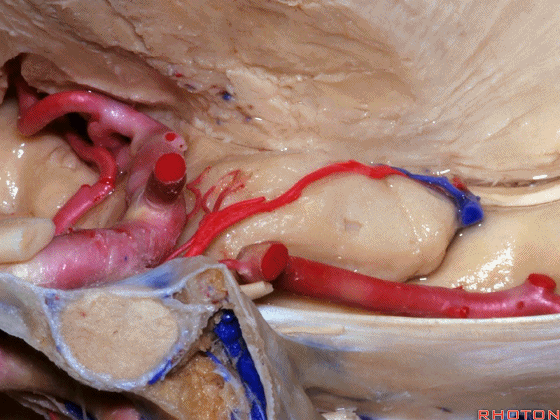
▼这是 半月沟
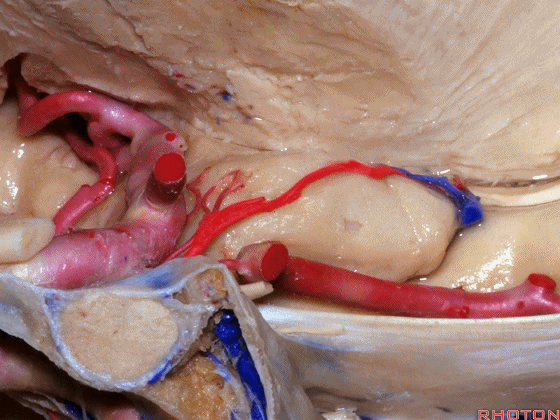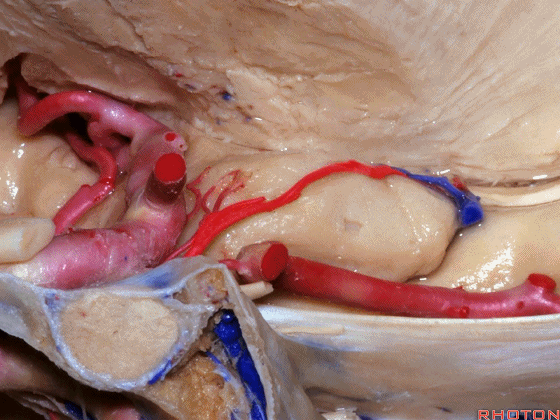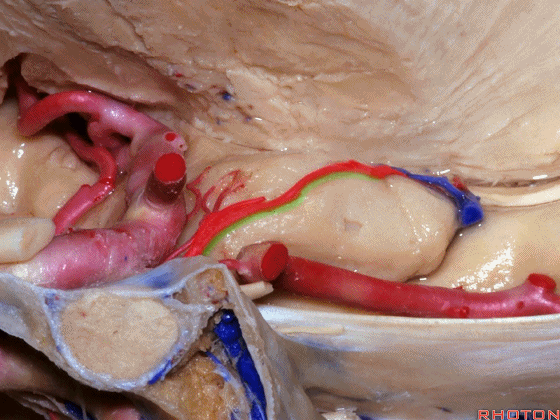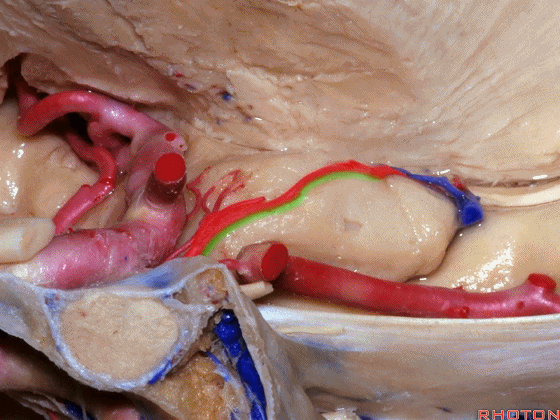
▼这是 下脉络点
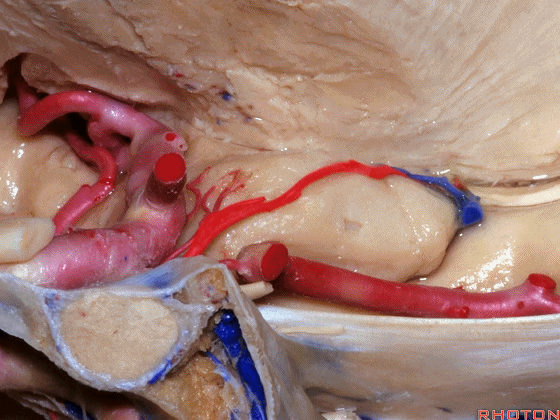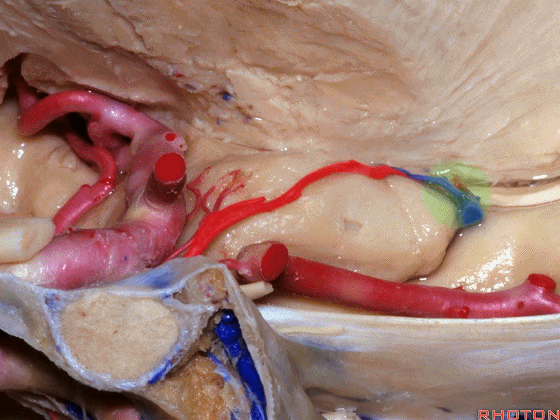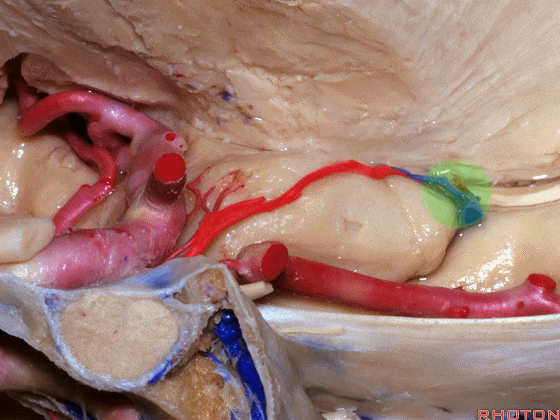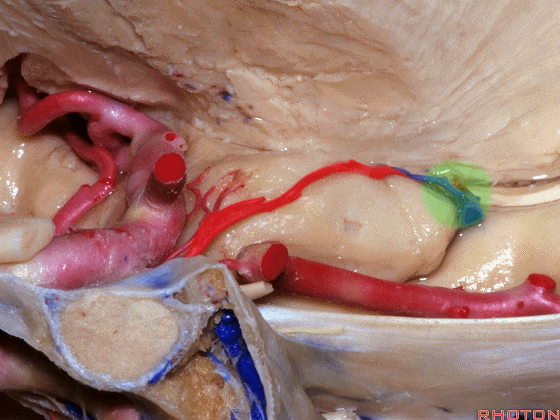
▼大脑中动脉 穿行于外侧裂谷(下图)
And then passing through this area, here, we see the middle cerebral, actually
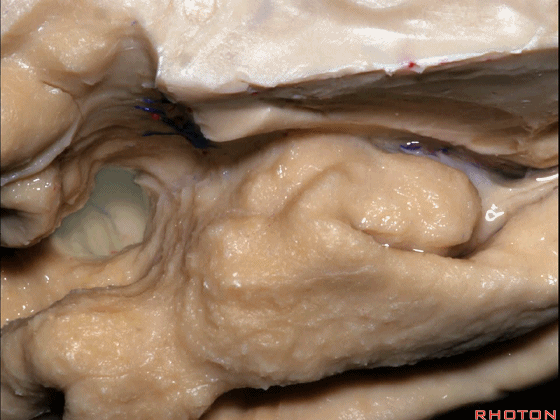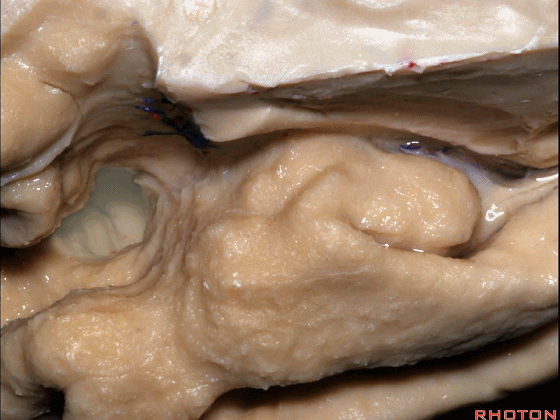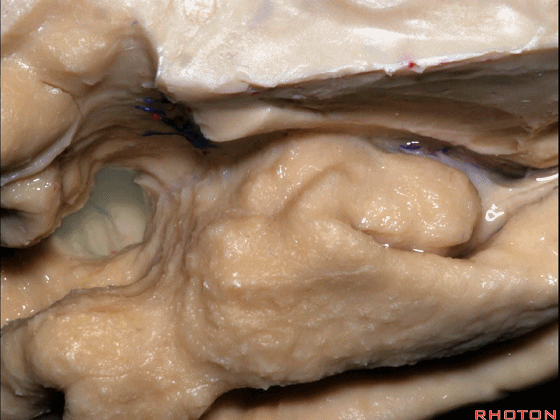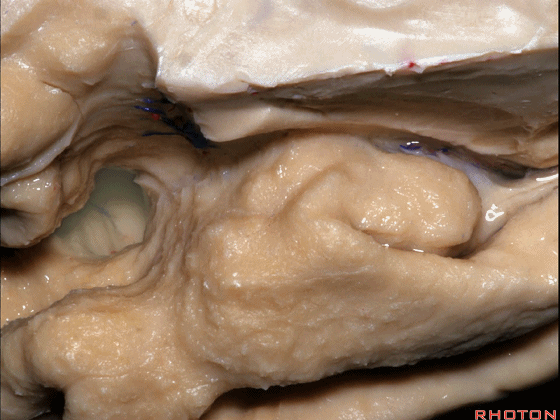
▼这是大脑中动脉,其发自颈内动脉
arise from the carotid,

▼这是 颈内动脉
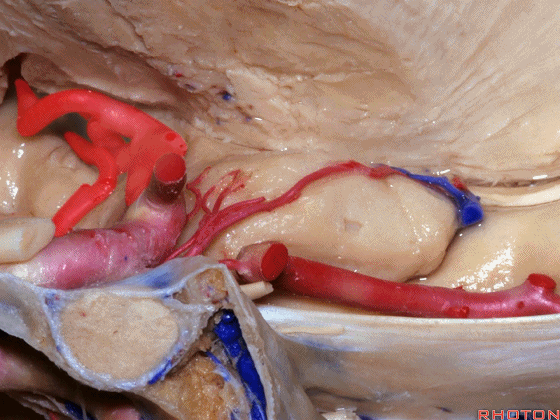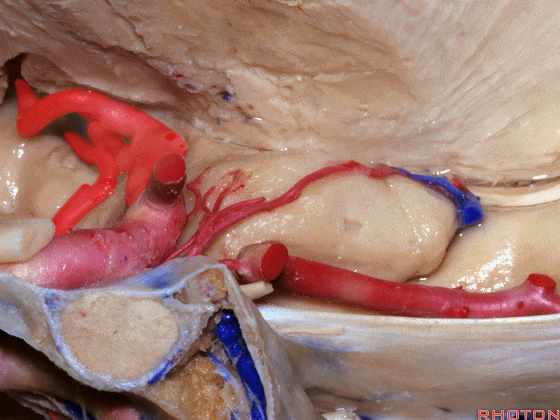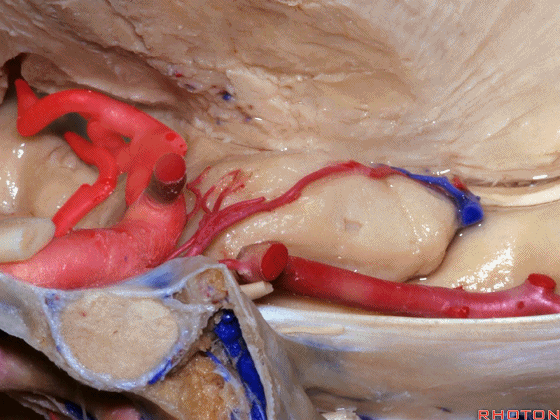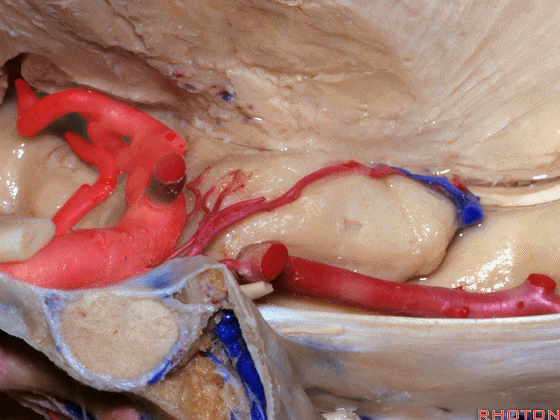
▼大脑中动脉 行经钩回前段(下图),后者含有杏仁核
pass along the anterior segment of the uncus that contains the amygdala,
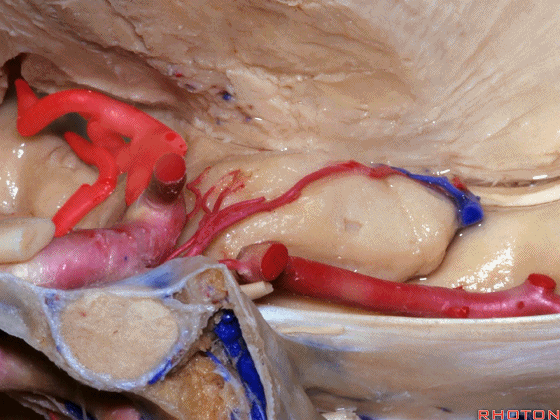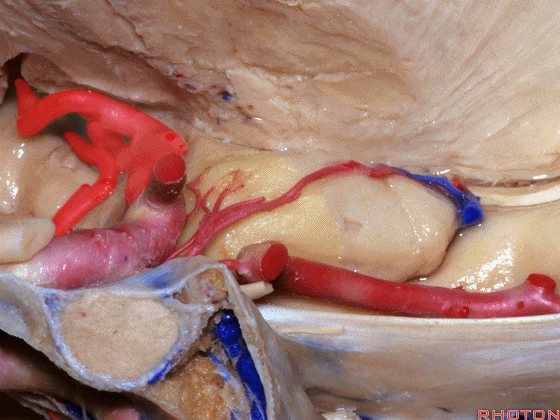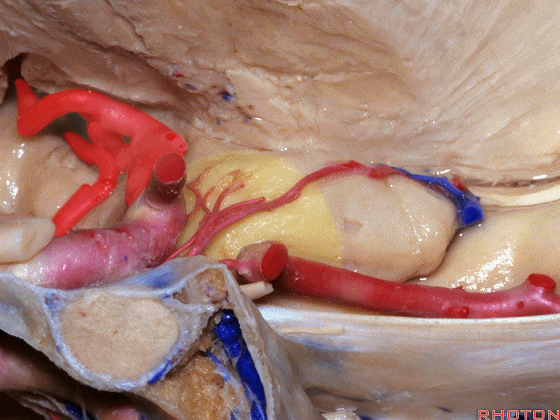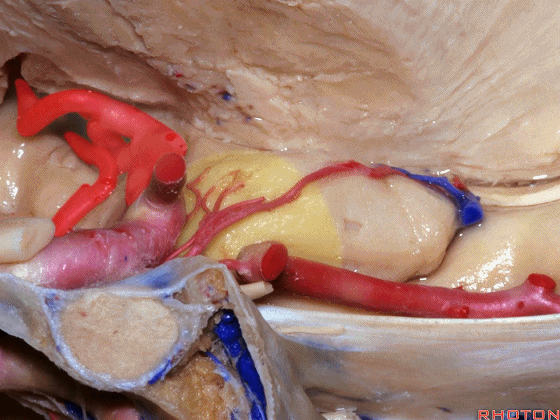
▼大脑中动脉 随后向外侧进入外侧裂(下图)。
and then runs laterally toward the Sylvian fissure.
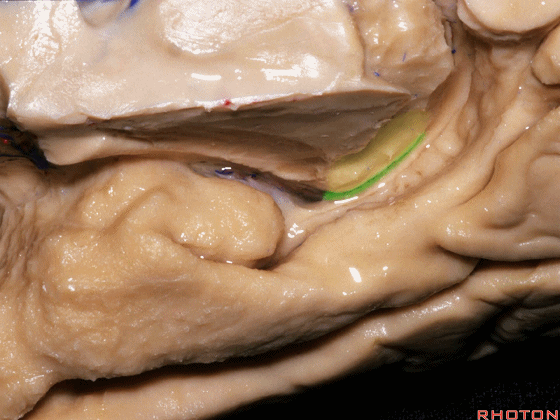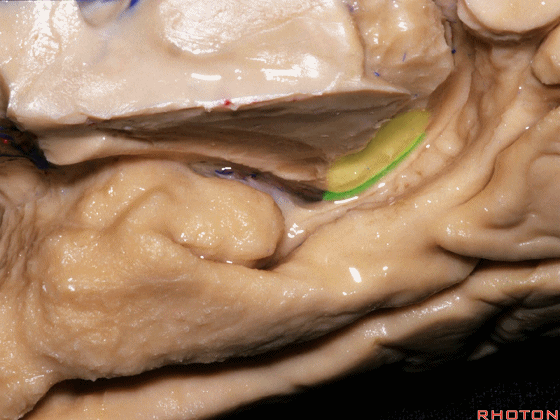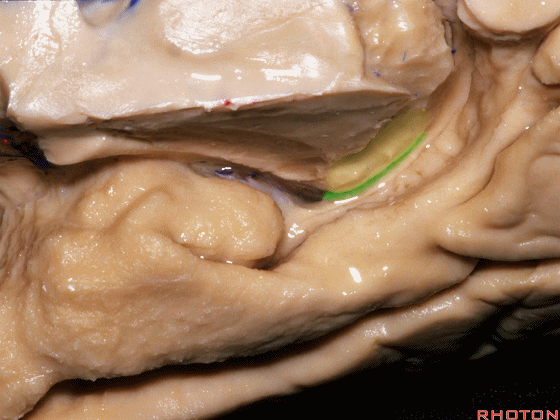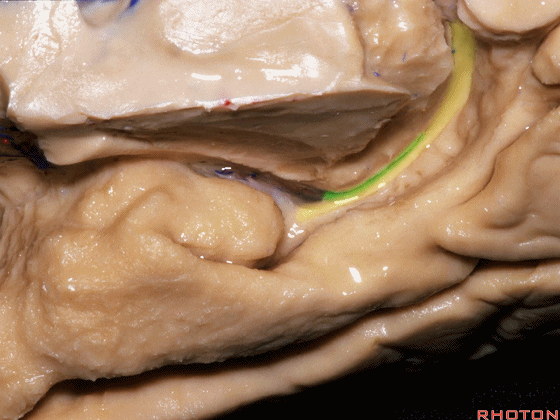
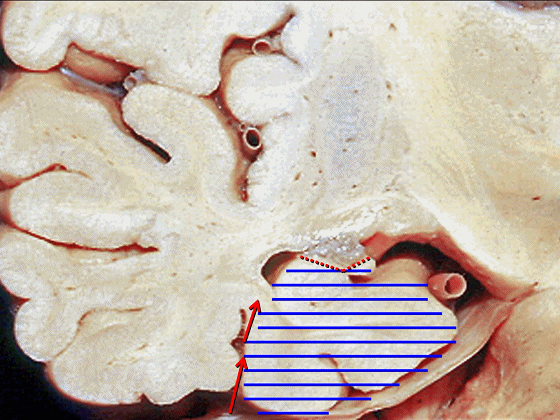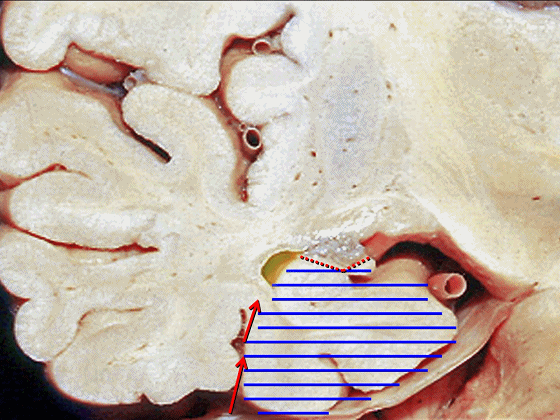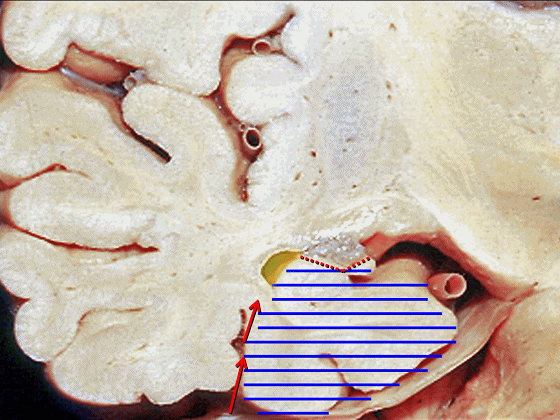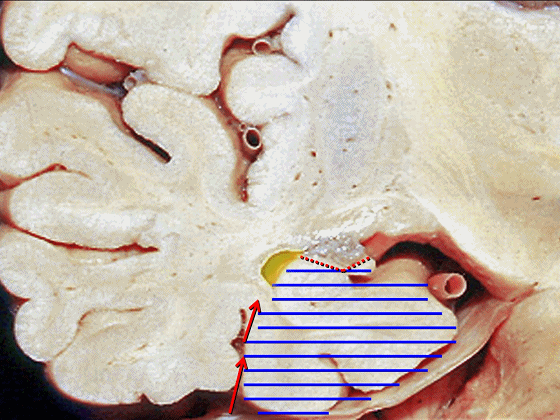
![]()
▼现在来看颞叶内侧面的中部。其构成环池的外侧界。
这一区域包含三层结构,下层(下图)位于侧副沟内侧 。
Now, middle part... of medial temporal lobe is here in the lateral margin of the ambient cistern, and this area has roughly three layers here, a lower layer here that is medial to the collateral sulcus
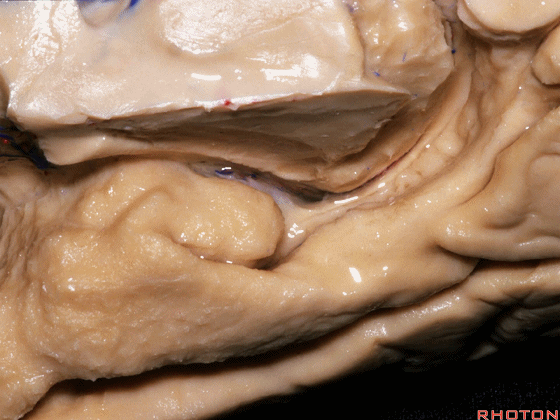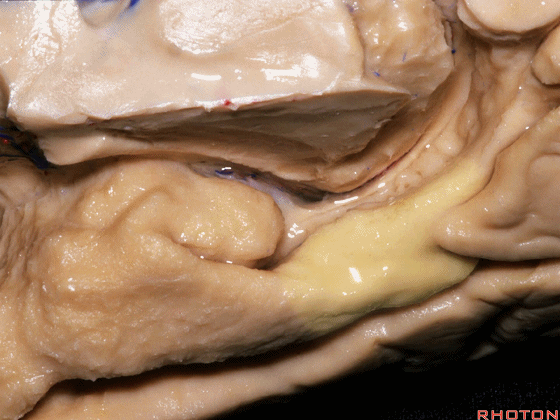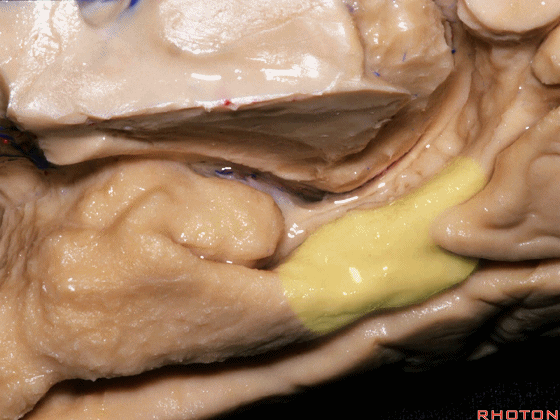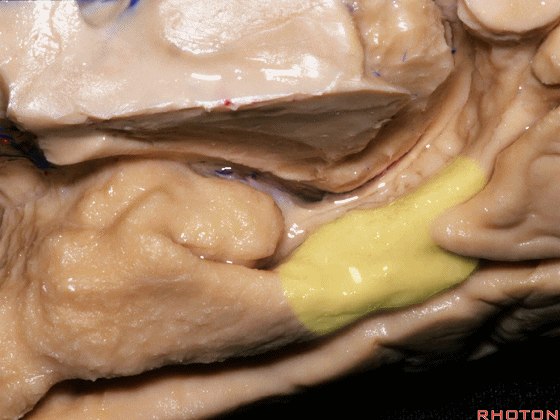
▼这是 侧副沟
collateral sulcus
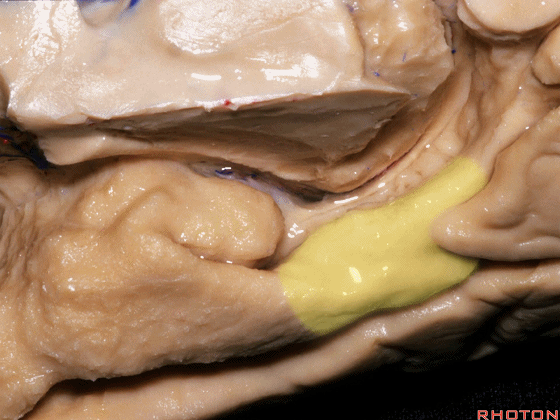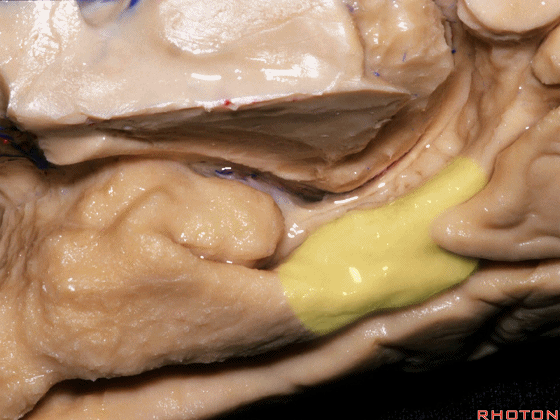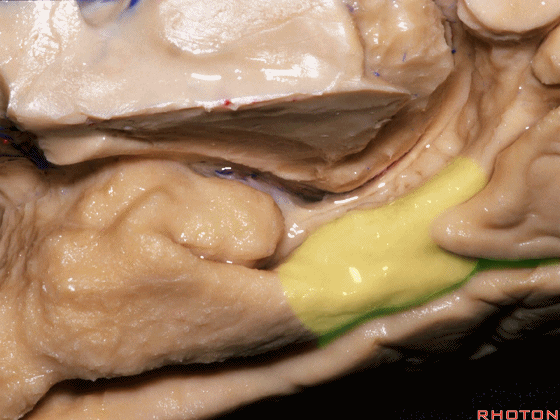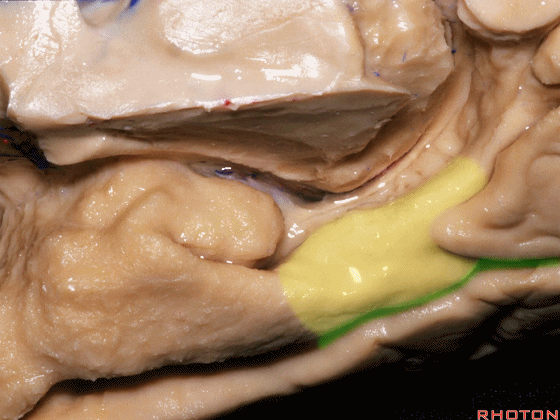
▼在其上方一层为齿状回(下图)
and then above that is the dentate gyrus
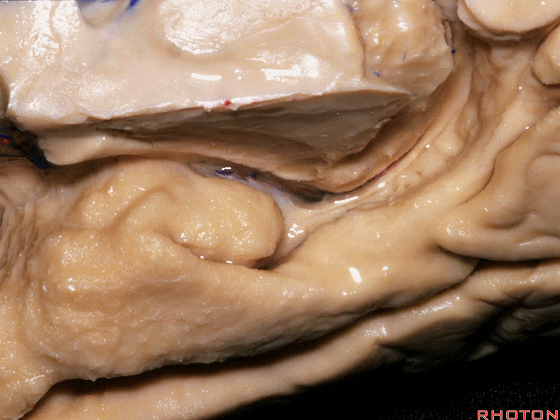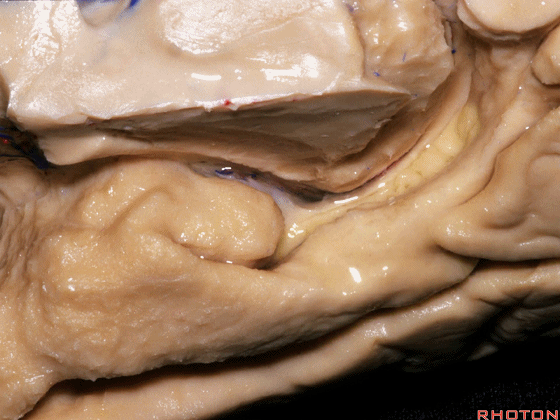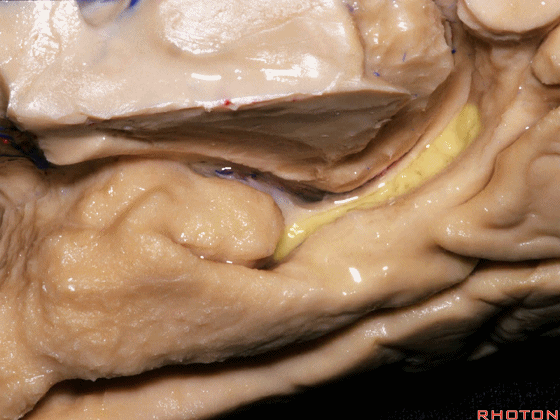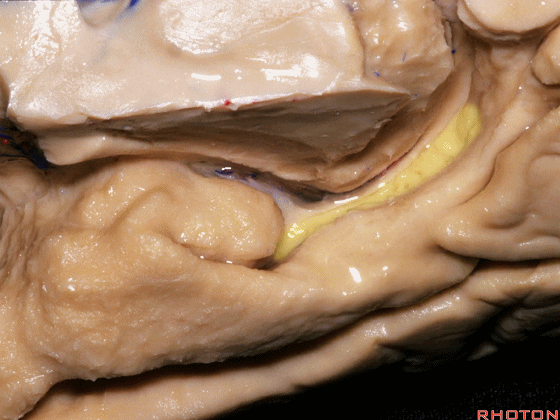
▼最上层为穹窿伞。
因此环池的外侧壁为这三层结构。
and above that is the fimbria.So three layers in this lateral wall of ambient cistern.
▼这是视束
Here we see the optic tract,
▼这是外侧膝状体,其位于环池顶。
and what is this? Lateral geniculate body here, in the roof of the ambient cistern.
▼这是下脉络点。
This is inferior choroidal point.
▼这是脉络裂
choroidal fissure
▼脉络裂 位于丘脑的 外侧膝状体 与 穹窿伞 之间。
And then choroidal fissure here between the thalamus, lateral geniculate and the fimbria of the fornix.
▼这是颞角(下图)冠状面的模式图
And temporal horn, if we look at it

▼其底壁内侧为海马(下图)
in the floor medially is hippocampus,

▼外侧为另一个底壁的突起,叫做 侧副隆起(下图)

▼侧副隆起 覆盖于侧副沟(下图)深部的表面
that overlies the deep end of the collateral sulcus that we call collateral eminence.

▼构成顶壁的是胼胝体毯部。
And then the roof is formed by tapetum fibers from the callosum.

▼这些毯部纤维将颞角顶壁与视辐射(下图)分开。
These tapetal fibers separate the roof from the optic radiations.

▼颞角顶壁内侧为尾状核 的尾
Medially you have the tail of the...caudate,

▼这是外侧膝状体
and then lateral geniculate body

▼这是脉络裂
choroidal fissure

▼这是 穹窿。 打开脉络裂的部位,通常是在穹窿侧,目的是保护内囊的豆状核下部,其内含有视辐射。
And always when we're opening the choroidal fissure, we want to open on the forniceal side,so that we preserve this sublenticular part of the internal capsule that contains the optic radiations.

▼脉络裂位于穹窿和丘脑之间。
and the choroidal fissure between the fornix and...between the fornix and the thalamus.

![]()
▼现在从下方来看颞叶内侧面,可见钩回前段(下图),其包含有杏仁核
So if we look at medial temporal lobe from below, we see anterior segment of uncus that contains amygdala,
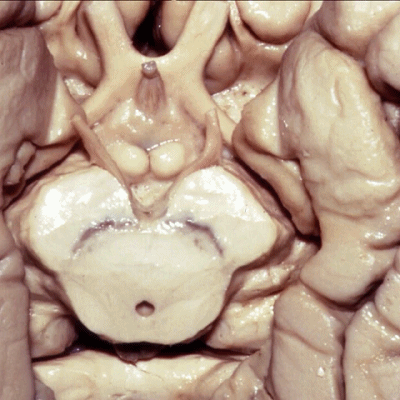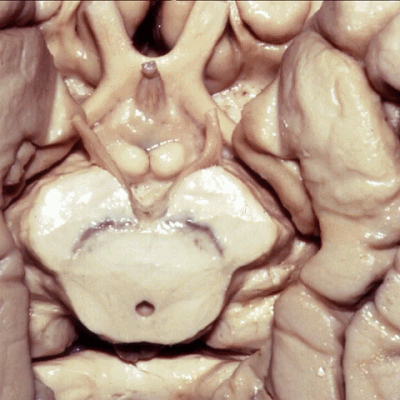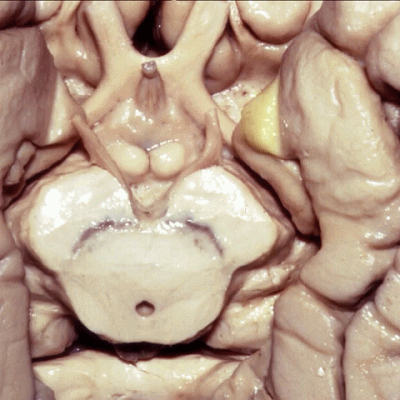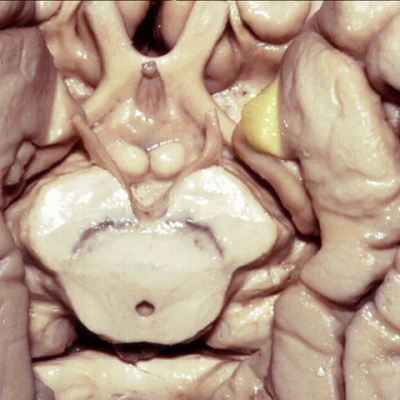
▼这是钩回后段,其内还含有内翻的海马头。
posterior segment of uncusIt contains the enfolded head of the hippocampus.
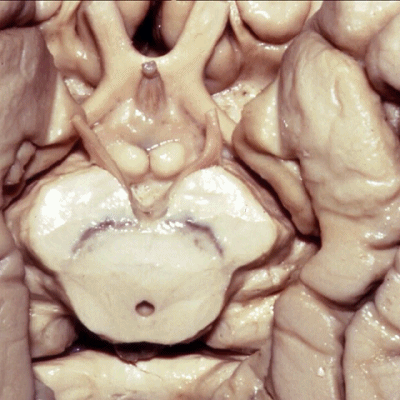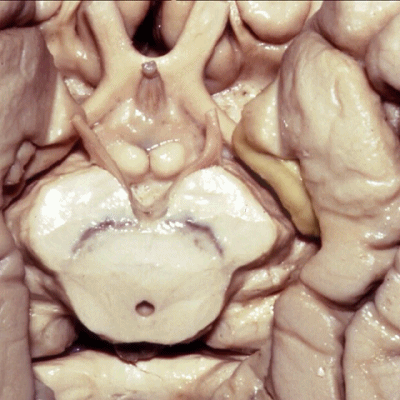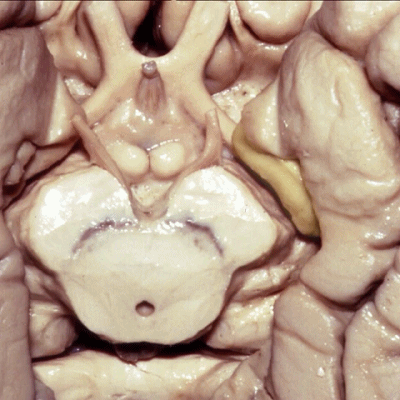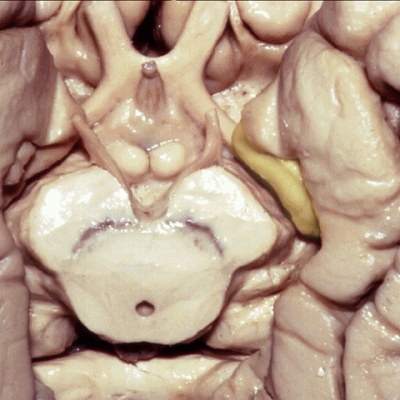
▼钩回后段面向大脑脚(下图),之间是脚池(下图)。
facing the peduncle across the crural cistern.
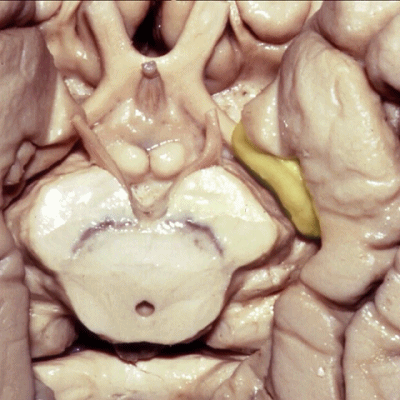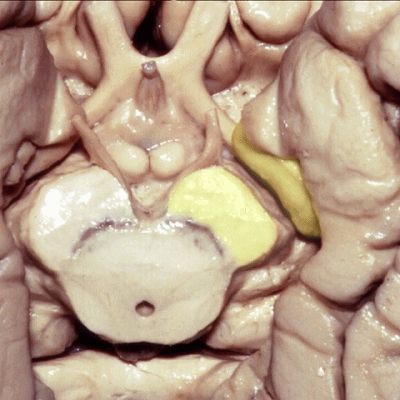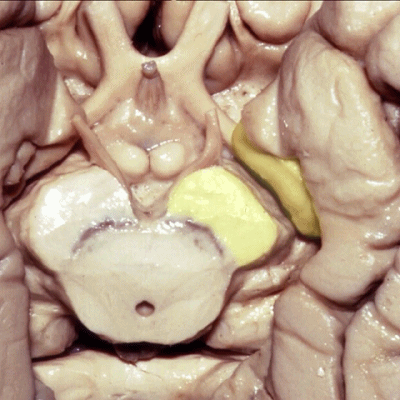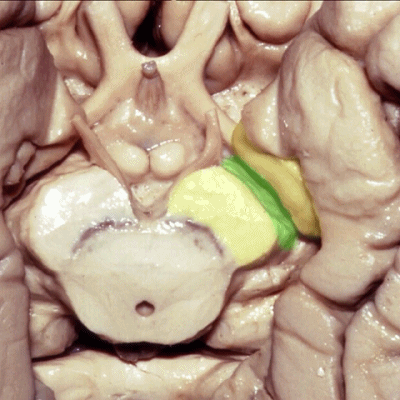
▼后方我们可见海马旁回
And then we come backwards and we have parahippocampal gyrus,
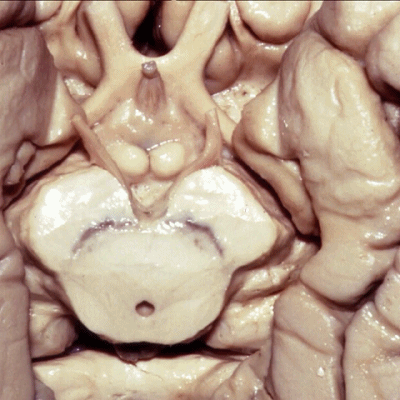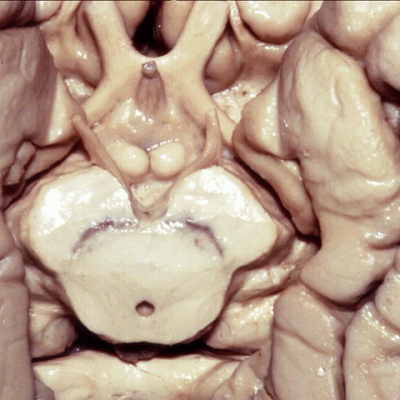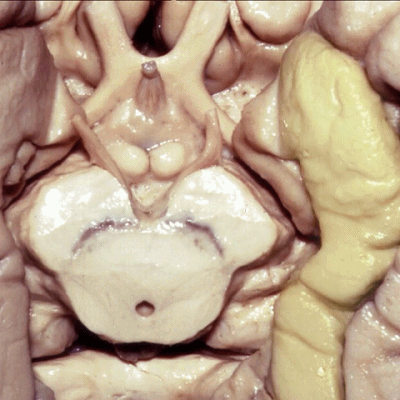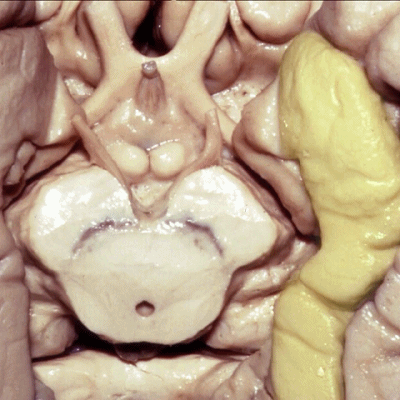
▼这是 侧副沟
collateral sulcus.
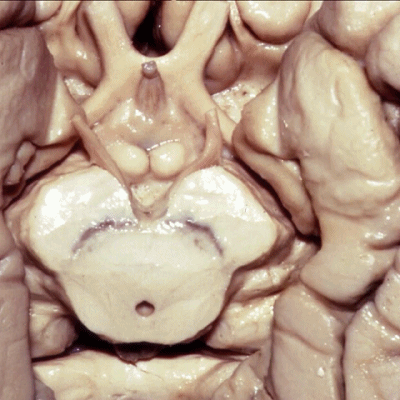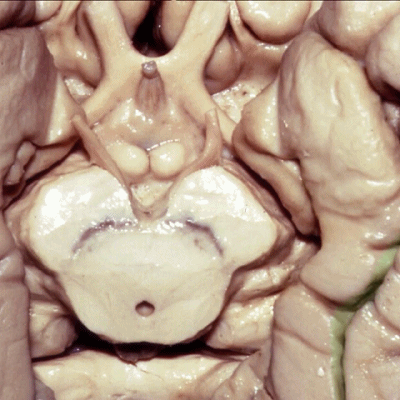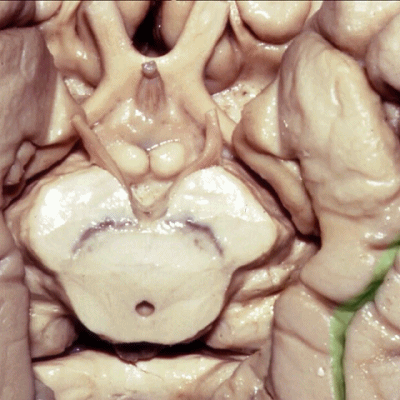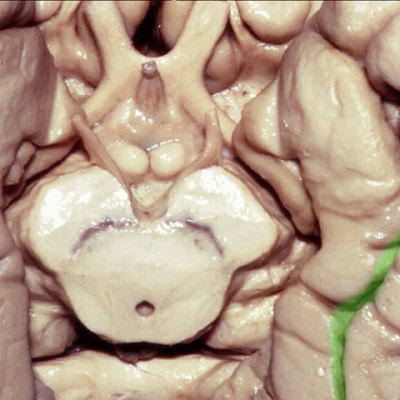
▼现在我们去除了海马旁回的内侧部,显露出齿状回(下图)。由此可知为何取名为海马。
And, here now we've removed the medial part of parahippocampal gyrus, and you see why this...how this... develop this hippocampal name or sea horse. We take off the lower...this part of parahippocampal gyrus and...we see dentate gyrus
▼这是 穹窿伞(下图) 和整个海马的形态。
fimbria, and this sea horse appearance.
▼这是边内回
And we see intralimbic,
▼这是 Giacomini带
Band of Giacomini,
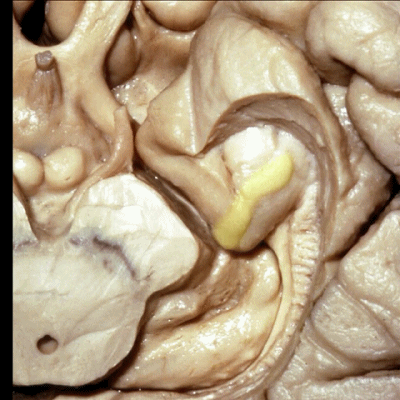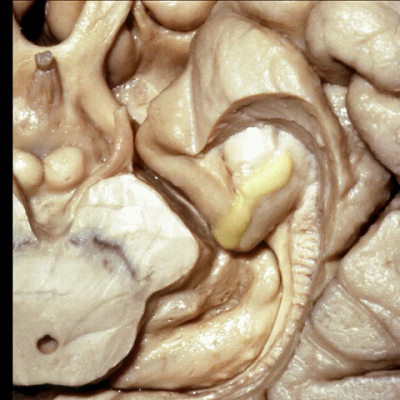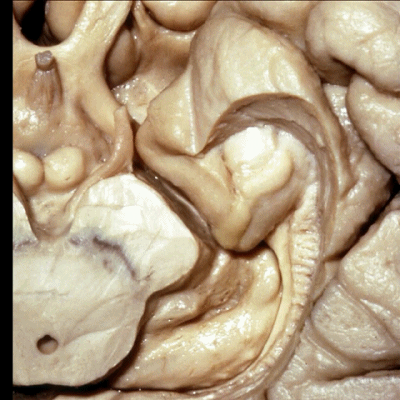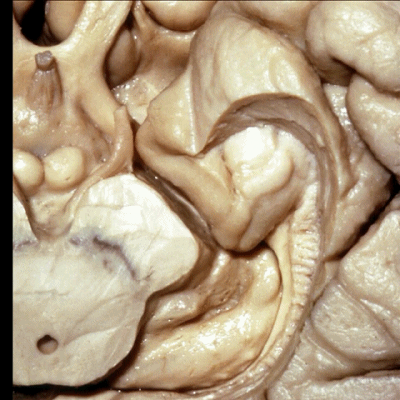
▼这是 钩状回
边内回、Giacomini带、钩状回 共同位于钩回后段。
uncinate gyri on that posterior segment of the uncus.
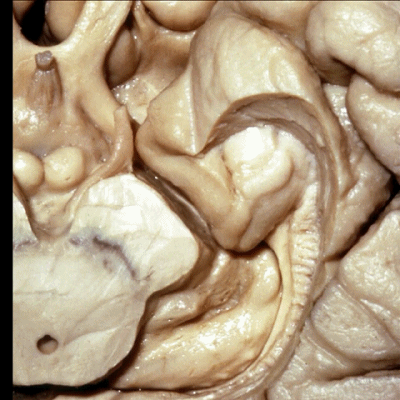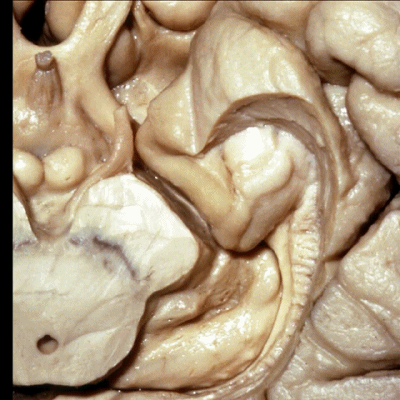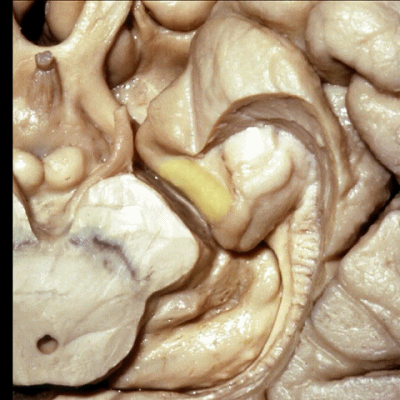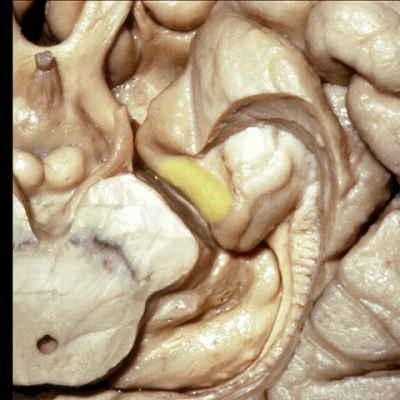
▼进一步,我们去除齿状回。从下方我们显露出杏仁核(下图),其构成颞角的前壁。
Looking from below we see the amygdala in the anterior wall of the temporal horn.
▼这是 穹窿伞
We preserve the fimbria here
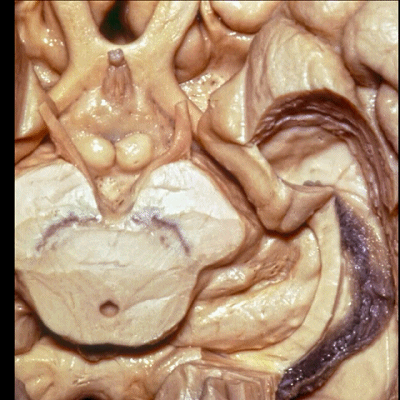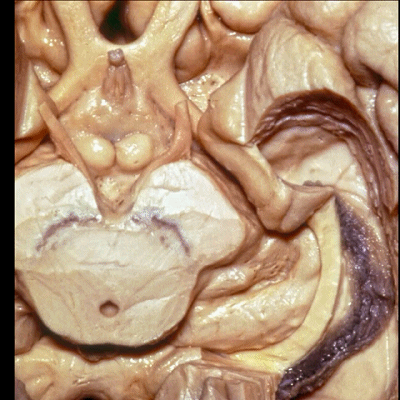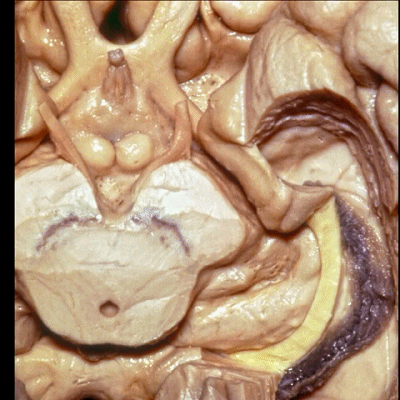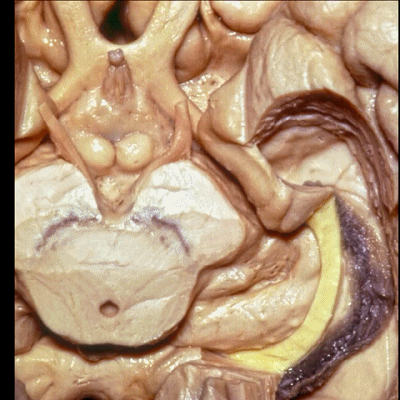
▼这是 脉络裂
choroidal fissure
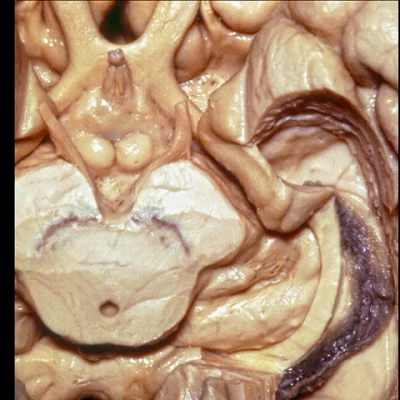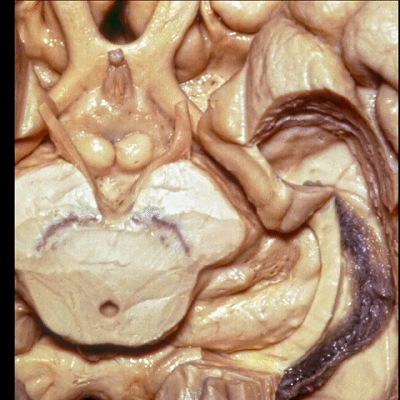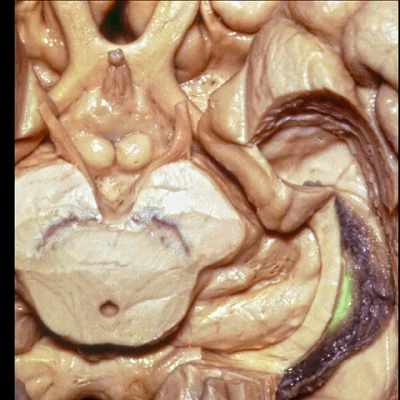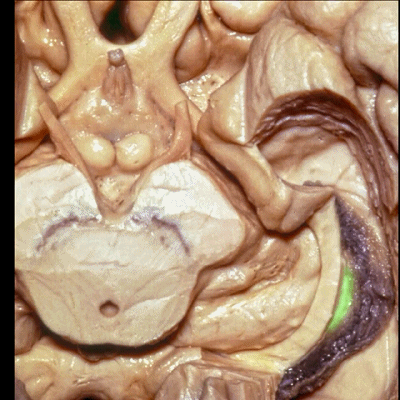
▼脉络裂向一侧附着于穹窿伞带(下图),另一侧附着于丘脑带(下图)
and the choroidal fissure is attached on one side to the tenia fimbria, on the other side to the tenia thalami
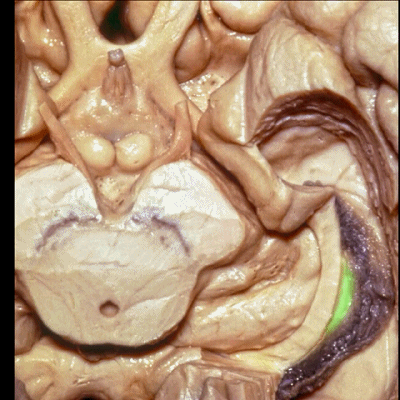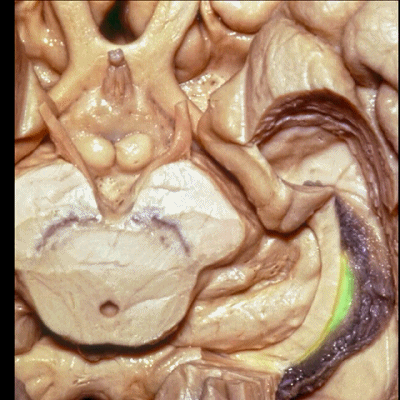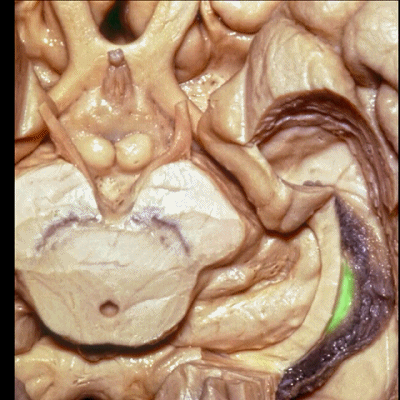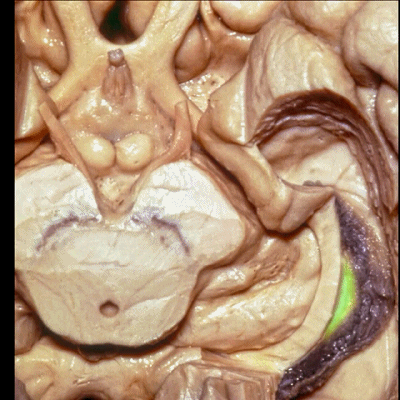
▼此部分丘脑 由丘脑枕(下图)、 外侧膝状体、内侧膝状体 组成。构成了环池的顶壁。
the thalamus in this area is made up of pulvinar, lateral and medial geniculate body in the roof of the ambient cistern.
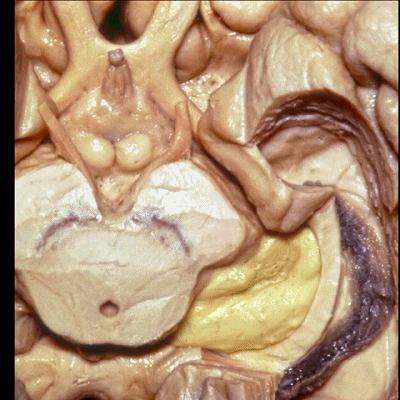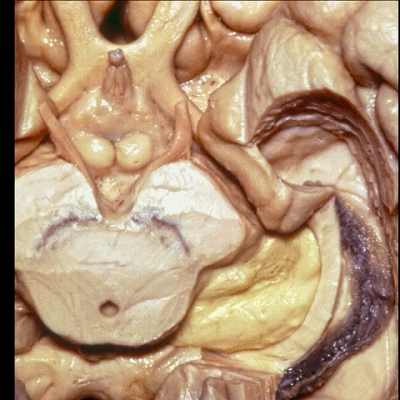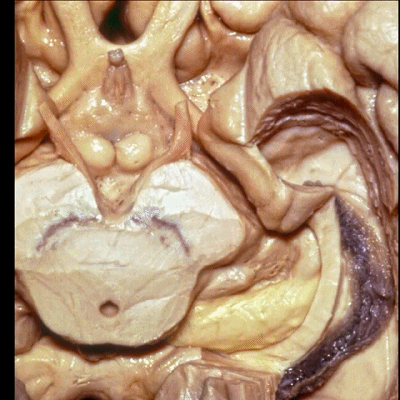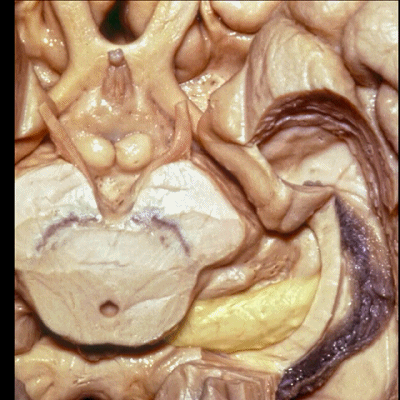
▼ 这是 外侧膝状体、内侧膝状体
▼继续去除穹窿伞,可直视颞角顶壁(下图)。
And then, if we take off the fimbria, we're looking at the roof of the temporal horn.
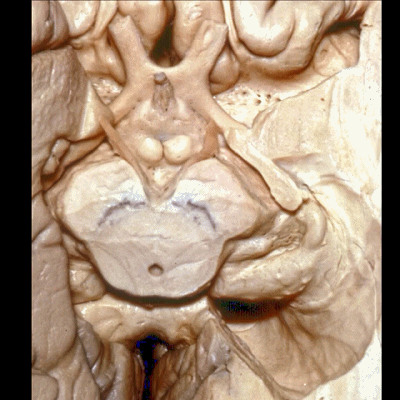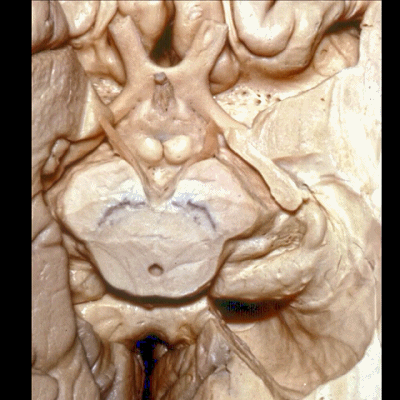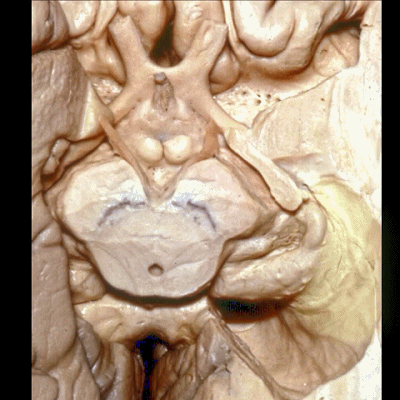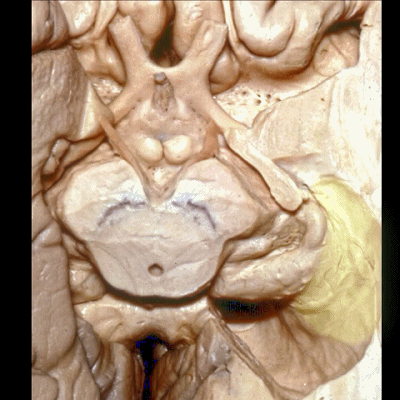
▼这是视神经、视交叉、视束、向后行至外侧膝状体。
We see the optic nerve,chiasm,tract come back to the lateral geniculate body.
▼这是 杏仁核 区域
This is the area of the amygdala.
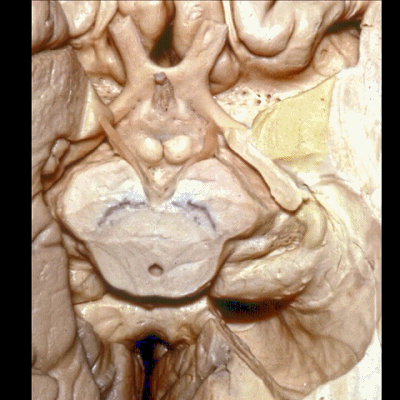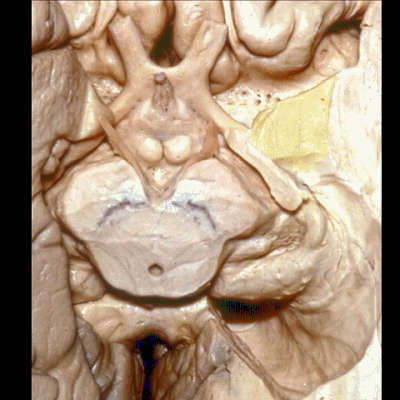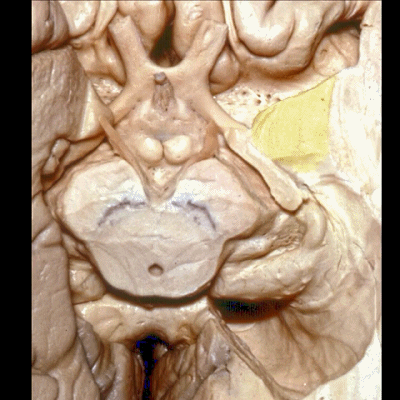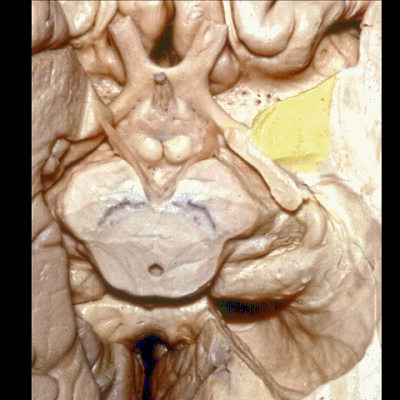
▼继续暴露深部结构。这是视束向后行至外侧膝状体。
And then if we go one step deeper... where here we see optic tract come back to lateral geniculate body.
▼这是 Meyer襻
Meyer's loop
▼Meyer襻向前迂行至颞角顶壁(下图)。
Meyer's loop loops forward in the roof of the temporal horn
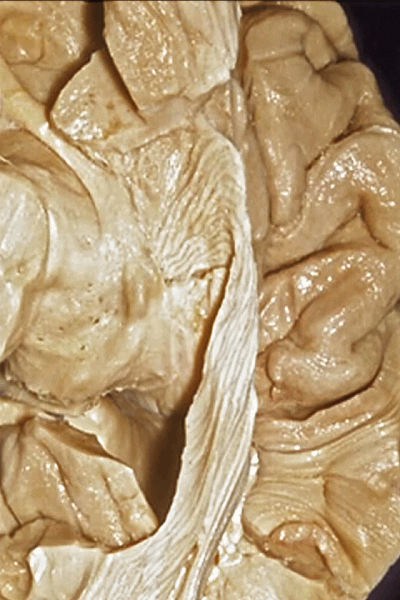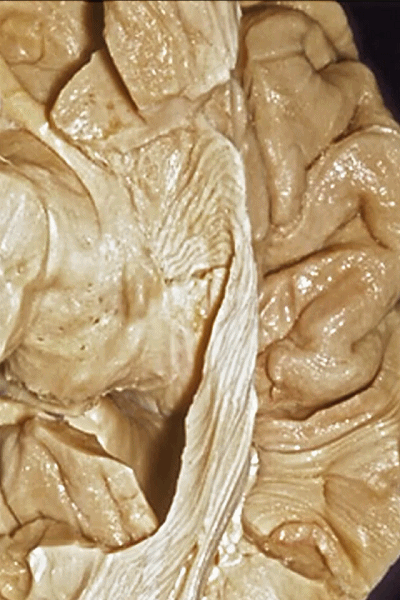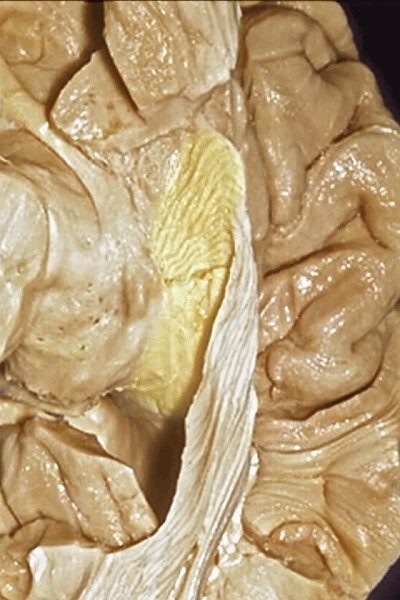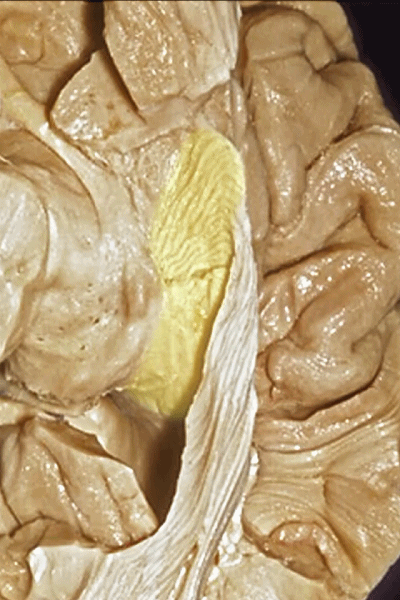
▼随后,视辐射向后绕行于颞角外侧壁(下图)
And then the optic radiations come back around the lateral wall of the temporal horn
▼视辐射向后终于此处的距状沟上下。
to end up back here along the calcarine sulcus.
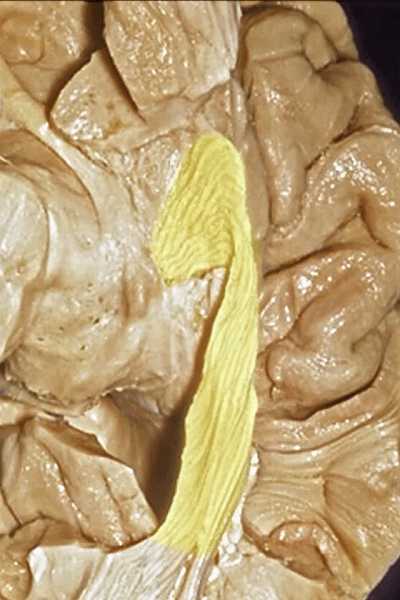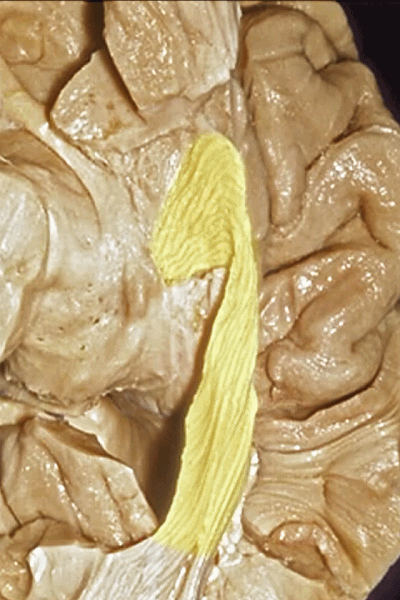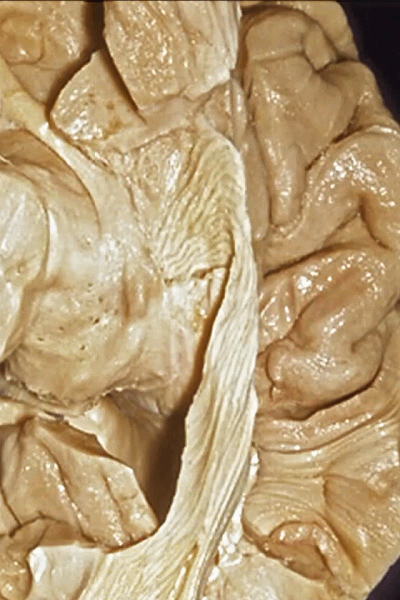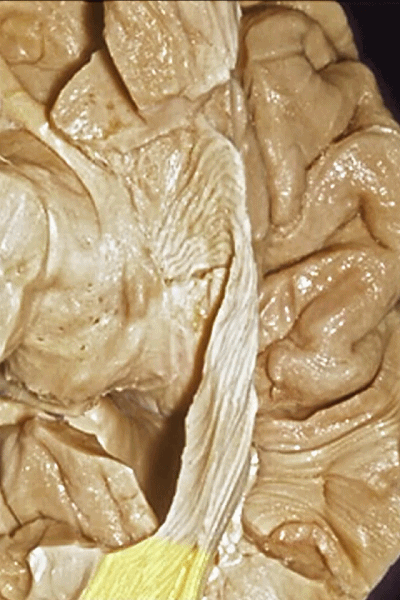
▼这样一层层地解剖即可暴露视辐射,其行经内囊的豆状核下部。
So that you can visualize this as you move layer by layer with the optic radiations,in the sublenticular part of the internal capsule.
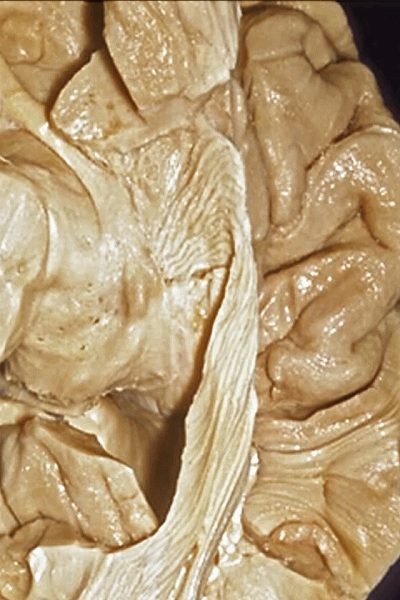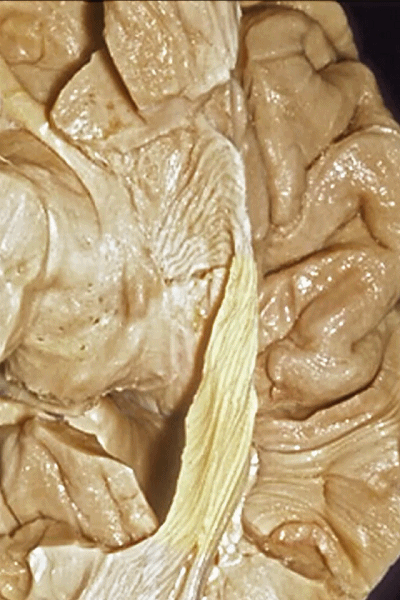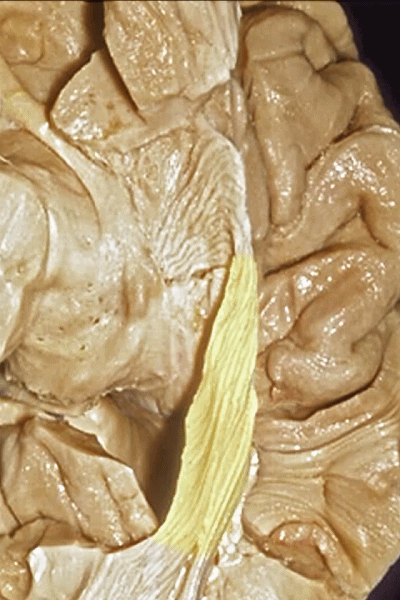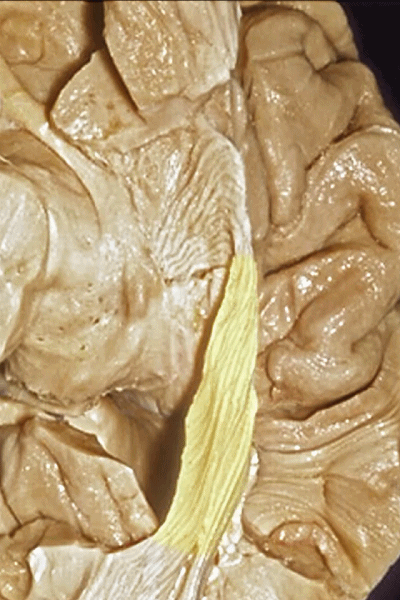
▼这些纤维位于颞角内脉络裂的丘脑侧(下图),这也是在穹窿侧打开脉络裂的原因。
And these fibers are running on the side of the...thalamic side of the choroidal fissure in the temporal horn.So we always want to open the fimbria side.

▼通过DTI成像技术,可见视交叉、视神经、视束。
Now, here with DTI, we see chiasm,nerve,optic tract.
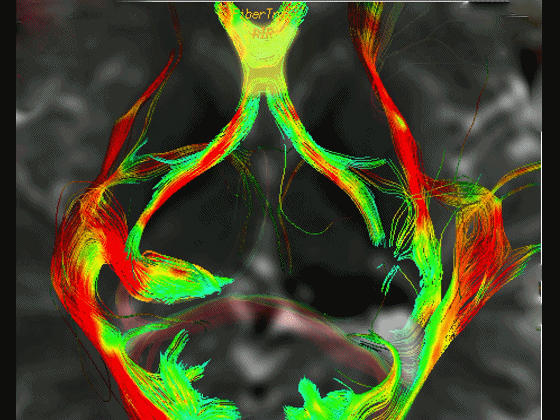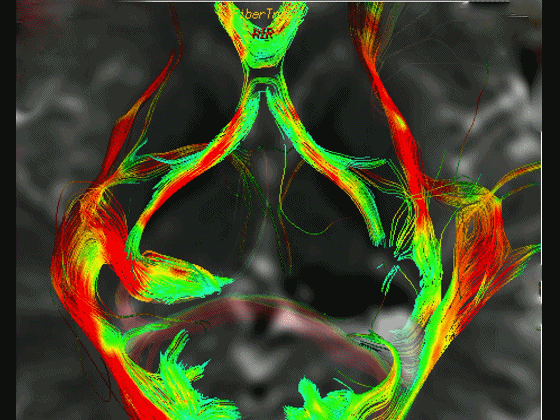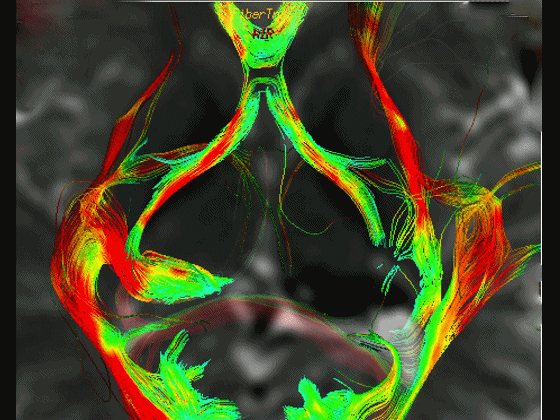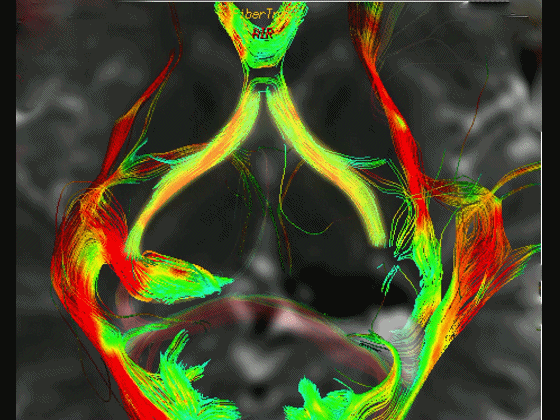
▼这是 外侧膝状体
What is this? lateral geniculate,
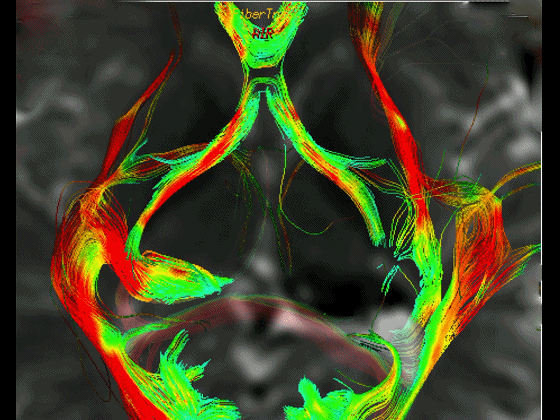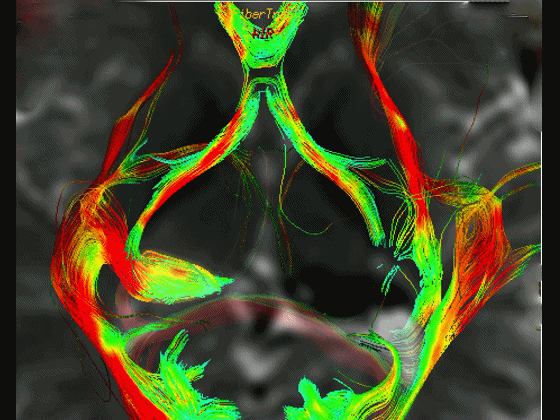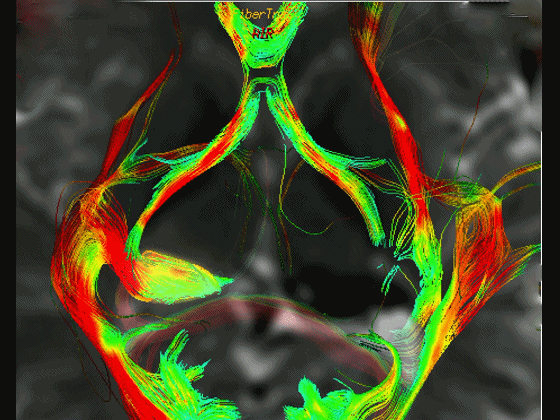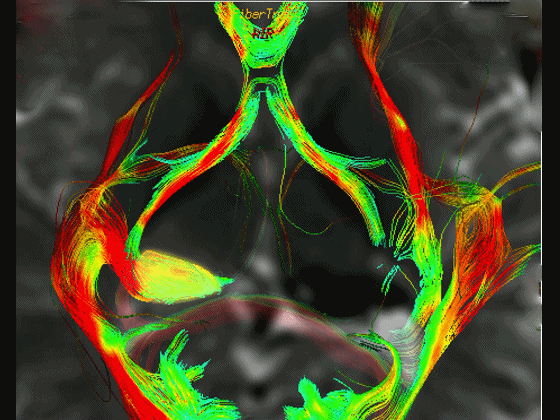
▼这是 Meyer襻
Meyer's loop.
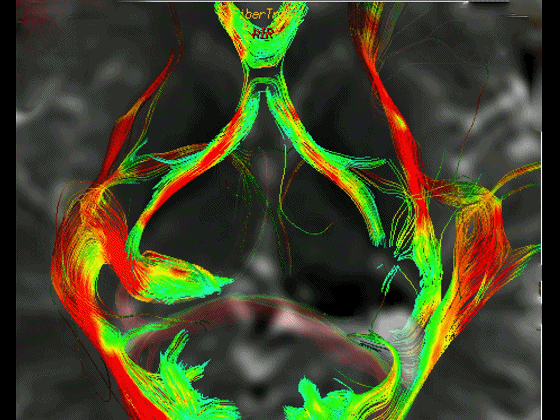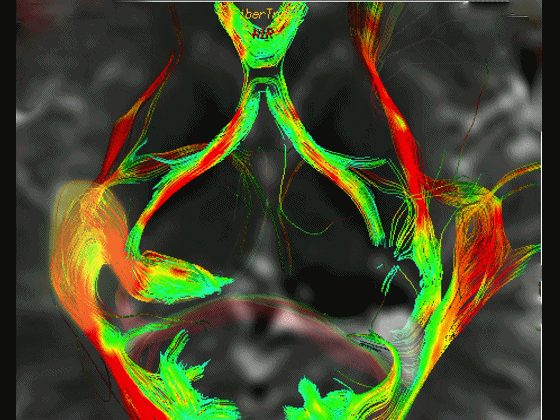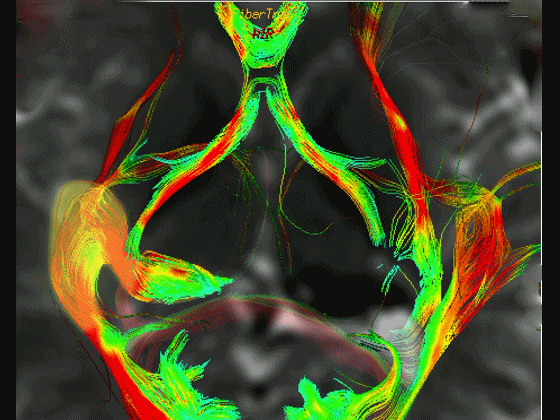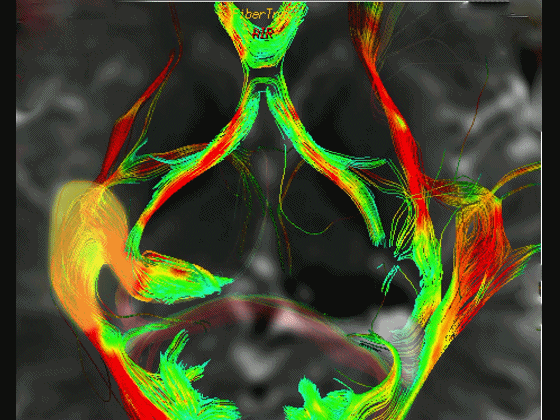
▼这是右侧的外侧膝状体,左侧的外侧膝状体缺如。
Where is the lesion? It's...here is the lateral geniculate, lateral geniculate.
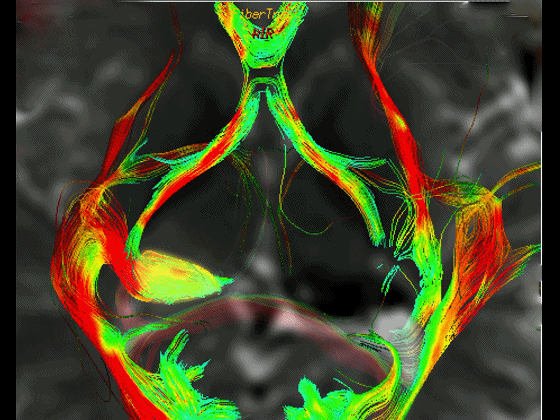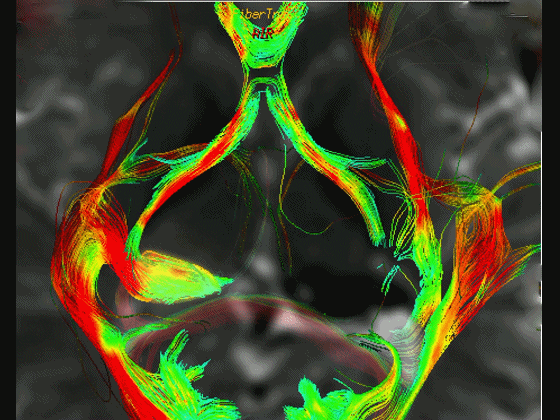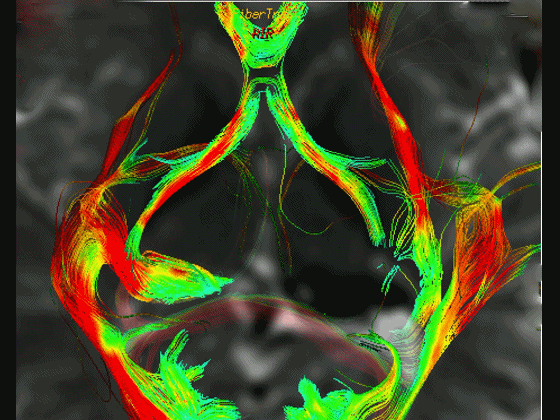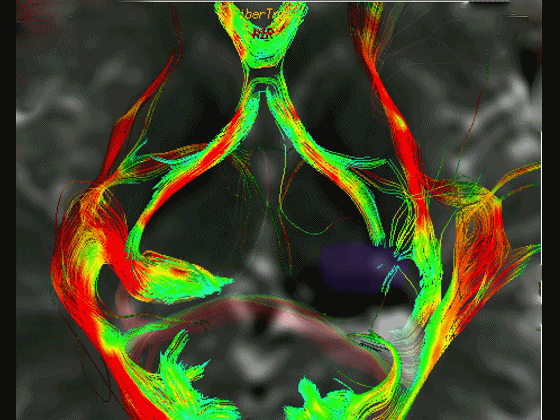
▼再来看一下 视束、外侧膝状体、Meyer襻
But just a view of...optic tract,lateral geniculate,Meyer's loop

▼Meyer襻向前迂行,通常可至颞角顶壁的前界。
looping forward usually to the anterior edge of the roof of the temporal horn.

▼这是一些影像学技术来显示视辐射。
So that...and just some of the imaging of optic radiations today.


![]()
▼之前已提到,钩回分成前段、后段、尖部。
这是钩回前段(下图),包含有杏仁核。
Now the uncus we said had an anterior segment, a posterior segment, and an apex,here we see anterior segment containing amygdala,
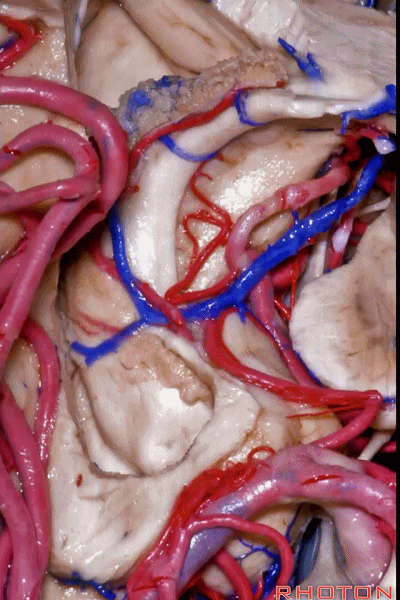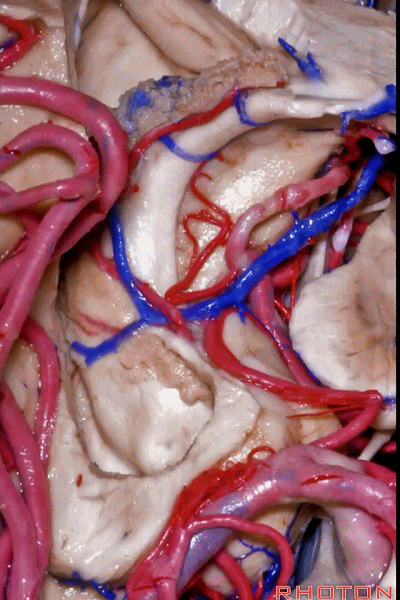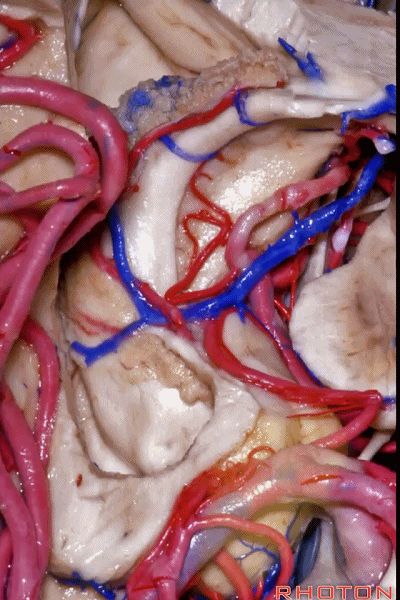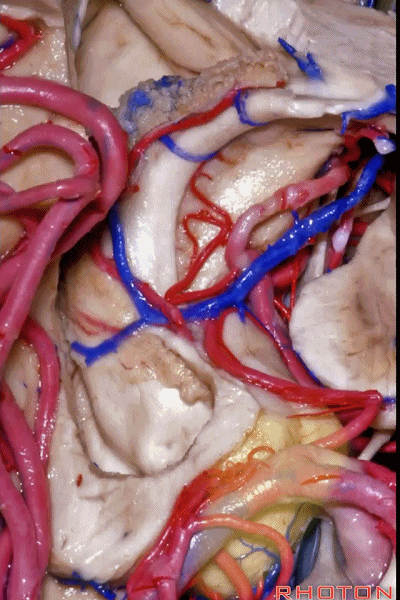
▼这是钩回后段(下图),包含有海马头
posterior segment containing head of hippocampus,
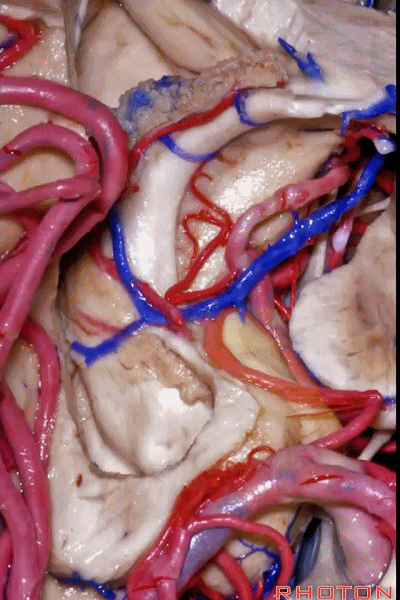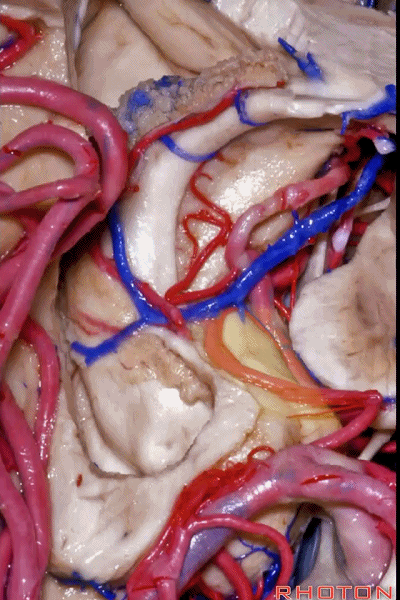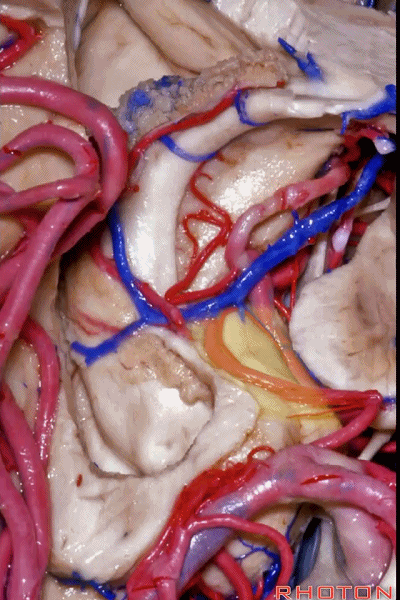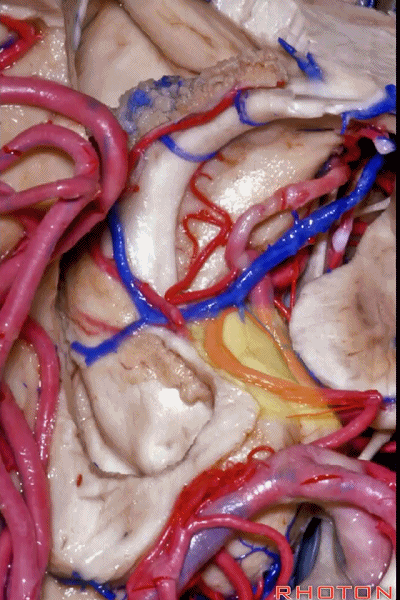
▼这是 钩回尖部,与动眼神经相邻。
and then an apex, that's lateral to the 3rd nerve
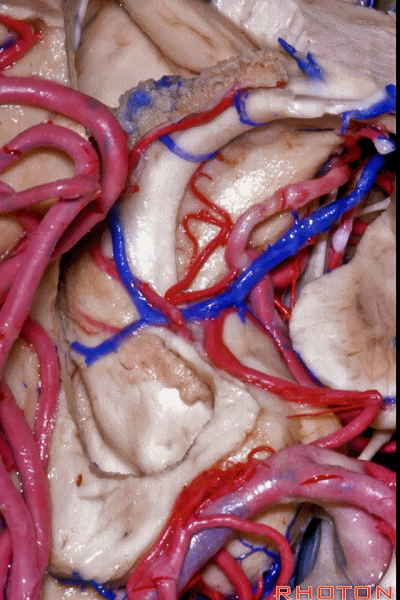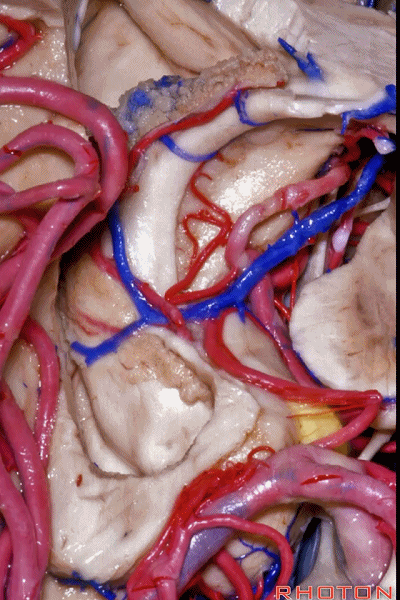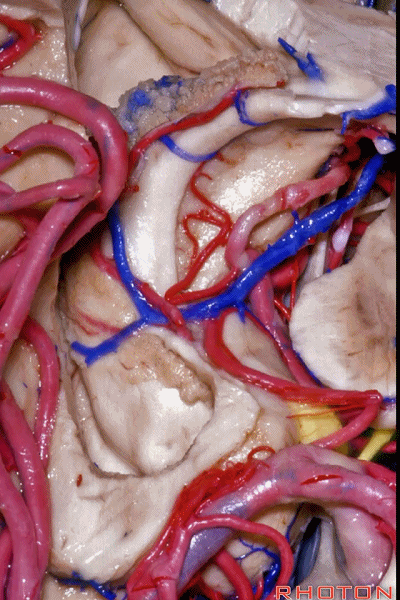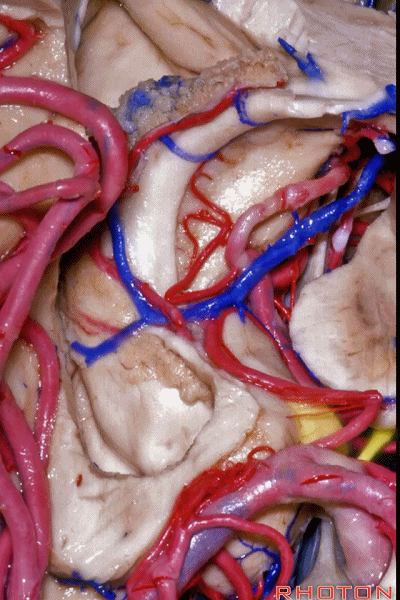
▼从外侧看,可见这一钩回隐窝(下图)。
And then, laterally we have an uncal recess.
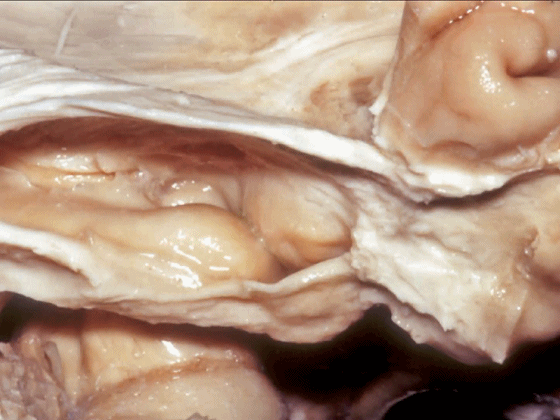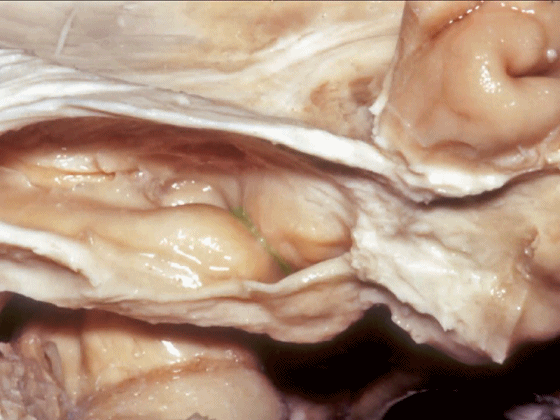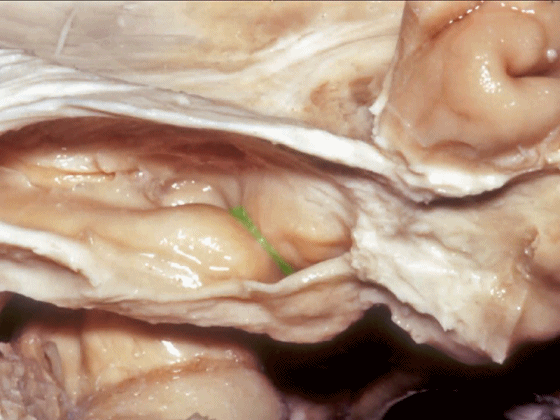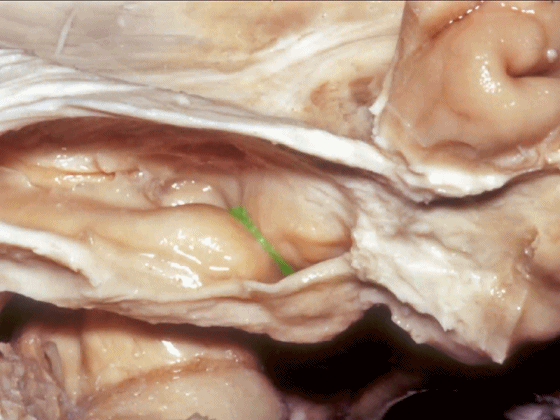
▼从外侧打开颞角(下图)
If you look into the temporal horn from lateral,
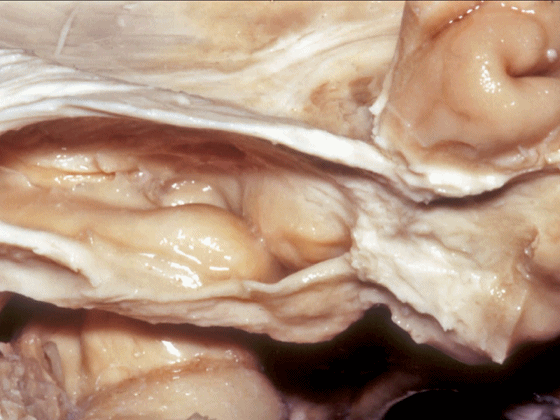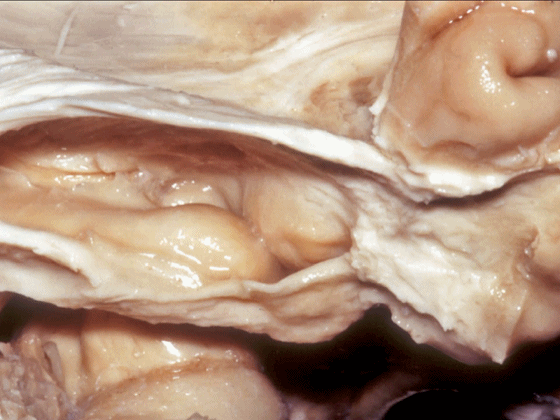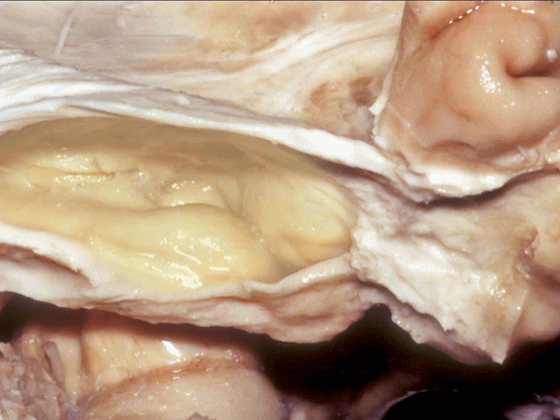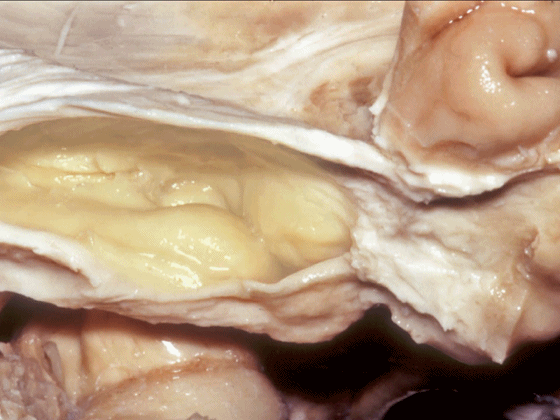
▼上方是视辐射
optic radiations above,
▼钩回隐窝 位于 杏仁核 与 海马头 之间(下图)。
而之前提到的钩回切迹,则在内侧面。
here is the uncal recess between the amygdala and the head of the hippocampus. And you've already seen the uncal notch as we look at the medial surface.
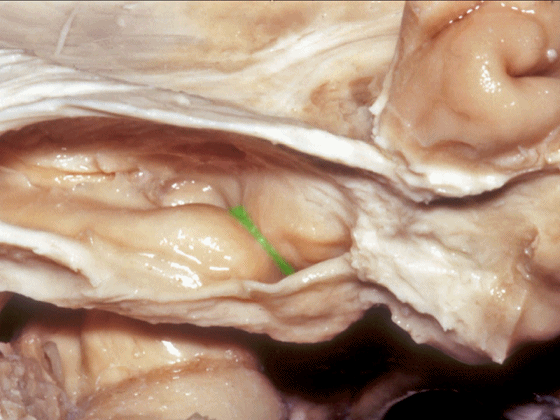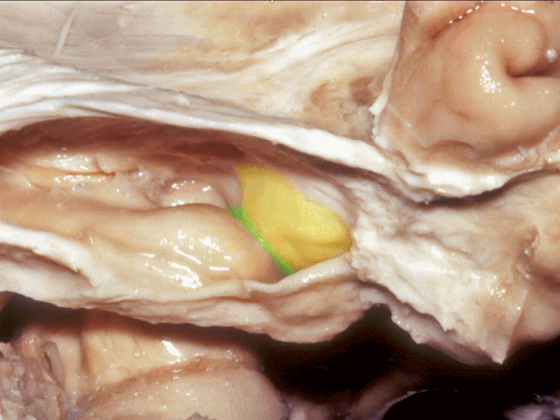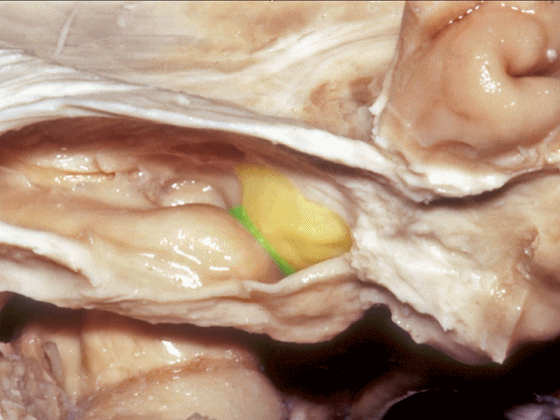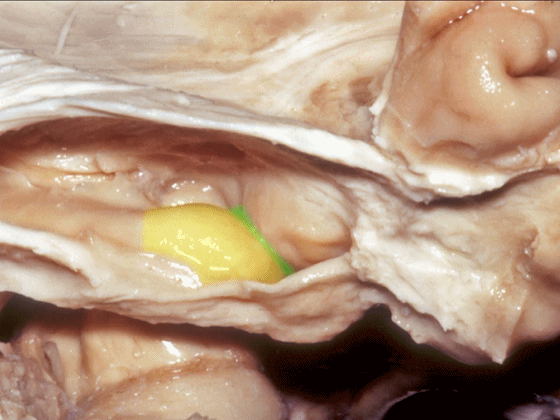
![]()
▼来看海马旁回,其包括三个面。
Now, parahippocampal gyrus, has three surfaces.
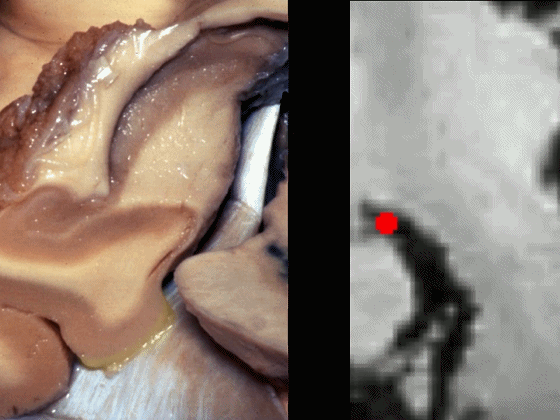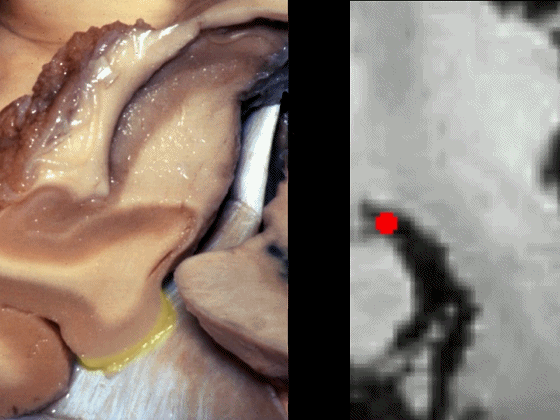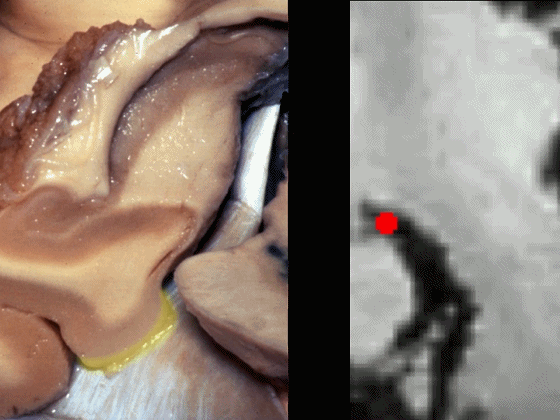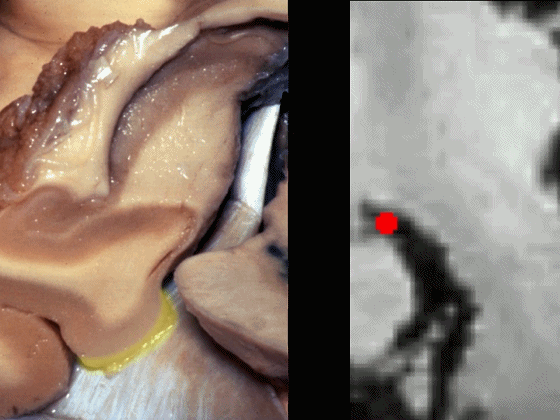
▼海马旁回下面相邻的结构为 中颅窝 和 天幕 。
It has a lower surface that faces the middle fossa and tent,
▼海马旁回内侧面呈弧形。
a rounded medial surface
▼海马旁回上面(下图) 位于 齿状回的内侧。
通常情况下,大脑后动脉(下图红点) 沿着海马旁回的上面走行(并非沿着下面和内侧面走行)。
and then an upper surface that is medial to the dentate gyrus.And often, the posterior cerebral artery runs not below,not medial,but on the upper surface of parahippocampal gyrus in this area.
▼这是 齿状回
dentate gyrus.
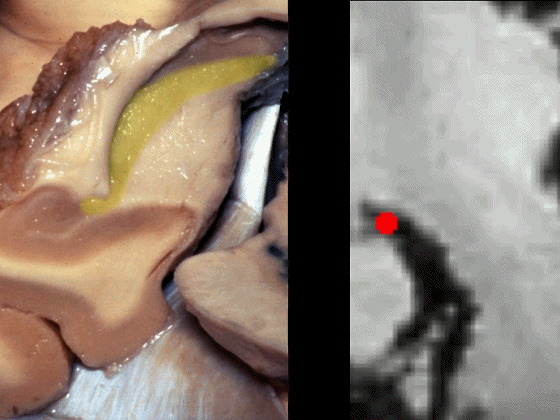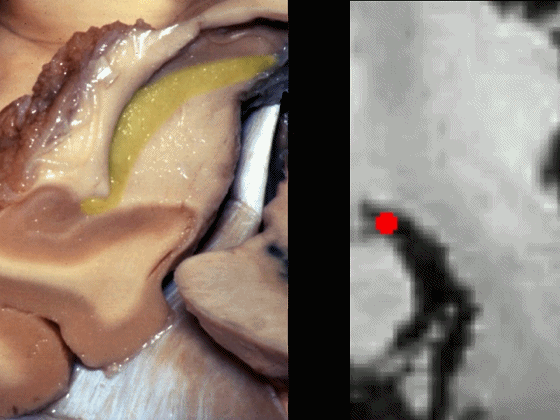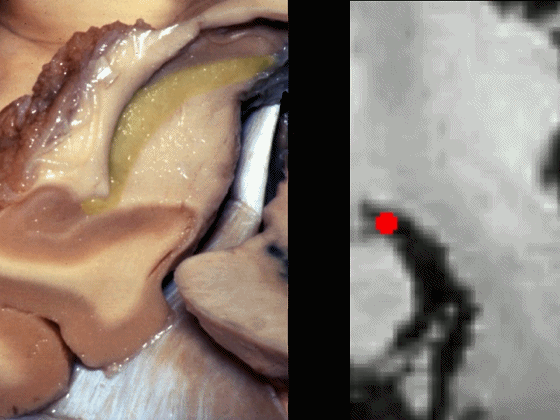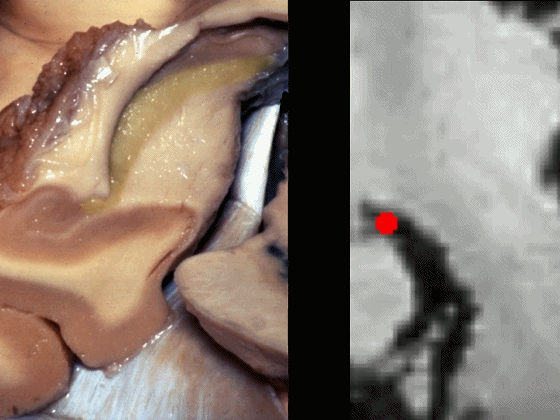
▼下图可见大脑后动脉走行于海马旁回的上面(下图)
Here we see it looping up toward that upper surface of parahippocampal gyrus
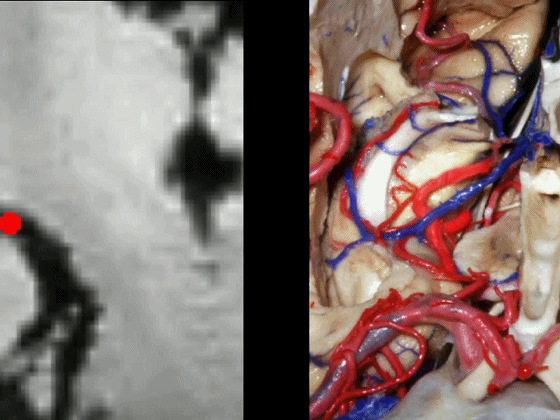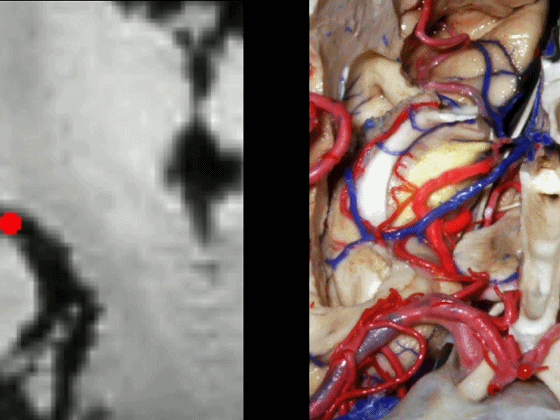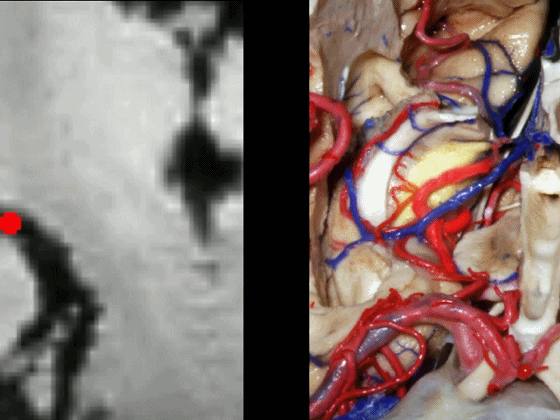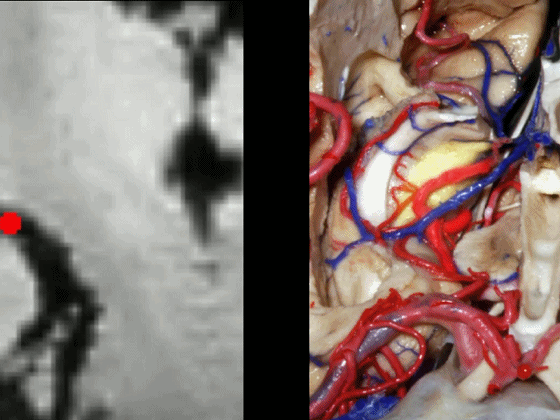
▼大脑后动脉走形于齿状回(下图)的内侧。
medial to dentate gyrus.
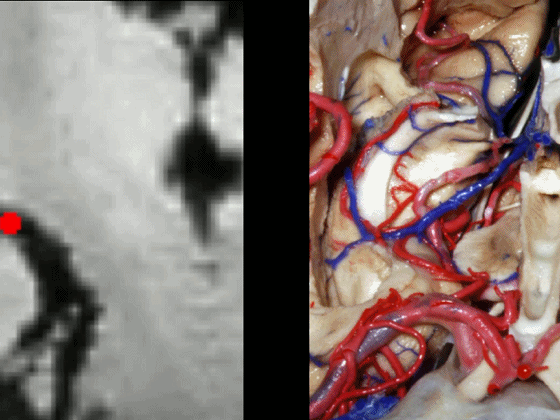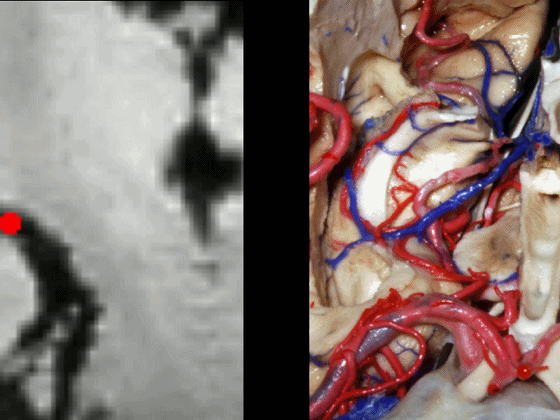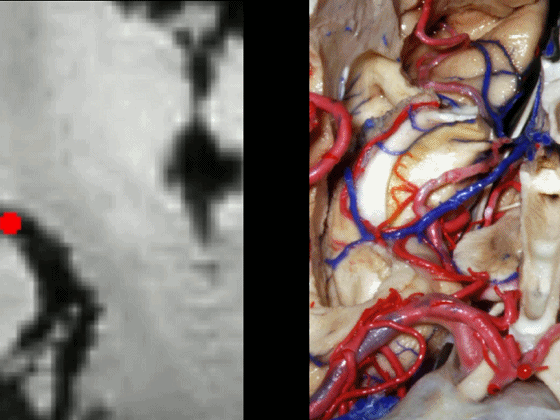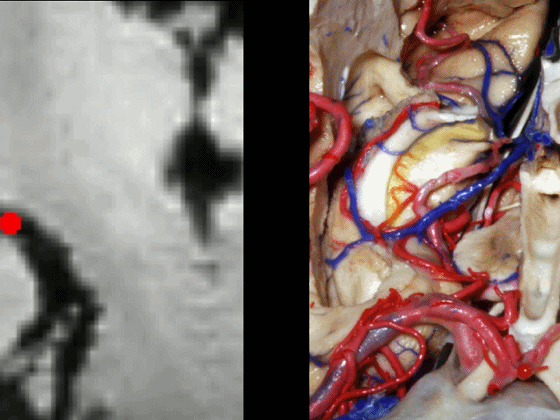
▼这从另外一个角度,可见动眼神经。
And here is just another view we're looking at 3rd nerve.
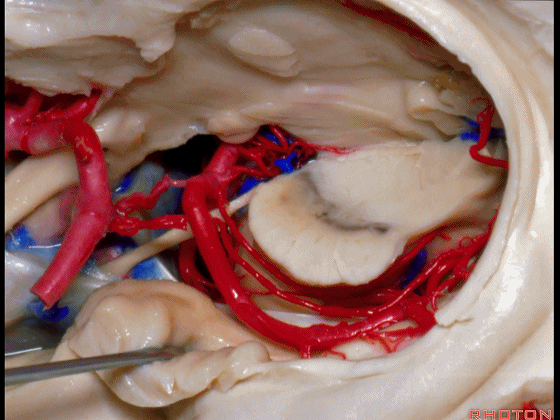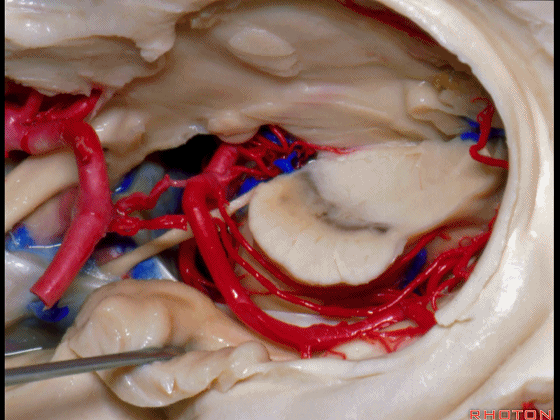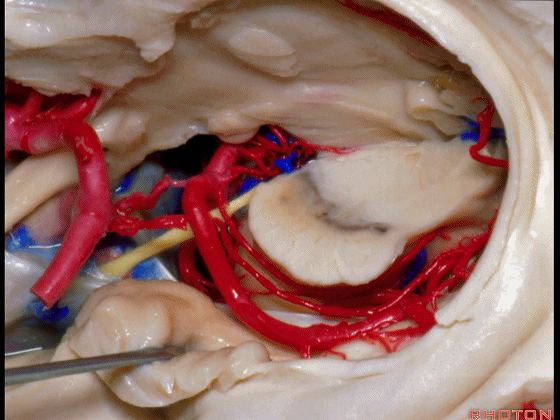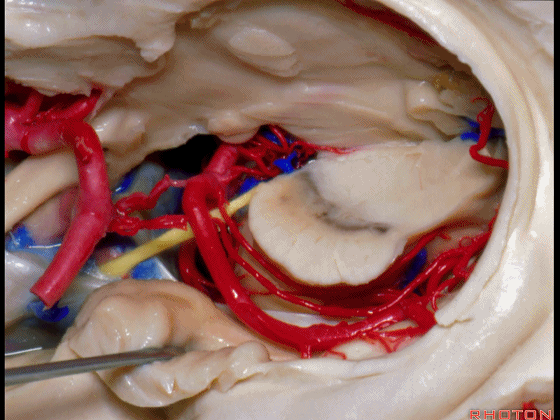
▼这是海马旁回的上面。
This is the upper surface of parahippocampal gyrus.
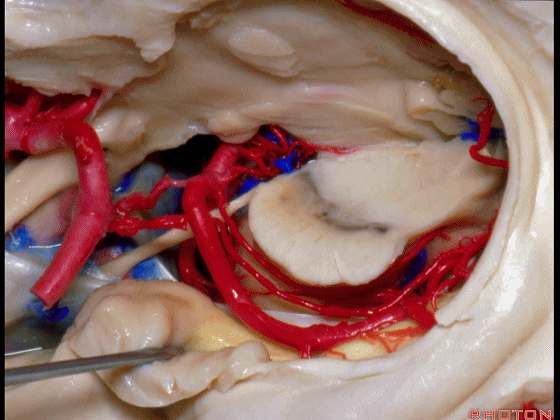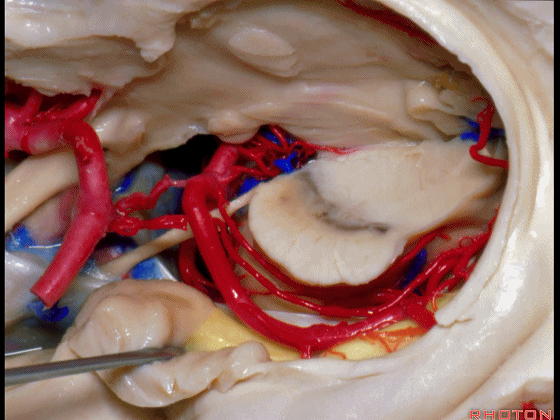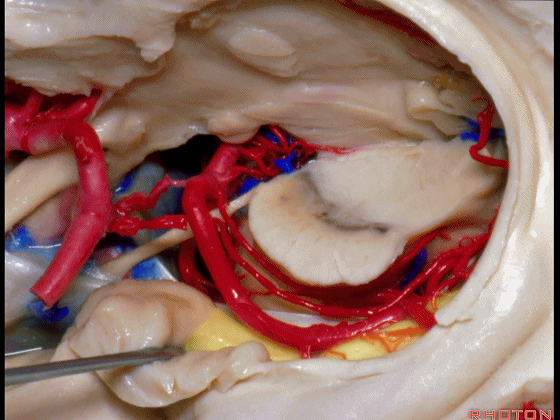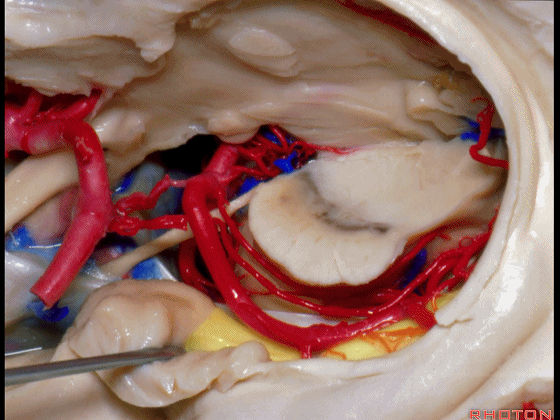
▼这是大脑后动脉。
So, and we see the posterior cerebral artery.
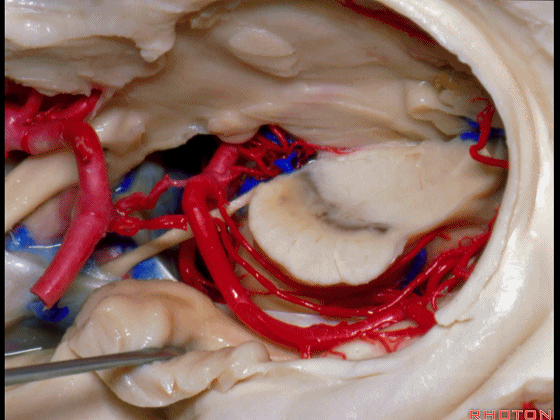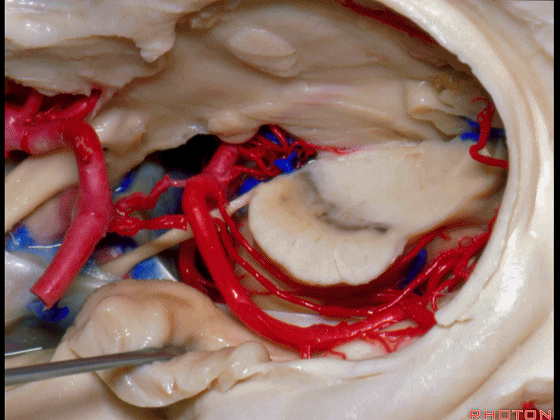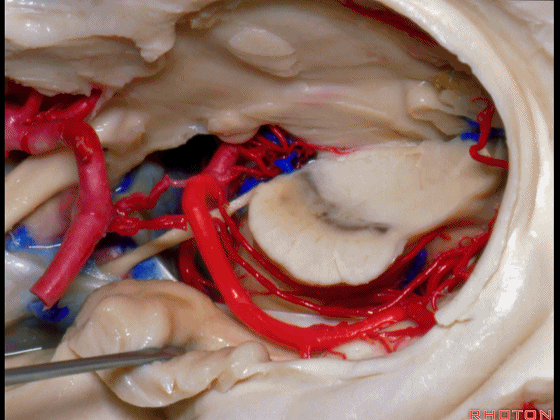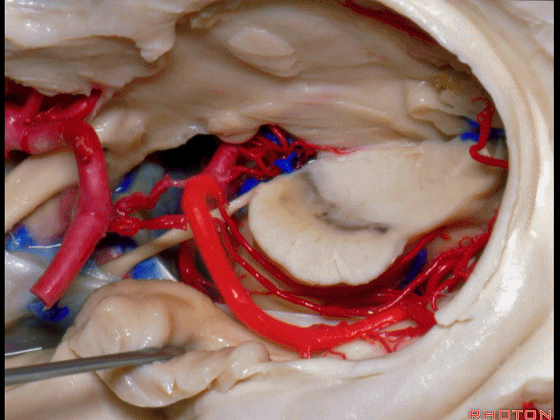
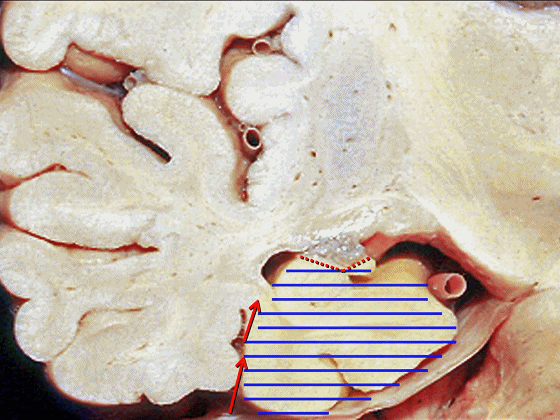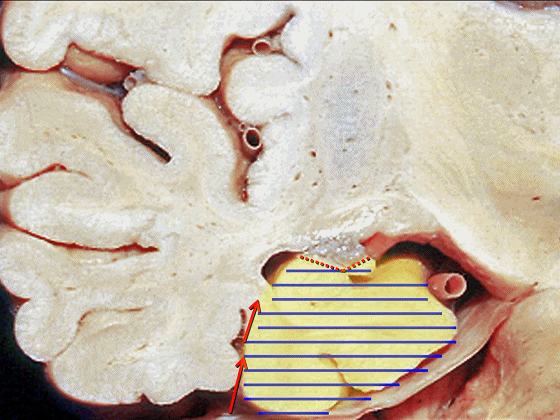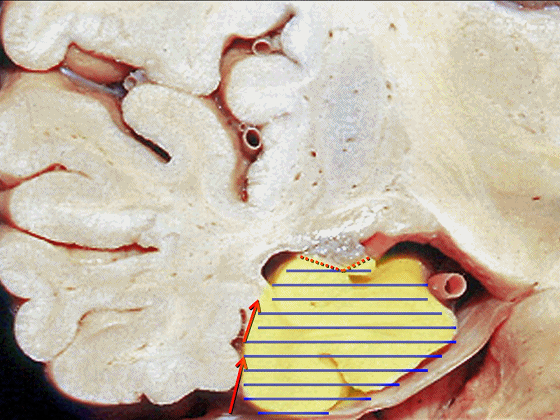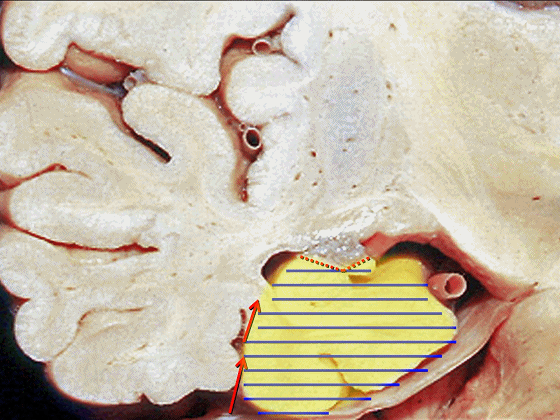
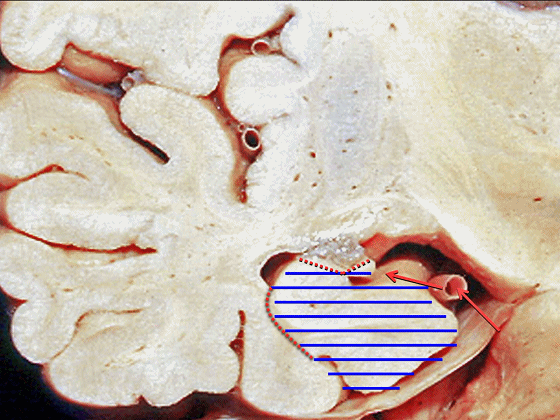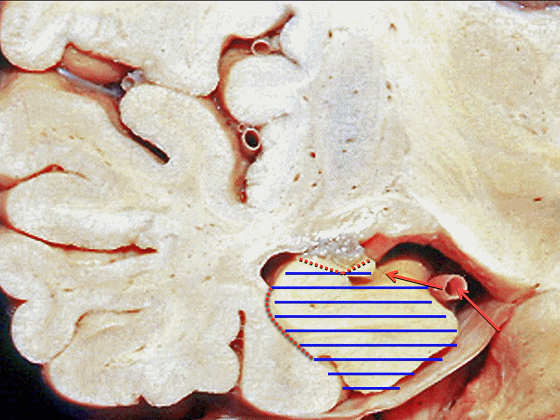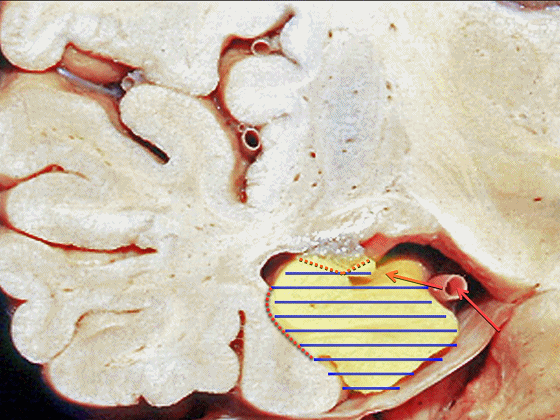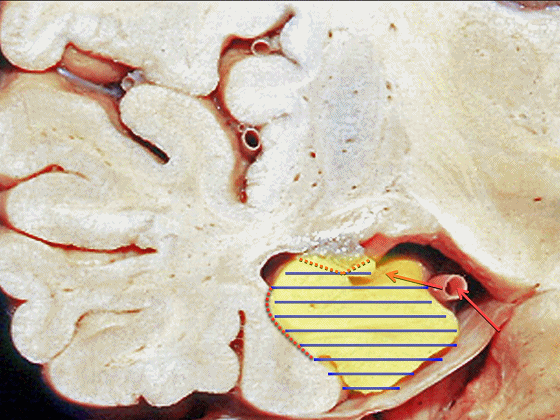
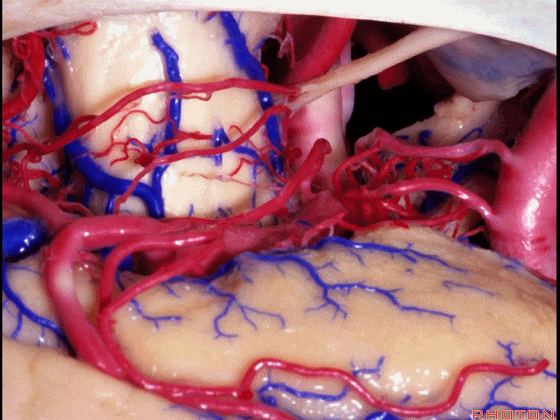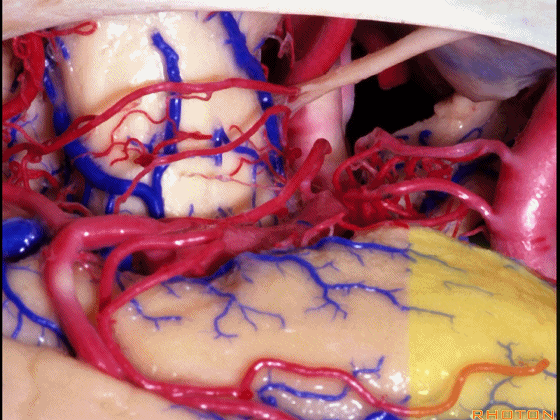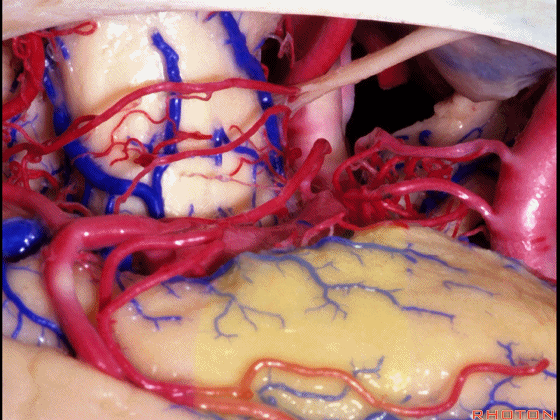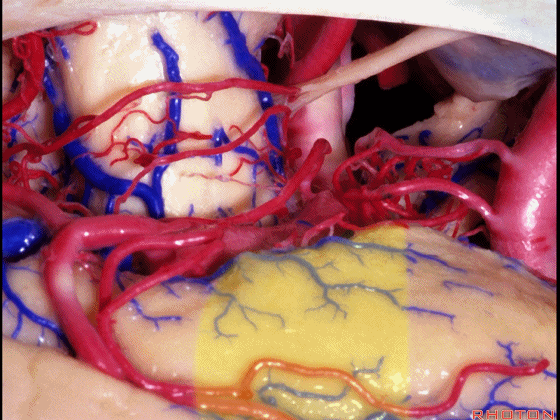
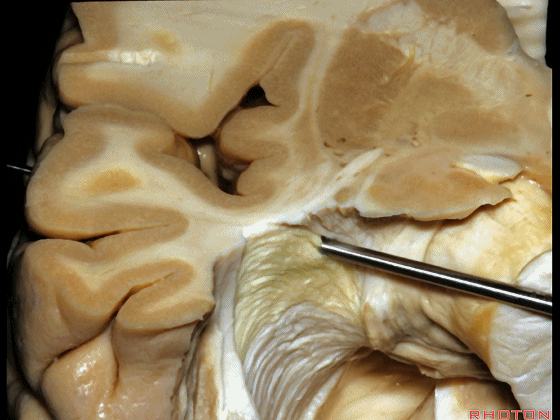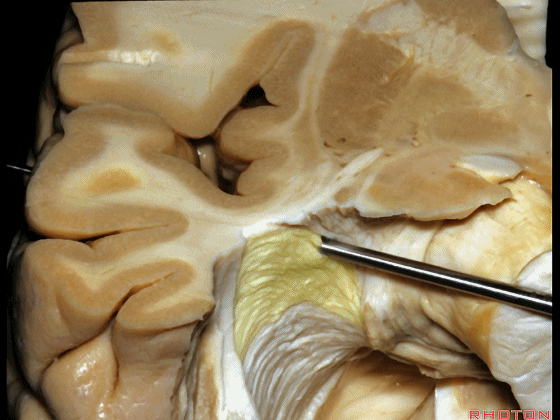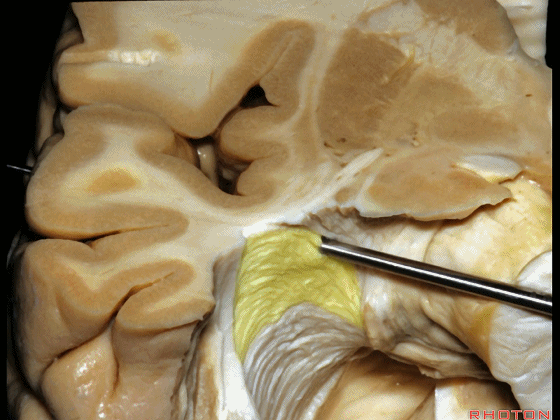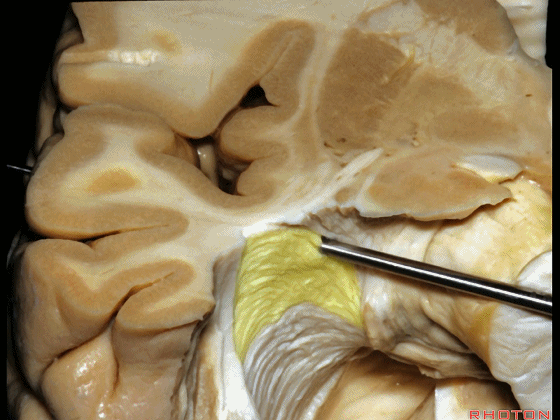
▼若选择了颞下入路暴露此处的病变,必然需要损伤颞叶的下部(下图)。
So that... if you're trying to reach pathology here,and you're coming in below the temporal lobe,you'll only reach that pathology when you've done great damage to the lower part the temporal lobe.
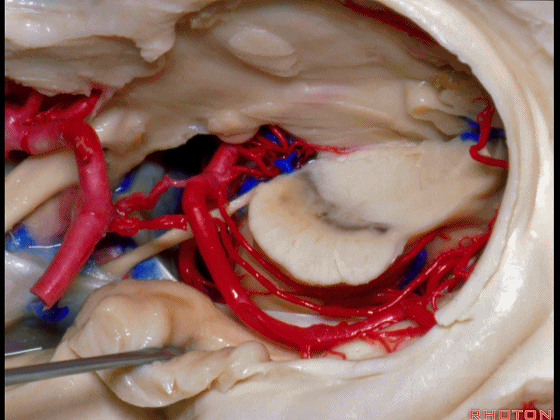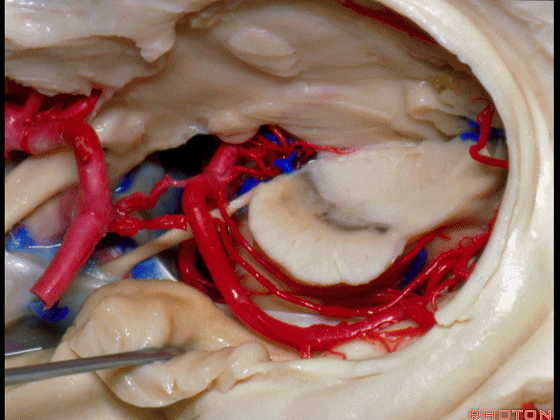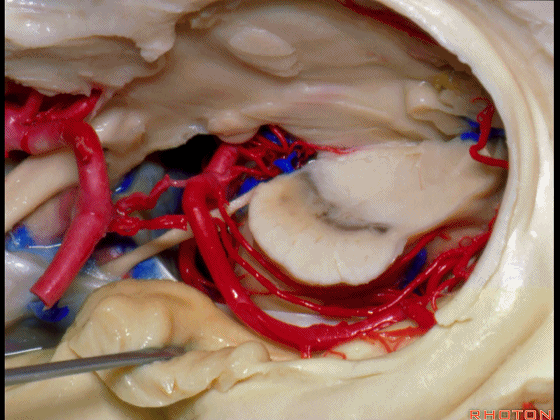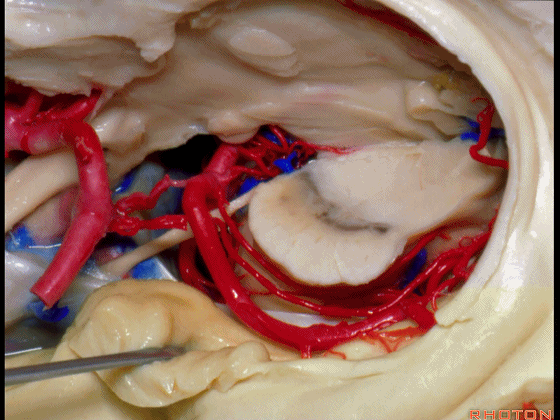
▼因此在这些情况下,可采取经颞角经脉络裂入路(下图)处理环池上部的病变。
So in some cases, it's easier to come through the temporal horn through the choroidal fissure to reach pathology in the upper part of the ambient cistern.
▼这是 环池上部
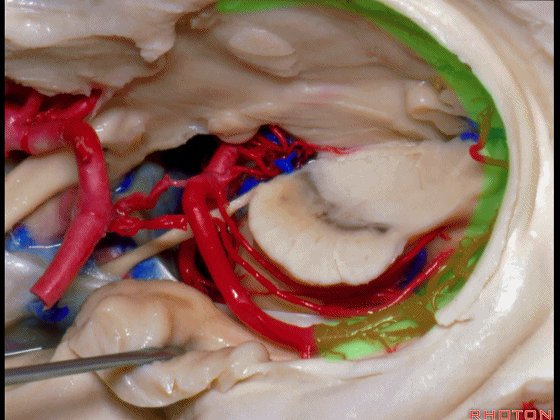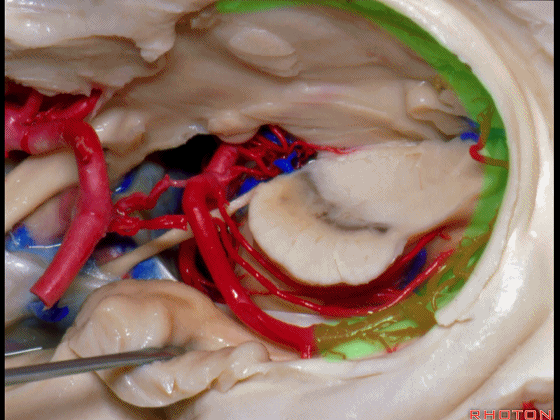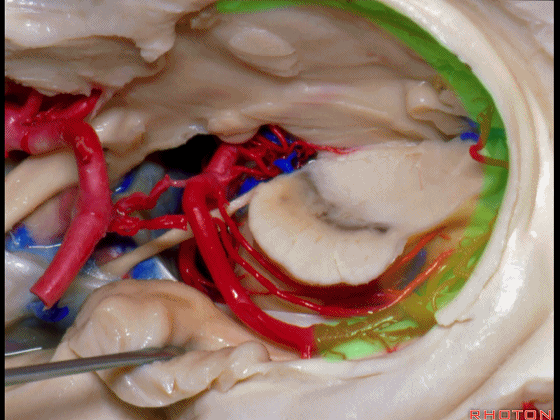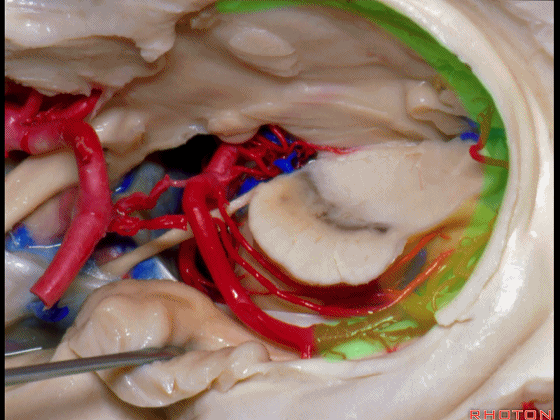
▼比如很多基底动脉高位分叉处的动脉瘤,其偏向一侧,位于颞角(下图)的内侧
And there're a number of these anuerysms on high basilar bifurcations that are tilted off to one side that sit medial to the temporal horn
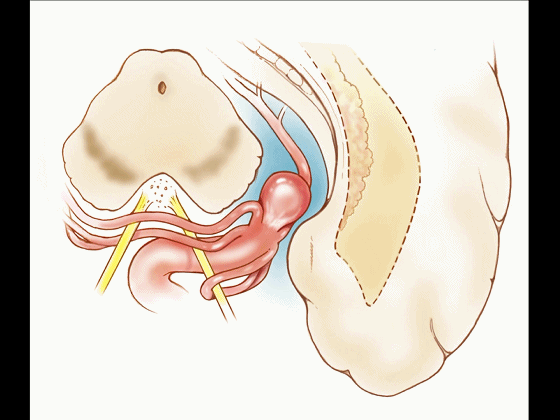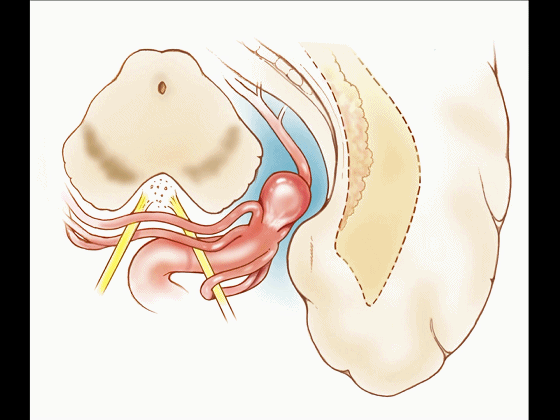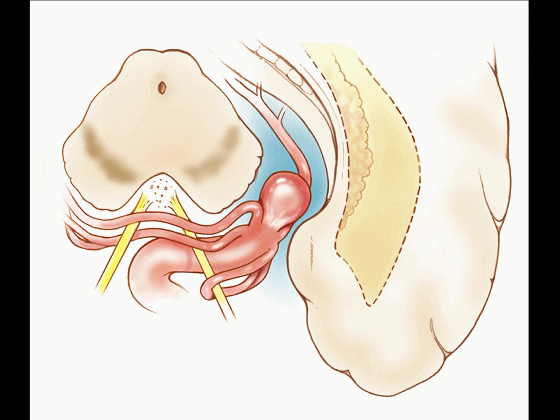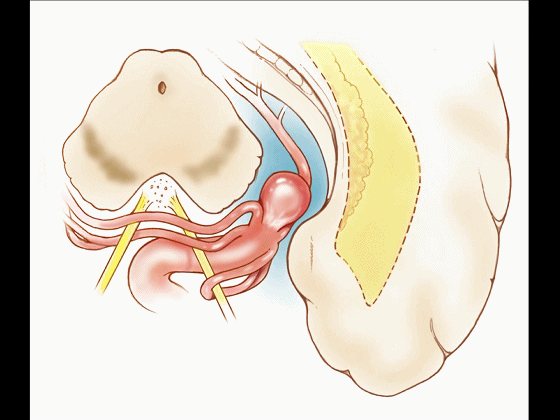
▼这时可通过经颞角经脉络裂入路处理。
and have been accessed by the transchoroidal approach through the temporal horn.
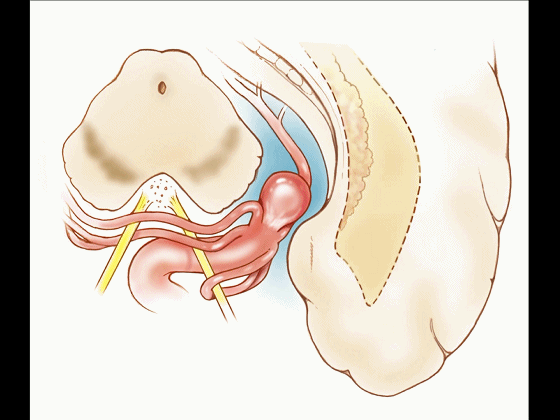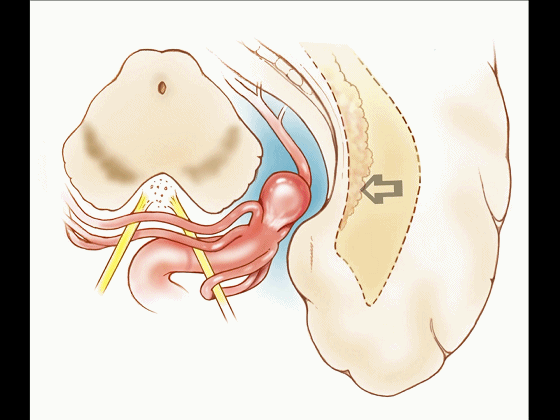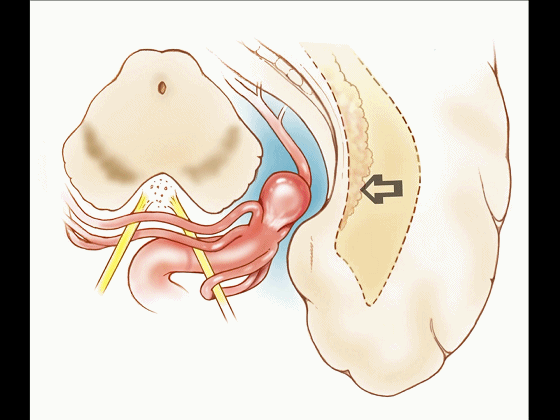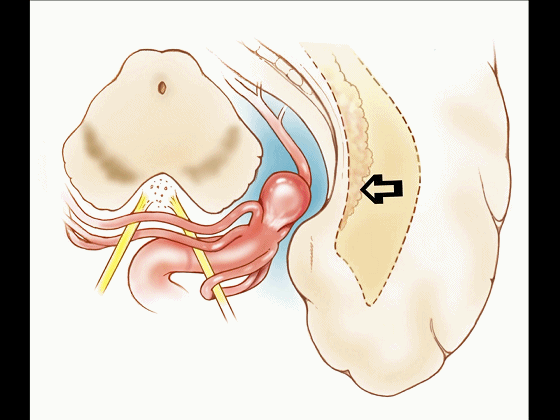
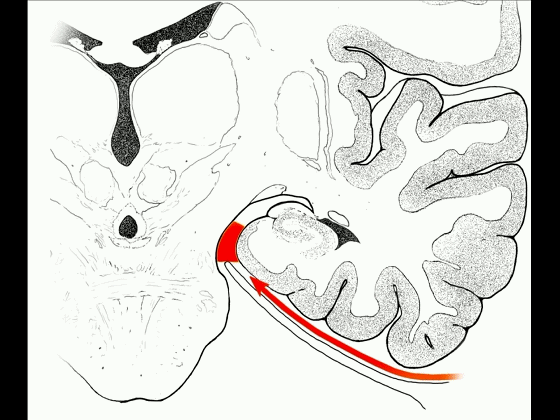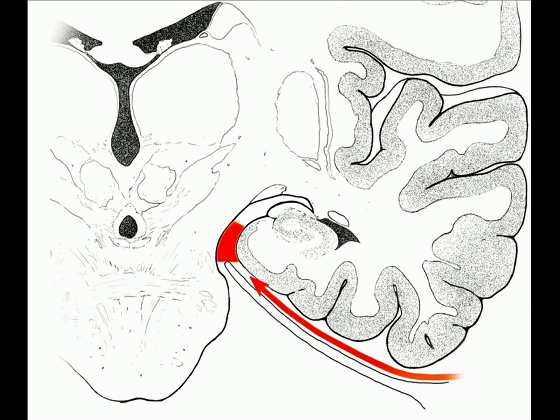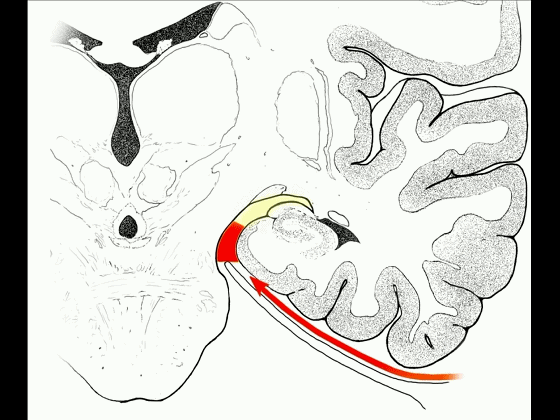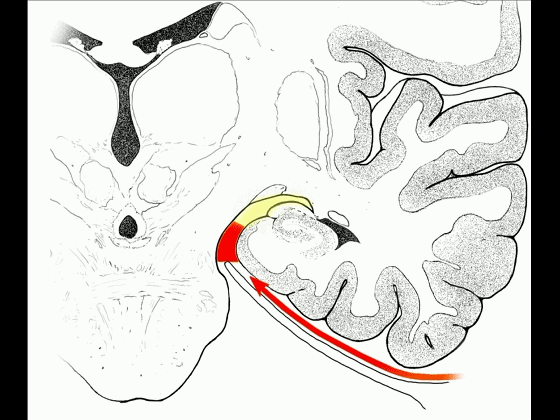
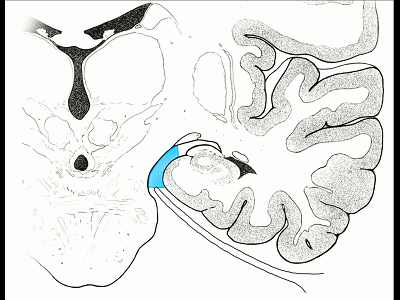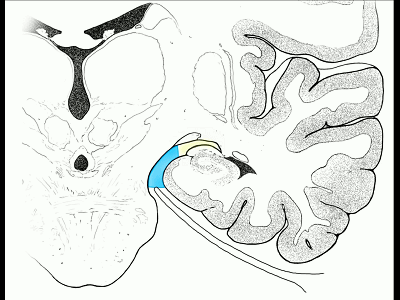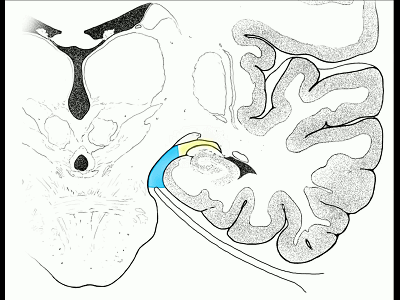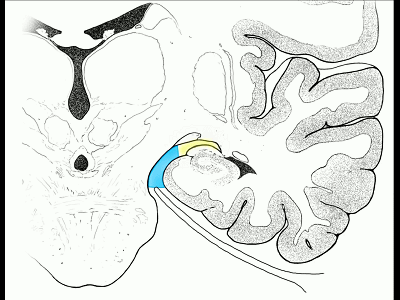
▼因此,暴露环池的入路选择可以是 颞下入路。
So one way of getting to ambient cistern is to come subtemporal.
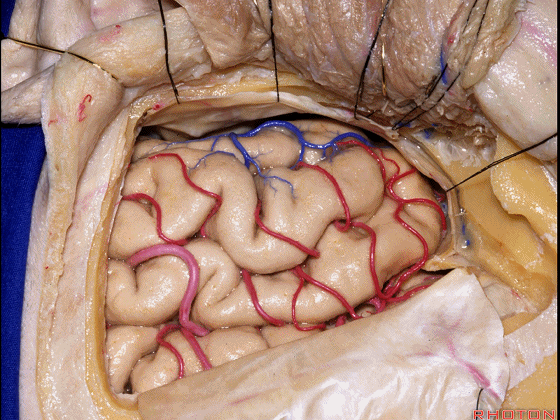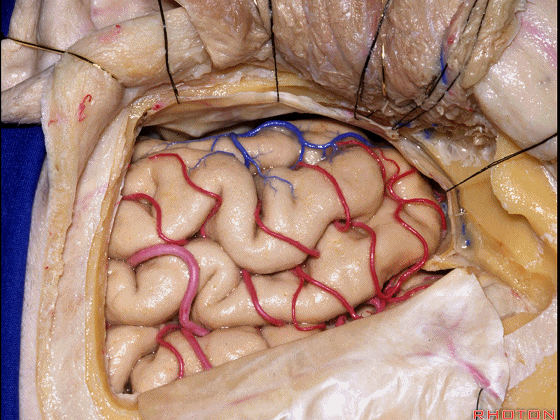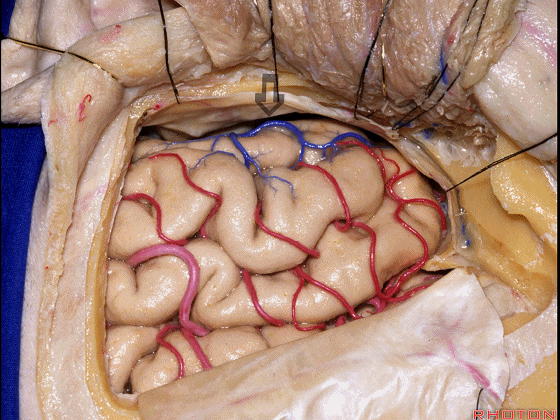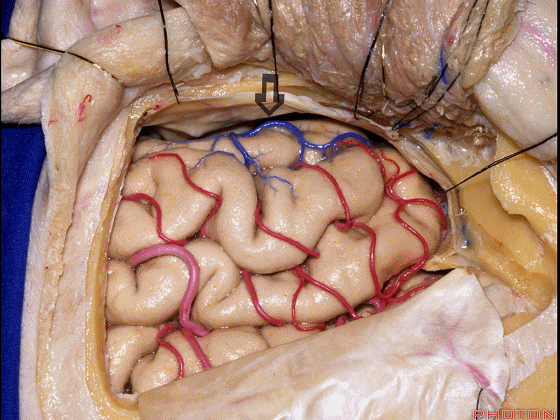
▼但是通过颞下入路,可暴露至 海马旁回内侧面的下部(下图红色部分),但不能暴露其上部,即环池上部(下图黄色部分)。
And, but if you come subtemporal,you can reach the lower part of the medial surface of the parahippocampal gyrus, but you can't reach this upper part, upper reaches of the ambient cistern.
▼另一种被广泛提及的入路是后方入路,其对环池(下图)的暴露,避免了对这些颞叶下方桥静脉的损伤。
Another way in a number of papers that have been published using the posterior approach to the area of the ambient cistern, and it avoids damaging these large bridging veins coming off the lower surface of the hemisphere.
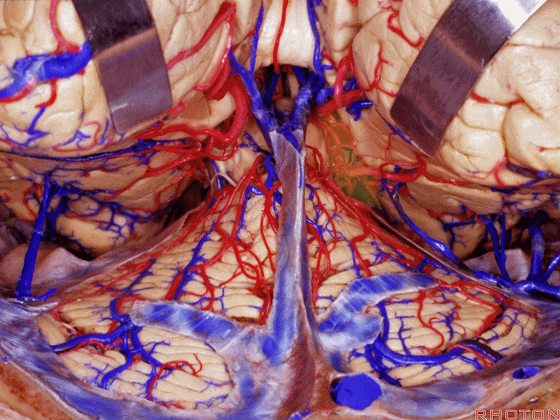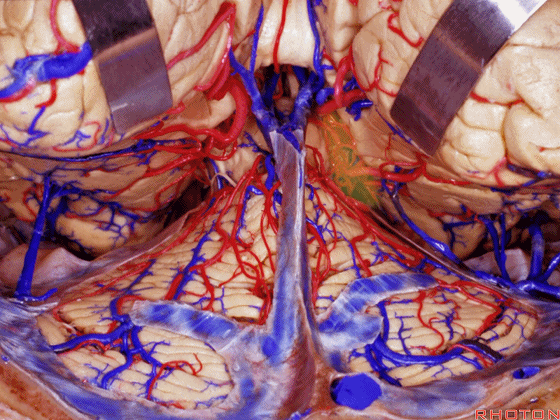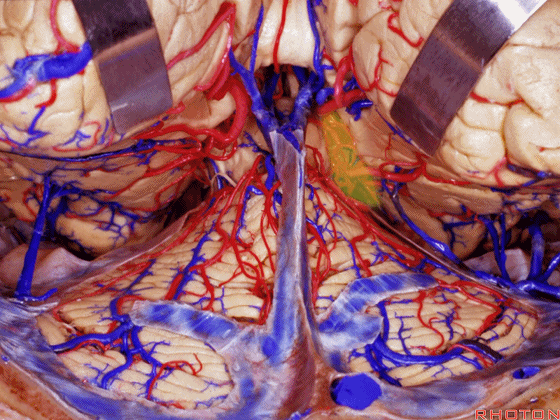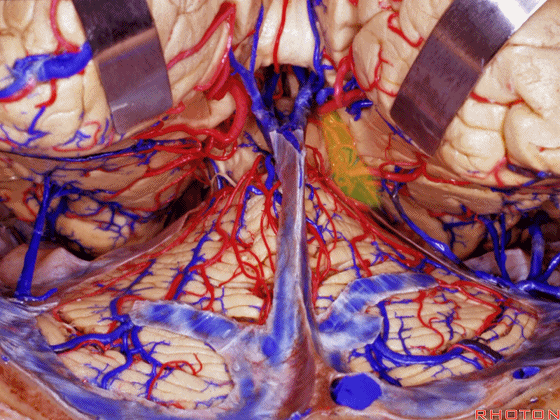
▼下图示 颞叶下方桥静脉
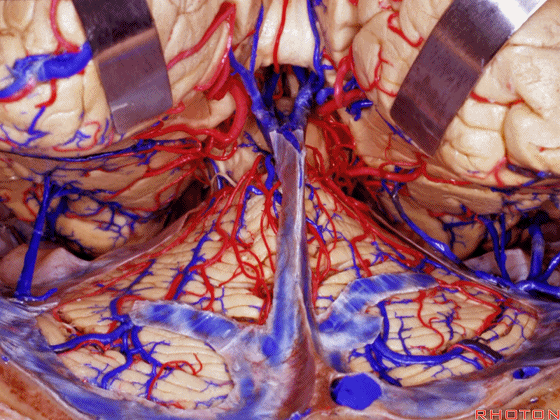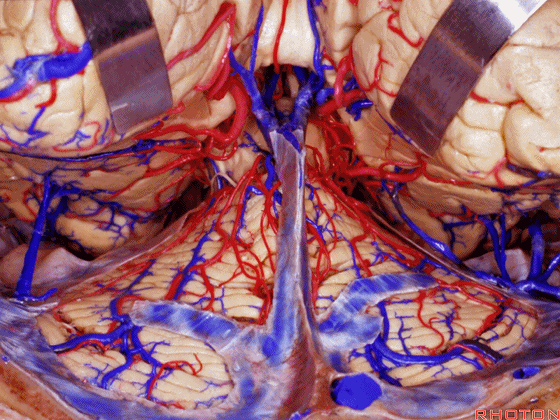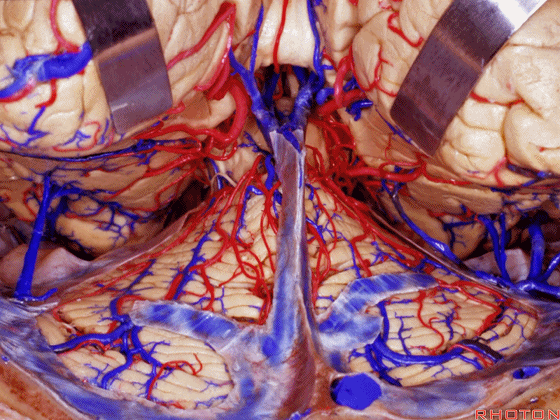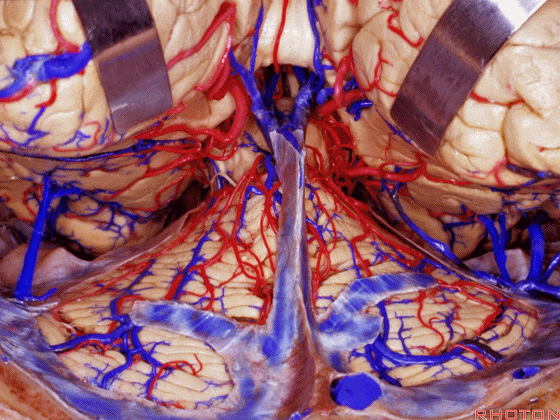
▼因此后方入路可暴露到更高的层面(下方蓝色部分),但仍然无法暴露环池的上部(下图黄色部分)。
You come posteriorly to the area of the ambient cistern. But coming posteriorly you can get a little higher,but you cannot reach the upper part of the ambient cistern.
▼而经脉络裂入路(下图),则可暴露至海马旁回的上面。
But coming through the choroidal fissure, you can reach this upper surface of parahippocampal gyrus.
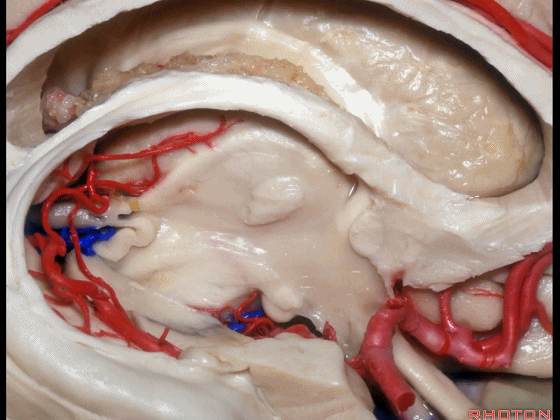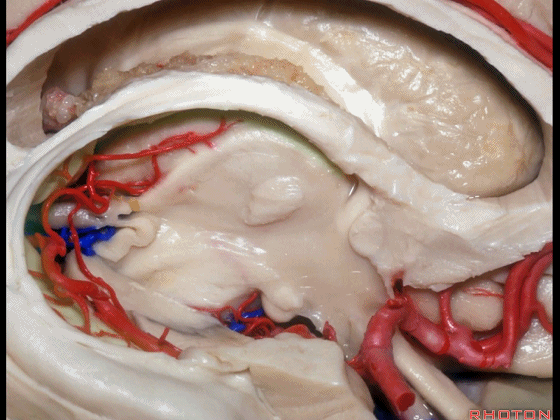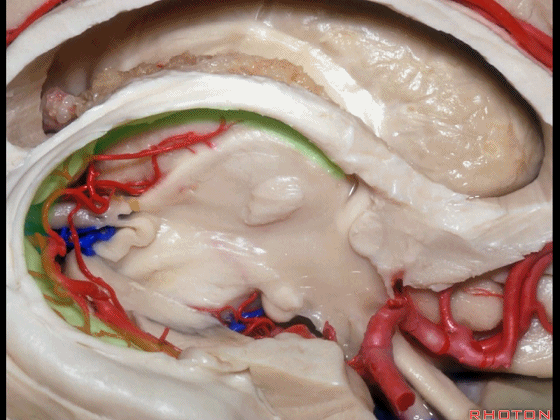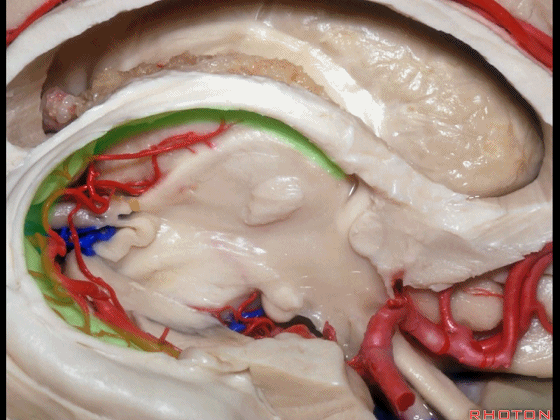
▼下图示 海马旁回
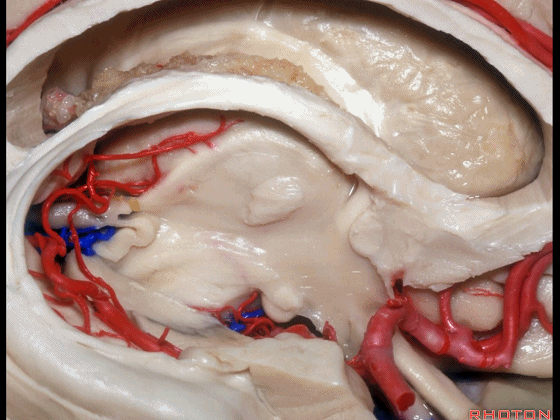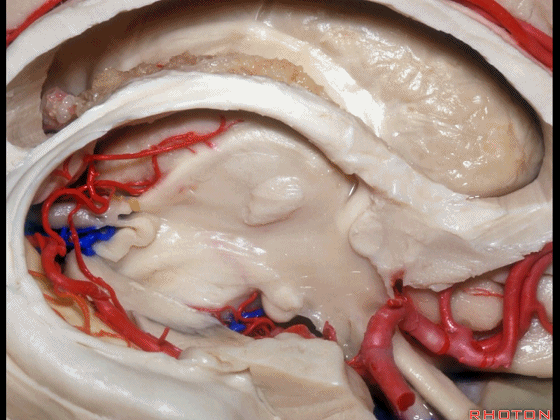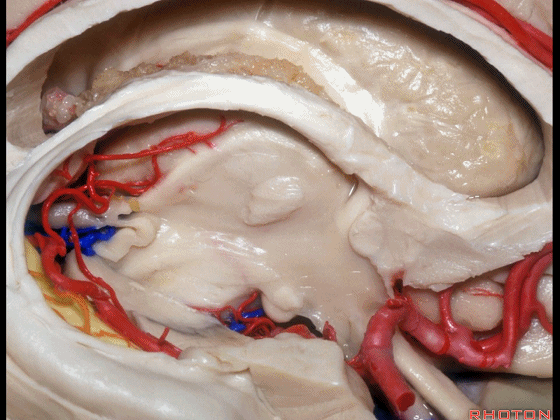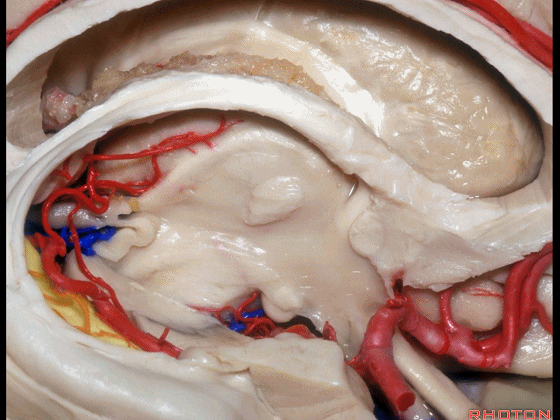
▼这里我们打开了脉络裂
And here we've opened the choroidal fissure and
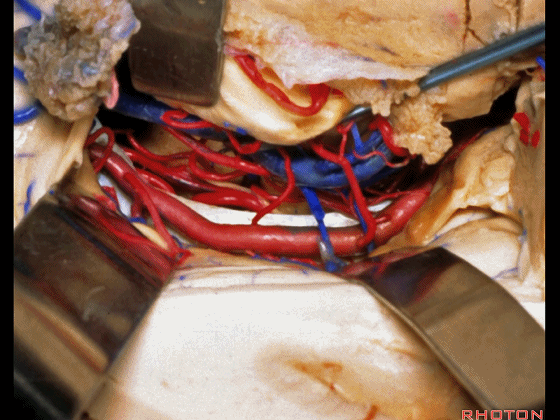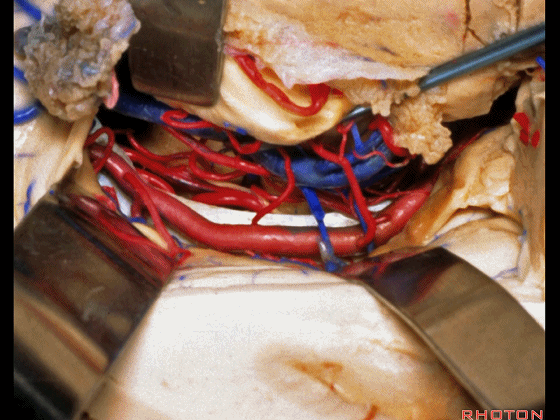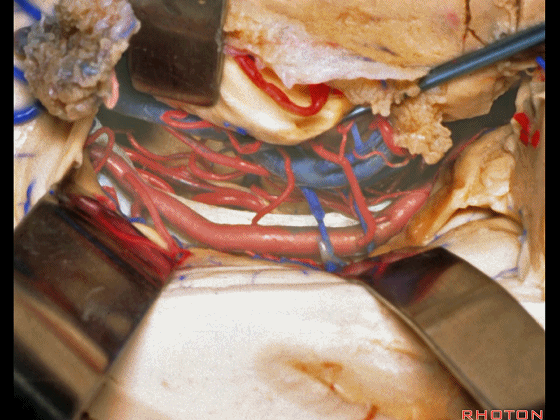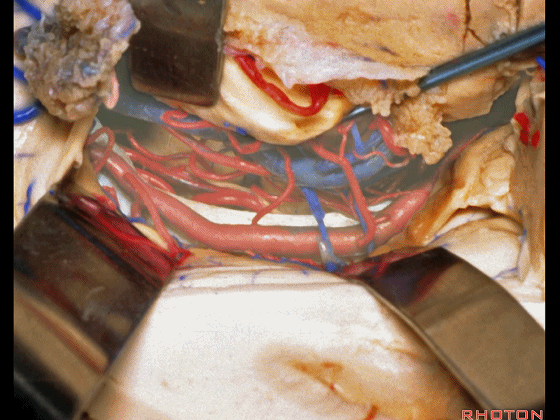
▼这是 海马
here is hippocampus.
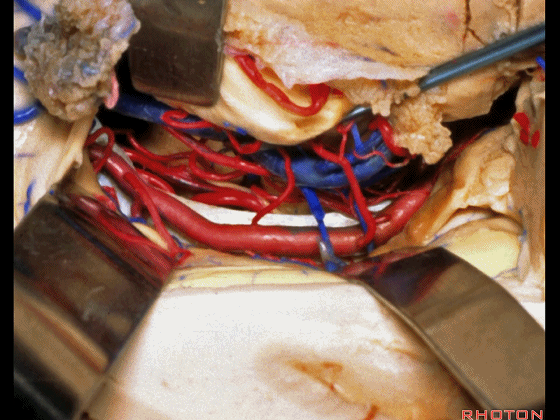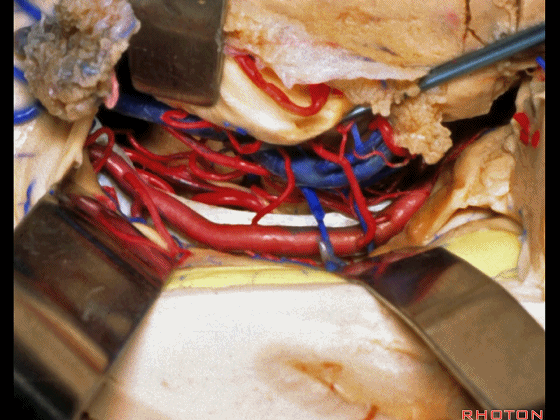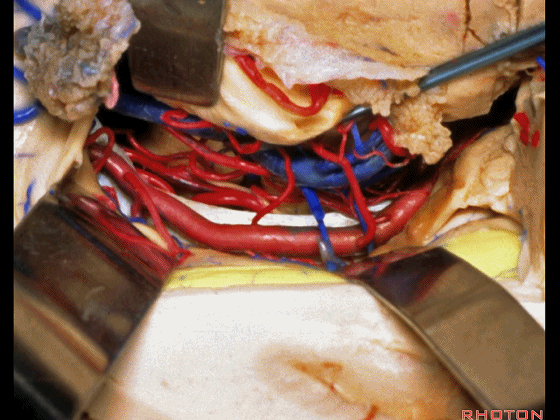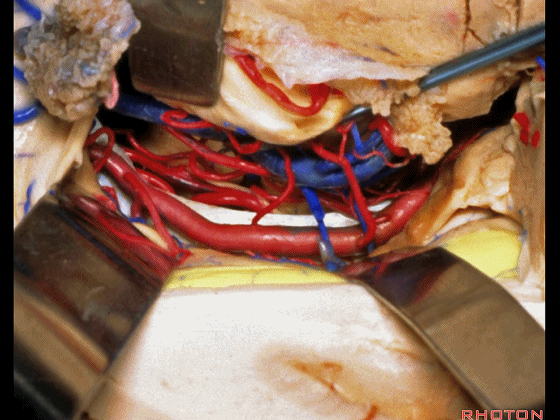
▼这是 丘脑
Here is thalamus,
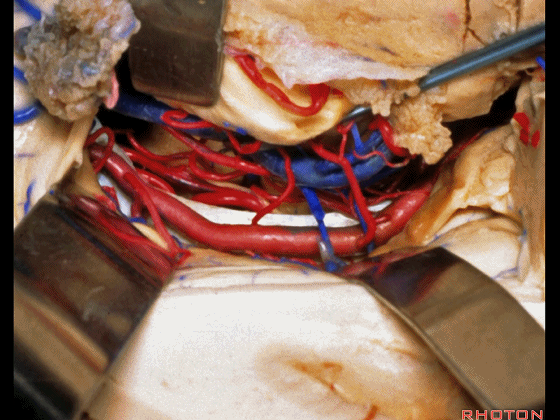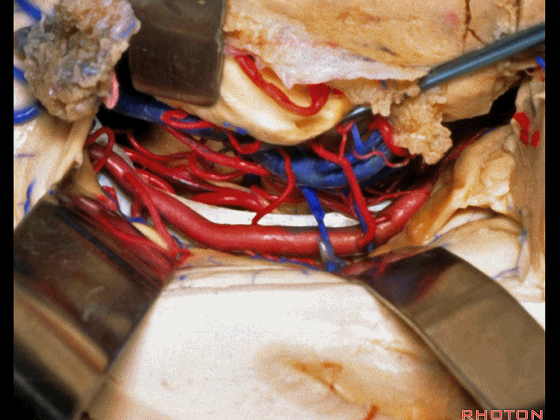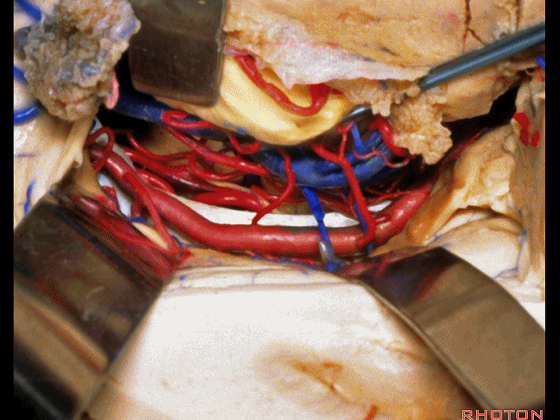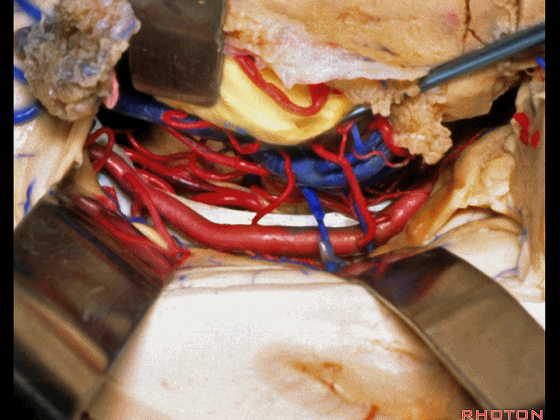
▼这是 外侧膝状体
and this is... lateral geniculate body.
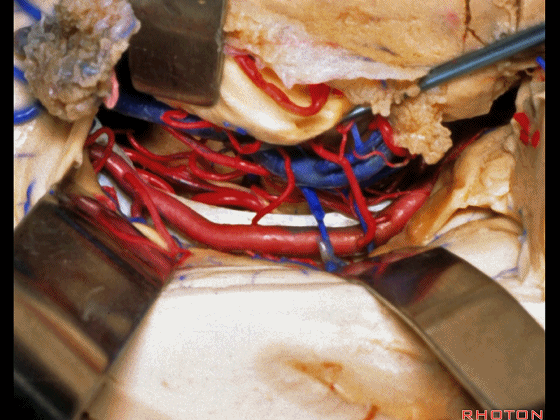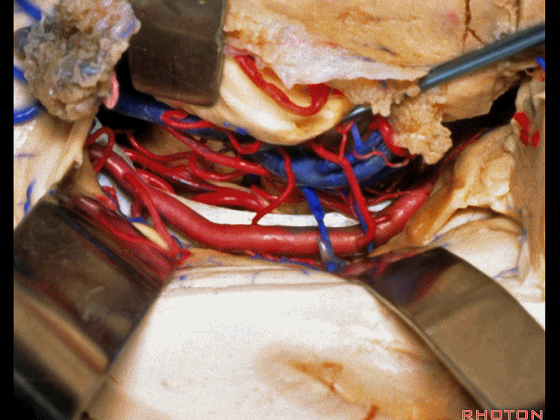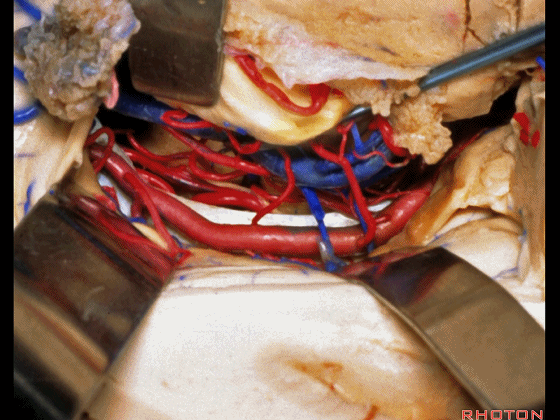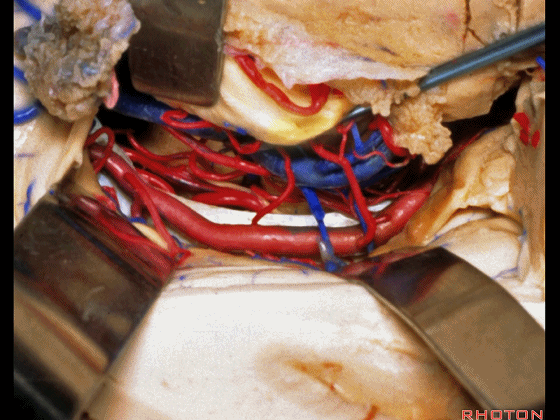
▼切开脉络裂时,始终将脉络丛(下方)留于丘脑侧。
We always, when we open the fissure, let the choroid plexus go with the thalamic side.
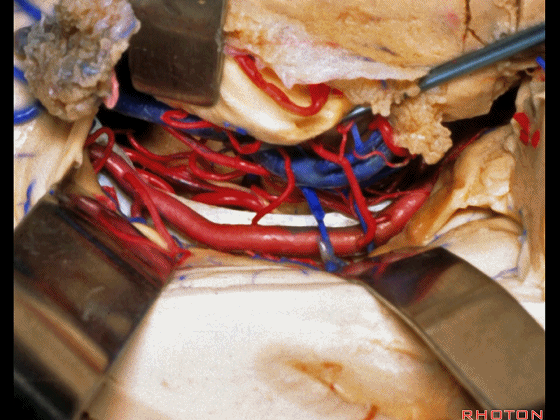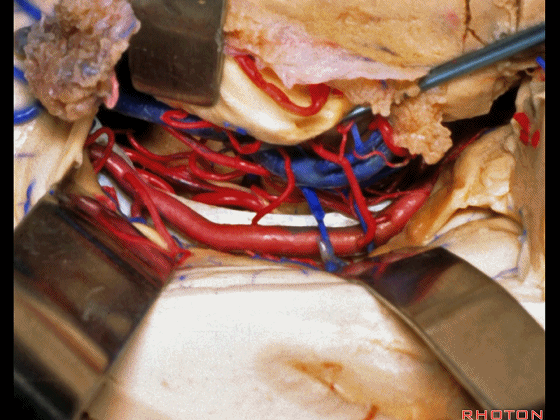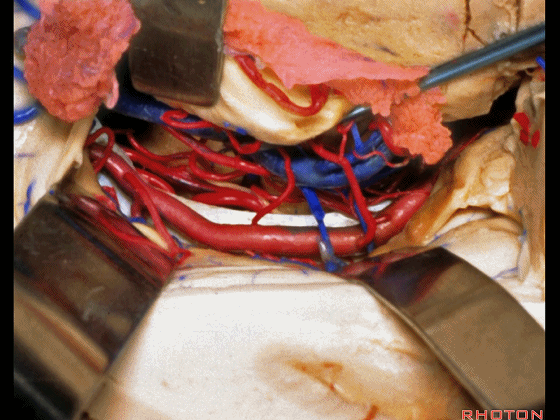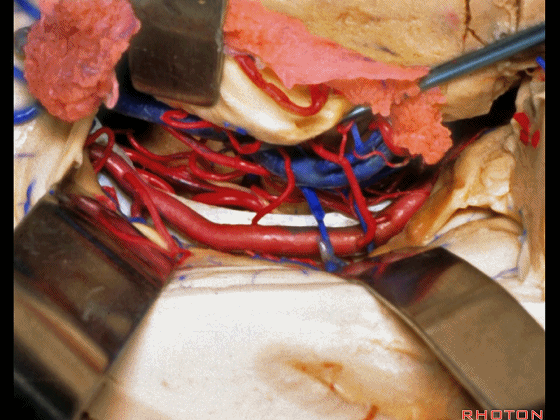
▼打开脉络裂,可见 大脑后动脉
We've opened through the fissure. We see posterior cerebral,
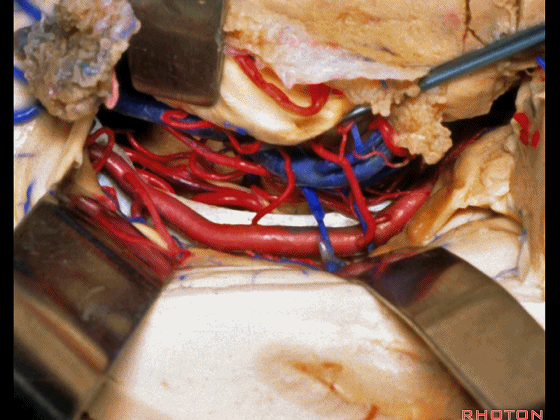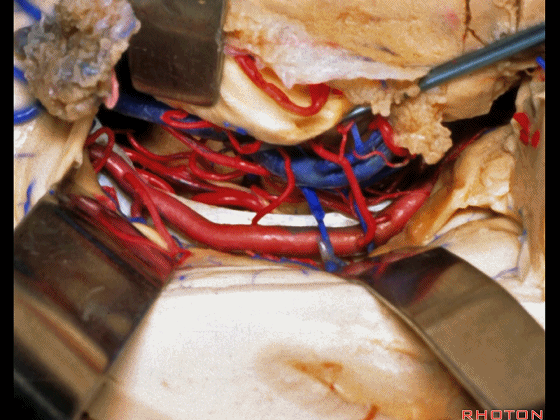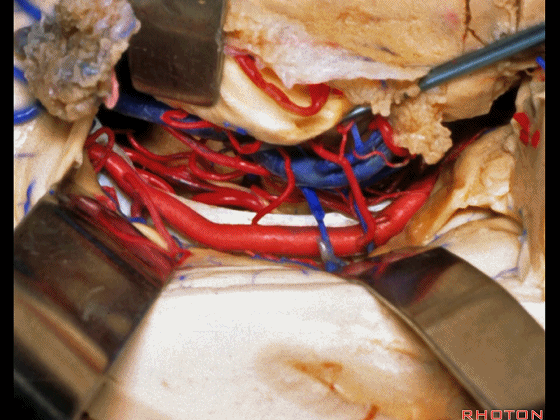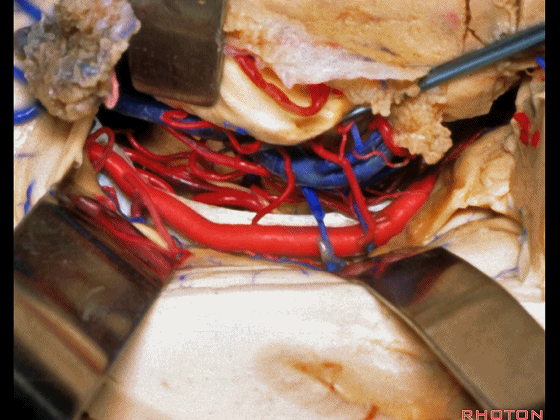
▼这是 天幕游离缘
tent edge
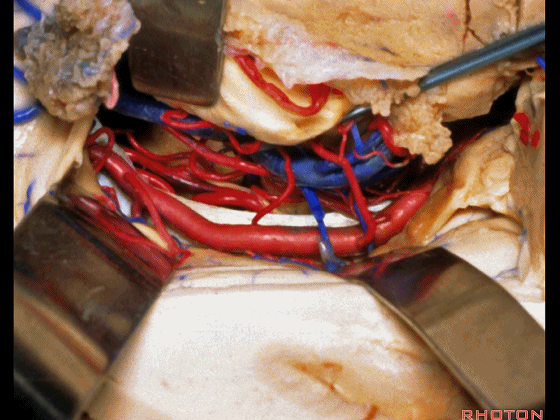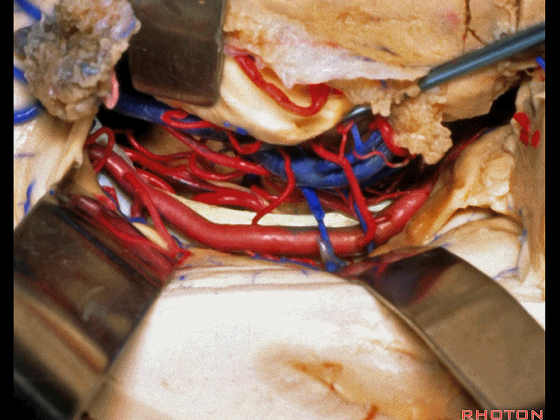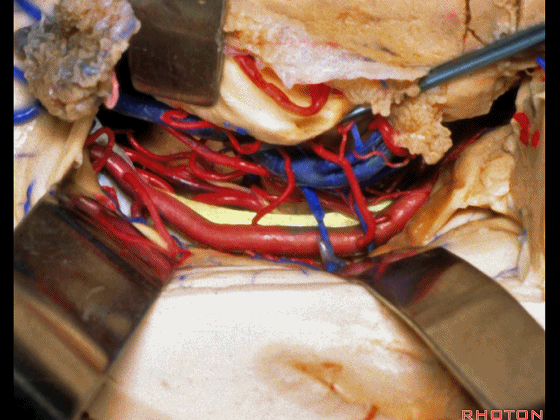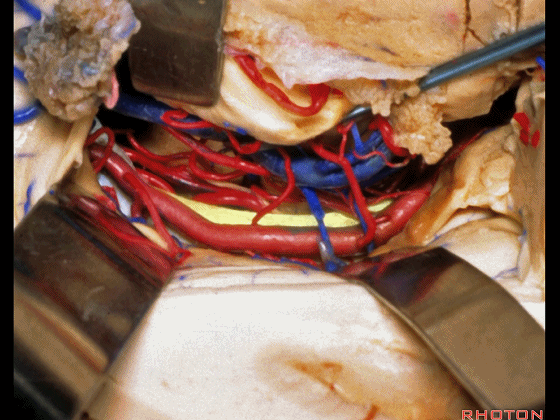
▼这是 滑车神经
a little bit of 4th nerve.
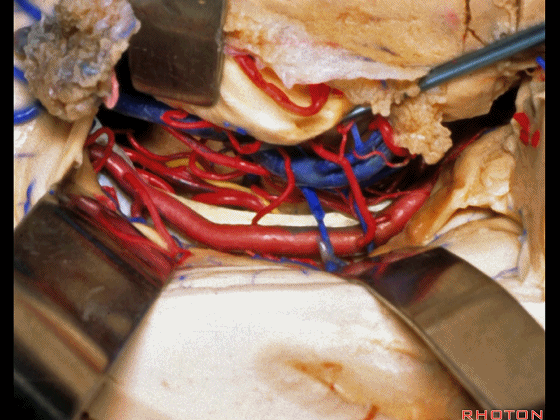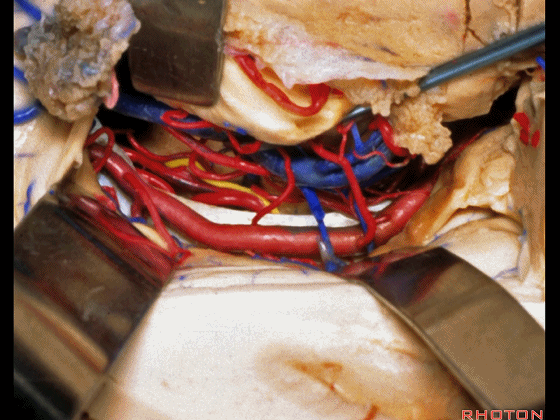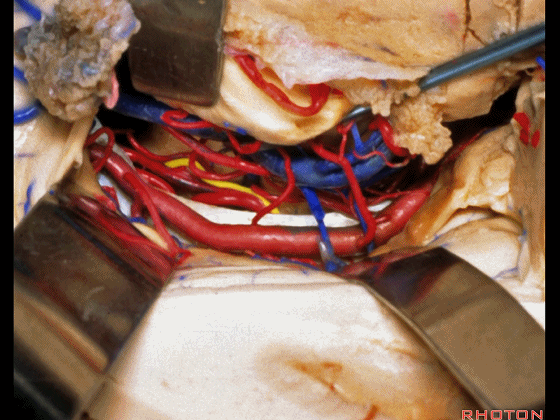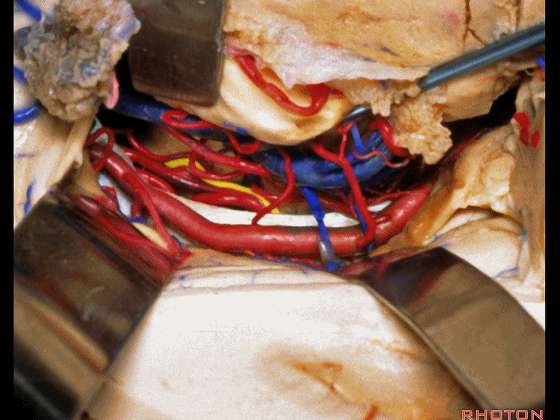
▼牵开这里的杏仁核
If you retract the amygdala here,
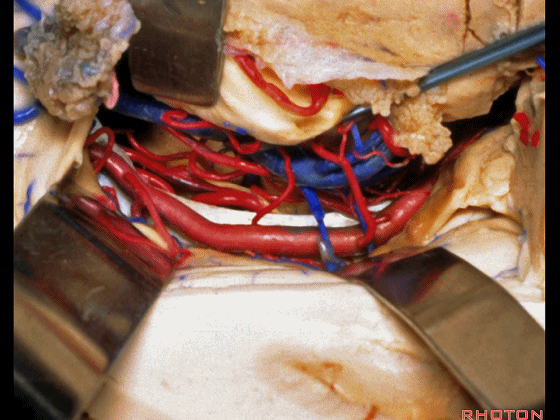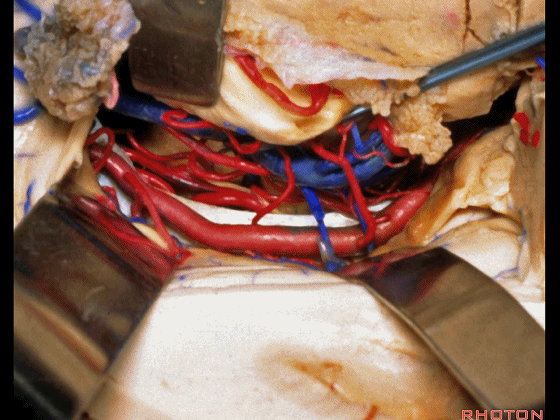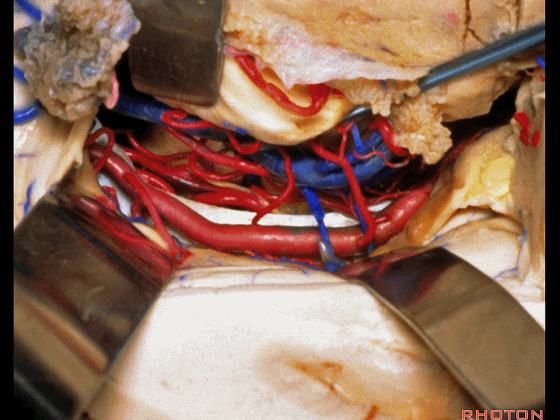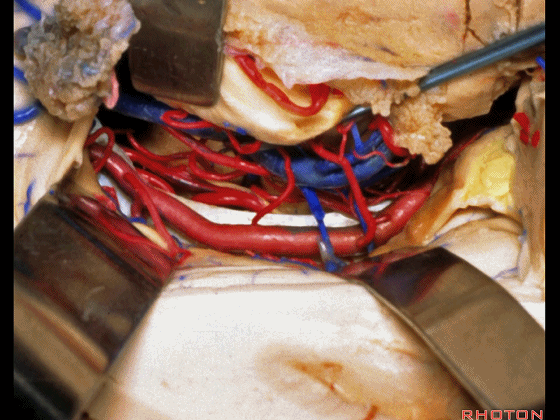
▼可向前暴露至基底动脉
you can reach forward to basilar,
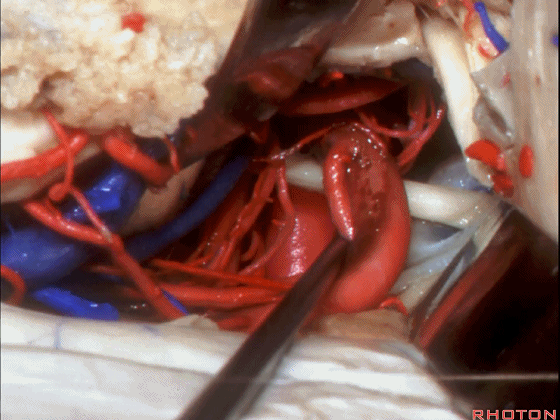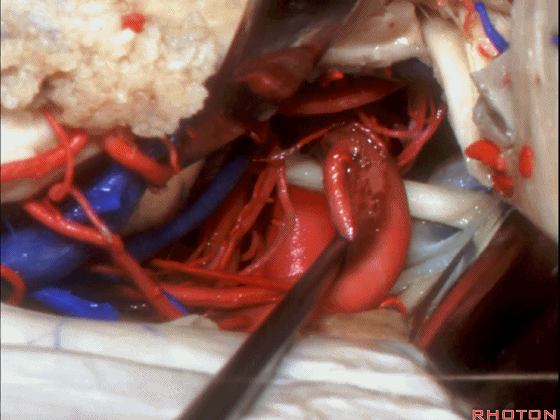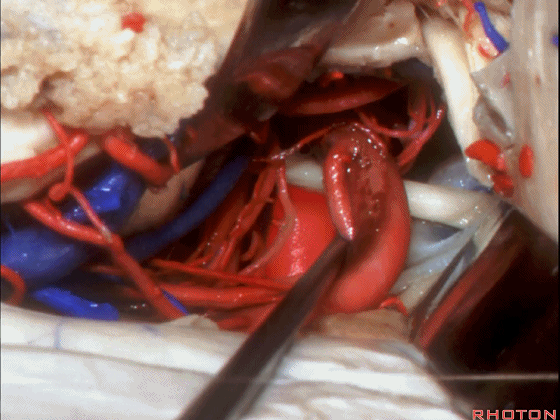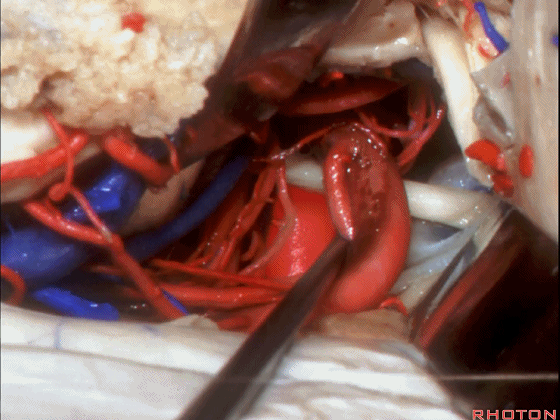
▼这是 基底动脉尖
basilar apex,
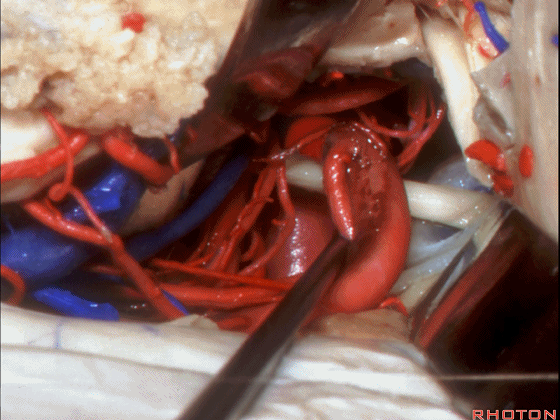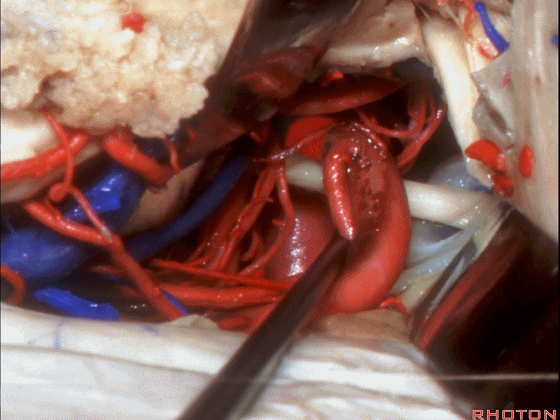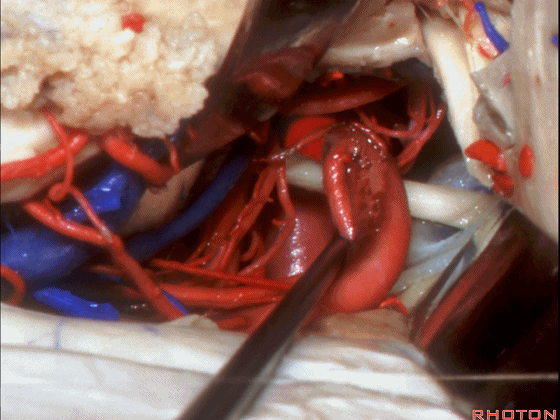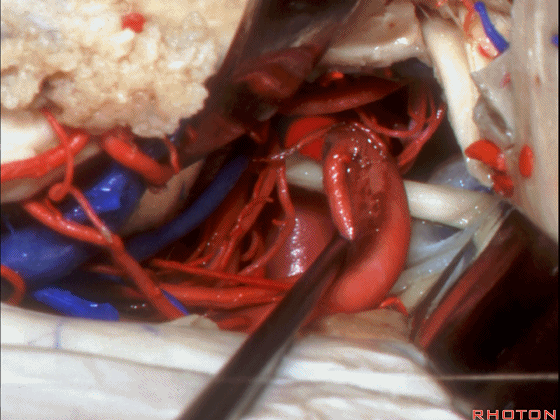
▼这是大脑后动脉 P1段、P2段、动眼神经
P1,P2, 3rd nerve.
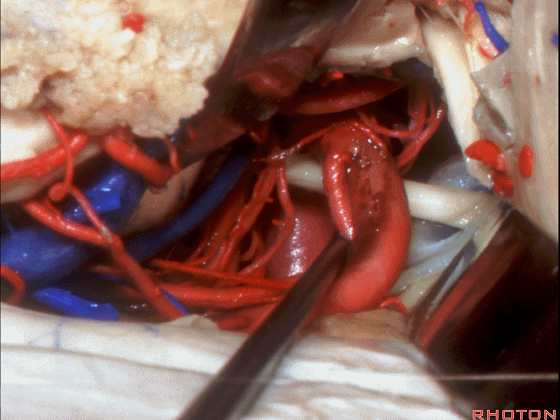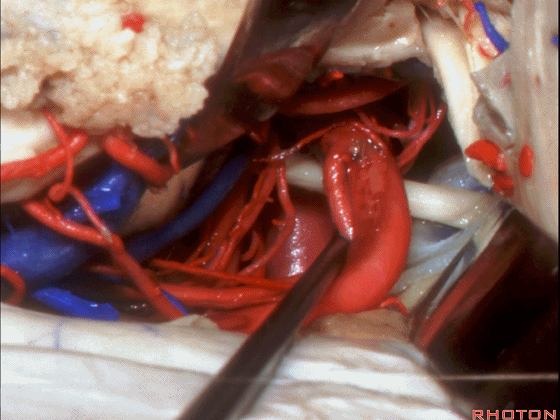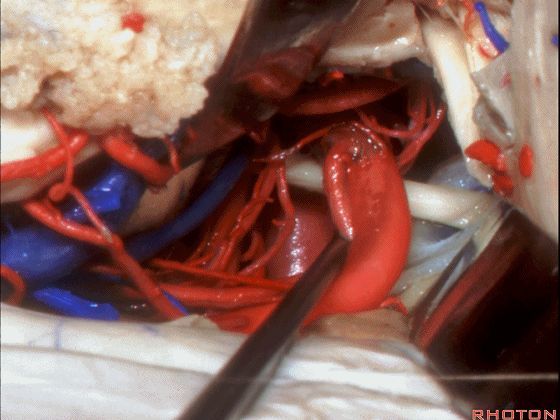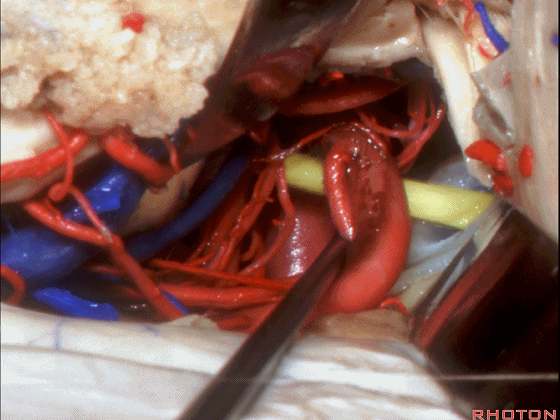
▼如果切开杏仁核,可显露颈内动脉(下图)
If you divide on through the amygdala, then for complicated pathology in this area, you have carotid,
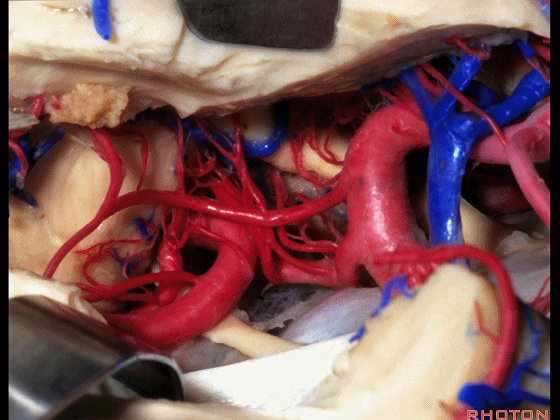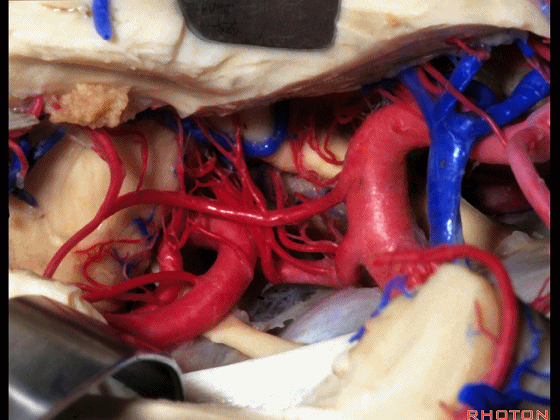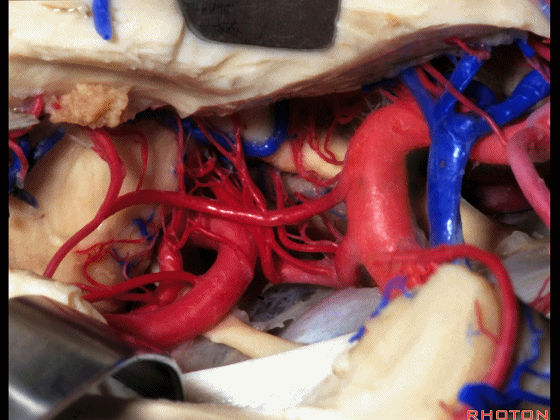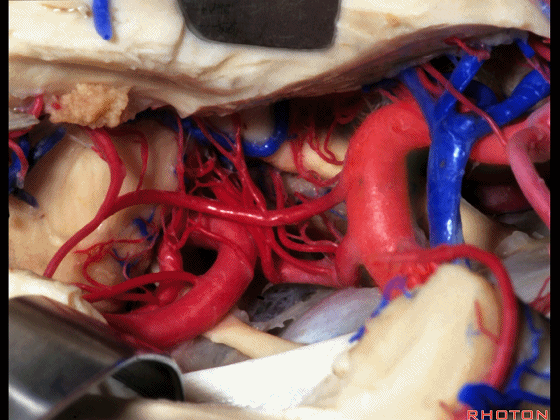
▼这是 后交通动脉
what artery...communicating,
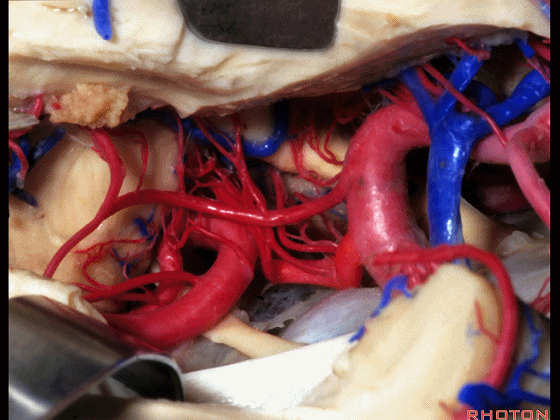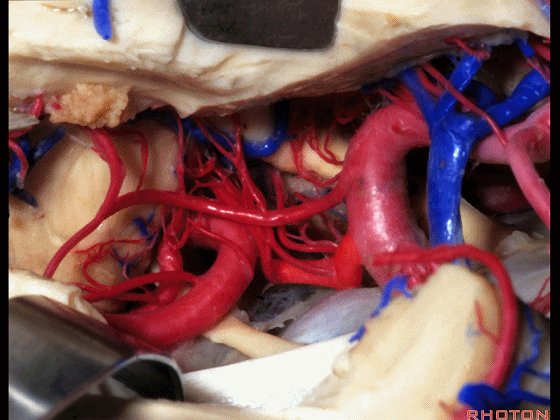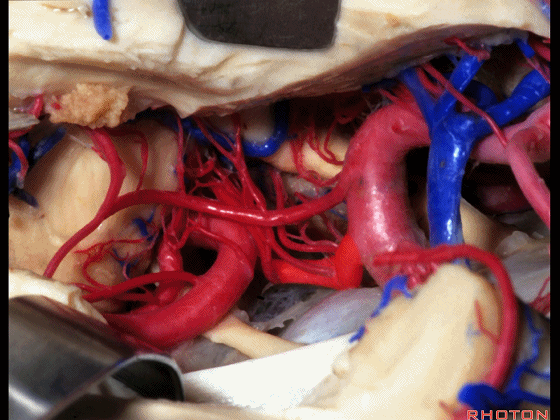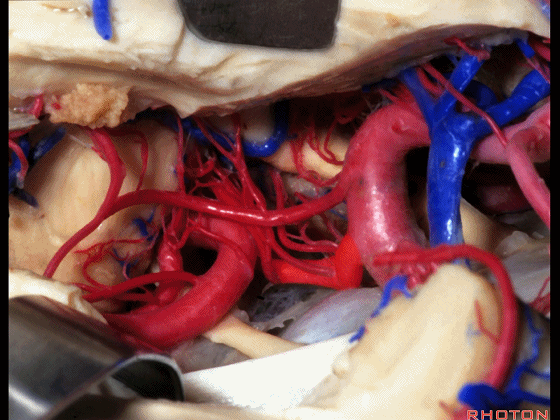
▼这是 脉络膜前动脉
choroidal artery
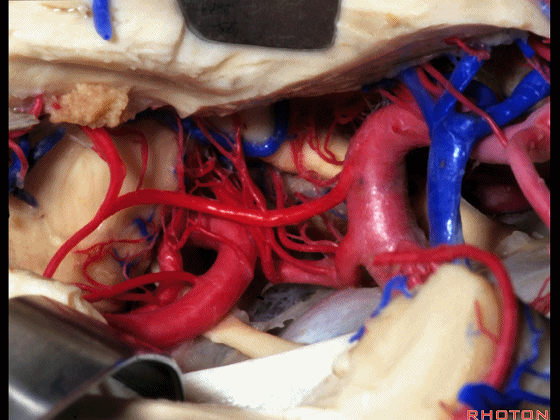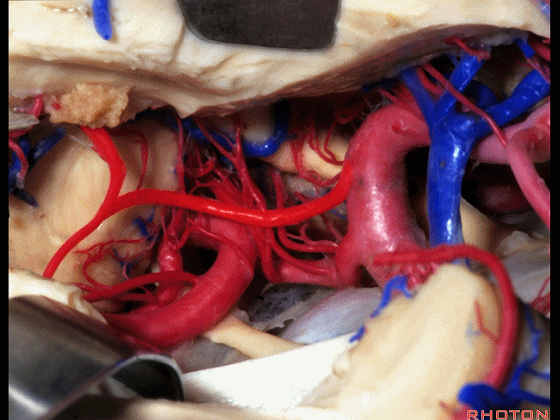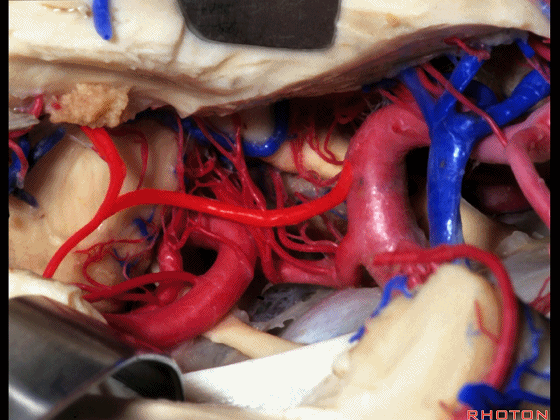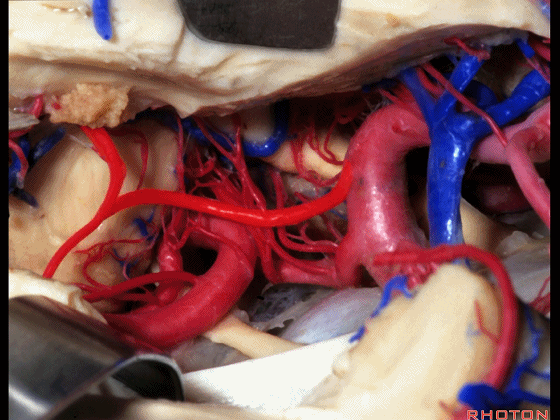
▼这是 大脑后动脉P1段、P2段
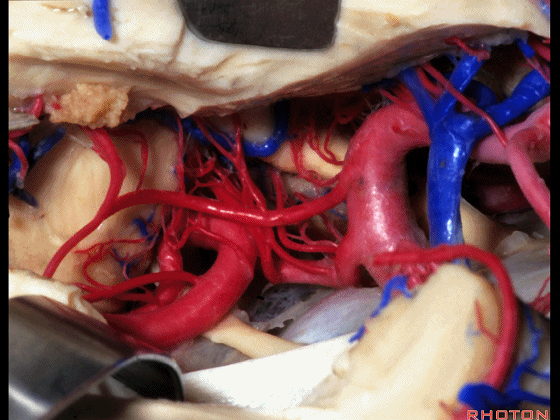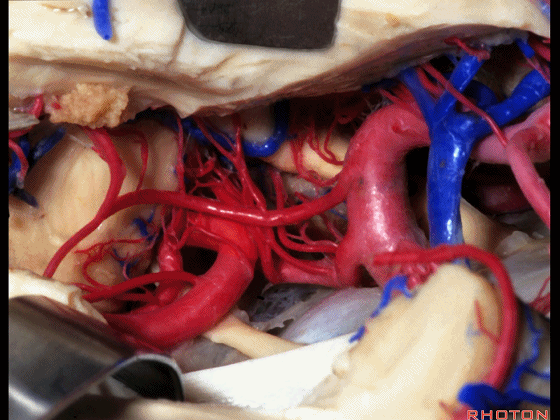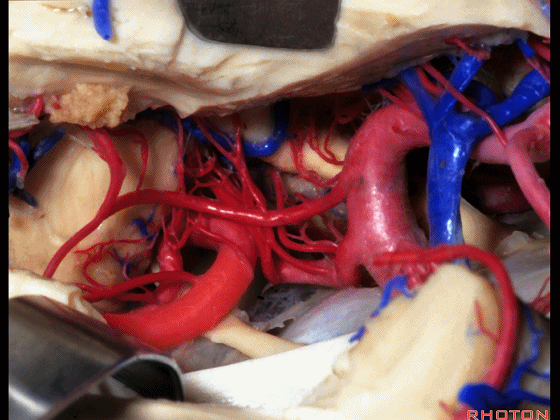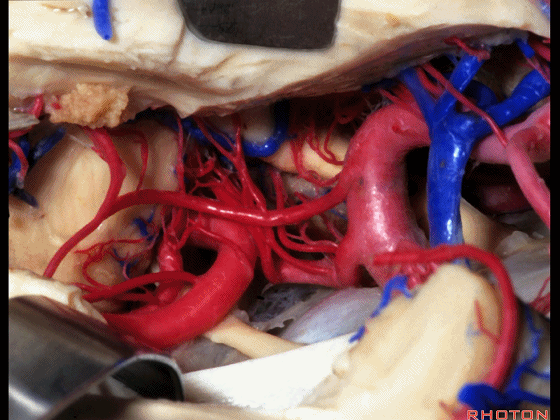
▼这是 脉络膜后内侧动脉(下图)发自大脑后动脉P1段
medial posterior choroidal arising from P1,
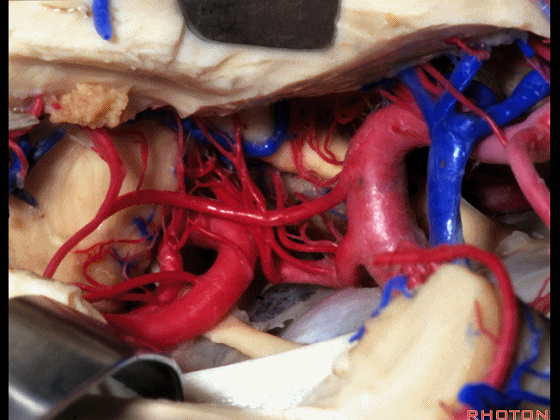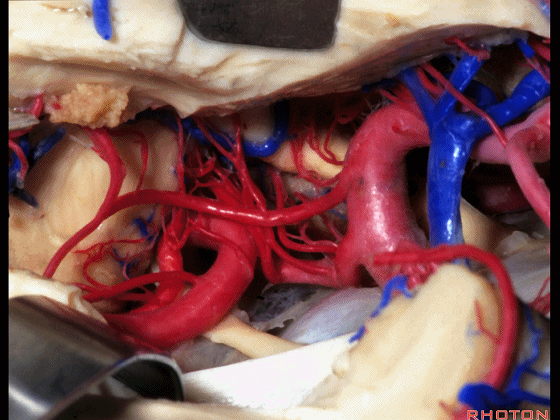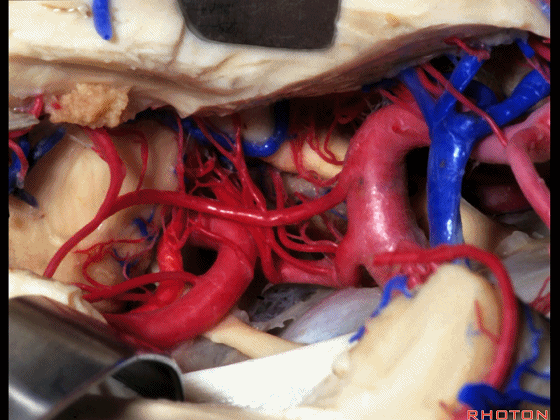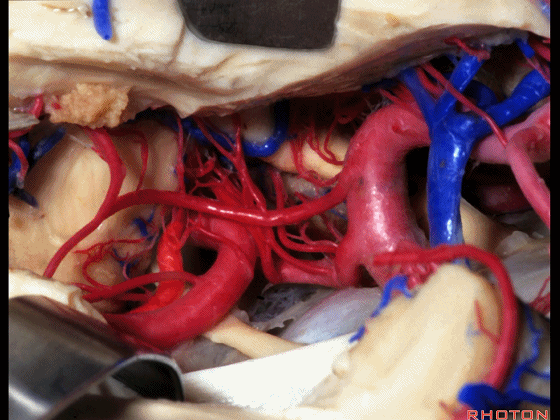
▼脉络膜后内侧动脉行经脚池、环池(下图),至四叠体池。
passing through crural,ambient,and quadrigeminal cistern.
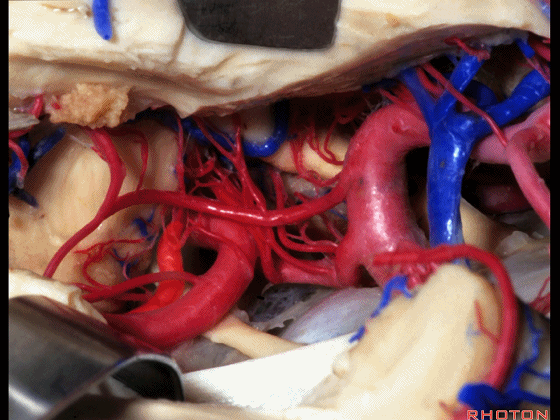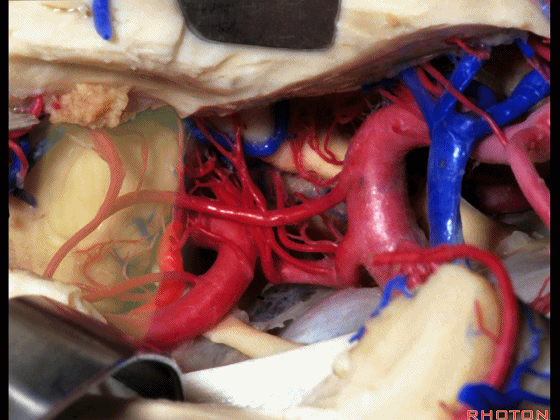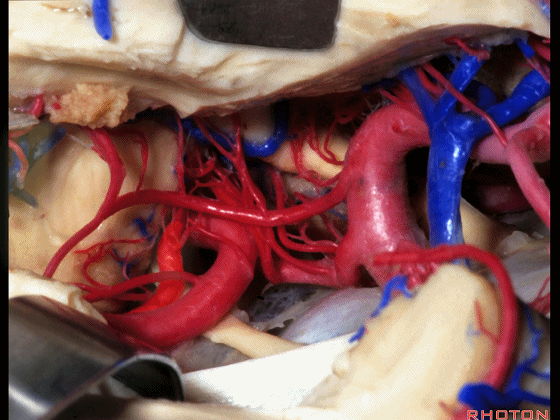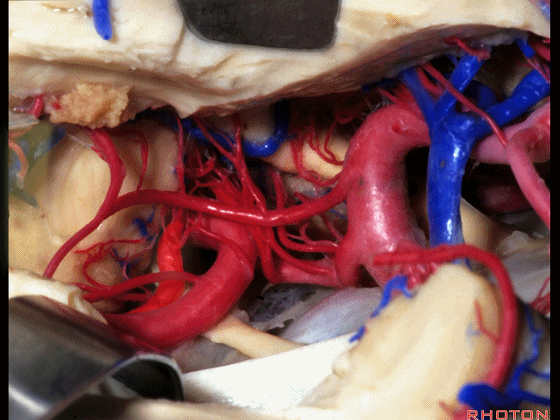
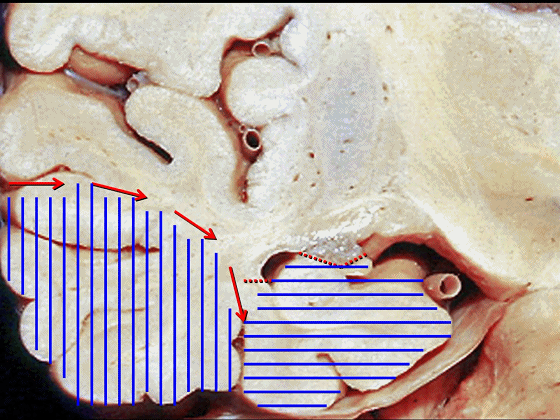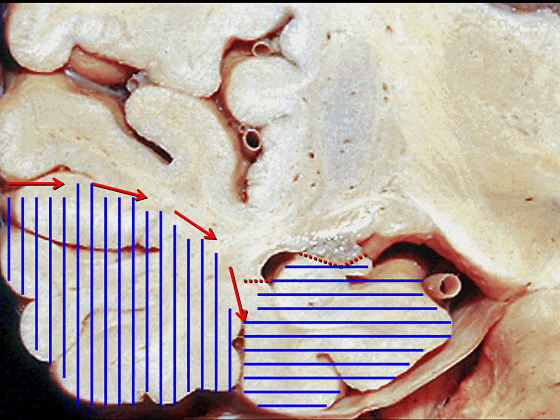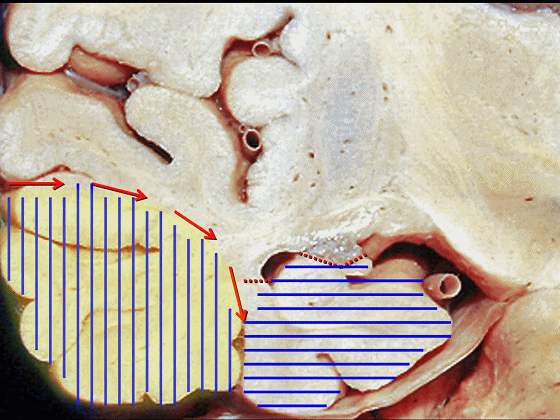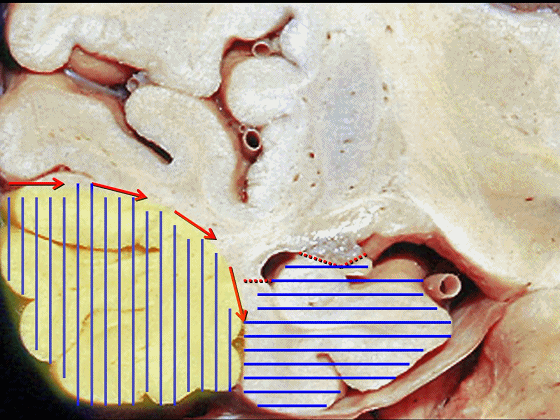
▼综上所述,颞下入路(下图)可暴露钩回的下面,无法暴露至很高的层面。

▼后方入路(下图)则可暴露至稍高的环池区域,但仍然无法暴露环池的上部。

▼但对于环池上部的病变,则往往需要经颞角暴露(下图)。

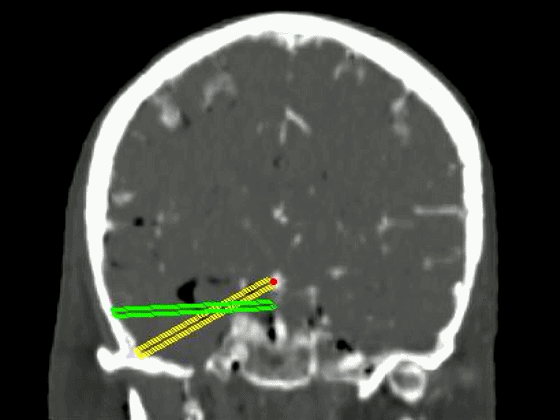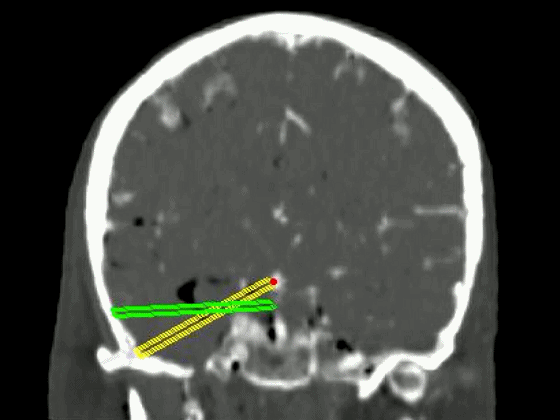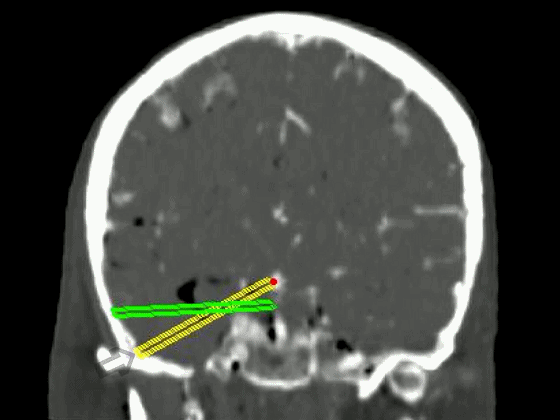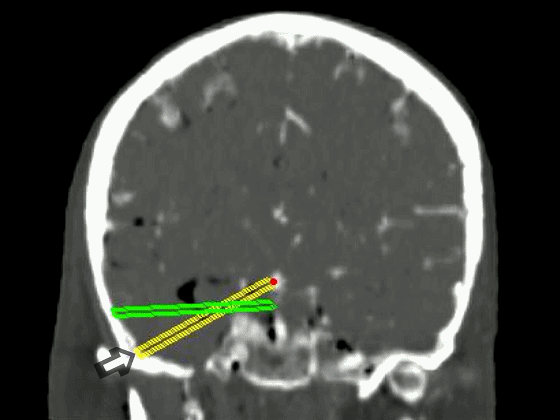
▼从影像来看。如果将颞肌下翻至颧弓上方(下图),仅能获得下图这一路径。
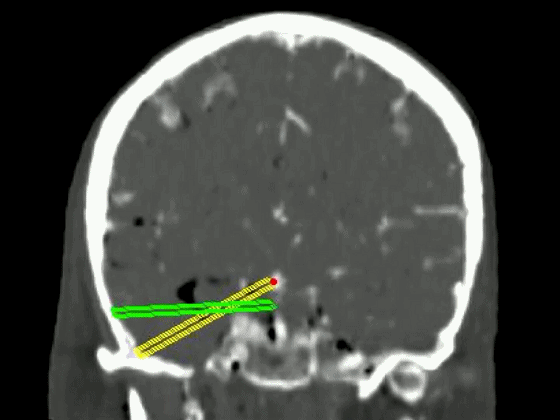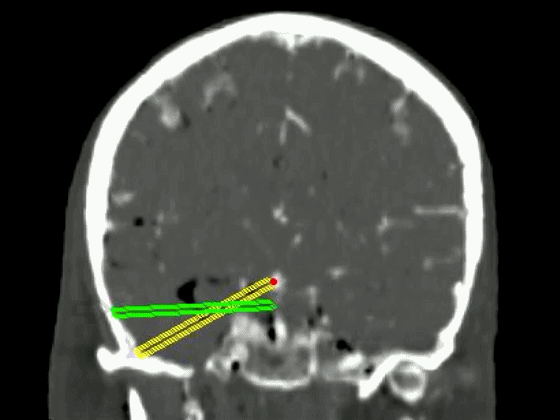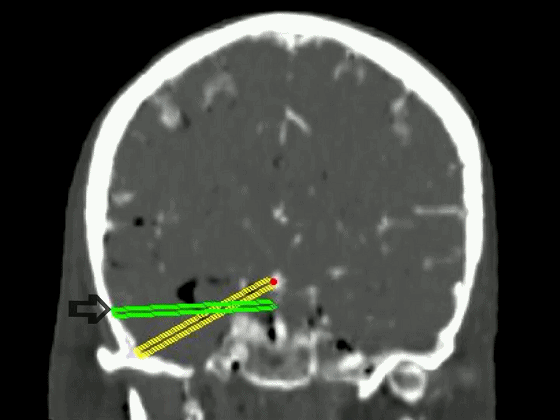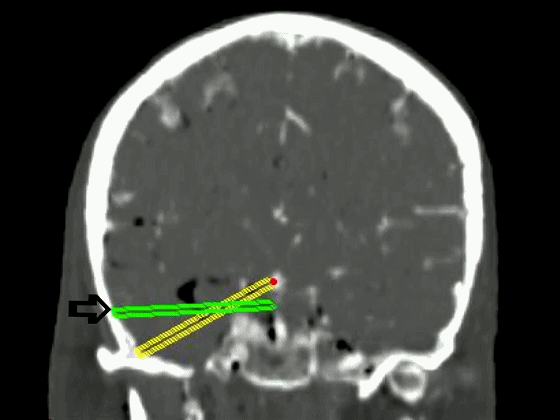
▼如果卸除颧弓,将颞肌继续下翻,则可获得一个更低的颞下入路,通向脚间池和环池。
If you divide the arch and fold the muscle down out of the way, you see what,a much lower trajectory you have below the temporal lobe,to the area of the interpeduncular and ambient cistern.
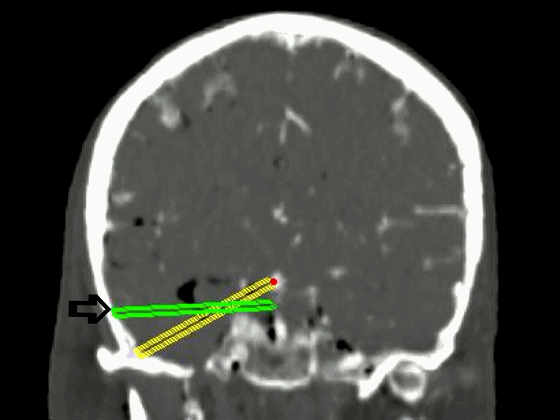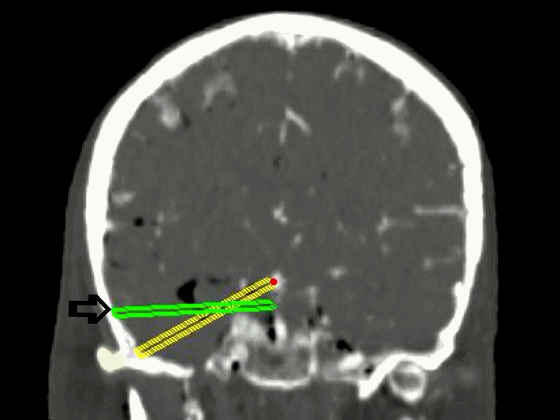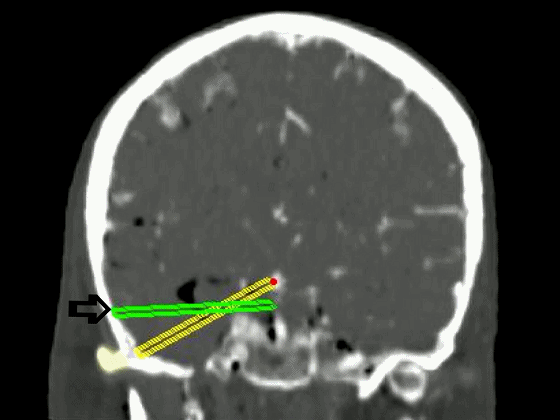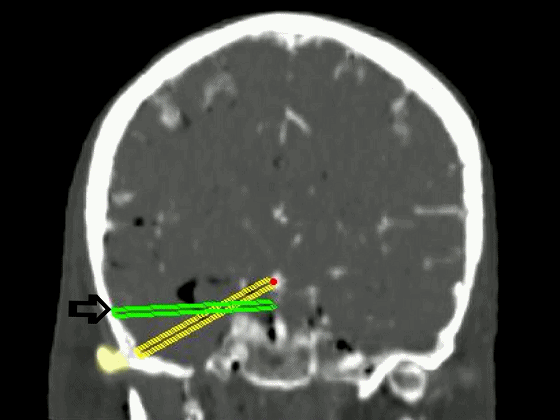
![]()
▼接下来讨论颞叶内侧面的静脉回流,其常常向后经脚池到环池到四叠体池,汇入Galen静脉。
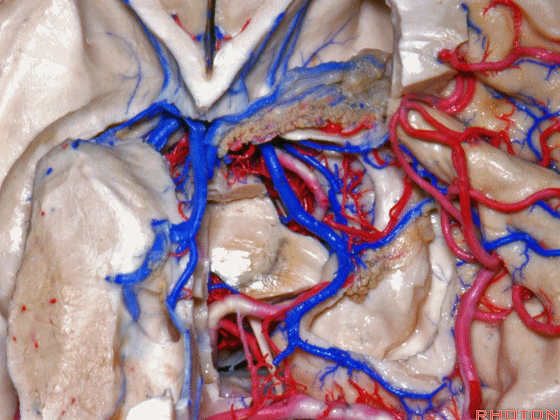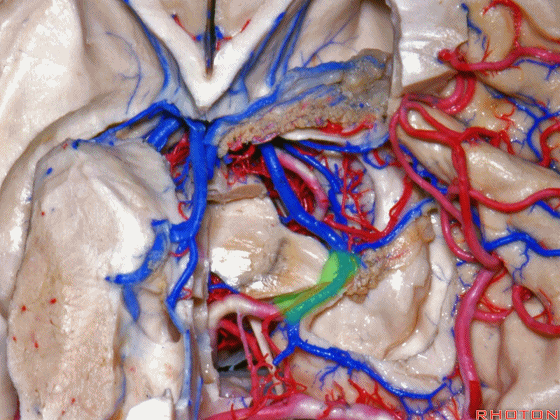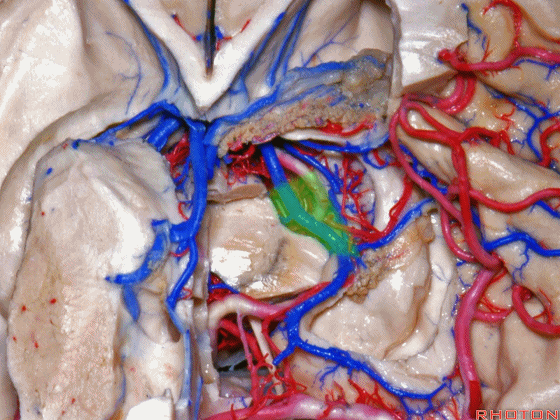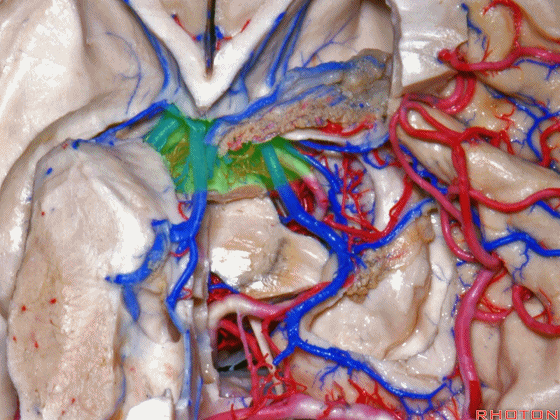
▼而引流颞角顶壁(下图)及视辐射 的粗大静脉,行经脉络裂的丘脑侧
And the large veins draining the roof of the temporal horn here that drain the optic radiations pass through the thalamic side,
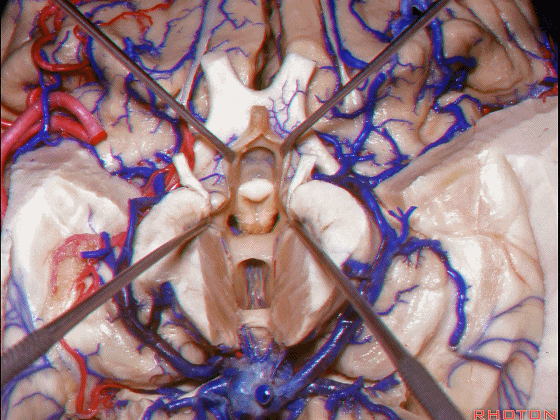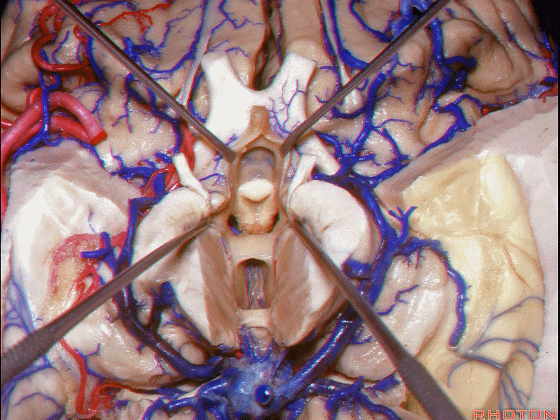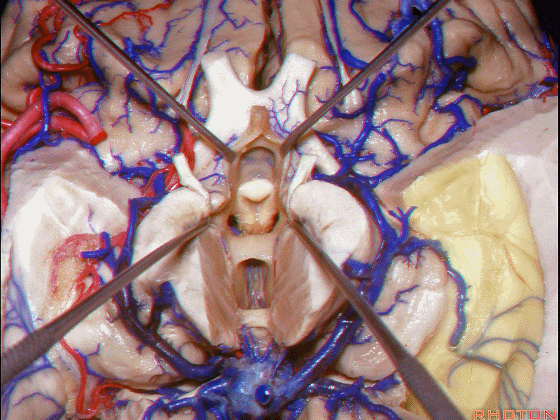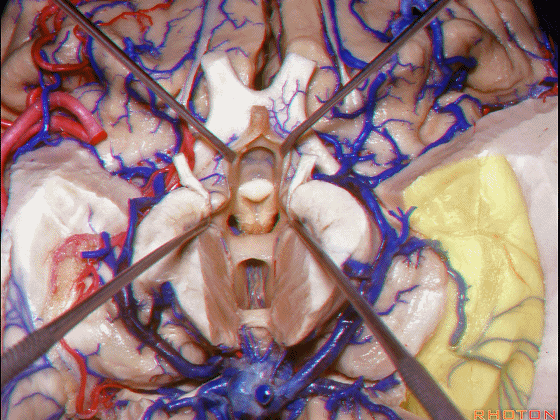
▼下图示丘脑
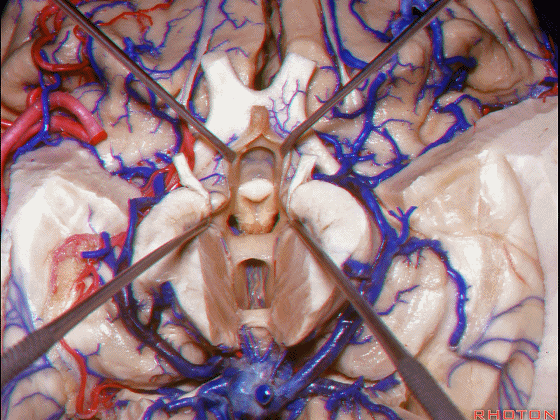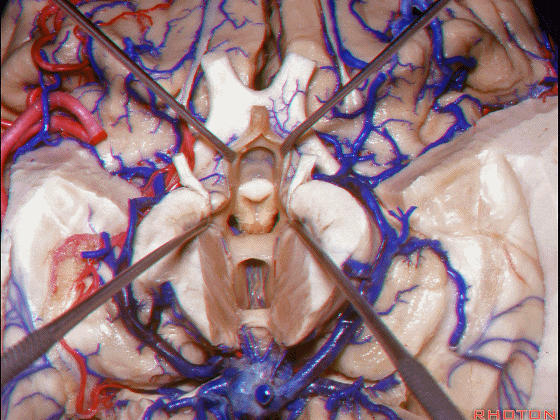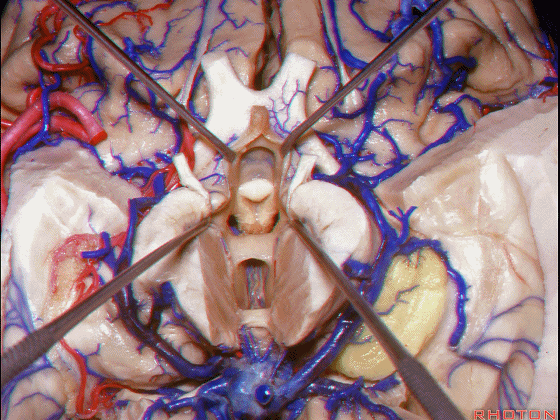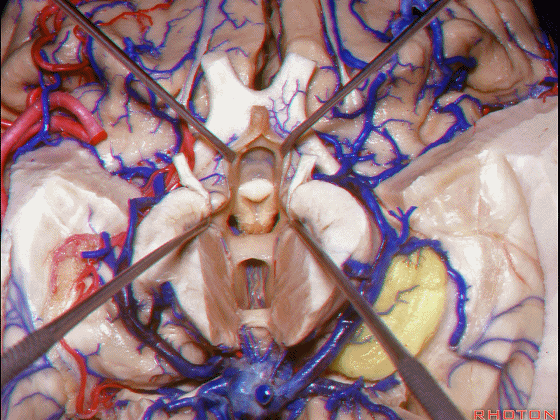
▼这是外侧膝状体侧的区域。
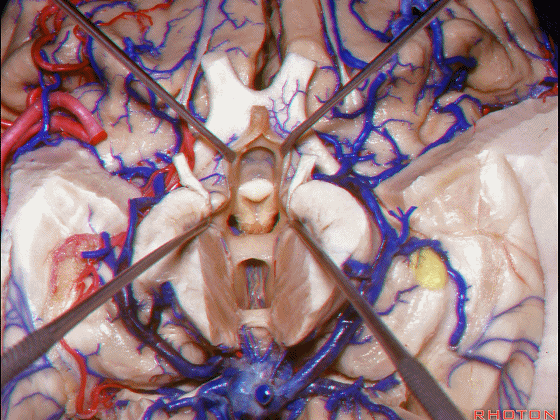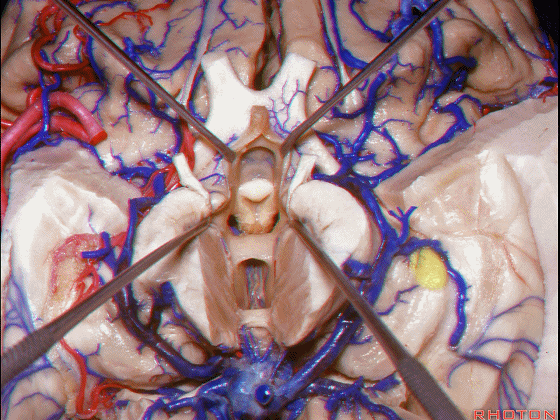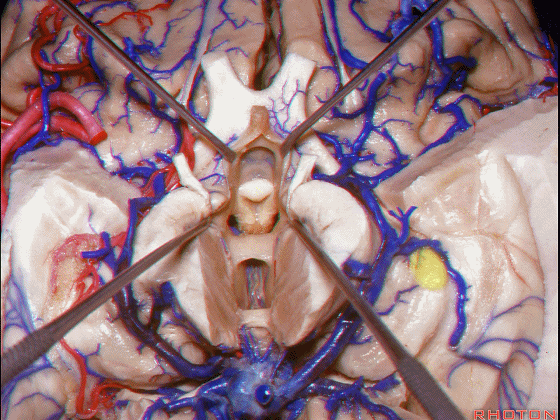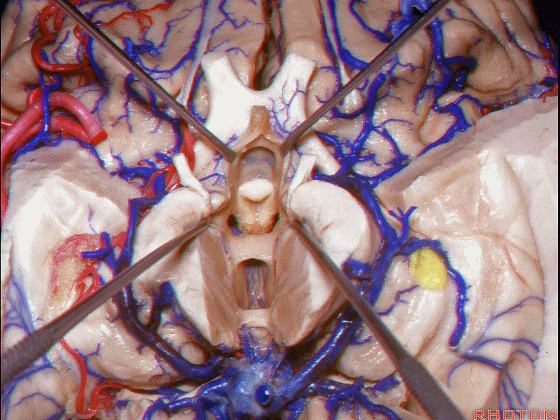
▼这是脉络裂处的静脉
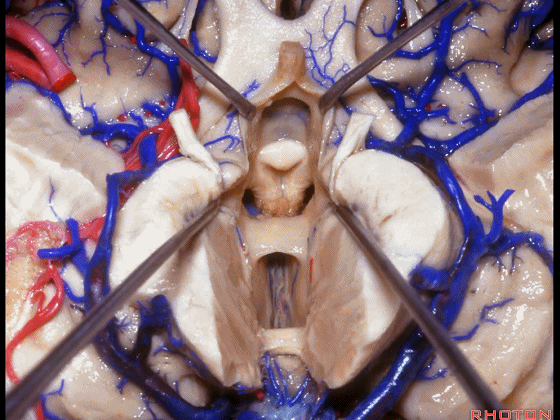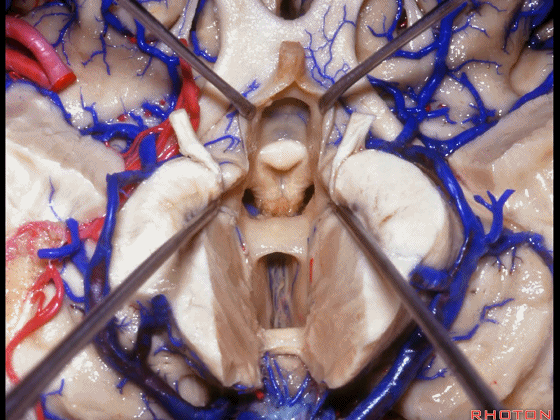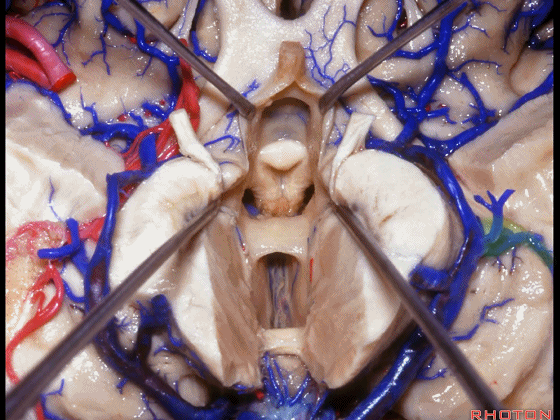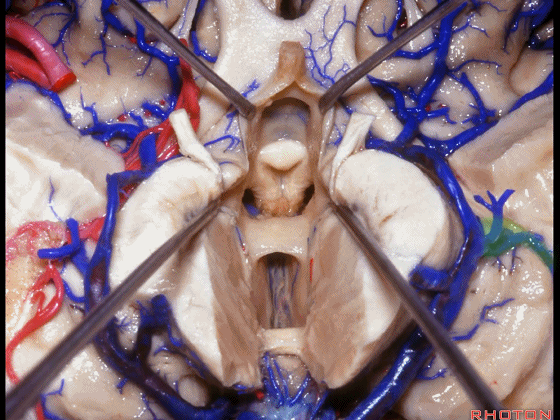
▼术中需时刻注意保护颞角顶壁的视辐射,并保护其静脉回流。方法即在脉络裂的穹窿侧切开伞部,以暴露环池或四叠体池。
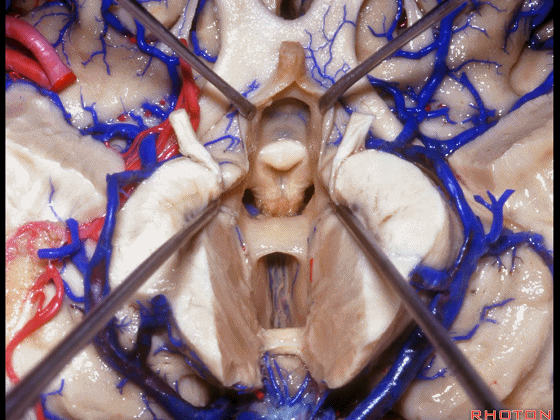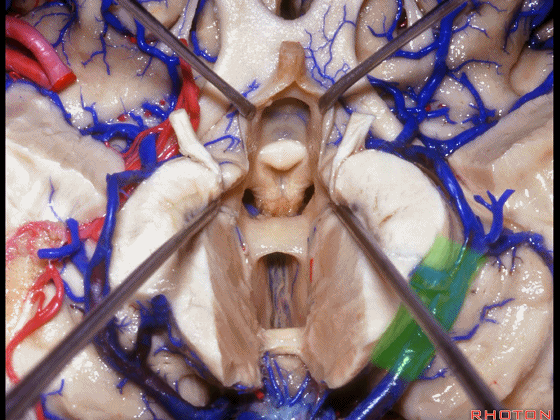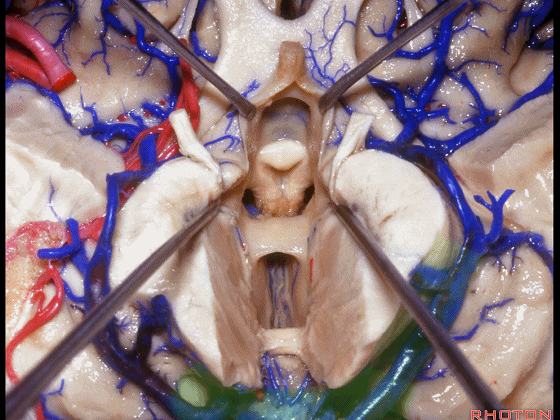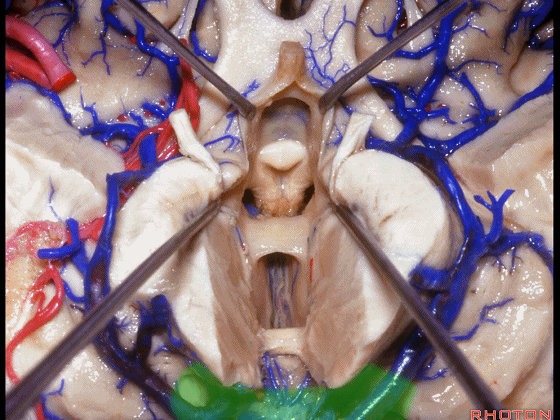
▼从下方来看第三脑室
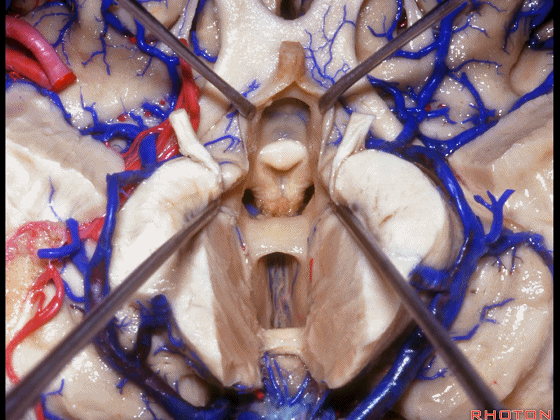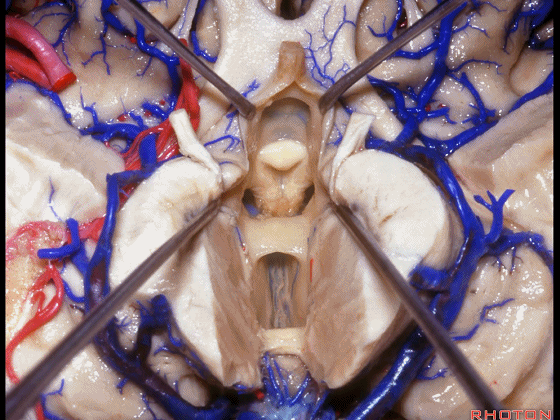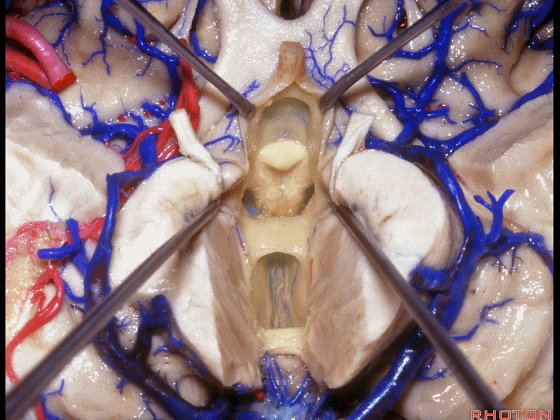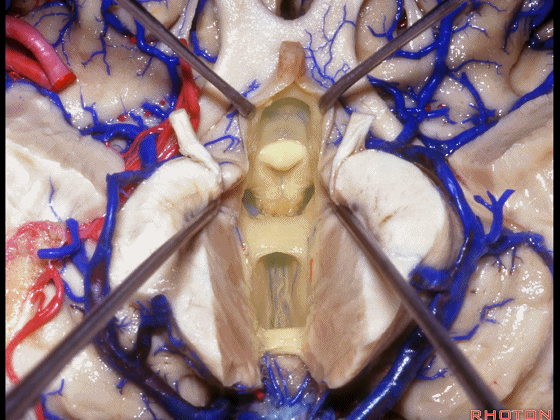
▼这是前连合
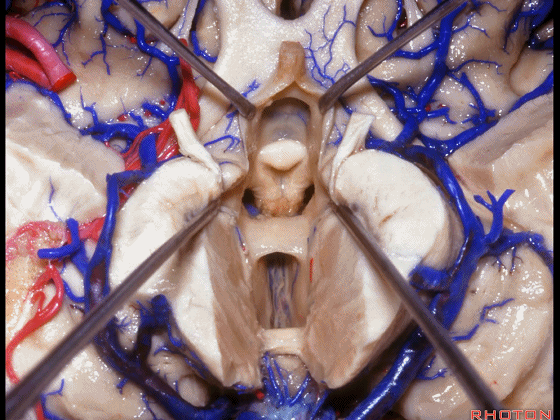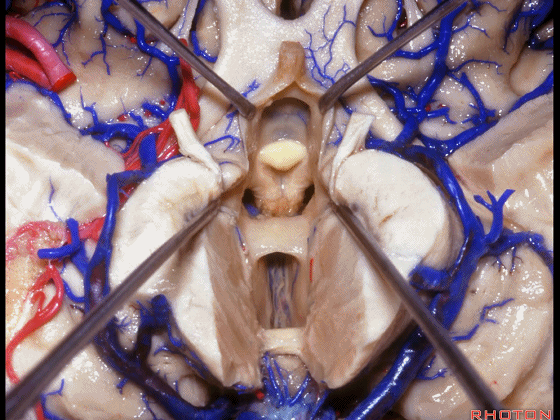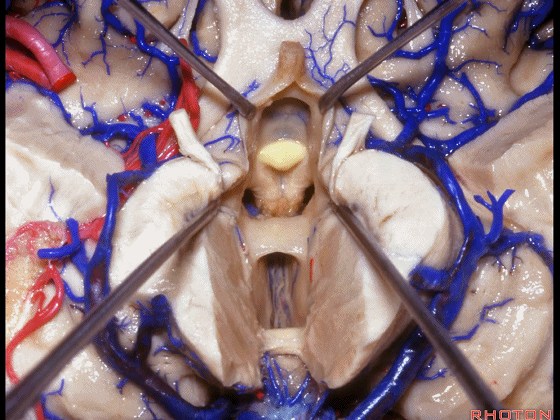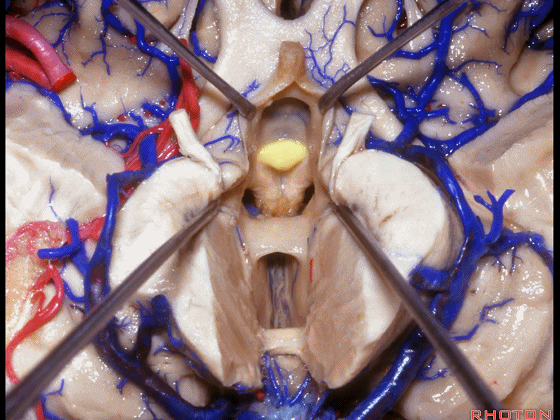
▼这是终板
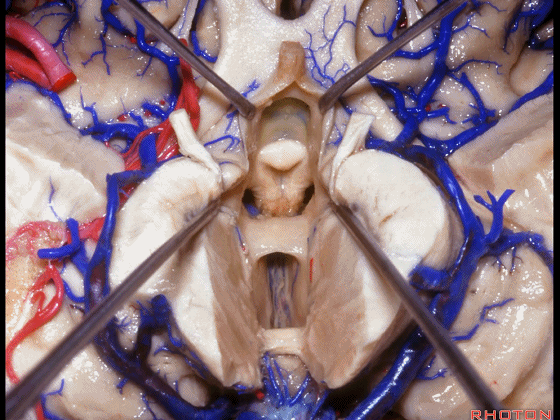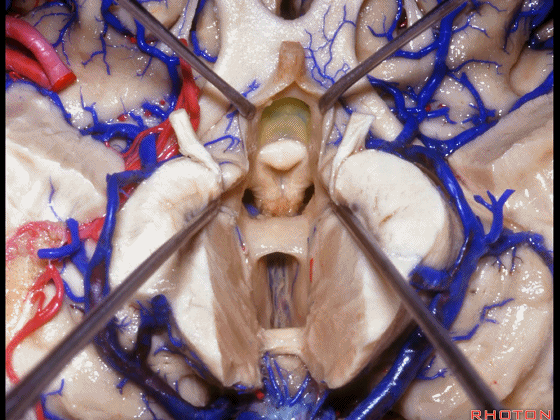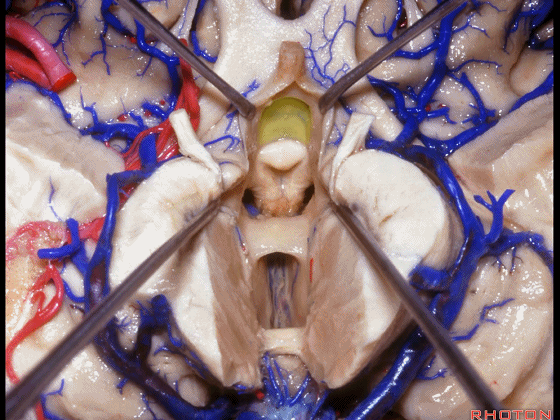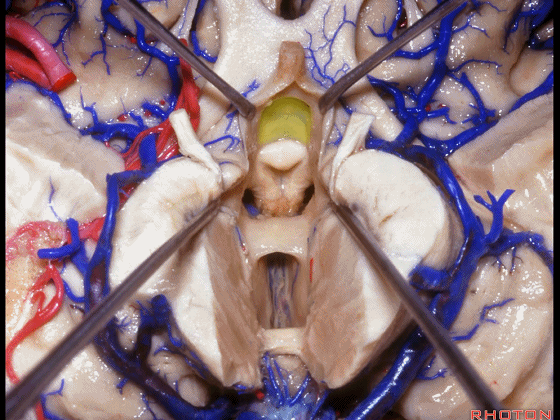
▼这是穹窿柱,其位于Monro孔前方。
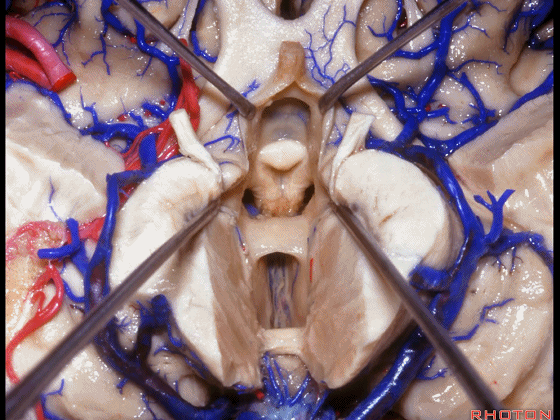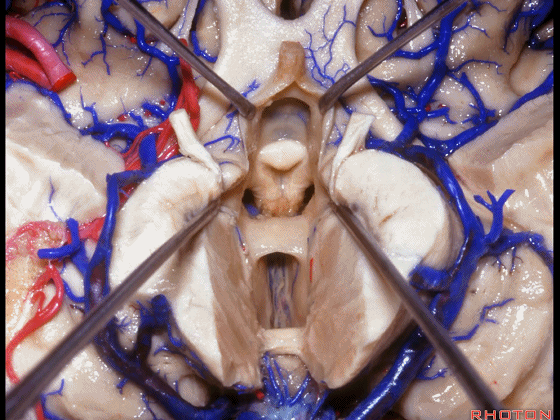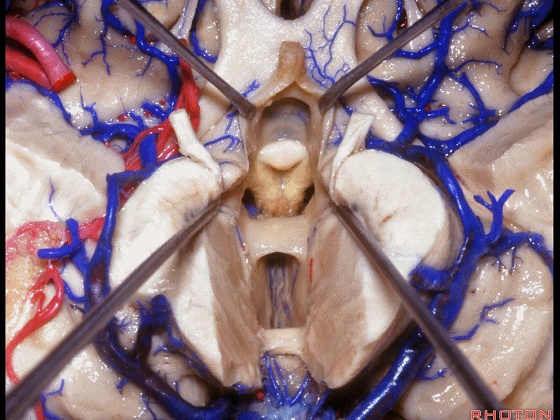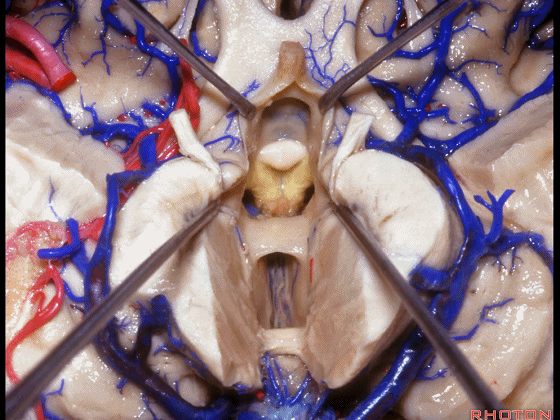
▼这是中间帆的下面。
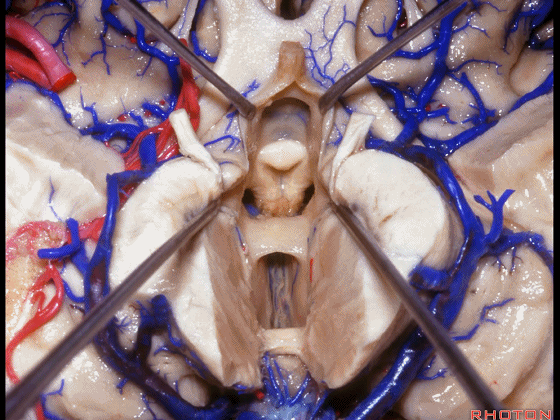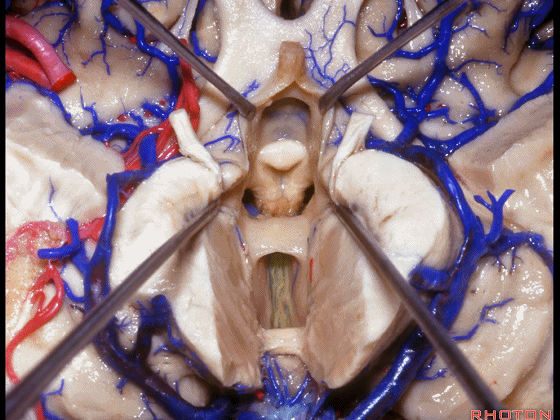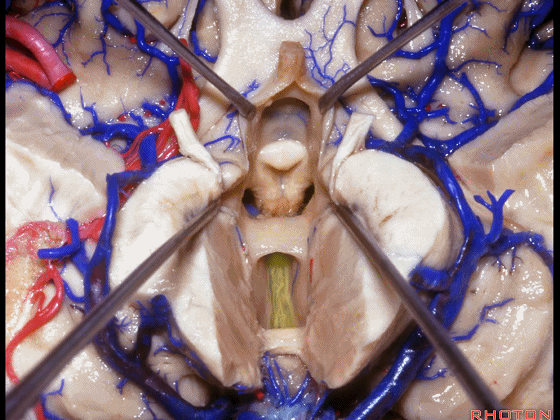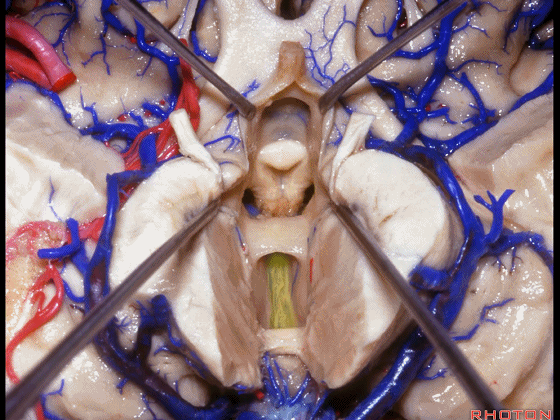
▼这是颞角、颞叶。
So, temporal horn,temporal lobe.
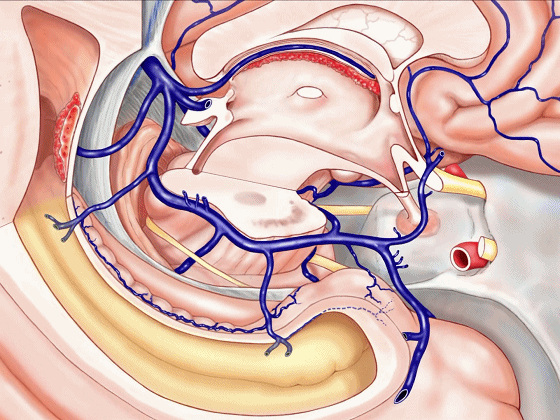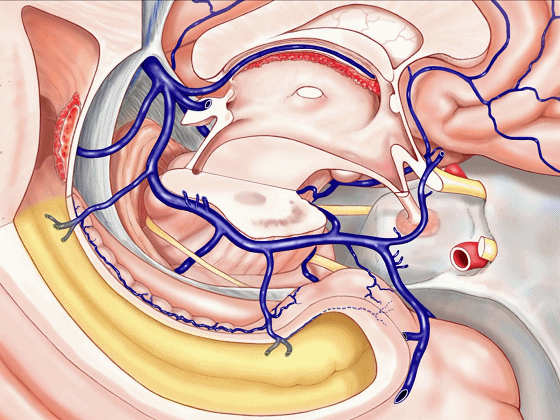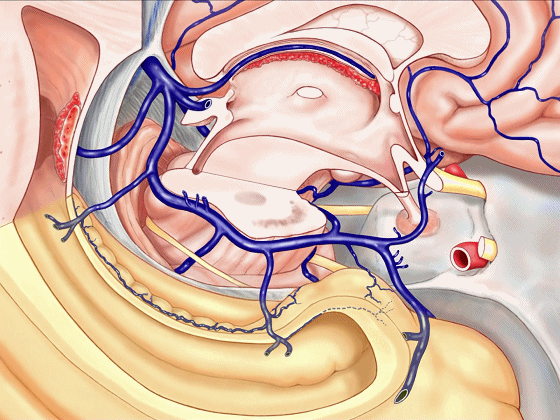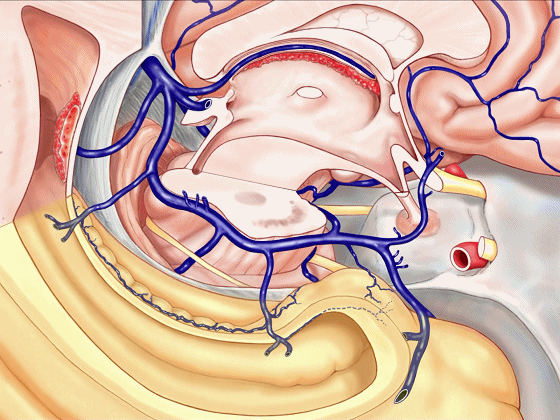
▼静脉系统通常向后回流,引流外侧裂深部(下方)、半球内侧面
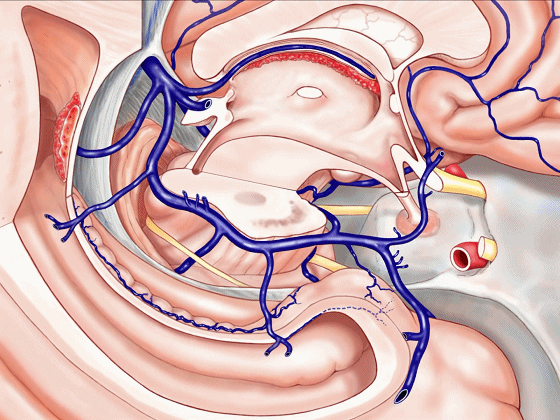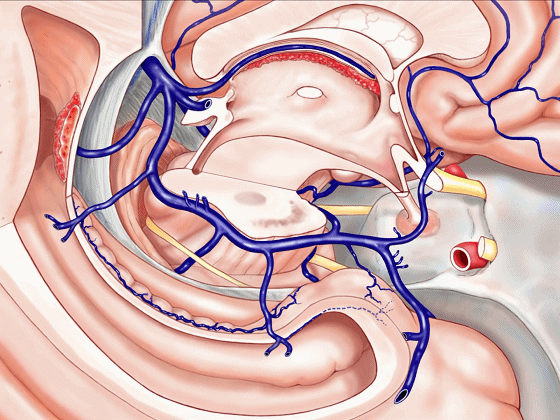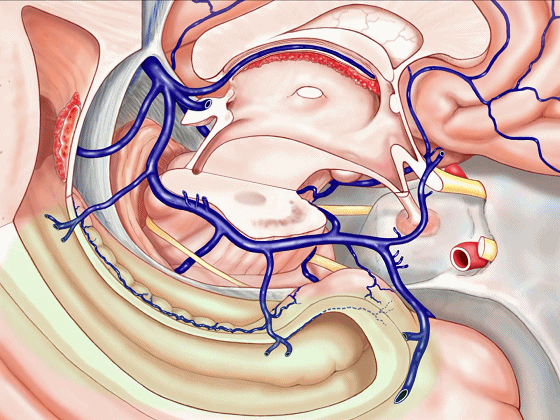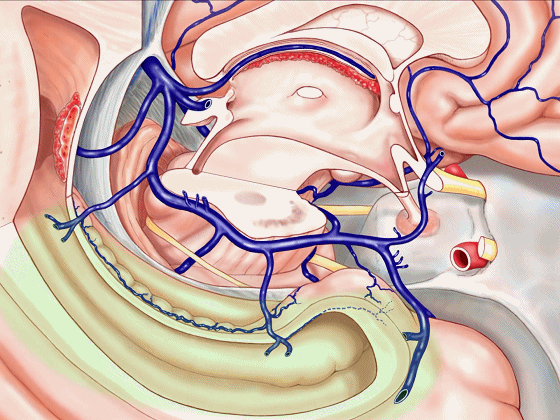
▼这是对侧半球内侧面

▼静脉向后经脚池、环池、回流至四叠体池。
▼但在处理血管性病变时,我们会遇到各种变异,比如钩回前段 回流至海绵窦,或流出外侧裂。
▼这一段血管(下图)可能发育不良。
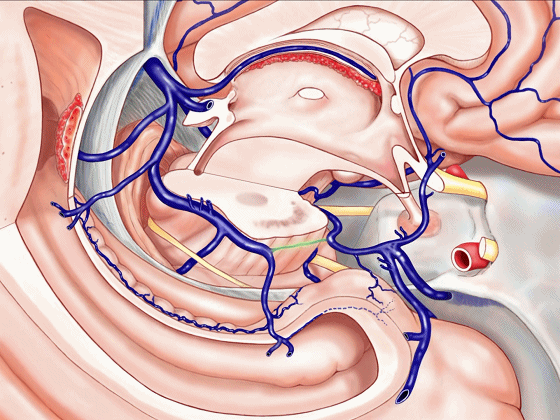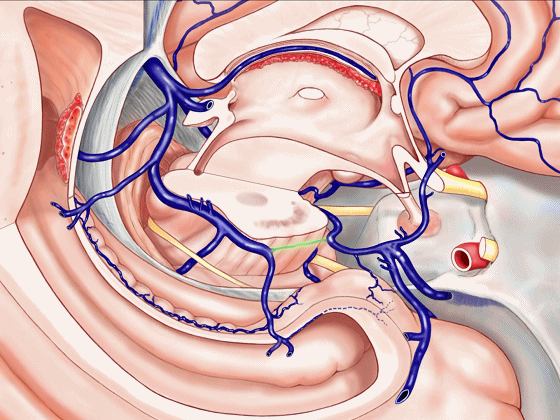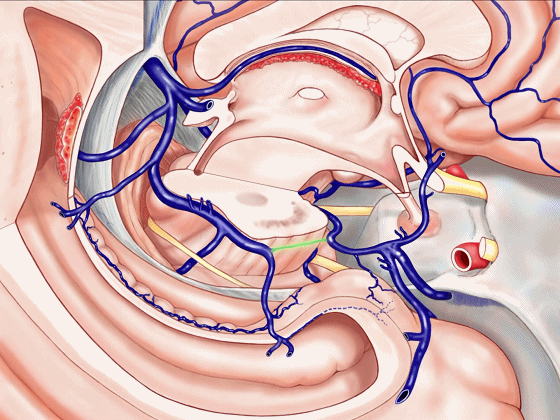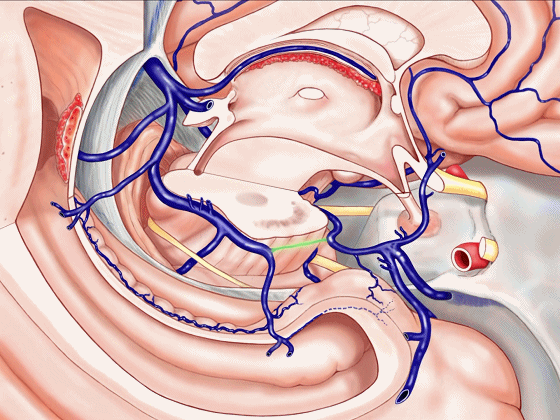
▼或者是这后方的一段血管发育不良,以至于大部分静脉血由中脑外侧静脉(下图)向下引流。
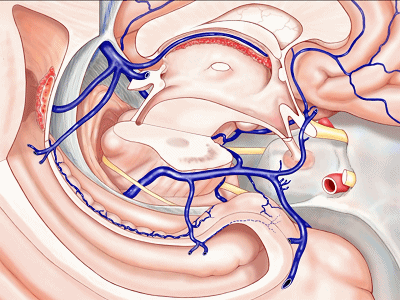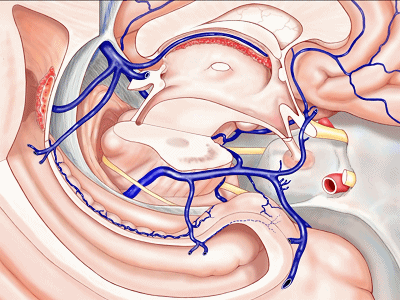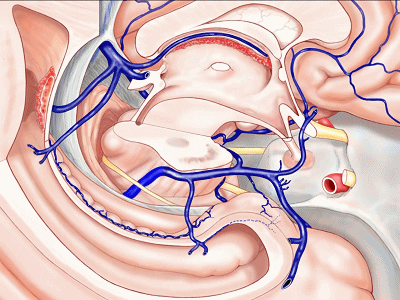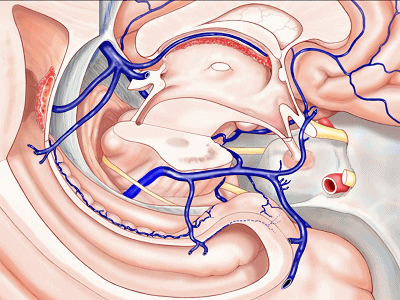
▼甚至可有多段静脉缺如。因此对于该部位的术前评估,尤其对于血管性肿瘤及AVMs,术前血管造影尤为重要,须弄清颞叶内侧静脉回流的方式。

▼最后,我再介绍几个用于颞叶内侧面的入路。一种是经颞叶下表面,沿着某一脑沟进入颞角(下图),以完成杏仁核-海马切除术。
And, to finish off I will just talk about a few approaches that are used to medial temporal lobe. One is to go through the lower surface here of the temporal lobe along one of the sulci to the temporal horn,and to complete an amygdalohippocampectomy.
▼另一种是通过前颞叶切除术,以暴露颞角,并切除颞叶内侧面。
Another is to do an anterior temporal lobectomy and then expose the temporal horn,and do the medial temporal lobe resection.
▼第三种入路是通过外侧裂向下经由岛叶下界沟进入颞角。这是Yasargil法进行杏仁核-海马切除术。
A third route that has been used is to come transsylvian down through the inferior limiting sulcus to the temporal horn...the Yasargil type of approach for amygdalohippocampectomy.

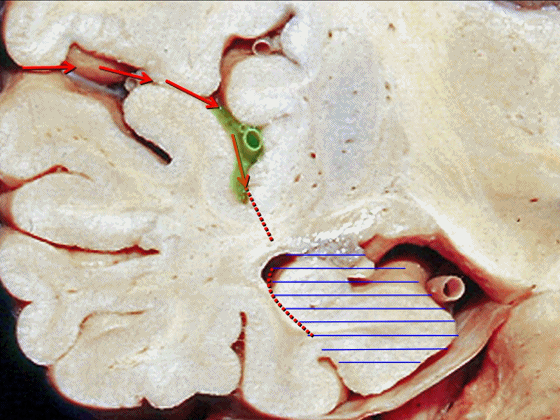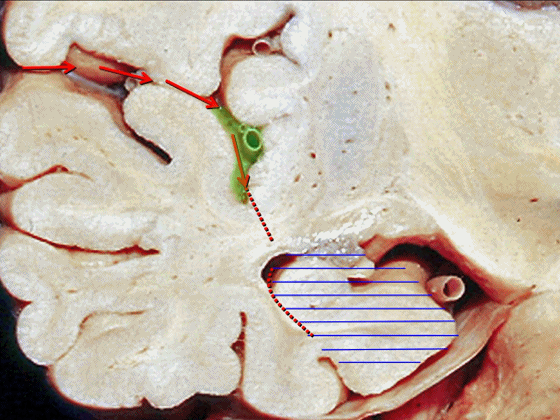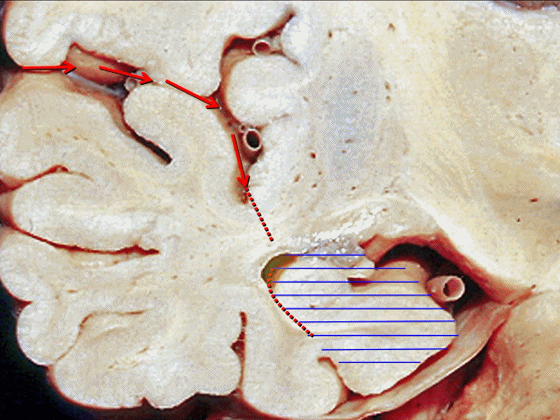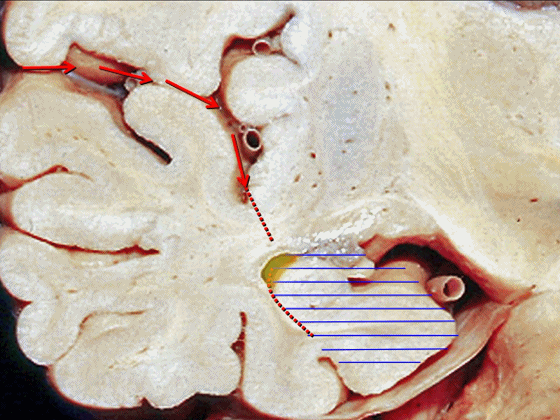
▼最后一种入路为经由脑池,即经脑池入路暴露颞叶内侧。
And the last one you can come through the cisterns,and do a transcisternal approach to medial temporal lobe.
▼我们在这里示范颞瓣开颅、暴露颞叶。
So, here is just the typical exposure of temporal lobe.

▼我们抬起颞叶,这是侧副沟(下图)
And one of the routes you can get in below the temporal lobe here, and say, collateral sulcus,
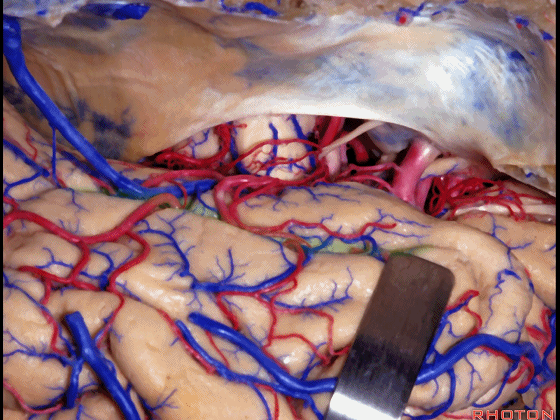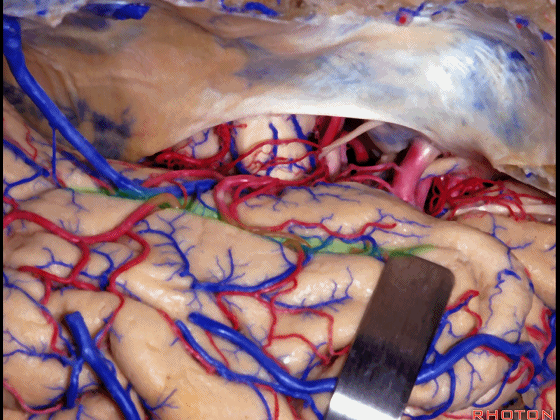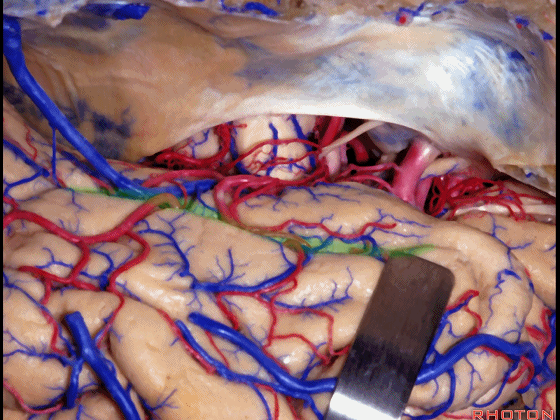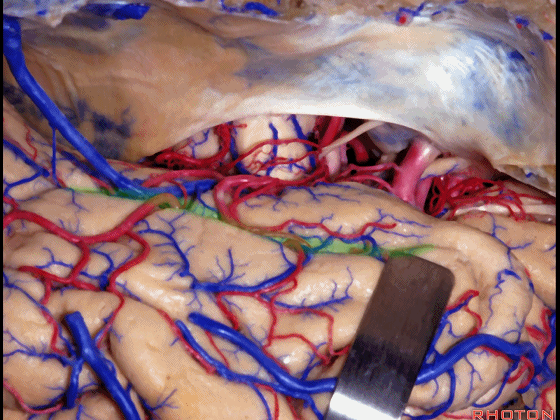
▼这是 梭状回
or lateral to fusiform gyrus here in this area.
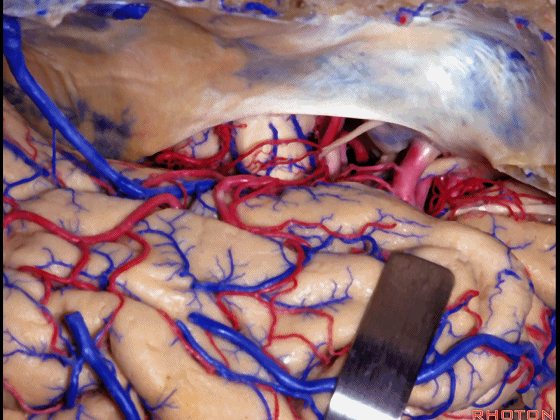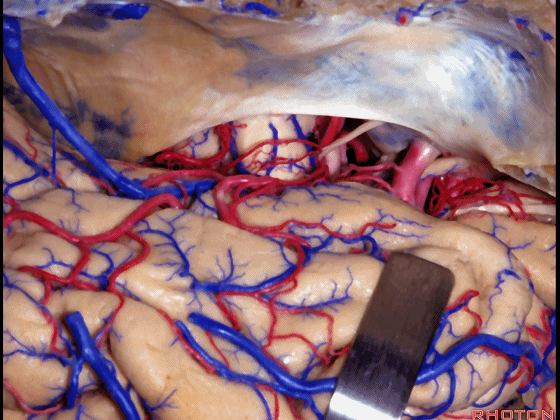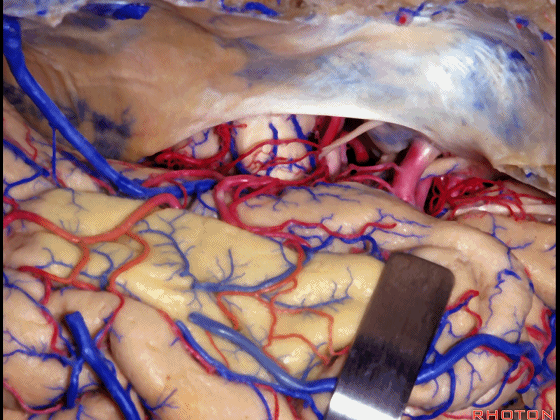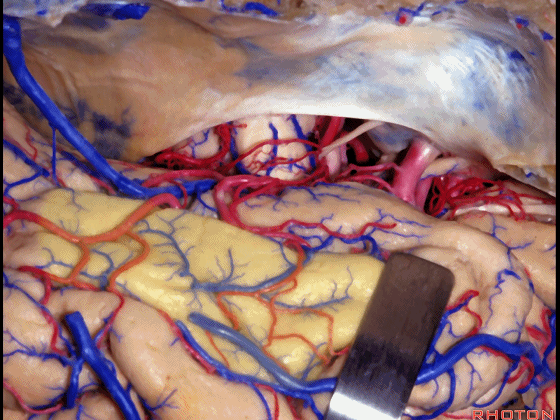
▼这里可见钩回前段、钩回后段
And here we see anterior, posterior segment of uncus,
▼这是 动眼神经,位于钩回尖端内侧
3rd nerve here, medial to apex of uncus,
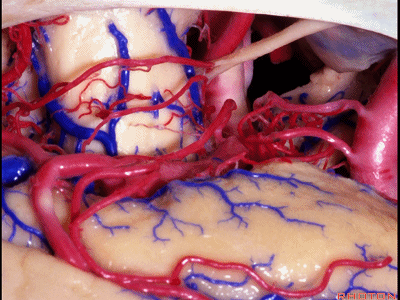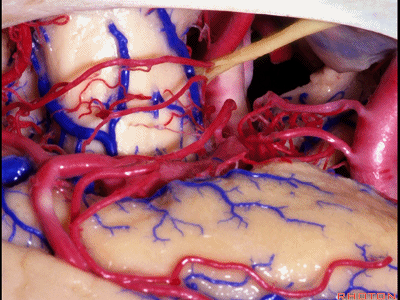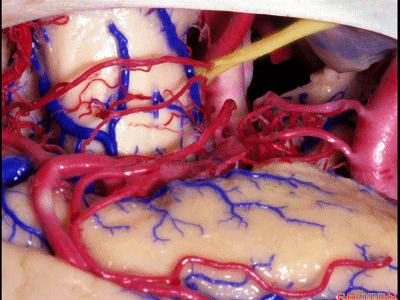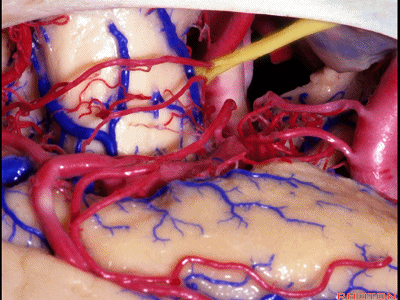
▼这是 钩回尖端
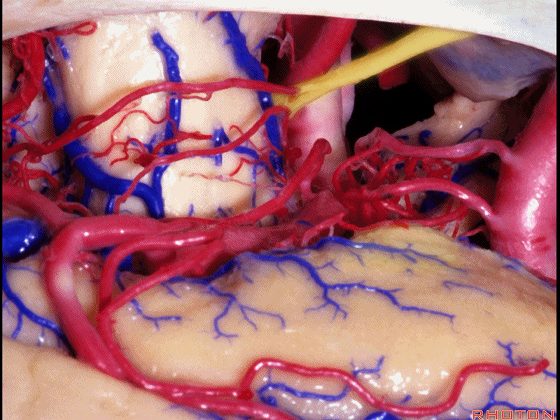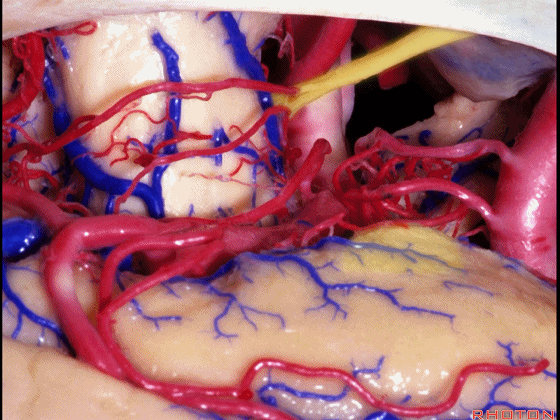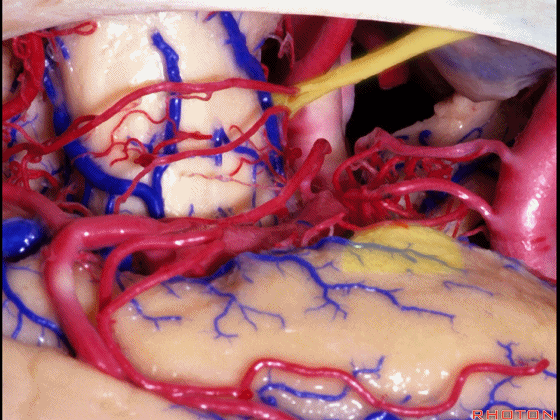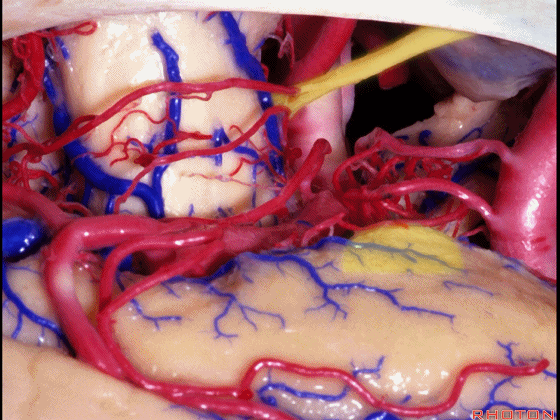
▼这是 后交通动脉
communicating,
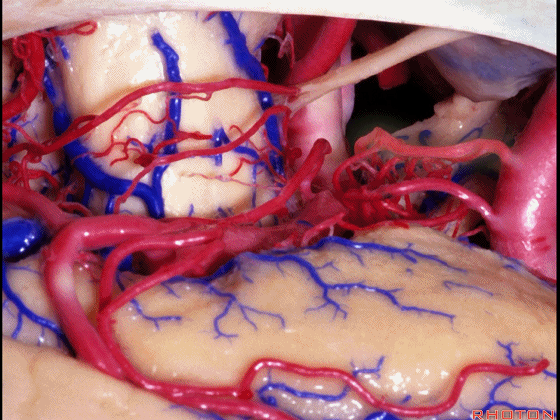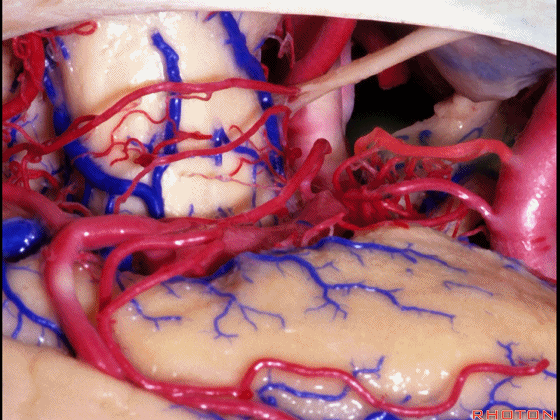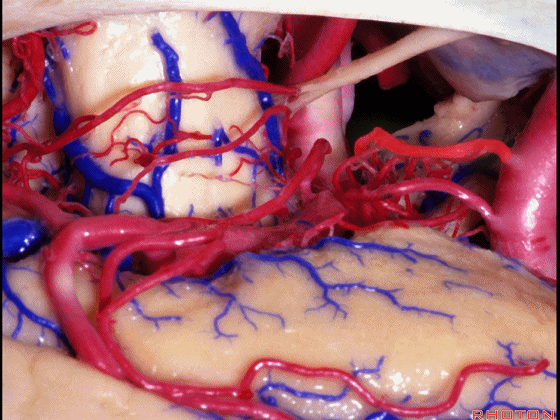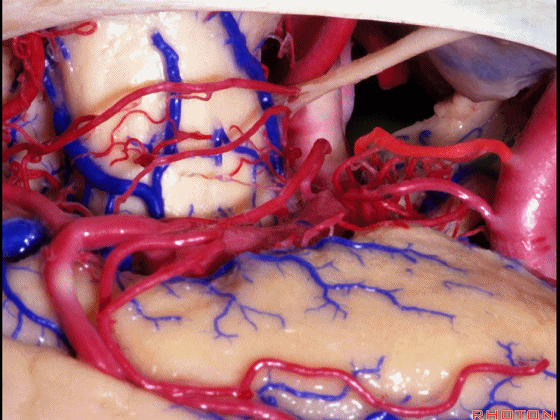
▼这是 脉络膜前动脉
anterior choroidal artery.
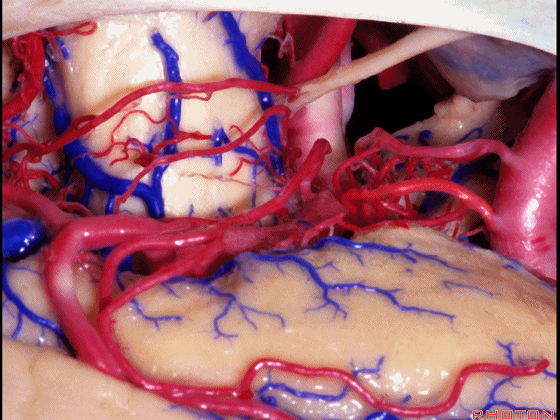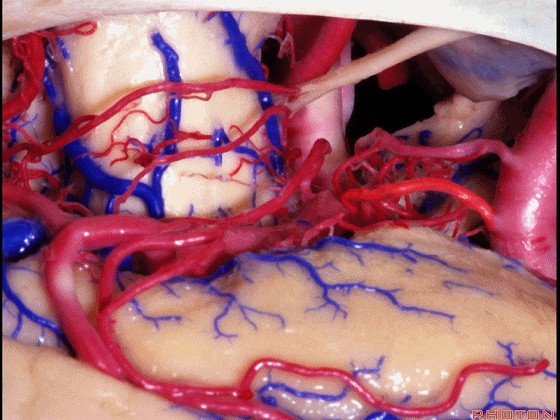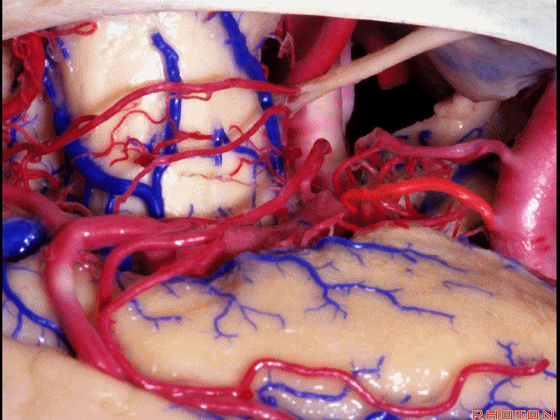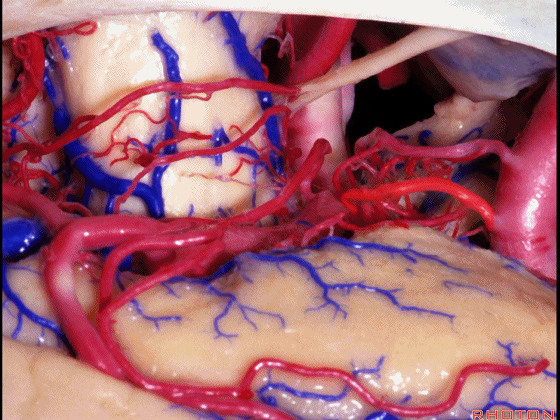
▼这里我们抬起颞叶。
And here we elevate the temporal lobe.
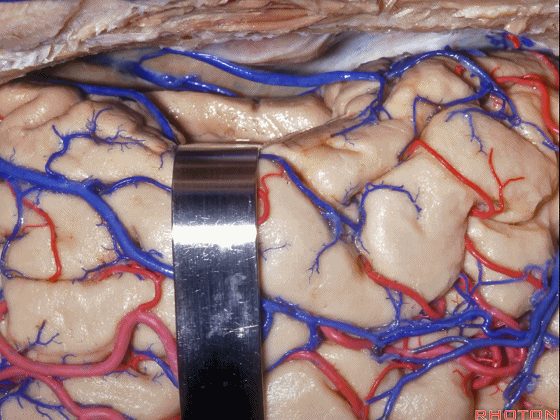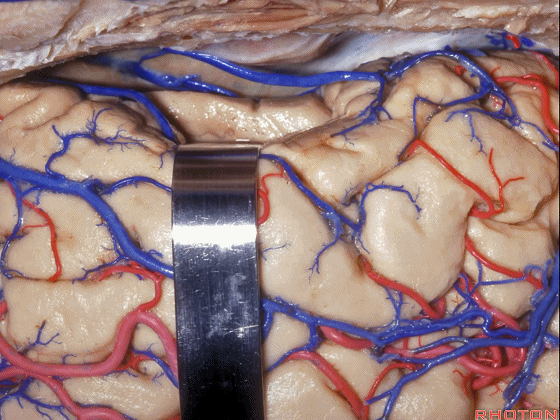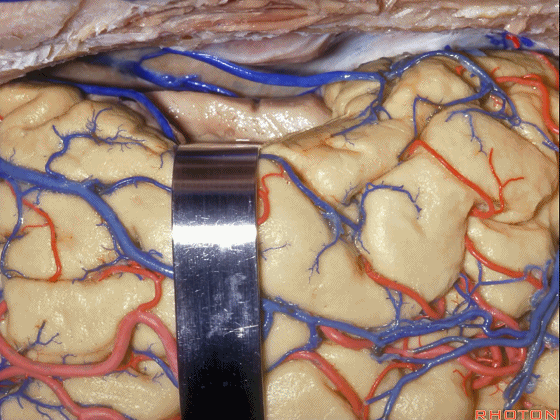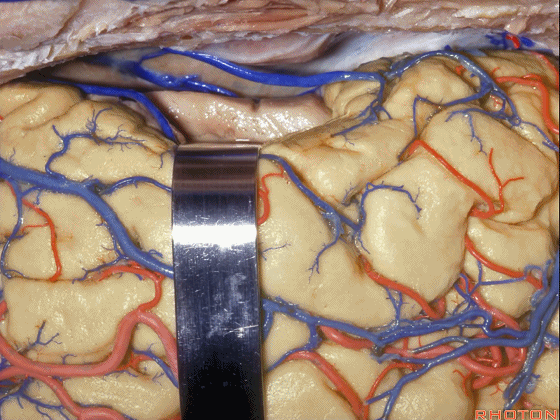
▼我们可打开一个脑沟进入颞角(下图)。
We can open into a sulcus to access temporal horn.
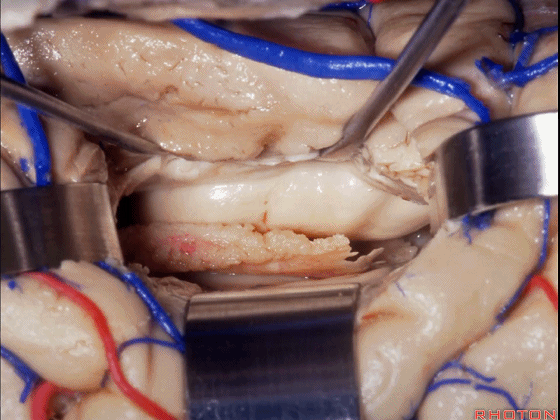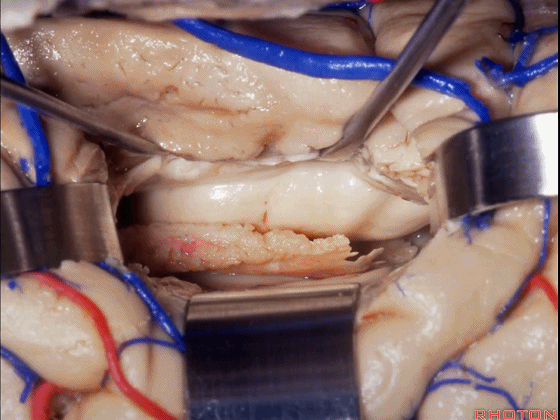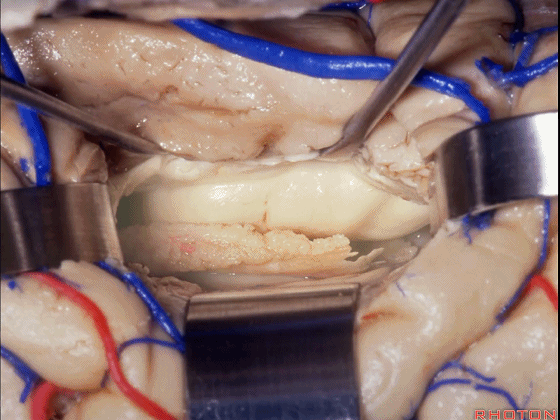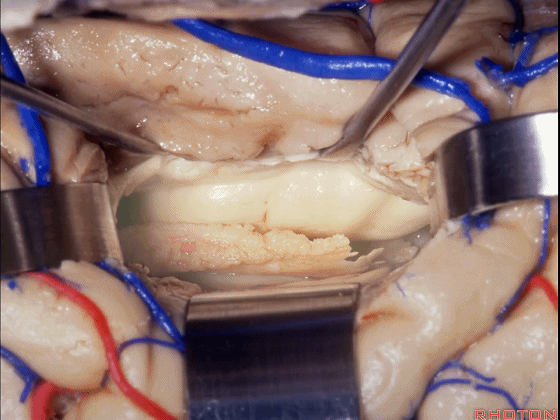
▼这是 海马、脉络丛。
Here we see hippocampus, choroid plexus.
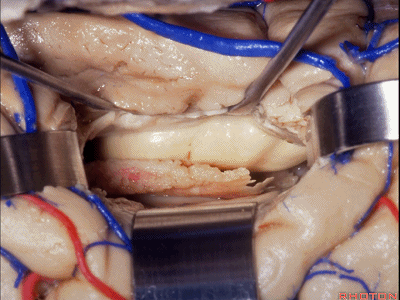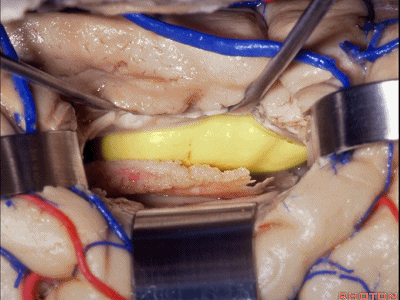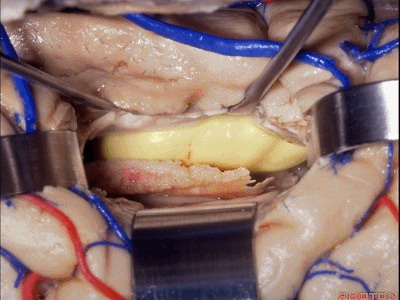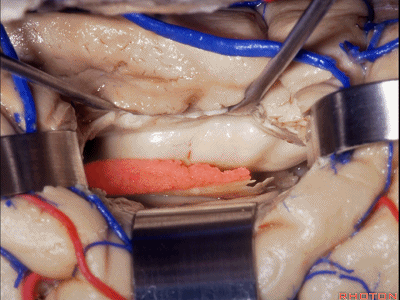
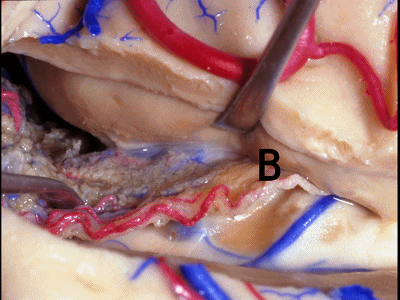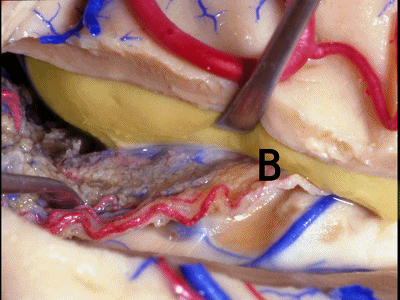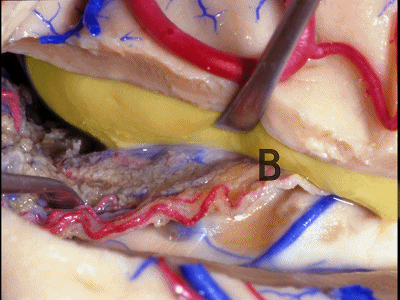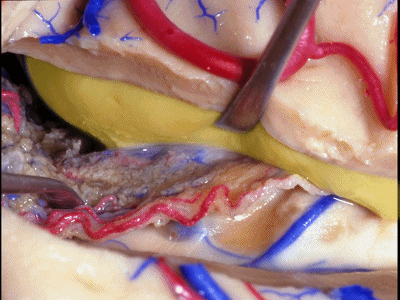
▼如果要打开颞角的脉络裂,你应该是B点切开。沿着穹窿伞,沿着脉络裂的海马侧,因为行经脉络裂的大静脉引流视辐射和位于颞角顶壁的内囊豆状核下部。
If you're going to open the choroidal fissure in the temporal horn, are you going to open at A or B? At B along the fimbria, along the hippocampal side, because the largest veins draining through the fissure drain the optic radiation and the sublenticular part of the internal capsule that is in the roof of the temporal horn.
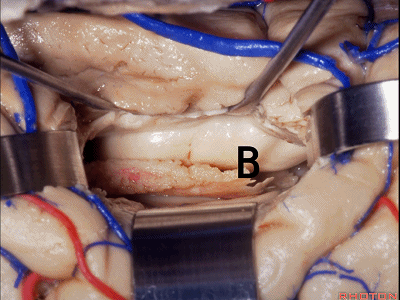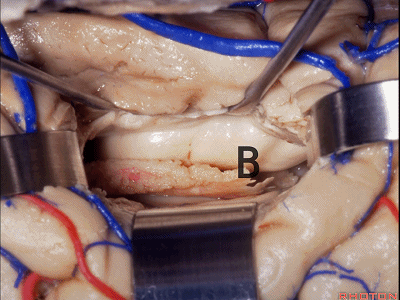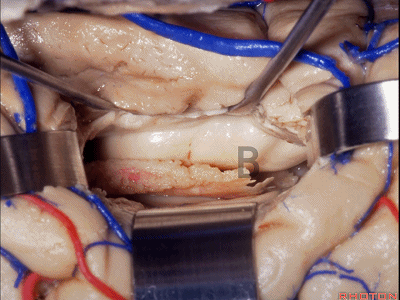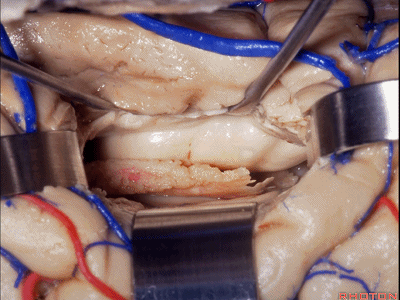
▼这里我们进入颞角、顶壁。
So here we've opened into temporal horn, the roof.
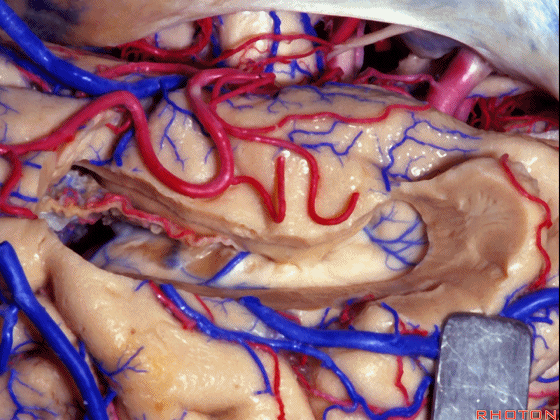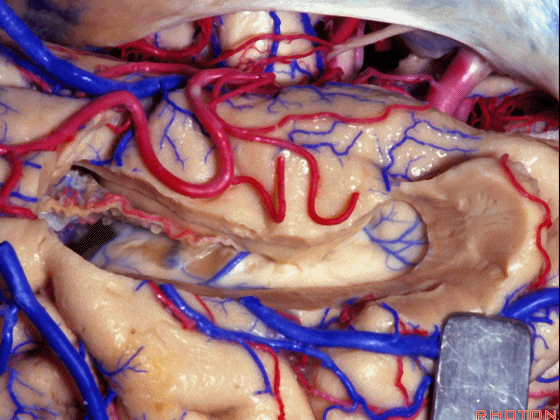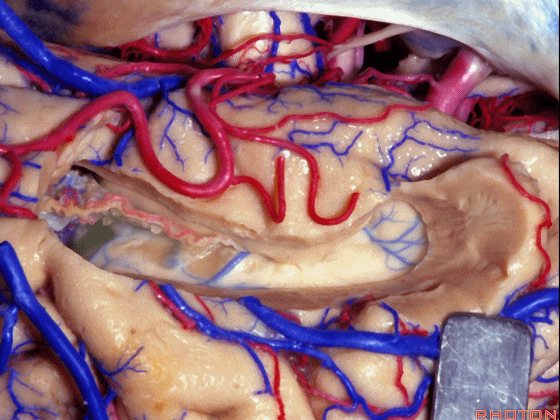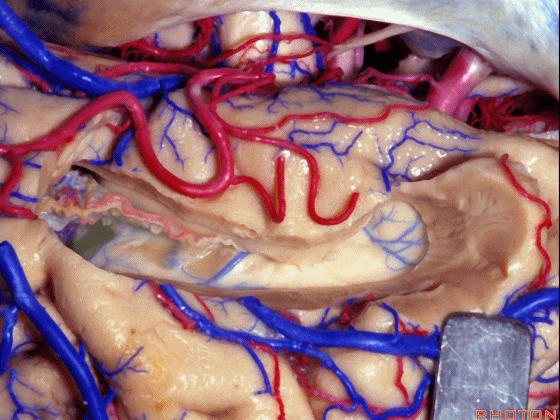
▼这是脉络丛。
Here we see the choroid plexus.

▼海马(下图)表面的静脉相对较少
There's relatively few vein that you see on the hippocampus,
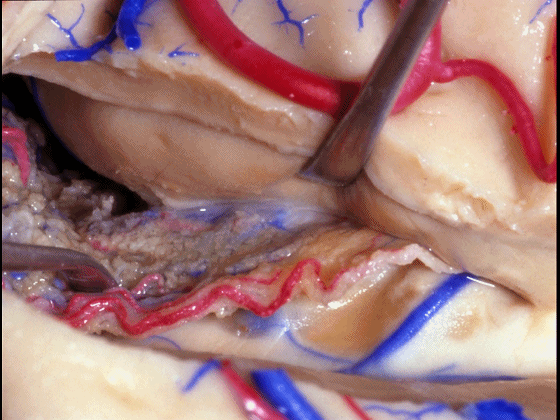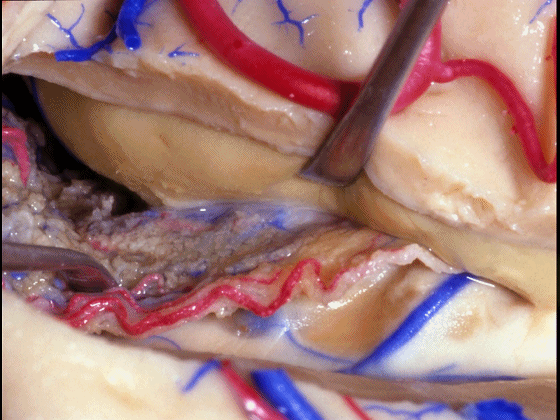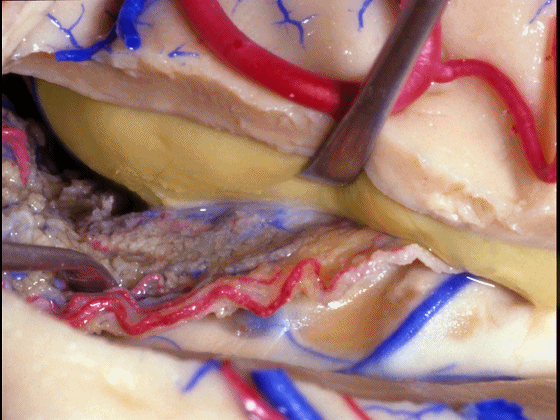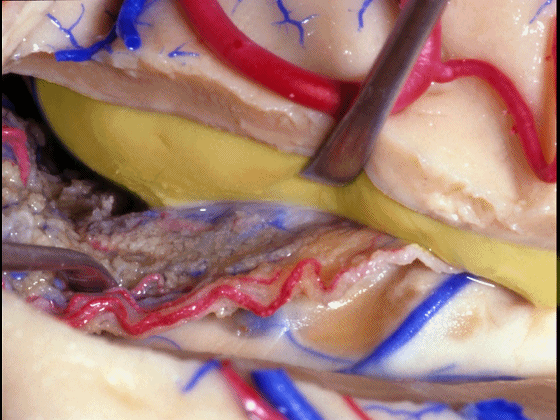
▼但引流顶壁视辐射(下图)的大静脉行经脉络裂的丘脑侧。
but the big veins draining the optic radiations in the roof pass through the thalamic side of the choroidal fissure.
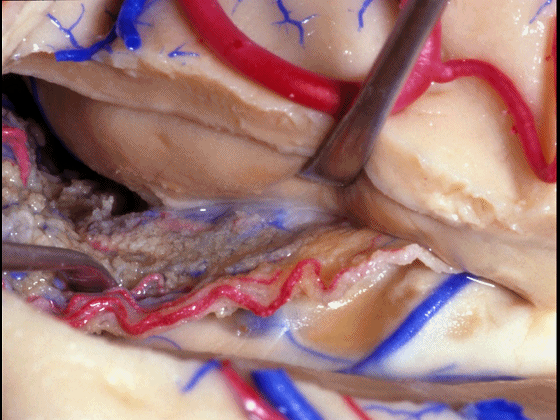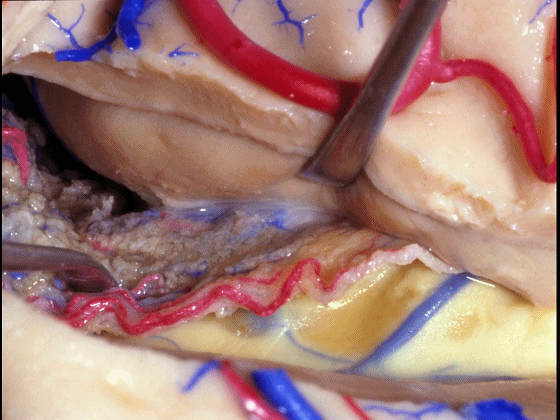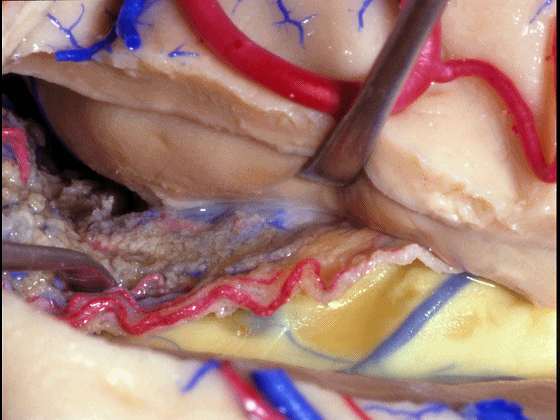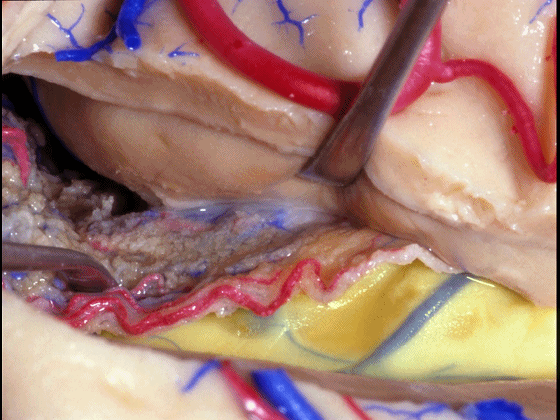
▼因此我们应该在B处打开脉络裂,应该沿着海马侧打开。
So are we going to open the fissure at Aor B? We'll open along the hippocampal side.
▼这里我们将脉络丛(下图)留于颞角顶壁。
Here we let the choroid plexus go with the roof.

▼这是外侧膝状体
Here's the lateral geniculate,
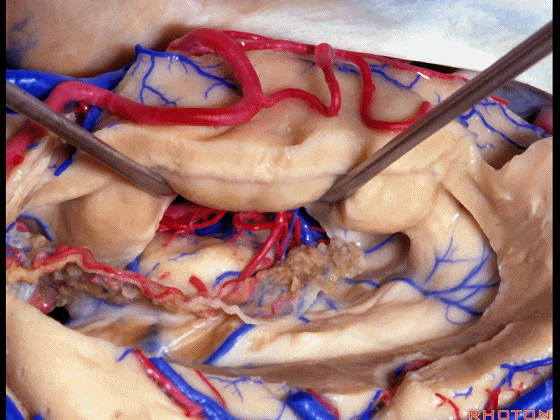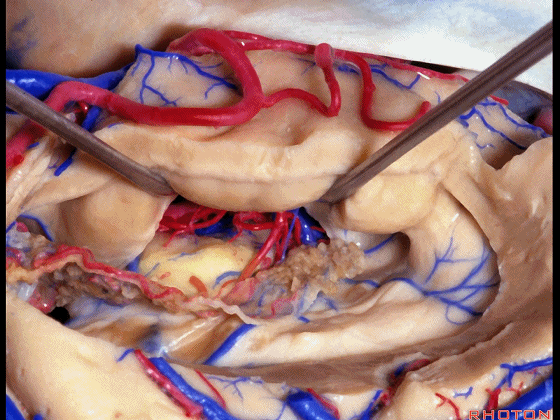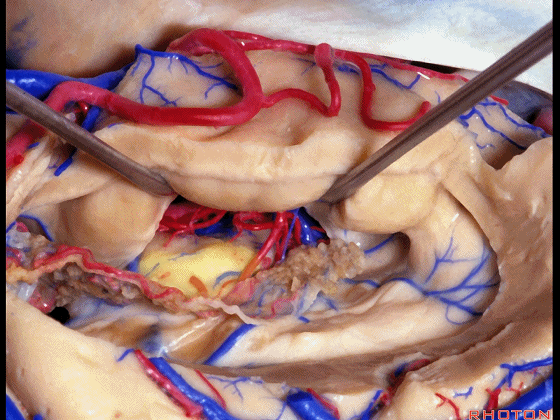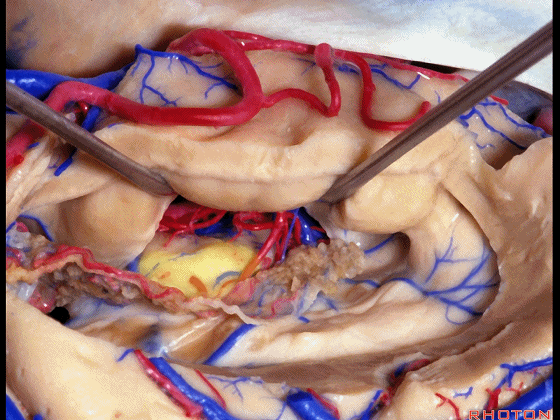
▼这部分视辐射即Meyer襻(下图)向前迂行。我们保护此处静脉。
the optic radiation, Meyer's loop are coming forward.We leave that venous drainage intact.
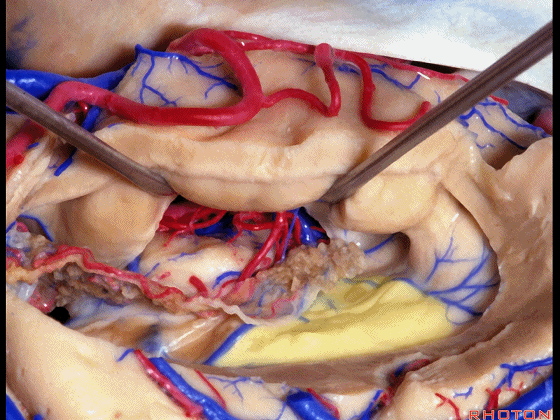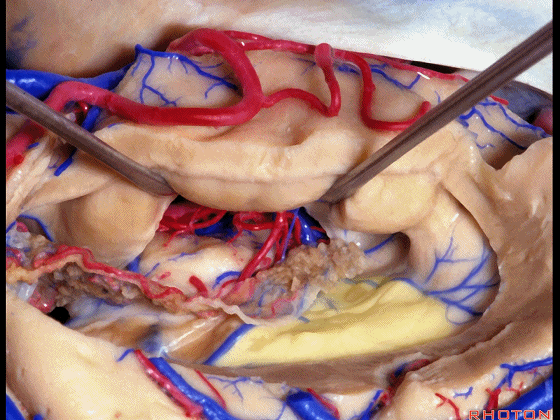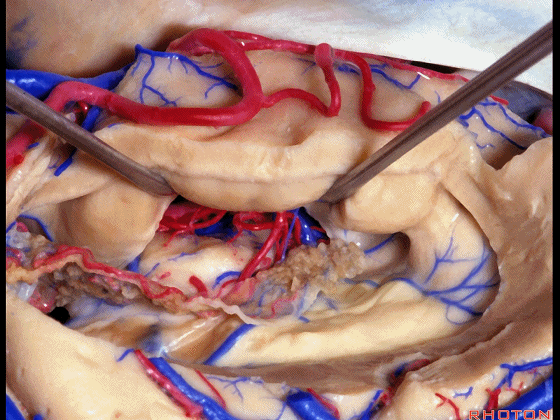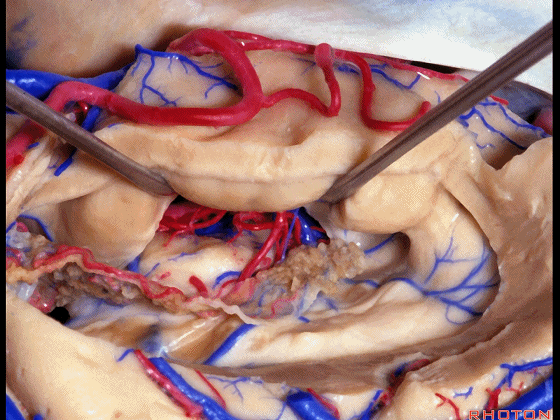
▼我们沿着穹窿伞缘(下图)
We go along the edge of the fimbria
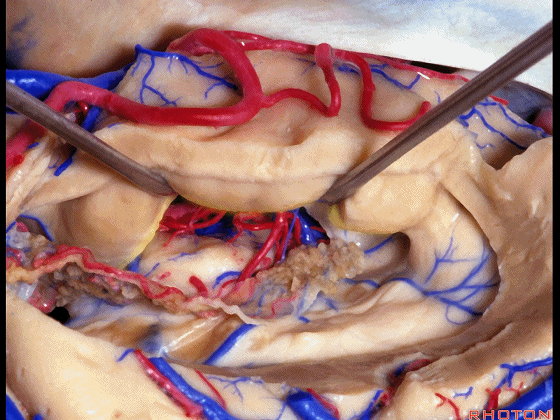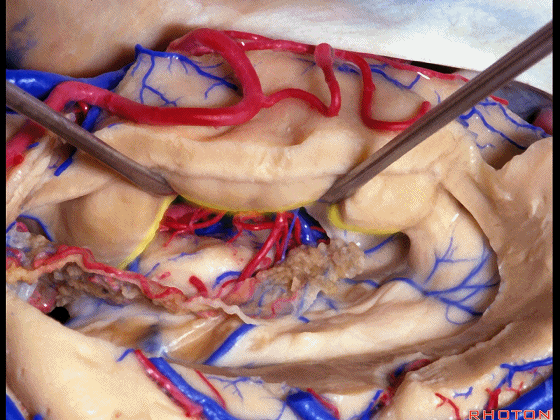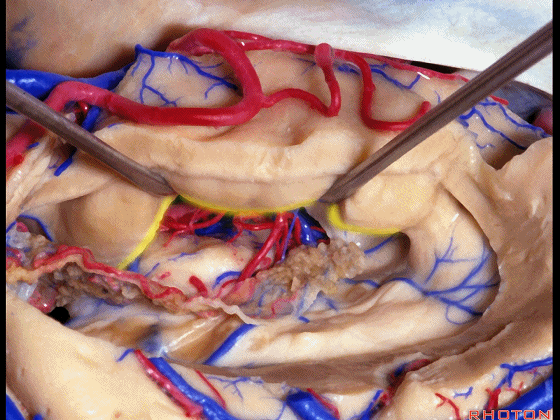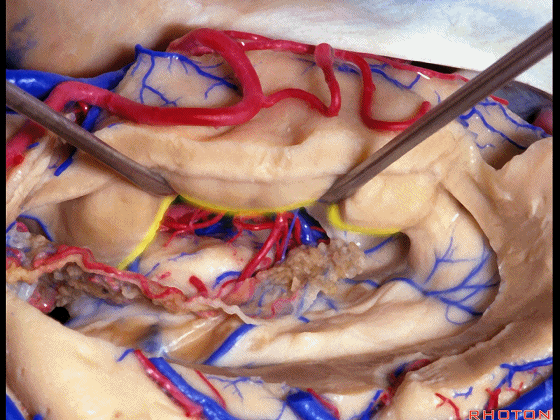
▼暴露外侧膝状体,进入环池。
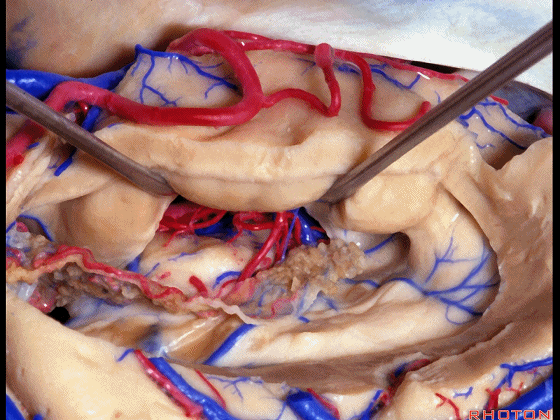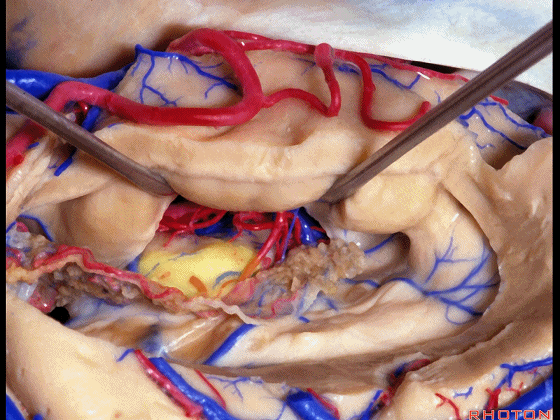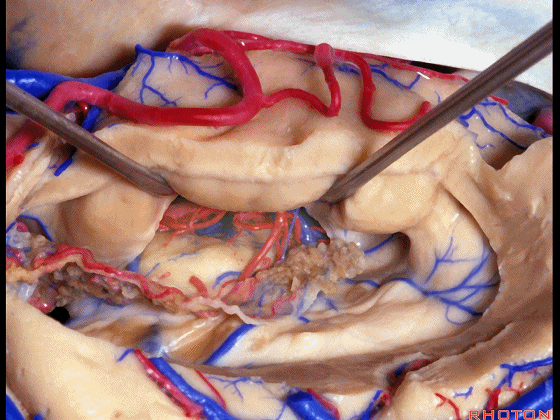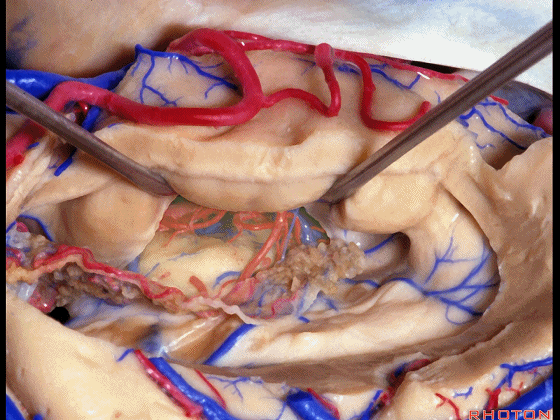
▼随后我们可切开杏仁核(下图),以完成颞叶切除术。
And then we can open through the amygdala here to complete a temporal lobectomy.
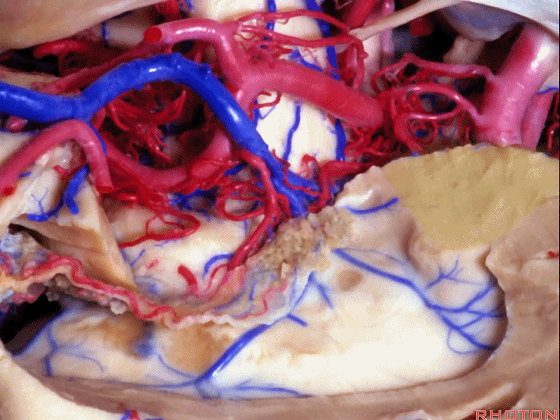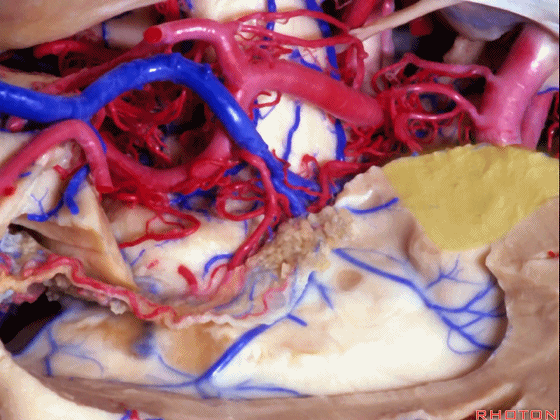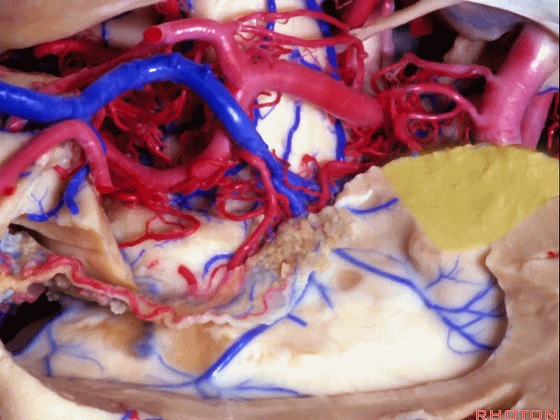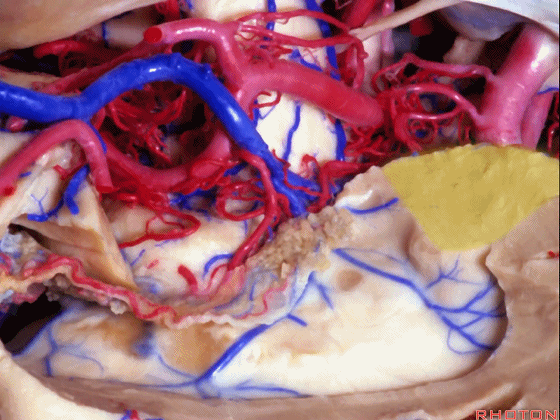
▼海马的后部(下图)最终融入禽距,其位于侧脑室房部的内侧部。禽距区域有视辐射。因此,海马的切除范围可向后至禽距前缘。
Well, at the back edge of the hippocampus, it blends into the calcar avis in the medial part of the atrium.And at the calcar avis you have optic radiations.So, we can resect hippocampus back to the anterior edge of the calcar avis.
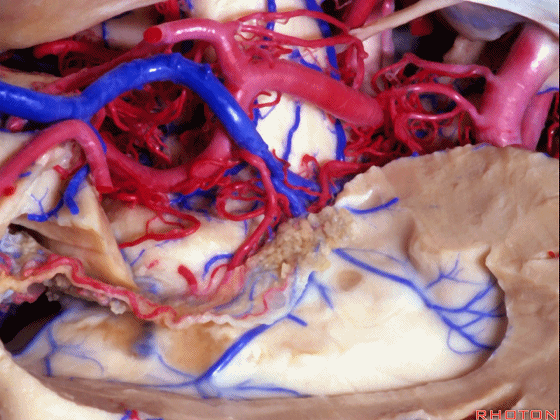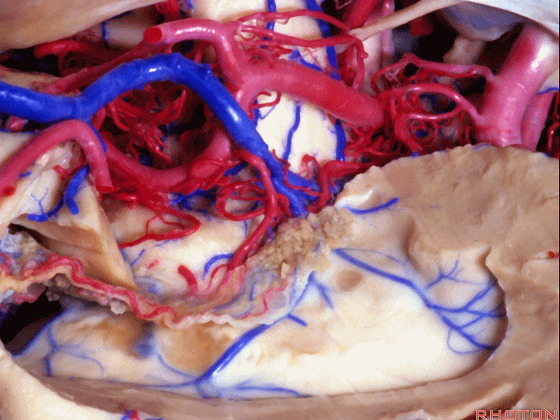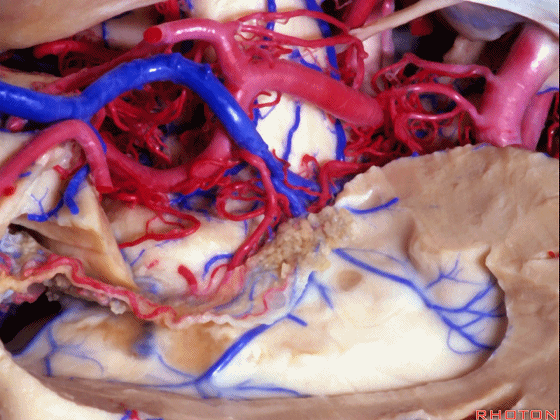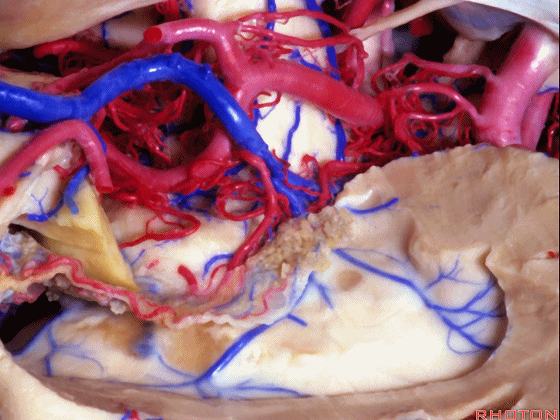
▼视辐射区域、外侧膝状体 均得以保护。
We see again, the area of the optic radiations,lateral geniculate,all preserved using this transchoroidal approach
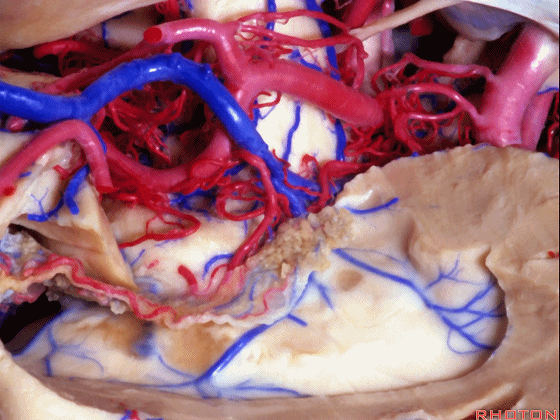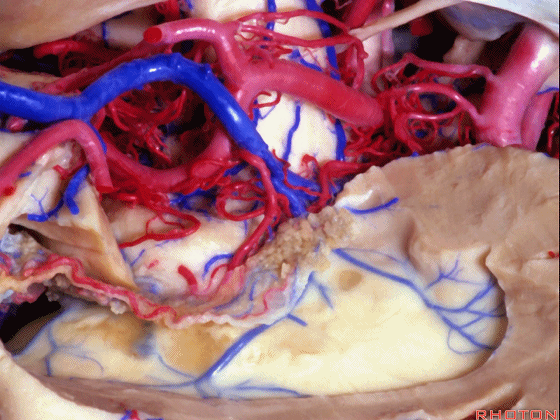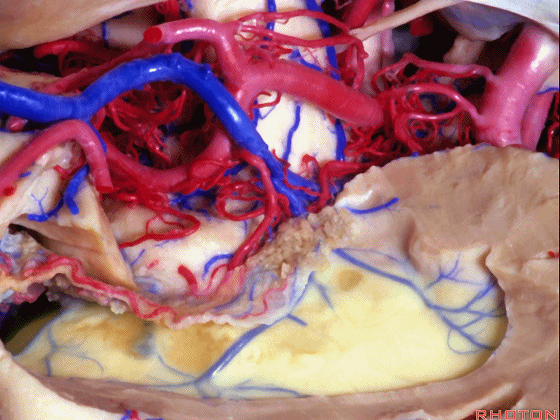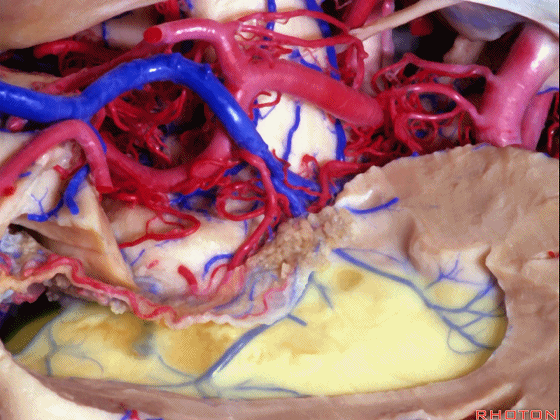
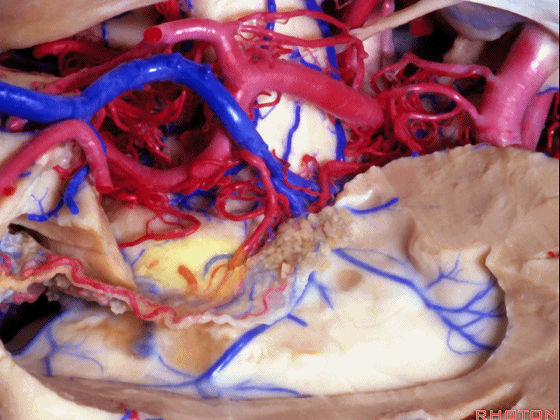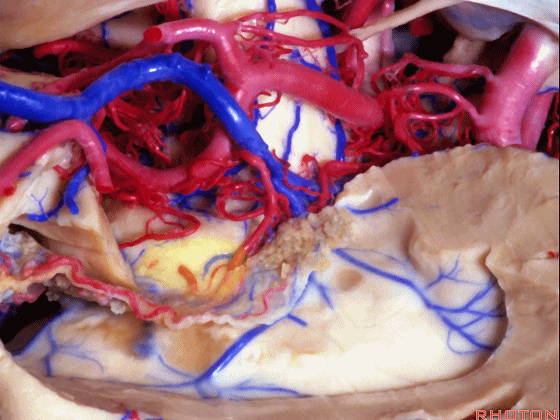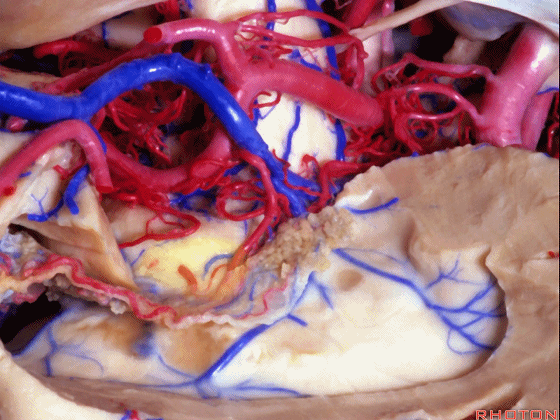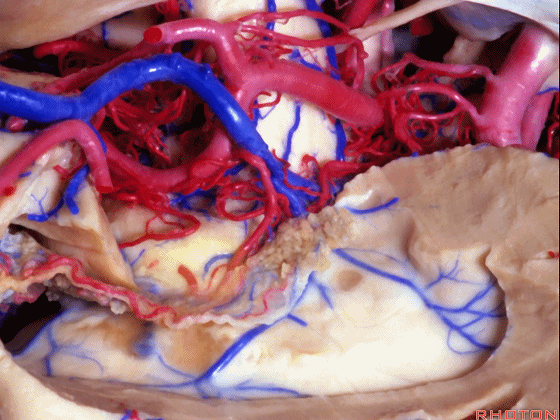
▼切开穹窿带或穹窿伞部(下图),即为经脉络裂入路。
through the tenia fornix or through the fimbria part of the fornix.

▼另一种进入颞角的入路是通过外侧裂。这是颞叶,额叶,岛叶
Now another way of going to temporal horn is coming transsylvian.Temporal lobe,frontal lobe,insula here,

▼这是大脑中动脉M2段。
▼可见岛阈
And in this approach we see limen insula,
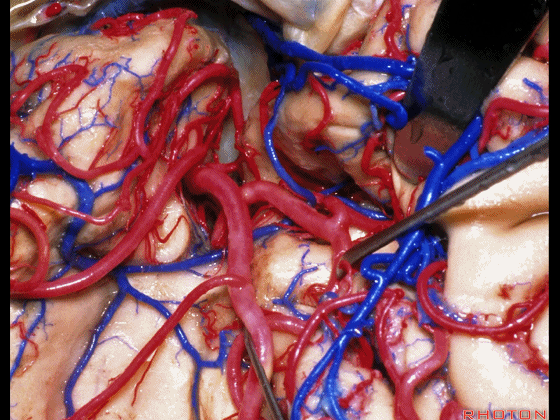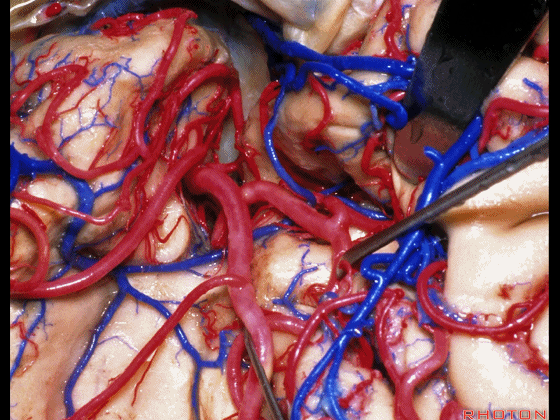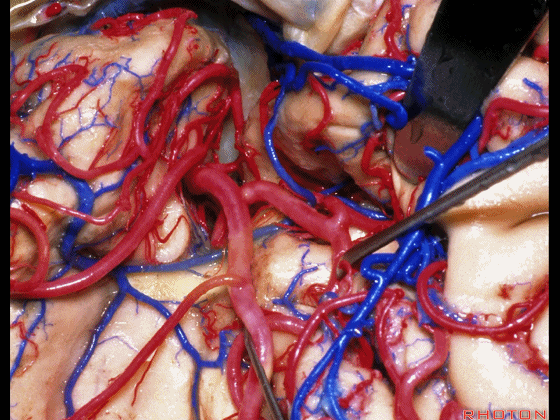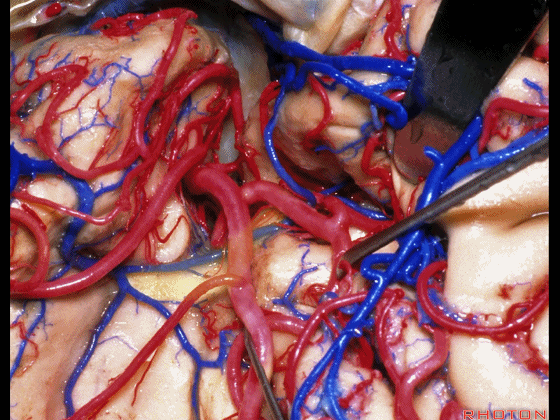
▼这是下界沟,其为岛叶的下界。
and then the inferior limiting sulcus along lower margin of insula.
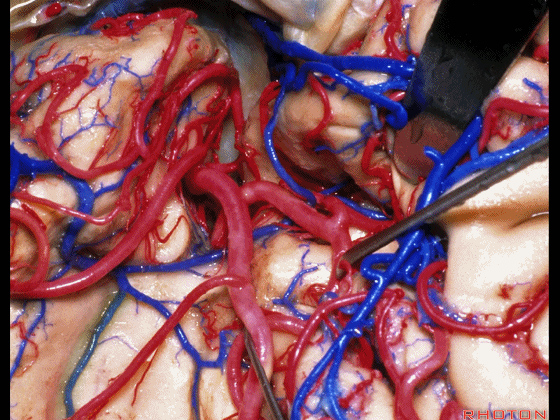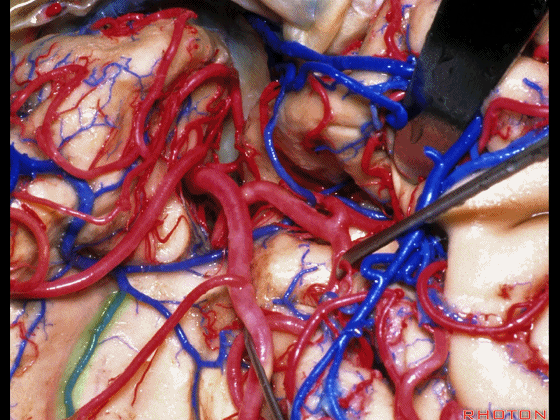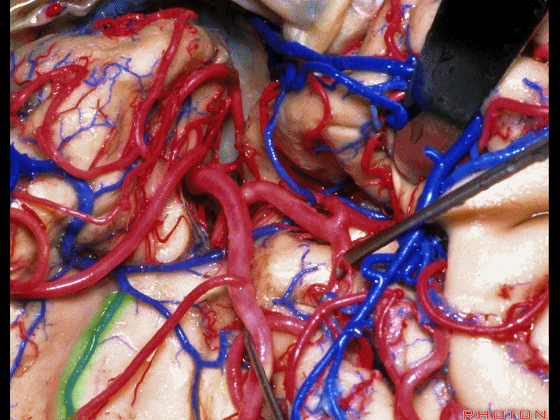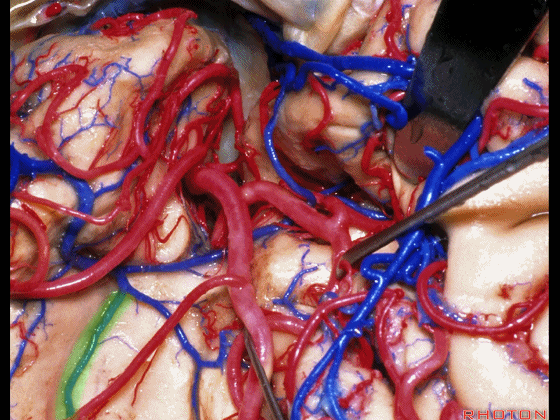
▼正如之前介绍的,切口位于岛阈(下图)后方的下界沟内。
And in the approaches that we has initially described, the incision is here behind the limen in the inferior limiting sulcus.
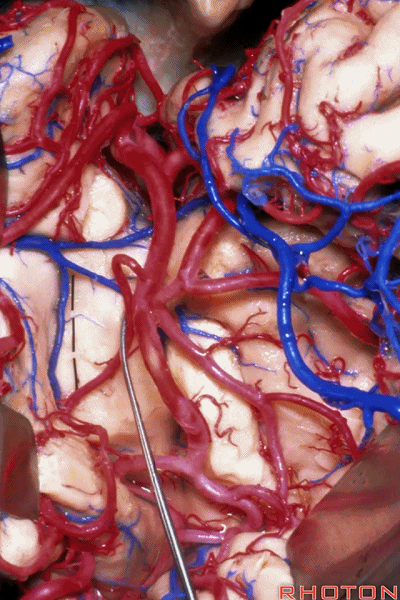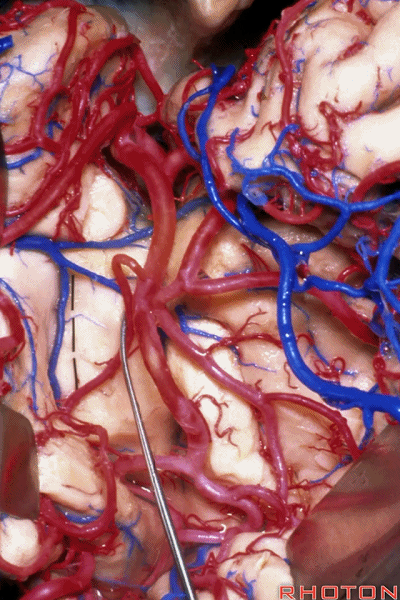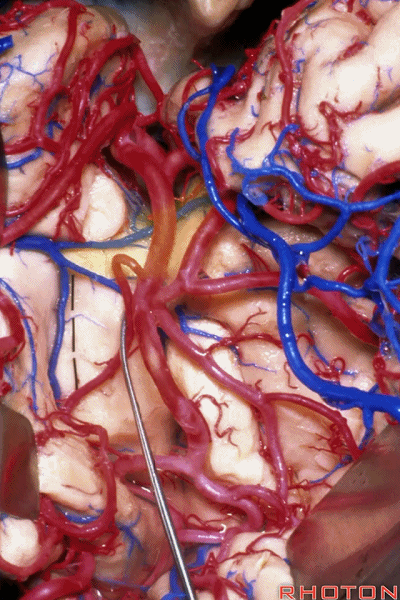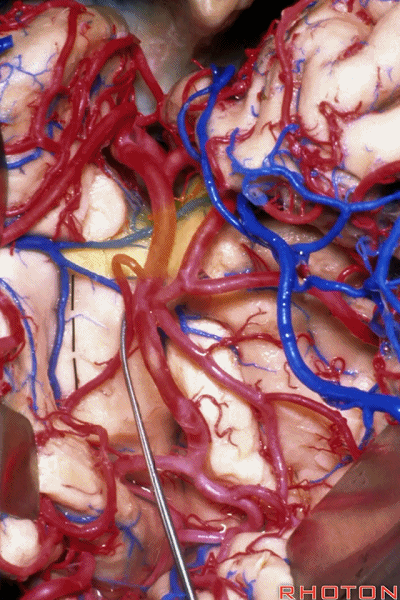
▼这是下界沟
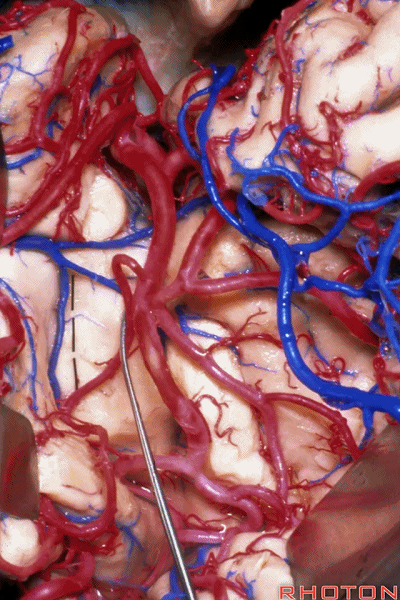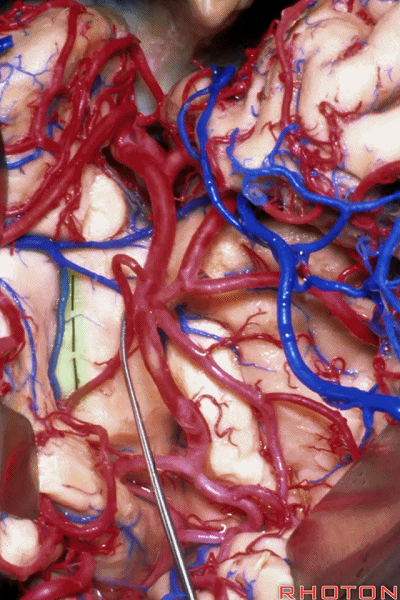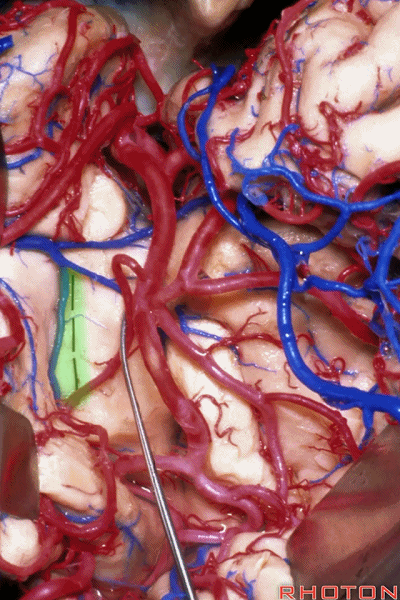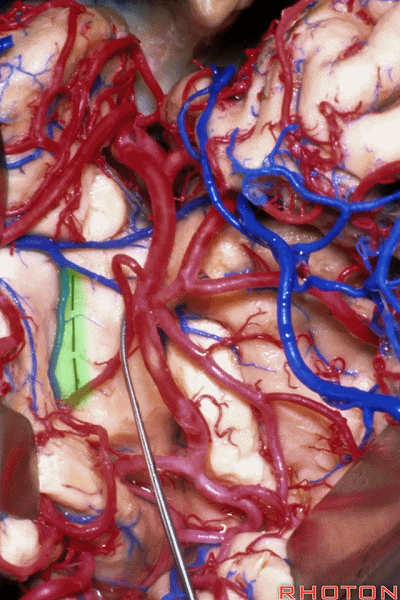
▼深入该区域约8mm深度即可进入颞角。可见海马(下图)
And you come through this area, at a depth of about 8 millimeters you enter the temporal horn.
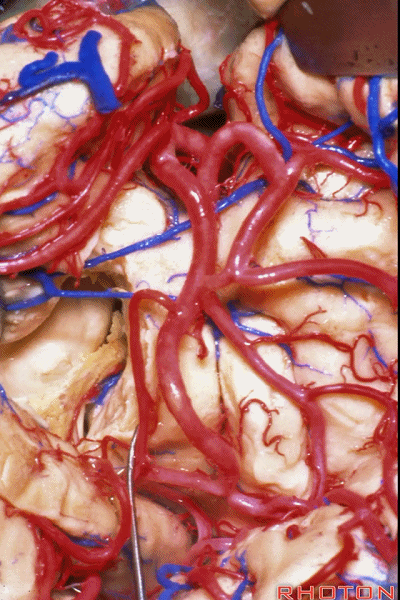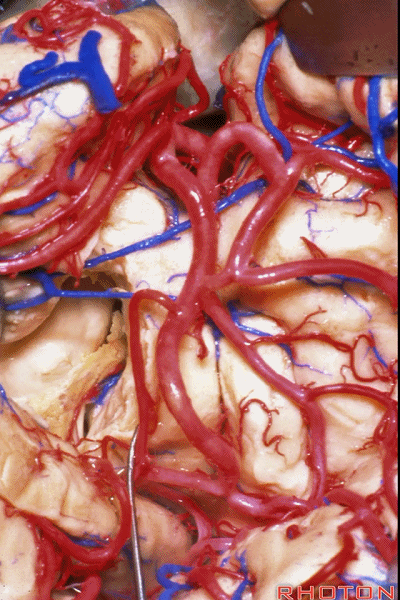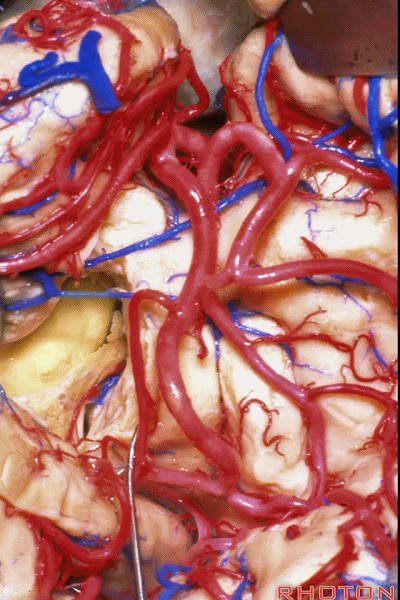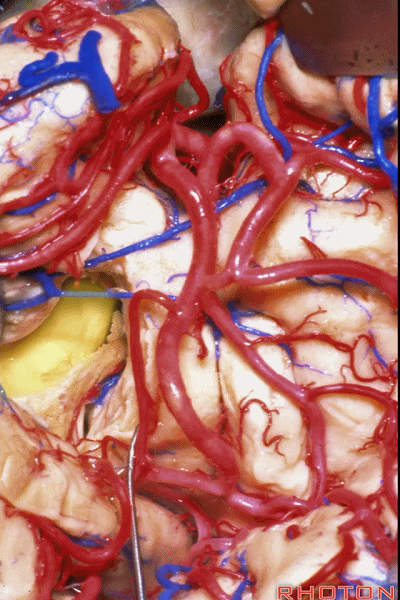
▼这是脉络丛。
choroid plexus.
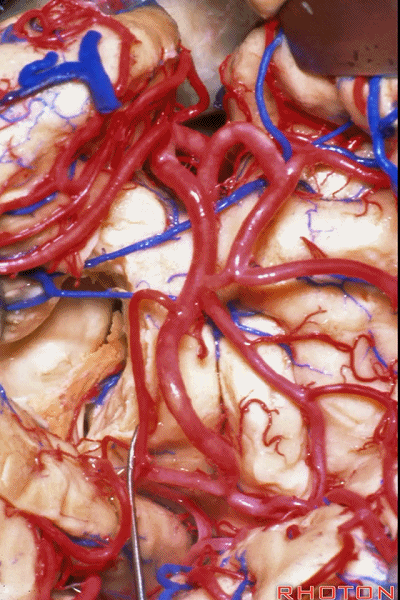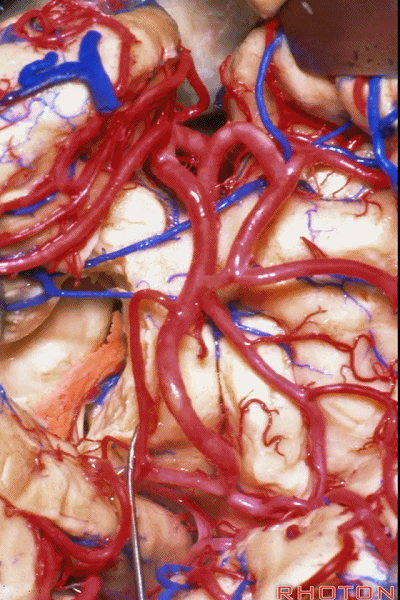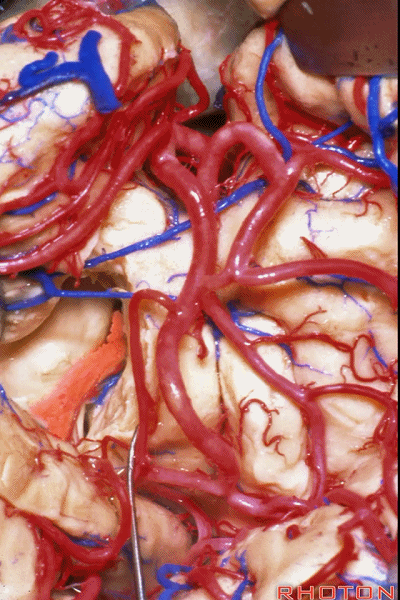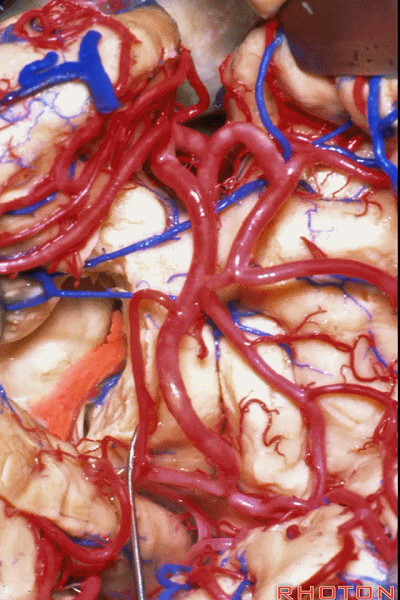
▼随后打开脉络裂(下图)。
And we've opened the choroidal fissure.

▼将脉络丛(下图)保留于顶壁。
We let the choroid plexus go with the roof.
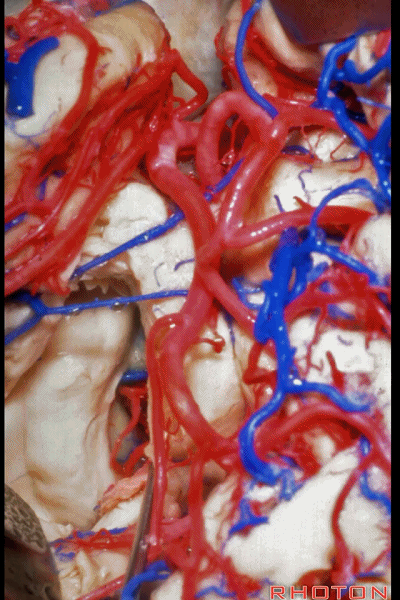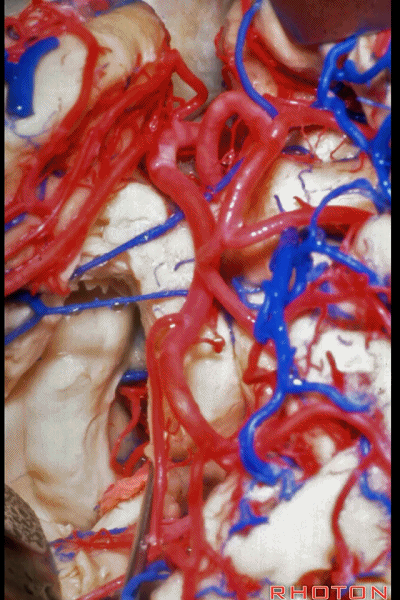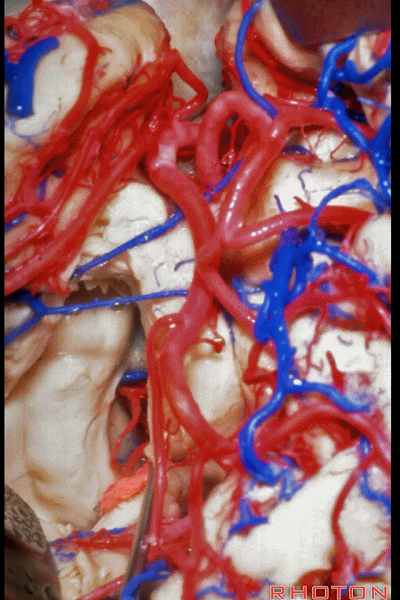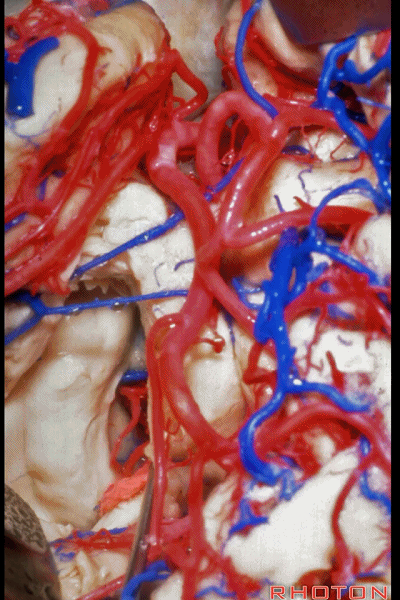
▼打开伞带即可暴露环池。
We've opened along the tenia fimbria to expose the ambient cistern.
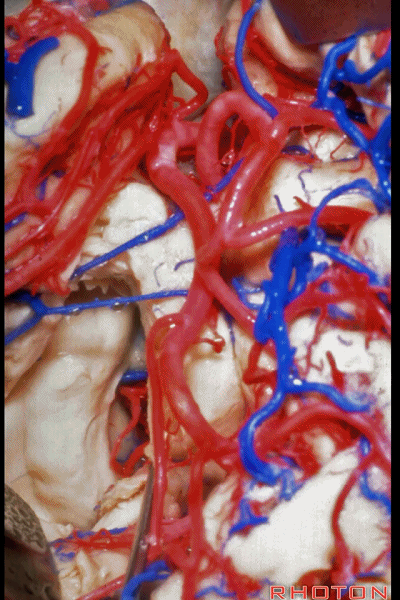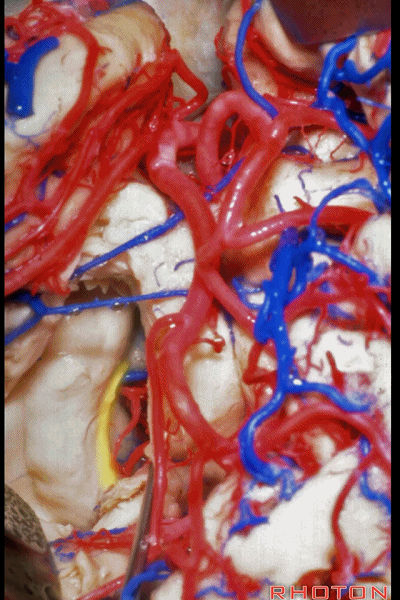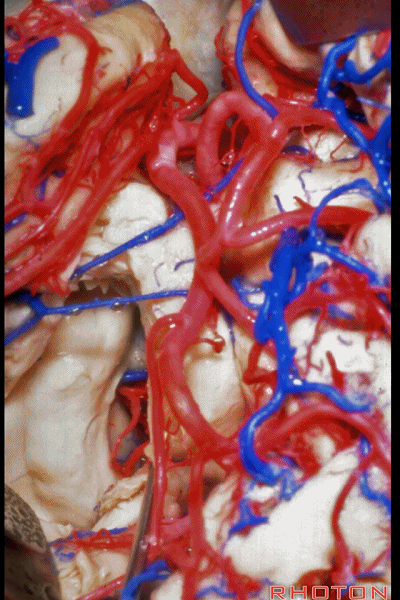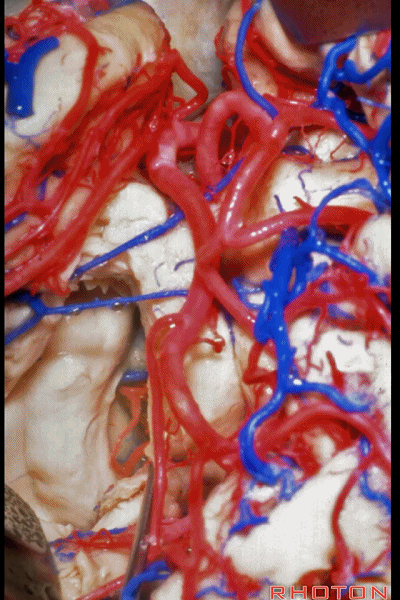
▼看看环池内的解剖。这是穹窿(下图)
And just a view into the ambient cistern. fornix,
▼脉络丛(下图)与顶壁,以及视辐射被保留
and here the choroid plexus goes with the roof with the optic radiations,
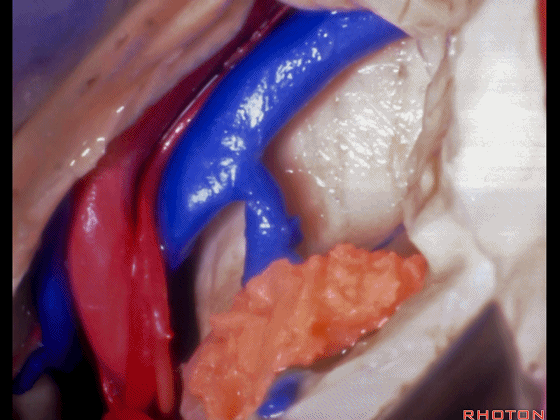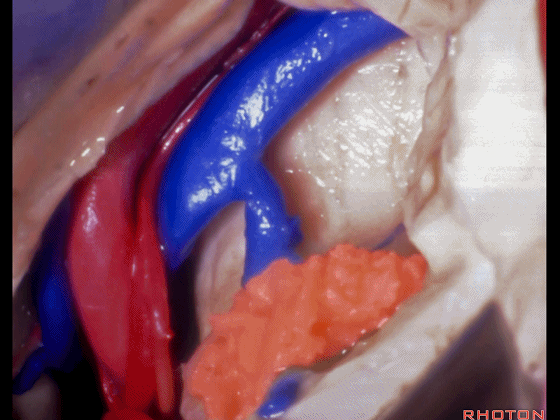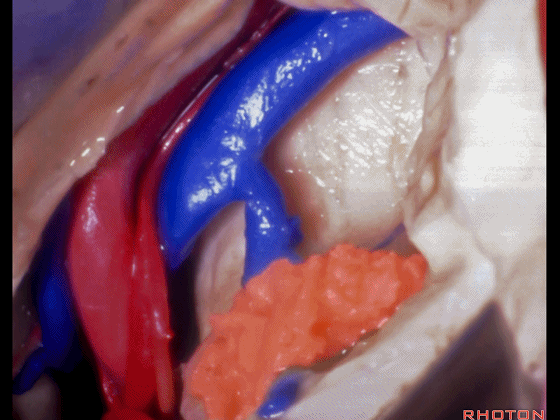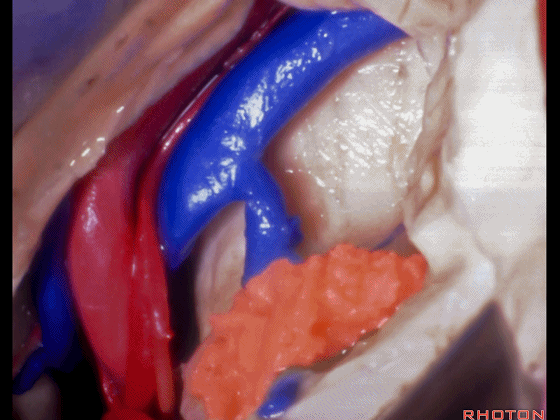
▼这是基底静脉
basal vein,
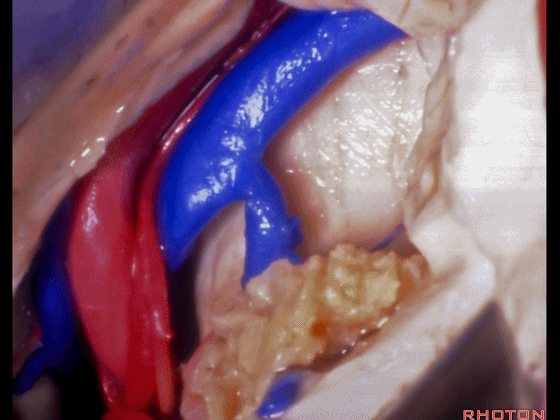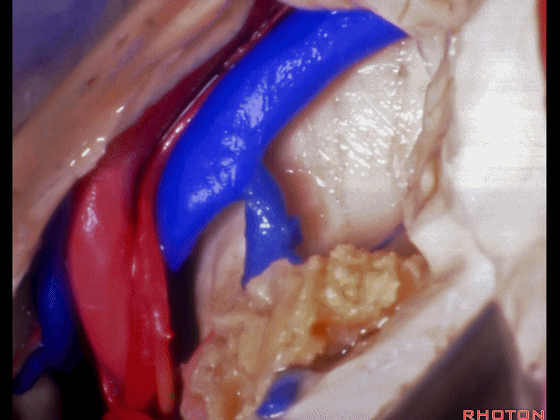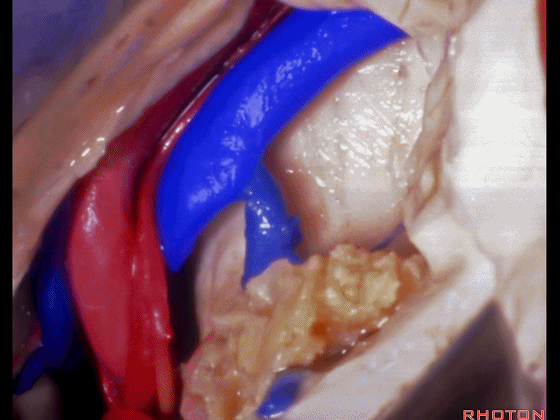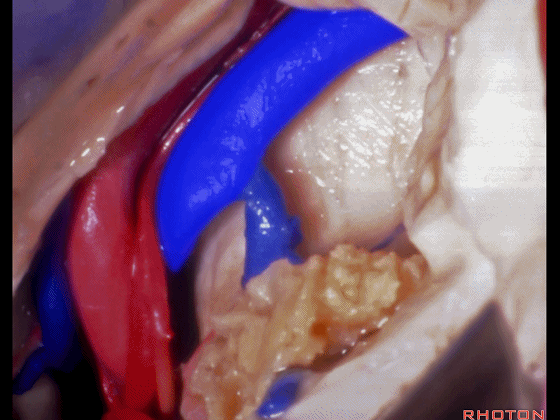
▼这是大脑后动脉。
posterior cerebral artery.
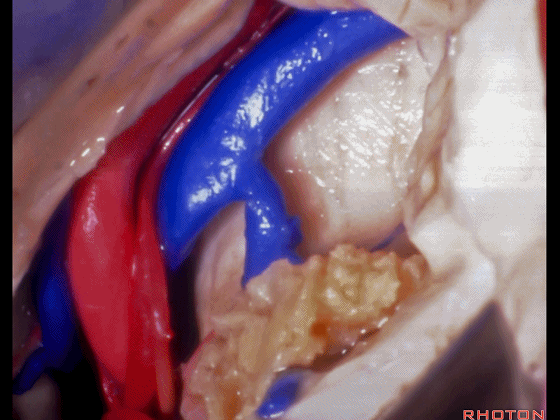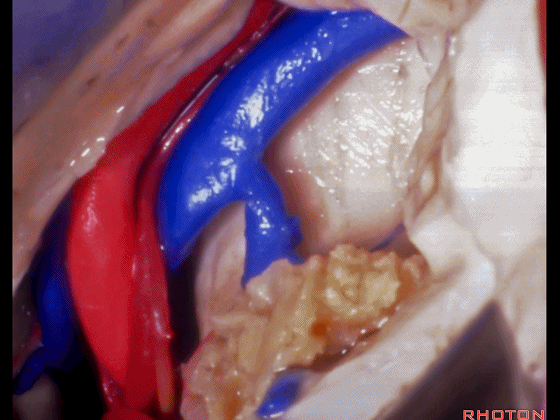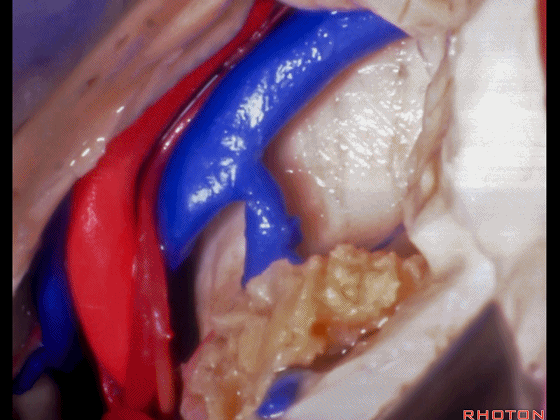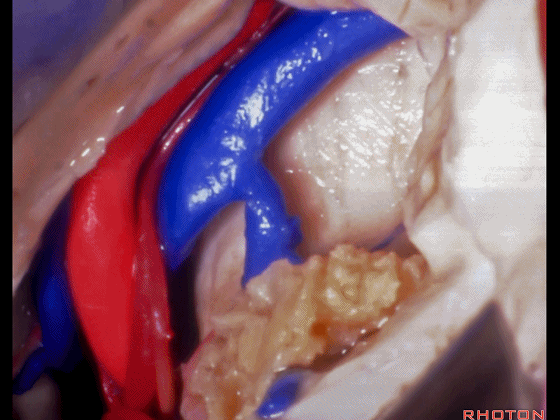
▼这是这一区域的另一视野。由此可完成杏仁核-海马切除术。
Just another view of that area. And then from here you can complete the amygdalohippocampectomy.

![]()
▼随着纤维束解剖研究的深入,我们意识到在岛叶(下图)下方、岛阈后方,沿着下界沟作此切口,则会遇到这区域的Meyer襻。
And but, as we started doing fiber dissections,we found that if you get in below the insula,here, behind the limen,and make an incision along the inferior limiting sulcus,you come along Meyer's loop in this area.
▼这是岛阈
▼这是下界沟
▼这是Meyer襻
▼这是下界沟
And here is inferior limiting sulcus,
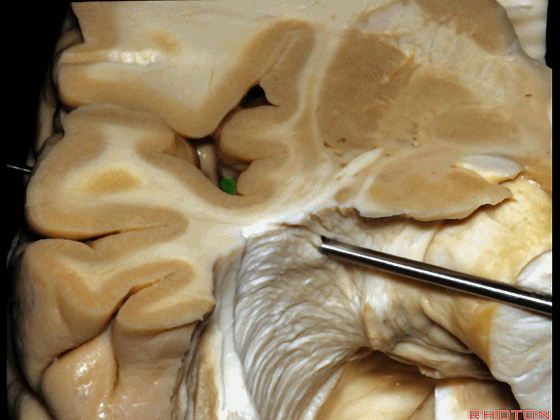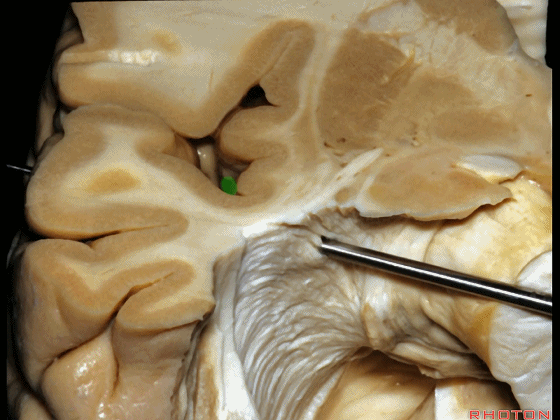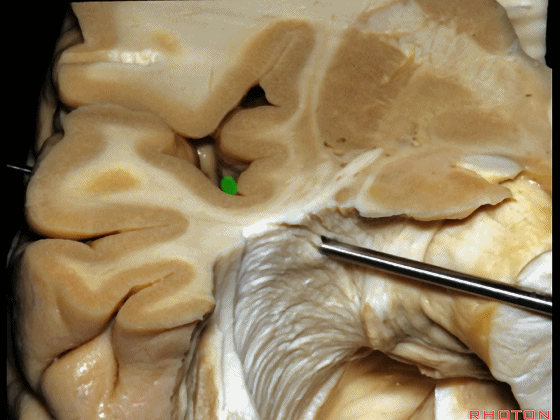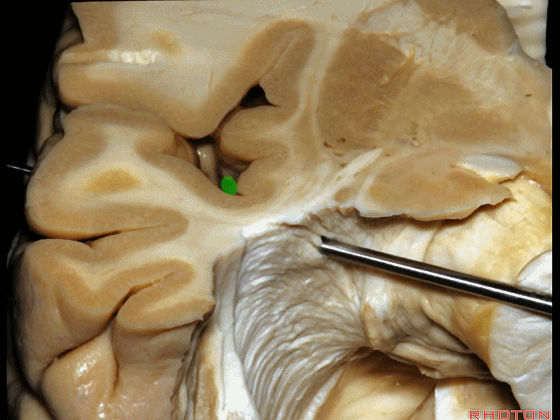
▼这是岛叶。
insula.
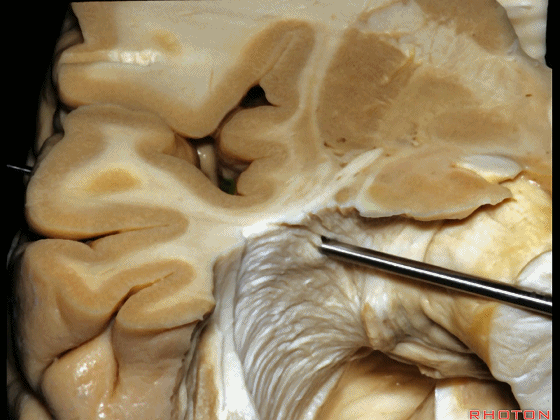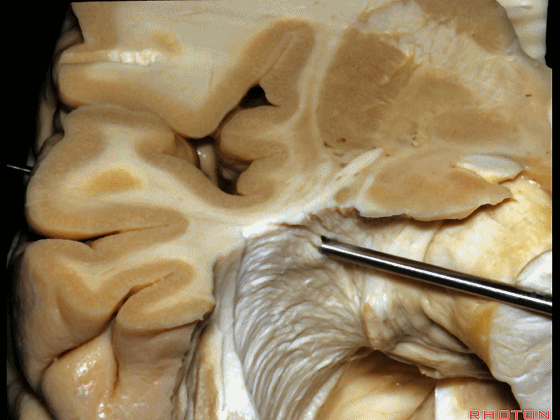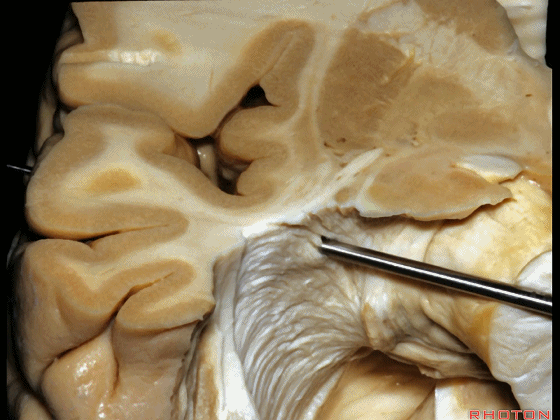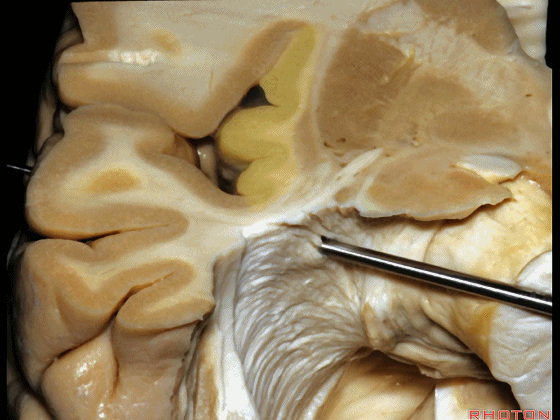
▼如果在此处切开,可见外侧膝状体
And if you divide through here,you see lateral geniculate,
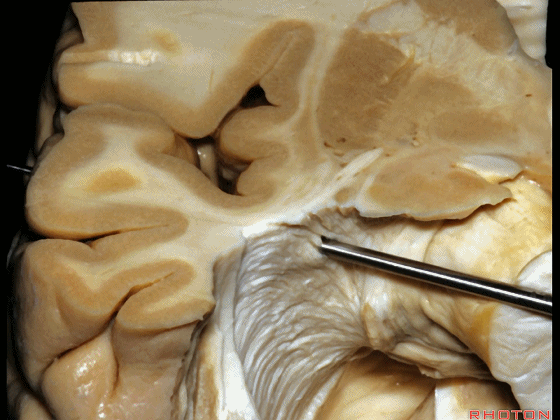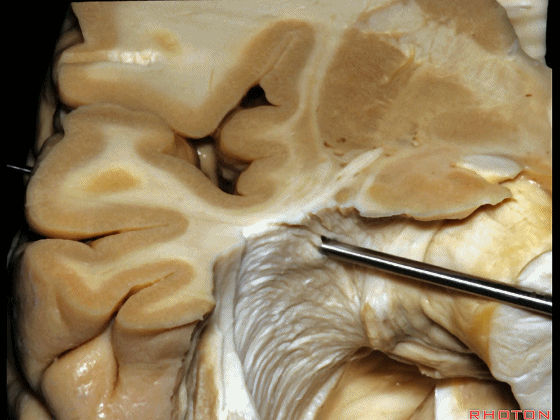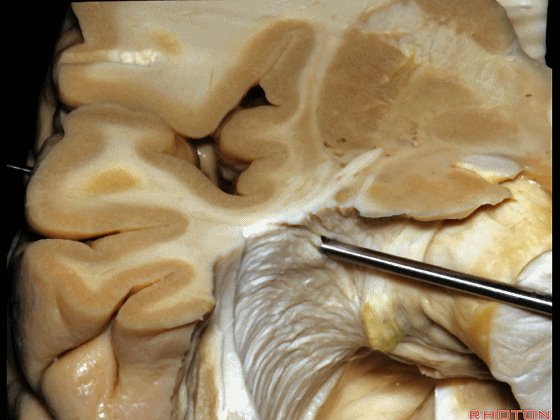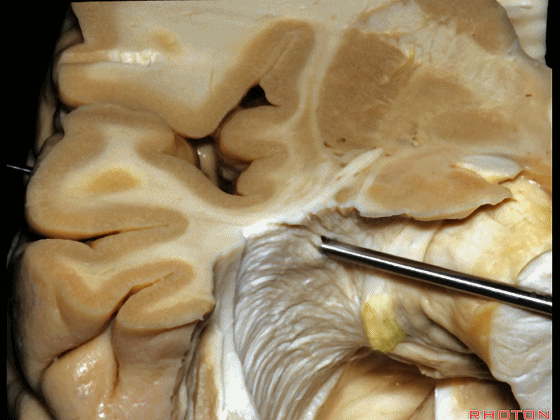
▼Meyer襻(下图)向前迂行。
Meyer's loop coming forward.
▼因此从下界沟切开,则可能会损伤Meyer襻。
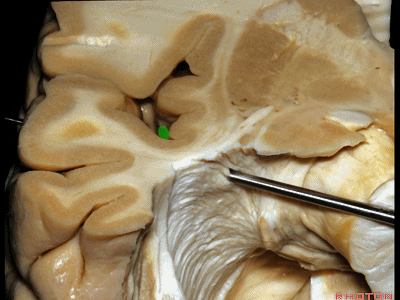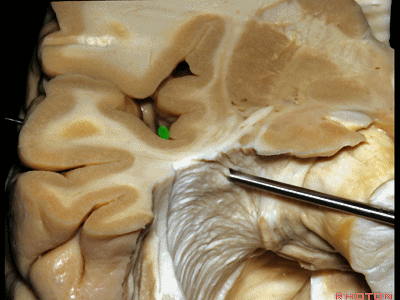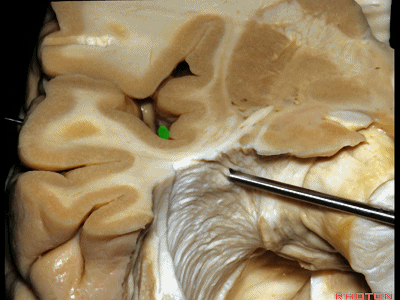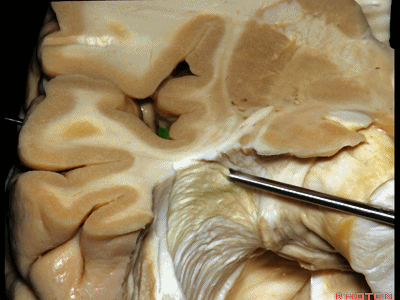
▼这是杏仁核
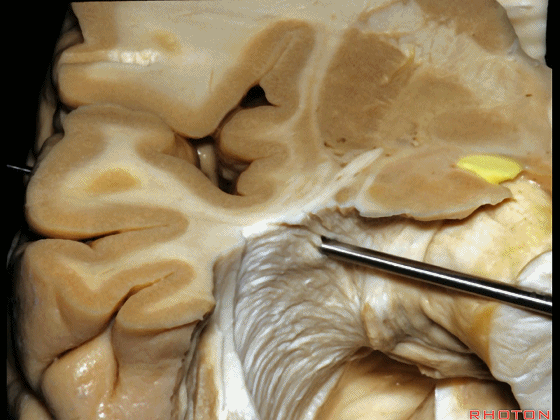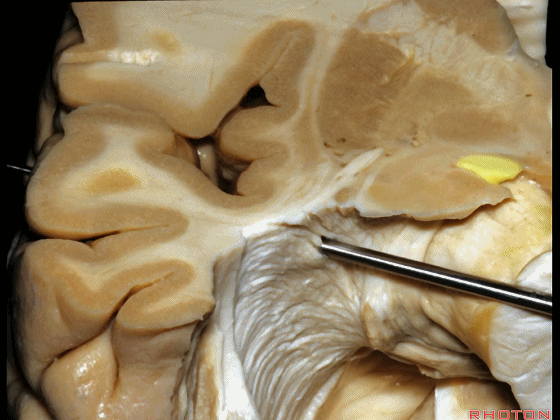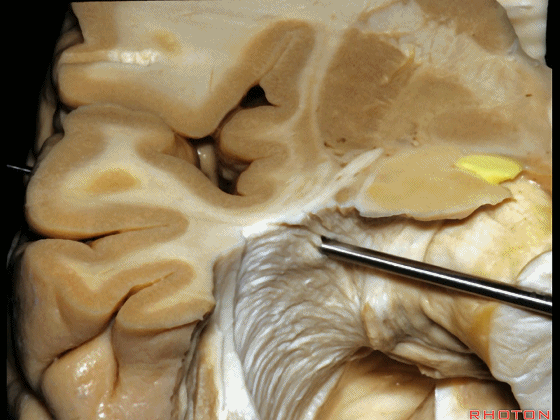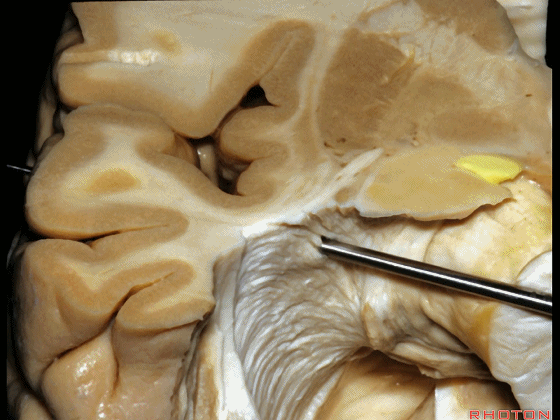
▼位于杏仁核上方的是视束,其向后行至外侧膝状体,并发出Meyer襻。
above amygdala, this is optic tract,coming back to lateral geniculate,giving rise to Meyer's loop.
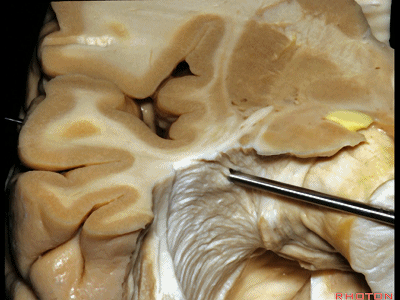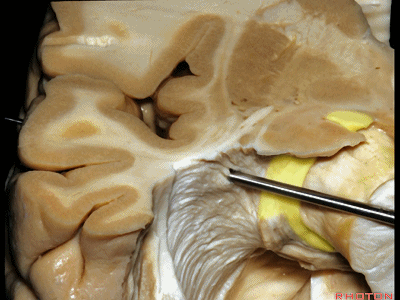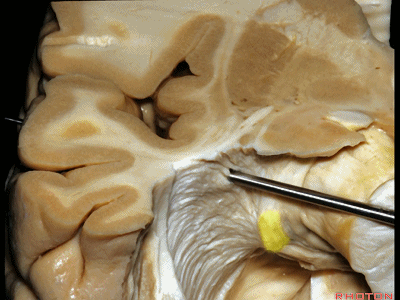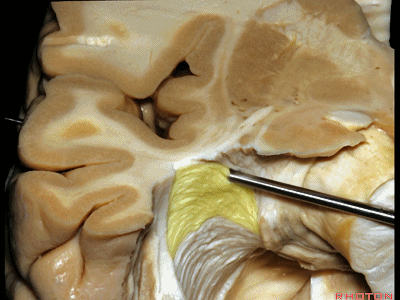
▼因此,与其从外侧切开此处,还不如经由钩回前段,经由杏仁核进入颞角,避开Meyer襻,从视束下方进入该区域。
And so, rather than coming through laterally here, you can come through the anterior segment of the uncus, here through the amygdala to the temporal horn,sparing Meyer's loop,and coming under the optic tract in this area.
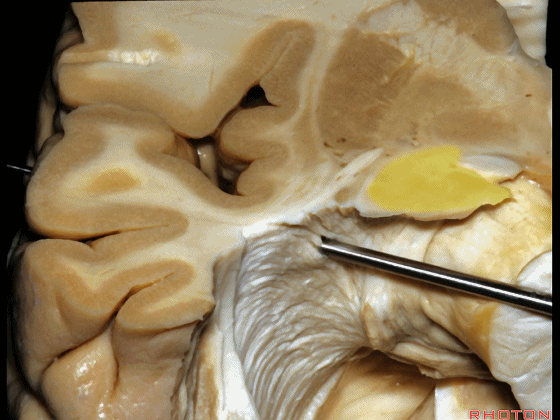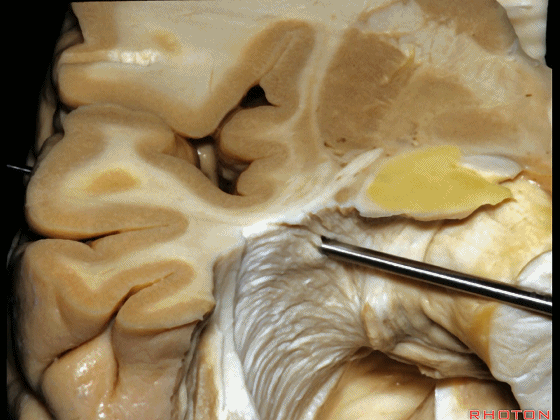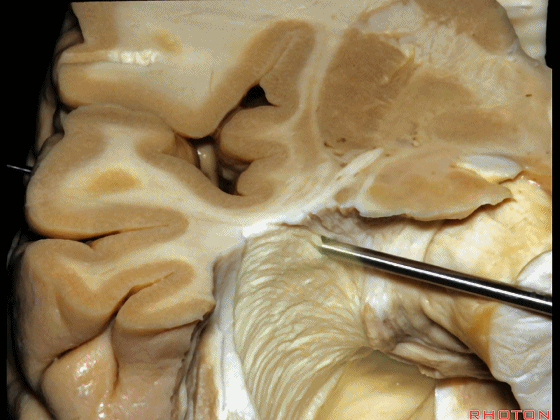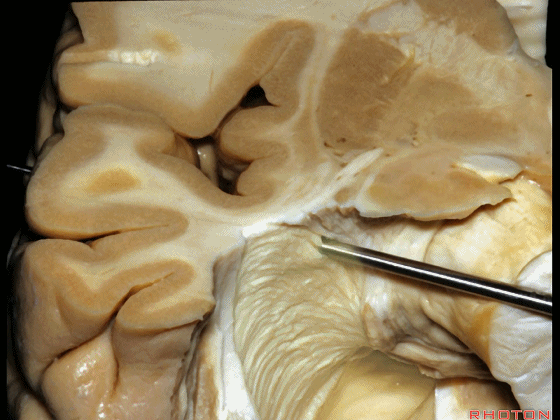
▼因此,从上方切开可经过这个安全地带,从Meyer襻和视束之间的这个V字形安全地带进入。
So that, there is a safe area coming from above between Meyer's loop and the optic tract,this V shape, safe area.

▼这是颞叶
here we have temporal lobe,
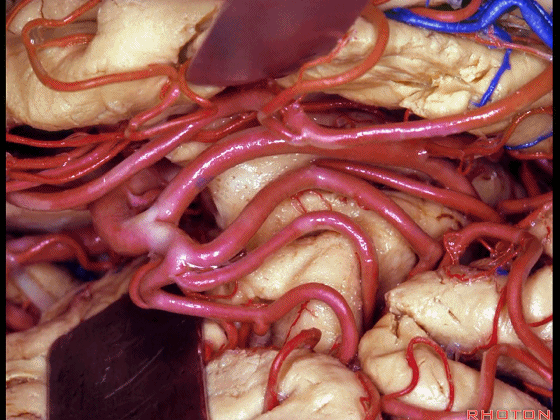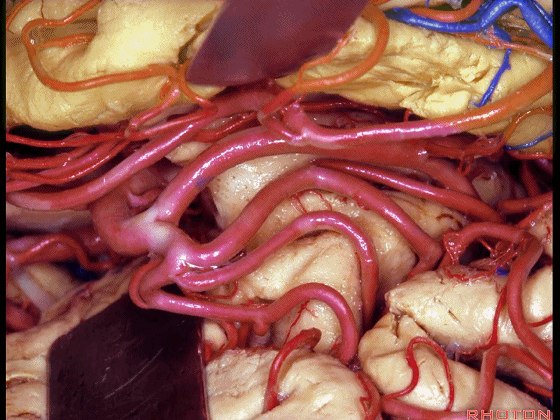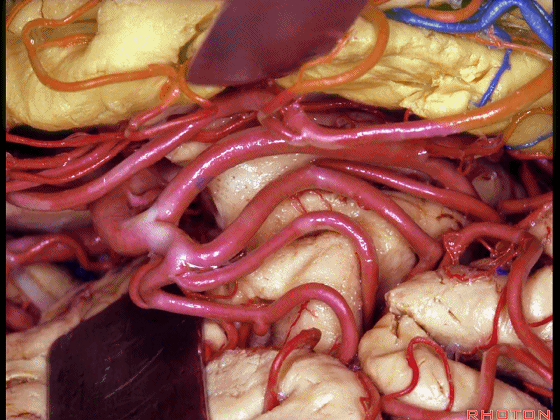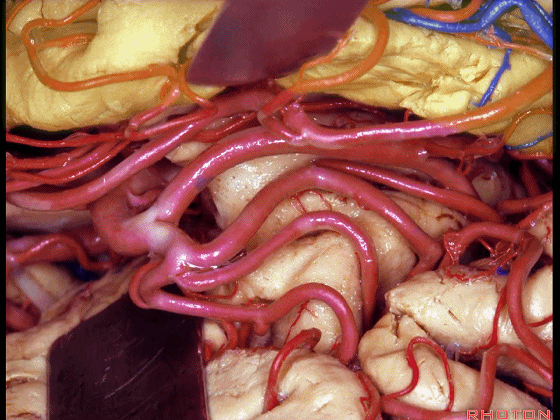
▼这是岛叶、额叶
insula, frontal lobe,
▼这是岛阈
limen in this area
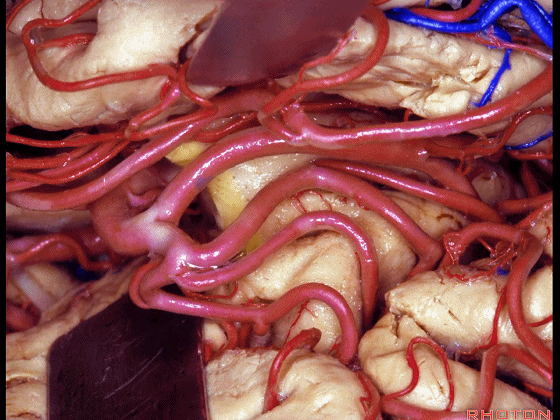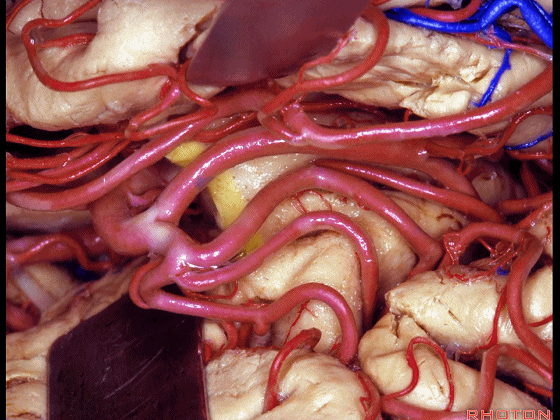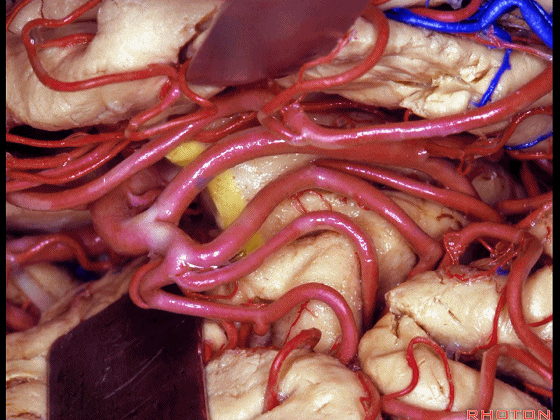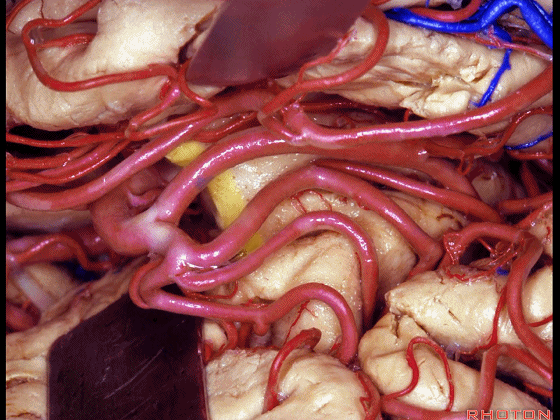
▼这是下界沟
inferior limiting sulcus.
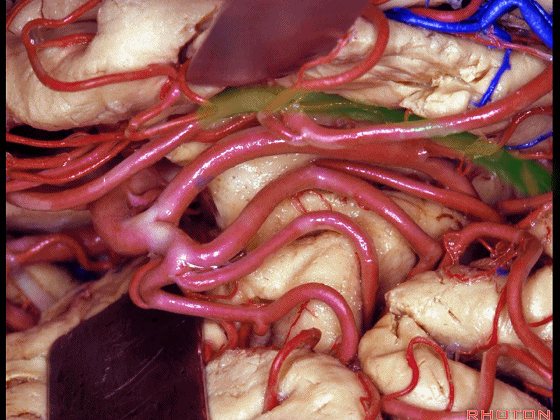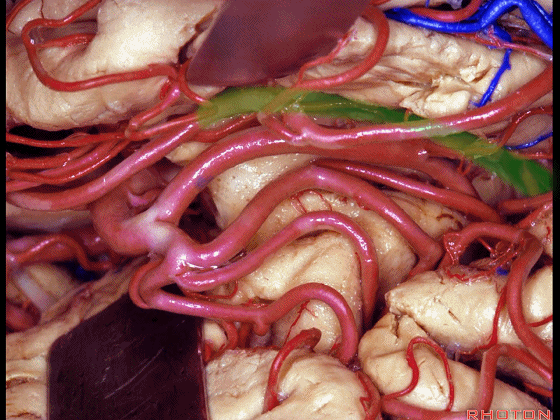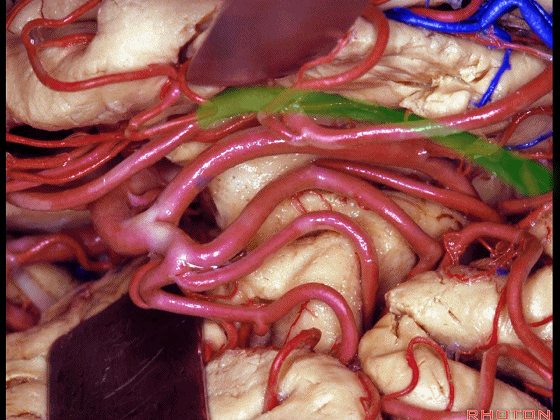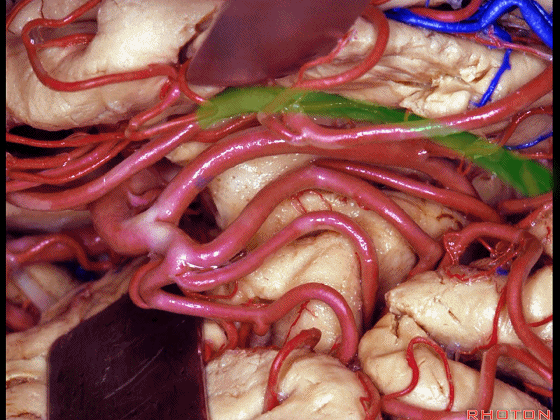
▼不要从下界沟(下图)进入
So rather than coming through the inferior limiting sulcus,
▼而是将此入路调整至钩回前段(下图),此处的杏仁核恰位于皮层下方。
we can shift the approach around to the anterior segment of the uncus,where the amygdala sits just below the cortical surface.
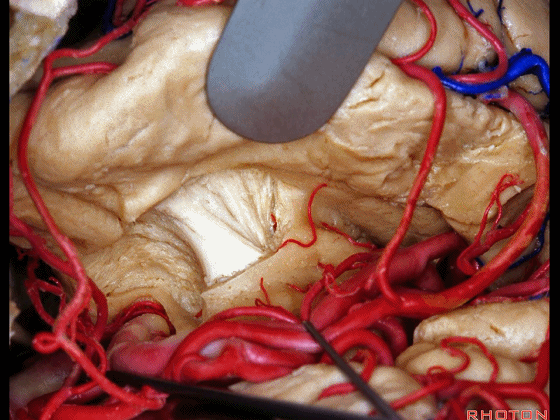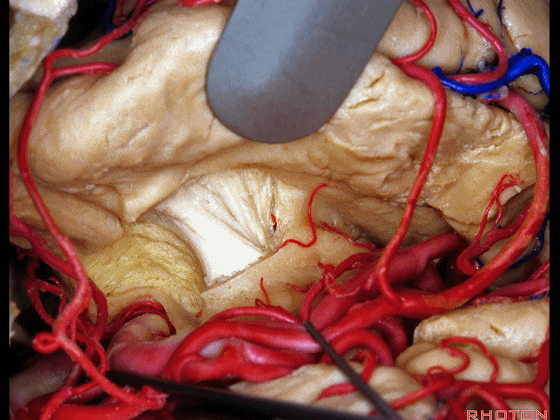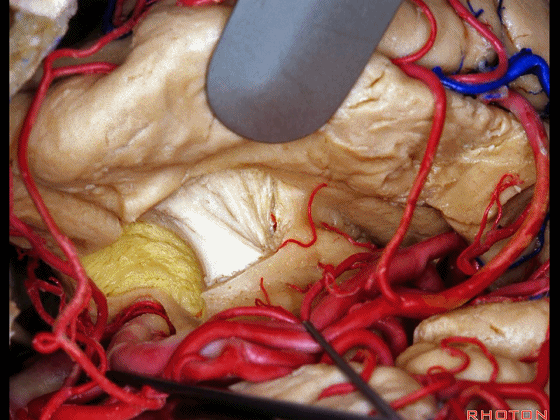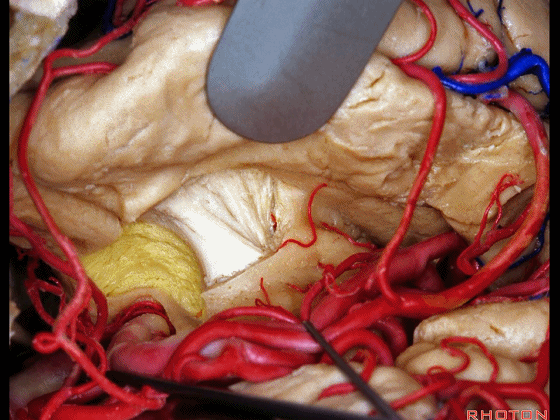
▼从而进入颞角(下图),完成杏仁核-海马切除术。
You can open into the temporal horn, and complete then, an amygdalohippocampectomy.
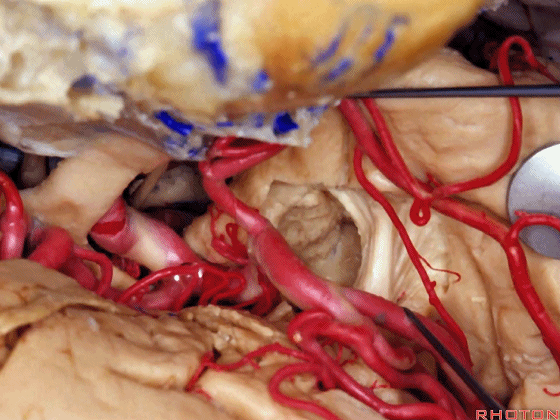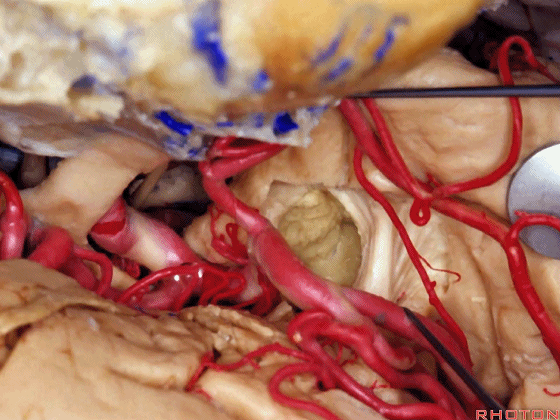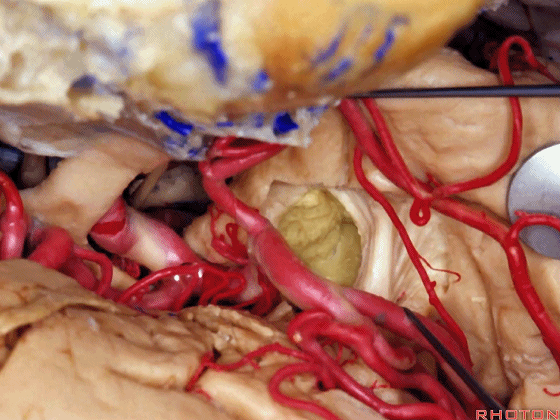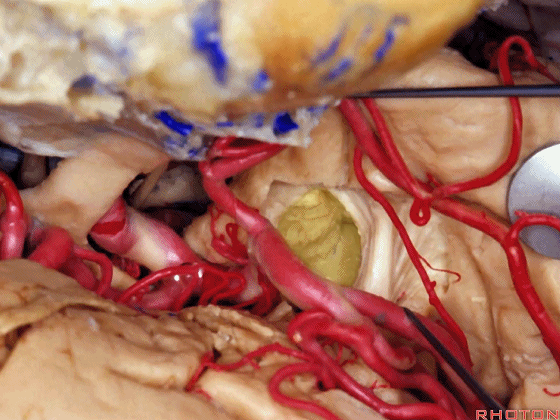
▼这是天幕游离缘
Here we see the...tent edge
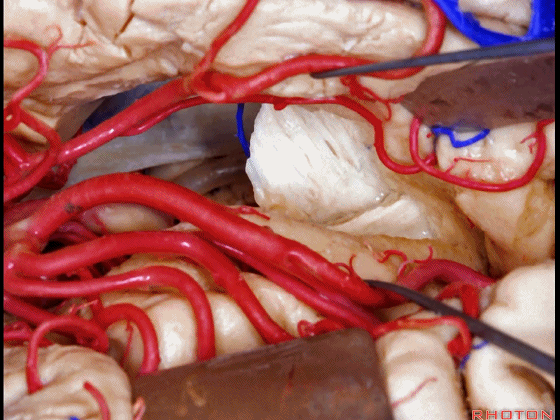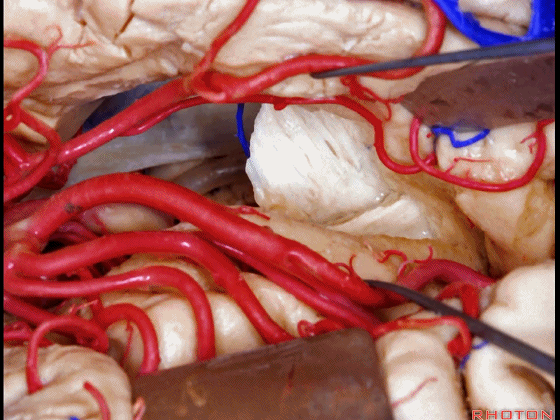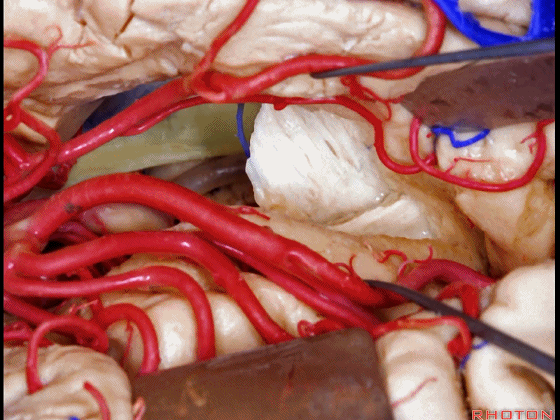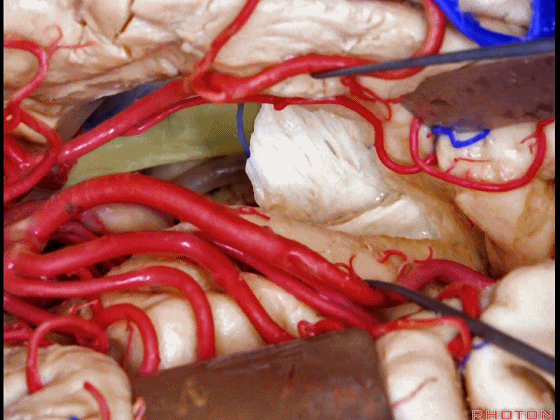
▼这是视放射纤维束(下图)。均得以保护。
the optic radiations of fiber dissection.They've been preserved.
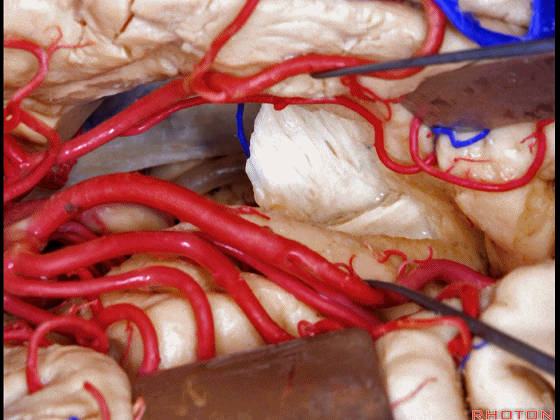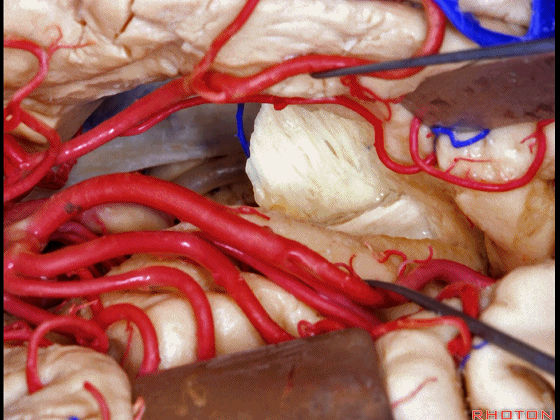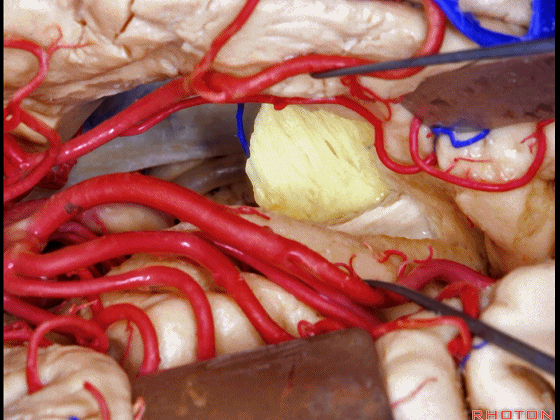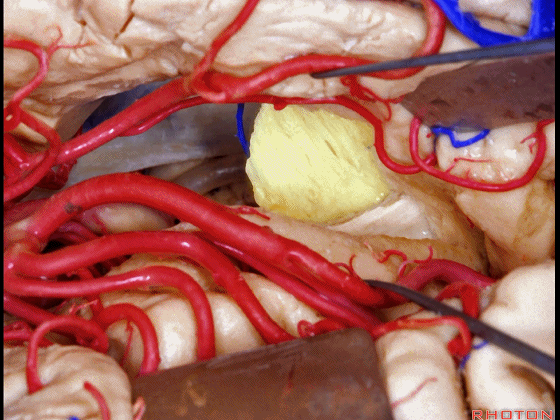
▼该区域最常用的入路还是经颞叶切除,以进入颞角。
The most common approach to this area is using a temporal lobectomy. You open into the temporal horn.

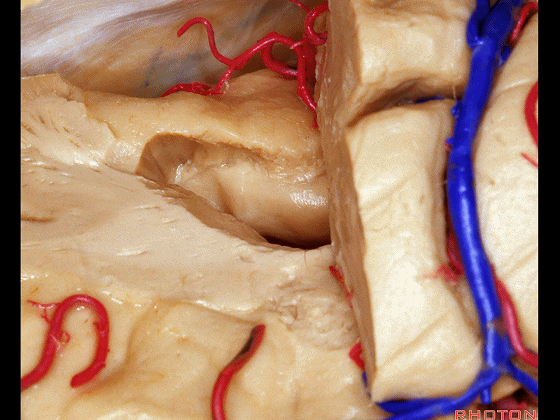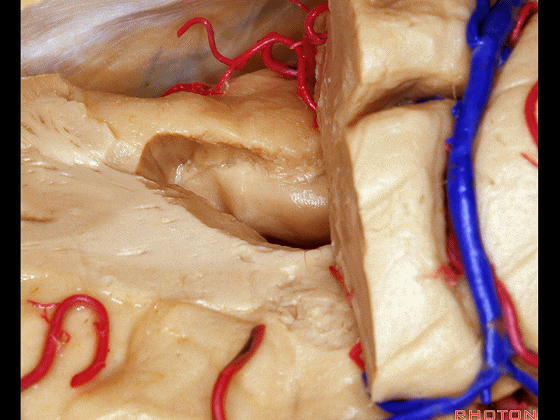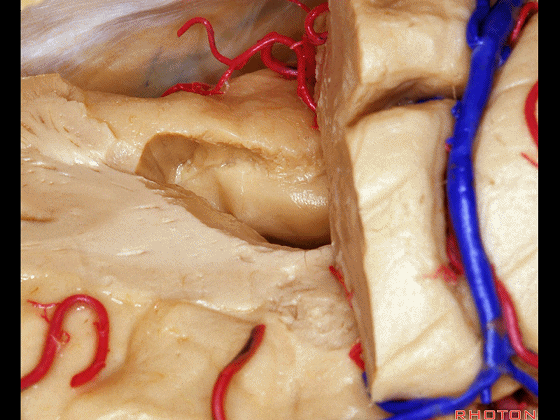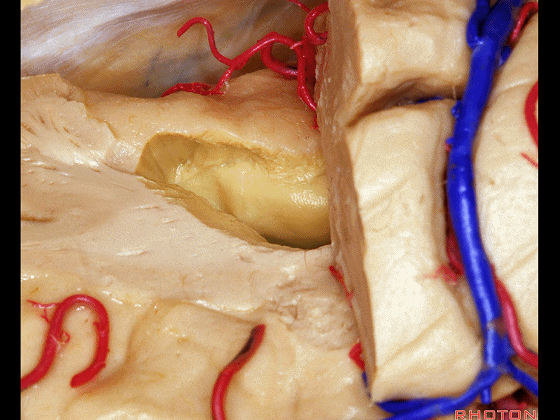
Here we've opened through the amygdala.
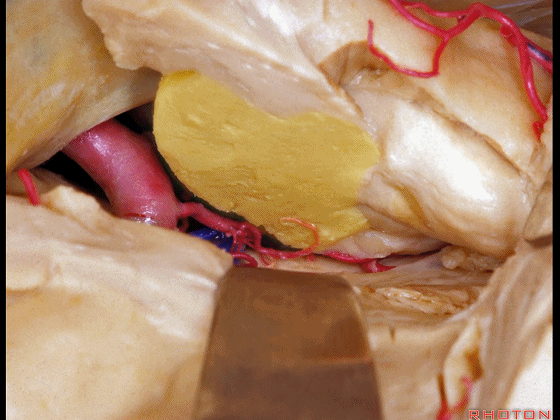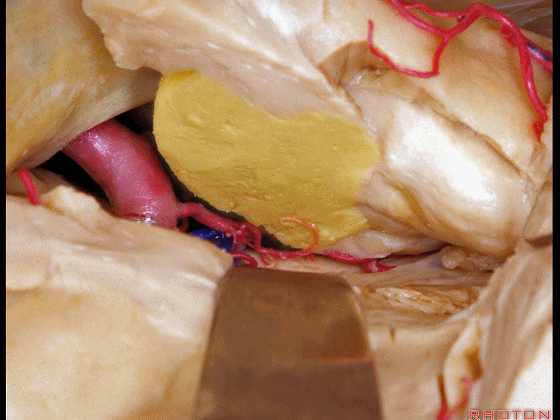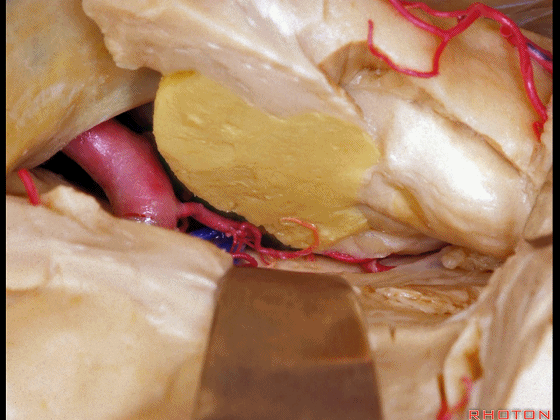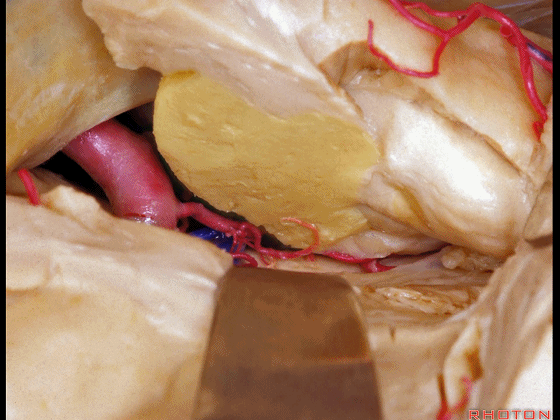
▼可见脉络膜前动脉(下图)向后进入下脉络点
We see the anterior choroidal artery passing back to the inferior choroidal point
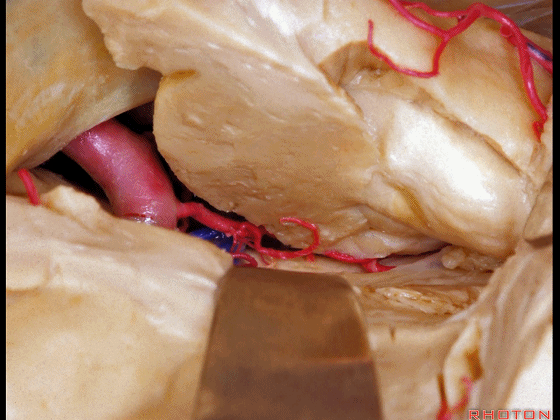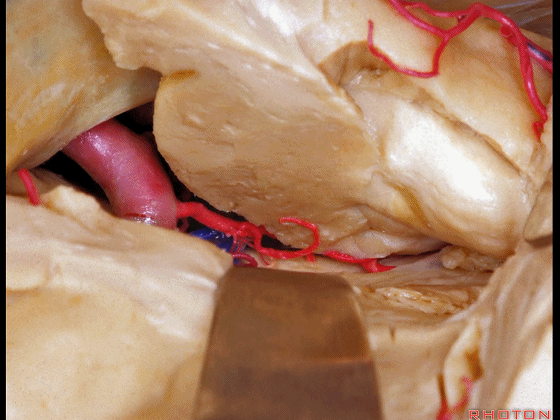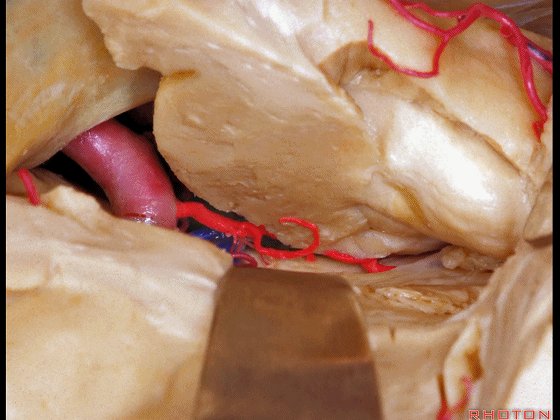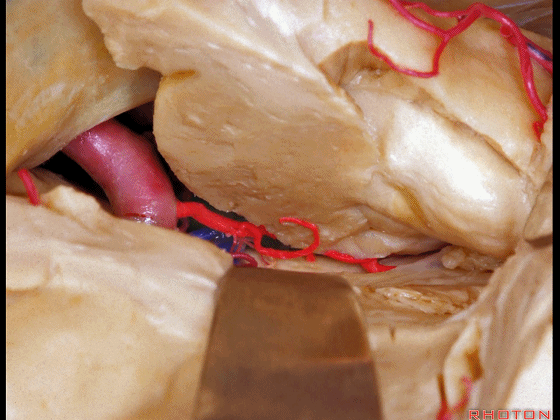
▼这是下脉络点
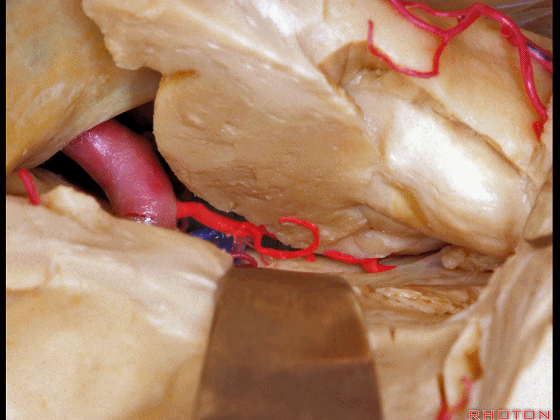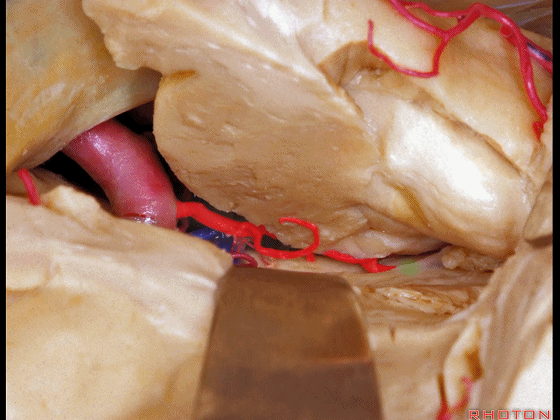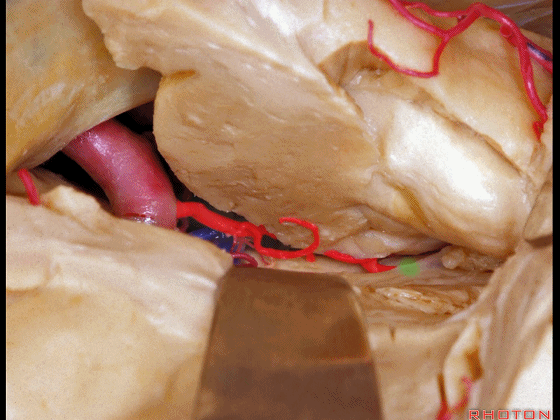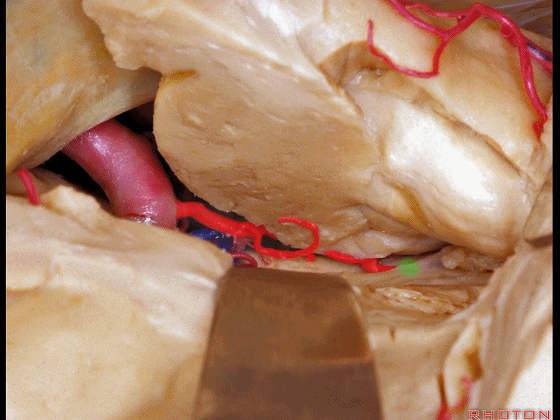
▼这是海马
the hippocampus.
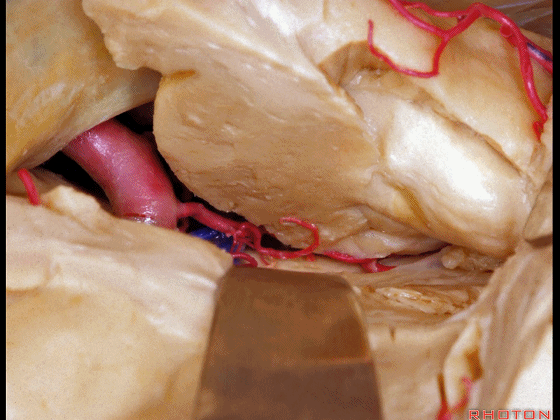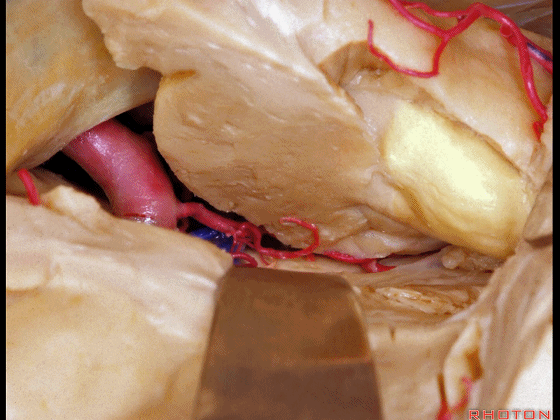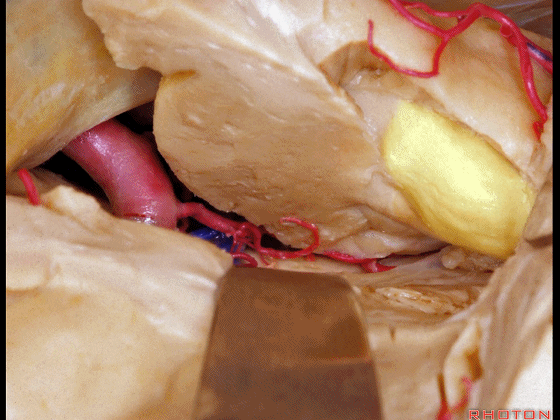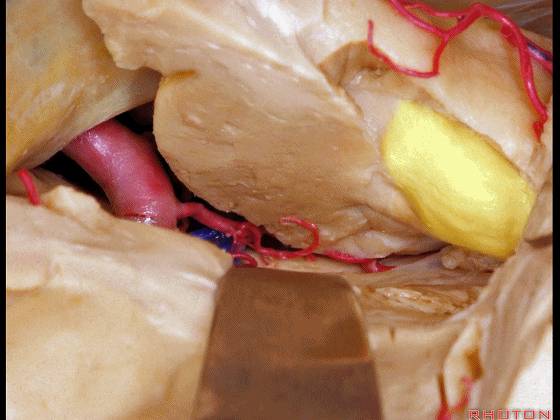
▼来看颞叶内侧面。这是穹窿伞(下图)
here is medial surface of temporal lobe,here, fimbria
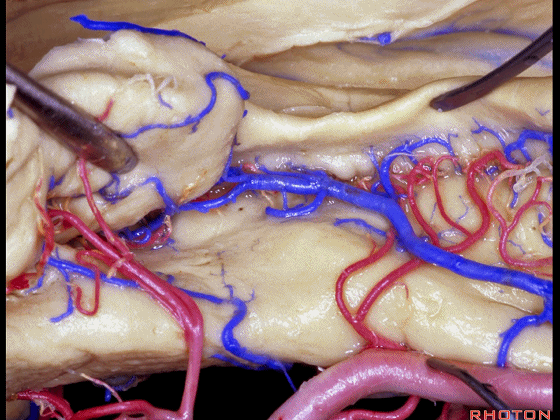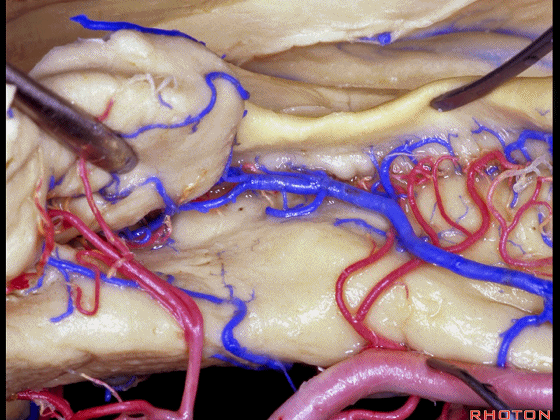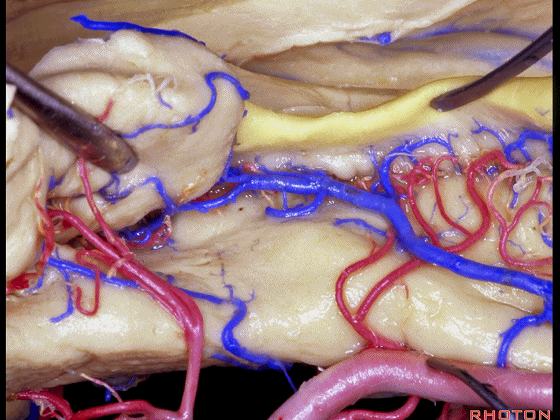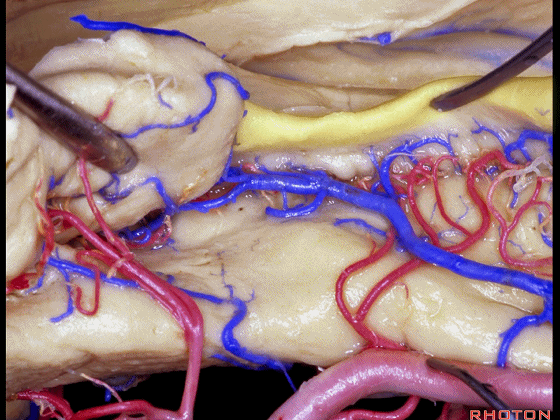
▼这是齿状回
dentate gyrus
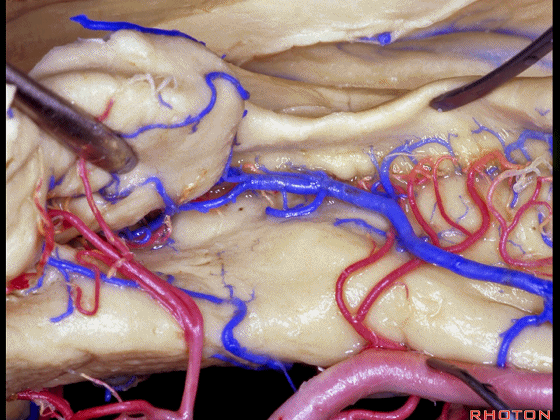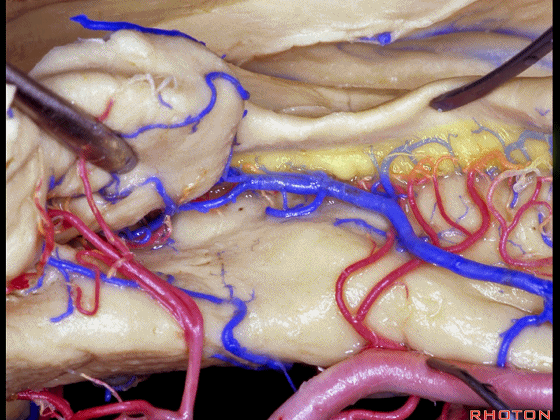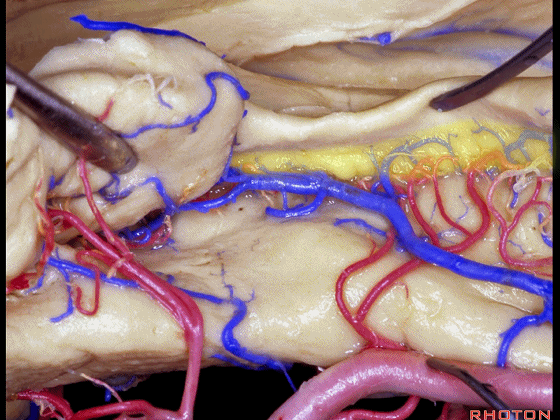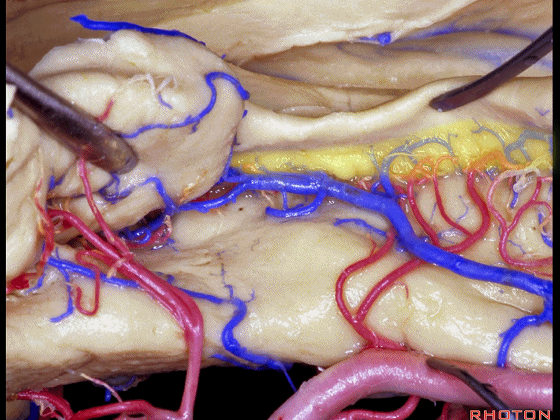
▼这是海马旁回
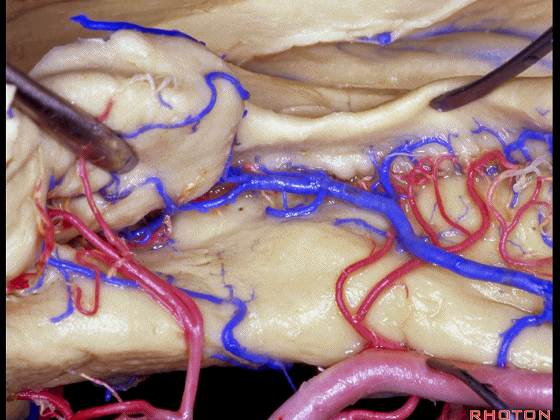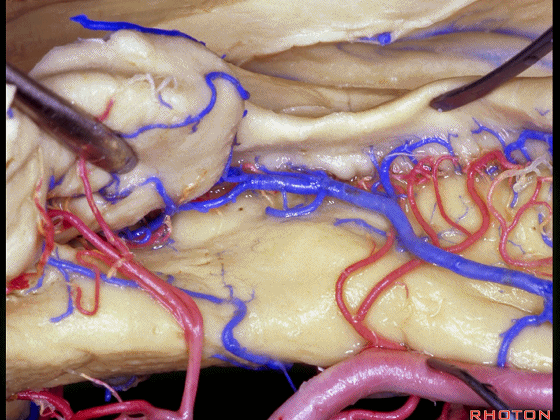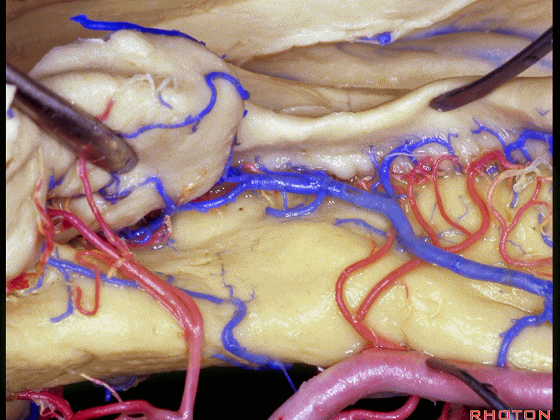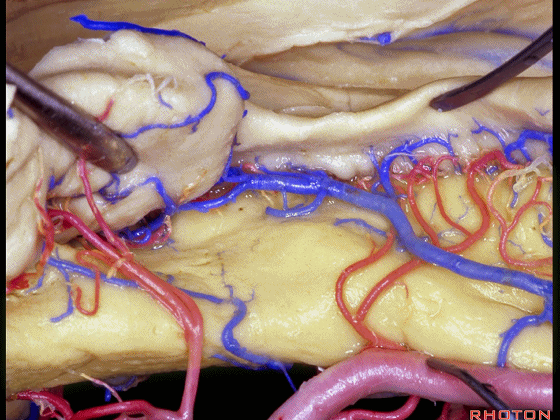
▼这是钩回后部(下图),其内含有海马头。
Here is posterior segment of uncus with the enfolded head of hippocampus.
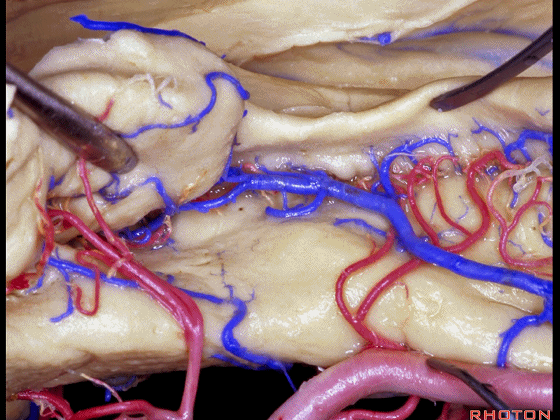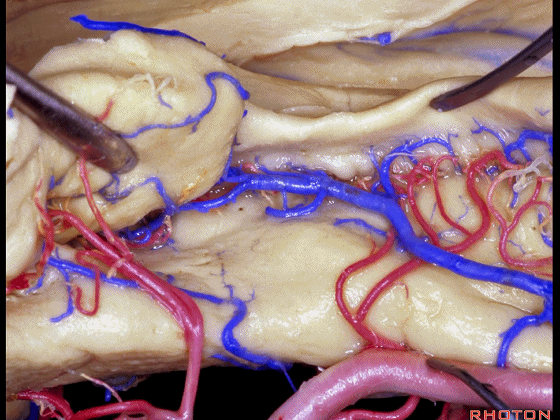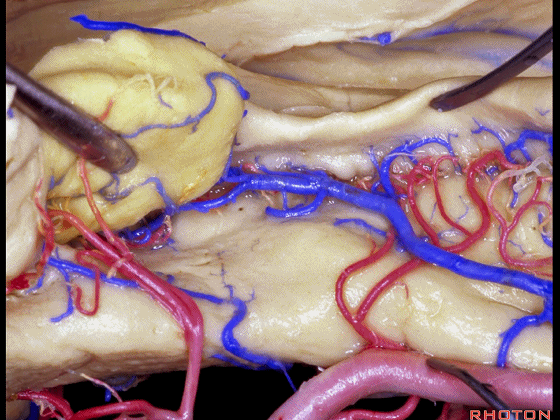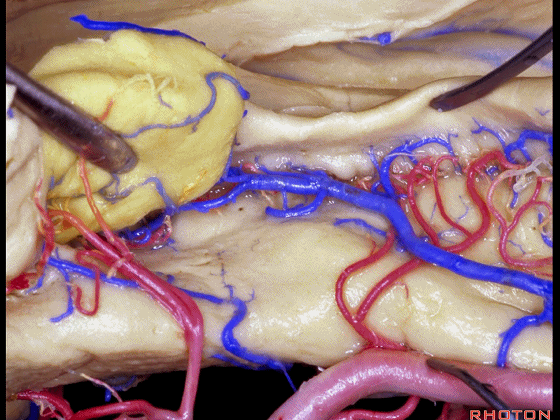
▼进行颞叶内侧面切除术时,我们不得不牺牲这些海马动脉(下图)。
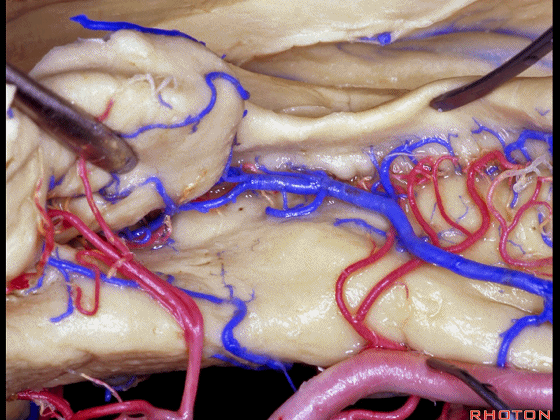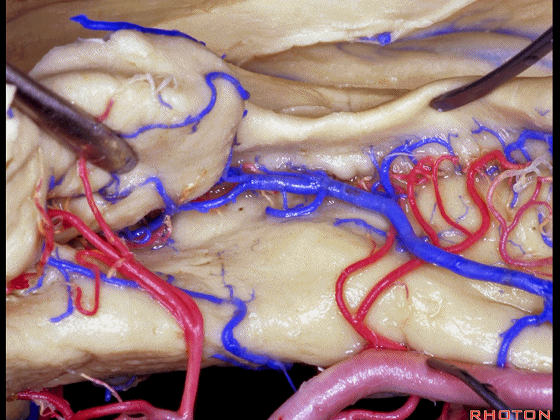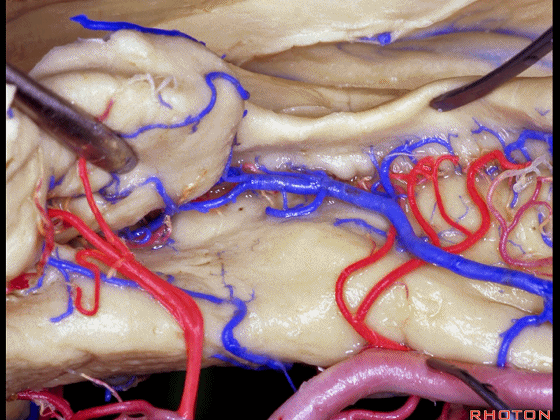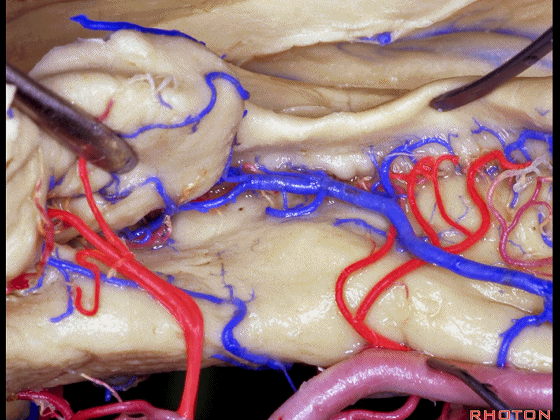
▼海马动脉走行于海马旁回(下图)和齿状回(下图)之间。
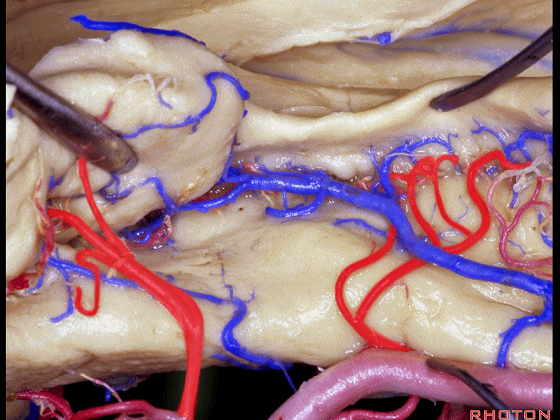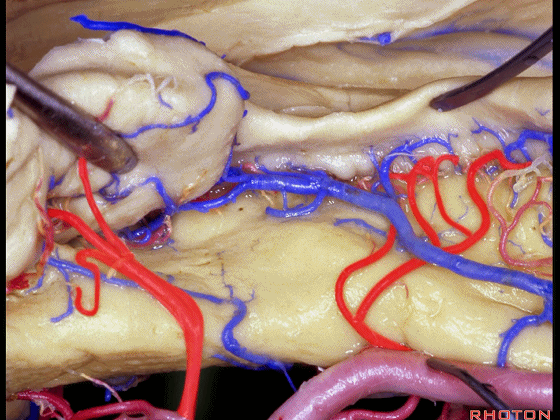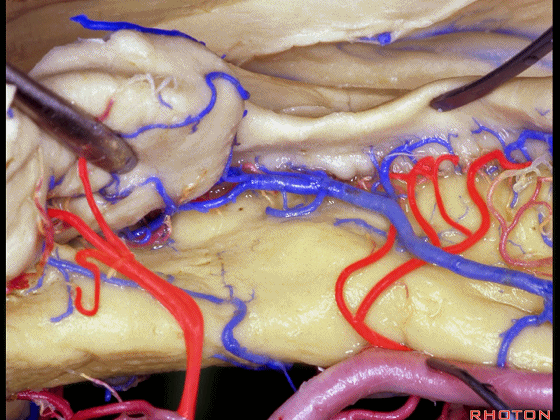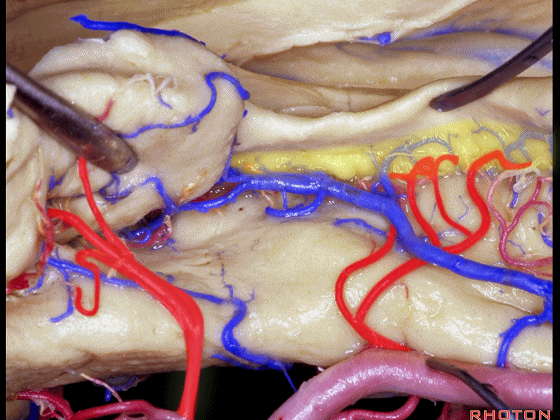
▼这些动脉行至颞叶外侧面。向后暴露即可见这些海马动脉,其会被牺牲。
while preserving these arteries that go to the lateral surface of the temporal lobe.So that as you open backwards you see these hippocampal arteries,we sacrifice those.
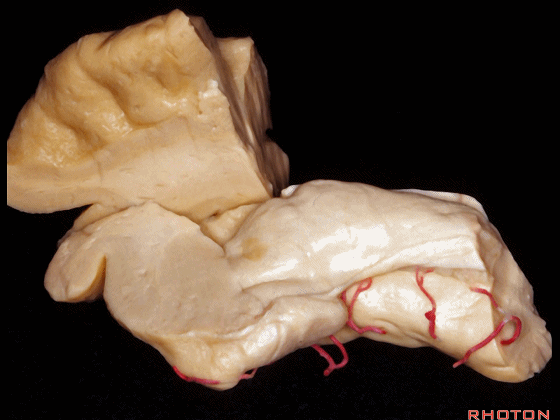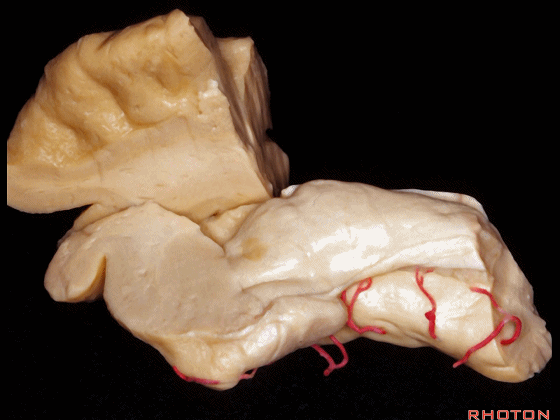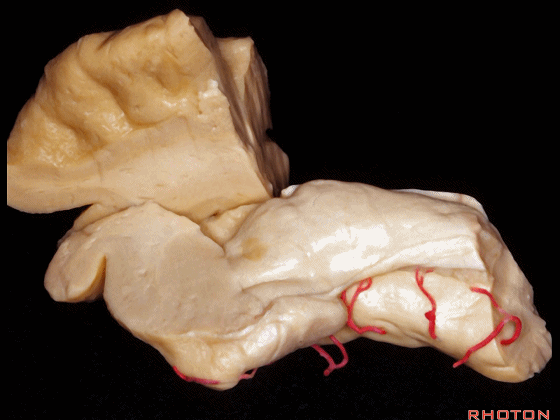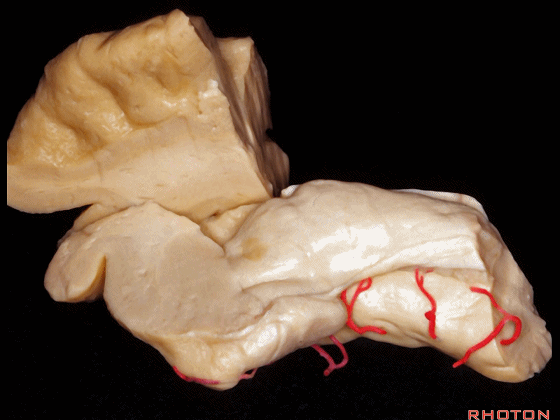
▼通过前颞叶切除术以暴露杏仁核、海马
amygdala,hippocampus in the anterior temporal resection.
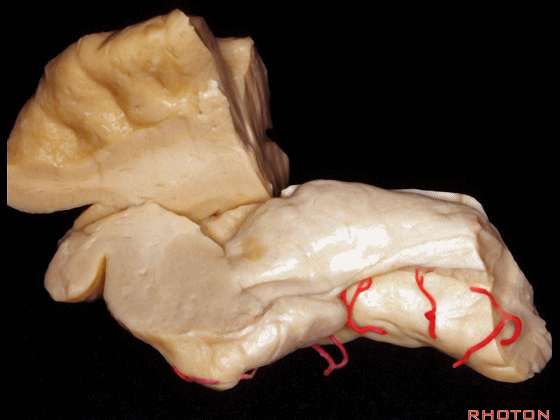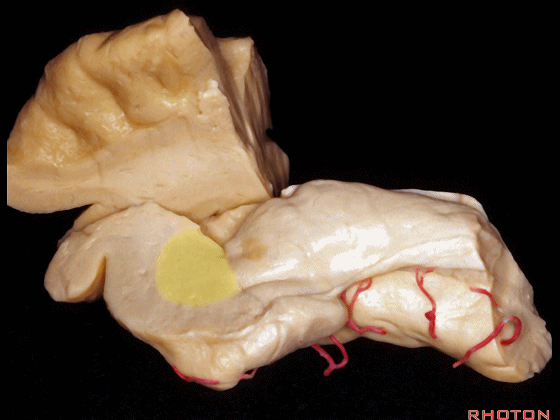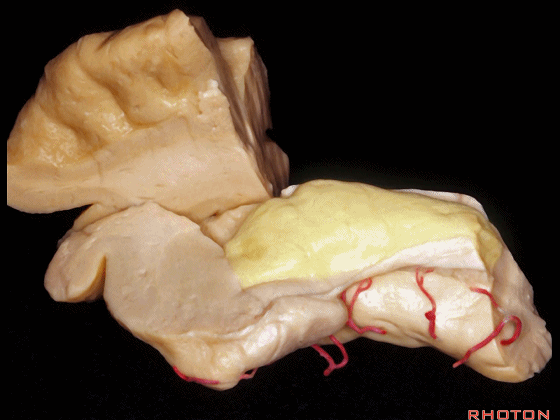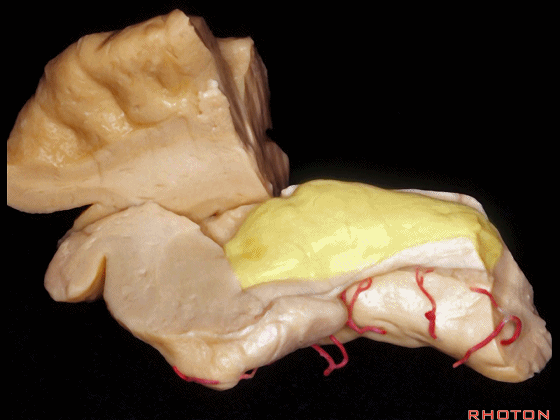
▼另一个该区域的入路是经脑池入路,从视神经外侧,贴着颈内动脉、M1段(下图)。
Another way of coming to this area is through the cisterns lateral to the optic nerve, adjacent carotid, M1.
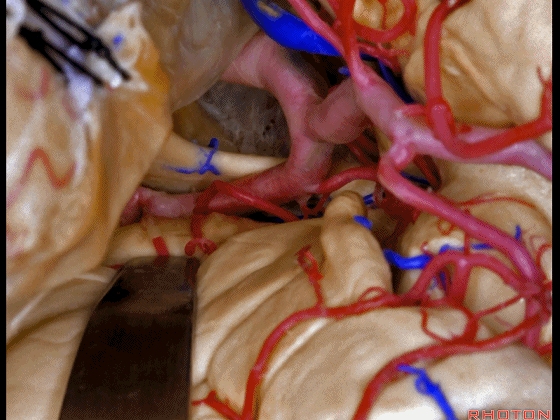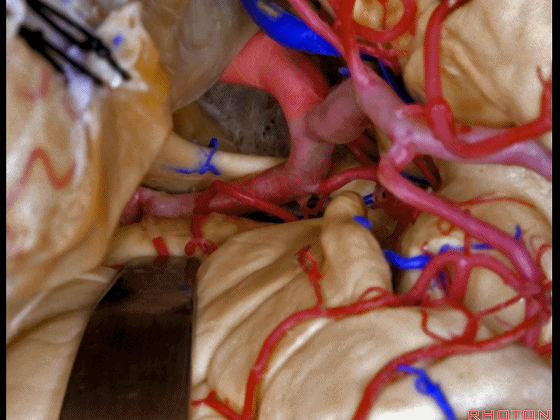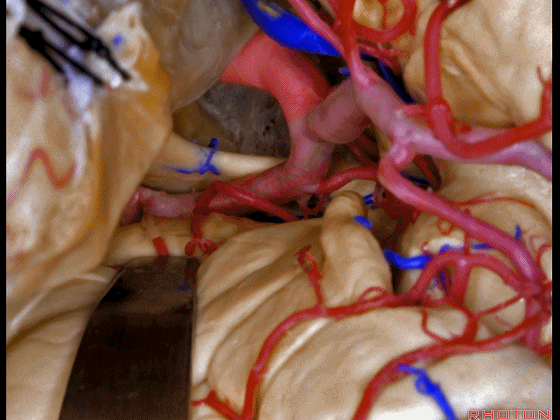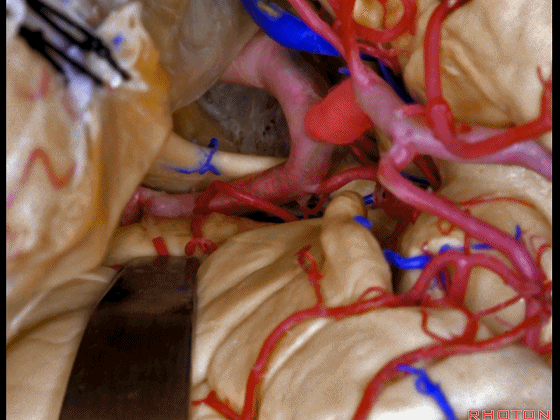
▼可见动眼神经、后交通动脉
You'll expose 3rd nerve, posterior communicating
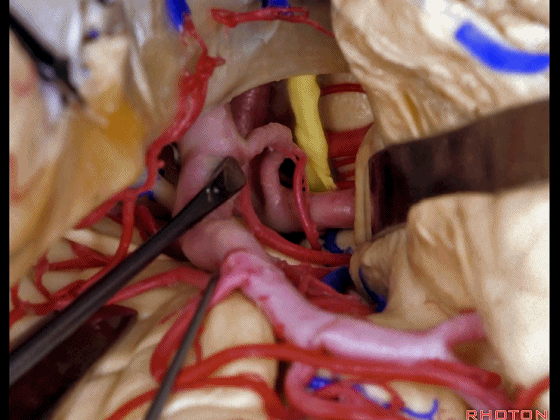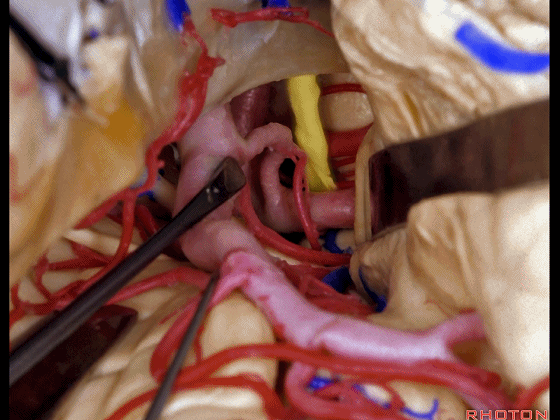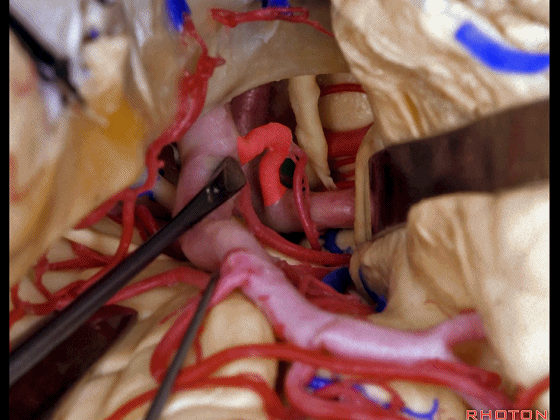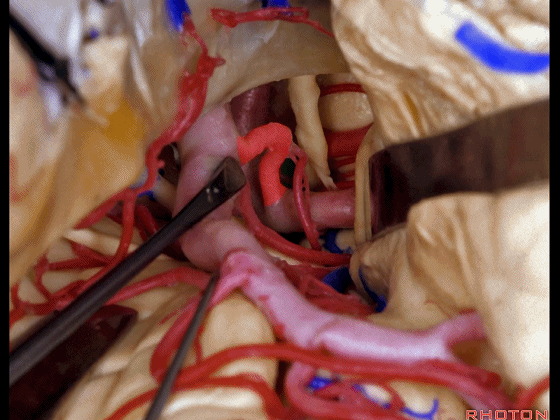
▼可切除杏仁核、海马前部,通过这个经脑池入路暴露颞叶内侧面的前部。
and you can resect amygdala, anterior part of hippocampus using this transcisternal approach to the anterior part of the medial temporal lobe.

▼这是动眼神经。可见大脑后动脉行于此处的脚池
Here's 3rd nerve. We see posterior cerebral artery in here crural cistern,
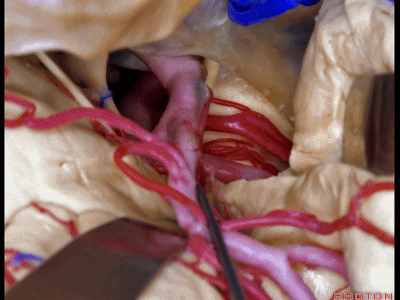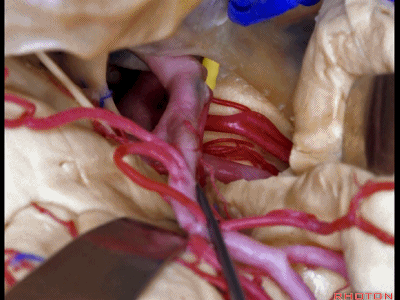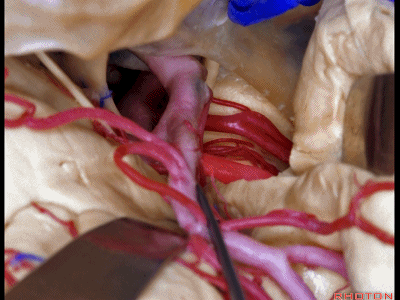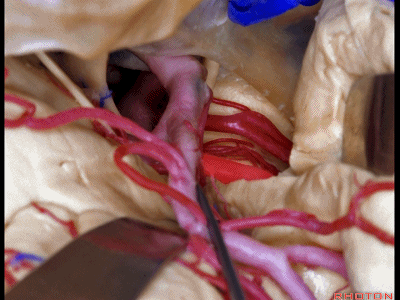
▼这是脚池、大脑脚。
以上就是用于暴露颞叶内侧面的各种入路。
crural cistern,cerebral peduncle.So these are come of the routes that we can take to medial temporal lobe.
更多精彩内容 请关注作者



