Rhoton解剖视频中《Cerebellopontine Angle and Fourth Ventricle》这一章节包含了幕下解剖的内容,包括小脑、第四脑室、幕下动脉、桥小脑角区等。为了完整展示幕下解剖,笔者加入《Internal Structures and Safe Entry Zones of the Brainstem》这一章节中的小脑解剖内容。本文内容与本公众号内文章《桥小脑角区解剖》(点击浏览)有部分重复。共150张图片。

笔者水平所限,错误之处请批评指正!
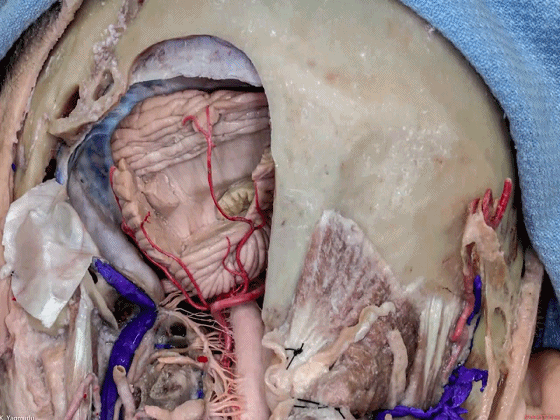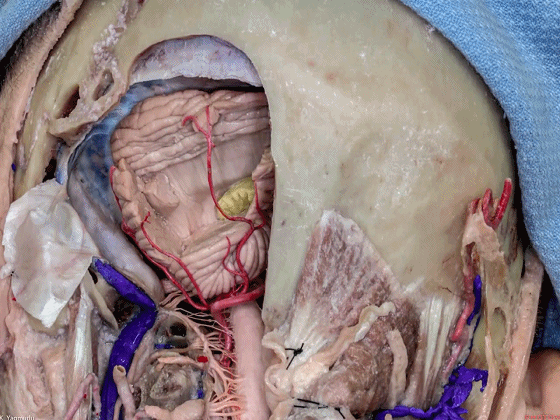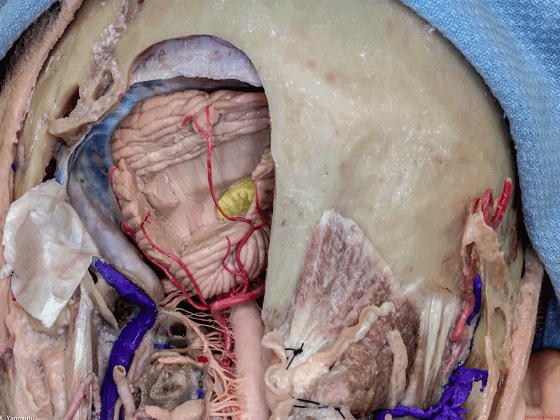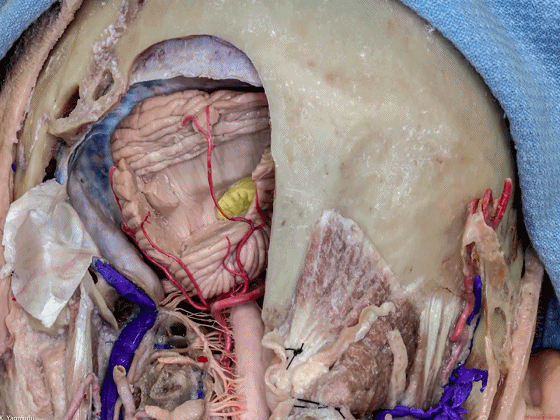
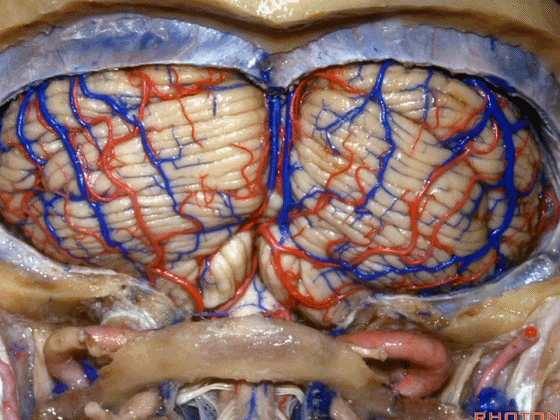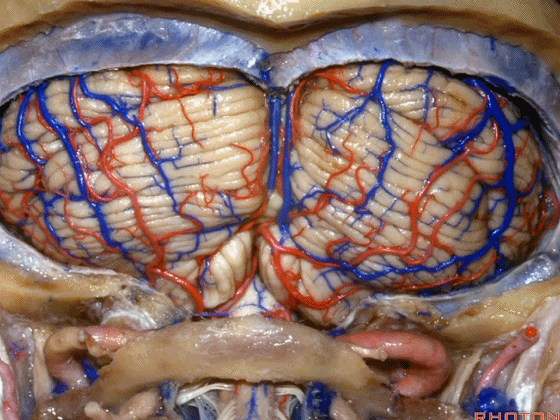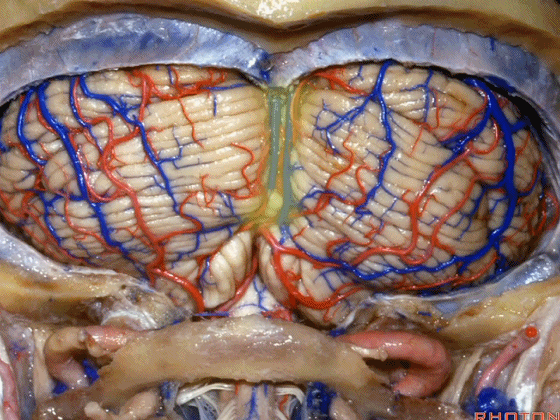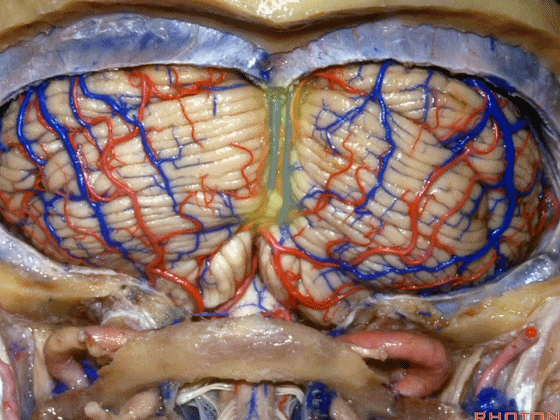
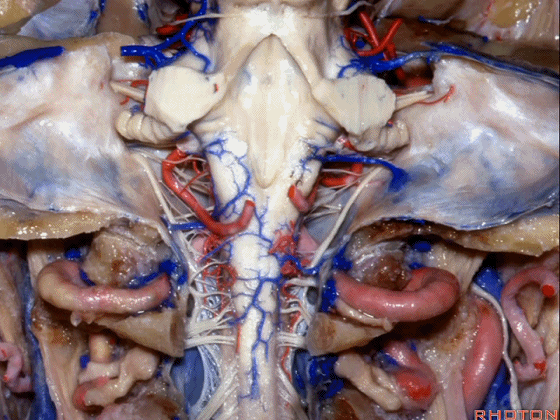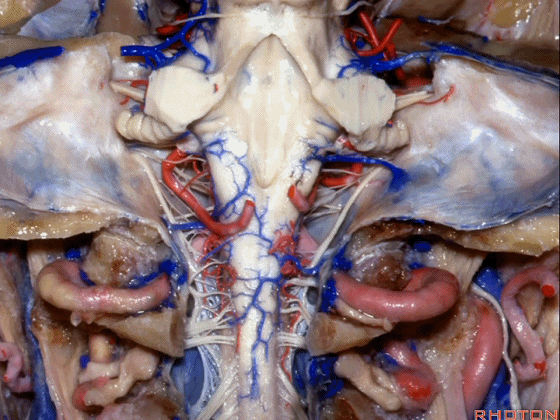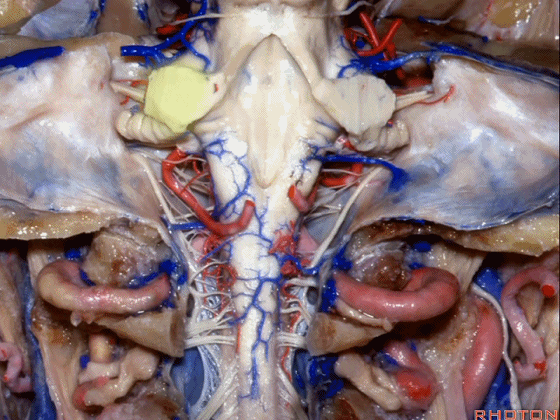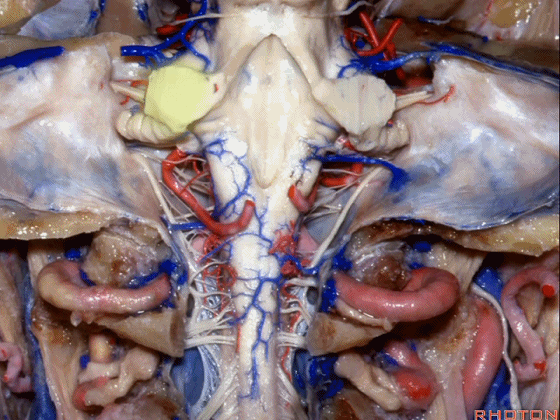
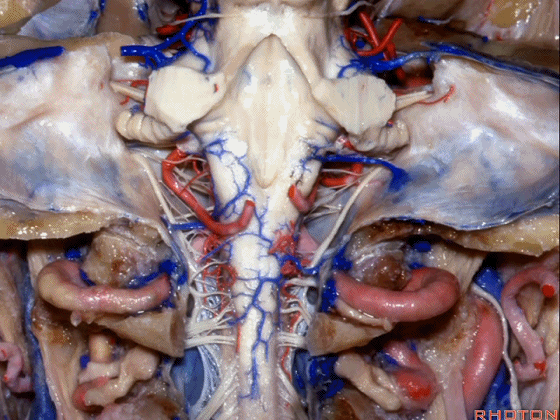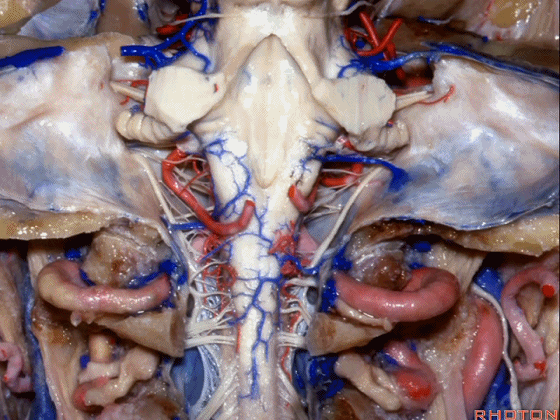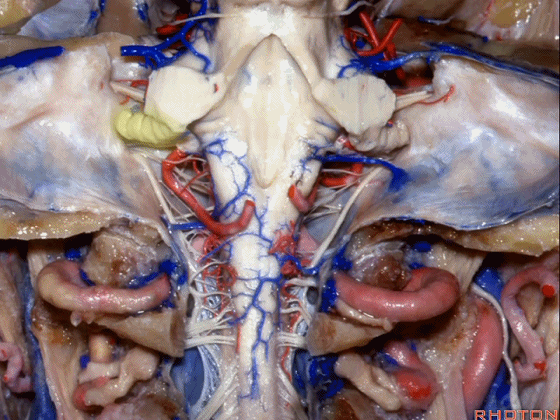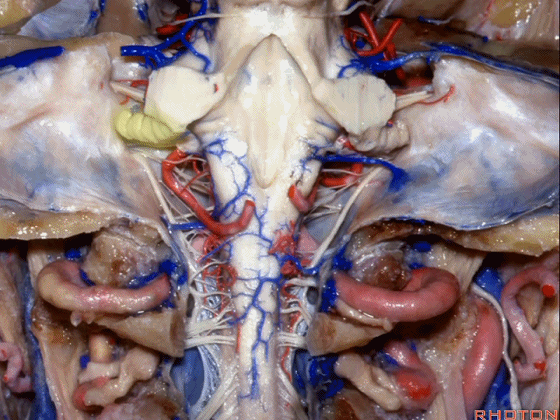
幕下解剖
Infratentorial anatomy
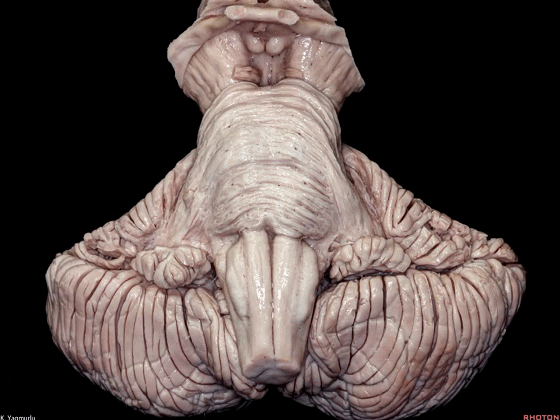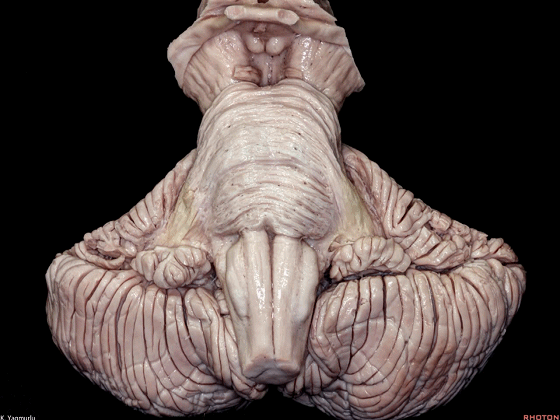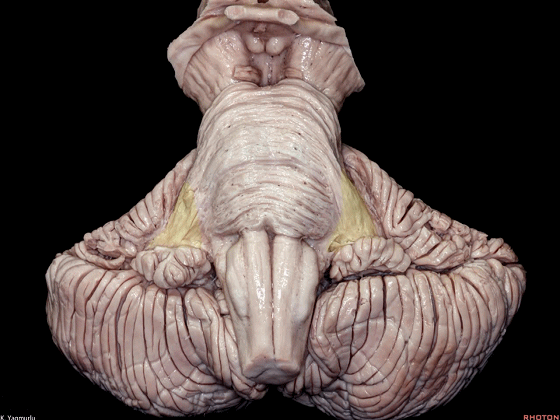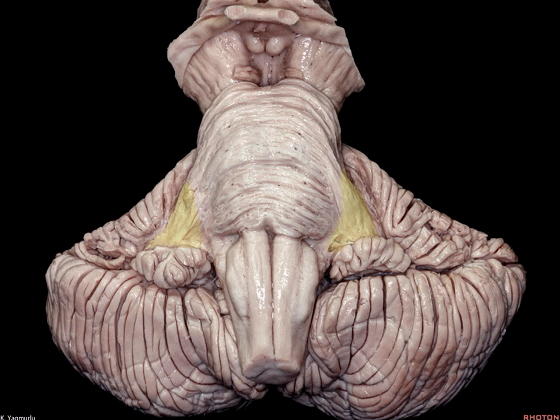
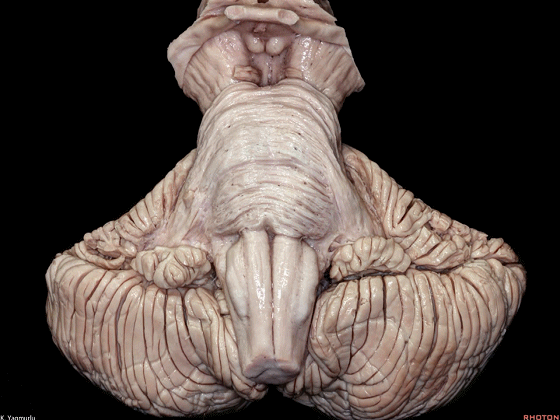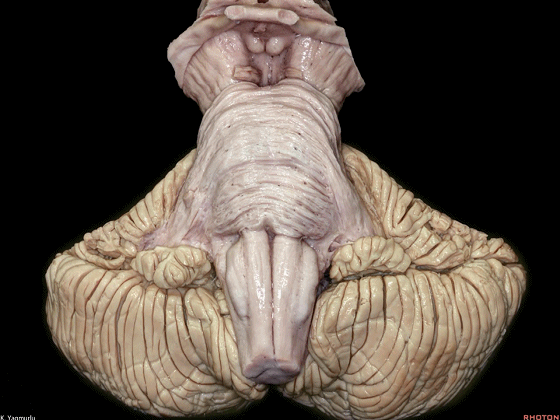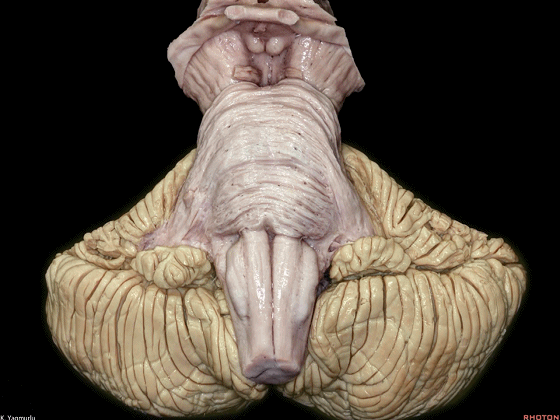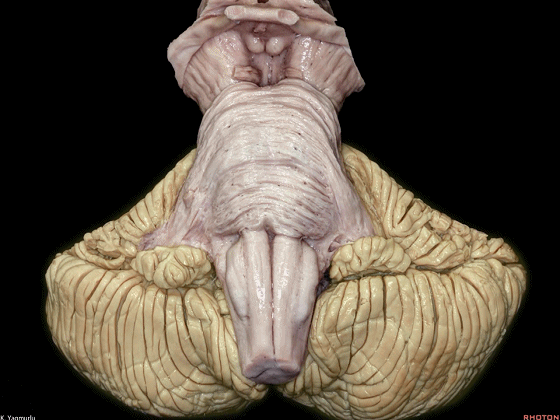
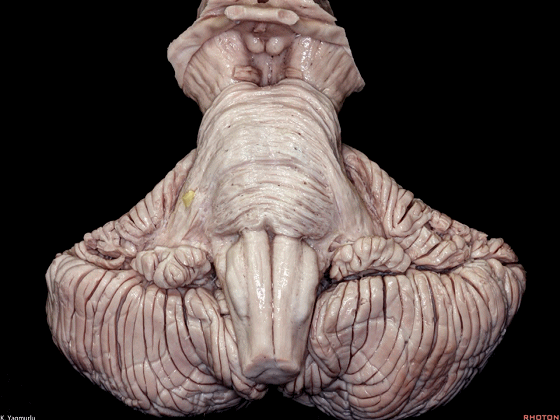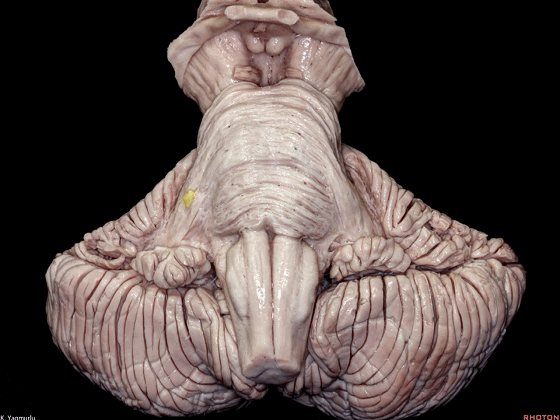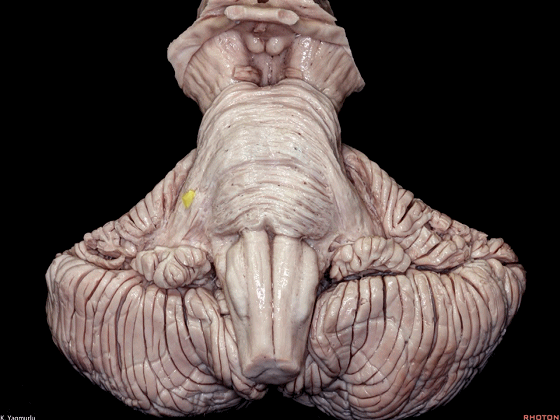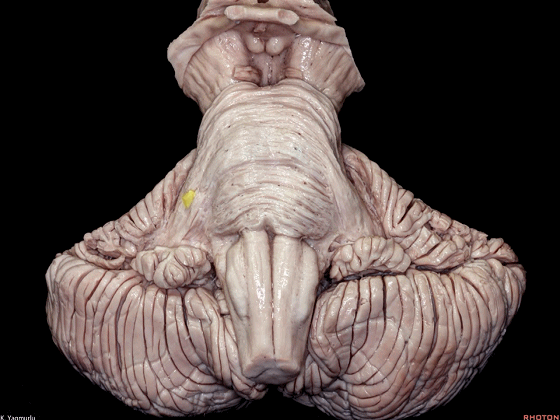
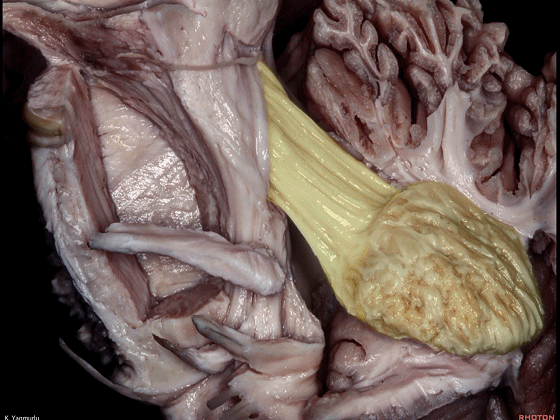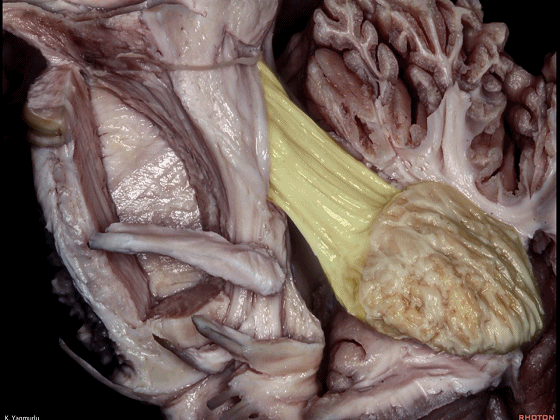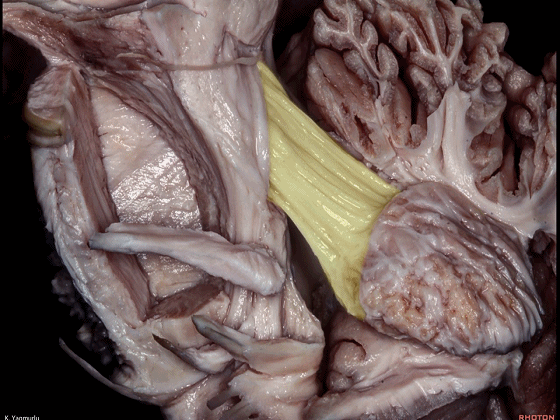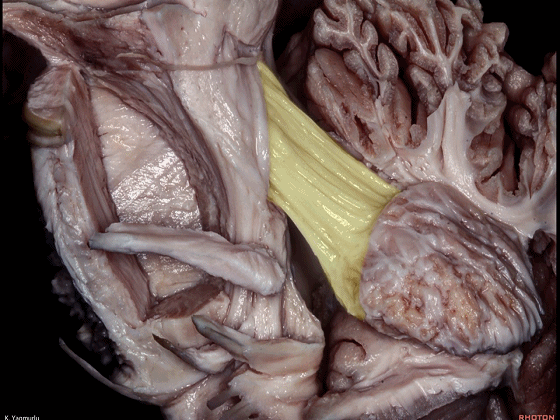
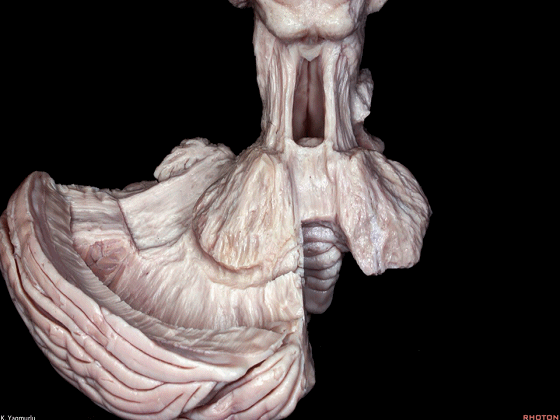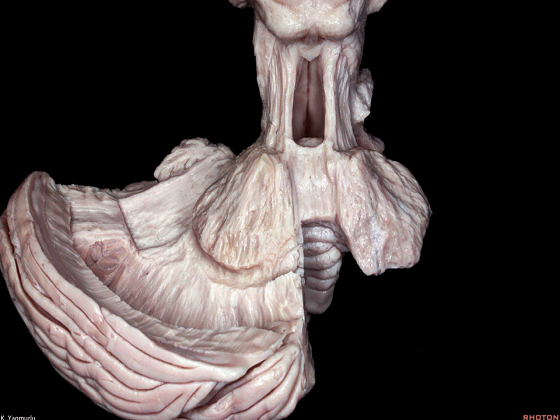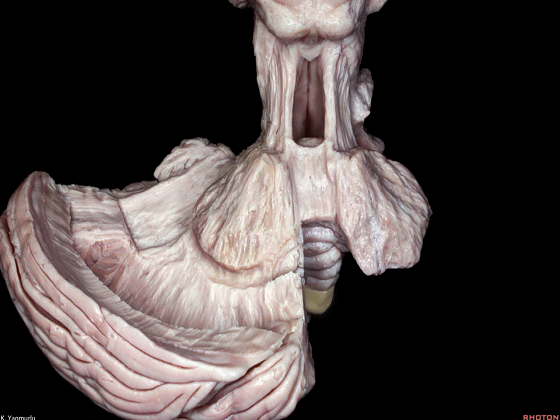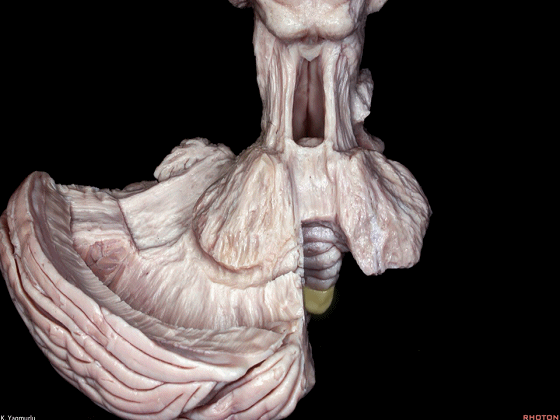
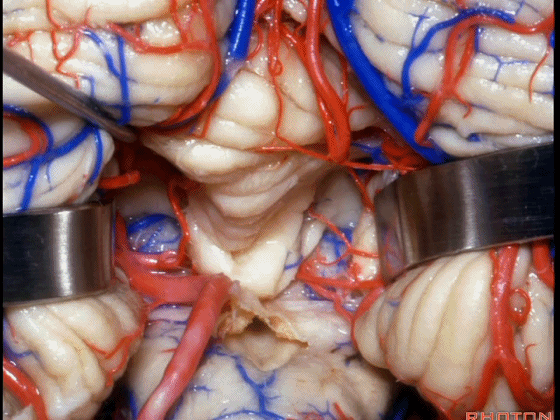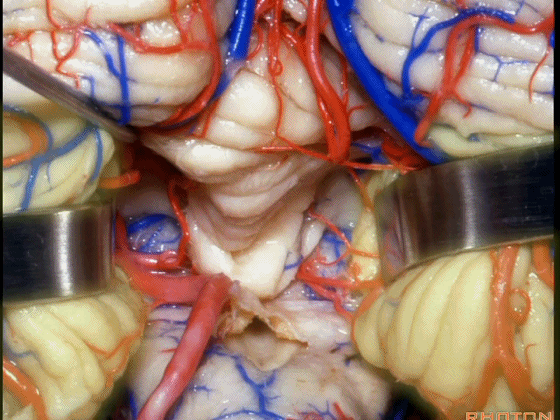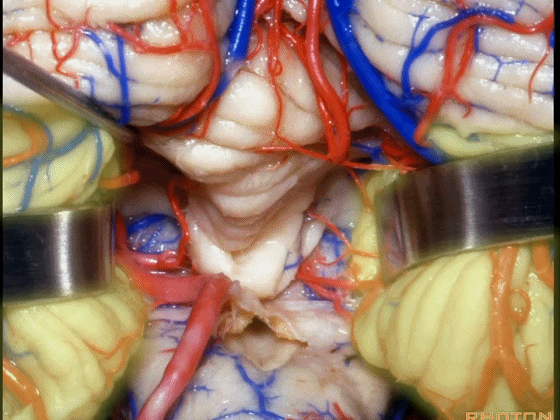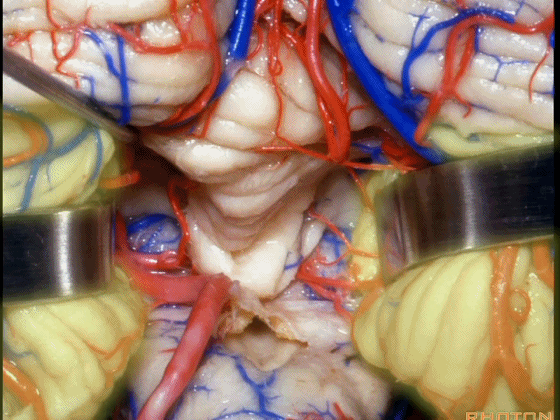
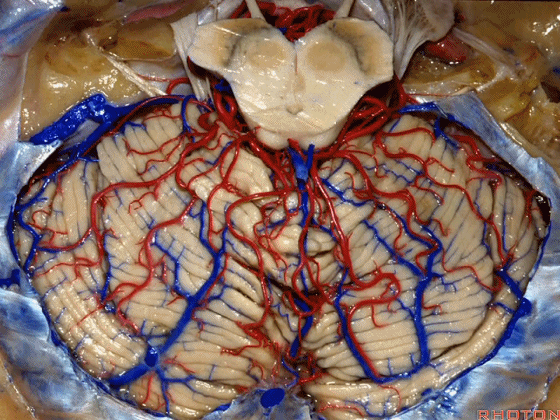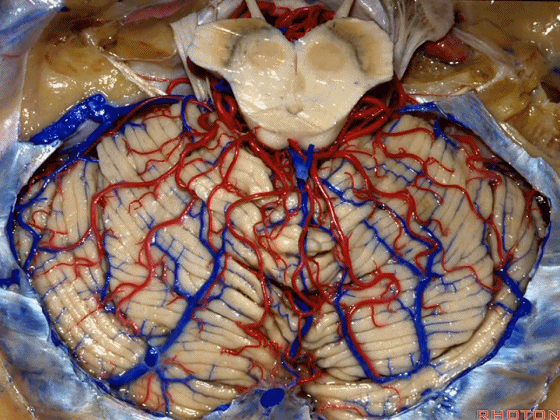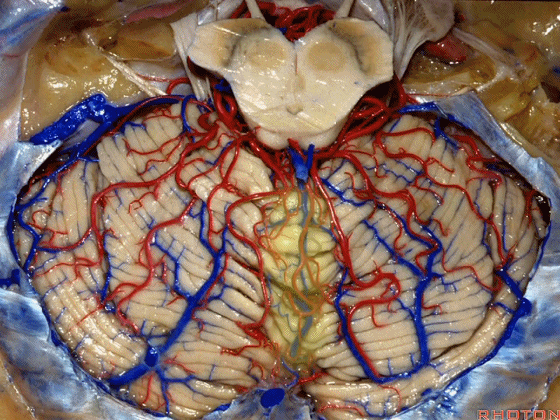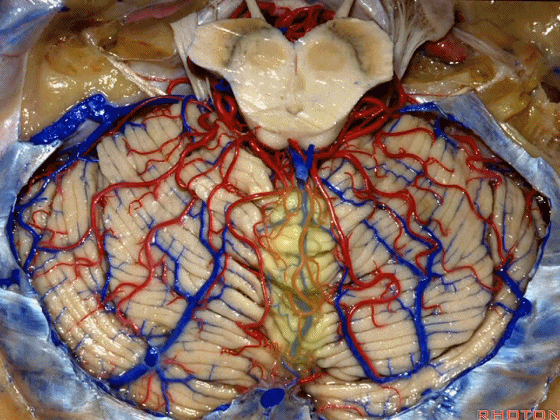
▼今天我们讨论幕下解剖,先来看小脑。
Let's go to the cerebellum first.
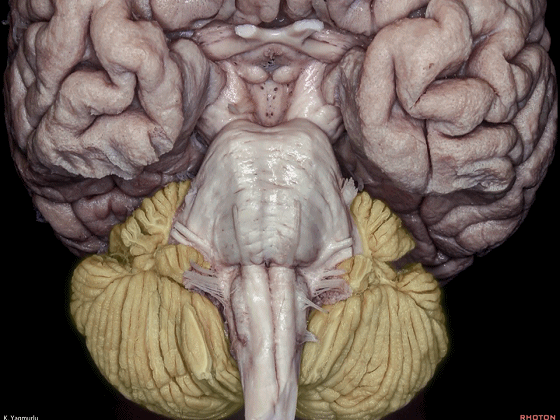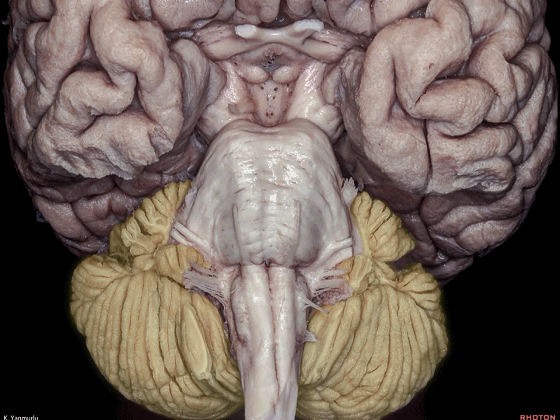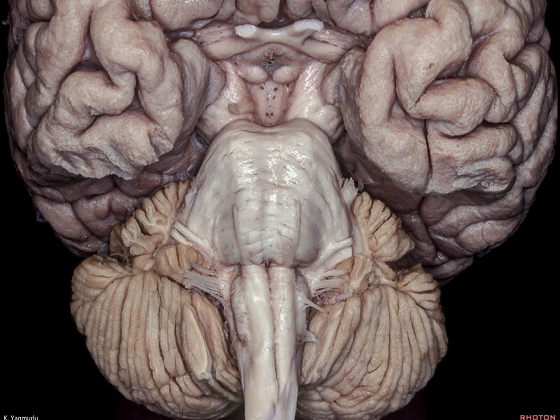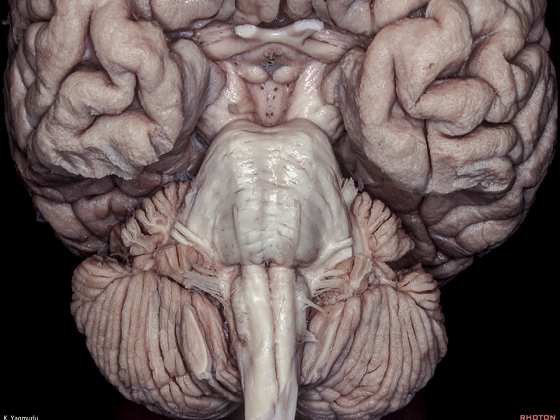
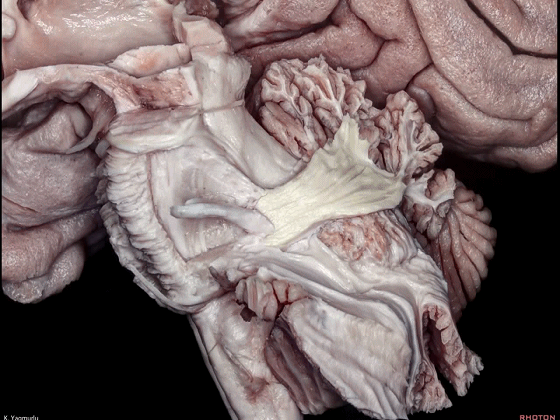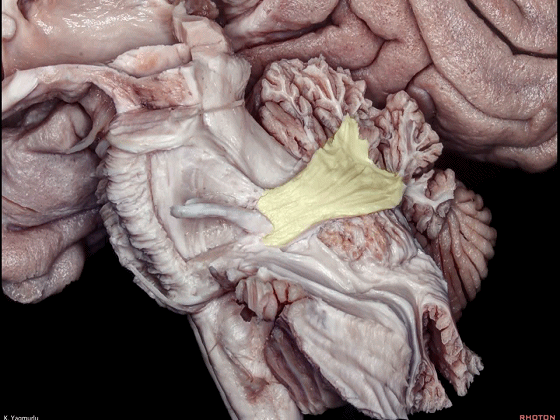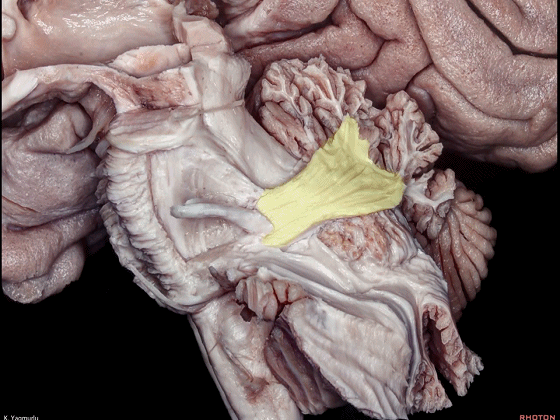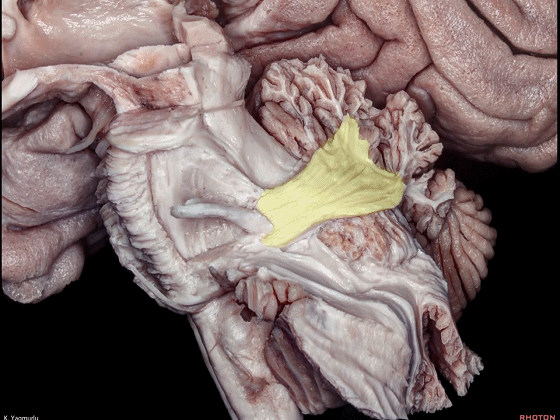
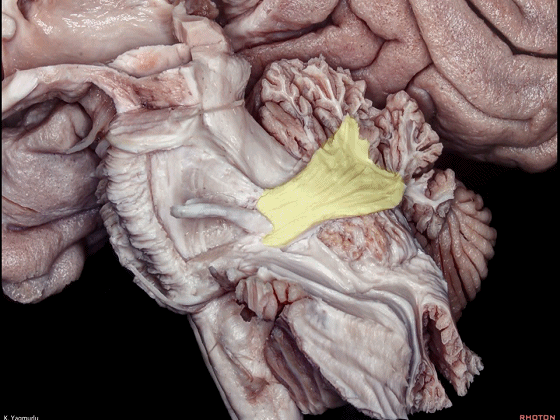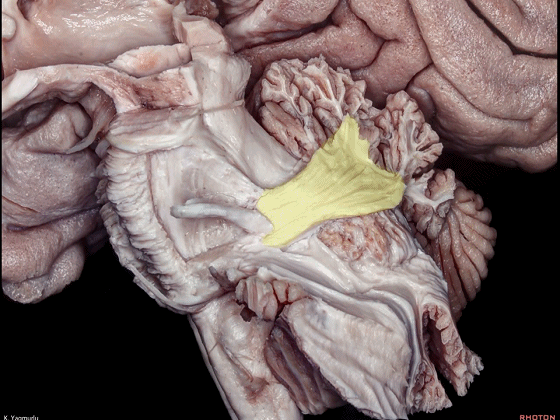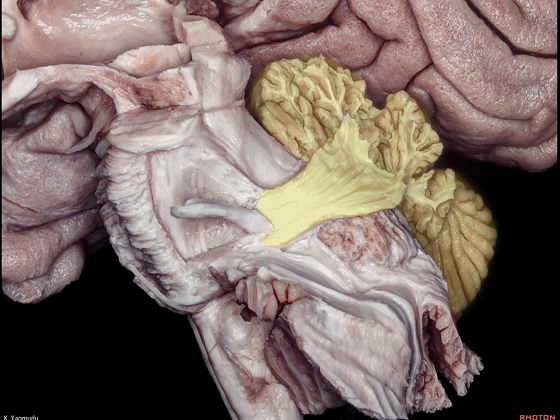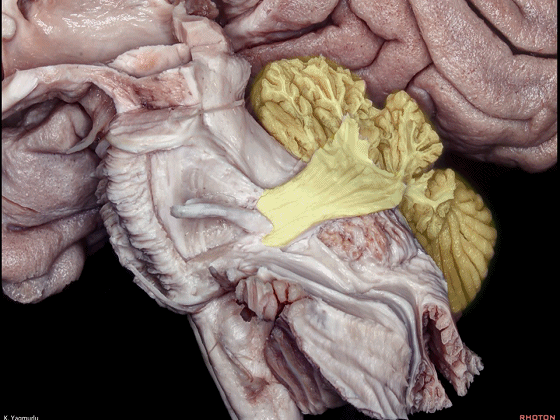
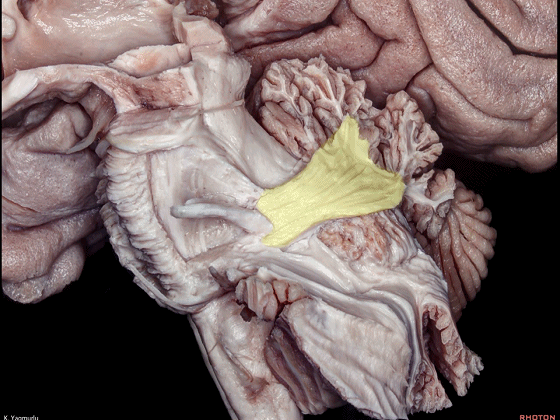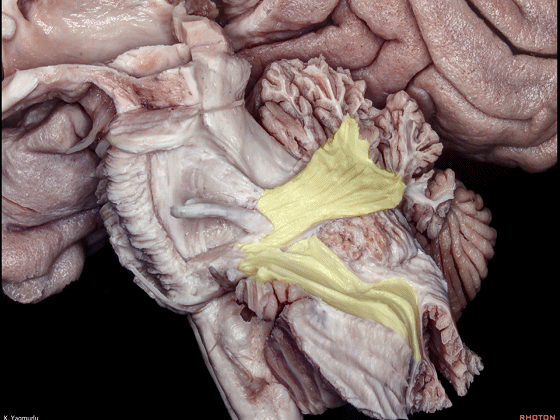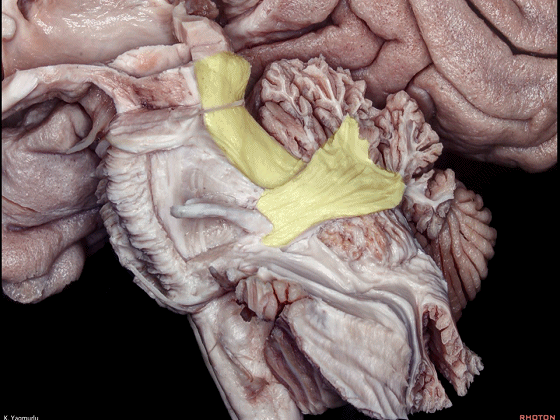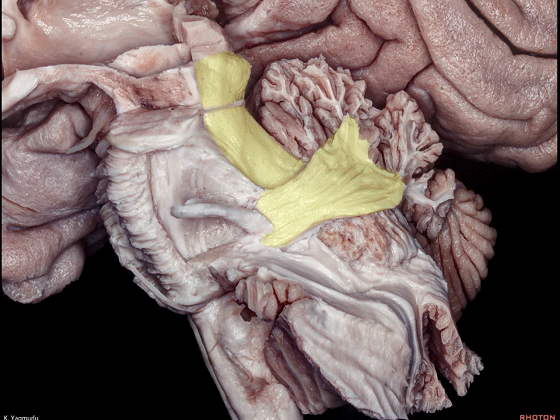
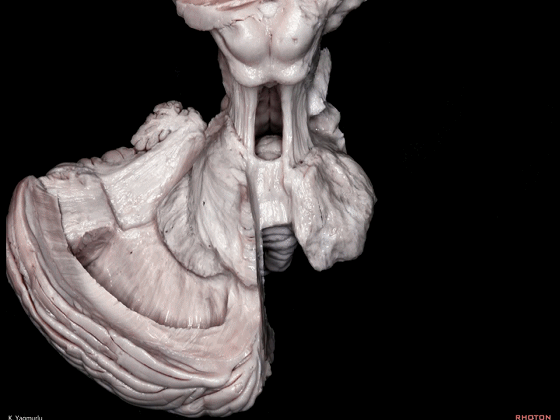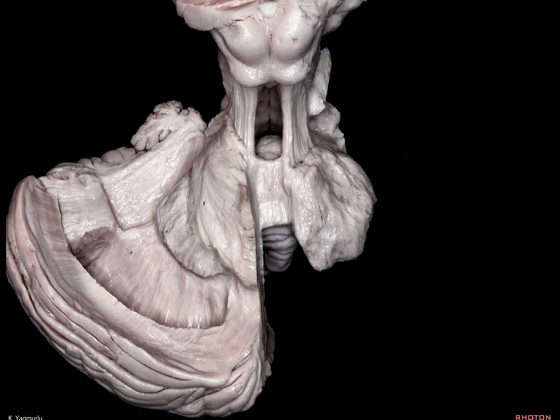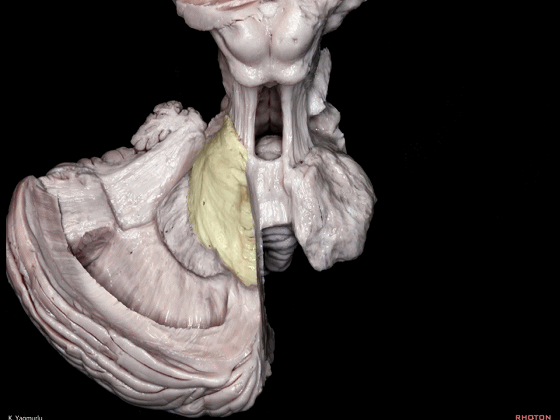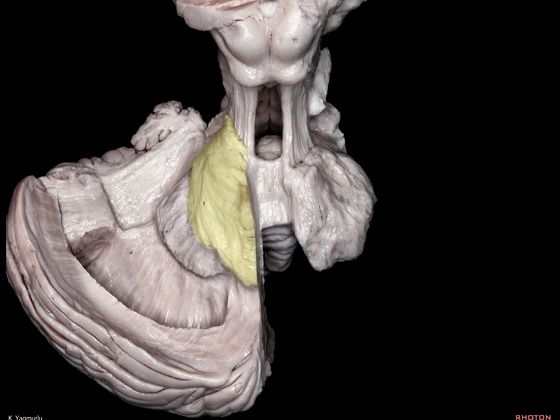
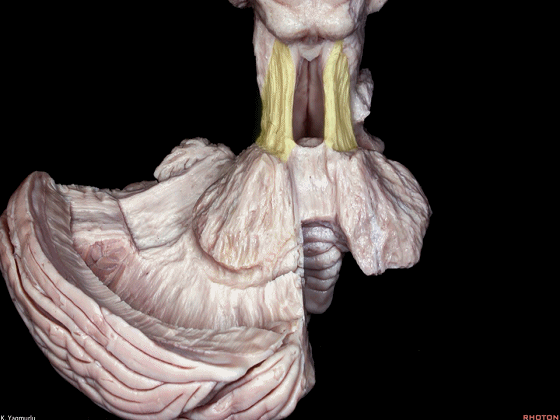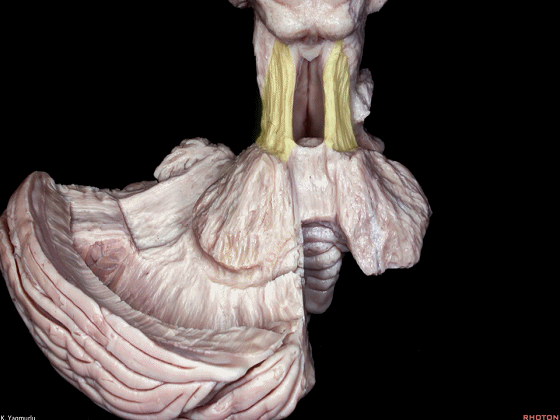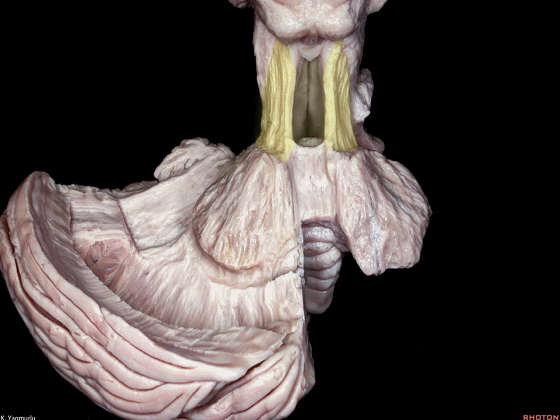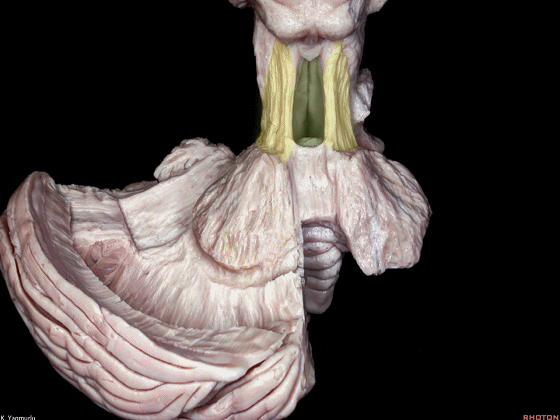
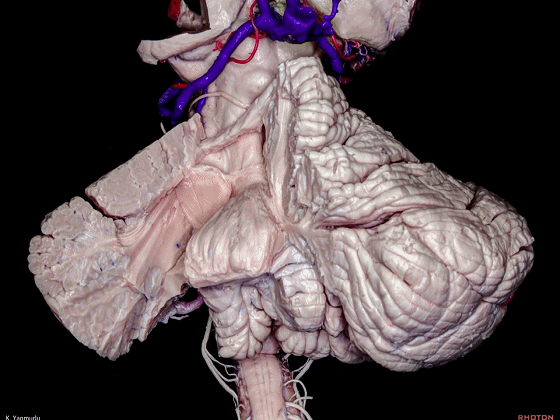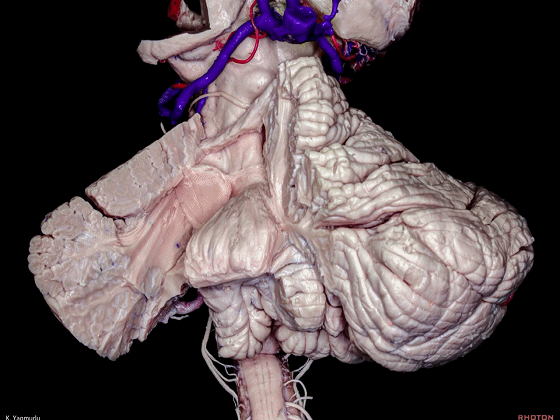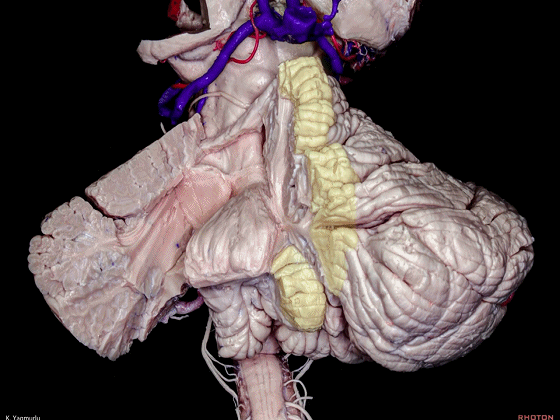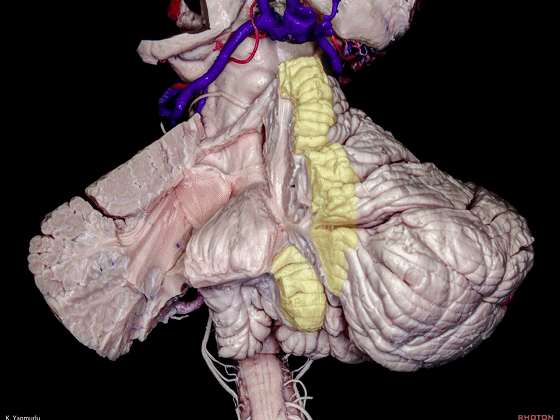
▼小脑的白质包括三组小脑脚:小脑上脚、小脑中脚、小脑下脚。
下图示小脑上脚。
The cerebellar white matter is formed by three cerebellar peduncles: superior,middle, and inferior.
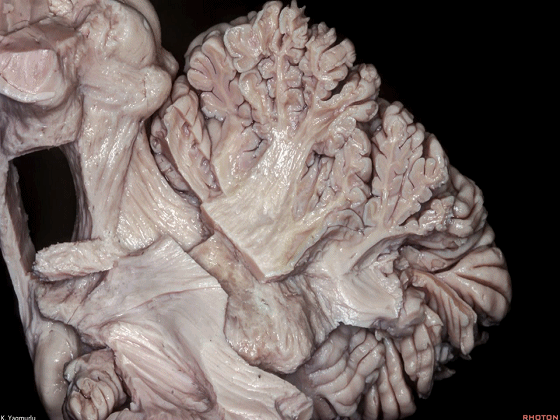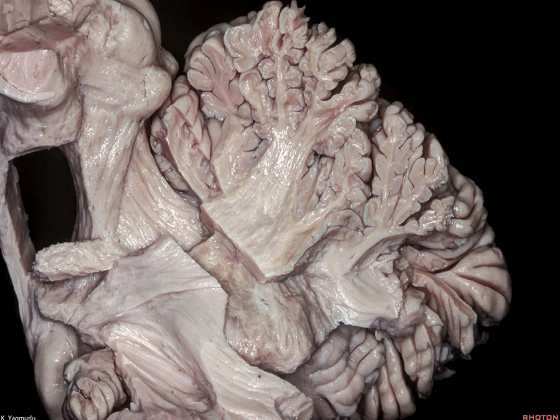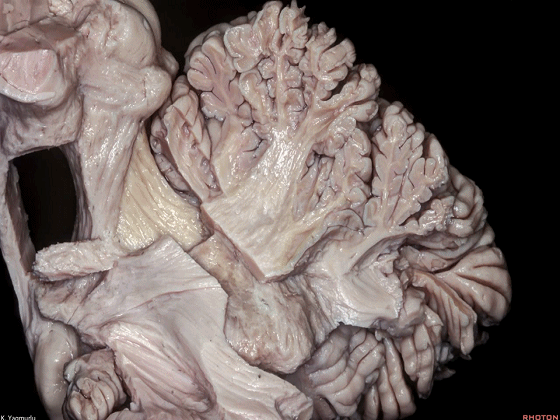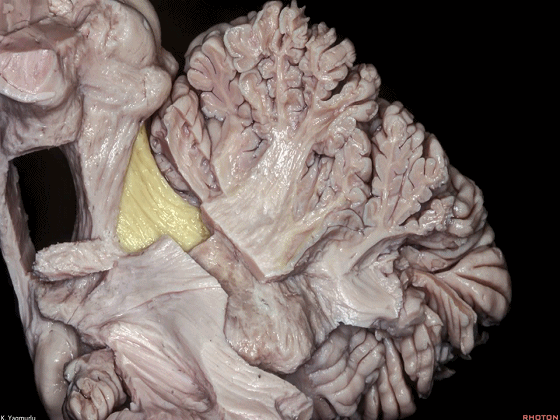
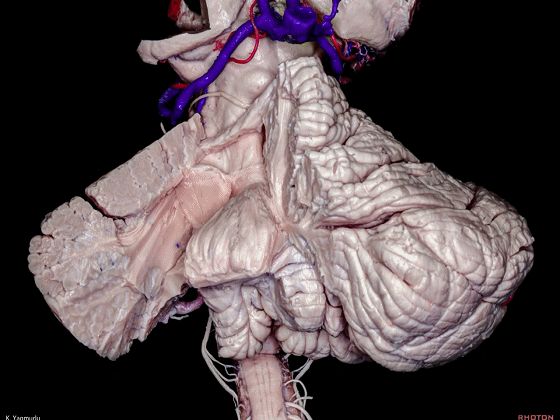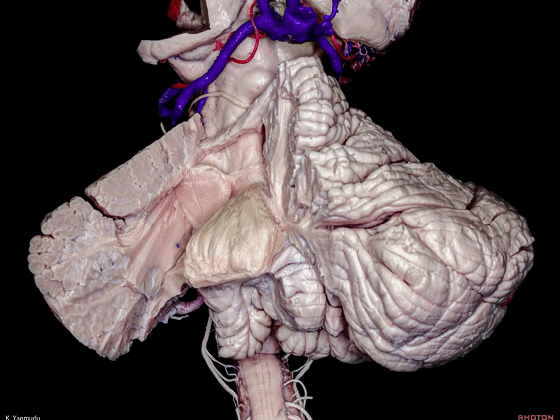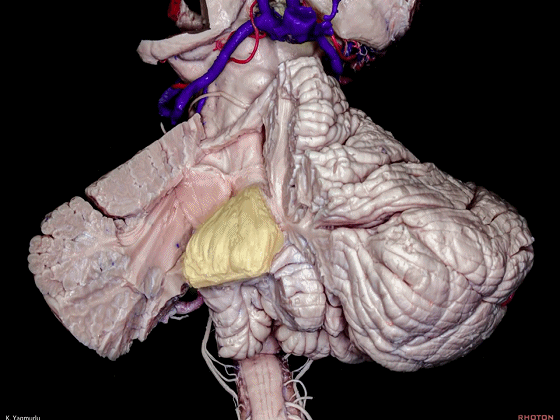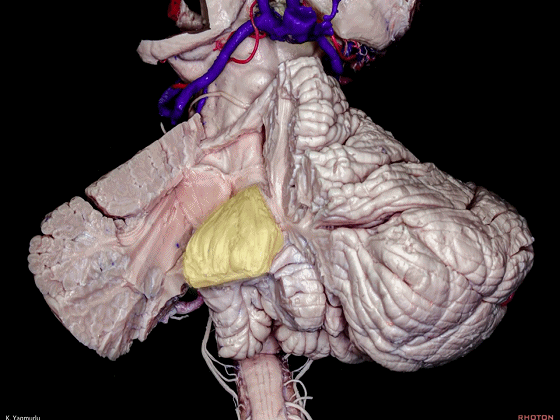
▼这是小脑中脚。
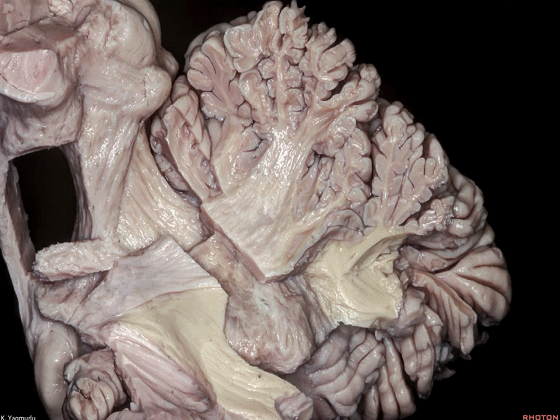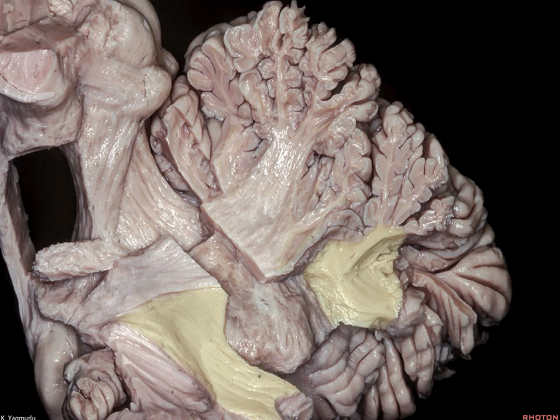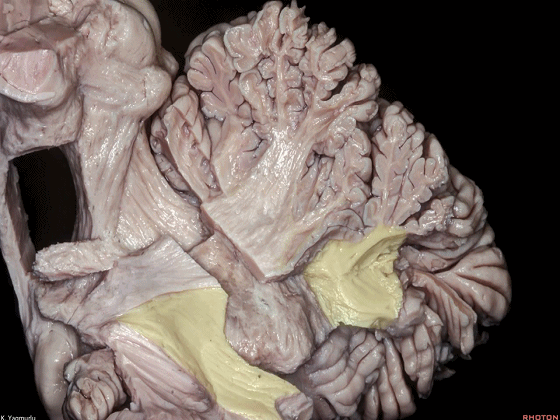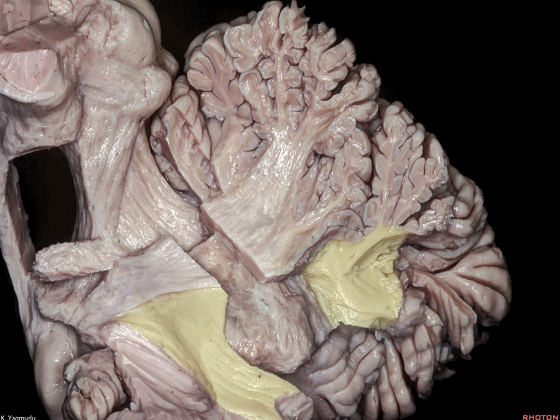
▼这是小脑下脚。
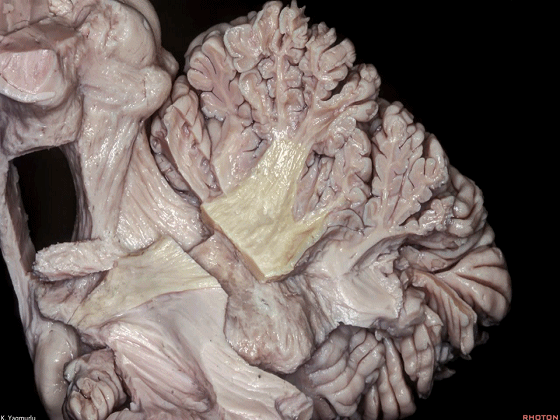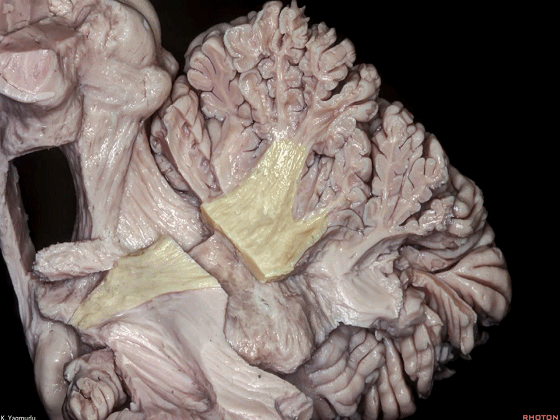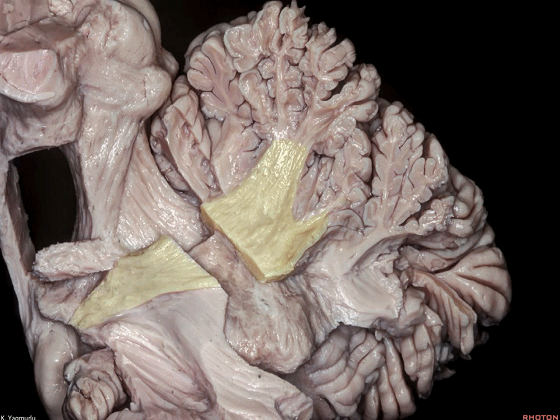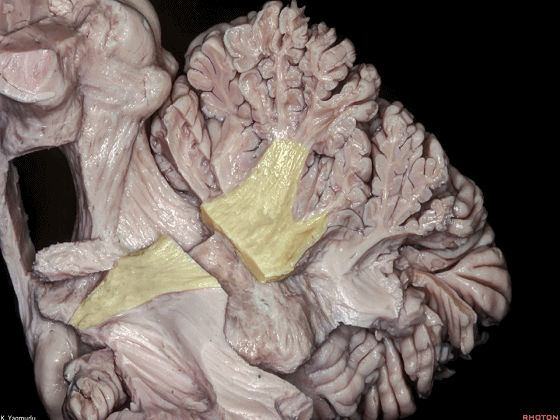
▼最大的是小脑中脚(下图)。
The largest one is the middle cerebellar peduncle,
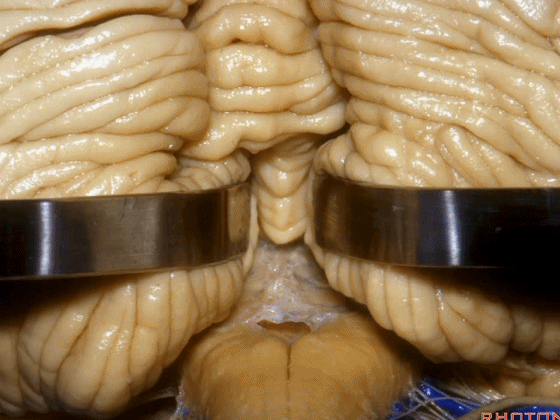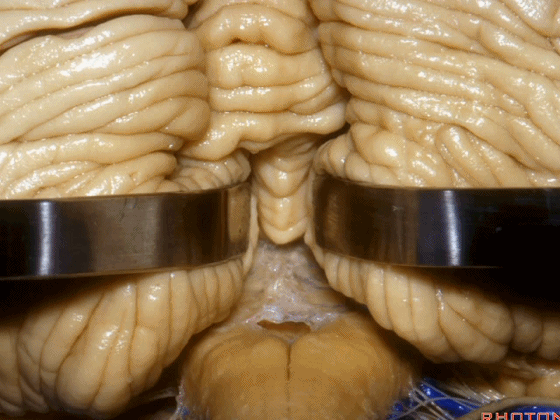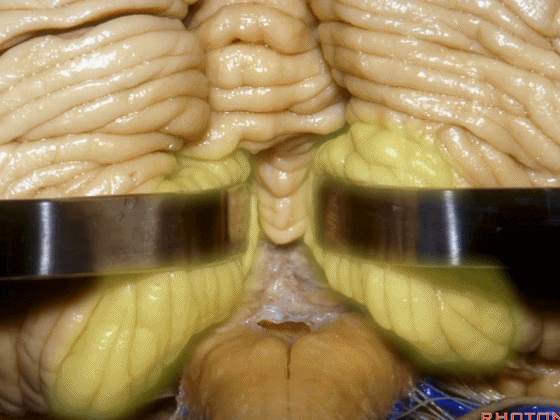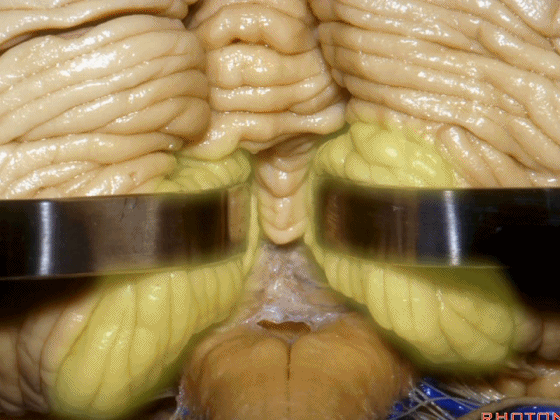
▼小脑中脚连接着小脑与脑桥。下图示小脑。
which connects the cerebellum with the pons.
▼下图示脑桥。

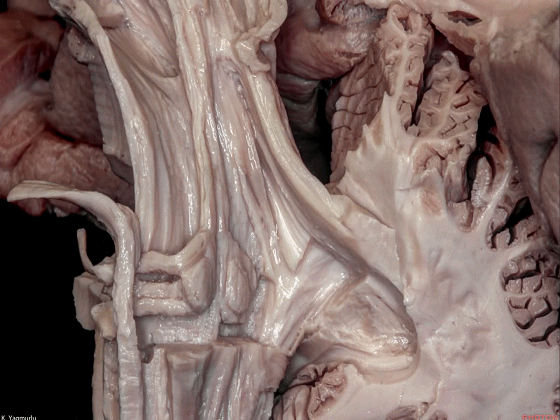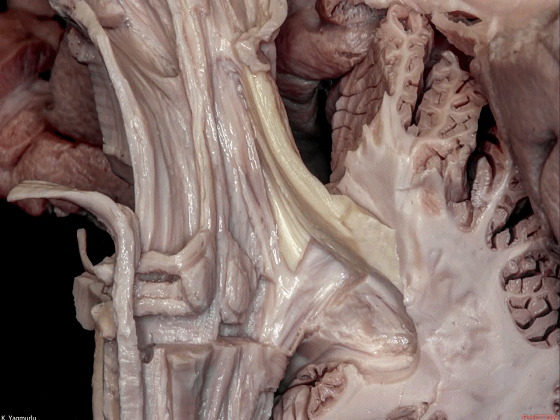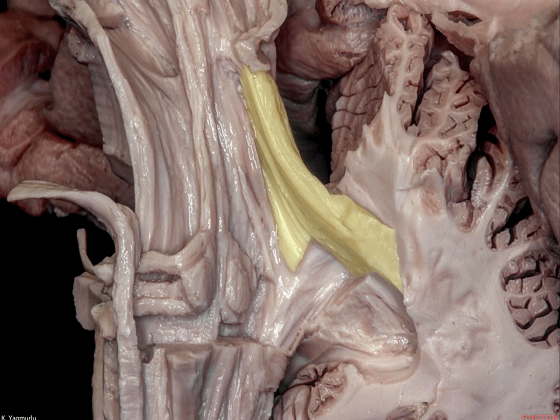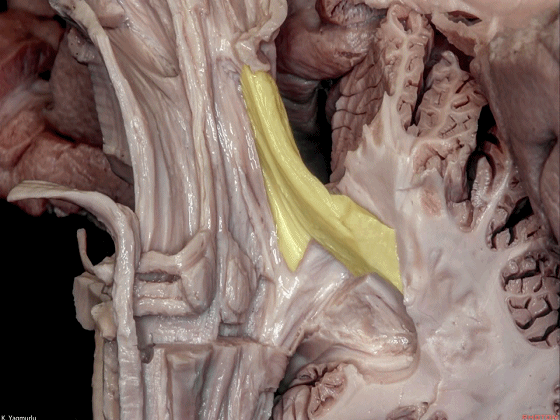
▼桥横纤维(下图)相聚集而构成小脑中脚。
The transverse pontine fibers collect together to form the middle cerebellar peduncle at the level of the trigeminal nerve.
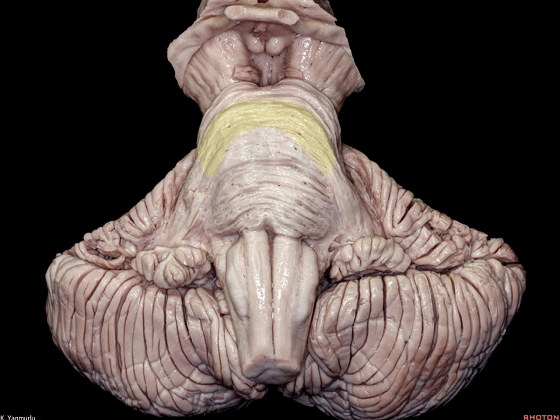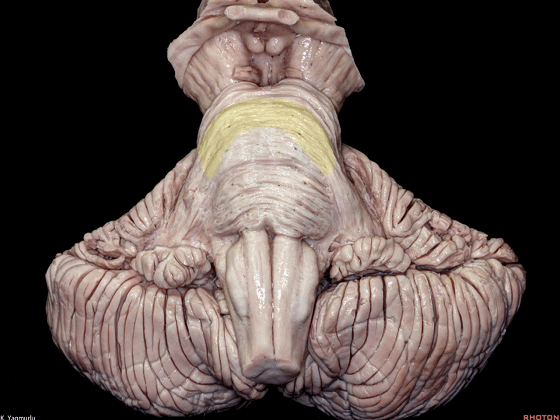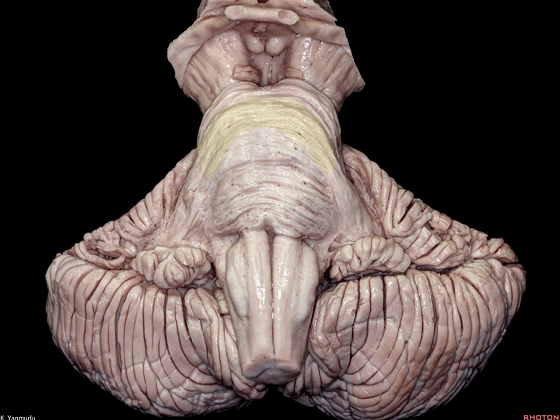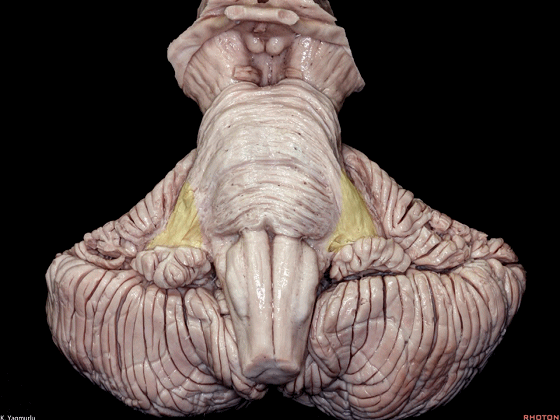
▼其层面恰同三叉神经(下图)。
▼小脑下脚(下图)连接小脑与脊髓。
The inferior cerebellar peduncle, which is a connection between the cerebellum and spinal cord,
▼下图示小脑。
▼小脑下脚穿行于小脑上脚(下图)和小脑中脚(下图)之间。
损伤小脑下脚和小脑中脚 可导致同侧共济失调。
The inferior cerebellar peduncle travels between the middle and superior cerebellar peduncles. Damage to the inferior and middle cerebellar peduncles may result in ipsilateral ataxia.
▼这是后面观。下图示小脑下脚。
This is a posterior view. The inferior cerebellar peduncle,
▼小脑下脚到达小脑蚓部(下图),途中越过齿状核上方。
The inferior cerebellar peduncle,reaches the cerebellar vermis by passing above the dentate nucleus.
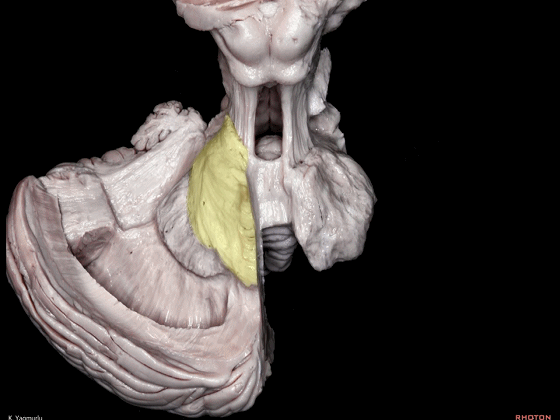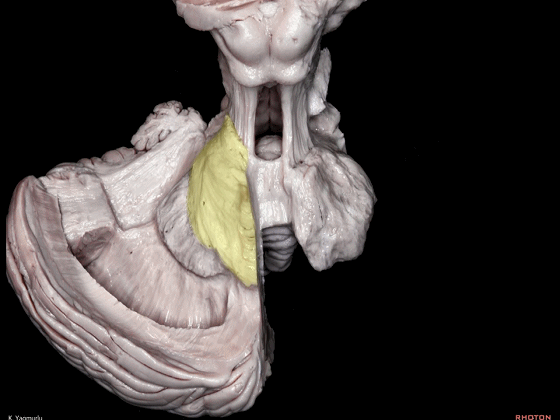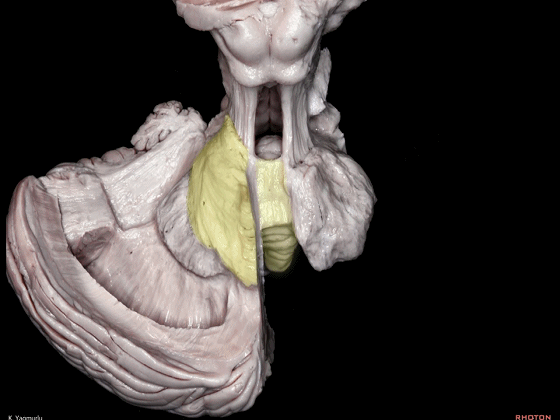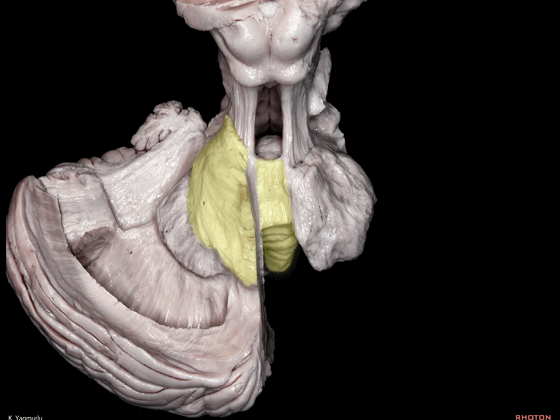
▼下图示齿状核。
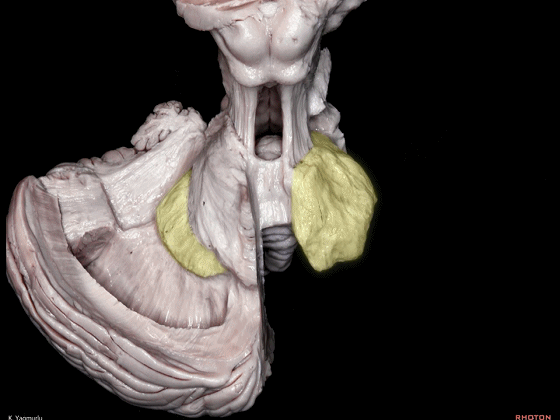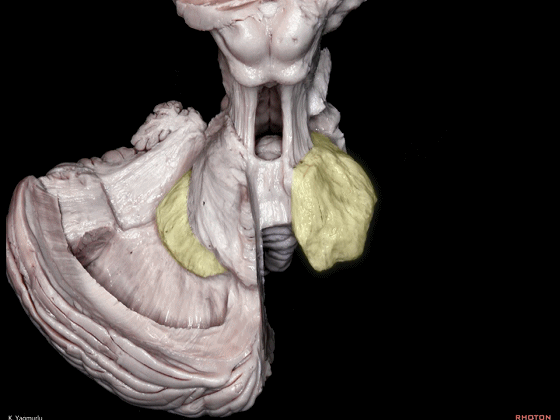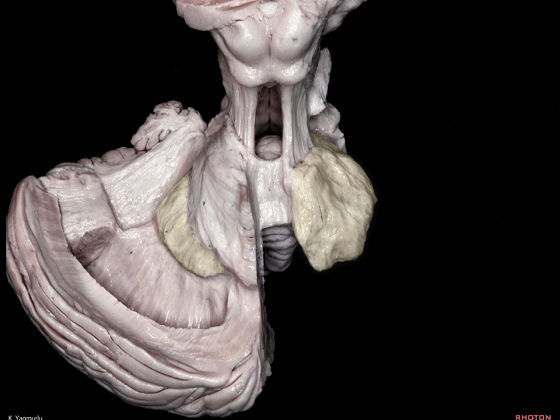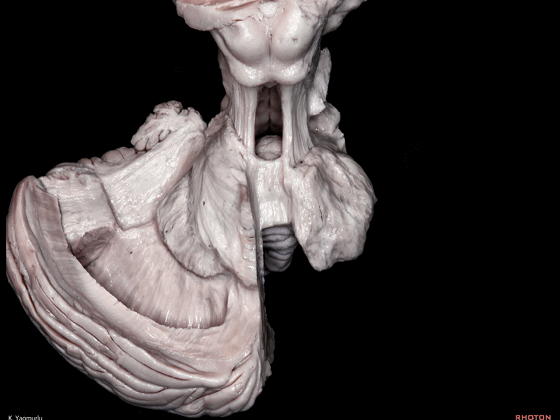
▼最后来看小脑上脚(下图),其连接着小脑与丘脑。
损伤小脑上脚可导致对侧的小脑性共济失调及震颤。
Finally, the superior cerebellar peduncle, the connection between the cerebellum and thalamus,Damage to the superior cerebellar peduncle may cause contralateral cerebellar ataxia and tremor.
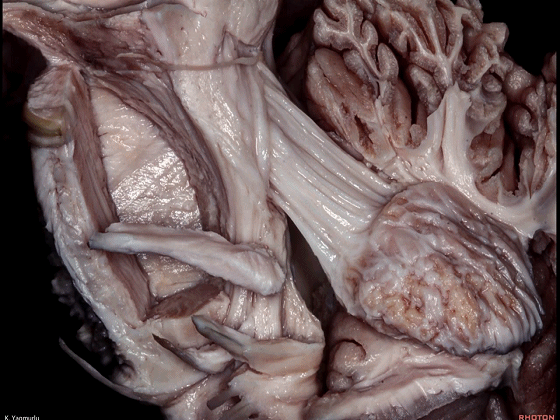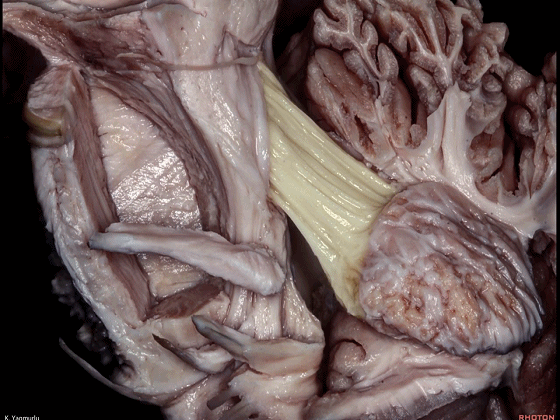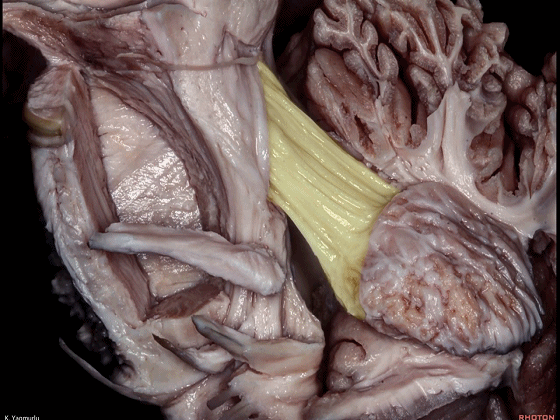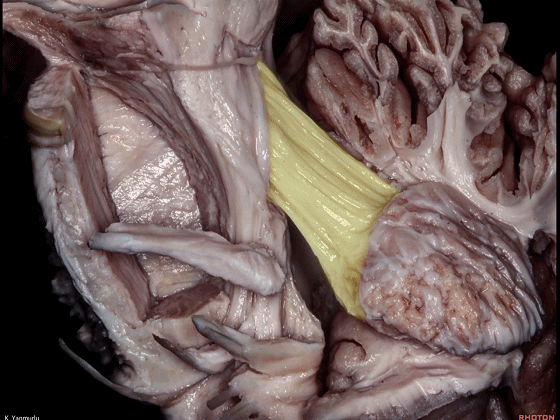
▼小脑上脚起自齿状核(下图),向上终于丘脑。
the superior cerebellar peduncle arises from the dentate nucleus and ascends up to the thalamus.
▼在中脑层面,小脑上脚的部分纤维 交叉后形成红核囊(下图)。
At the level of the midbrain,some fibers of the superior cerebellar peduncle decussate to form the capsule of the red nucleus.
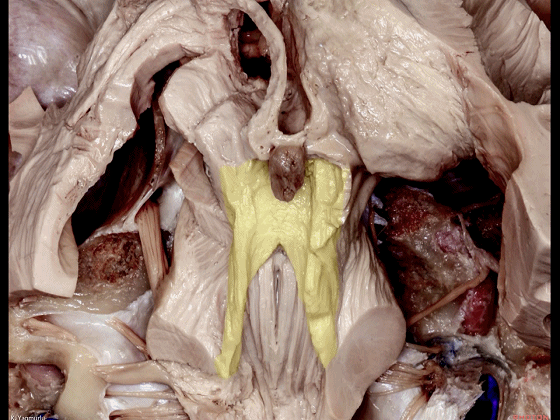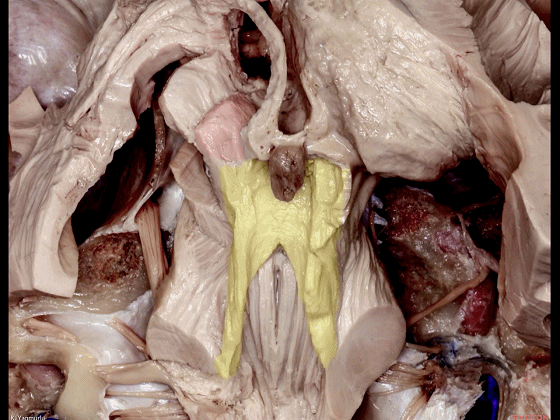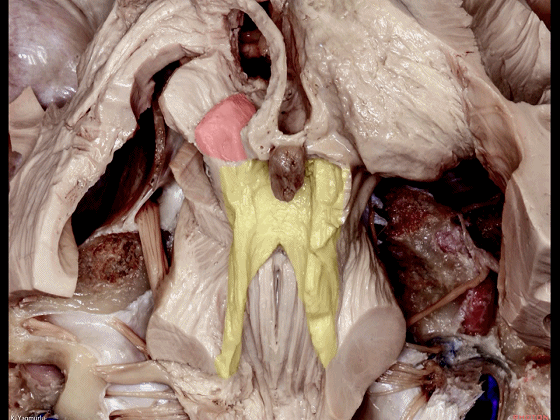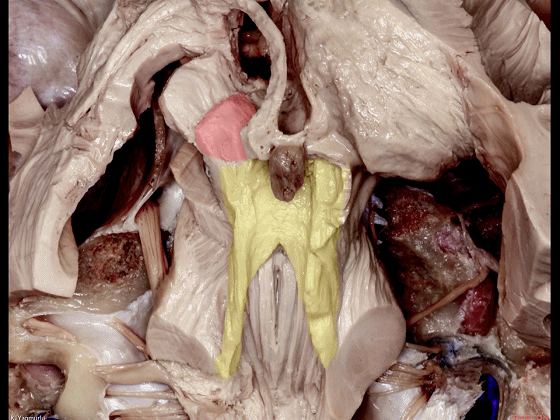
▼随后止于丘脑(下图)。
before reaching the thalamus.
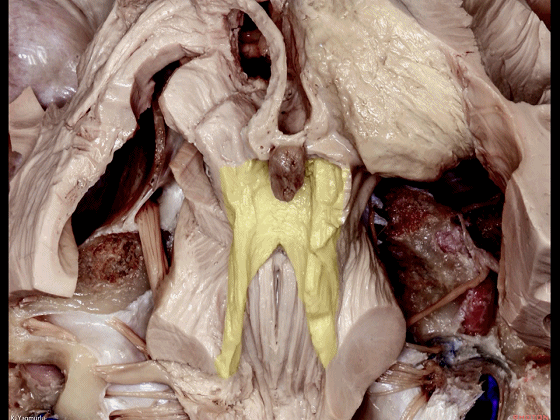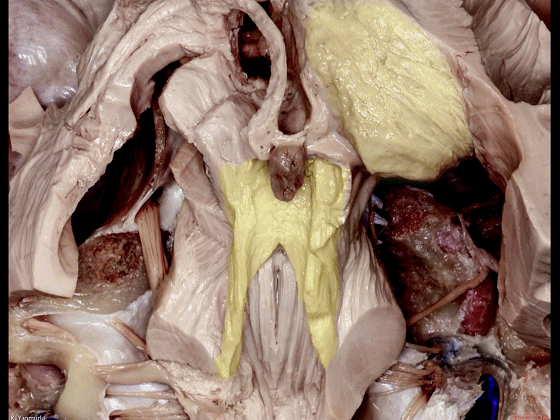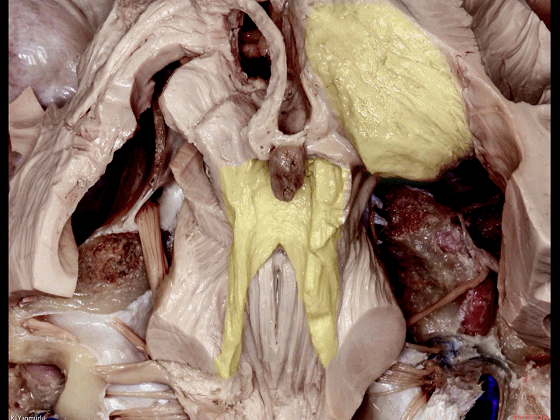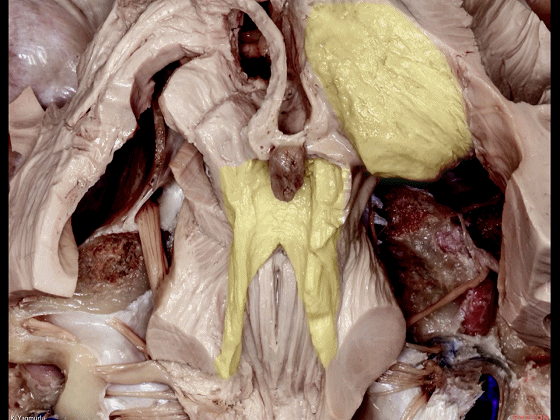
▼小脑上脚构成第四脑室外侧壁的上半部。
The superior cerebellar peduncle forms the superior half of the lateral wall of the 4th ventricle.
▼小脑下脚构成第四脑室外侧壁的下半部。
and the inferior cerebellar peduncle forms the inferior half of the lateral wall of the 4th ventricle.
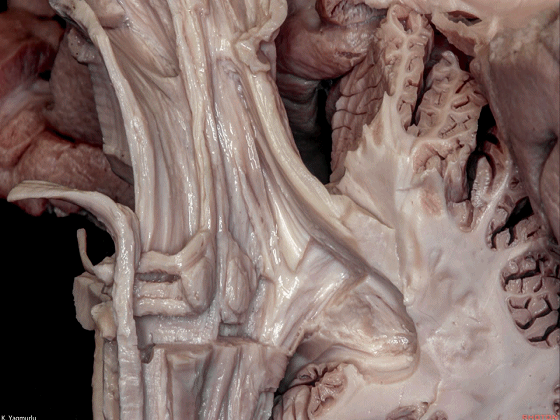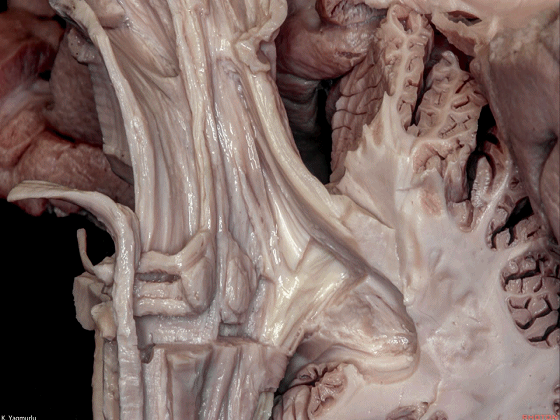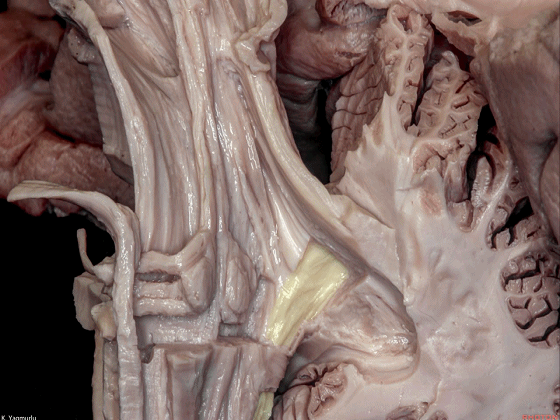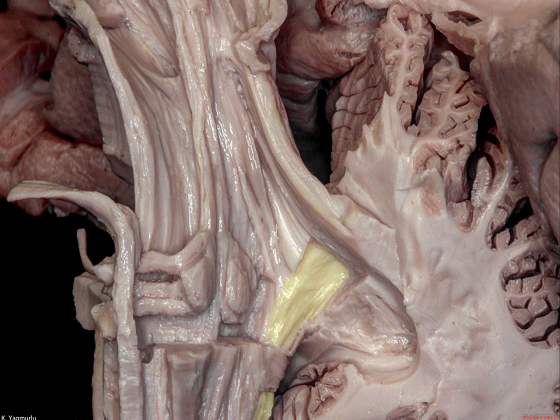
▼来看小脑的后面观。这是蚓垂。
We are looking at the cerebellum from posterior. The uvula.
▼这是蚓锥体。
pyramid.
▼这是小结。
nodule.
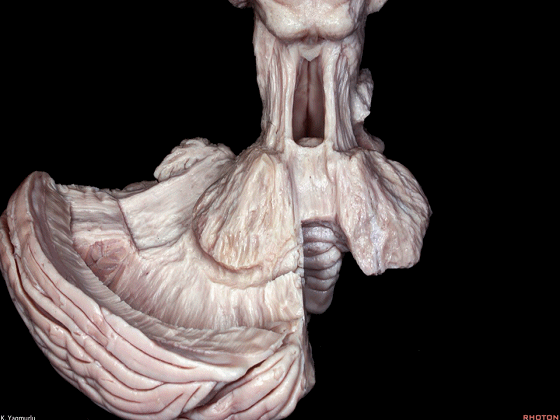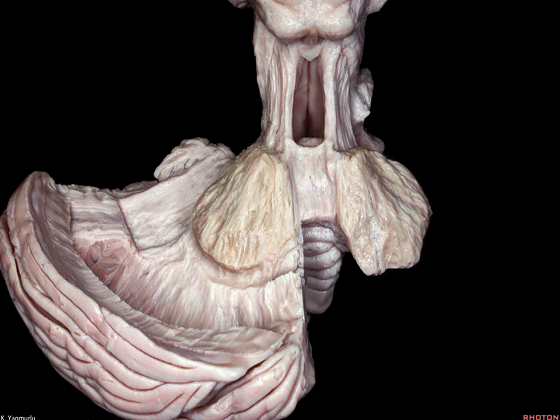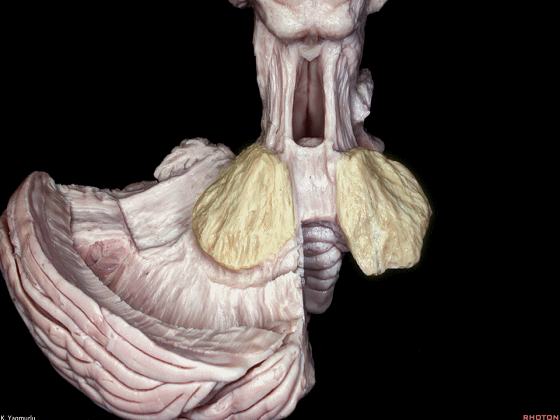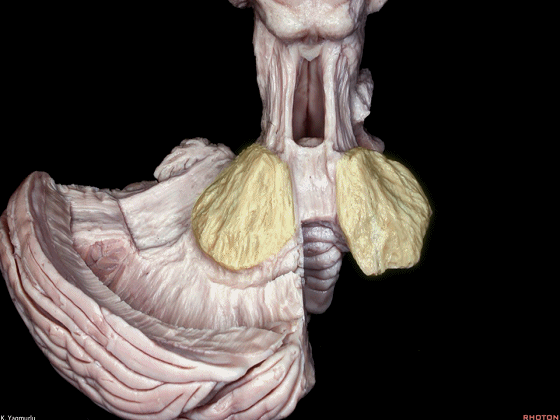
▼成对的齿状核(下图)在中线旁两侧。小脑的传出纤维主要起自齿状核。
whereas the paired dentate nuclei are located next to the midline on each side.The dentate nucleus is the major outflow of the cerebellum.
▼此处可见,第四脑室外侧壁的上半部由小脑上脚构成。
Here, one can see the forming of the lateral walls of the superior half of the 4th ventricle by the superior cerebellar peduncles.
▼这是后面观。损伤齿状核(下图),可导致平衡障碍,以及肢体自主运动时的意向性震颤。
The posterior view. When the dentate nucleus is damaged, equilibratory disturbances, often accompanied by intention tremor during voluntary movement of the extremities, can be seen.
▼经小脑蚓入路中,分离蚓部下半部可导致小脑性缄默症。下图示小脑蚓。
During the transvermian approach, splitting the inferior portion of the vermis may also play a role in cerebellar mutism.
▼这是 小脑蚓部的下半部。

▼齿状核(下图)位于小脑半球的上内侧部。
The dentate nucleus is located at the superomedial position in the cerebellar hemisphere.
![]()
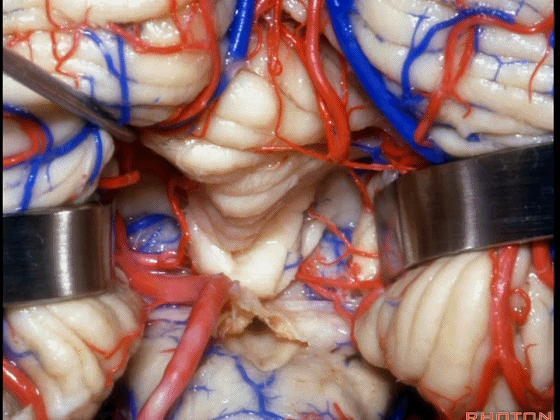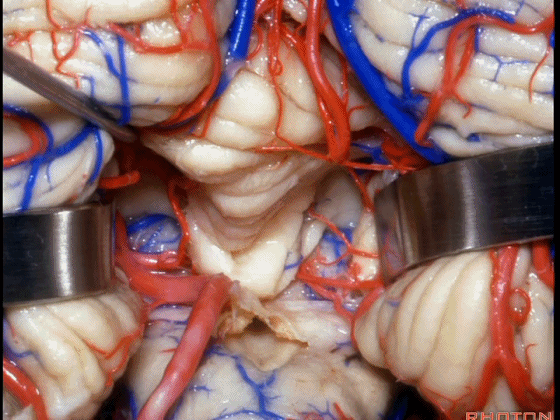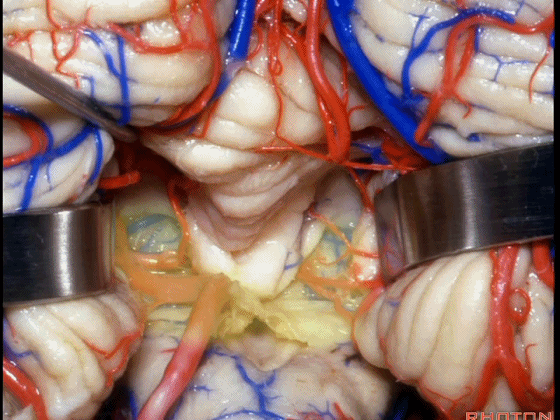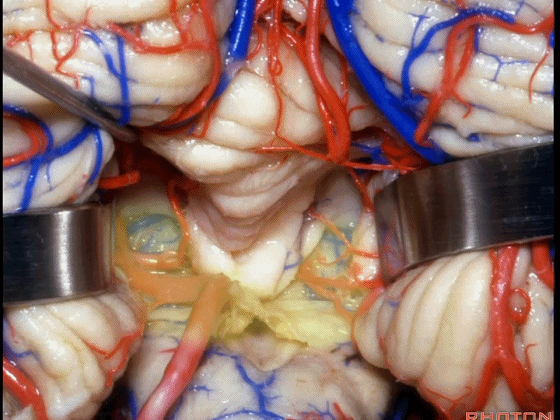
▼接下来我们开始讲解第四脑室。这是小脑蚓的小舌。它就像五官科医生让病人发“啊”声时看到的悬雍垂。
Well I just wanna talk a little bit about 4th ventricle. And, what subdivision of vermis is this?Uvula. It's like ENT, when you say "Ahh...".
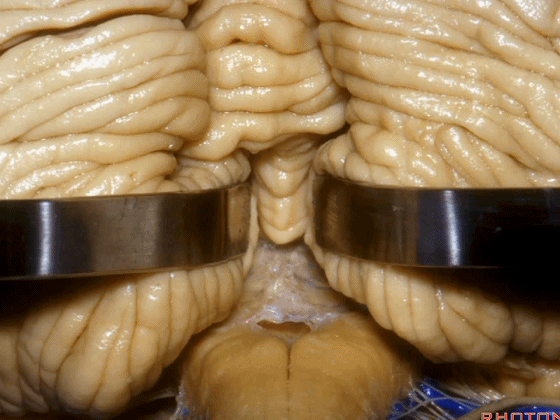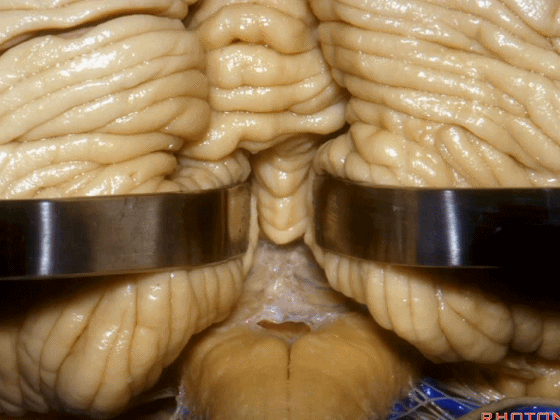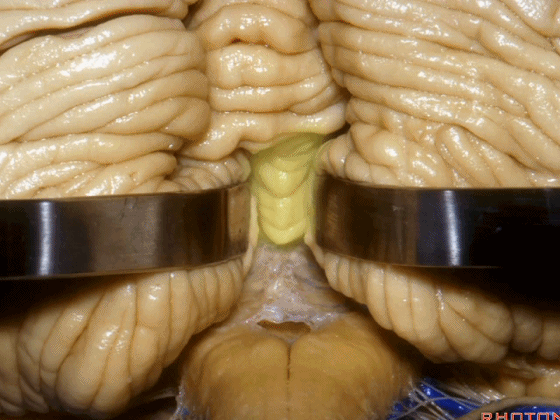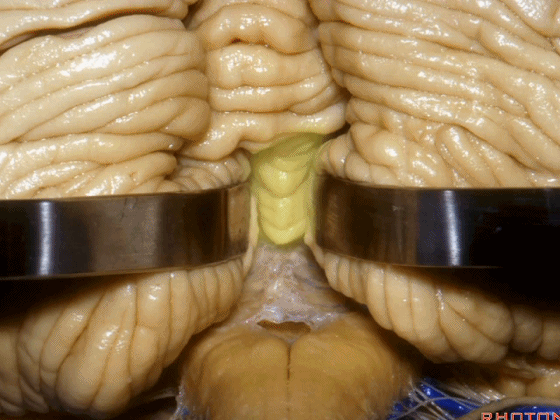
▼小舌位于两侧小脑扁桃体(下图)之间。
The uvula hangs down between the tonsils.
▼在过去,进入第四脑室的入路常需切开小脑蚓(下图),而这会造成缄默综合征,尤其在儿童及年轻患者中多见。
And in the past, when we went to 4th ventricle we split the vermis, but that can cause a mutism syndrome,especially in children and young people.
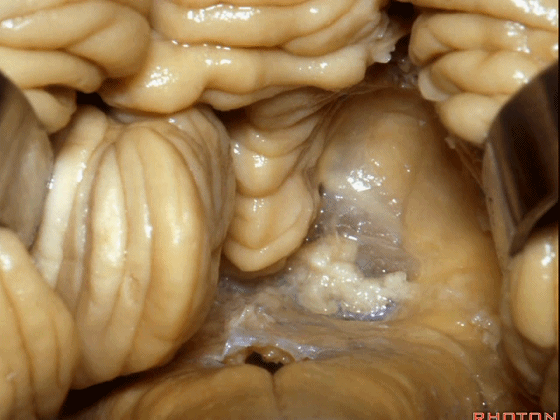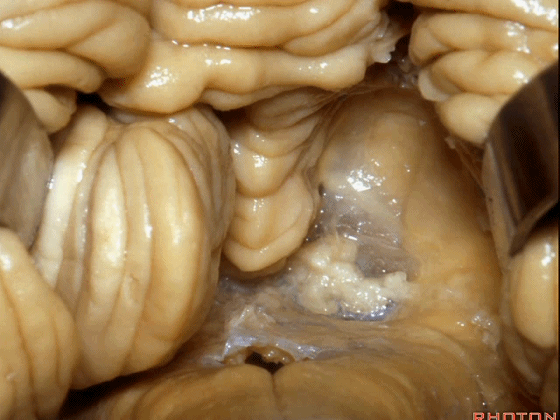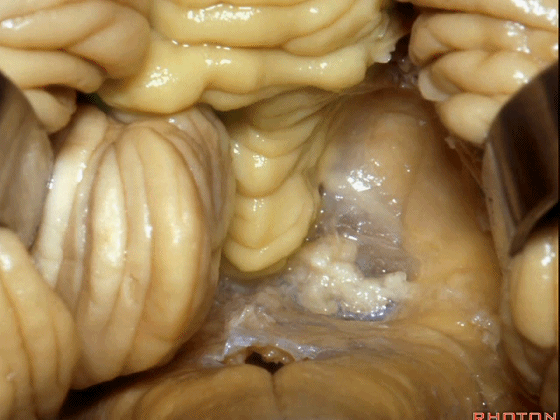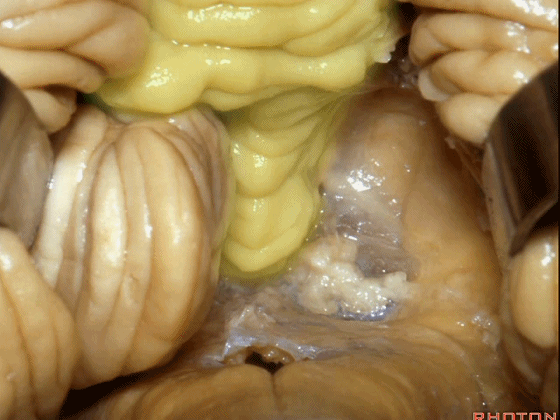
▼而我们发现,牵开小脑扁桃体(下图),即可见 第四脑室顶的下半部分由下髓帆和脉络膜组成。
And we found if we retract the tonsil, you see the inferior half of the 4th is made up of the inferior medullary velum and the tela choroidea.
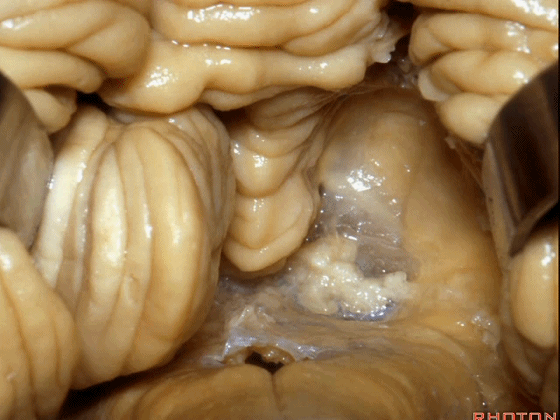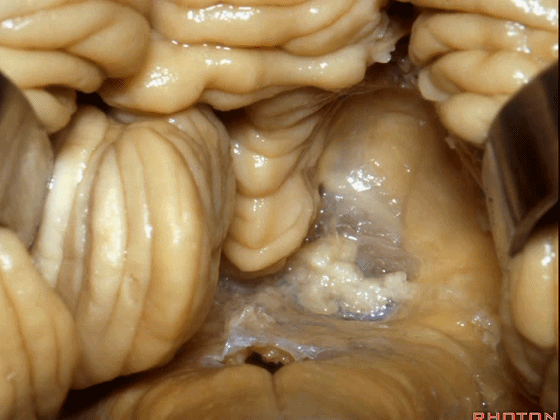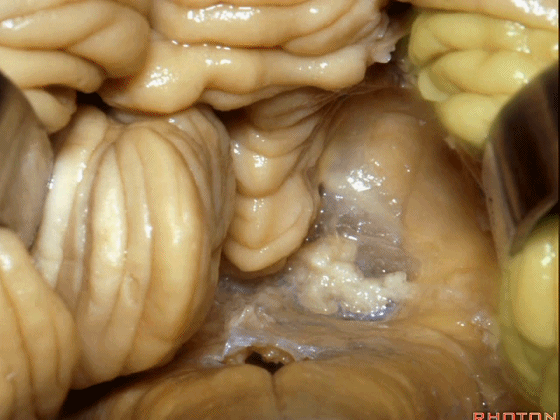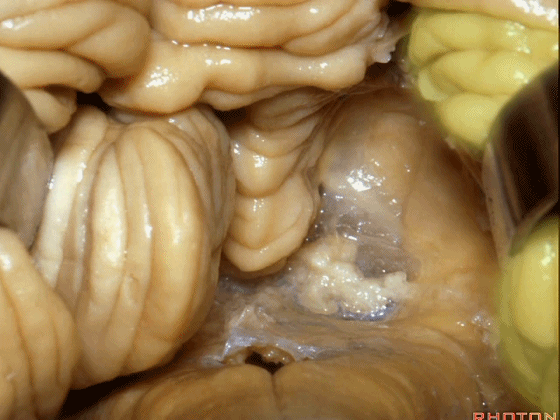
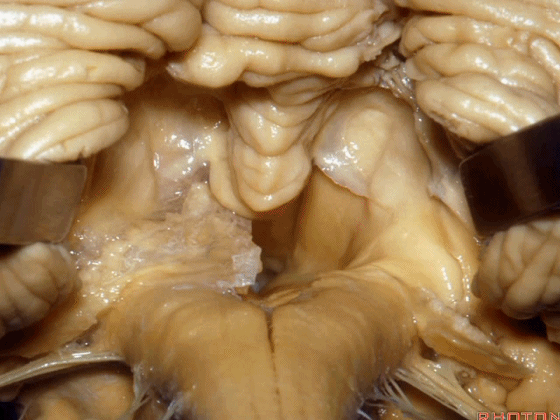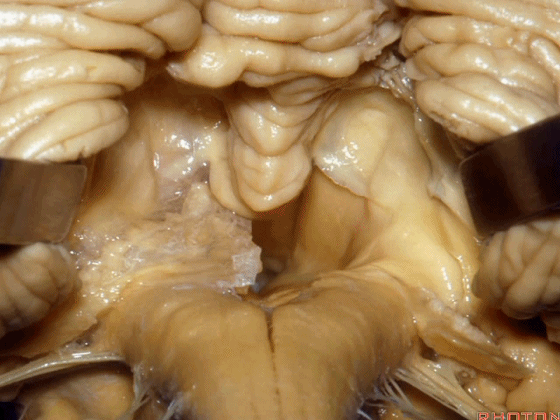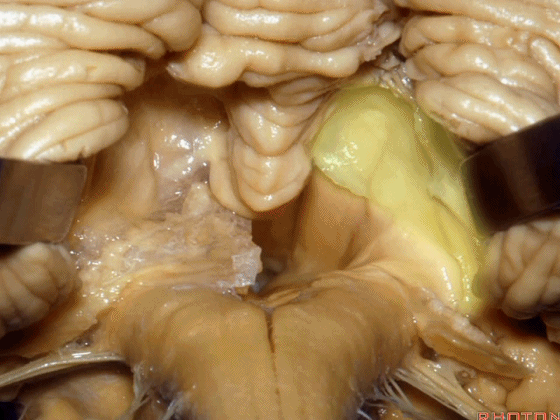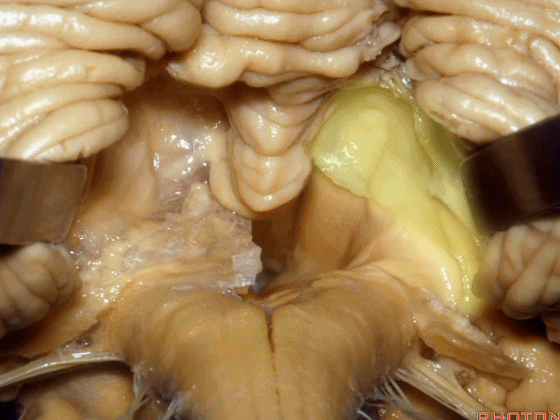
▼这是下髓帆,从小结延伸至绒球。
inferior medullary velum that sweeps from the nodule to the flocculus.
▼这是脉络膜。
tela choroidea.
▼ 脉络丛起源于此。
in which the choroidal plexus arises.
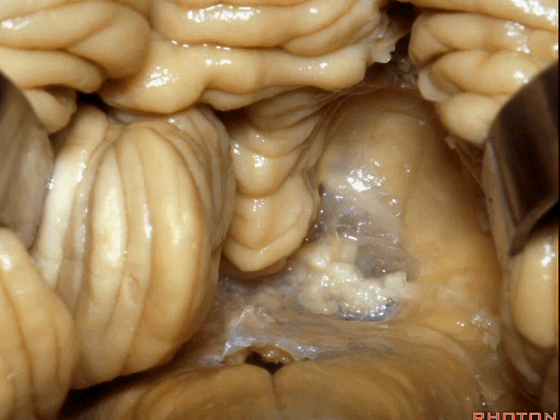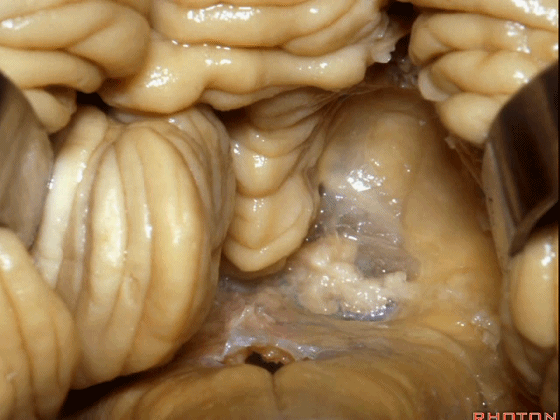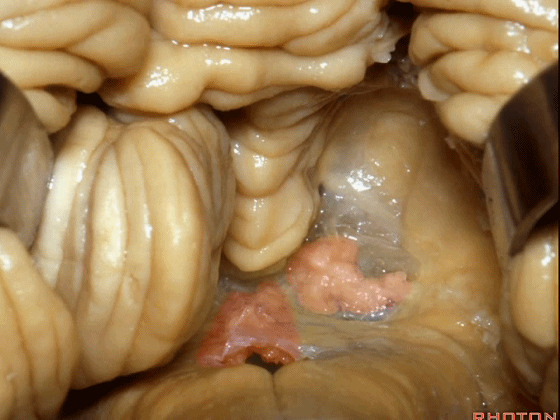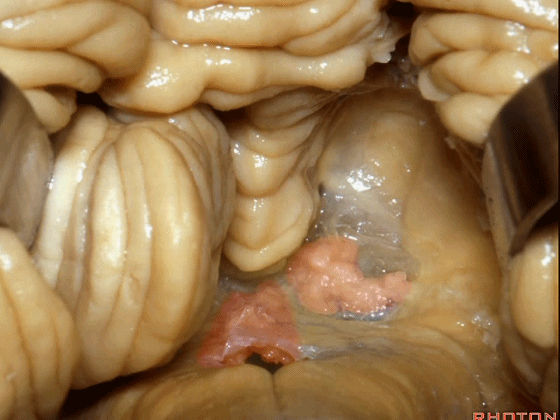
▼当我们打开脉络膜,我们可以一直暴露到中脑导水管(下图)。
And here we've opened the tela that forms the lower half of the roof of the 4th,and that gives a view all the way up to the aqueduct.

▼这是菲薄的下髓帆。
Here's the paper-thin velum.
▼下髓帆向外延伸至绒球。下图示绒球。
that sweeps lateral to attach to theflocculus.
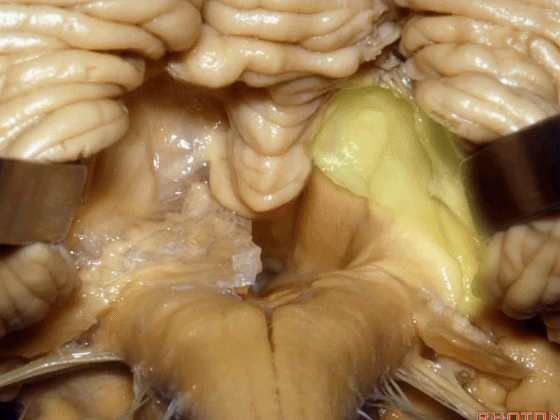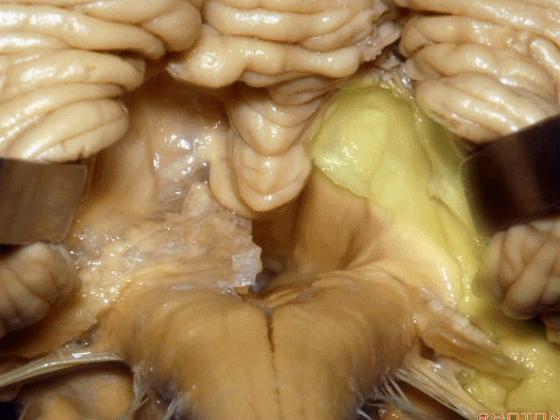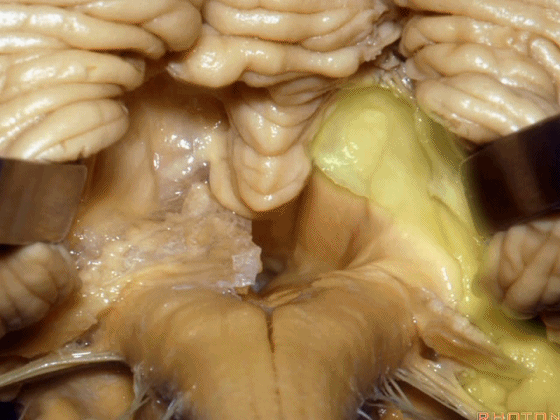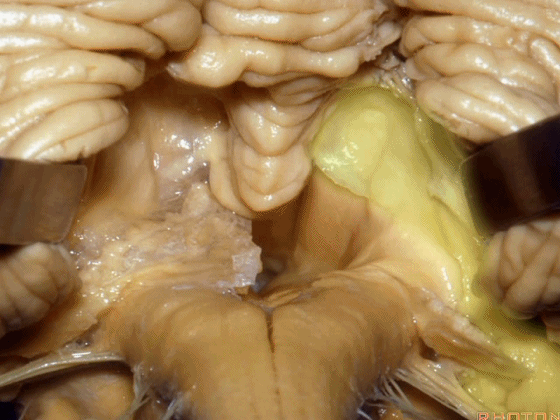
▼因此,对于第四脑室病变,我们不必切开小脑蚓(下图),避免缄默综合征。
So that, if we have a lesion in the 4th,we don't split the vermis.
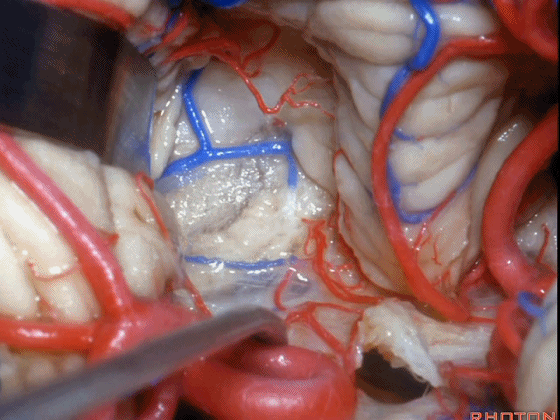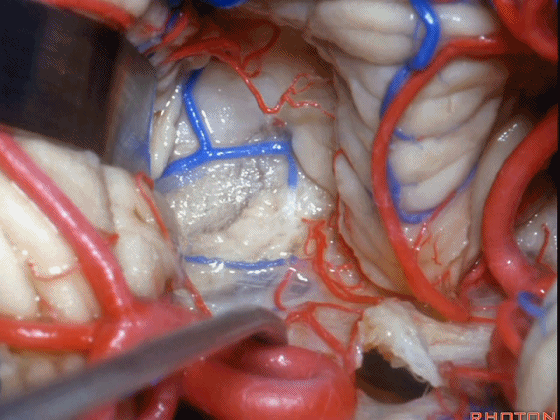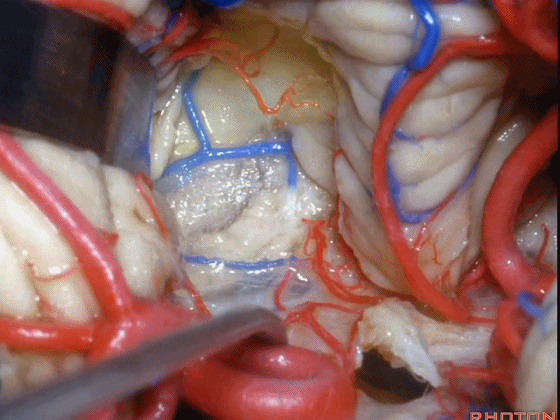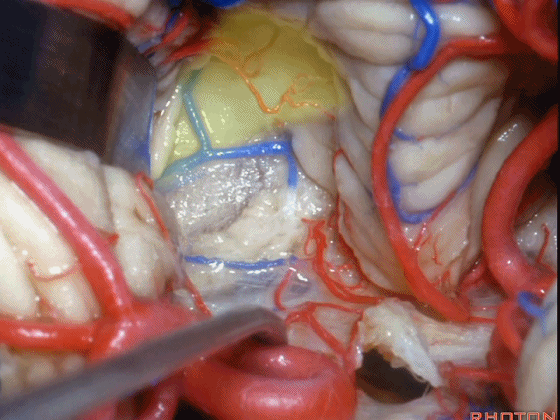
▼我们贴着小舌(下图),牵开扁桃体,显露出脉络膜和下髓帆。
We go here adjacent to uvula. You retract the tonsils and you see the tela and the velum.
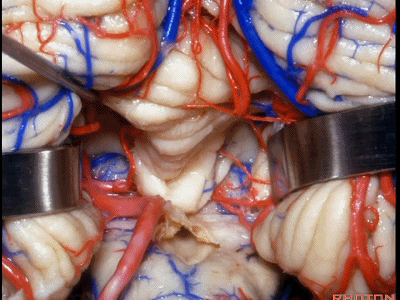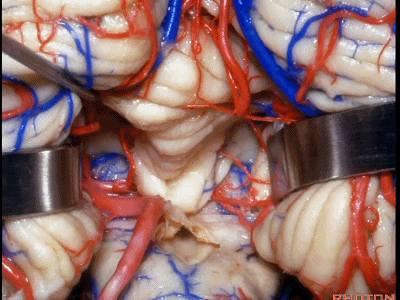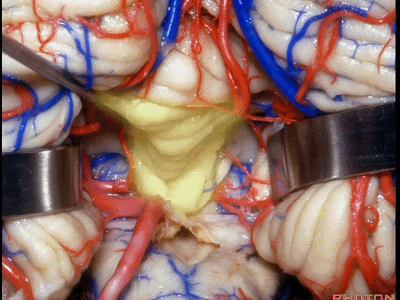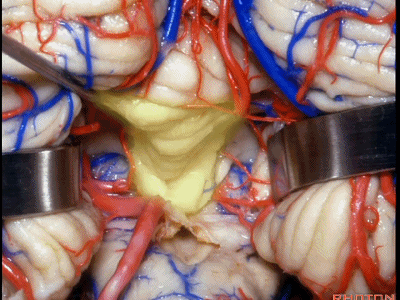
▼下图示扁桃体。
▼下图示脉络膜。
▼下图示下髓帆。
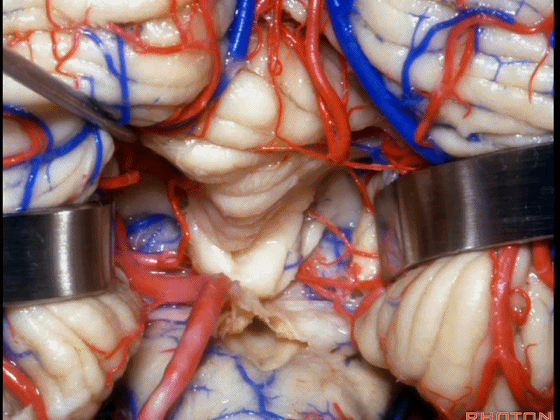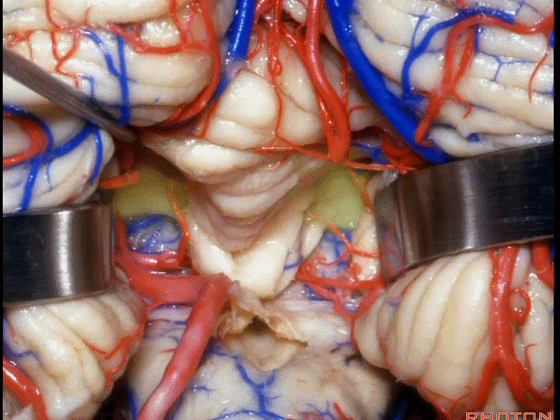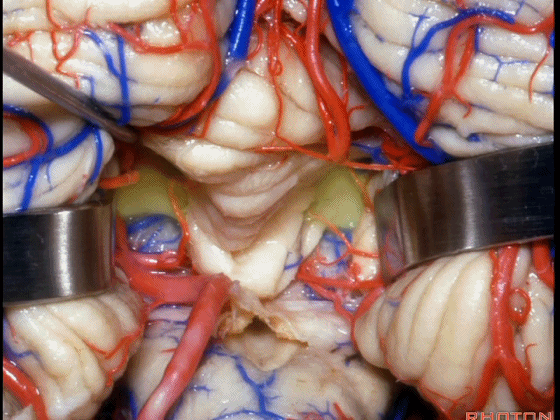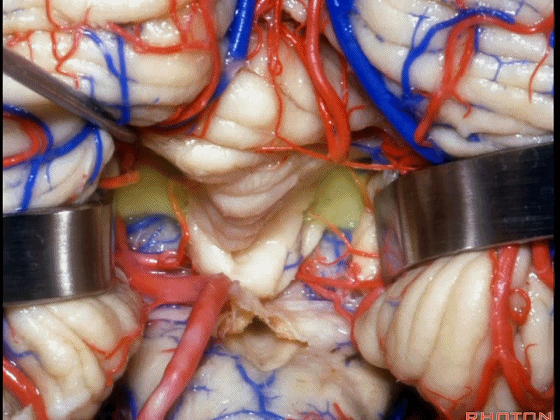
▼在小舌的一侧,可显露出脉络膜(下图),和下髓帆。
And you can get in and off to one side of the uvula. Here we see tela,and velum.

▼这是下髓帆。
▼打开脉络膜即可获得足够的视野直至中脑导水管(下图)。
And you open the tela, you have a view all the way up to the aqueduct.
▼若需进一步暴露上外侧隐窝或小脑上脚、下脚,我们可打开下髓帆(下图)。
If you need access to the superolateral recess or the part of the pedunclar mass made up of the superior and inferior peduncle,you can divide the velum.
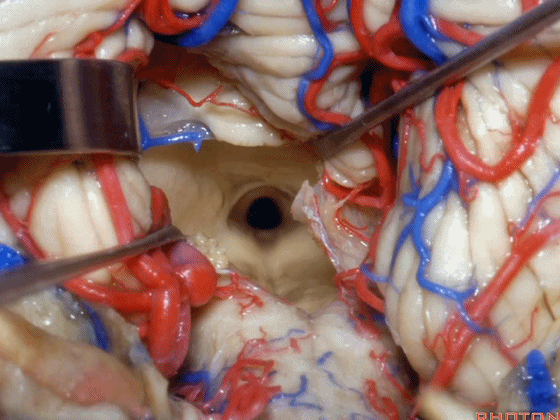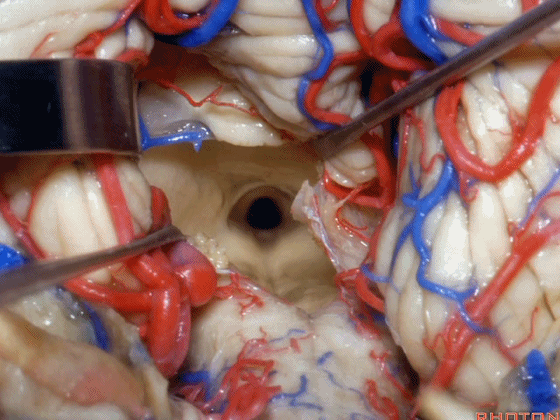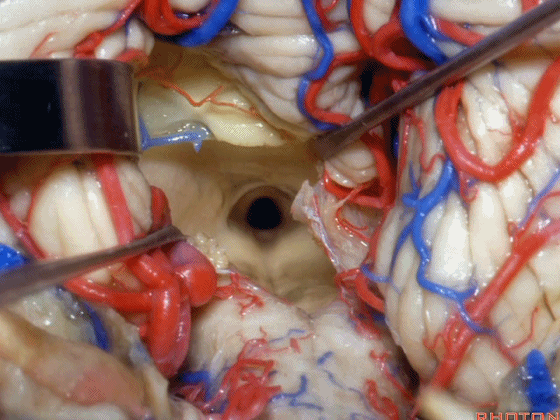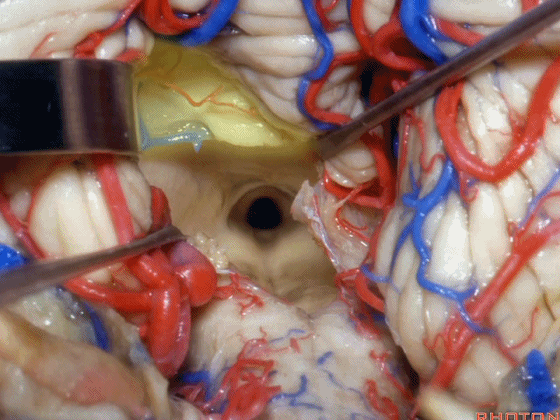
▼从而显露上外侧隐窝。
and that gives access to the superolateral recess.
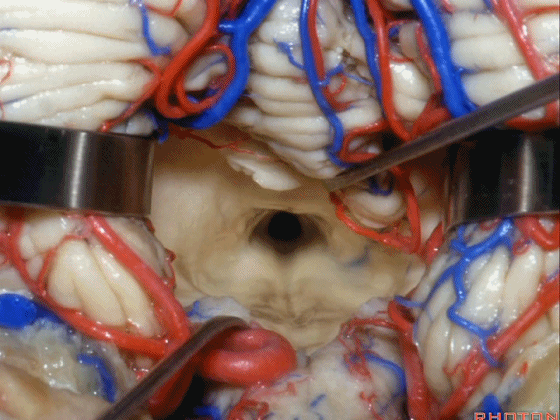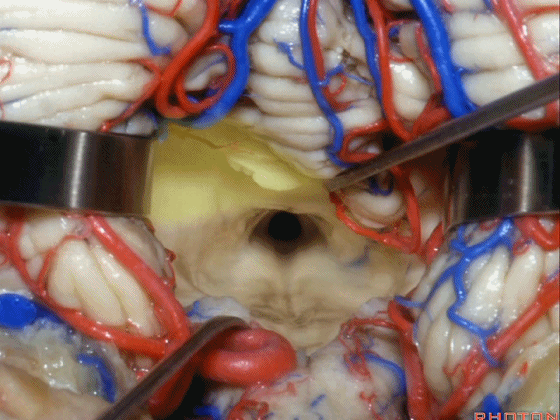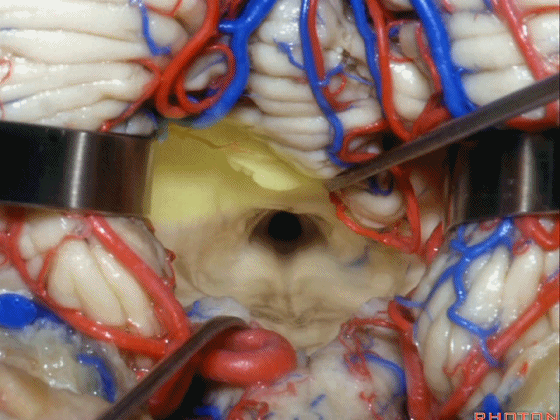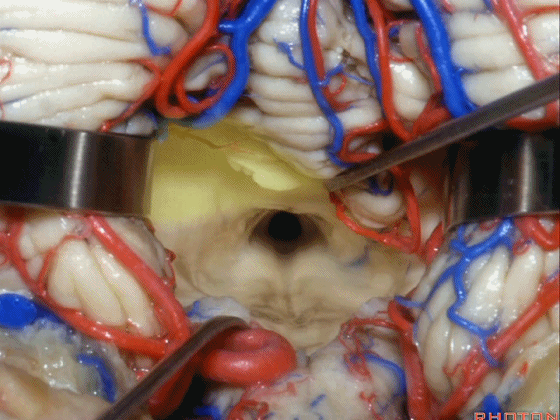
▼侧隐窝的顶壁即由 下髓帆 和 脉络膜 构成,下图示下髓帆。
the lateral recess is roofed by velum and tela.
▼下图示脉络膜。
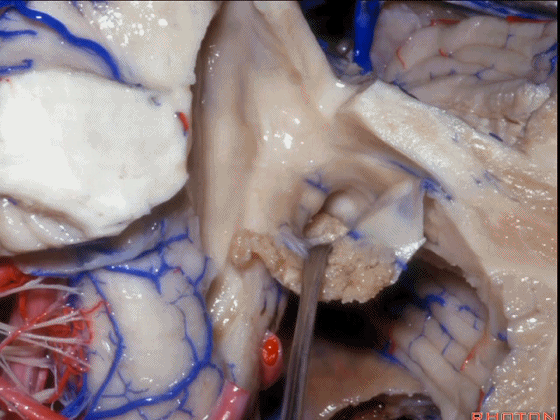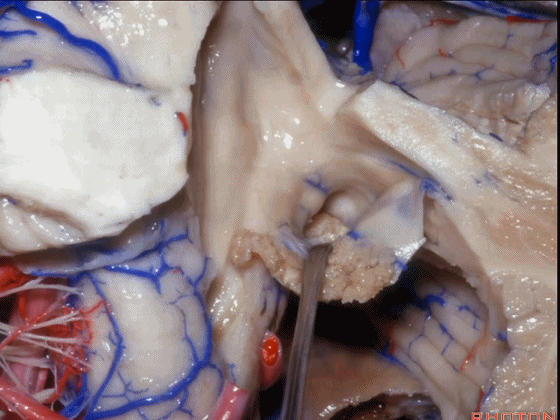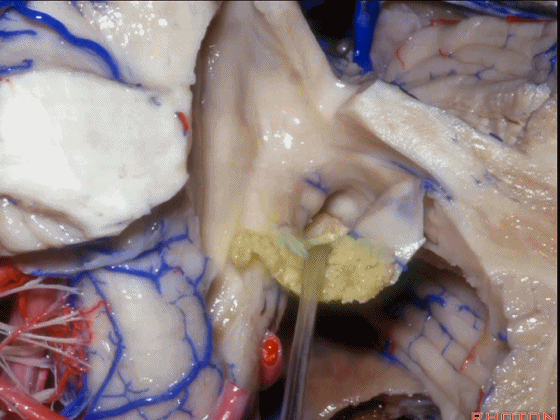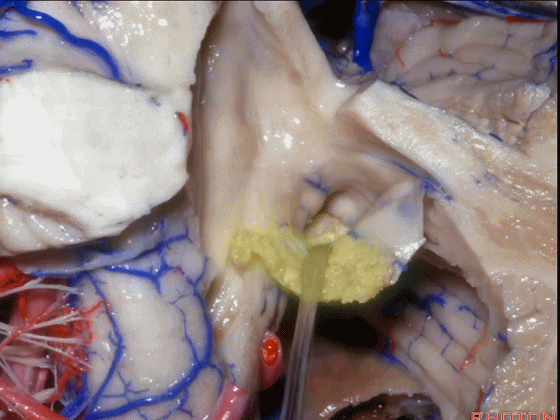
▼如果病变再向外侧进一步侵犯至侧隐窝外,需要抬起扁桃体(下图)。
And then, if the pathology extends out the lateral recess.. and all you have to do to open the lateral recess is elevate the tonsil.
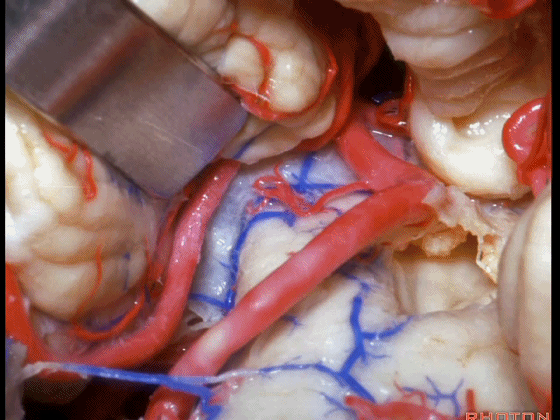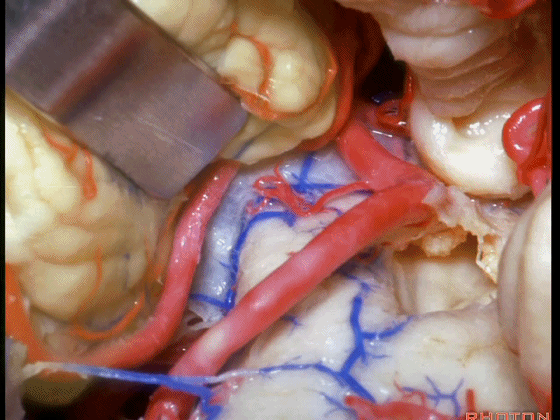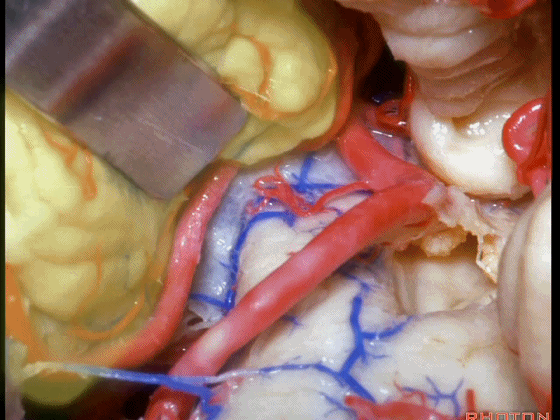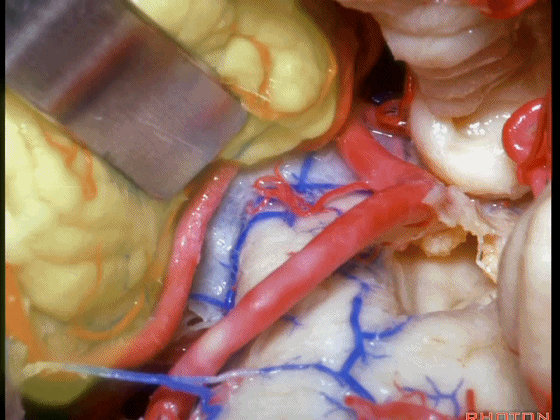
▼切开脉络膜。
open the tela .
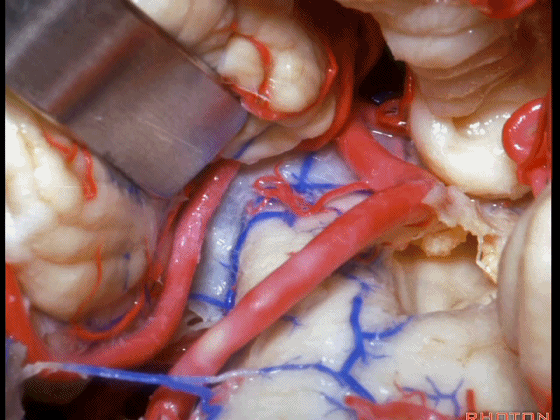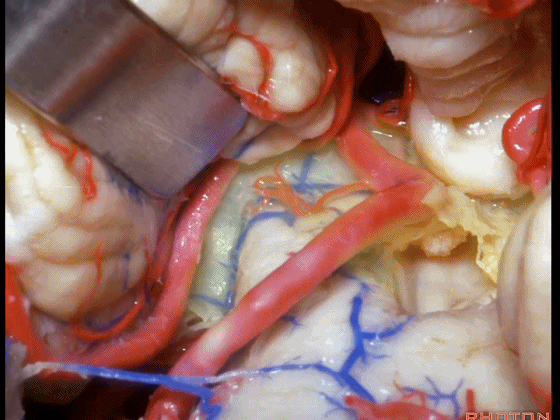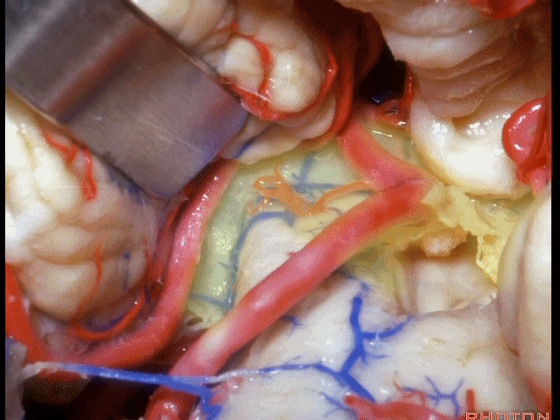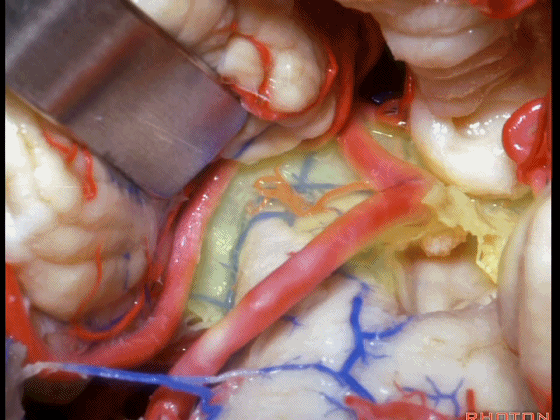
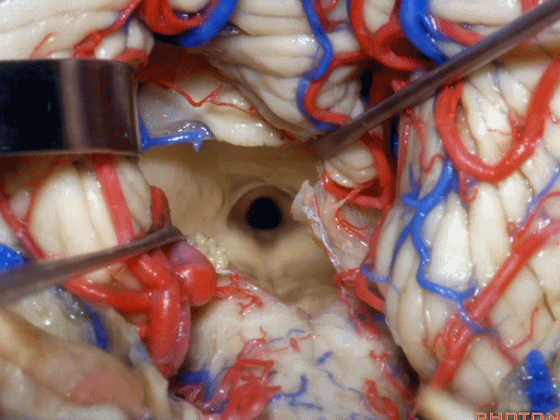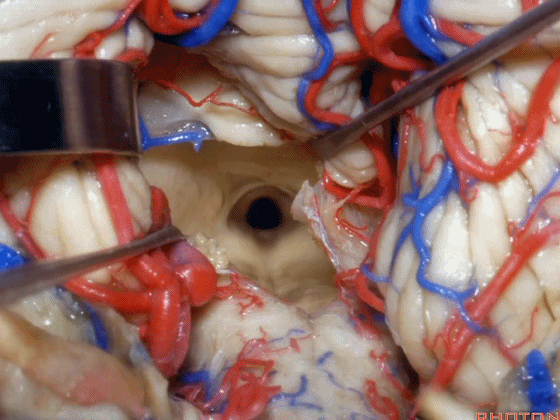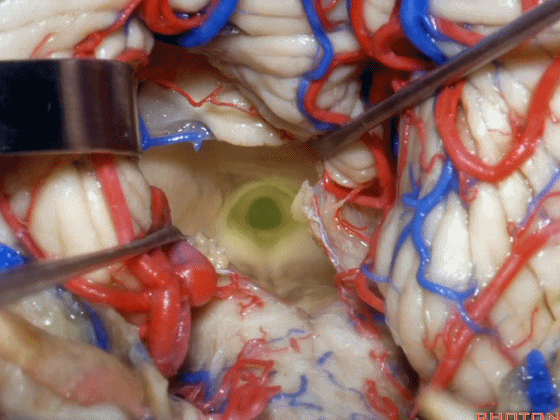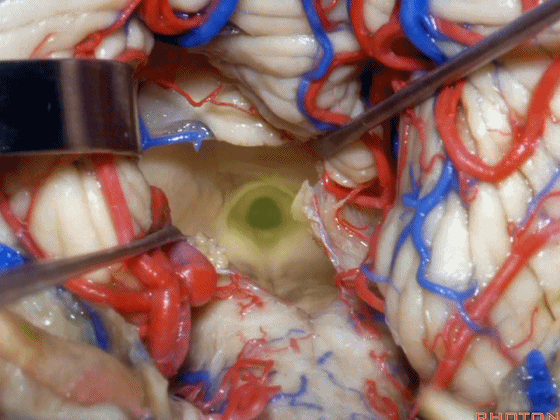
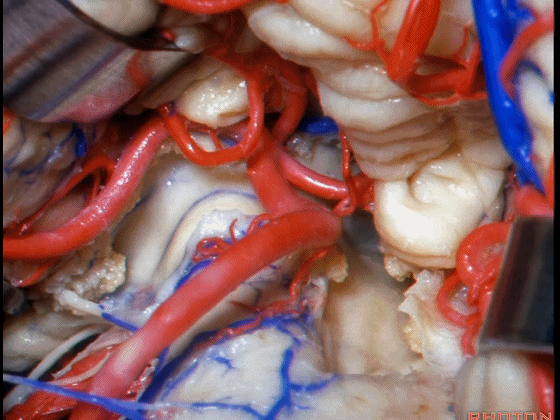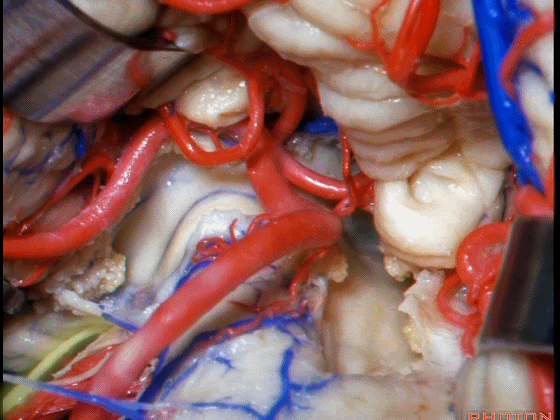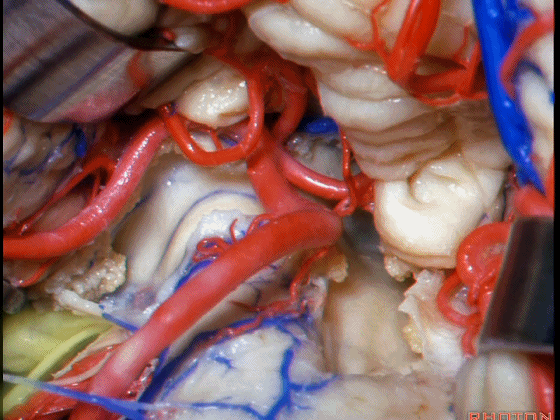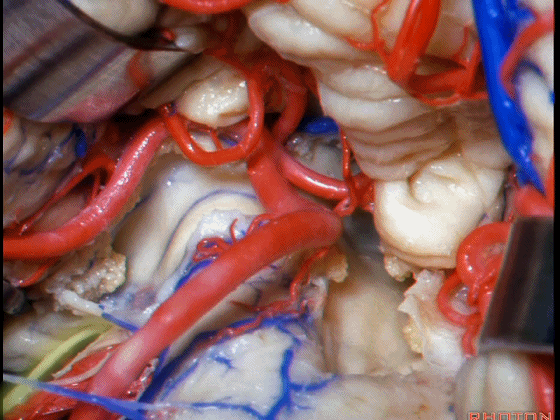
▼从Magendie孔暴露至Luschka孔。下图示Magendie孔(正中孔)。
from Magendie to Luschka.
▼这是Luschka孔。
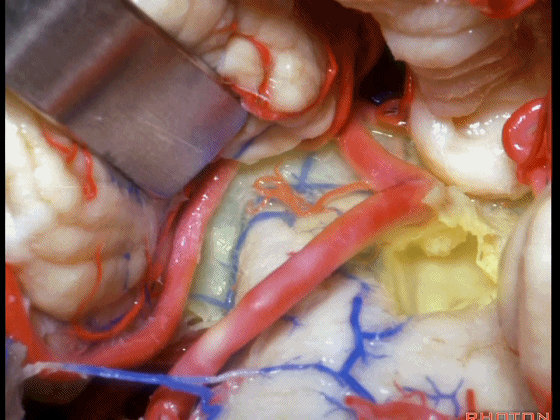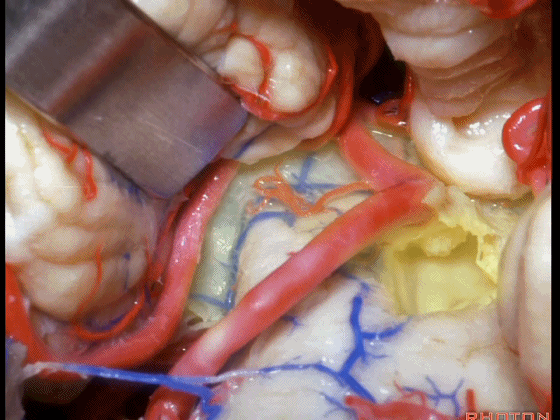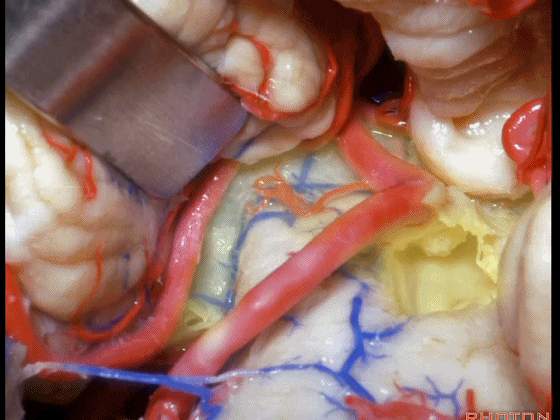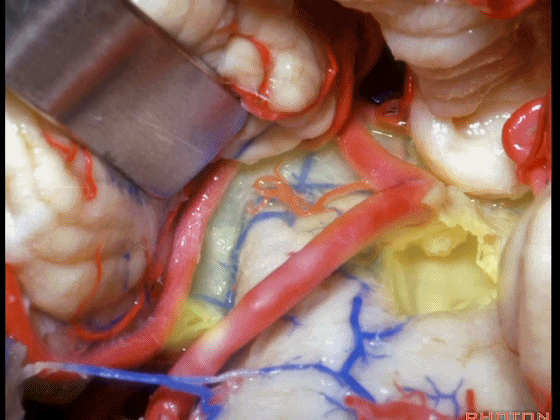
▼即可完全暴露侧隐窝(下图)。
and you have access to all of the lateral recess.
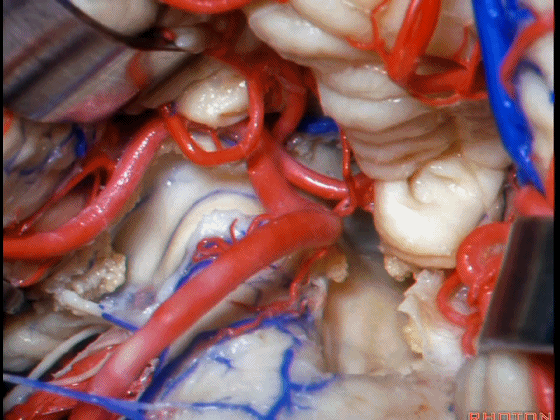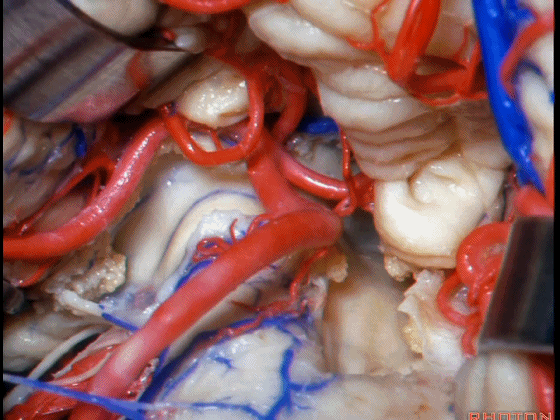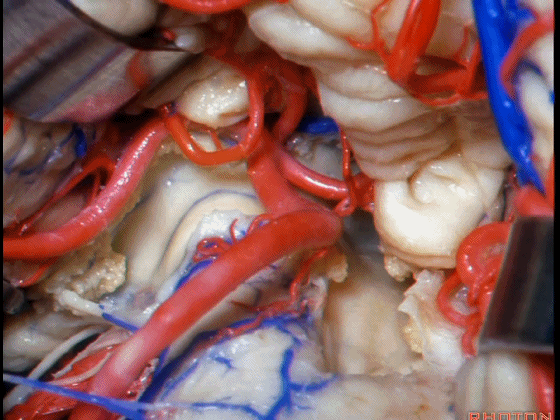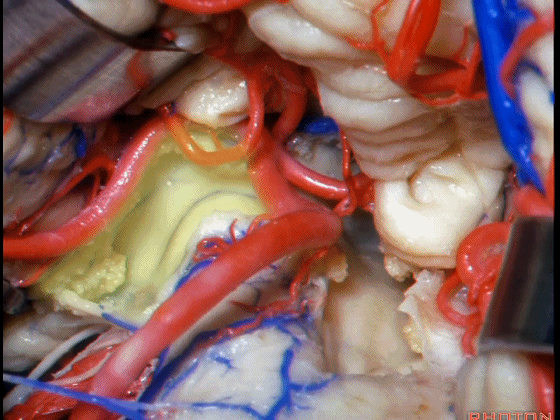
▼这是Luschka孔。
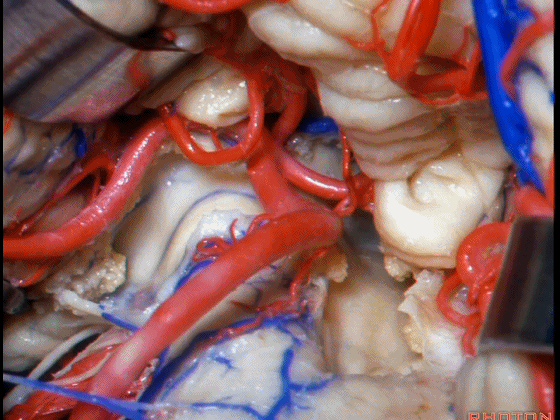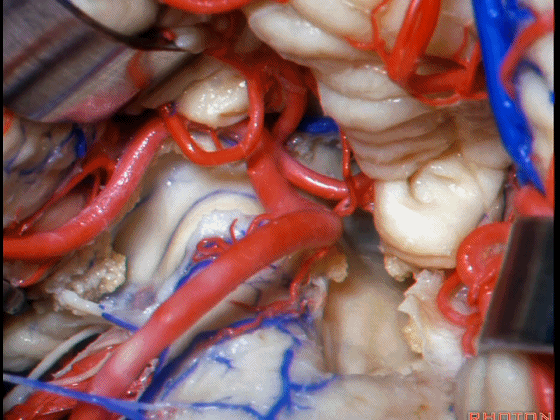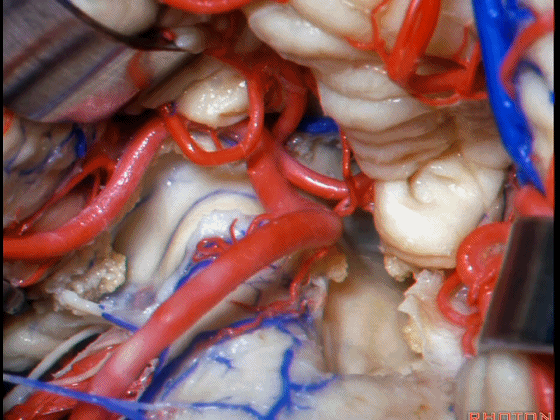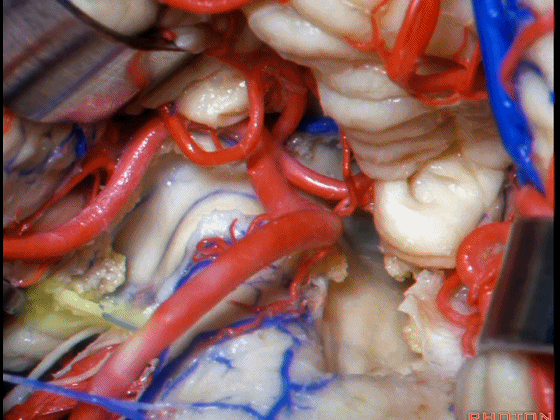
▼Luschka孔在舌咽神经(下图)后方,紧邻绒球(下图)。因此对于第四脑室病变,膜帆入路是首选。这在小儿神经外科中运用普遍。
So for pathology in the 4th, we use telovelar approach. It's become common in pediatric neurosurgery for 4th ventriclar tumors. Here's Luschka behind IX, adjacent the flocculus.
▼如今只有一种情况下我会切开小脑蚓,那就是蚓部肿瘤。
The only time I split the vermis today is if the tumor is in the vermis. And.
▼这里,我们打开脉络膜,这是蜗背侧核(下图)。听觉植入常被放置在侧隐窝。在这下方是蜗腹侧核。因此我想该术式应是尽量将其置于上述两神经核之间。一些术者从侧方经Luschka孔暴露。但若肿瘤造成了脑干扭曲,有些术者也会从下方抬起扁桃体,打开侧隐窝,即当脑干扭曲时选择从下方置入植入物。
So here we've just...we've opened the tela. That's dorsal cochlear nucleus. They actually put the brainstem implant in the lateral recess. Just below this is ventral cochlear nucleus. And, I think they try to set it right on the junction of the two. Some people do it from lateral through Luschka. If the brainstem is real distorted with the tumor, I know some people come back down here and go, lift up the tonsil and open the lateral recess, and stick it in from below if the brainstem is real distorted.
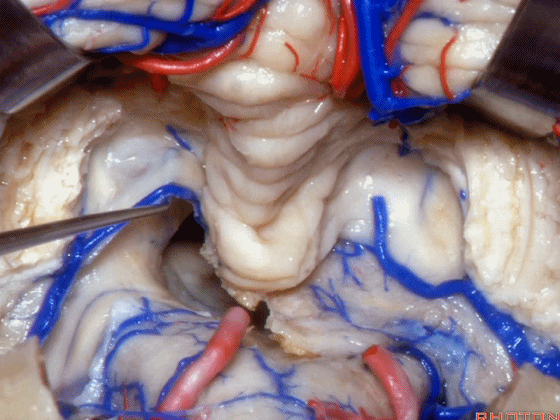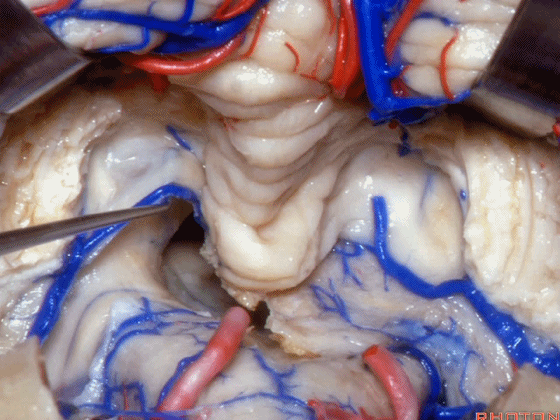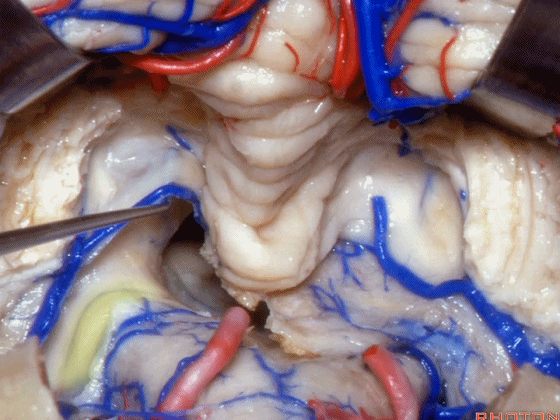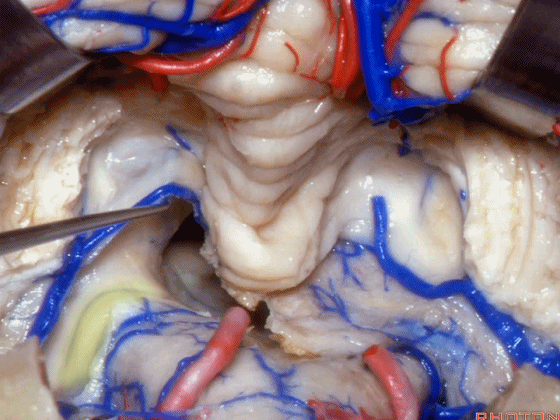
▼这是该区域的总览,这是 小舌。
Here we just see a view of all of this area. This isthe uvula.
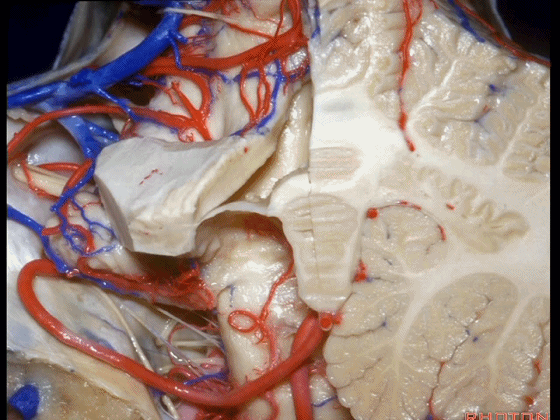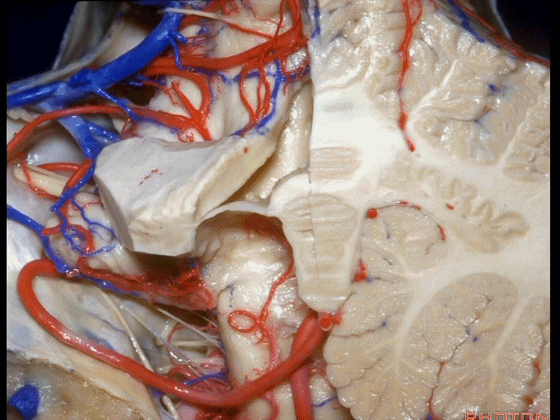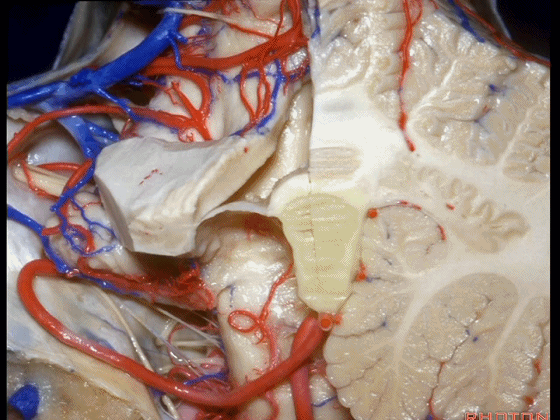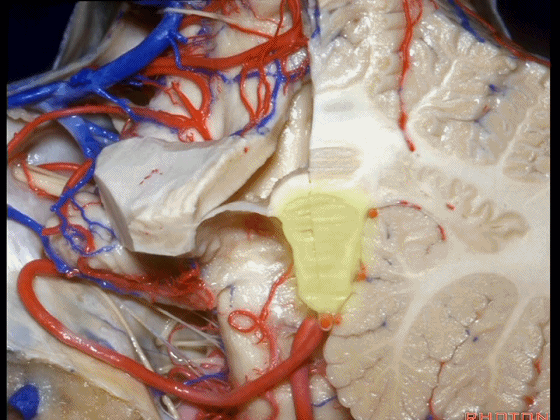
▼这是 蚓部的小结。
the nodule of the vermis.
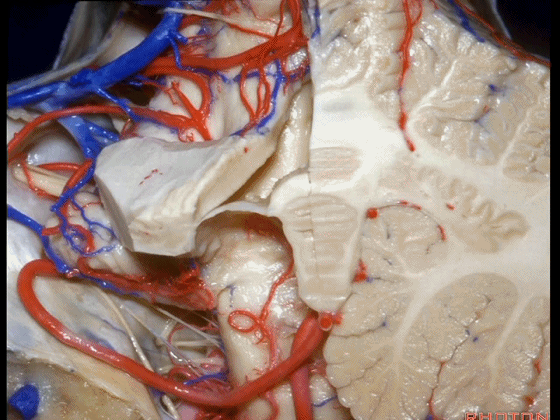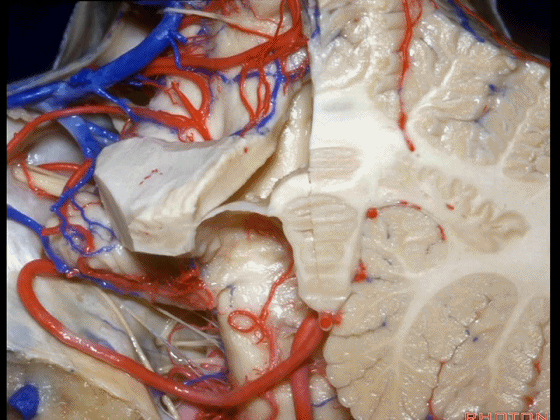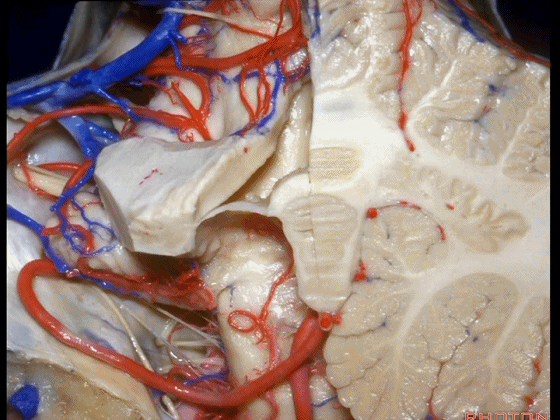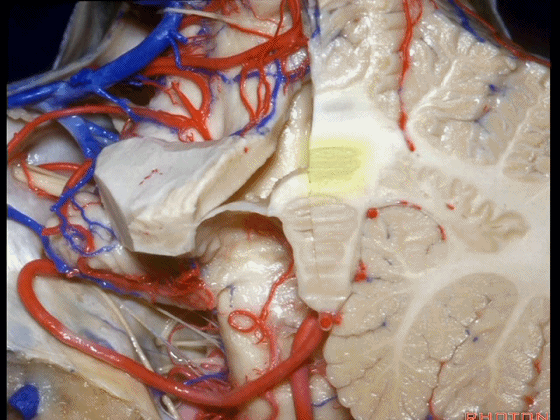
▼这是下髓帆。
Here's the inferior medullary velum.
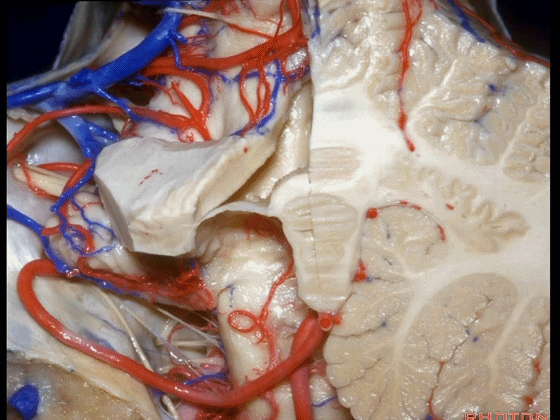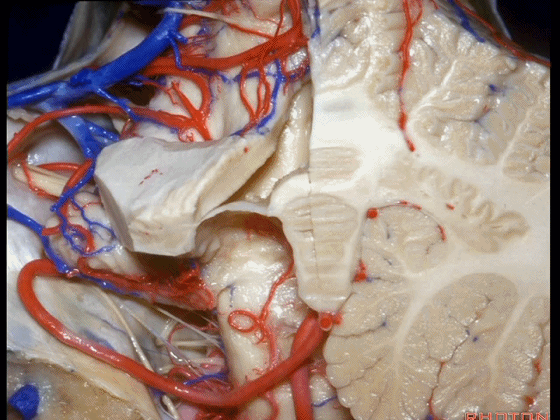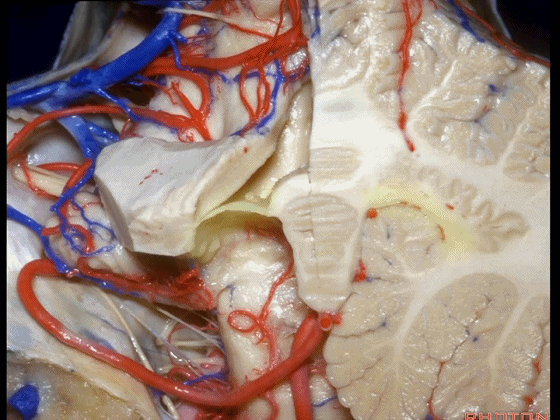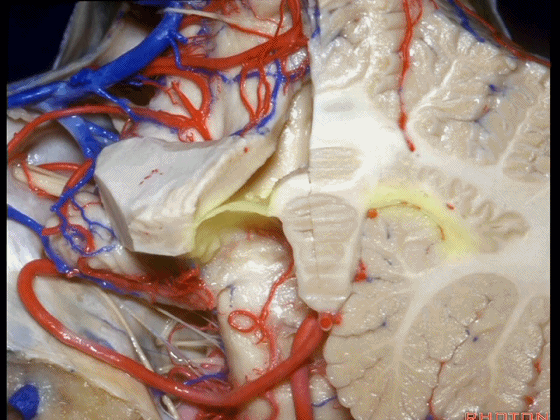
▼下髓帆向两侧延伸并覆盖扁桃体头部(下图)。
the inferior medullary velum that sweeps laterally and caps the tonsil.
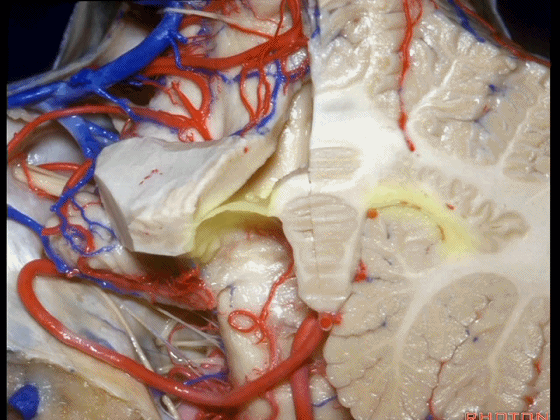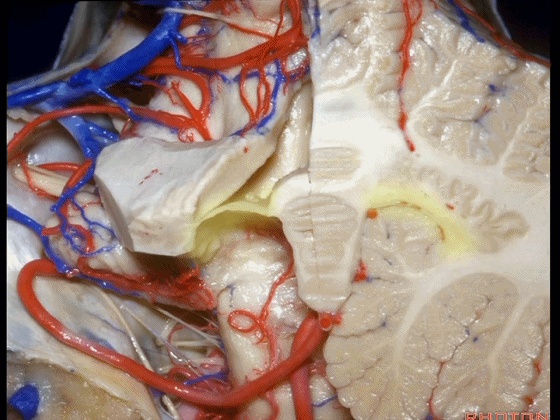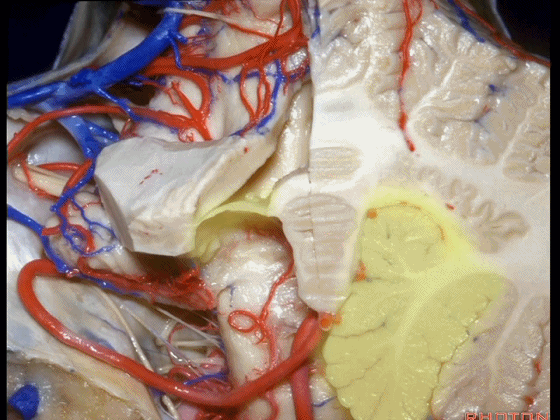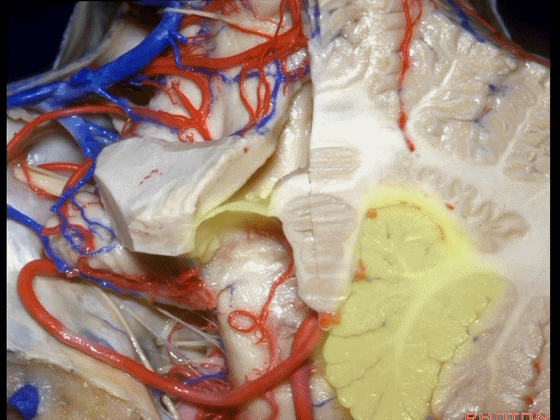
▼这是小脑后下动脉。
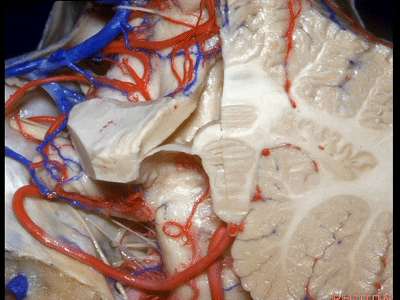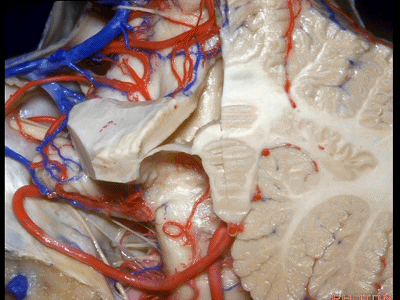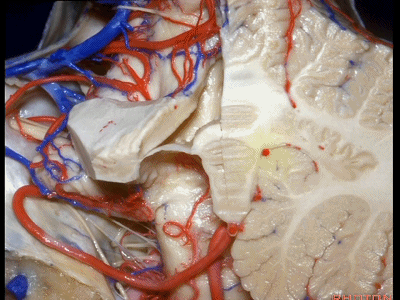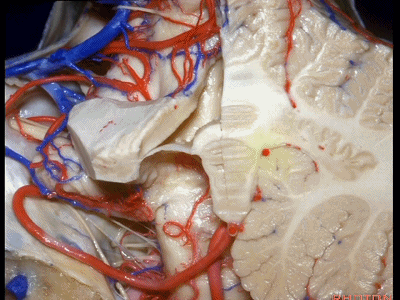
▼小脑后下动脉常常走行于下髓帆和扁桃体头部之间。
But often these trunks of the PICA run between the velum and the cranial pole of the tonsil.
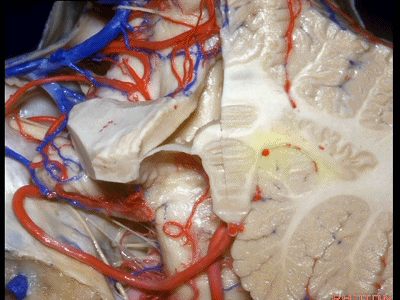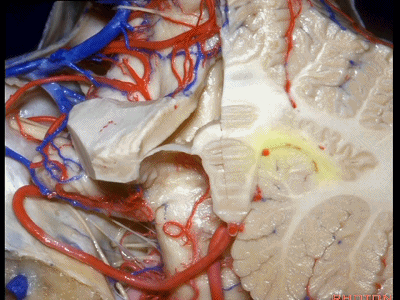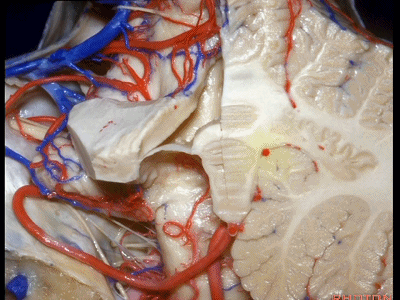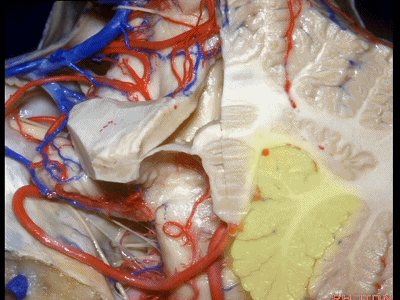
▼这是齿状核。在处理扁桃体头部时,需时刻谨记切勿伤及齿状核,其包绕扁桃体的头部,它们之间仅隔着下髓帆。
And anytime you're dealing with the cranial pole of the tonsil, you wanna stay out of the dentate nucleus that wraps around that cranial pole of the tonsil just above the inferior medullary velum.
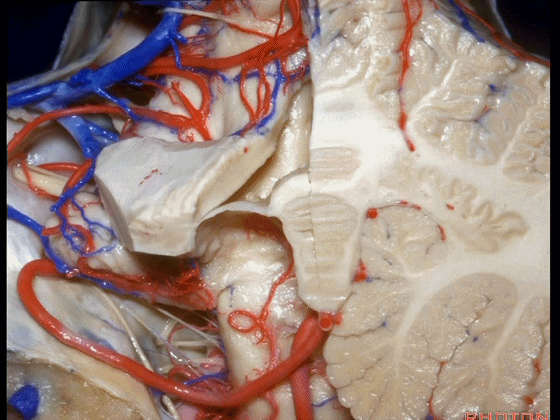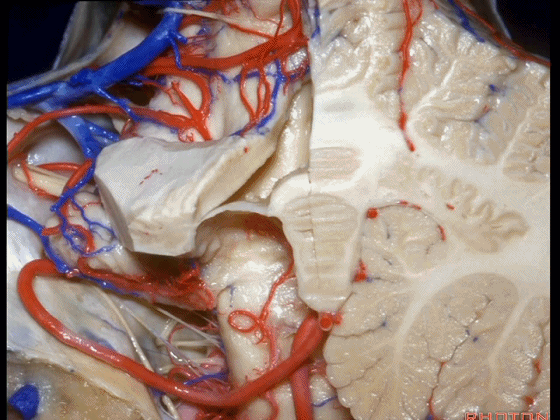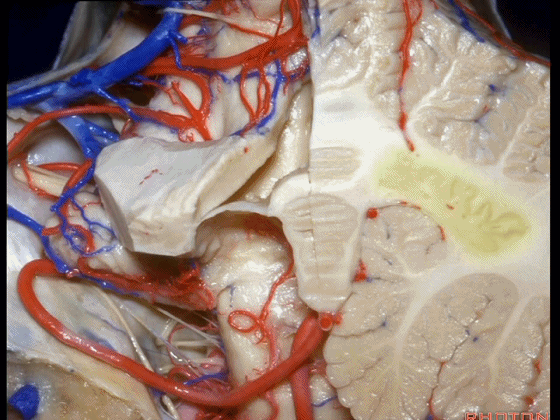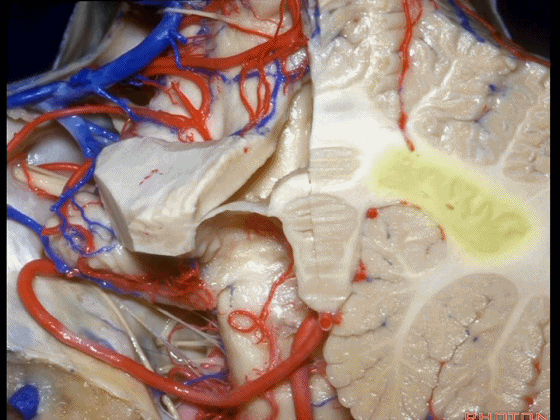
![]()
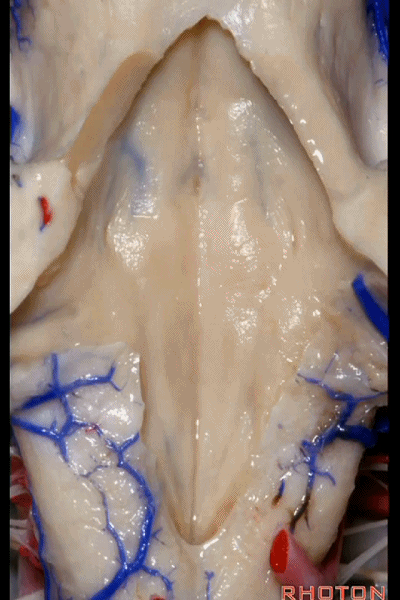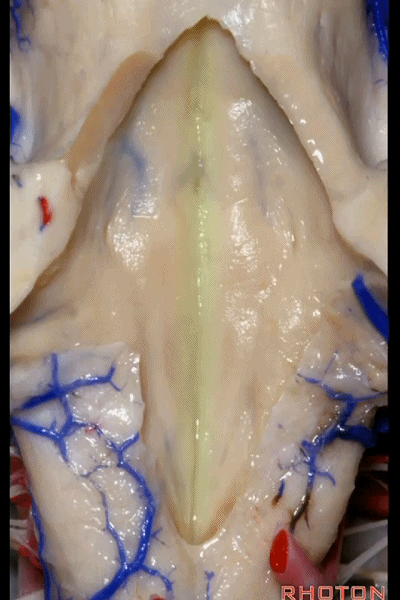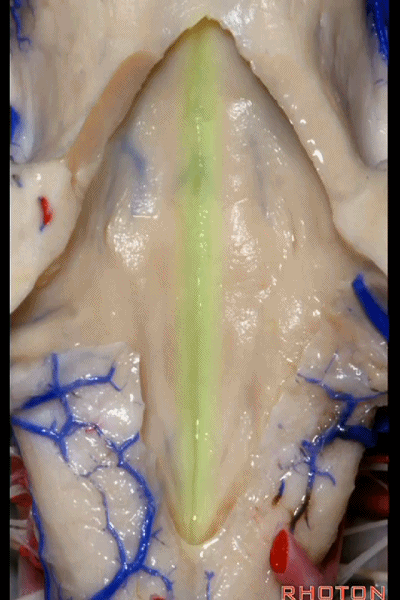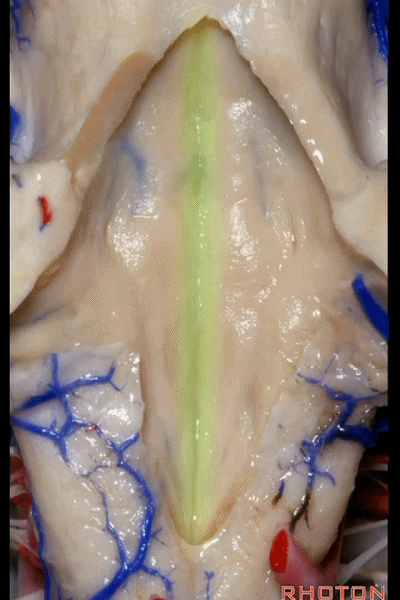
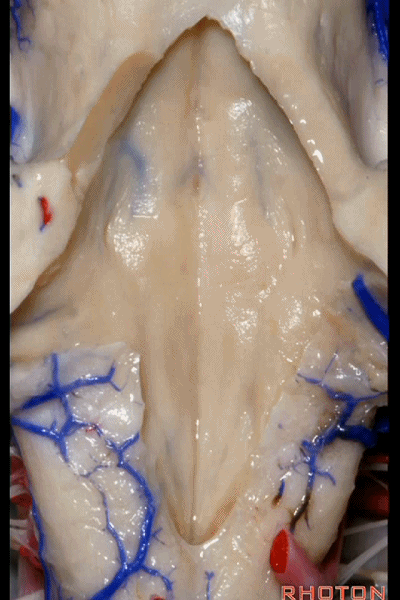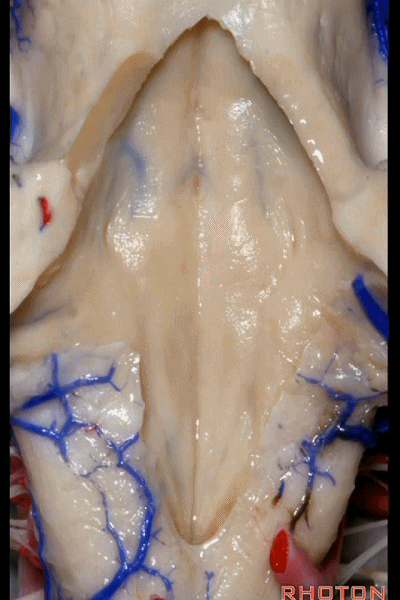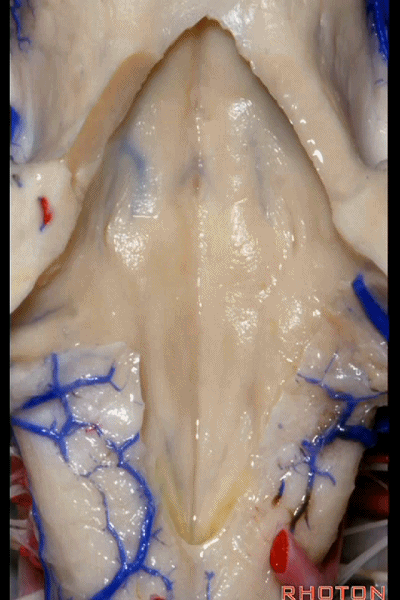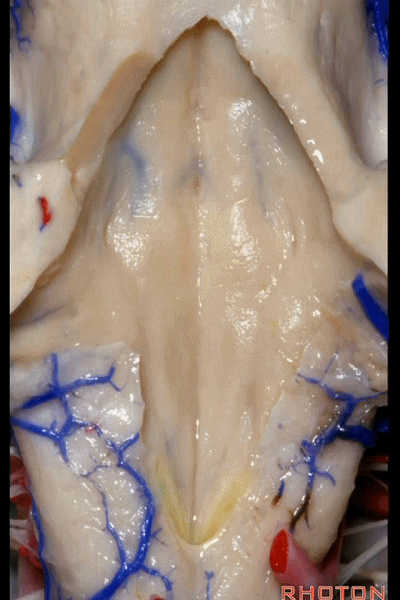
▼再来看看四脑室底。
here we see the floor of the 4th.
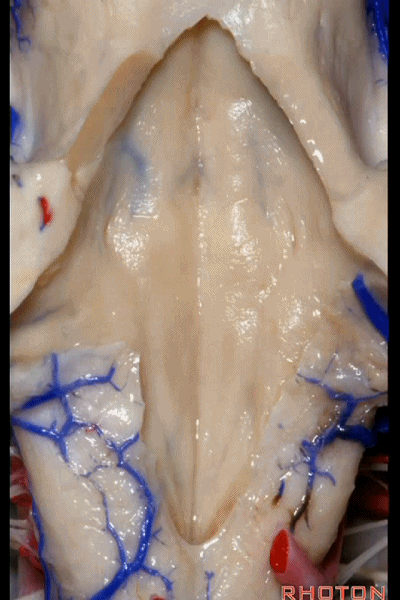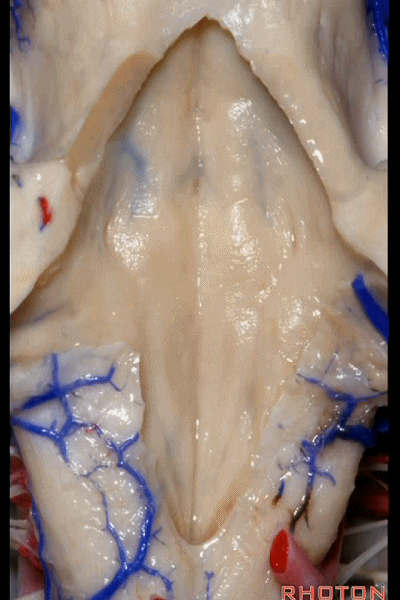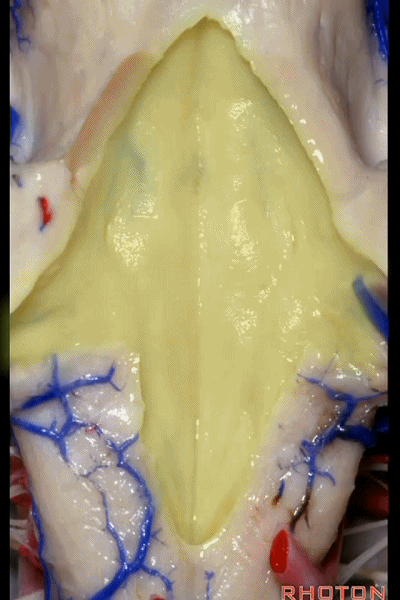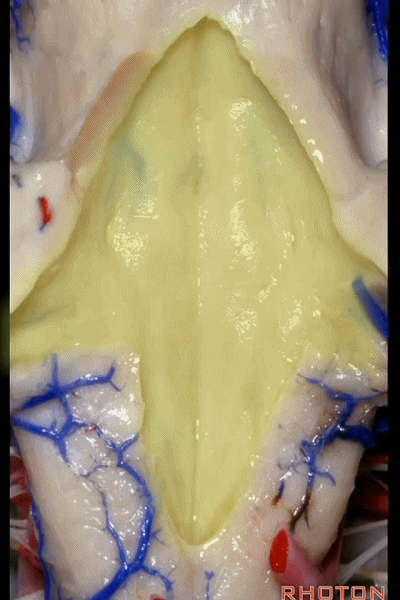
▼这是正中沟。
the median sulcus.
▼这是 面丘。
facial colliculus.
![]()
▼这是舌下神经三角。
Hypoglossal.
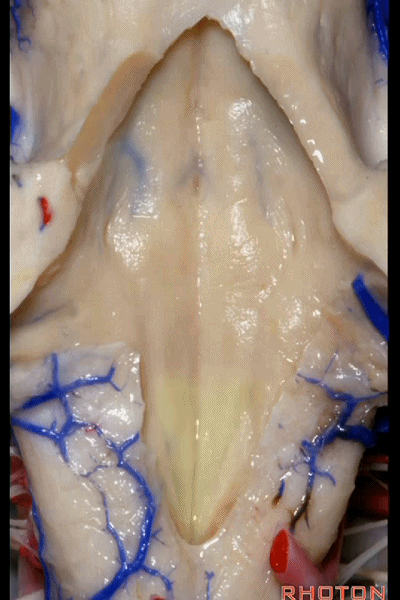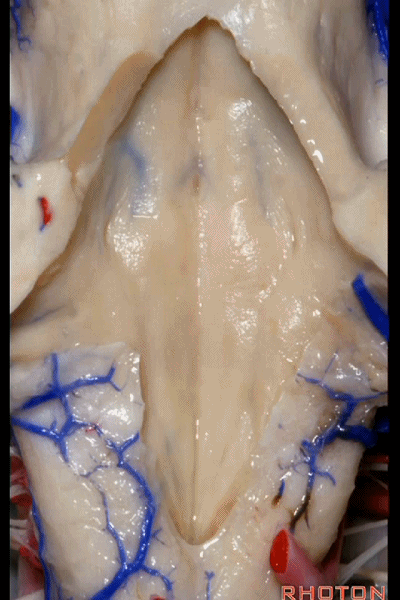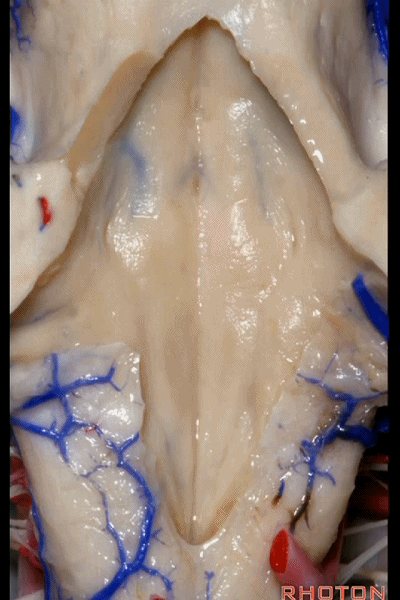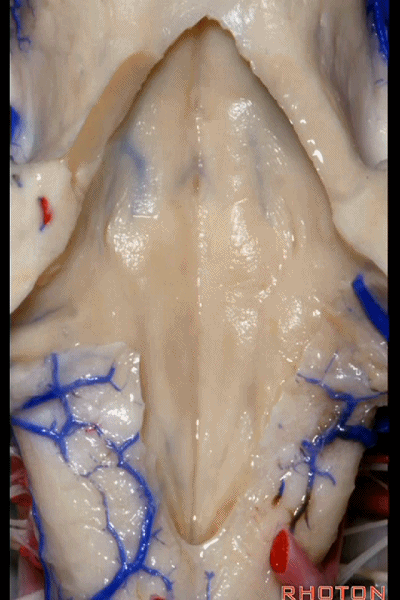
▼下方是迷走神经三角。
below, vagal.

▼再下方是最后区。
这个区域层层叠加犹如笔尖样,因此被称为写羽。
and then below, area postrema that gives this area a "pen nib" appearance that lead to it being called the calamus scriptorius.
![]()
▼现在我们加上颅底,这是面听神经。
we're working in this area here, at VII and VIII.
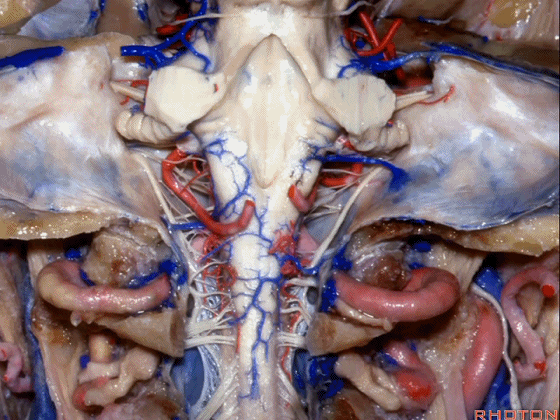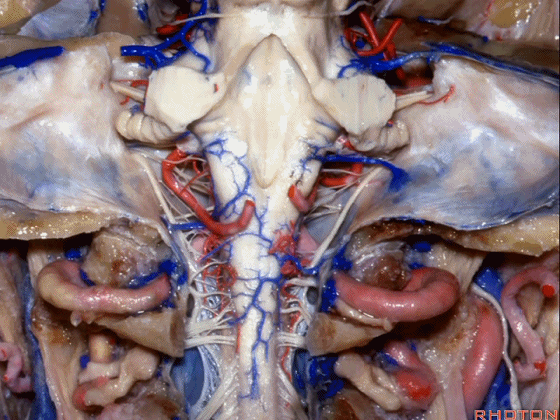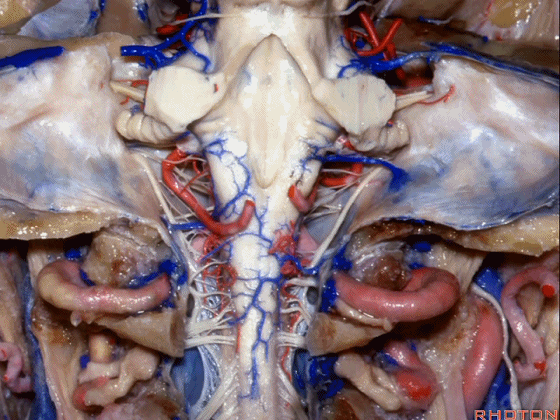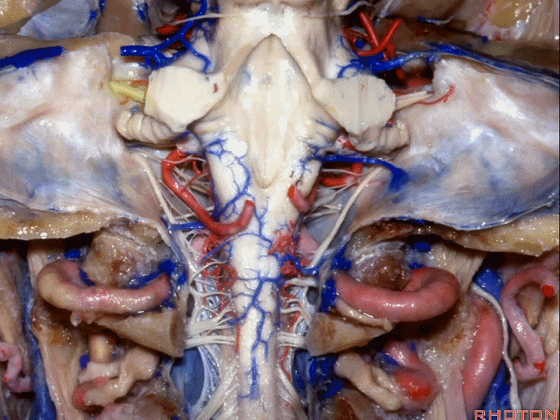
▼这是舌咽、迷走、副神经。
IX, X and XI.
▼位于副神经前方的舌下神经。
you see XII here in front of XI.
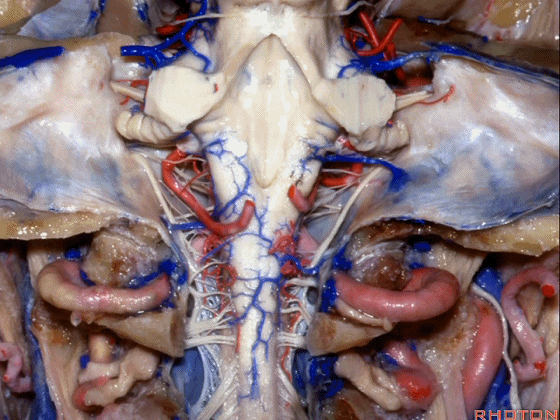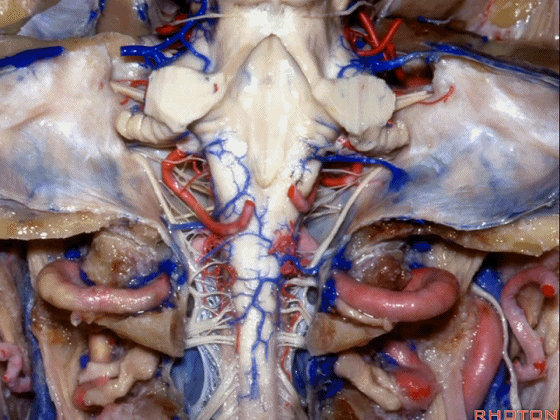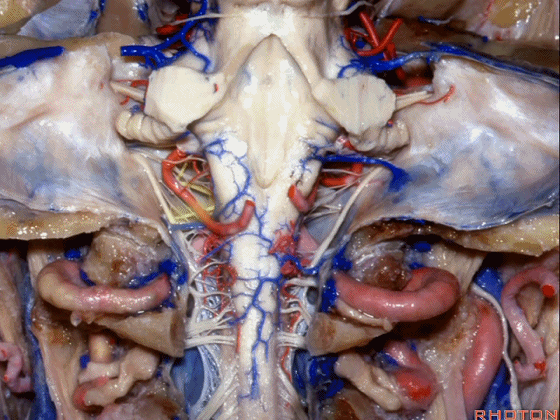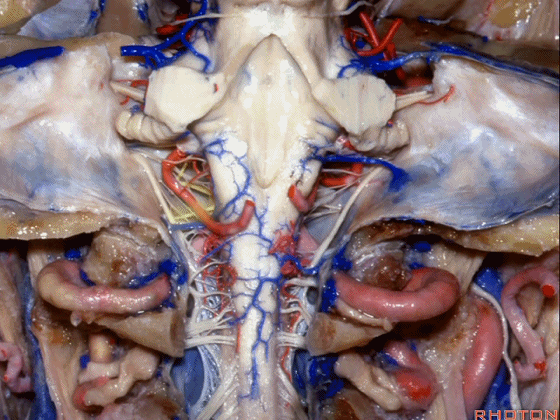
▼这是枕髁。
condyles.
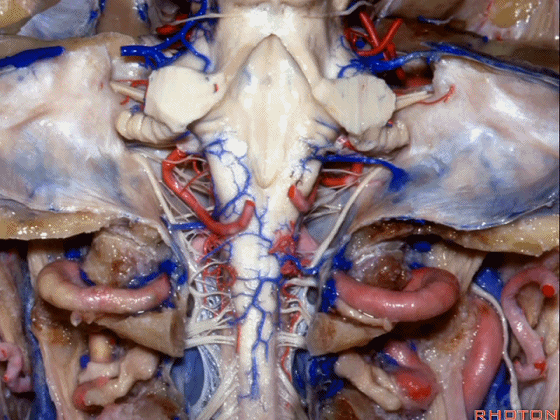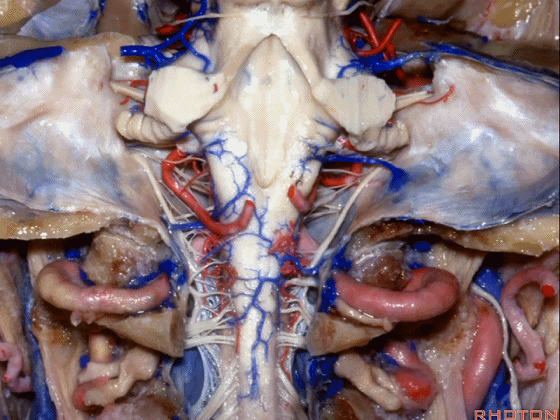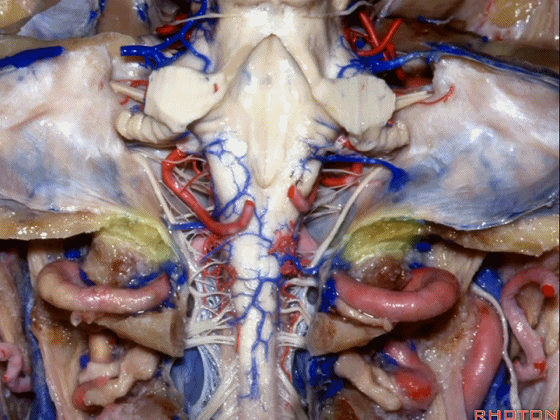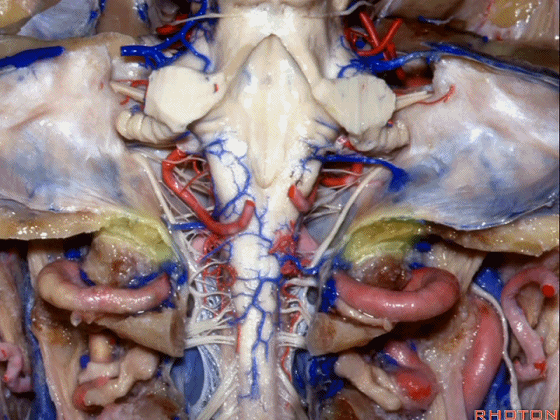
▼这是第四脑室。
here is 4th ventricle.
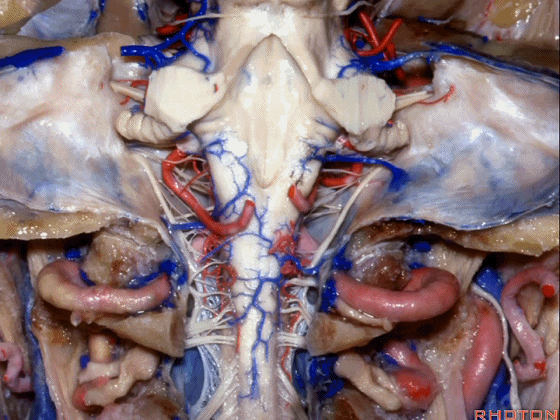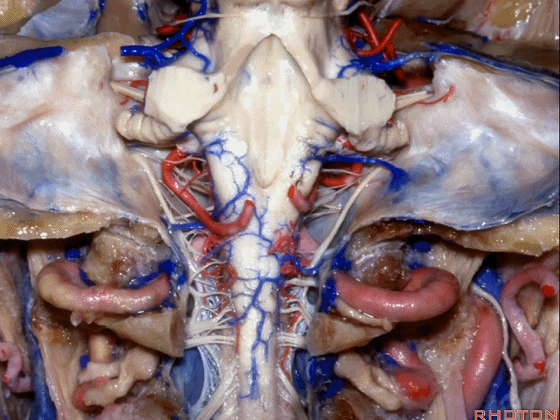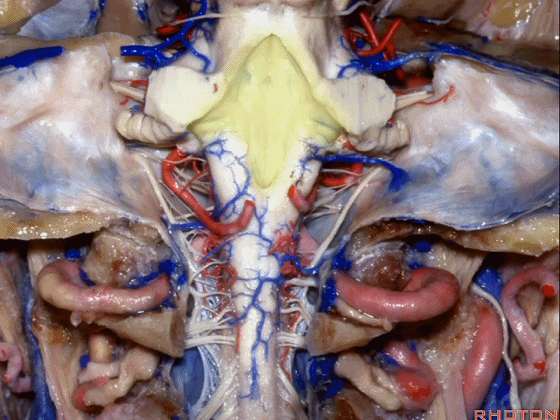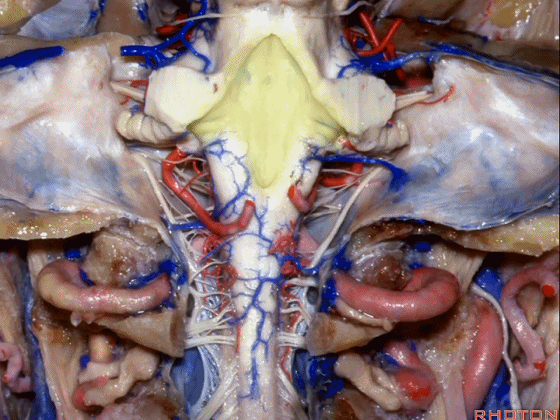
▼小脑脚中的哪部分与第四脑室直接相邻?在处理小脑脚内侧部的海绵状血管瘤时,与第四脑室相邻的这部分是小脑上脚 和 小脑下脚。下图示小脑上脚。
And what part of the peduncular mass makes up the part of the peduncle and faces the 4th ventricle? If you're dealing with cavernoma in this medial part of the peduncular mass that faces the 4th, all of that is made up of superior or what peduncle is this?Inferior.
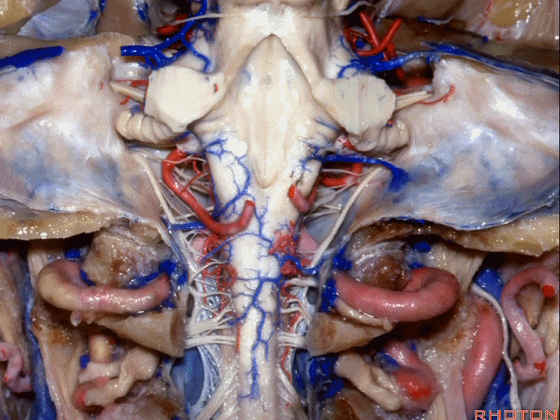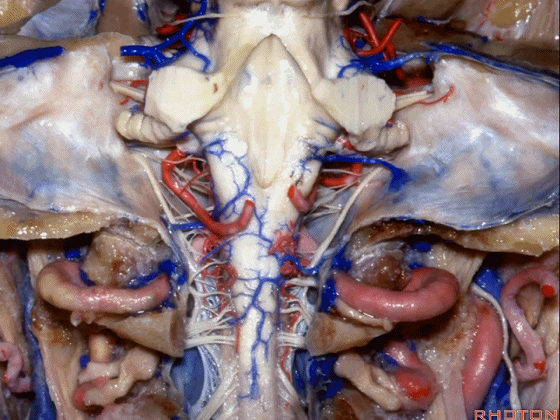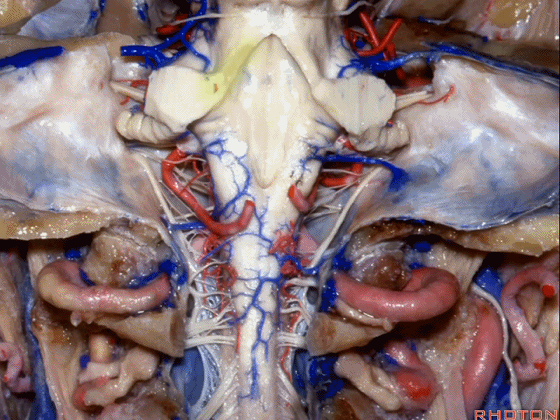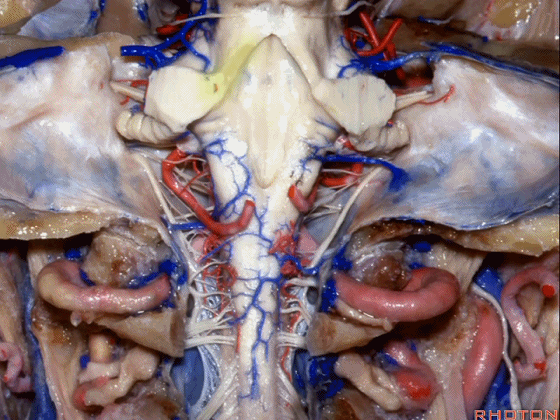
▼这是小脑下脚。
Inferior peduncle.
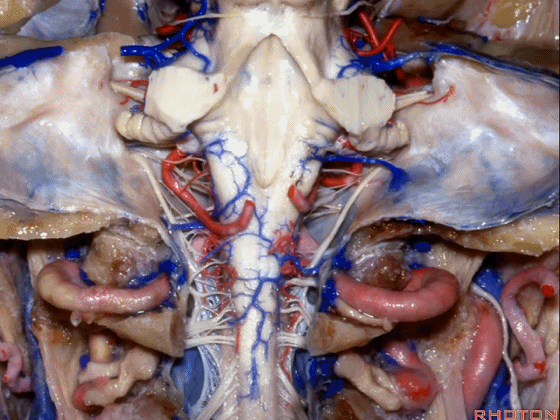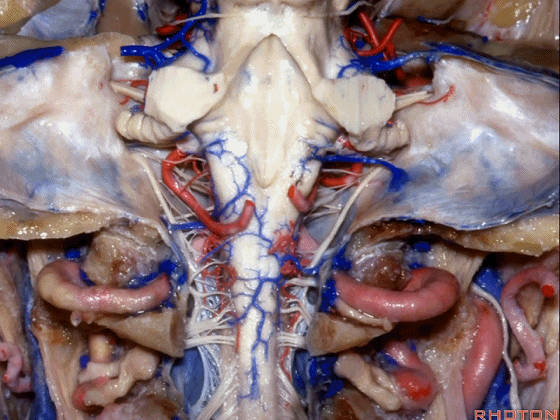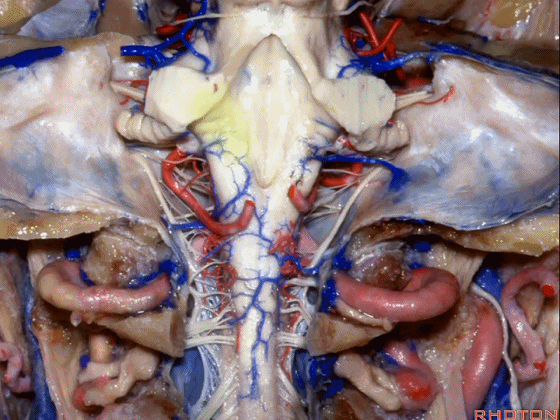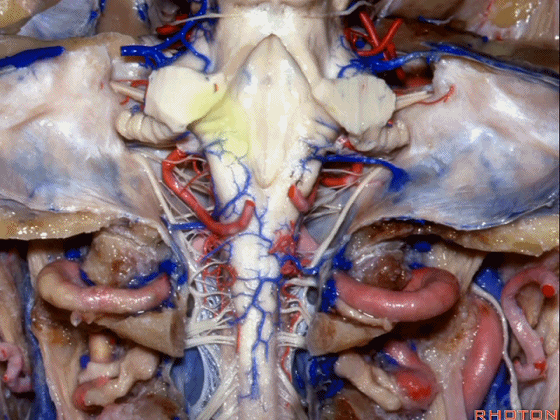
▼因此,对于小脑上脚和小脑下脚的病变,常需由第四脑室侧隐窝(下图)暴露。
for lesions in superior or inferior peduncle, we commonly come through the lateral recess of 4th.
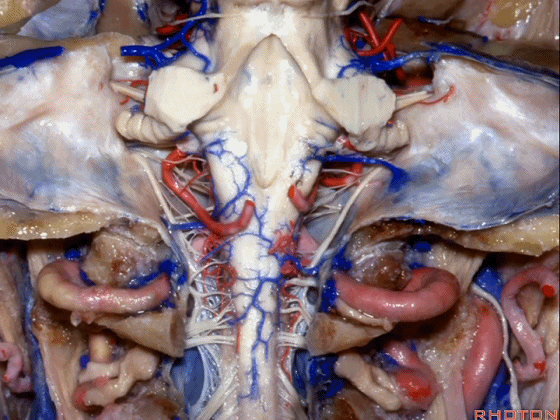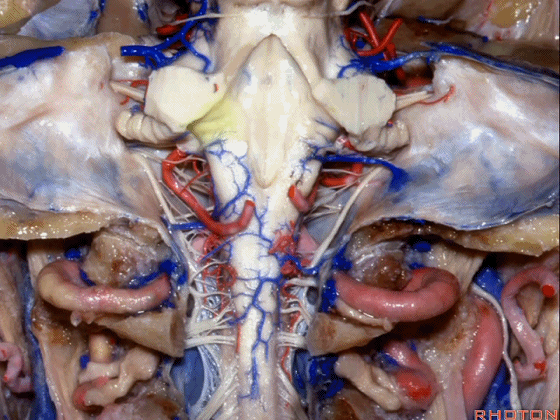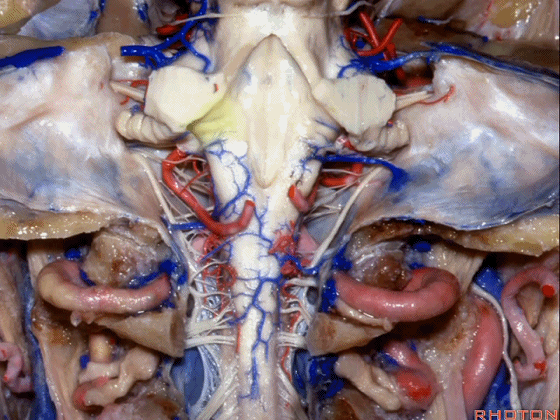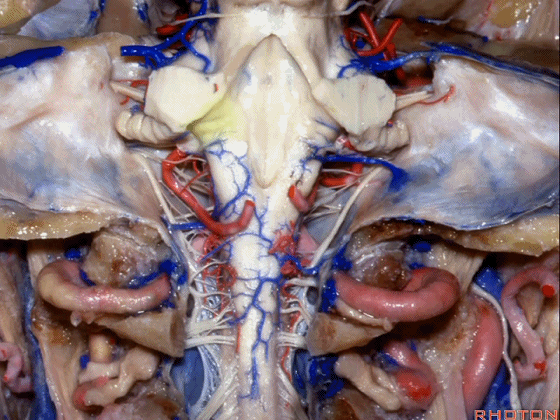
▼小脑中脚(下图)的外侧面与脑池相邻,对于此处的病变,我们常从侧方经乙状窦后入路暴露。
For a lesion in the middle cerebellar peduncle that is lateral facing the cisterns,we commonly come in retrosigmoid from lateral.
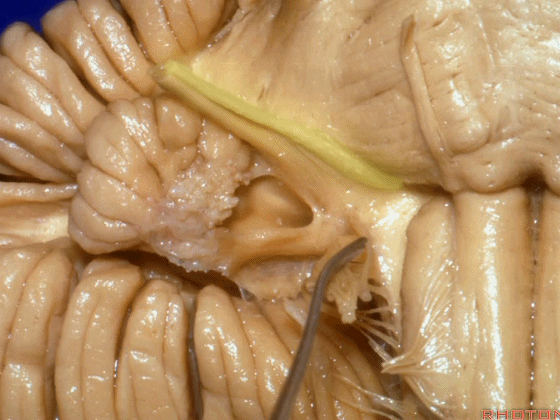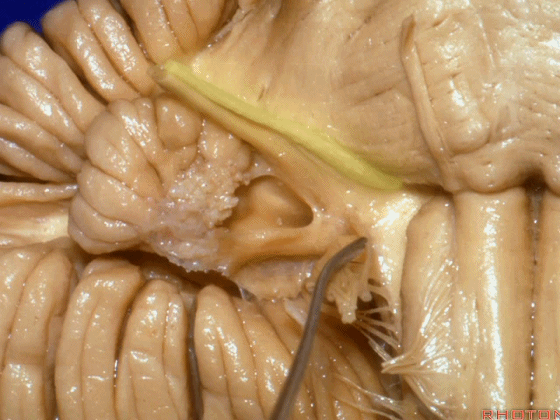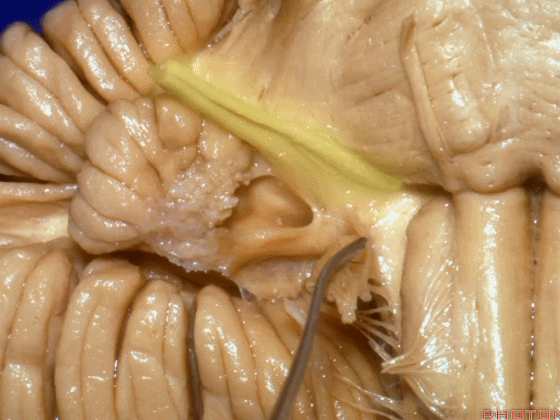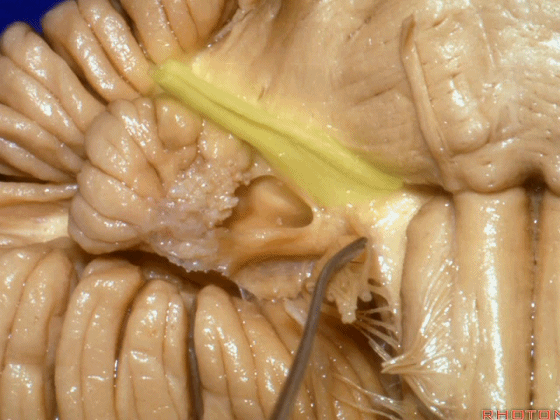
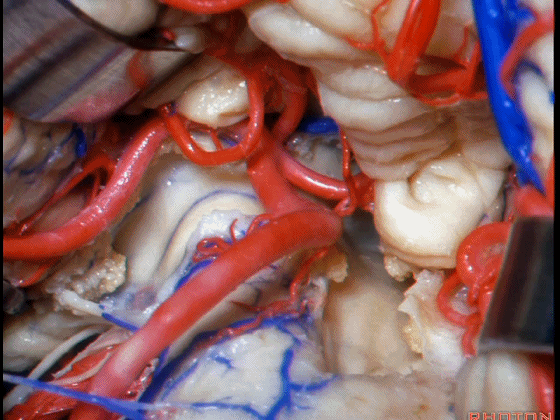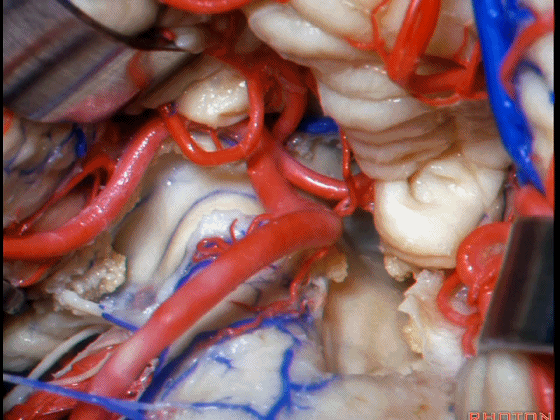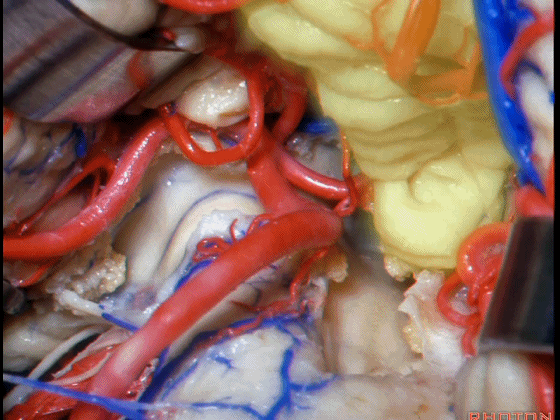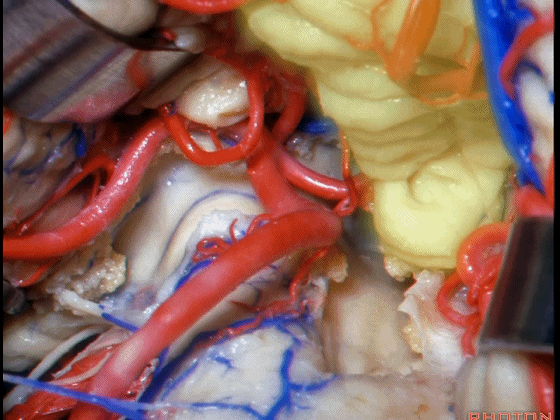
▼下图这个结构是小脑绒球(flocculus ['flɒkjələs])。我曾在各种会议中问及很多医师,但是不止一位不知道我问的就是小脑绒球,而它正是桥小脑角区的一个重要解剖标志。
And this is...flocculus. I used to be able to ask thousand surgeons in the meeting what that was and...not a single person who look in the CP angle dozens of times really look at the flocculus, but it's an important landmark in CP angle.
▼这是右侧 舌咽、迷走、副神经。
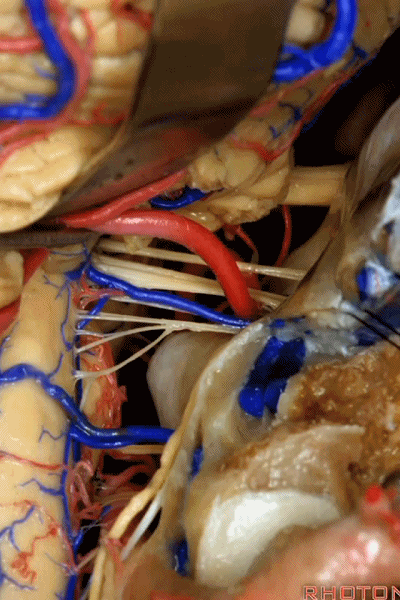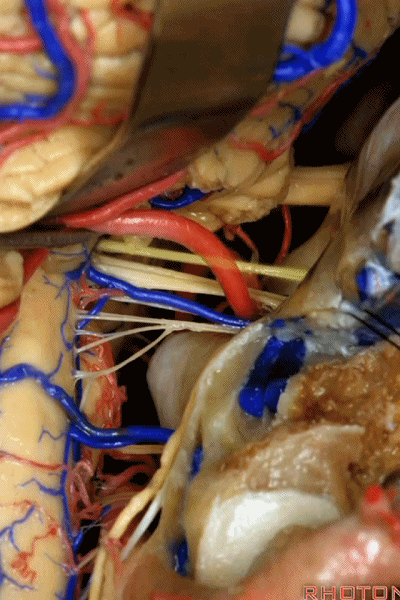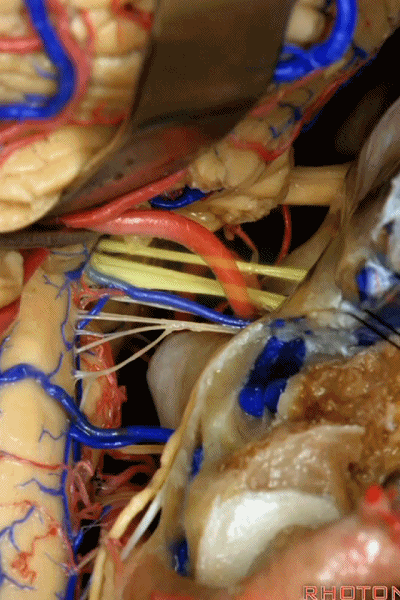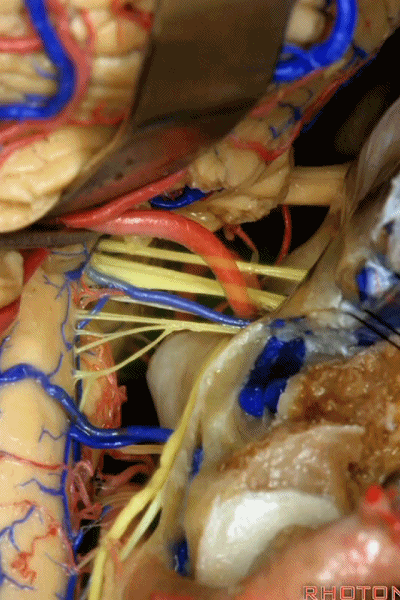
▼这些在舌咽、迷走、副神经间走行的静脉是岩下静脉,它们常与后组颅神经缠绕。
And then the veins that you wanna watch for down at IX, X, XI are these inferior petrosal veins. And, they are often mixed in with these nerves.
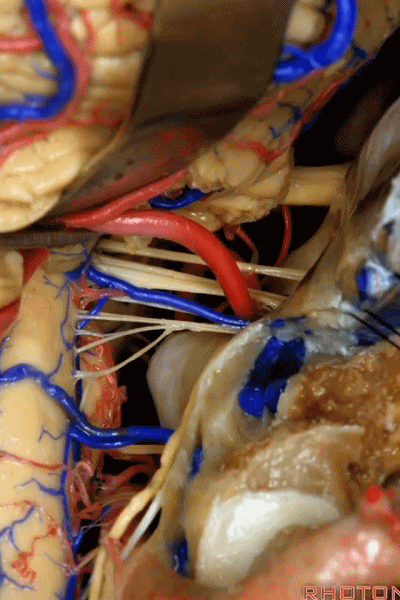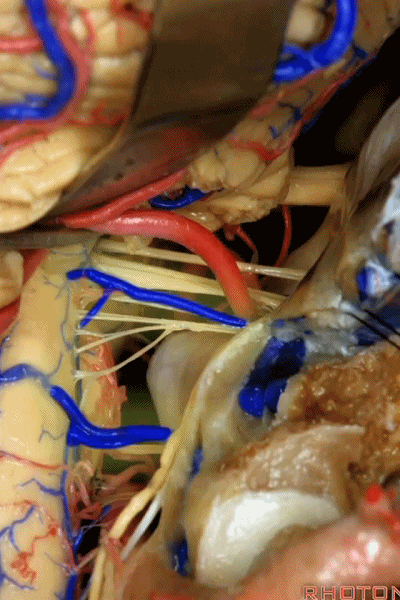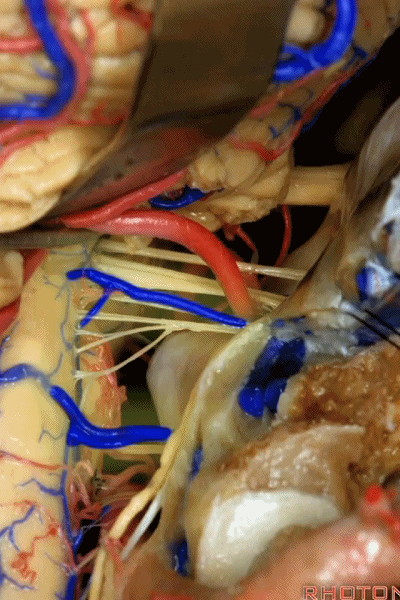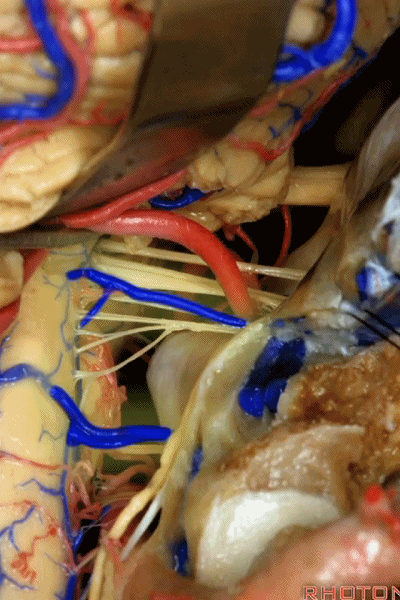
▼我每次牵开小脑时,都会注意这些静脉 。
Whenever I elevate the cerebellum, I look for these.
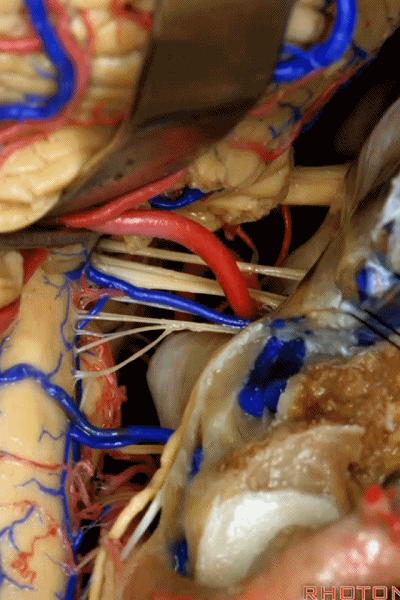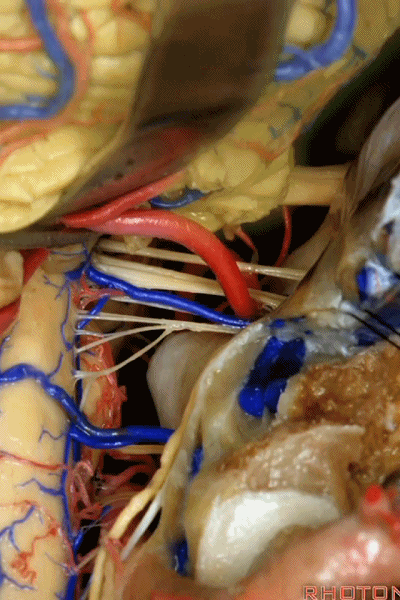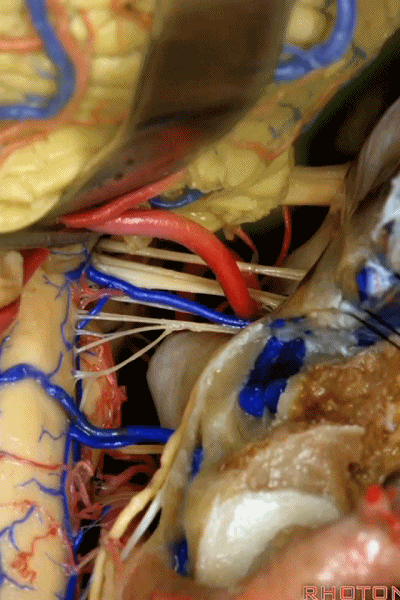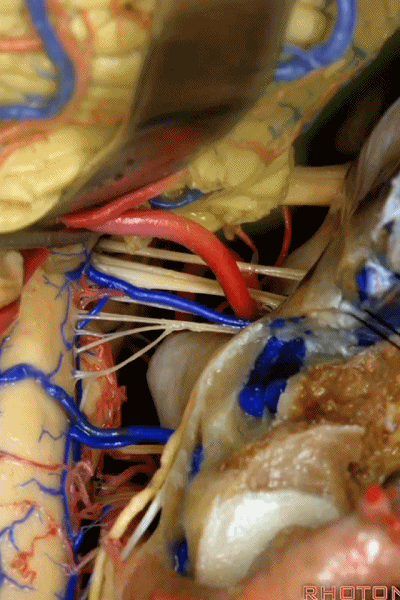
▼因为细小的牵拉即可造成出血,出血点在舌咽和迷走神经之间,而用明胶海绵和双极进行止血时,就容易损伤这些神经。因此,如果我遇到这些静脉,而我需要进行牵拉操作,那么为了保护神经,我干脆使用双极处理掉这些静脉。
because if you stretch them or tear them and when you get a clot around IX and X, and you put in cottonoids and bipolar, it's easy to damage these nerves. So if I see these veins and I'm gonna stretch them,then I usually protect the nerves and just bipolar it and get it out of the way.
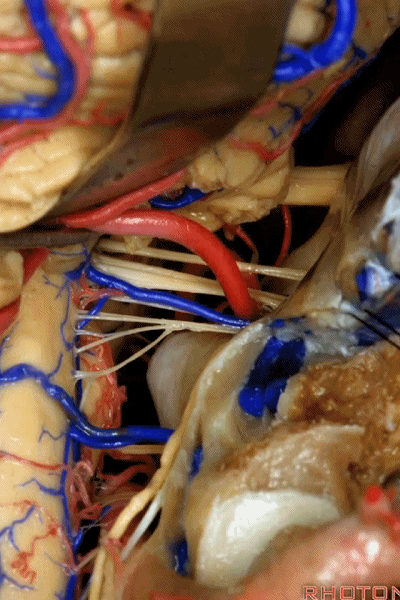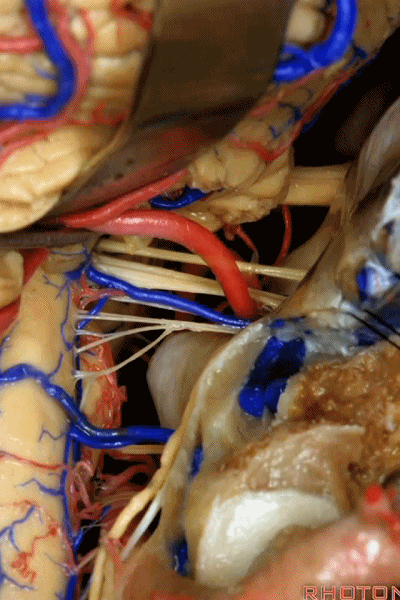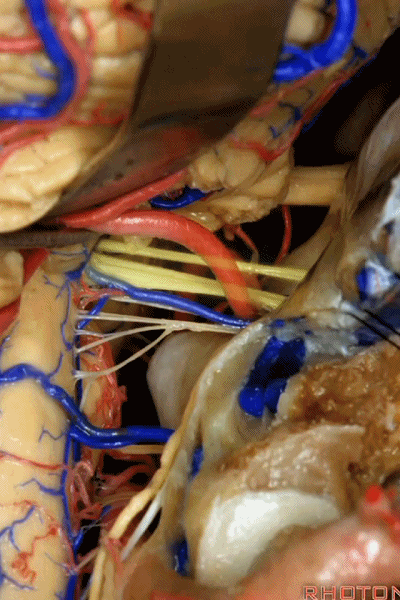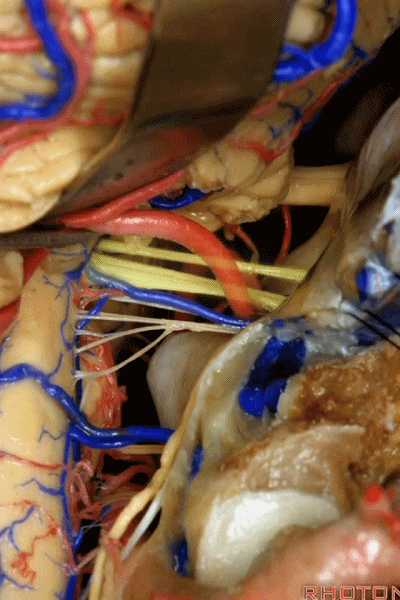
![]()
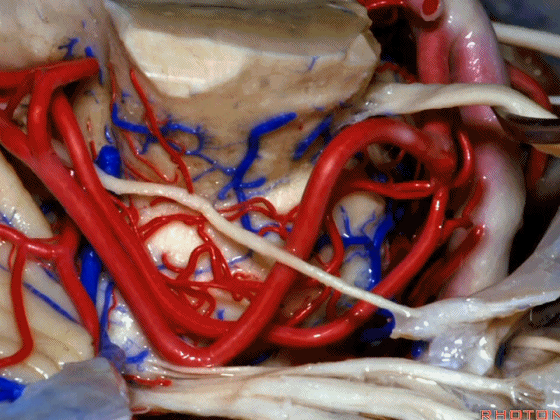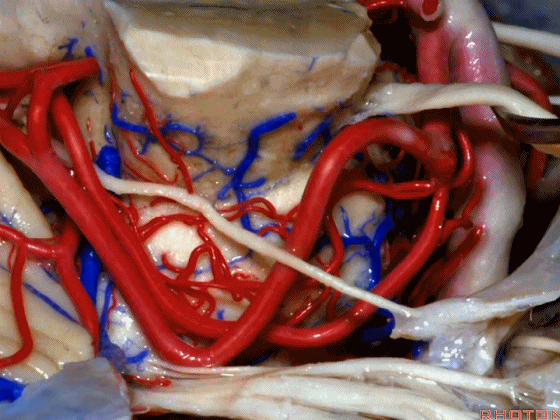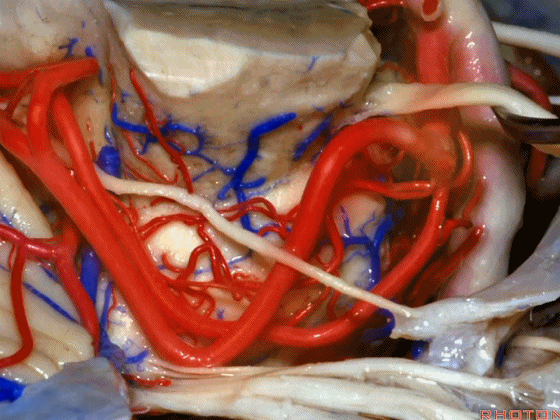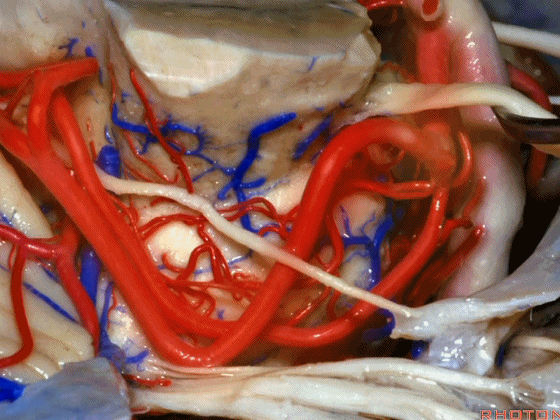
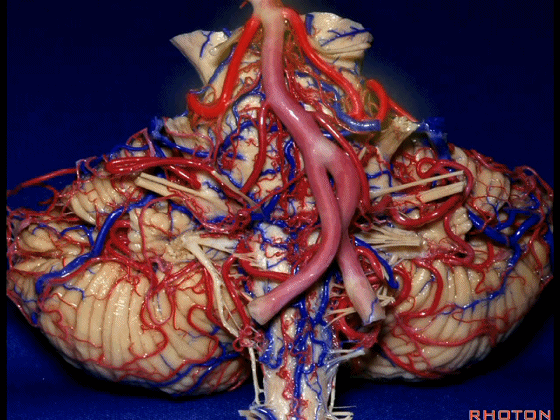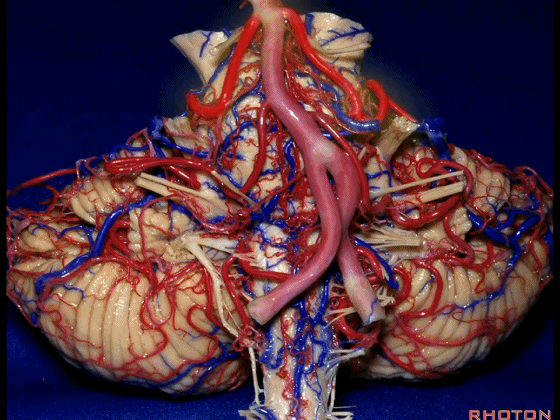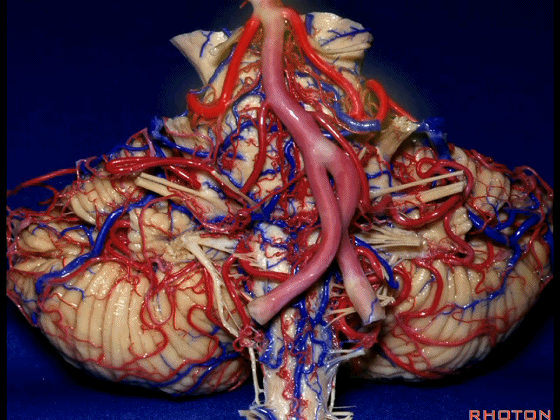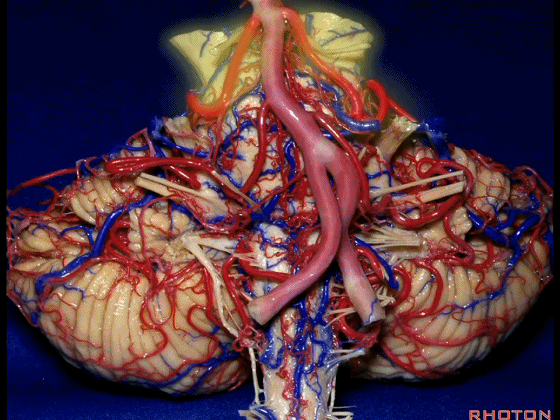
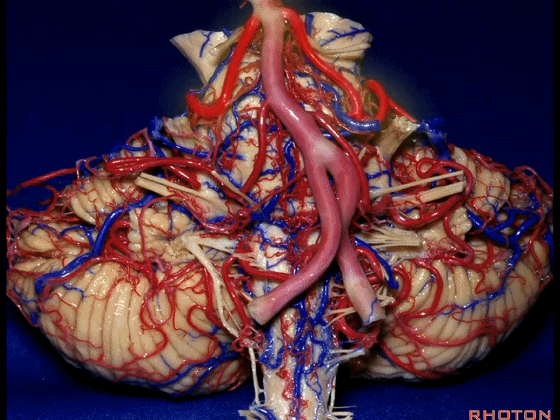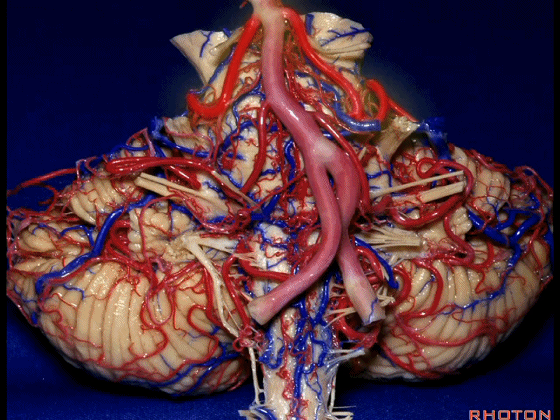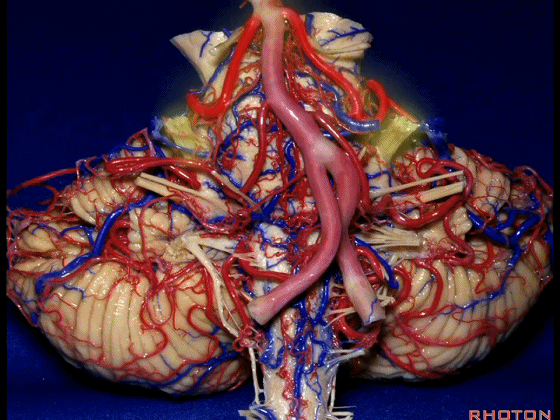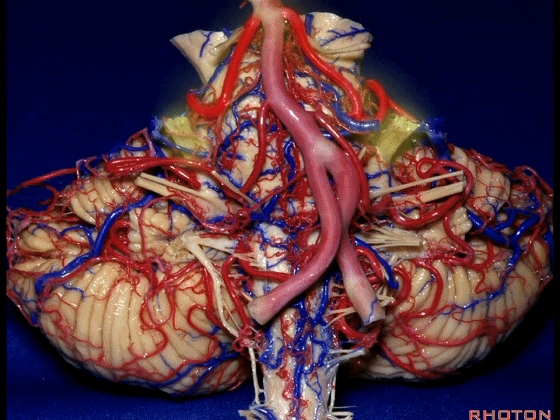
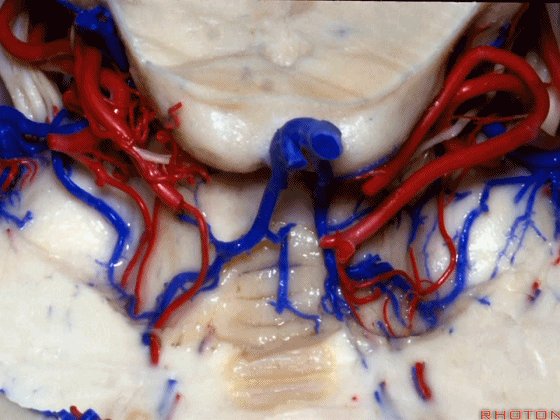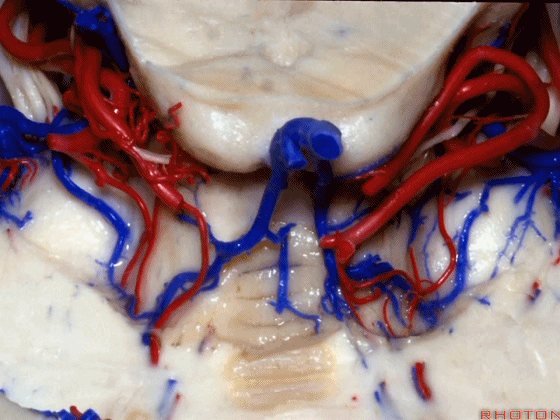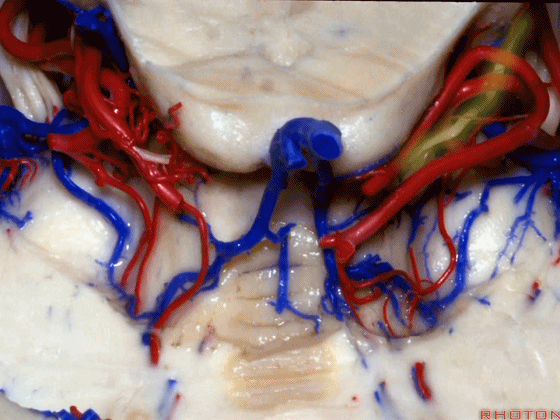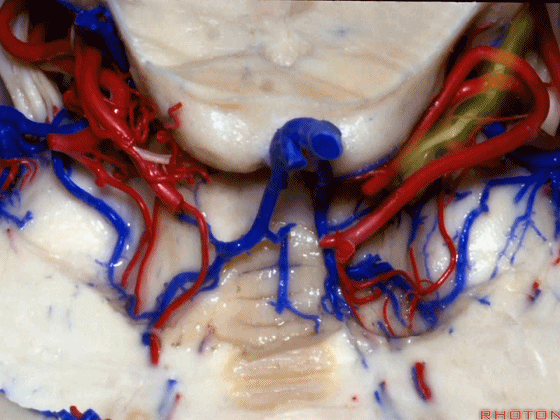
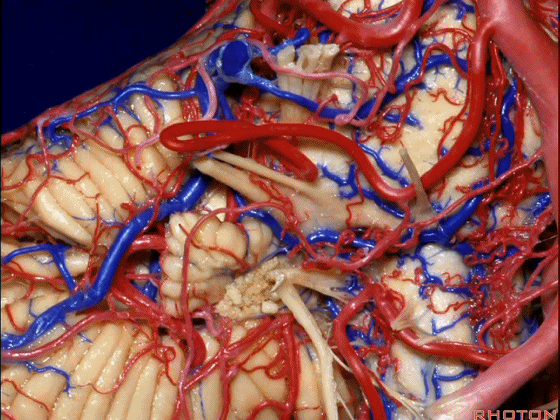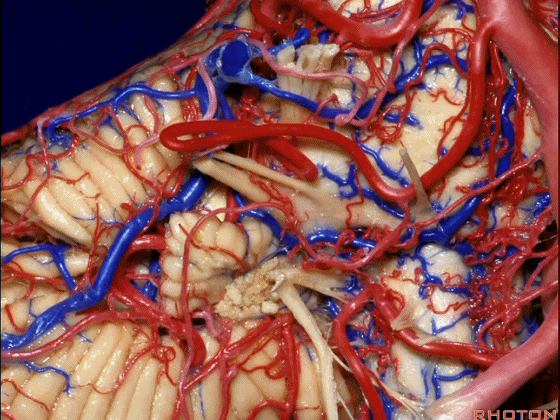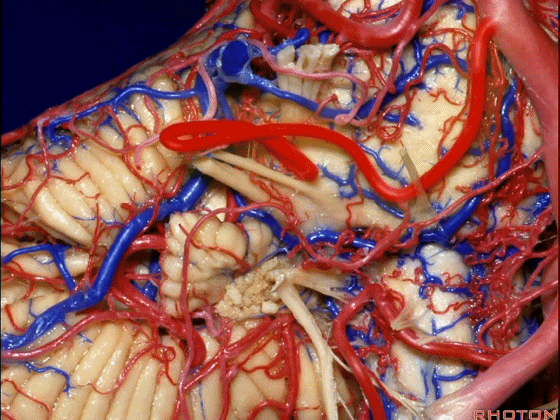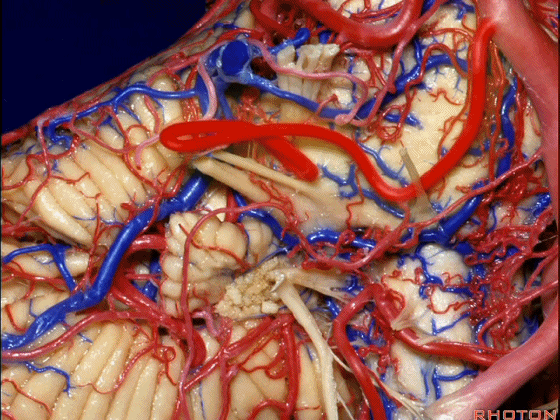
▼幕下的神经血管复合体,涉及三对重要血管:小脑上动脉、小脑前下动脉、小脑后下动脉。
这是小脑上动脉 SCA。
And we build this complex three arteries:SCA, AICA, PICA.
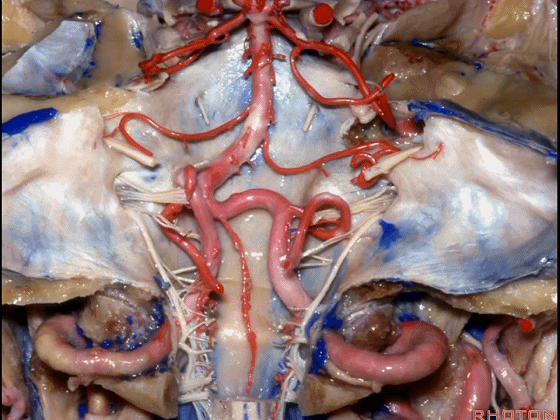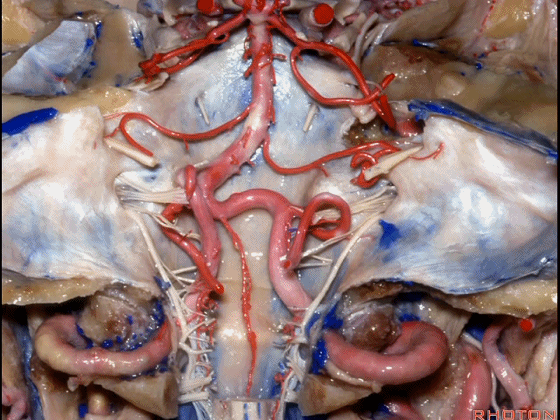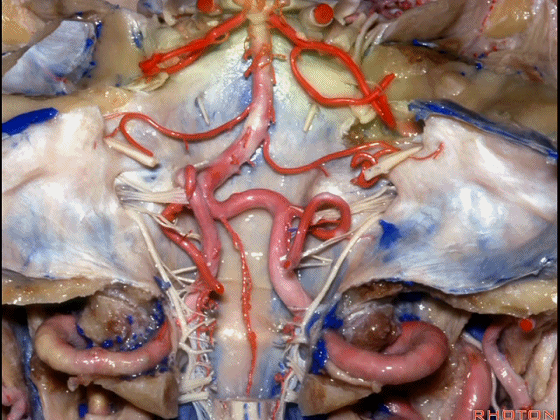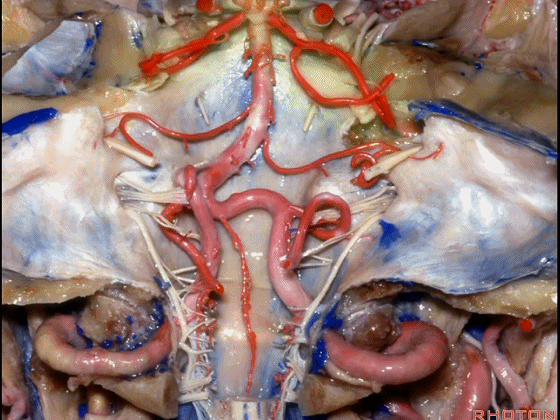
▼这是 小脑前下动脉 AICA。
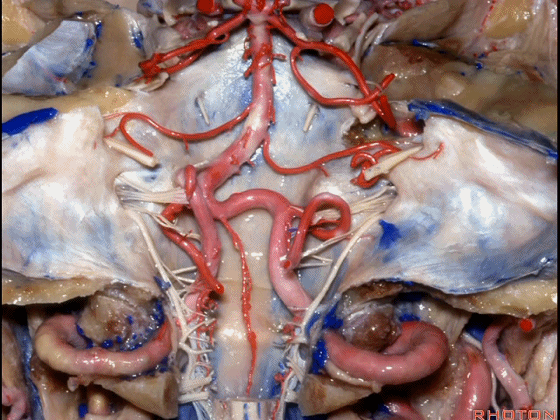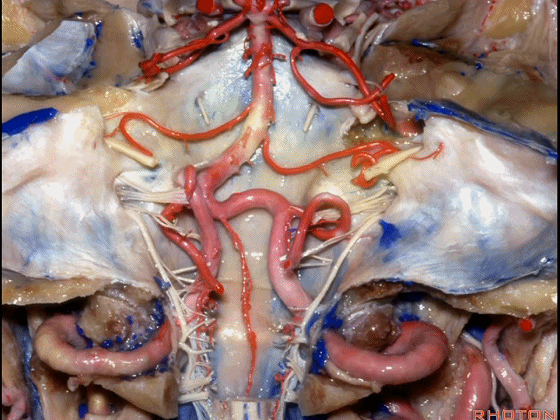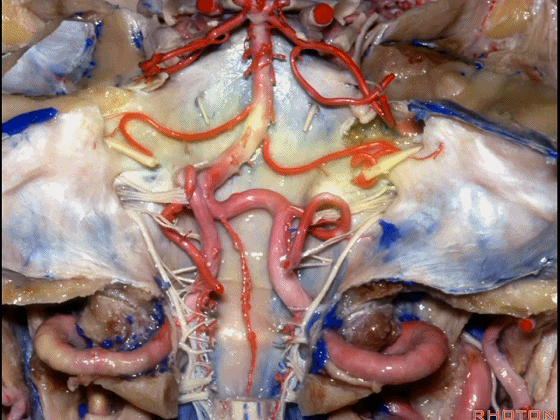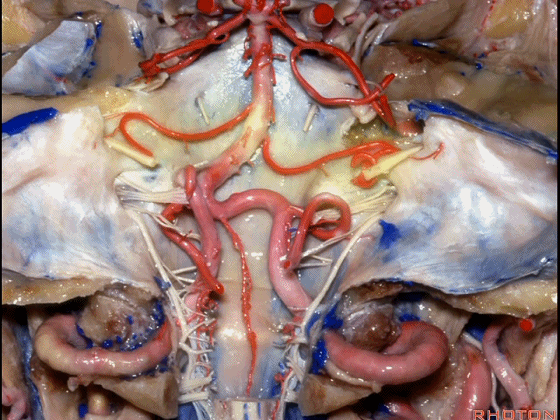
▼这是 小脑后下动脉 PICA。

▼现在来看上神经血管复合体。小脑上动脉自中脑水平发出。
The SCA arises at midbrain level.
▼小脑上动脉走行在 动眼神经和滑车神经下方,三叉神经上方。
it passes below III and IV, above V.

▼随着年龄的增长小脑上动脉常常向下迂曲。其通常以单一主干起源,随后分为两支,头干(下图)通向蚓部,尾干供应小脑半球幕面。
And with age it often loops downward. It arises usually as a main trunk that divides into a rostral trunk to the vermis, a caudal trunk to the hemisphere.
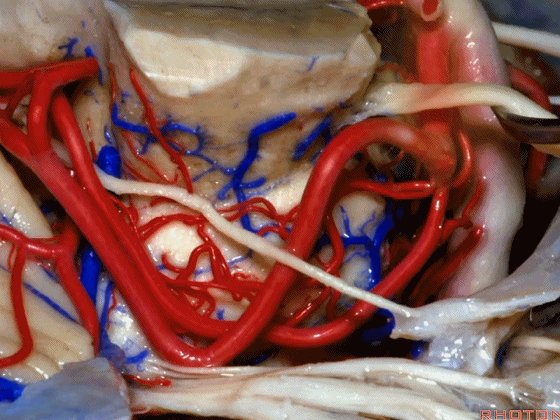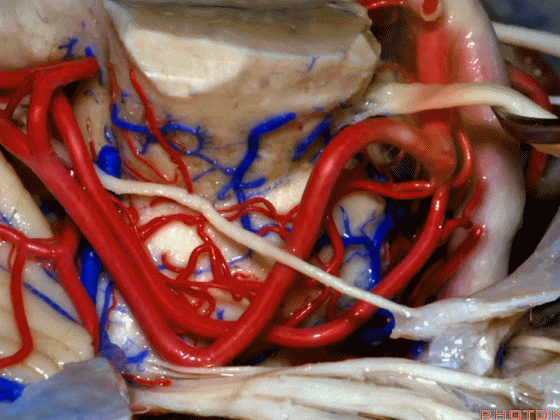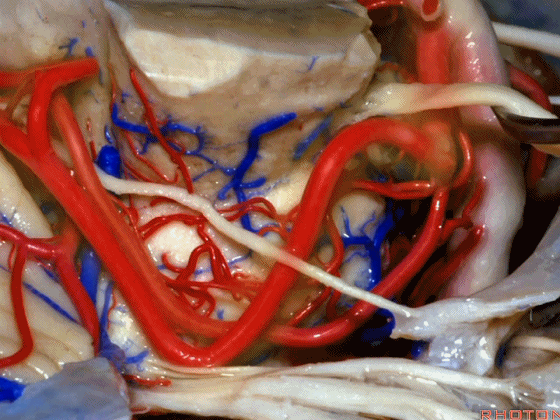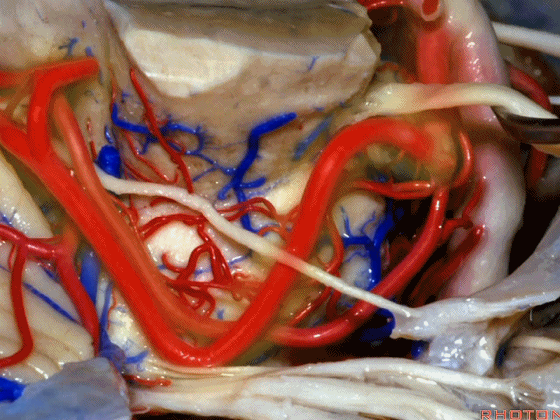
▼这是 小脑上动脉 尾干, 供应小脑半球小脑幕面。
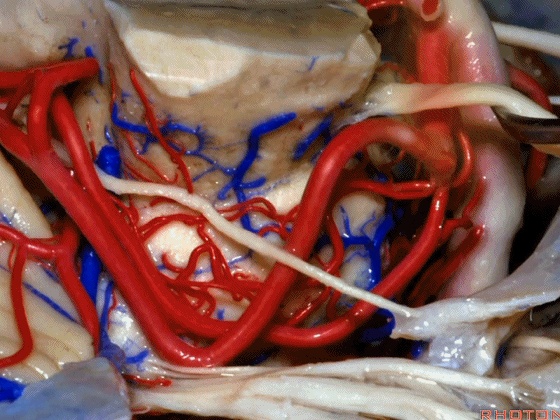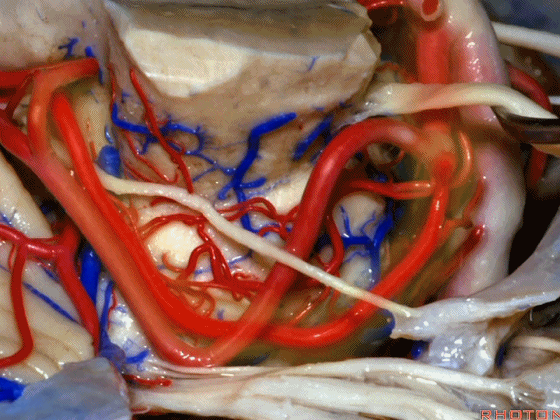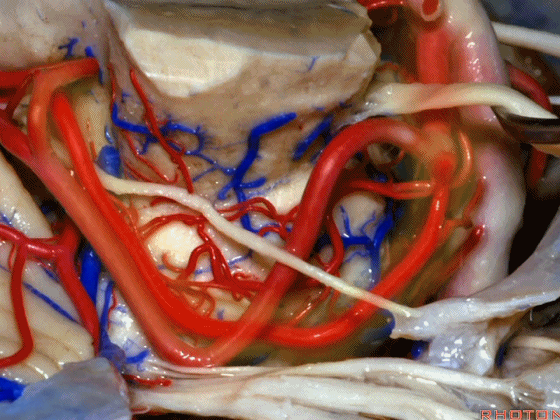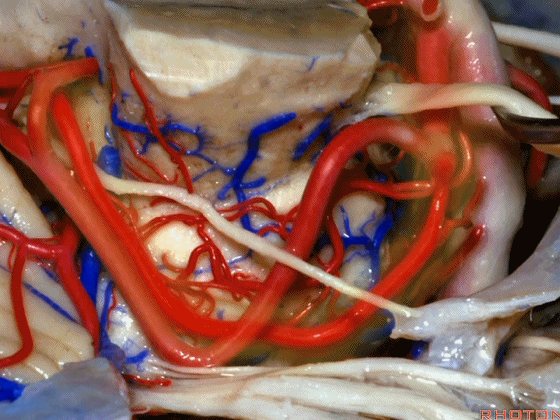
▼这些动脉干都有可能在脑干旁压迫三叉神经。而这正是三叉神经痛微血管减压术中最常见的情况。
And any of these trunks can compress the trigeminal nerve here right adjacent to brainstem. And that's the most common finding in the vascular decompression operation for trigeminal neuralgia.
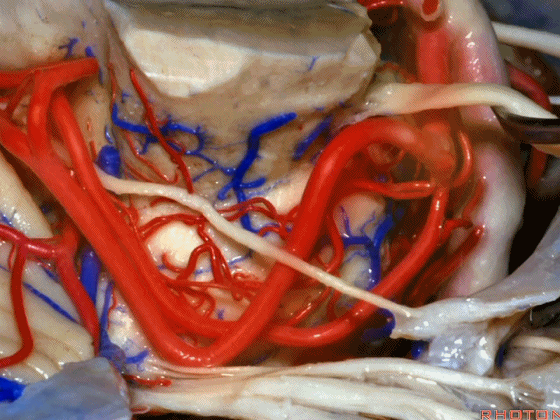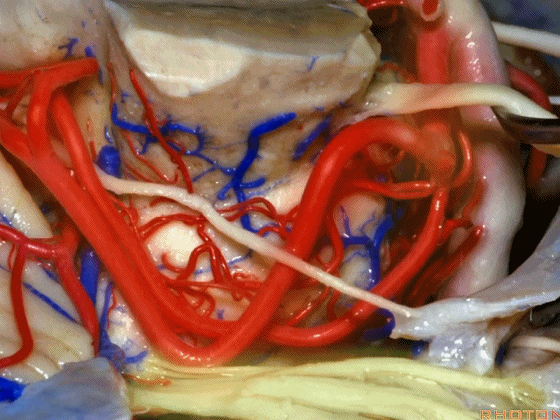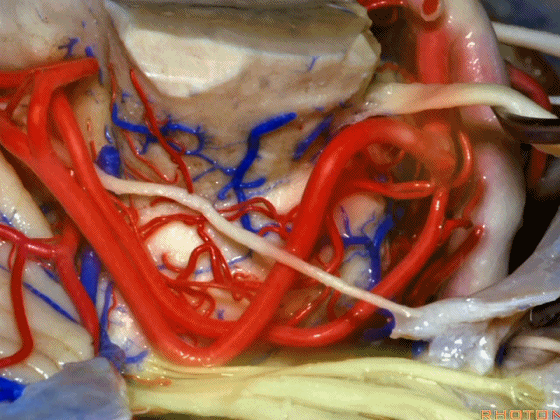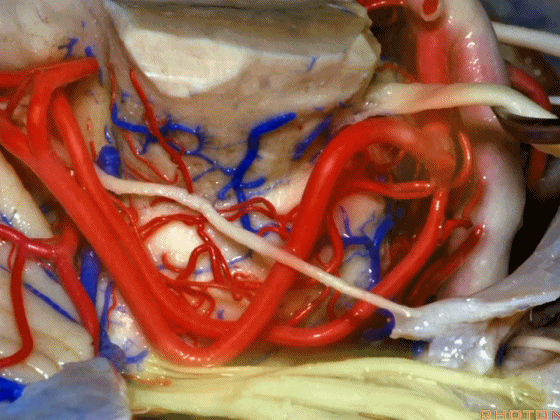
▼在三叉神经痛微血管减压术中,通常情况下,年轻人群的小脑上动脉起自中脑水平,并绕行于下部中脑(下图)。
And here's what happens in trigeminal neuralgia,normally, early in life, this SCA arises at midbrain level,and it circles the lower midbrain.
▼而随着年龄增长,这条动脉向下迂曲,术中可见其从上方压迫三叉神经,或更为向下迂曲而从腋下压迫三叉神经。
But with age, this artery loops downward and in trigeminal neuralgia we find it, often find it sitting here on top of the trigeminal nerve, or loop down into the axilla of the trigeminal nerve.
▼术中有时会牺牲这些岩上静脉或其属支,以暴露三叉神经。
And when you sacrifice these superior petrosal veins or the tributaries, to get to the trigeminal nerve.
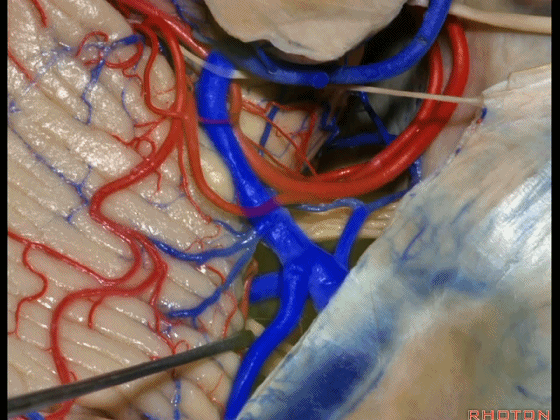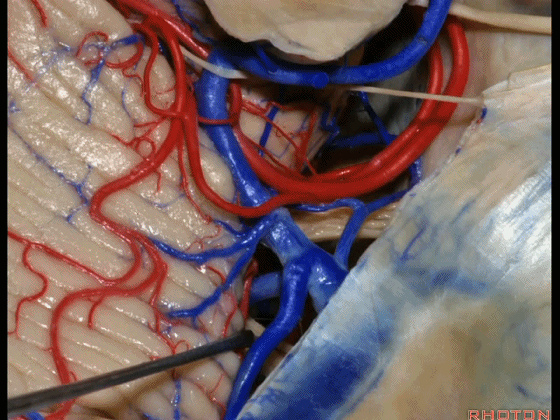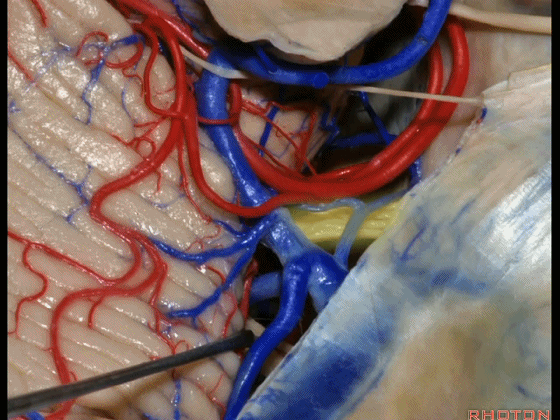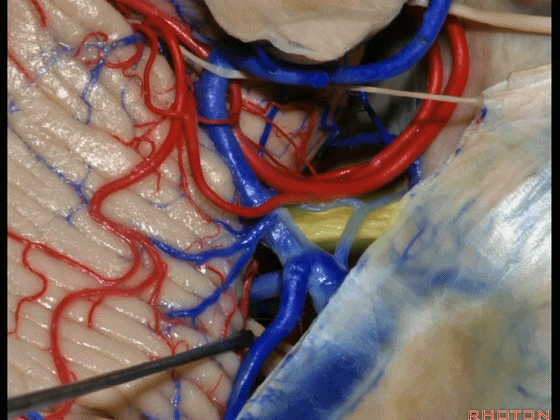
▼因此在幕下侧方入路中,接近岩上窦(下图)时,需非常小心地分离出每一支小脑上动脉的分支,它们会在蛛网膜下腔中,与静脉相粘连缠绕。
when you do the lateral infratentorial approach coming adjacent to superior petrosal sinus, always be careful to dissect out any trunks of superior cerebellar artery that may be involved in the arachnid, binding the artery to the veins.
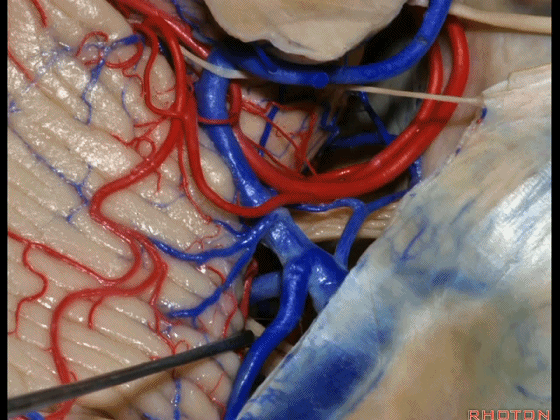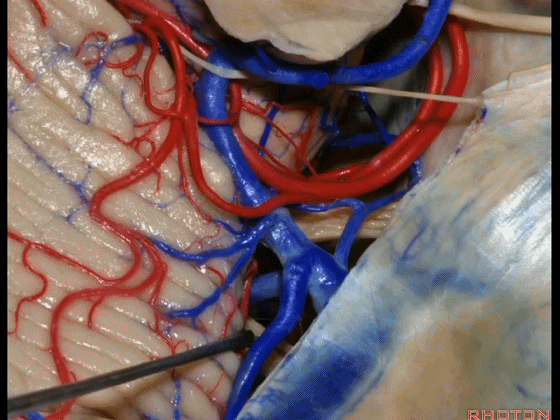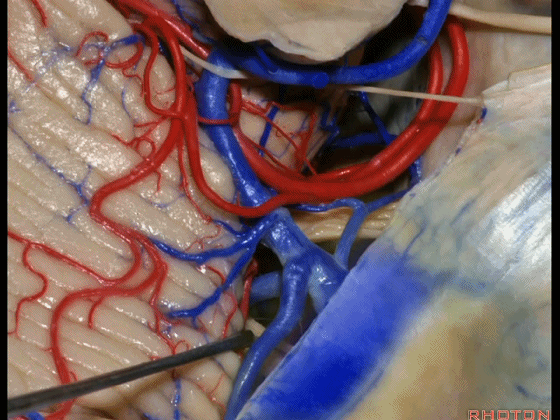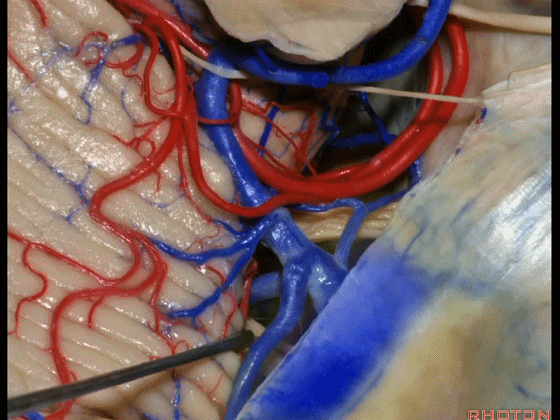
▼许多术后发生梗塞的病例往往被考虑为损伤静脉引起的静脉性梗塞,而我认为其实是损伤了小脑上动脉的分支引起的动脉性梗塞。因此在处理这些静脉时仔细操作。
I think a number of cases that are called venous infarction from taking the veins are actually arterial infarction from taking a trunk of the SCA. So be very careful in sacrificing these veins.
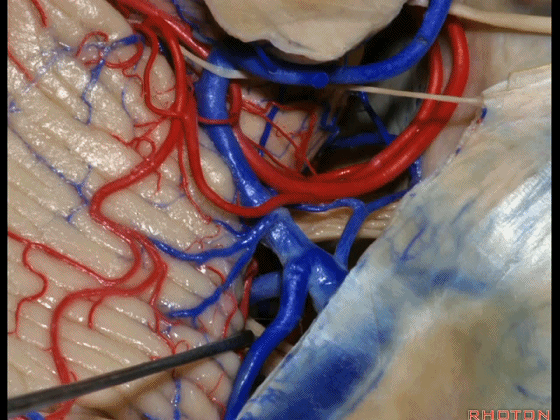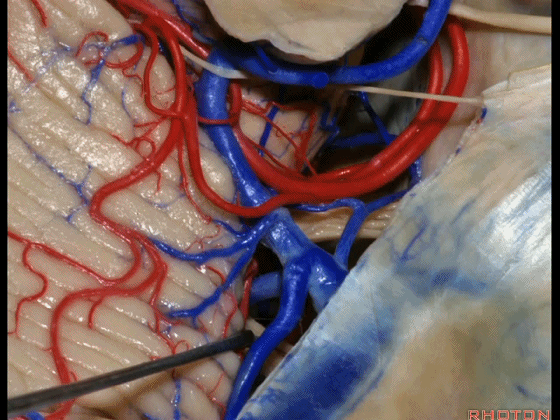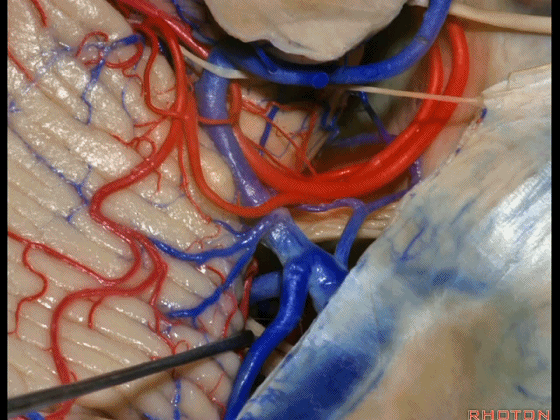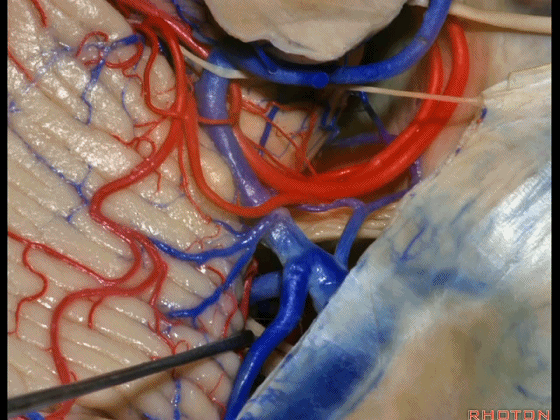
▼这些小脑上动脉的分支,穿行在小脑中脑裂中。
And these arteries as they come around the SCA, they dip into the the cerebello-midbrain fissure.
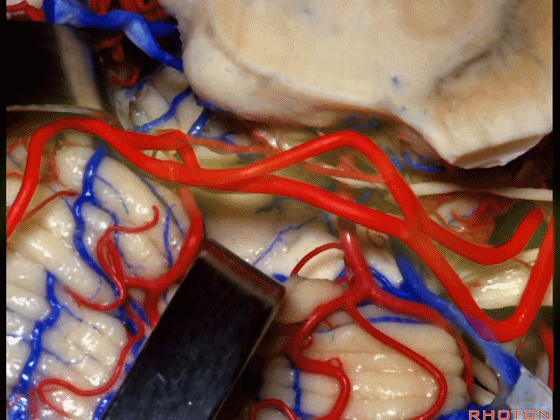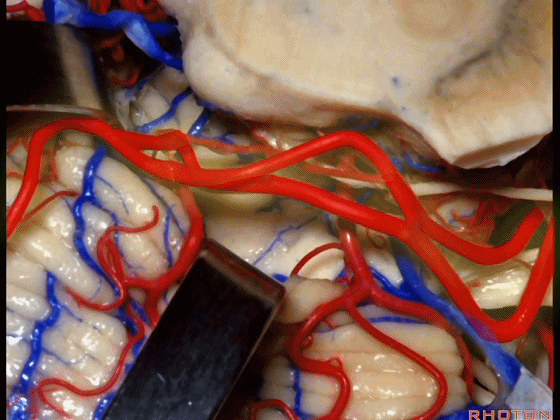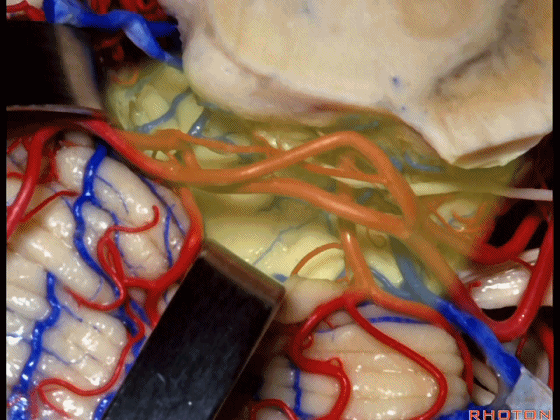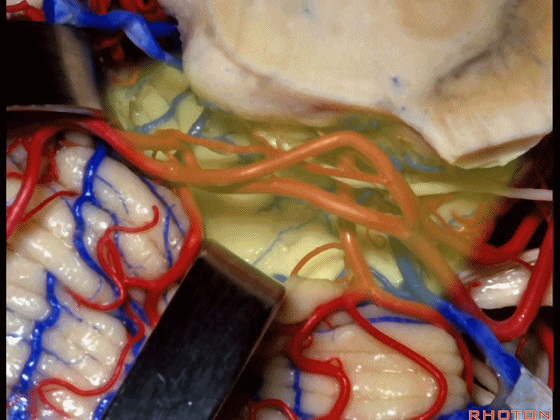
▼小脑上动脉 环绕 中脑。
So this is upper complex, SCA encircling midbrain.

▼小脑上动脉 深入 小脑中脑裂 (cerebello-midbrain fissure 下图)之中。
It dips into this fissure.

▼小脑上动脉 主要供应 小脑半球的小脑幕面。
and supplies this tent shaped surface.

▼小脑半球的小脑幕面最上部是 上蚓部。
that has the vermis at the upper side of it.
▼这些小脑上动脉的分支在小脑中脑裂内呈现一系列发卡样转弯,并与滑车神经(下图)相互缠绕。
where it has a series of hairpin turns. It's intertwined with the 4th nerve.
▼随后其向下发出分支供应小脑上脚(下图),以及齿状核,后者是小脑出血的最常见部位。
And then it sends its branches down the superior peduncle, then to the dental nucleus, the most common site of cerebellar hemorrhage.
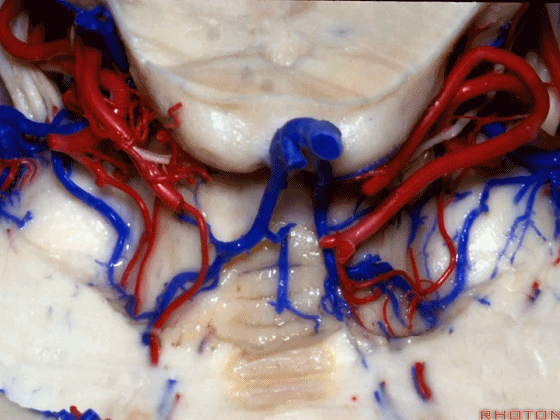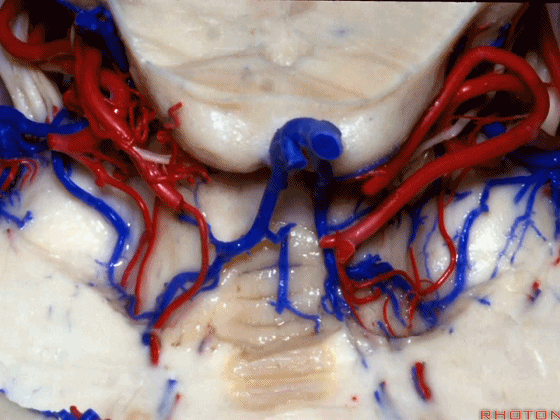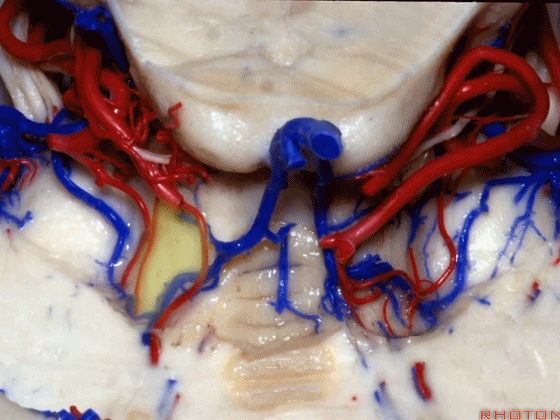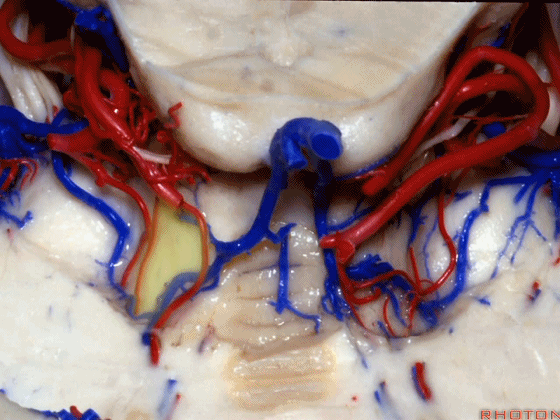
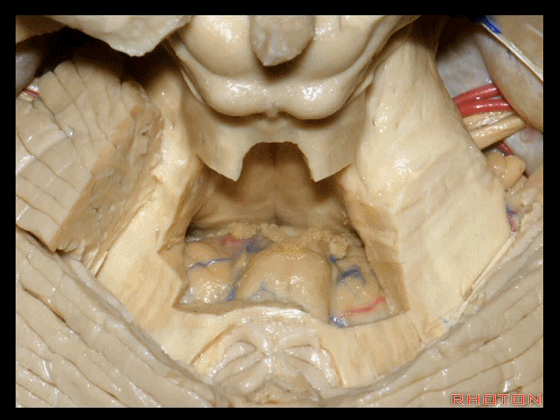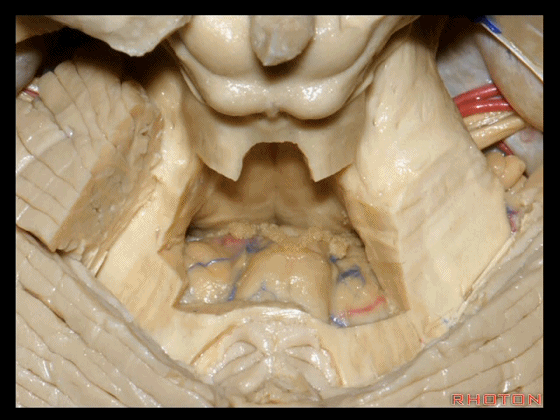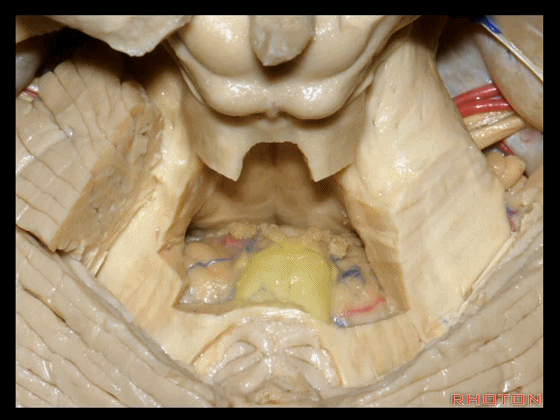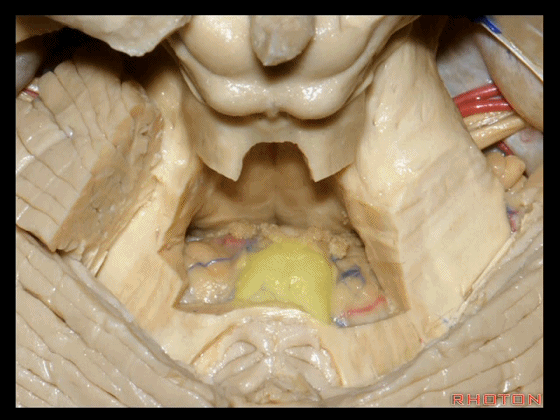
▼这里我们切开了蚓部的小舌和上髓帆,这是面丘。
Here we've opened up the lingula of the vermis and the superior medullary velum. And what is this? Facial colliculus.
▼从下往上突入的这个结构是蚓部小结。
And what is this bulging up from below? This is nodule bulging up with.
▼随之一起突入的还有下髓帆(下图)。
inferior medullary velum.
▼这是脉络膜,脉络丛起源于此。
tela in which the plexus arises stretches around it.
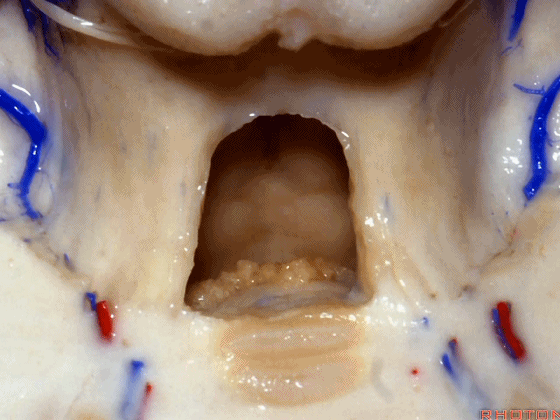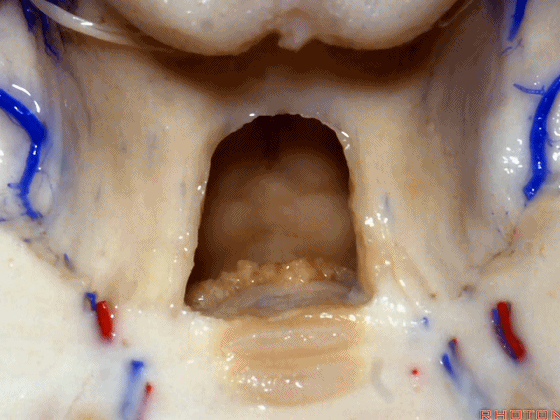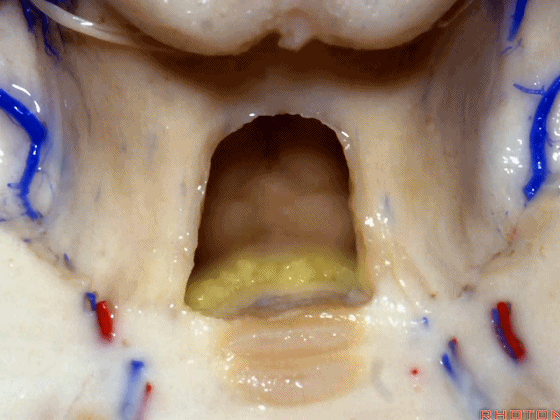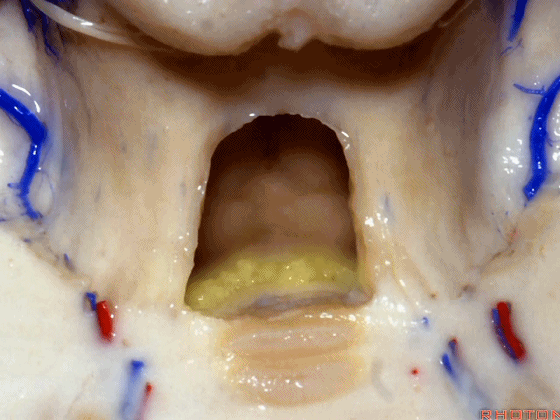
▼这是蚓部小结。
▼若向蚓部小结两侧继续切开,透过下髓帆(下图),可见小脑扁桃体的头部。
And if we open up a little bit more lateral to the nodule, we'll see through the inferior medullary velum. That is the cranial pole of the tonsils.
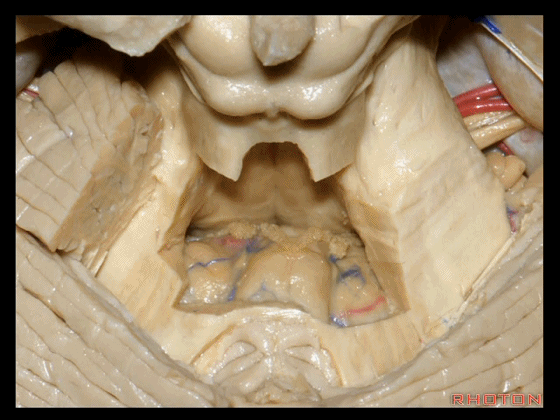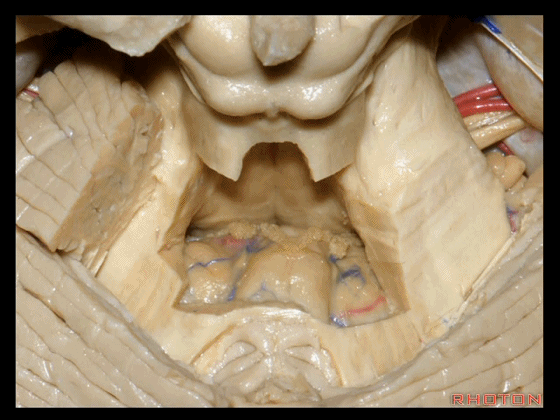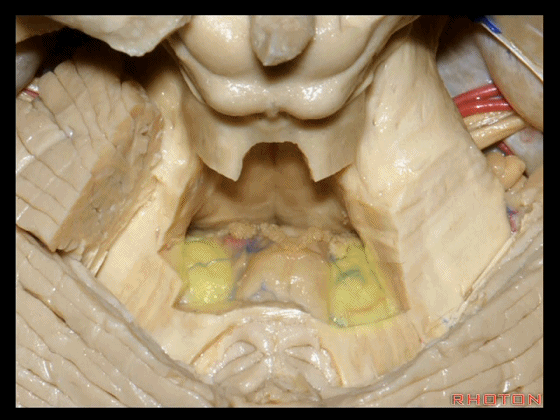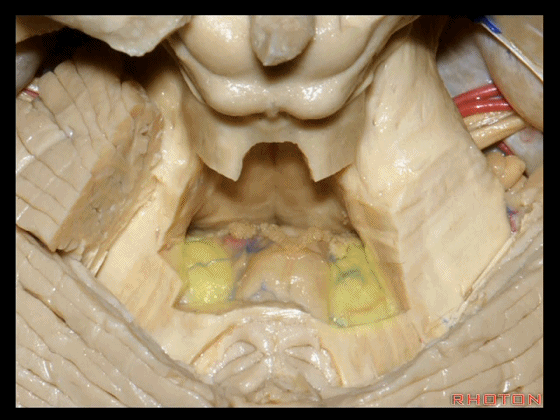
▼下图示绒球。
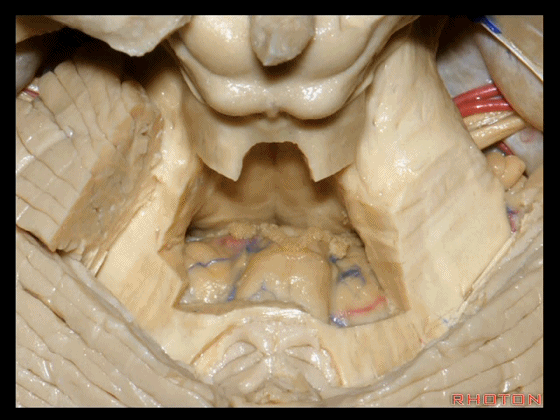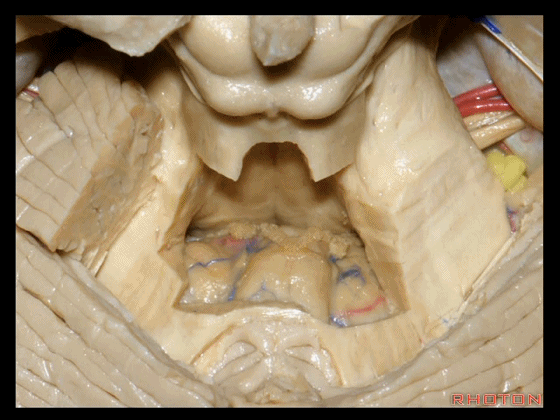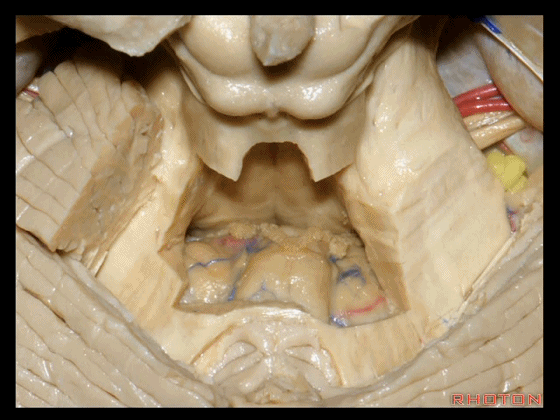
▼下髓帆将 小脑绒球 与 蚓部小结 相连,从而构成称为原小脑的绒球小结叶。
The flocculus and the nodule are connected. What connects them?The inferior medullary velum to complete that primitive flocculonodular lobe of the cerebellum.
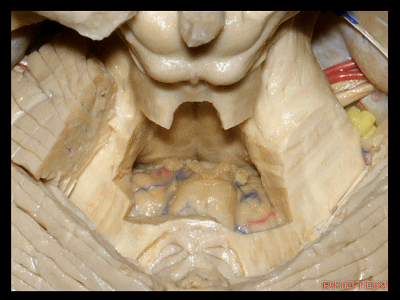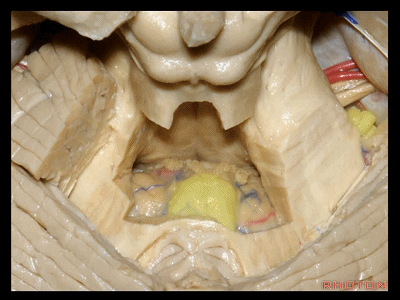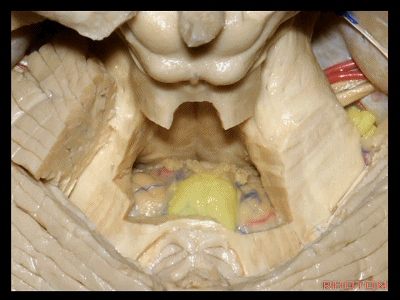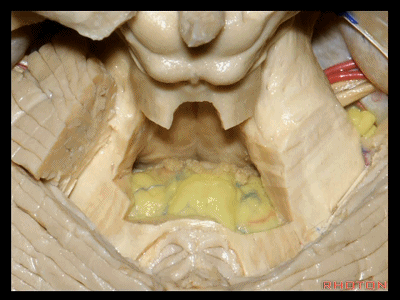
▼绒球小结叶,由一层菲薄的下髓帆(下图)连接。
So this is the flocculonodular lobe connected by the paper-thin velum.
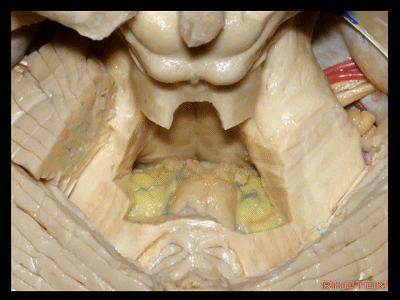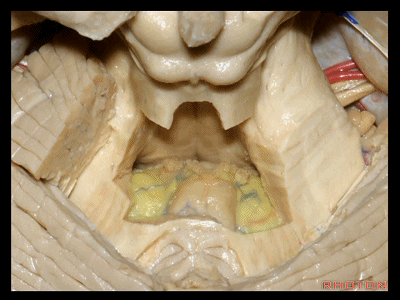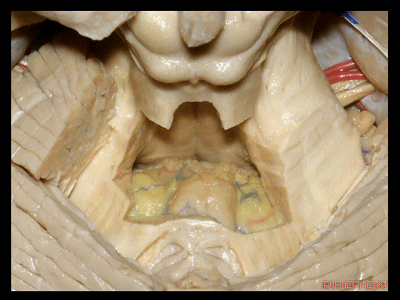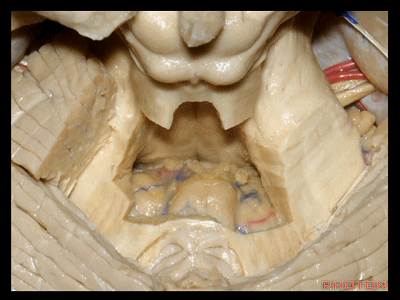
▼我们常可看到小脑后下动脉的头侧襻(下图)向上迂曲走行于下髓帆和扁桃体之间。
And often you see the cranial loop of the PICA looping up between the velum and the tonsil.
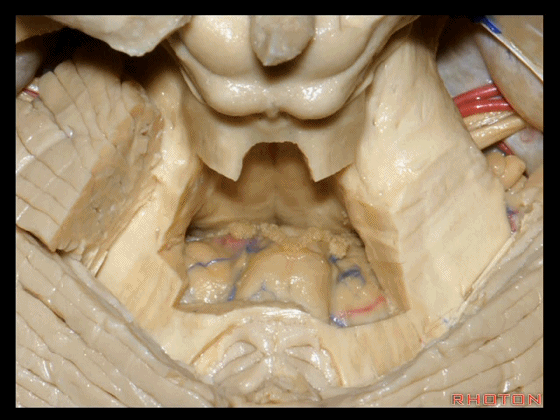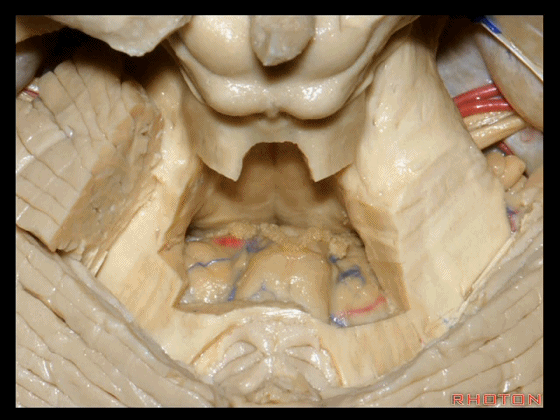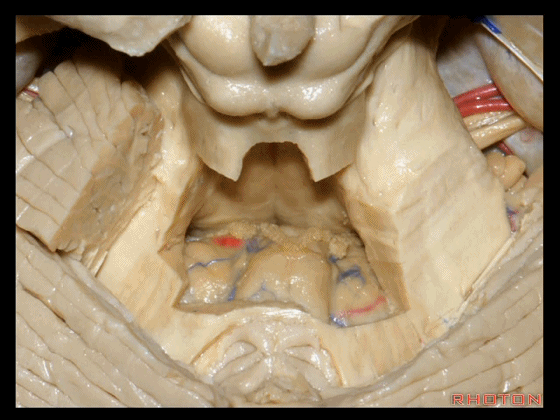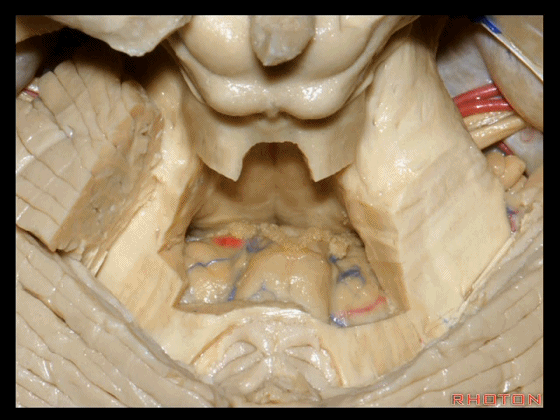
▼这个位于扁桃体头部周围的裂隙称为 膜帆扁桃体裂(扁桃体上裂)。
in what we call the telovelotonsilar cleft around the cranial pole of the tonsil.
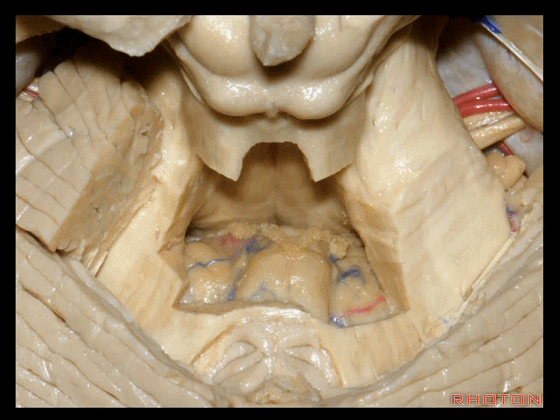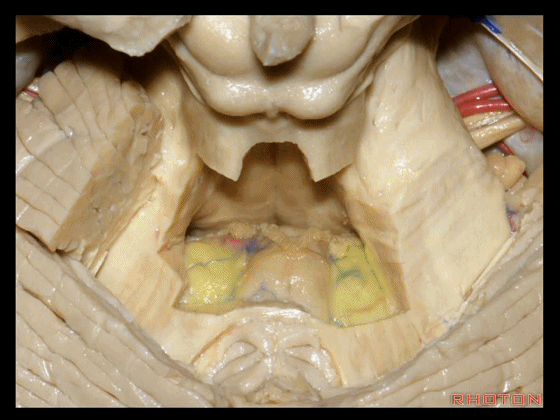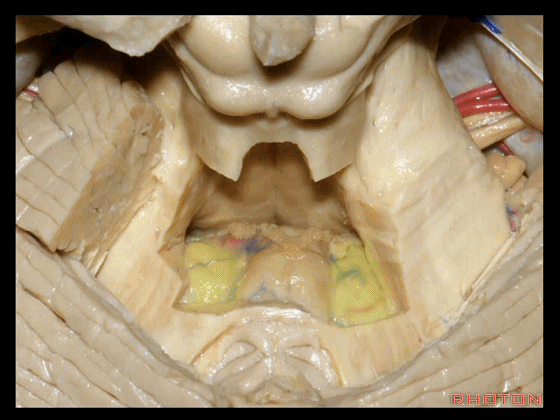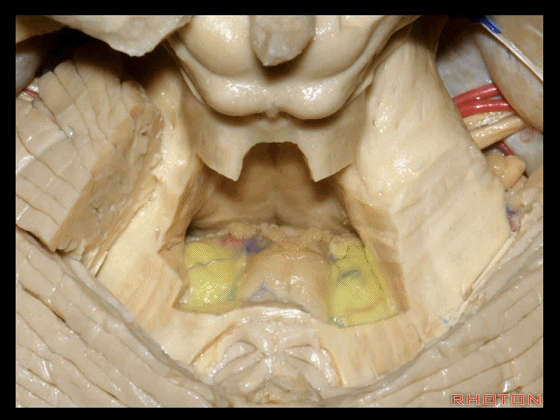
▼下面来看第二对 神经血管复合体:小脑前下动脉,起自脑桥水平。
And just AICA arises at pontine level.
▼小脑前下动脉 越过 外展神经。
passes by..what nerve? VI.
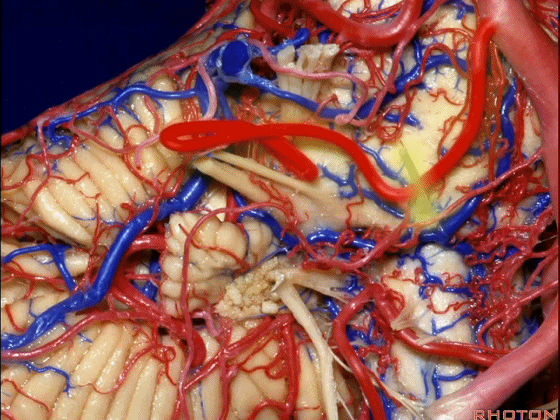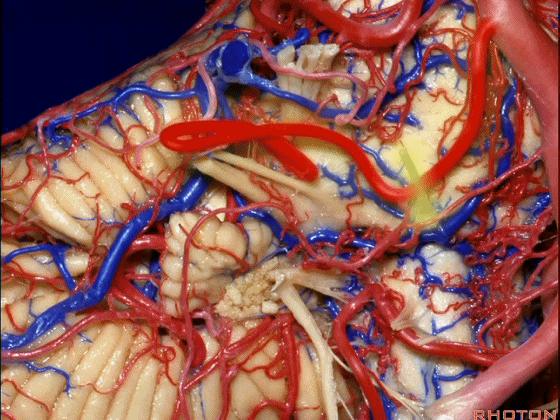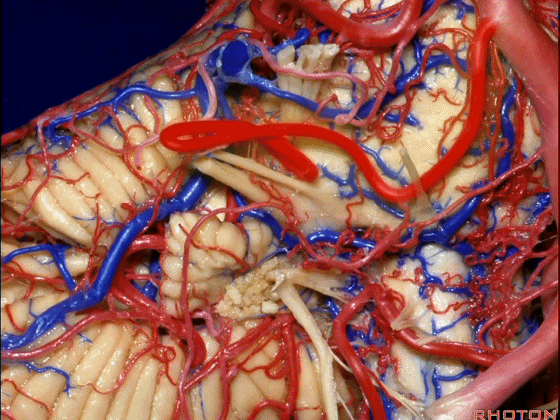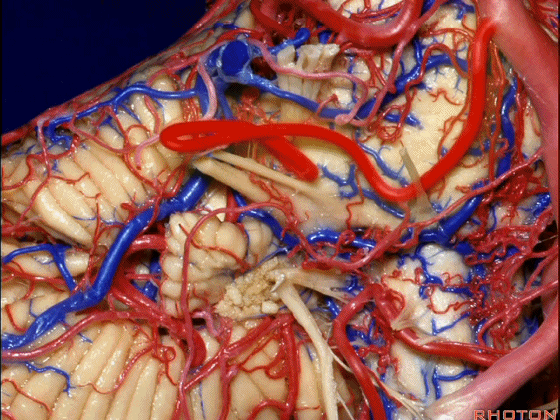
▼随后小脑前下动脉越过 面神经、以及前庭蜗神经。
Then VII, then VIII.
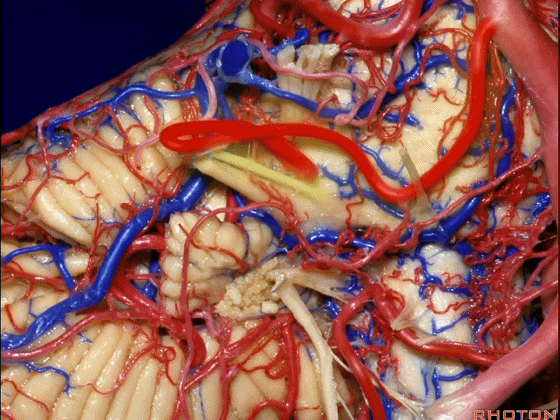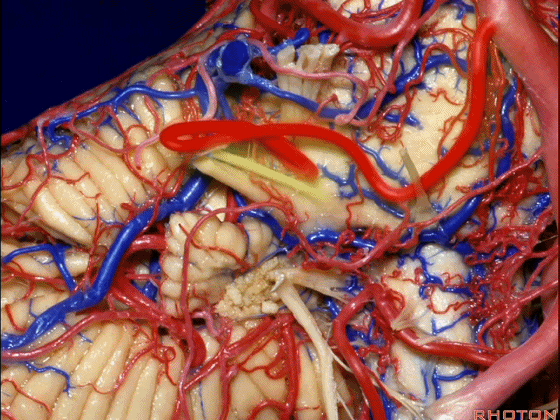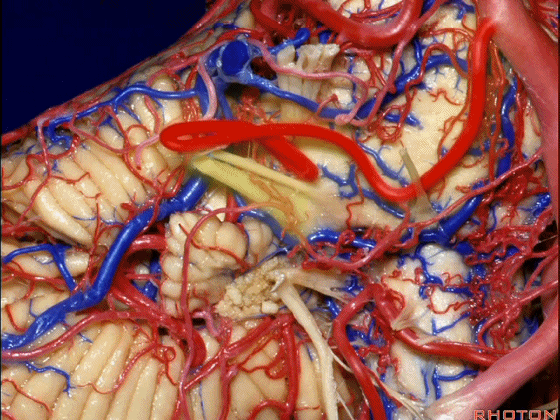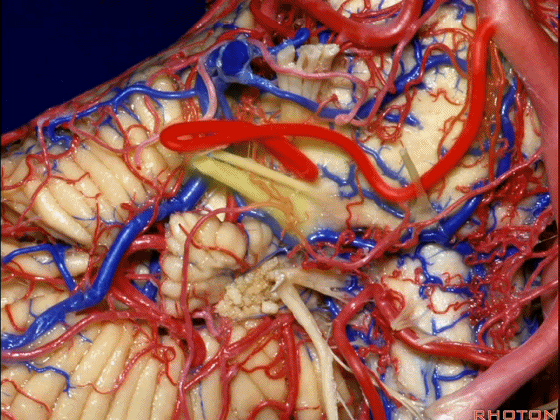
▼随后深入到的裂隙即所谓的 桥小脑裂 或 桥小脑角。小脑中脚构成桥小脑裂的底。随后,AICA供应小脑岩面的血供。
and then it dips into this cleft that we call the cerebellopontine fissure or angle. In the base of that cleft is the middle cerebellar peduncle. And then it supplies the surface that faces the back of the temporal bone.
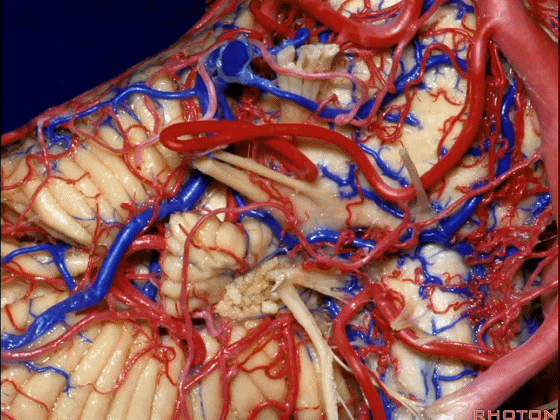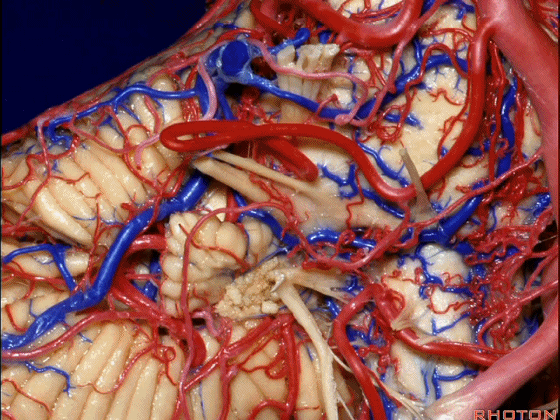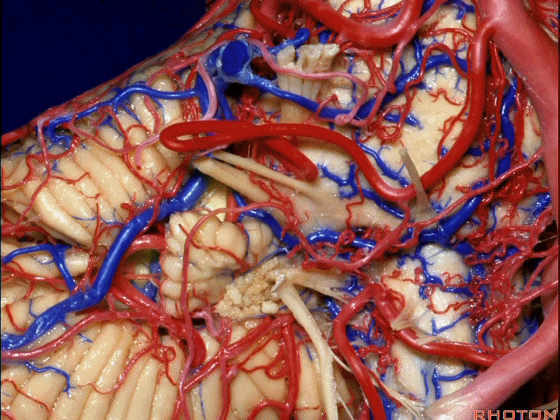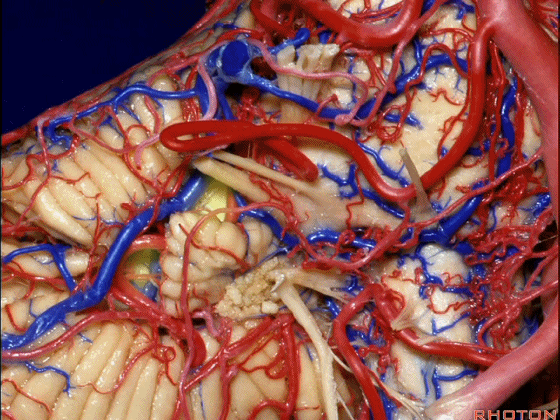
▼这是面神经、前庭蜗神经。
Here's VII and VIII.
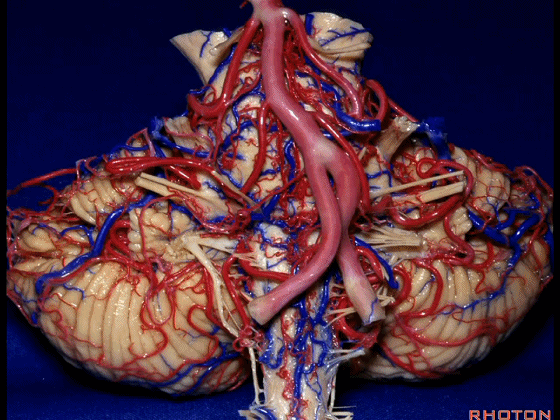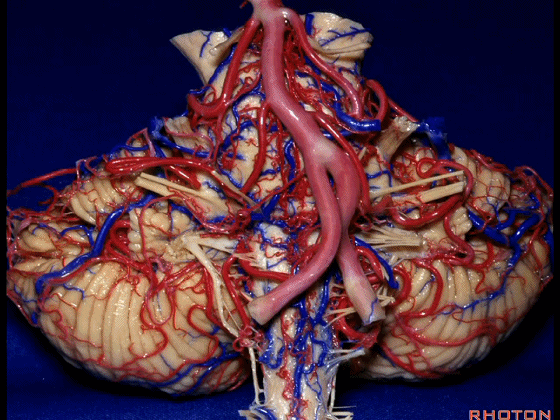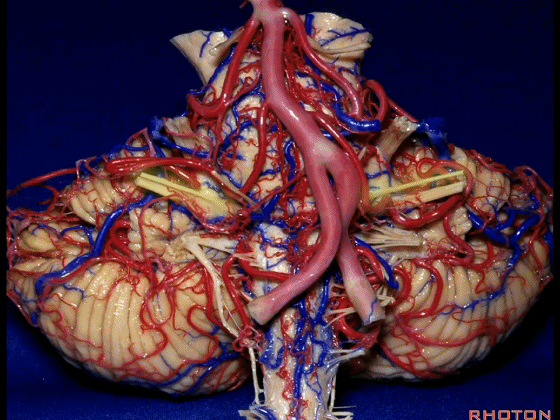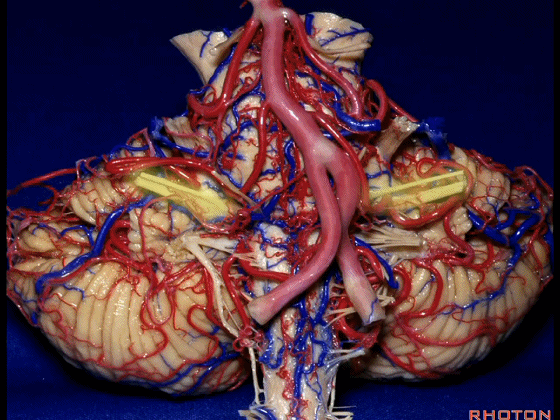
▼这是小脑前下动脉。
The AICA is here.
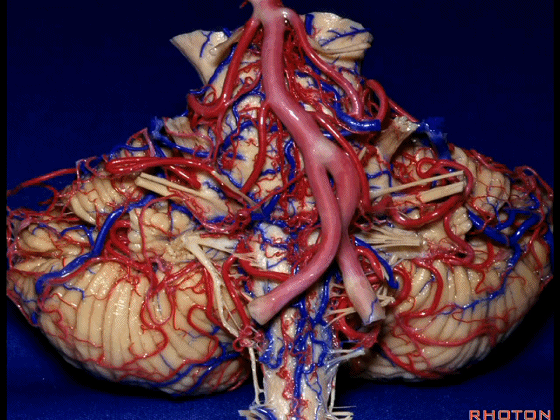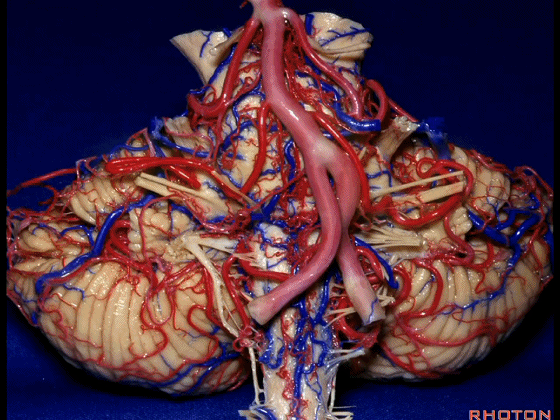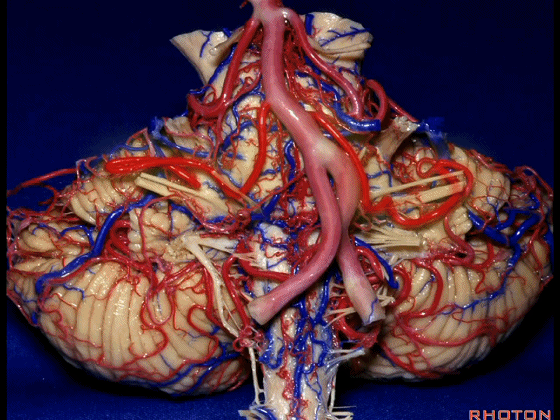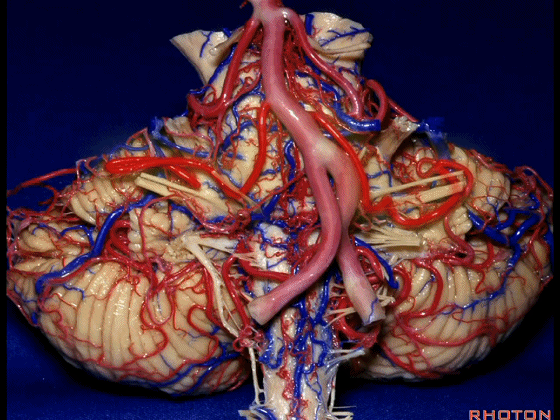
▼再让我们看看面肌痉挛术中所见。小脑前下动脉(下图)可向下迂曲压迫面神经。
And here's what can happen in hemifacial spasm.You can have an AICA loop down here next to VII at the junction with the brainstem.
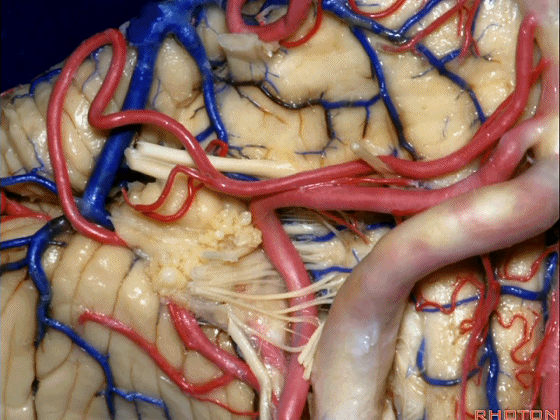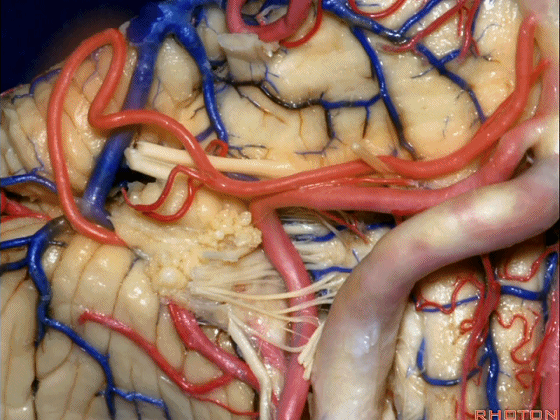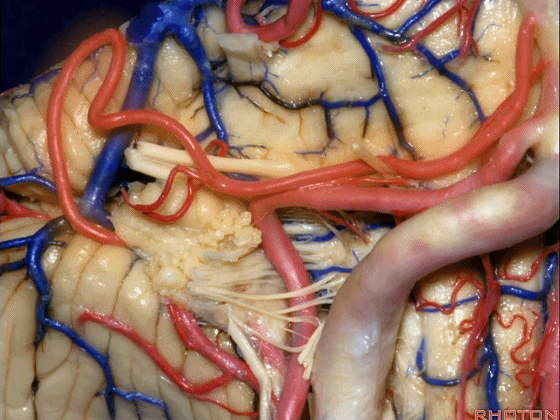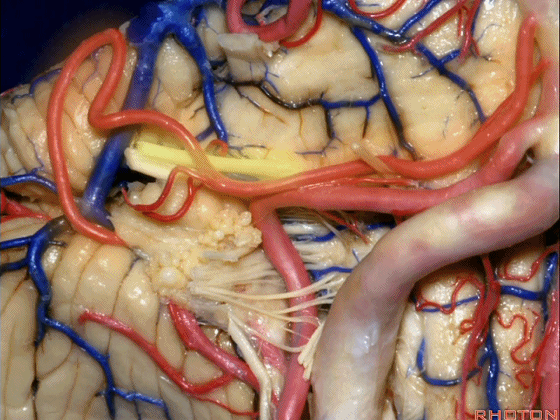
▼约另一半病例,则可见小脑后下动脉(下图)向上迂曲压迫面听神经。
Or in about half the cases, the PICA will loop upward under VII and VIII.
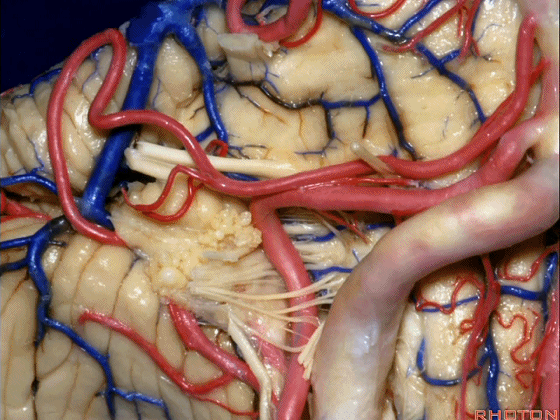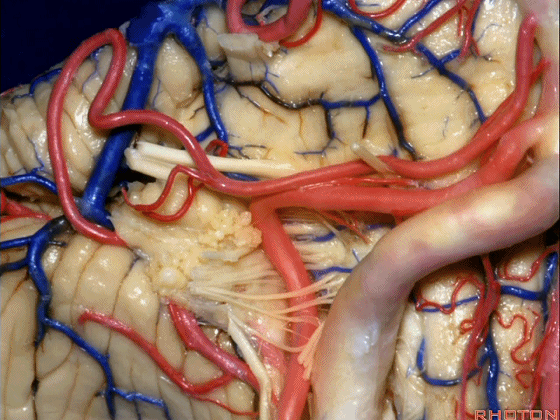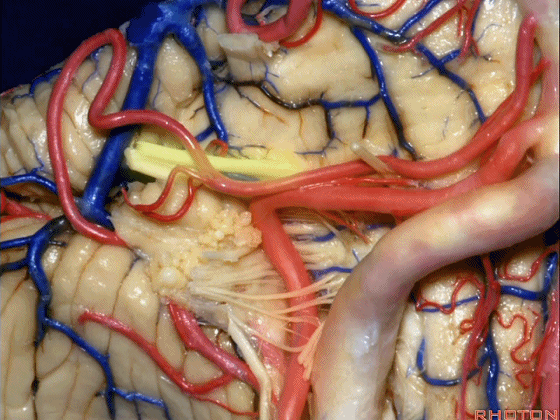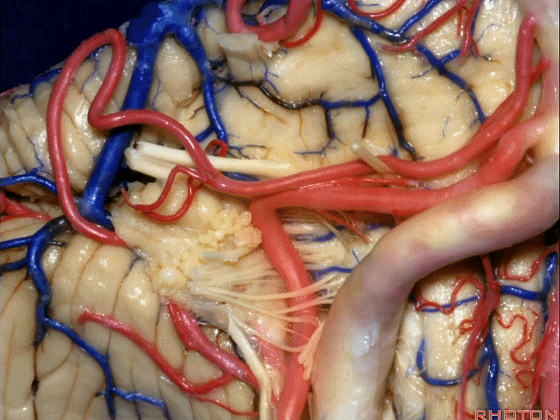
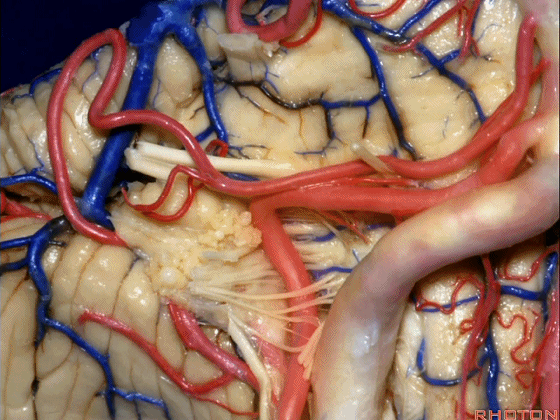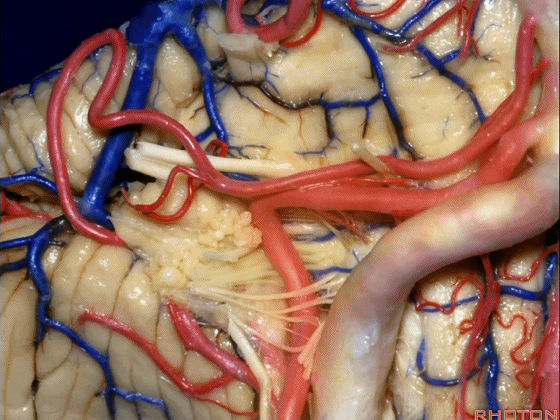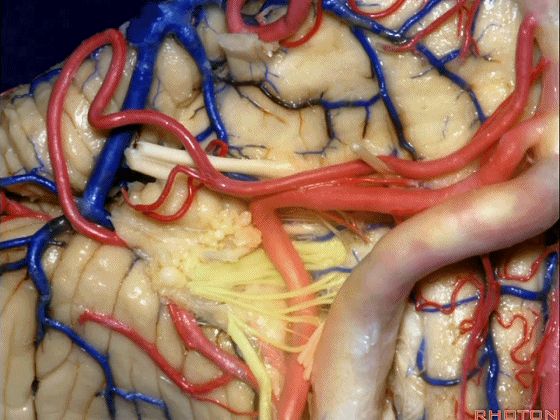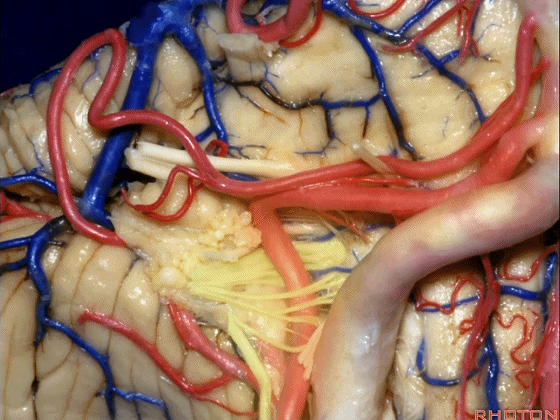
▼小脑后下动脉(下图)随后下行并从背侧穿行于舌咽神经与迷走神经之间。
and then it'll pass downward and it then passes dorsally some place between IX and the rootlets of XI.

▼小脑后下动脉可从背侧走行,此处(下图)看起来似乎在迷走神经和副神经下方,然后行向背侧。实际上它可穿行于舌咽神经至副神经之间的任何部位。
It can be passing dorsal.Here it looks like it's below between X and XI that it passes then dorsally to the nerves. But it can be any place between IX and XI.
![]()
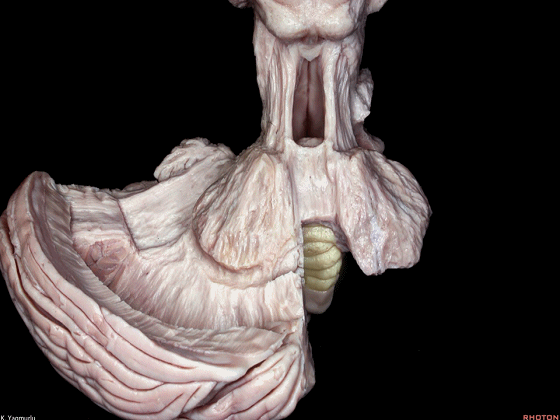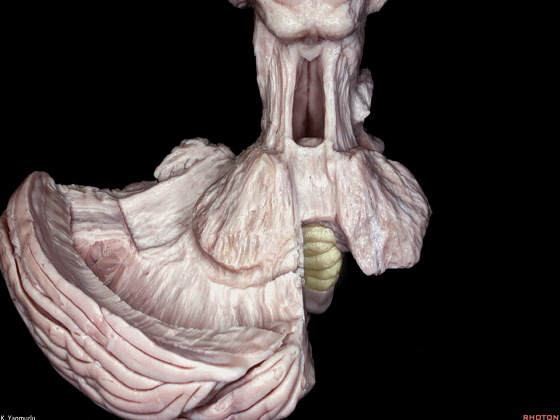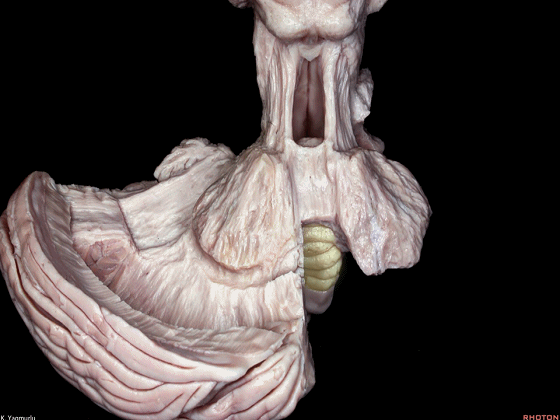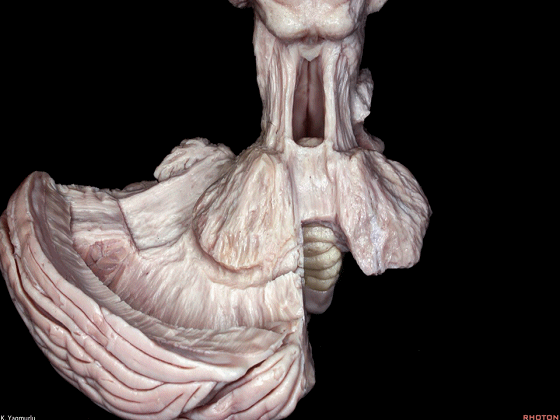
▼我们继续来看 桥小脑角区(下图),它是小脑岩面包绕脑桥形成的。
Here we come down now we're looking at the CP angle. here where the petrosal surface folds around the lateral margin of the pons.
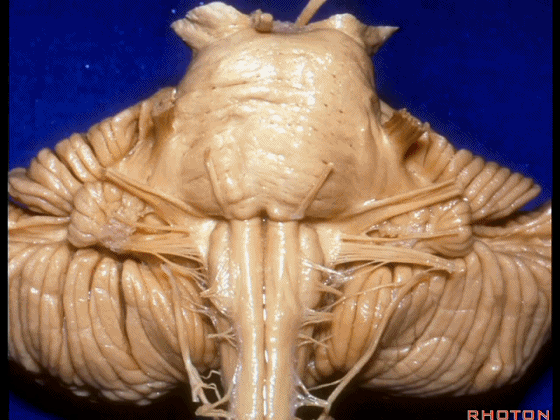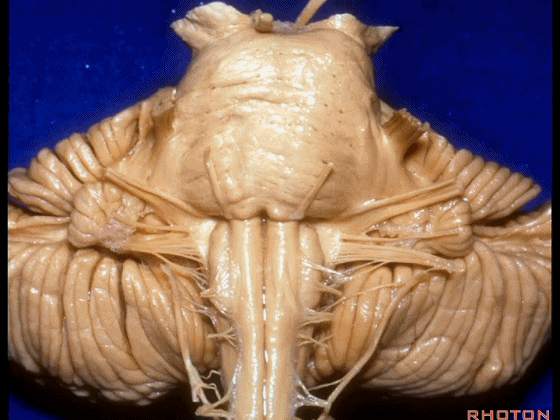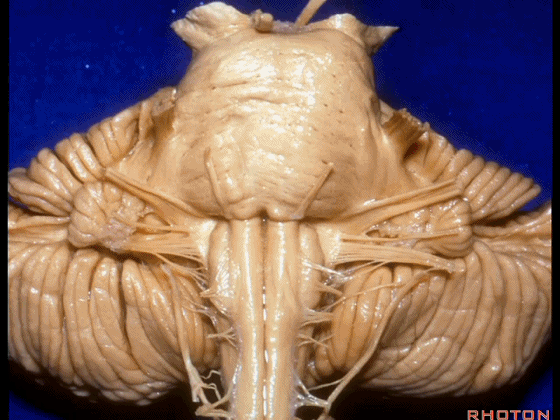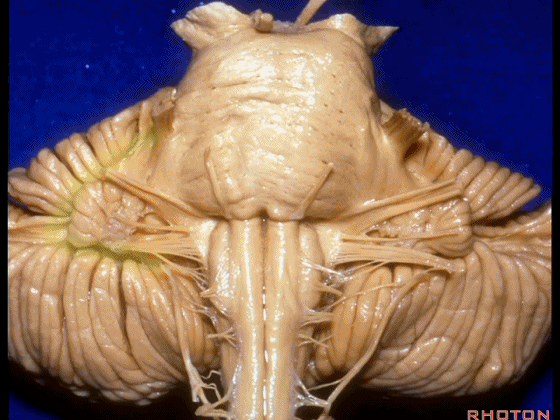
▼这是面神经(下图),从桥延沟的外侧端发出,走行于 脉络丛 及 绒球 的稍上方。
And here we see VII arising at the lateral end of the sulcus between the pons and medulla and slightly above the choroidal plexus and flocculus.
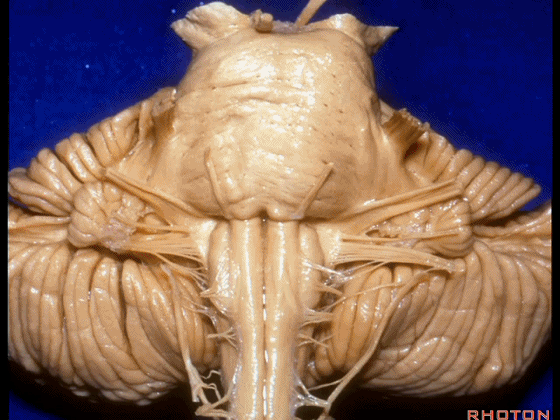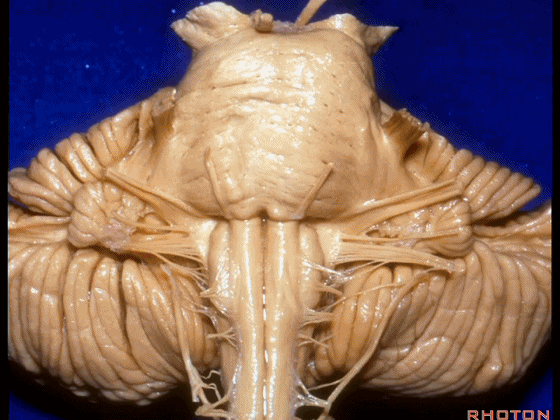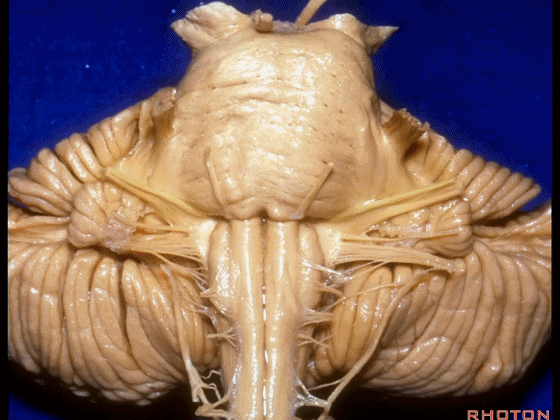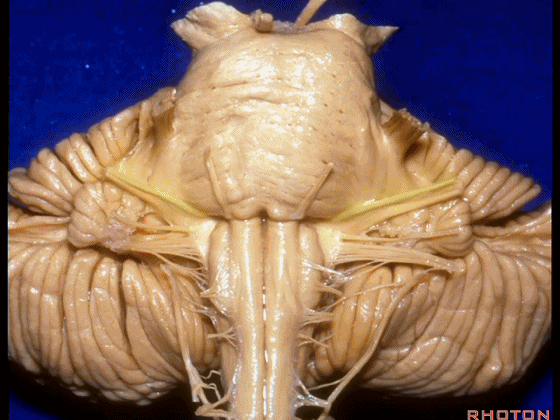
▼这是 脉络丛(choroidal plexus)。
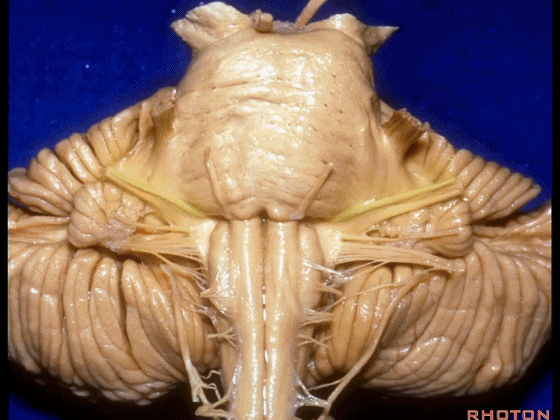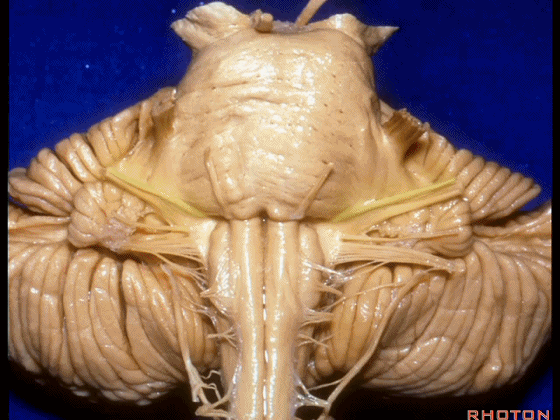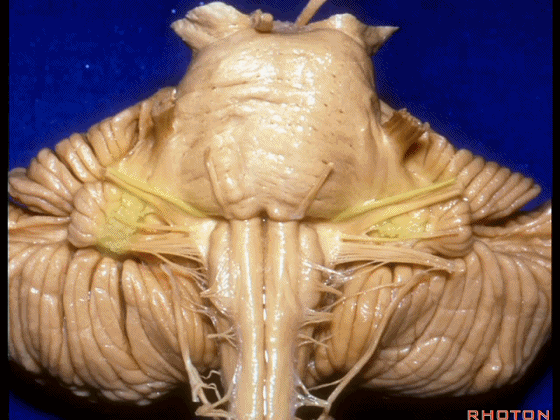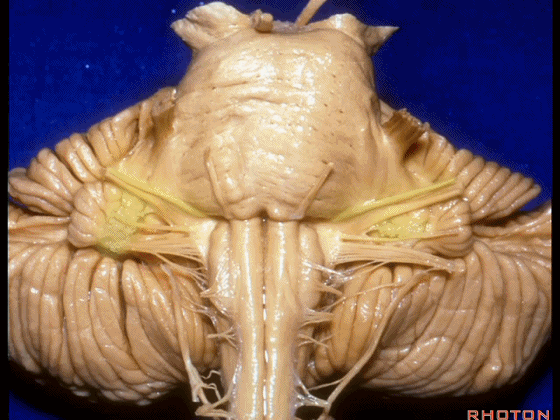
▼这是 小脑绒球(flocculus ['flɒkjələs])。
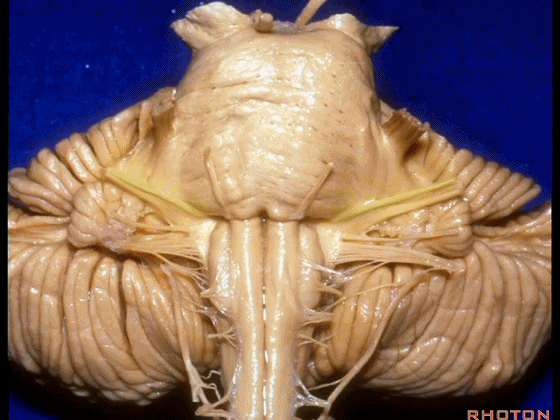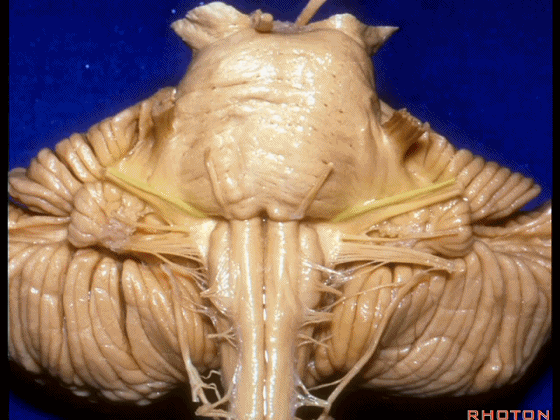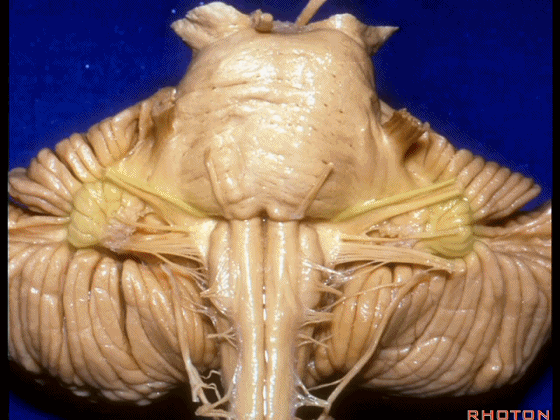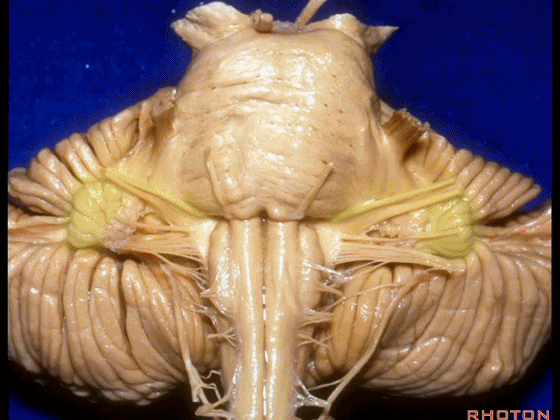
▼这是Luschka孔(第四脑室外侧孔,位于第四脑室两侧外侧隐窝尖端,与位于菱形窝下角尖部正上方的第四脑室正中孔一起引流第四脑室的脑脊液至蛛网膜下隙)。
hanging out Luschka.
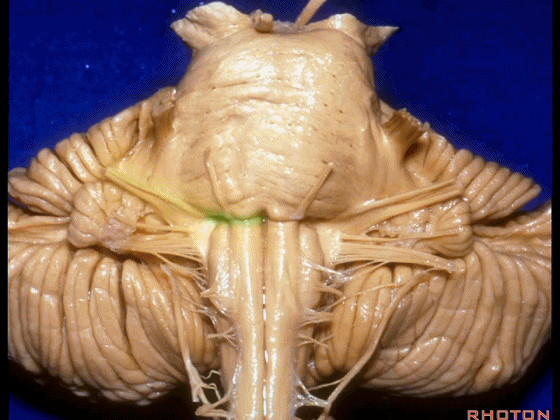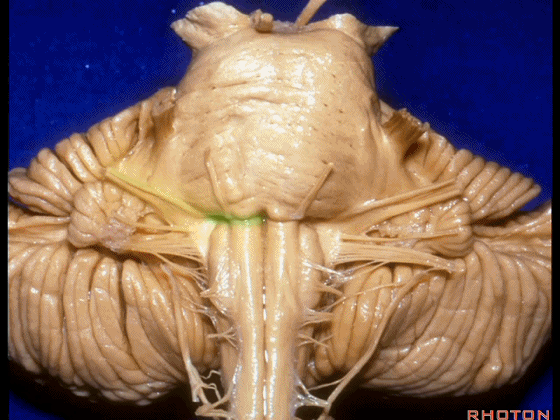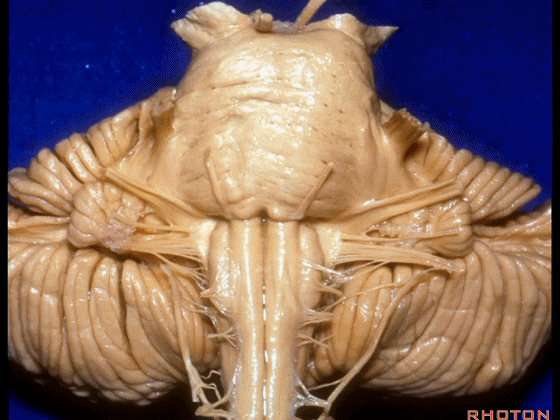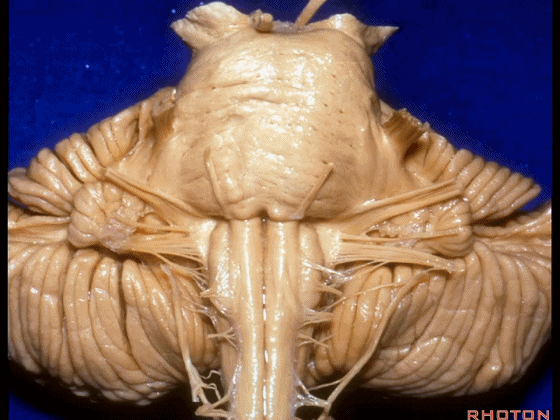
▼我们沿舌咽、迷走、副神经(下图)作一连线,并向上延长2~3毫米,即为面神经进入脑干处。
And if you draw a line along, down along the arch of the IX, X, XI, and project that line up 2 or 3 millimeters, that's where VII enter the brainstem.

▼面神经进入脑干处,位于桥延沟的外侧端(下图)。
at the lateral end of the sulcus between the pons and medulla.
▼这里可见舌下神经位于橄榄核前方。
And here we see XII on the front of the olive.
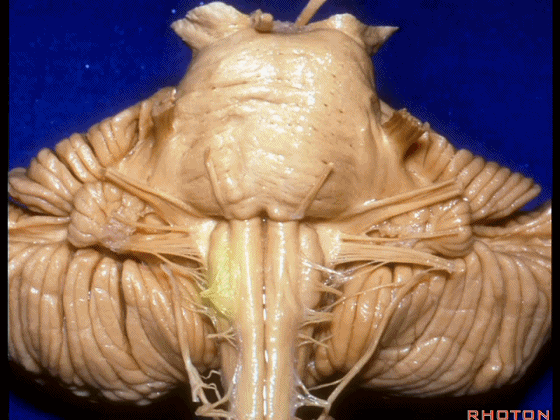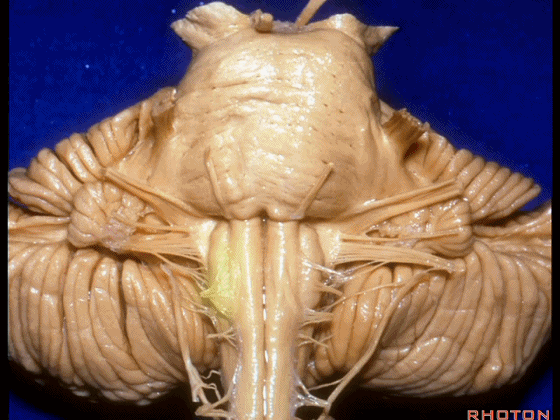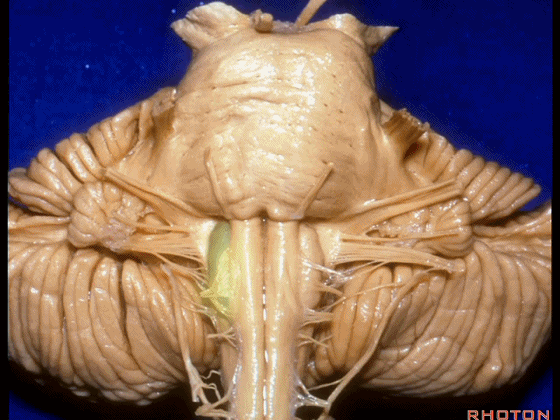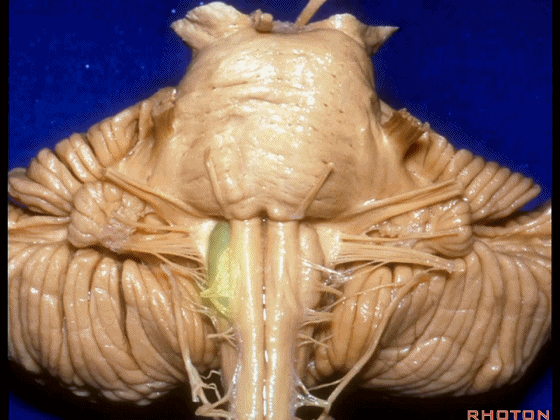
▼而舌咽、迷走、副神经从橄榄核后方发出。
and IX, X, XI arising on the back of the olive.
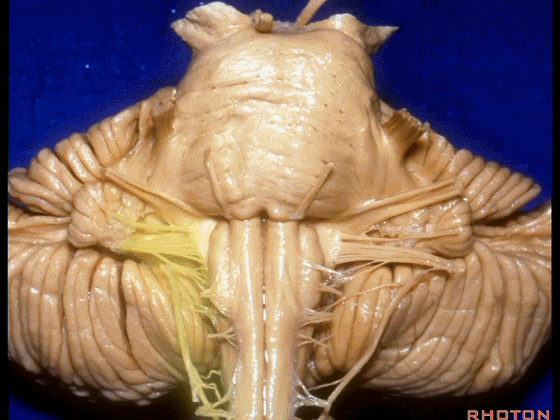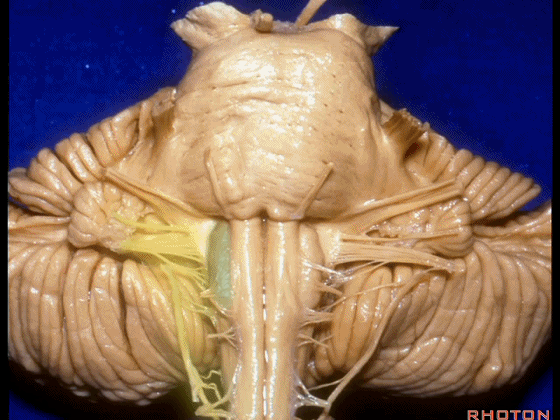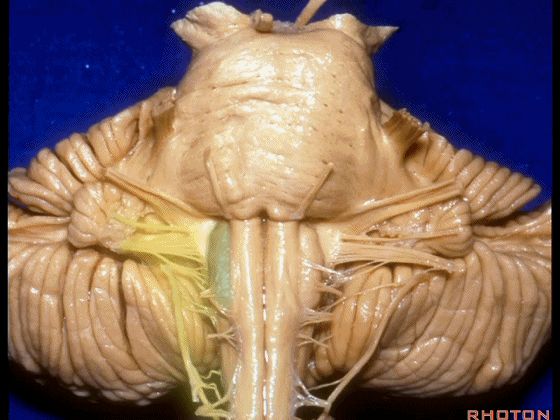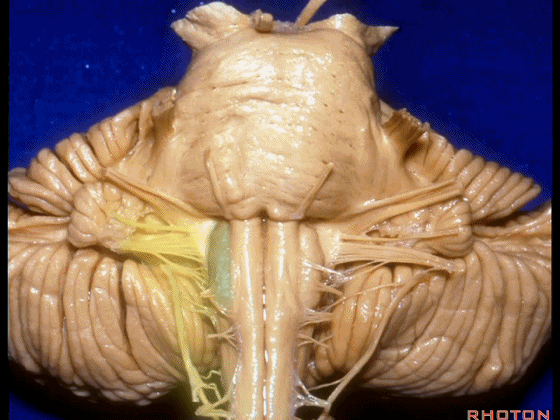
▼外展神经 从 桥延沟内侧段 发出。
We see VI arises in the medial part of the pontomedullary sulcus.

▼三叉神经 从 脑桥中部 水平发出。
and V arises at mid pontine level.
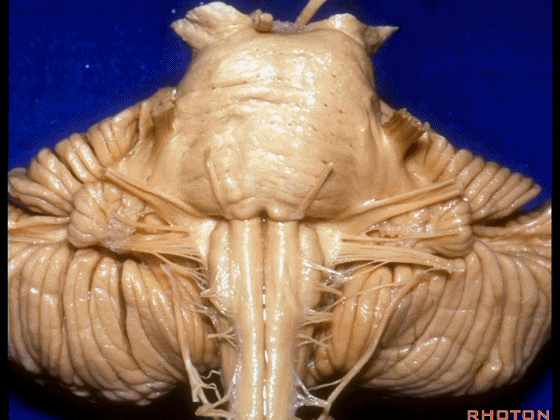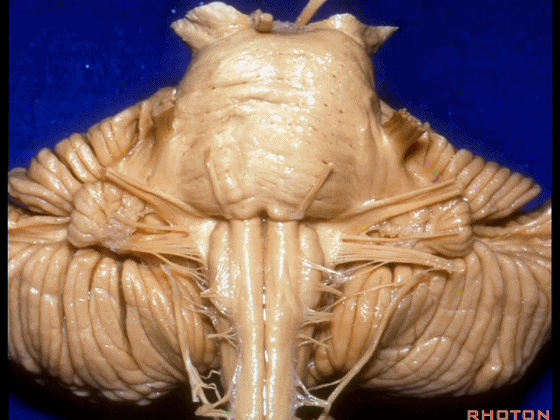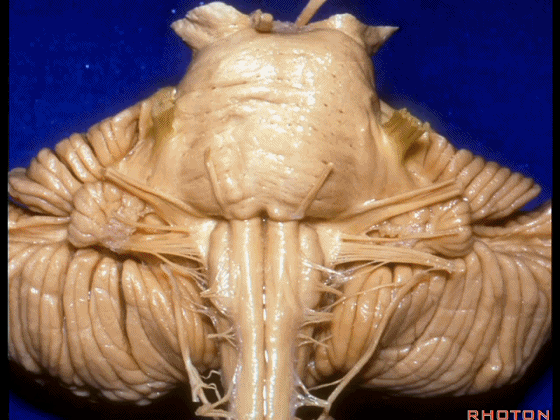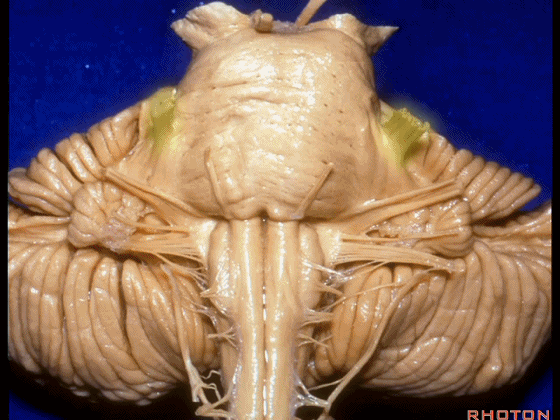
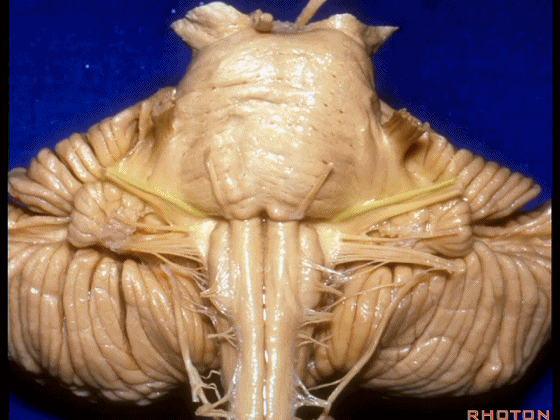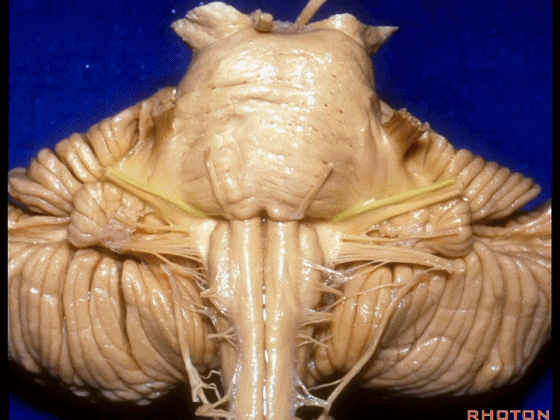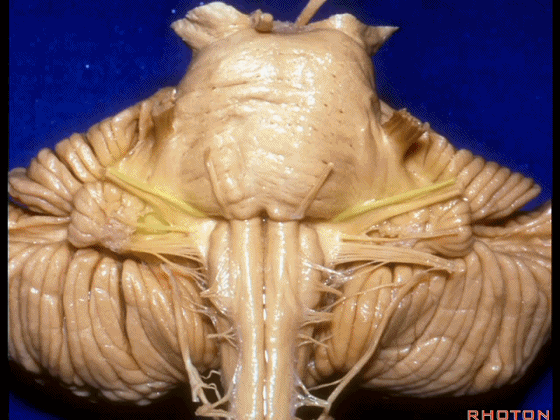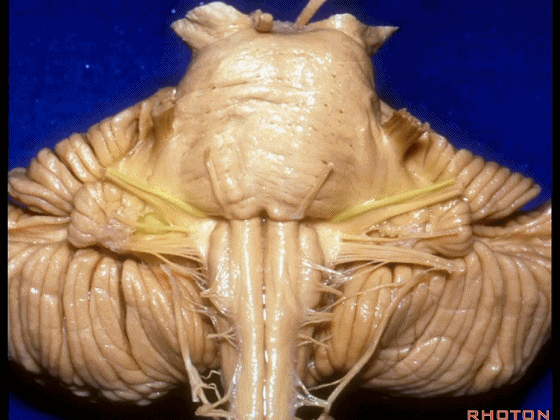
▼这是桥小脑角的局部观,下图示 Luschka孔。
So, here's just CP angle. Luschka.
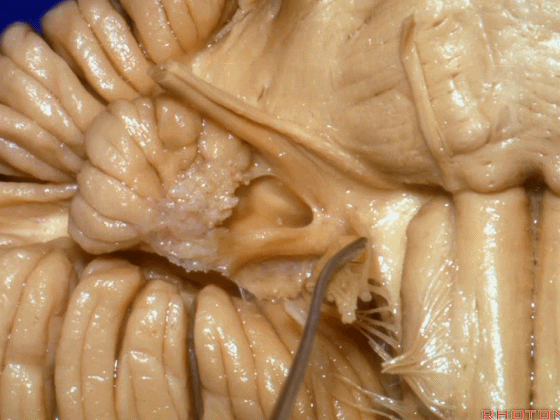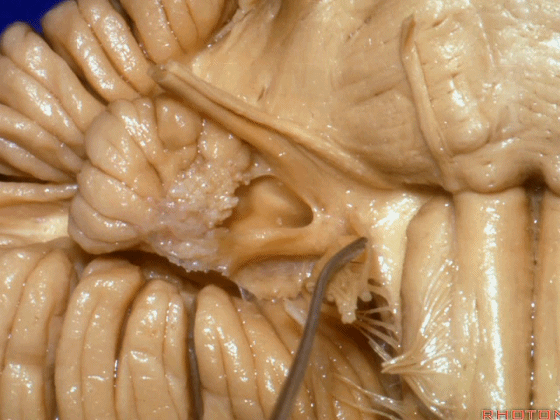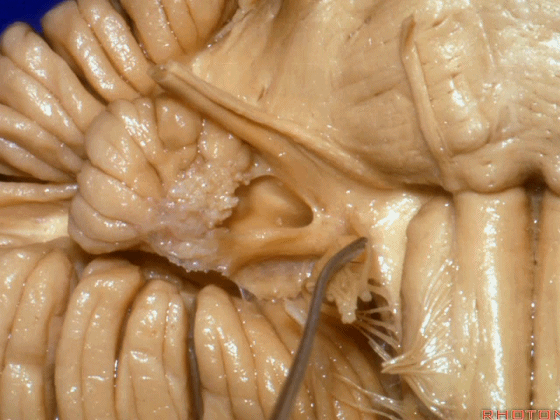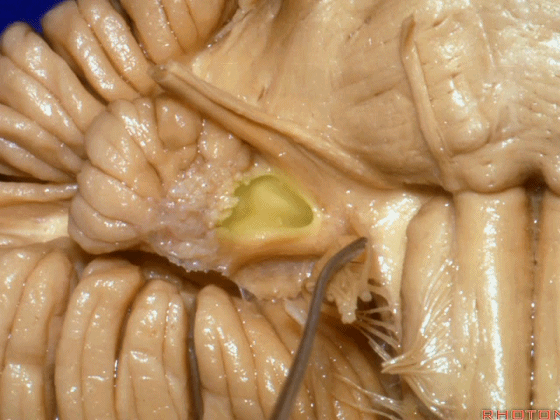
▼面神经、前庭蜗神经。
VII、VIII.
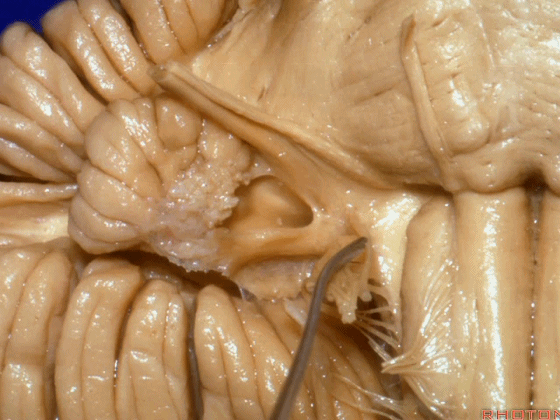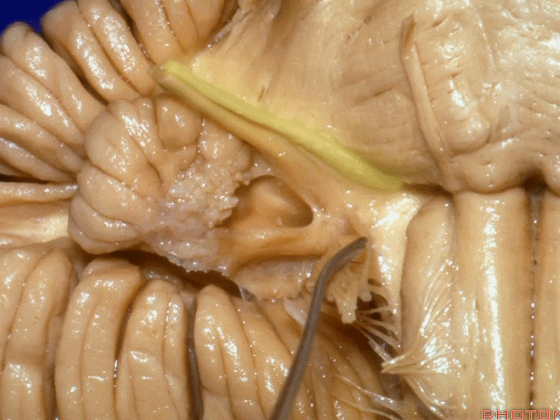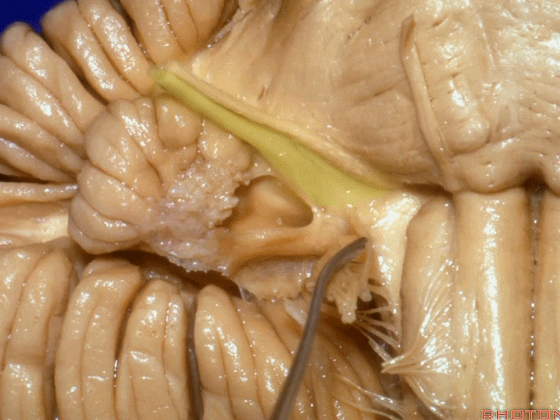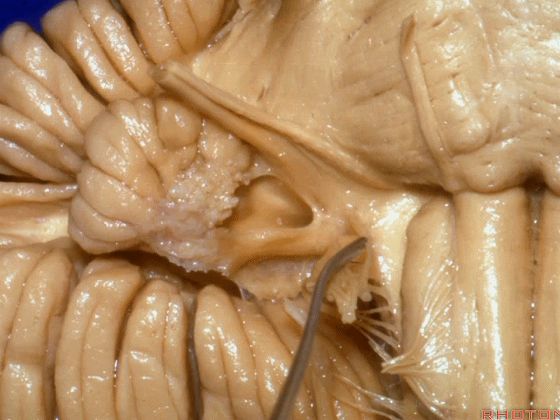
▼沿舌咽、迷走、副神经作一连线,向上延长2~3毫米,即为面神经进入脑干处。
You draw a line along the origin of these rootlets, go up 2 or 3 millimeters, and that's where VII enters the brainstem.
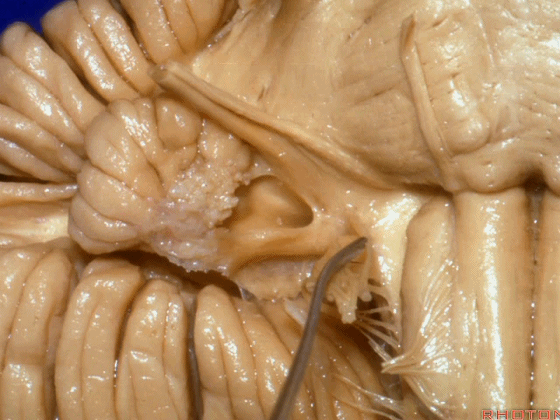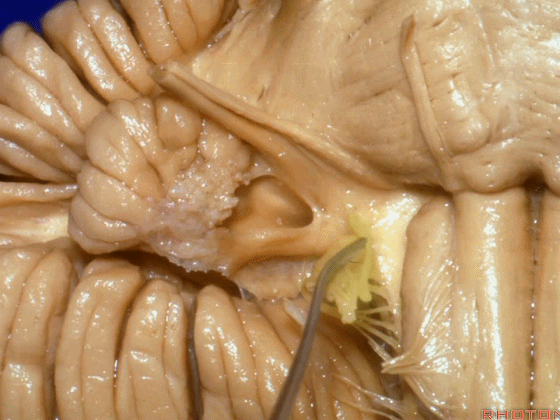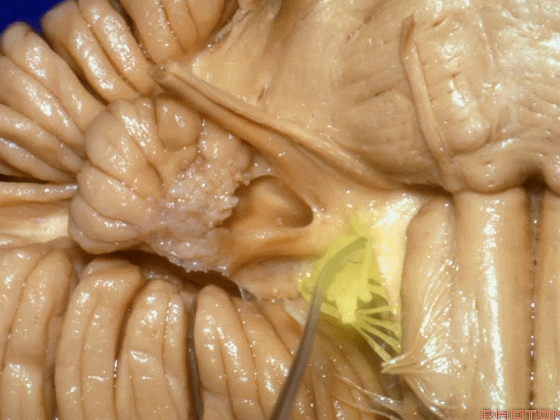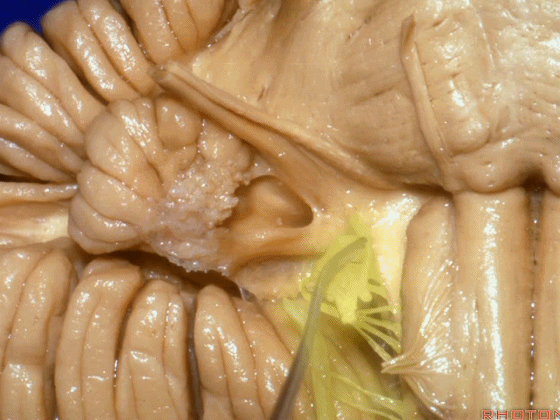
▼面神经进入脑干处。
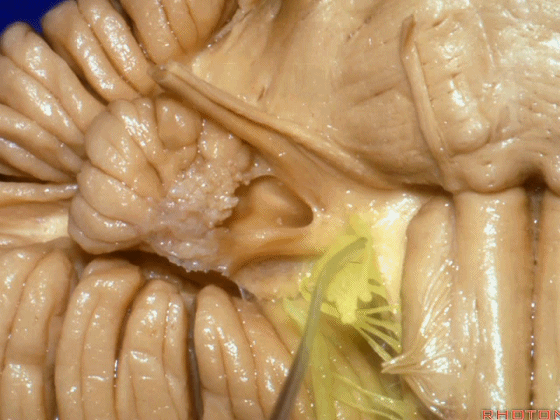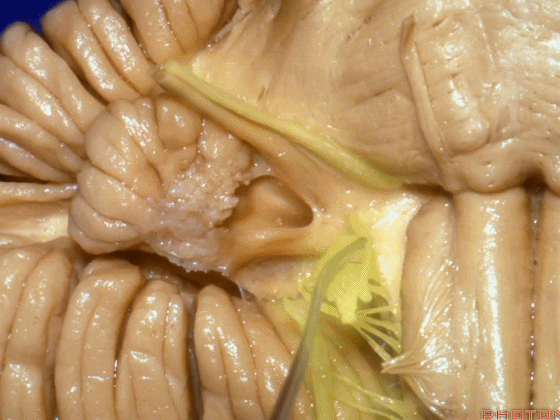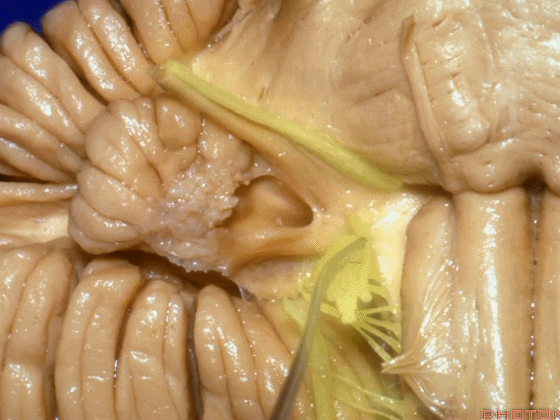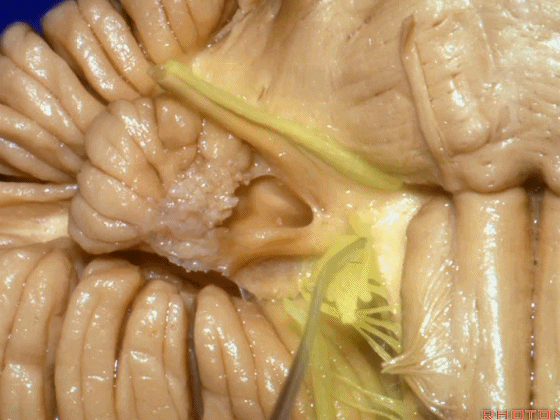
▼面神经位于前庭蜗神经的前方。
in front of VIII.
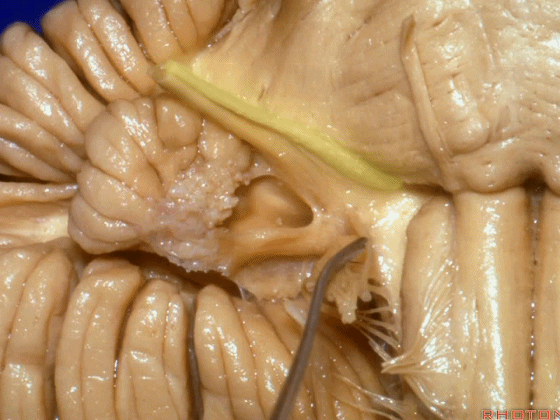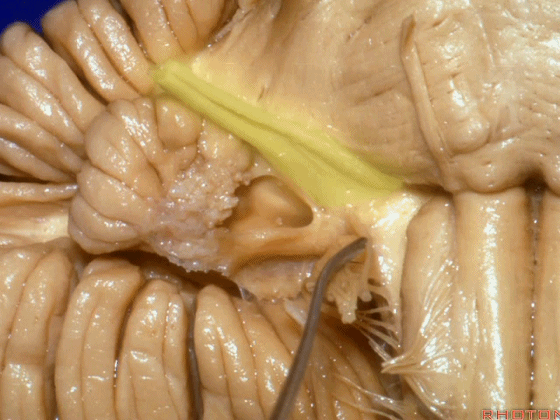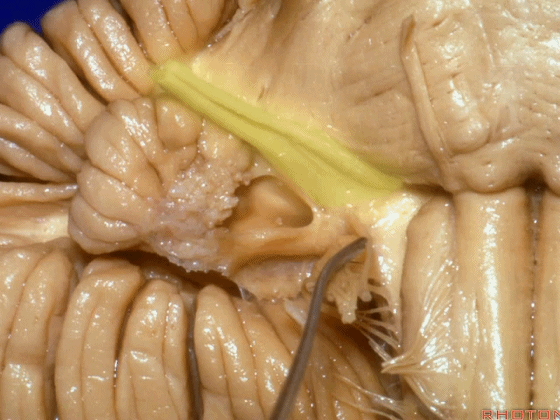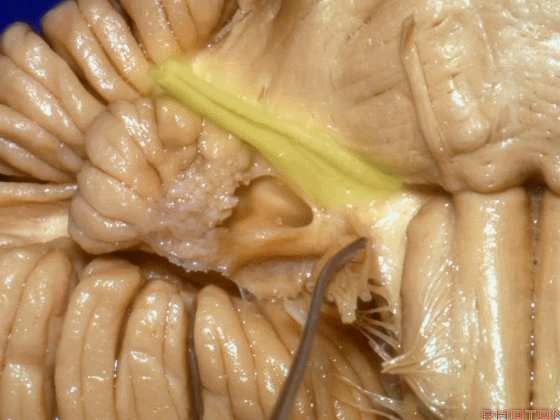
▼当从下图这个方向进行 绒球下入路时,在舌咽神经后方,向上即可见面神经。
And for the infrafloccular approach you come in this direction, behind IX, you look up and you see VII here.
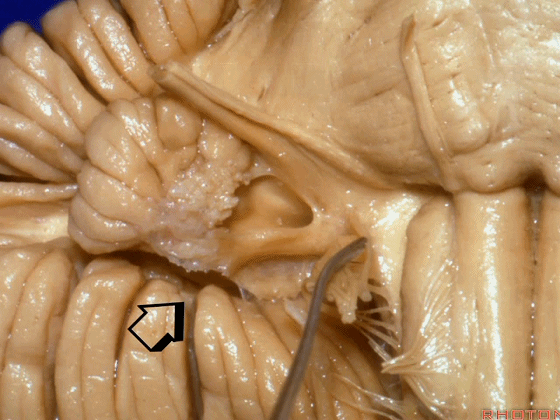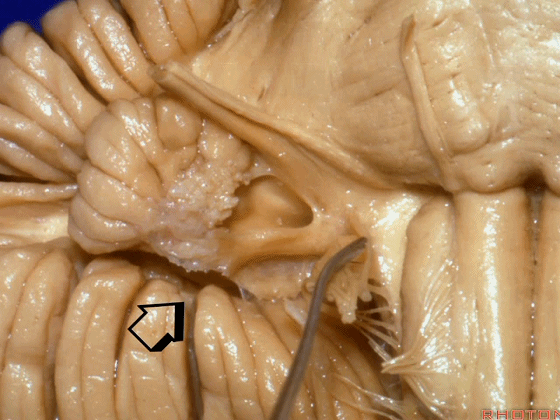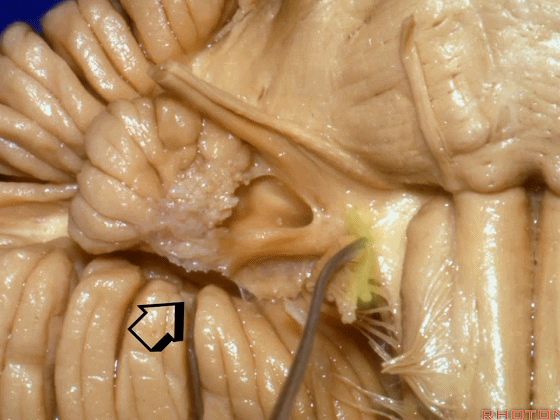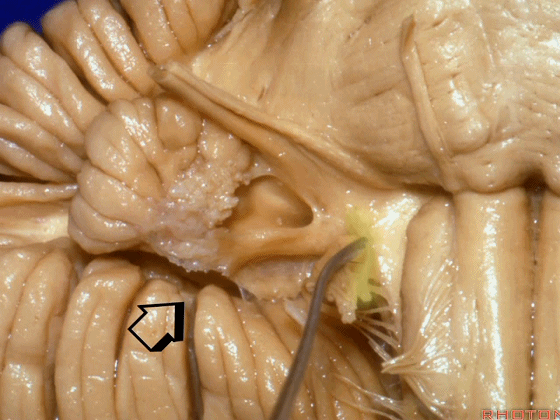
▼绒球下入路这一视角中,面神经似乎位于前庭蜗神经下方,实际上位于其前方。
As the view makes it look like it's below VIII, but it's really in front of VIII.