本篇为Rhoton解剖视频《Head and Neck Anatomy for Neurosurgeons》这一章节,由Rhoton实验室的Dr. Maria Peris-Celda女士讲解,国内广受好评的《罗顿颅脑颈部解剖彩色图谱》便是由Maria女士主编。对颈椎手术、颅内外血管搭桥、颈动脉内膜剥脱、颈静脉孔病变等感兴趣的医师来说,头颈部解剖是必须要掌握的。笔者将《前颅底(2)》中的“经口入路部分”亦归入本篇,共264张图片。
笔者水平所限,错误之处请批评指正!

头颈部解剖
Head and Neck Anatomy for Neurosurgeons
▼今天我们来讲头颈部解剖。头颈部的界限:上界为下颌骨下缘、乳突尖、枕外粗隆;下界包括胸骨的颈静脉切迹、锁骨、第7颈椎的棘突。
So today we are going to review some aspects of the head and neck anatomy that are relevant for neurosurgical approaches and pathologies. The boundary between the head and neck runs along the inferior border of the mandible, as well as the tip of the mastoid, and the external occipital protuberance. and the neck terminates inferiorly at the jugular notch of the sternum, the clavicle, and the spinous process of the 7th cervical vertebra.
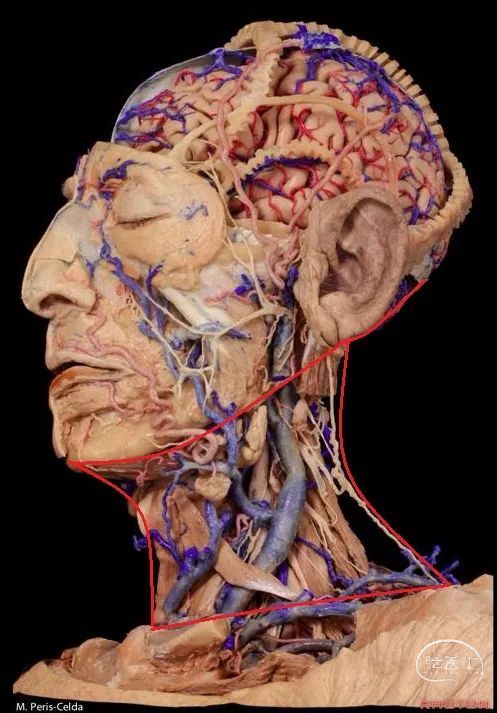
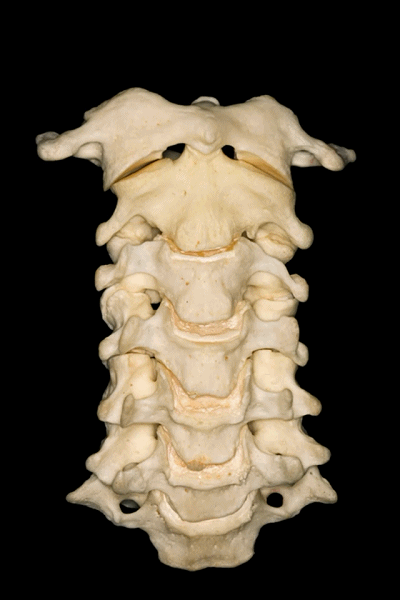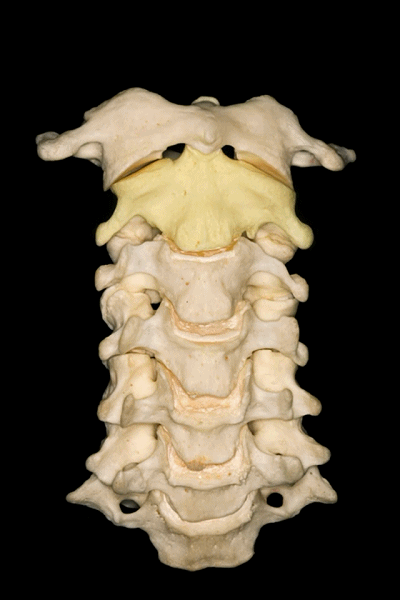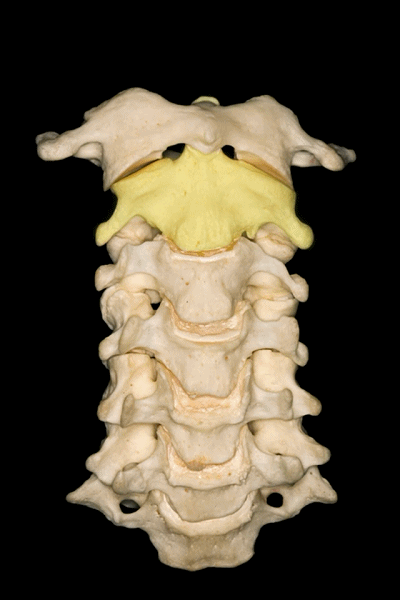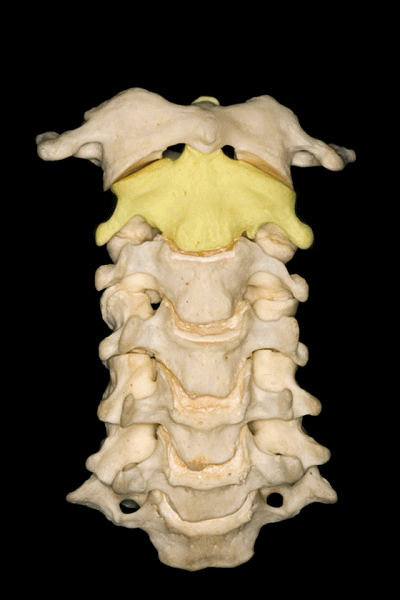
▼首先来学习颈椎的解剖,七个颈椎骨是颈部的重要构成。上两个颈椎骨的形态明显异于其余五个,它们是C1(寰椎 atlas 下图),C2(枢椎 axis)。
First we are going to look at the anatomy of the cervical vertebra as a basic structure of these regions. Here we see the seven cervical vertebrae that forms part of the...here neck. The first two have a very different configuration than the other five vertebrae in the first C1 or atlas, and the second C2 or axis.
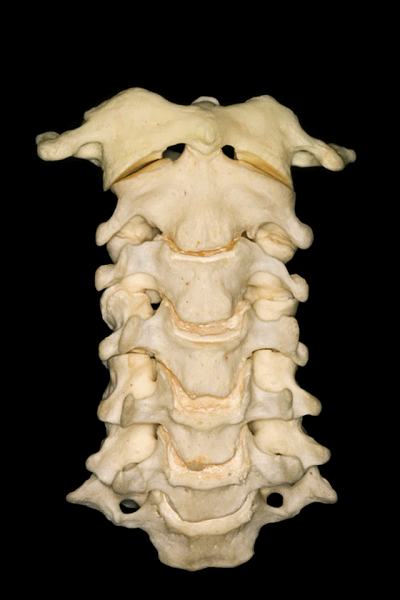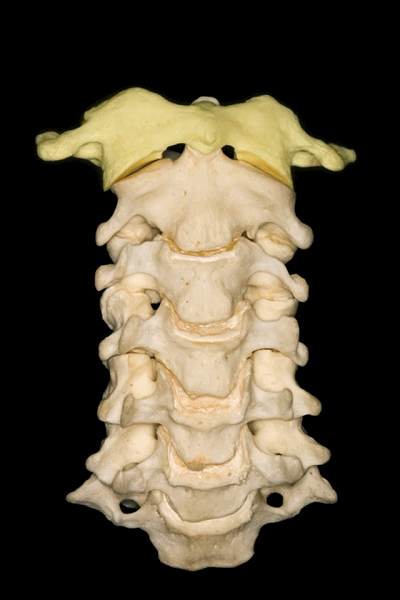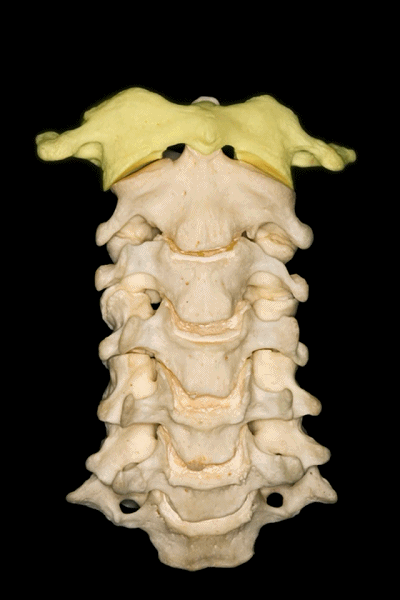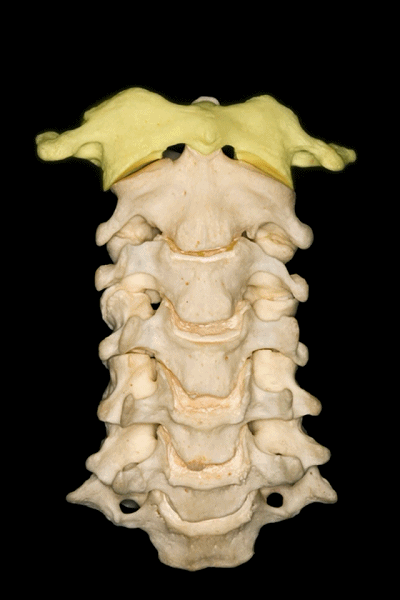
▼下图示 枢椎 axis.
▼所有颈椎均与椎动脉关系密切,后者行于第7颈椎前方,随后穿行于上六个颈椎横突孔内。
And all of them are closely related to vertebral artery which passes anterior to the seventh cervical vertebra, and then inside or through the transverse foramina of the upper six cervical vertebrae.
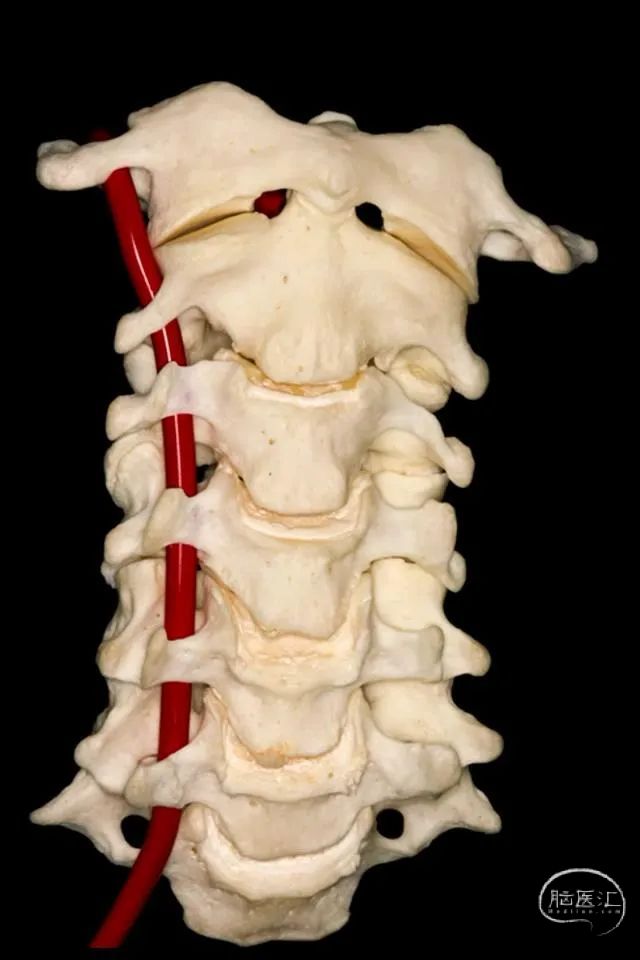
▼这里可辨别出椎动脉的三个分段。第一段(V1),从椎动脉起自锁骨下动脉处至第6颈椎的横突孔。
And we can distinguish three segments of the vertebral artery here. The first segment or V1 is from its origin in the subclavian artery in the right or left side to the foramen transversarium of the sixth vertebrae.
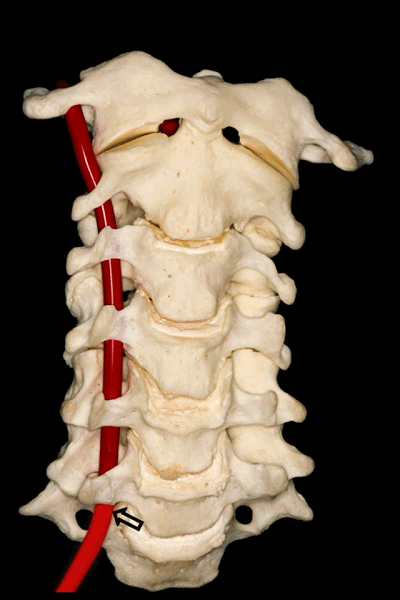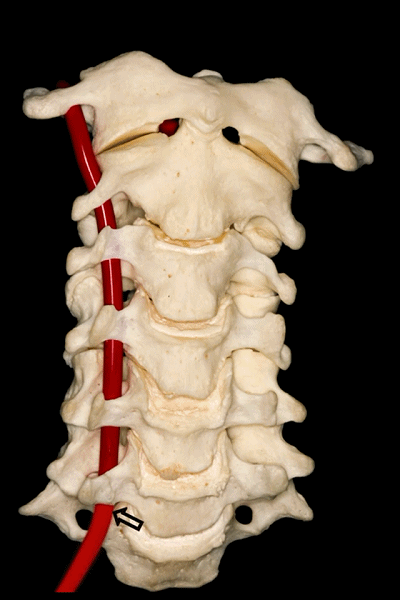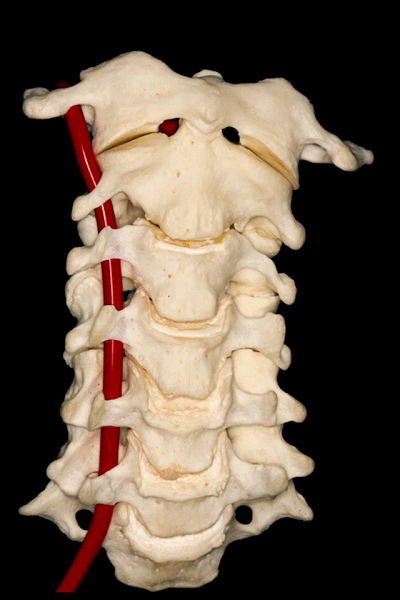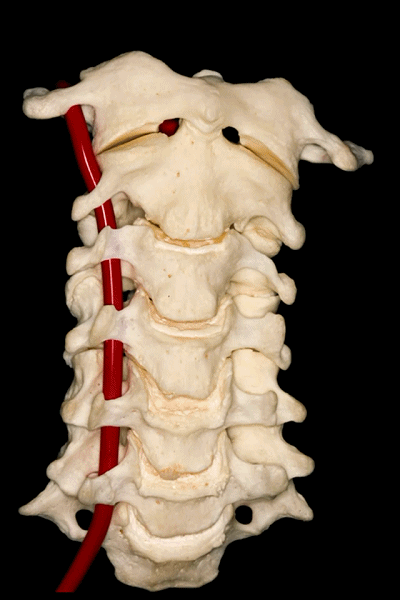
▼第二段(V2),穿行于第2至第6颈椎的横突孔内。
Then the second segment or V2 runs through the transverse foramina of C2 to C6.
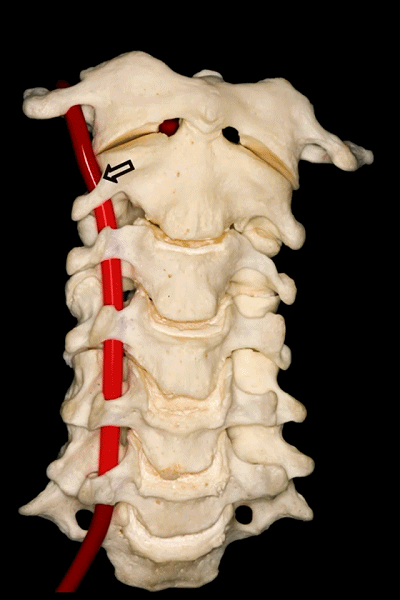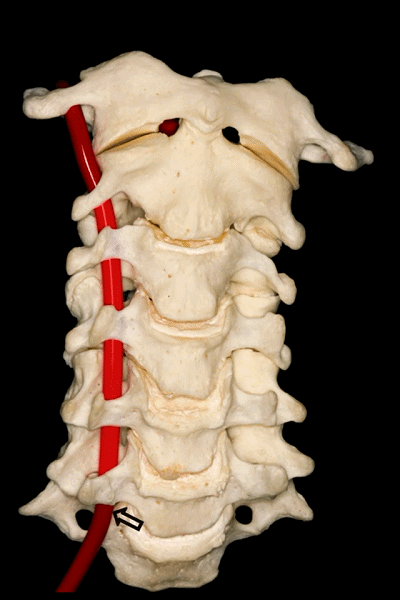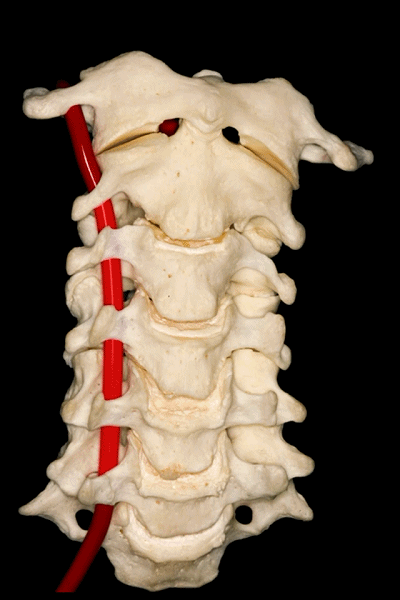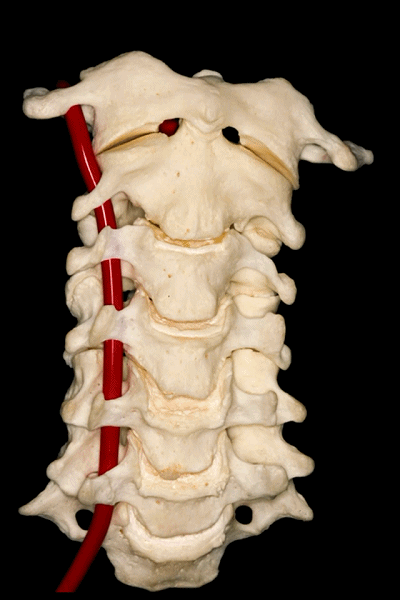
▼第三段(V3):下图显示了部分V3,该部分行于枢椎横突孔以上,随后向上穿过寰椎横突孔。枢椎横突孔是向下倾斜,异于其他横突孔的水平方位。
And then, the third segment that we can see in this picture partially runs above the transverse foramina of C2, which is oblique and different from the transverse horizontal position of the other transverse foramens, and then goes up and passes through the transverse foramina of C1. But we don't see this segment completely.
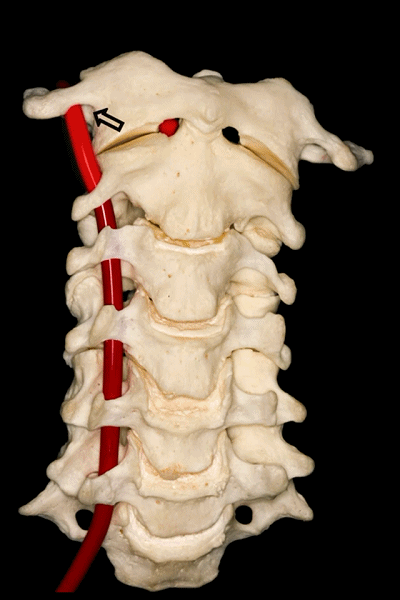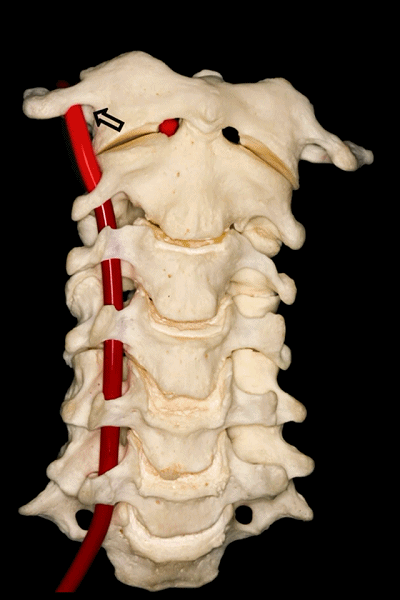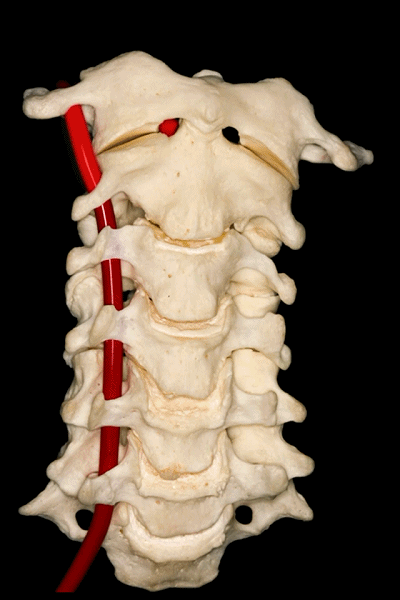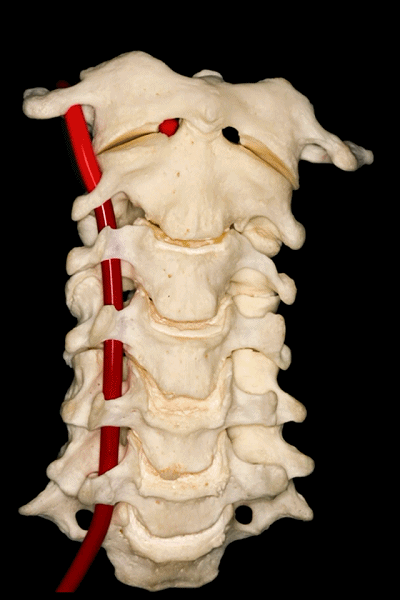
▼下图可见上述的V3段继续绕行于寰枕关节,随后穿硬膜入颅而成为V4段。
And in this view, we see that this segment, the V3 segment continues around the atlanto-occipital junction, before it enters the dura mater and then forms the V4 segment.
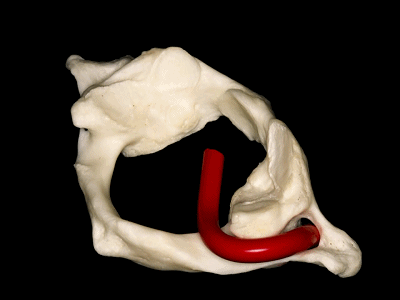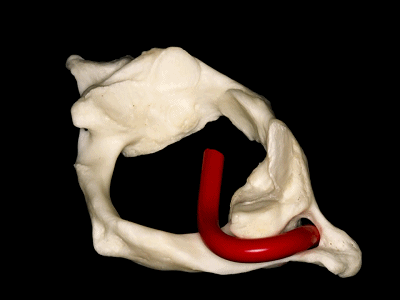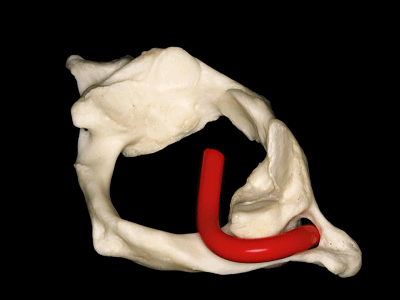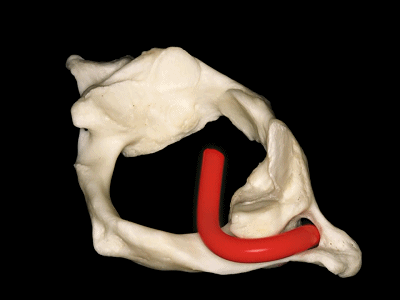
▼这是寰枕关节(侧块)
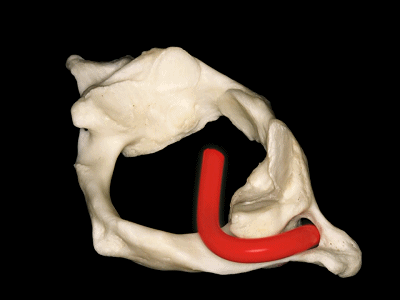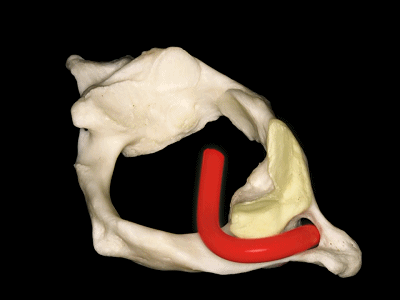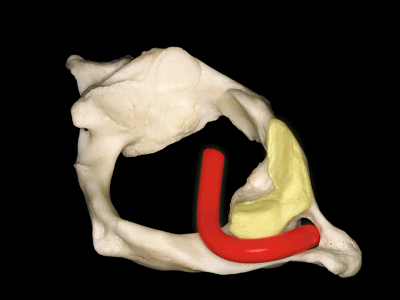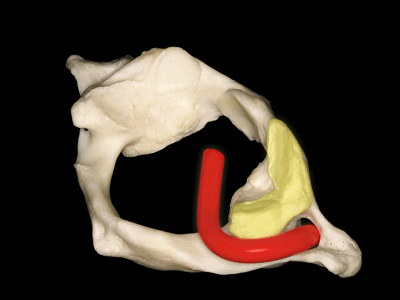
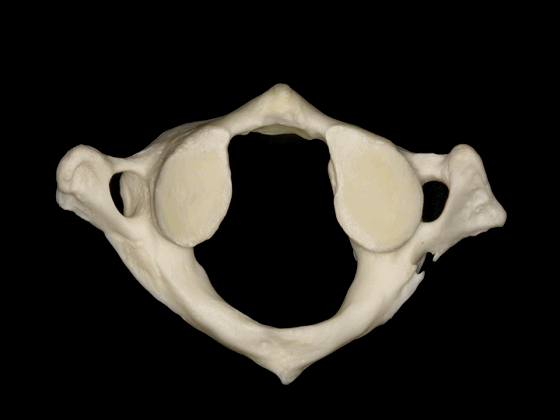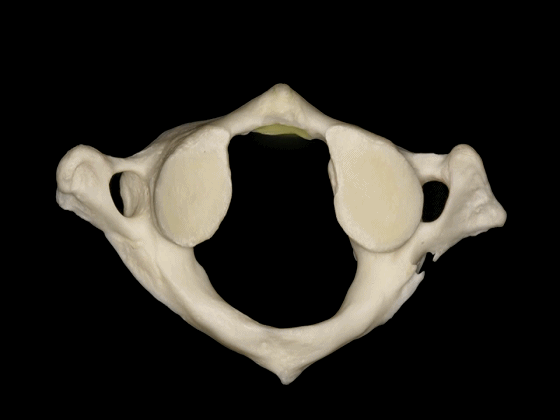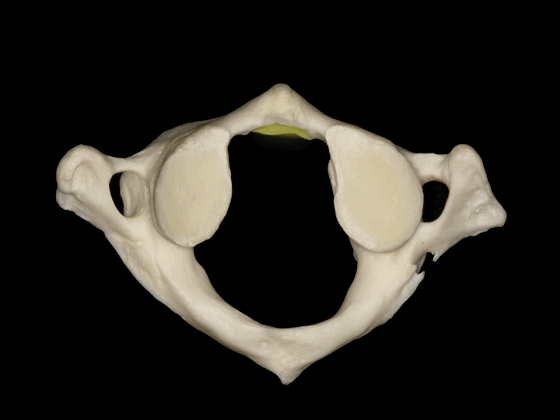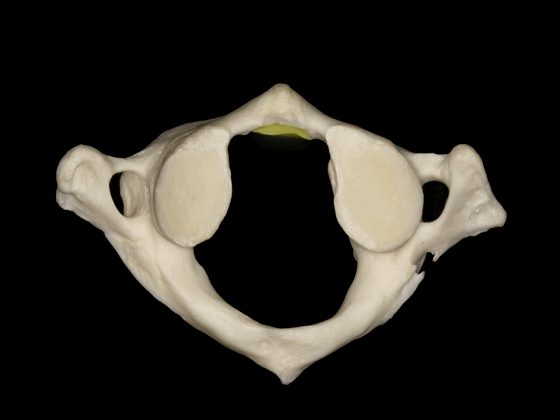
▼这是上面观,可以看出,寰椎是最宽的颈椎。其结构的特殊性在于独有的前弓(下图)
So we see here the firs cervical vertebra or atlas which is the widest one. And in the view from above...and this is unique in having nobody has an anterior arch,
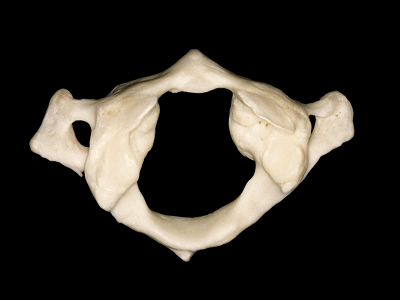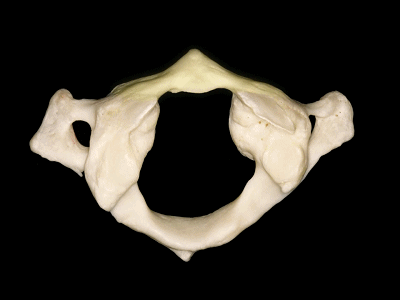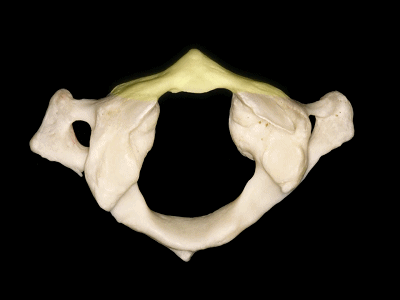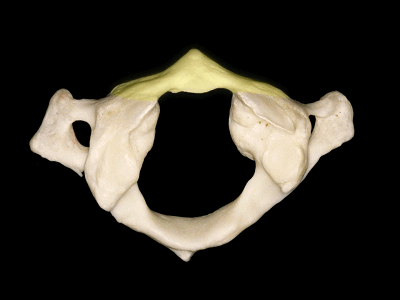
▼前弓上有前结节(下图)
with an anterior tubercle
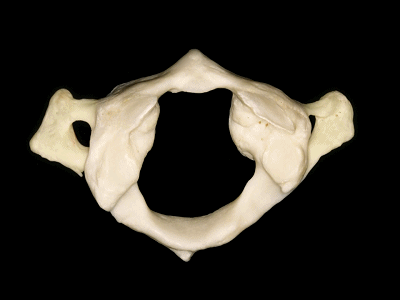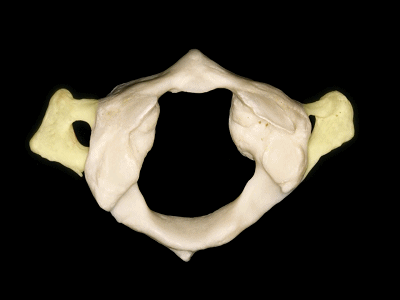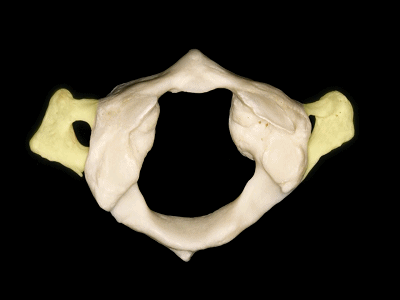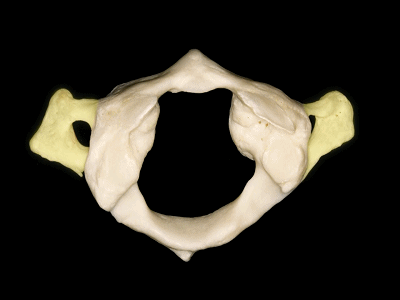
▼这是后弓
▼后弓上有后结节(下图)
with a posterior tubercle
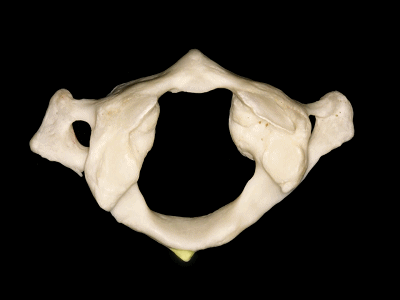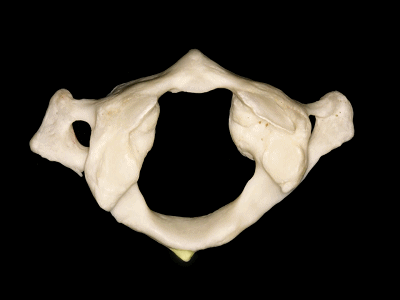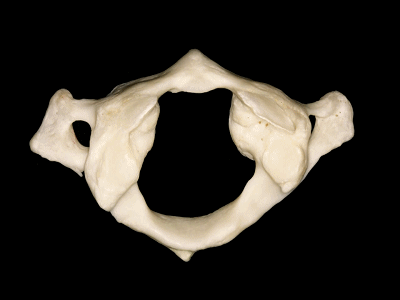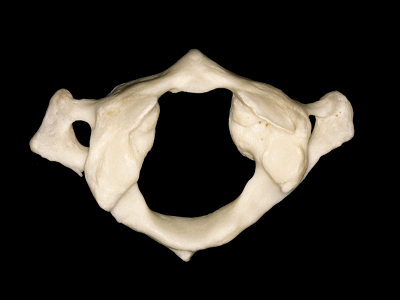
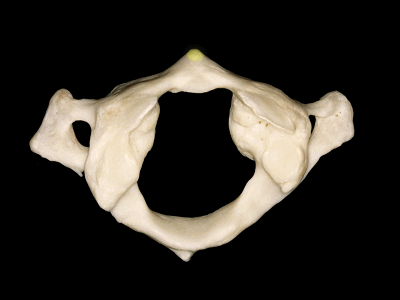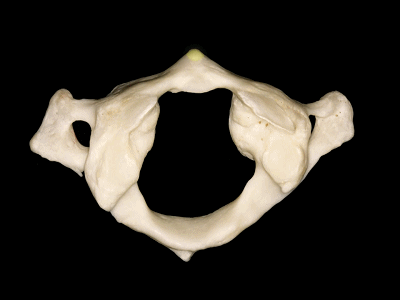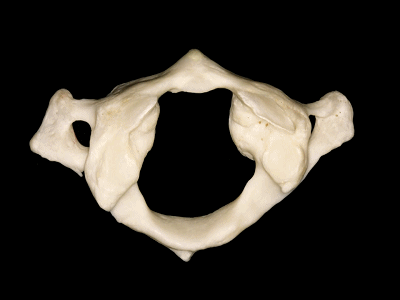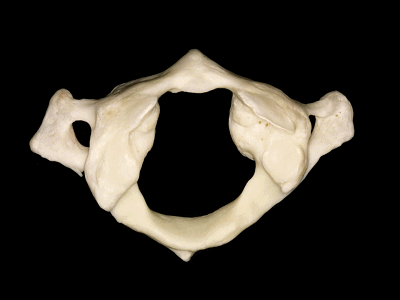
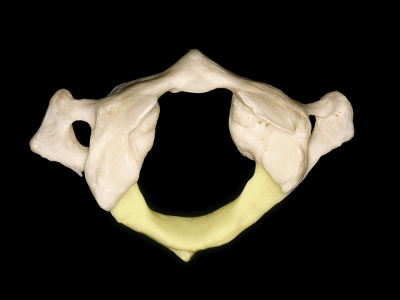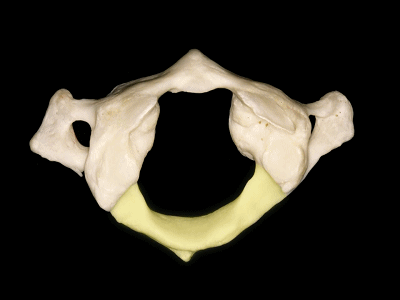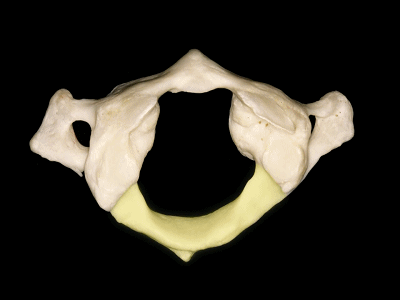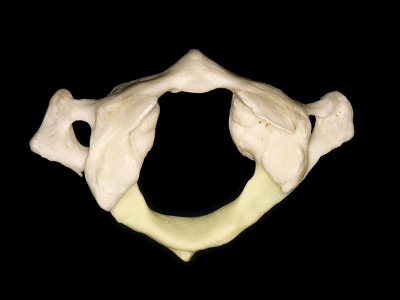
▼这是横突,以及横突孔
and a transverse process, with a transverse foramen,
▼这是侧块 ,其上关节面与枕髁形成寰枕关节。
and a lateral mass in which we can see,the superior articular facet for the occipital condyle.
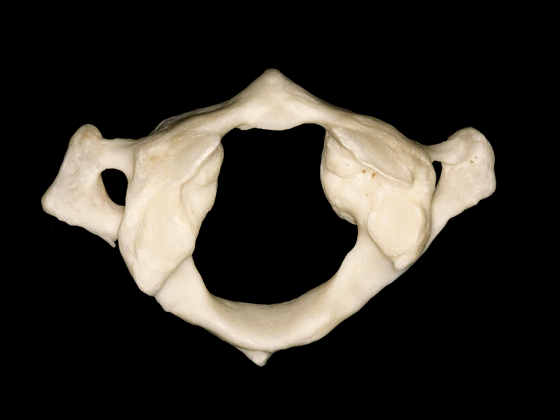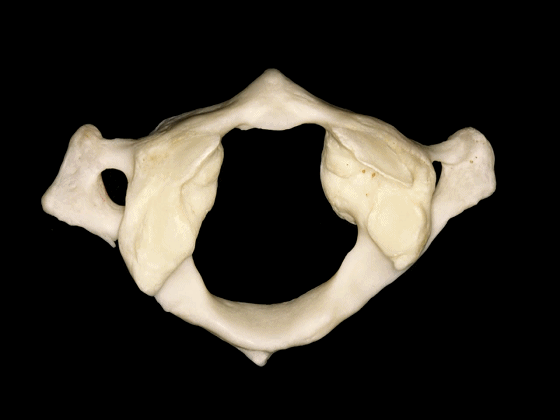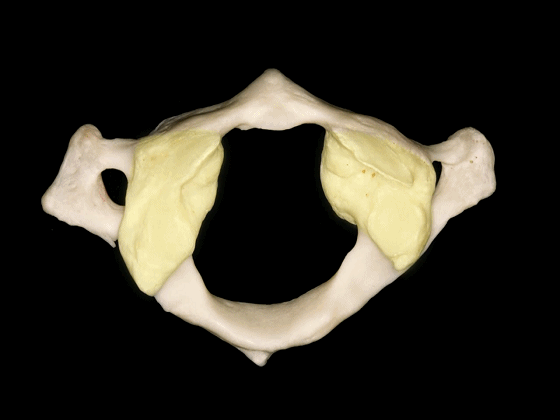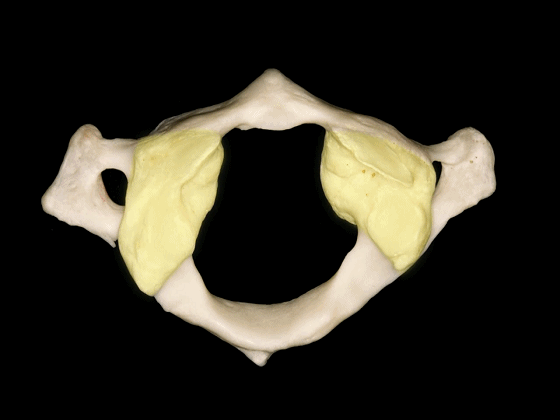
▼这是枕髁的下面观,其关节面与寰椎侧块形成关节。
In an inferior view of the occipital condyle, we see the articular surface for the lateral mass of the atlas.
▼这是后面观,可见寰枕关节,以及椎动脉的V3段,位于寰椎关节外侧。
And here we see a posterior view of the atlanto-occipital junction, with the V3 segment of the vertebral artery, which is lateral to the lateral atlanto-occipital joint
▼椎动脉的V3段从枢椎横突孔穿出,穿过寰椎横突孔,随后绕行于寰椎侧块(下图)。
passing through a transverse foramen of C2, transverse foramen of C1, and then around the lateral mass of the atlas.
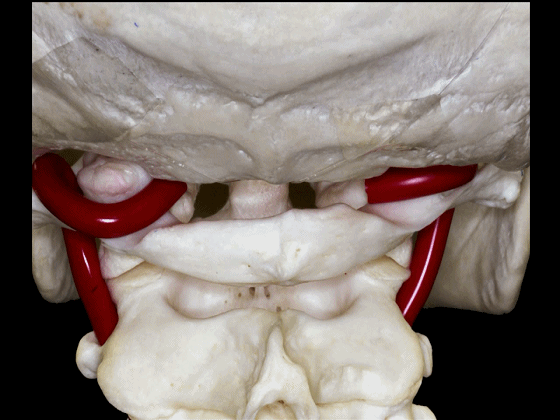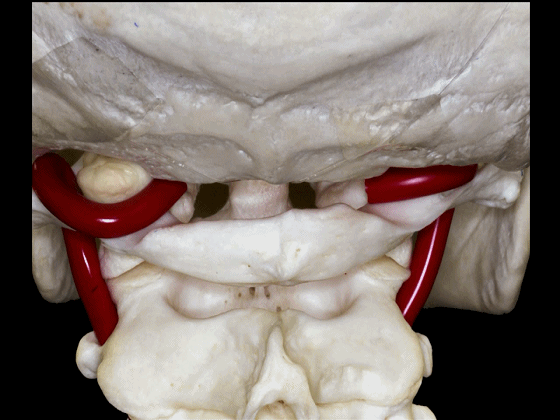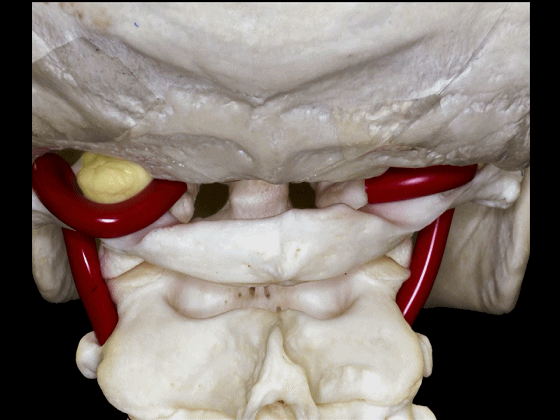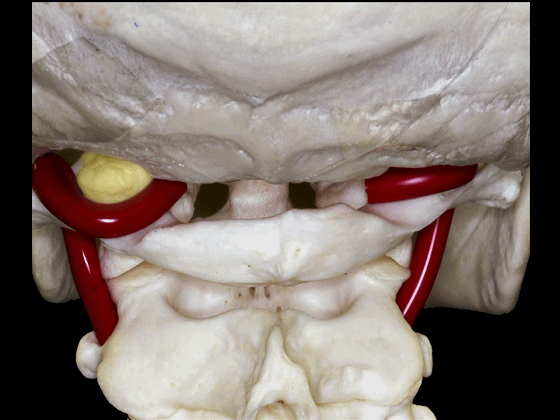
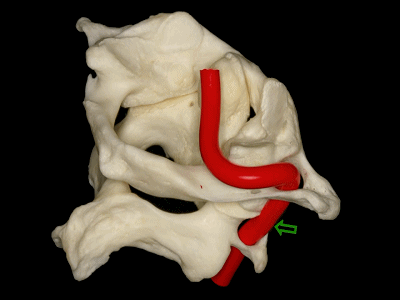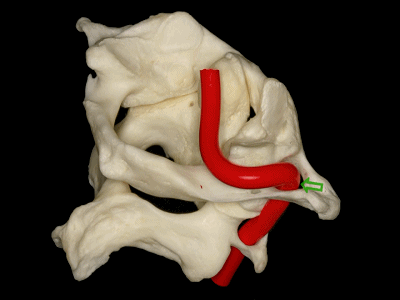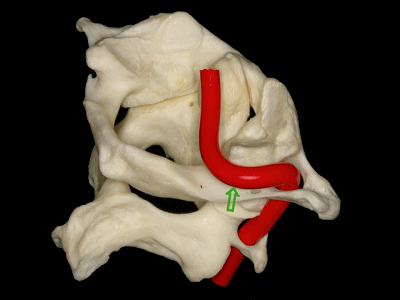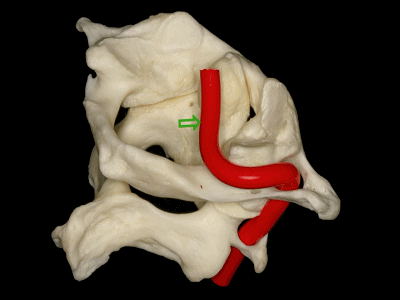
▼椎动脉V3段斜位观
Here's an oblique view illustrating the V3 segment of the vertebral artery with three portions:
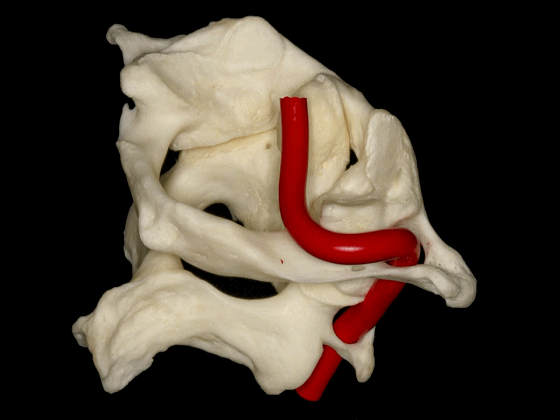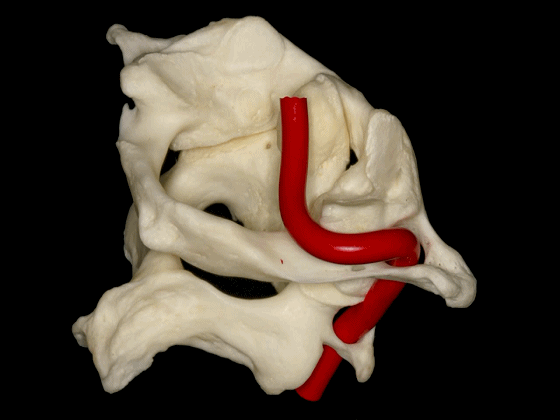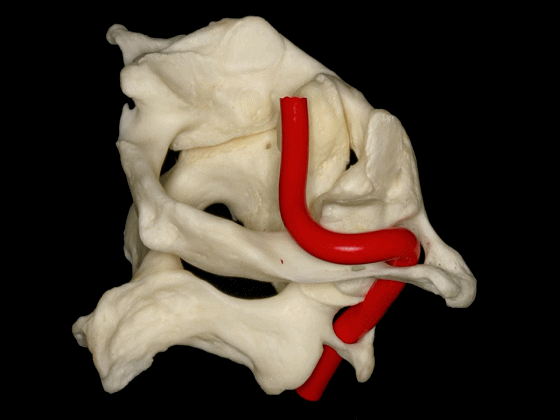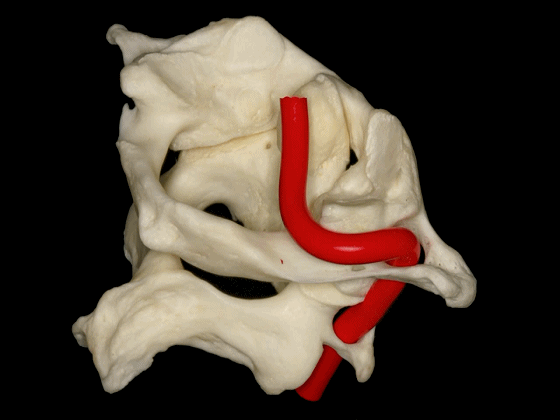
▼椎动脉V3段三个部分:垂直部位于枢椎横突孔与寰椎横突孔之间;水平部绕行于寰椎侧块;斜部为穿经硬膜进入颅内前的一段。
a vertical portion between the transverse foramen of C2, and C1, then a horizontal portion around the lateral mass of the atlas, and an oblique portion which is going to reach the dura mater and enter intradurally.
▼这是下面观,寰椎在前方和两侧与枢椎形成关节,其前方的关节面(齿突凹下图)与齿突形成关节。
So in a view from below, C1 articulates anteriorly and laterally with C2, has a facet anteriorly to articulate with the odontoid,
▼两侧的下关节面(下图)与 枢椎上关节面 形成关节。
and two inferior facets to articulate with the superior facets of C2.
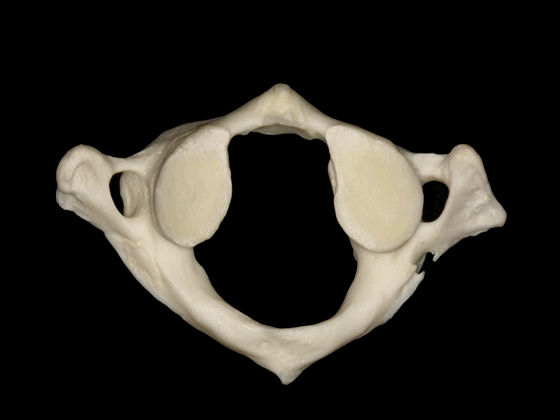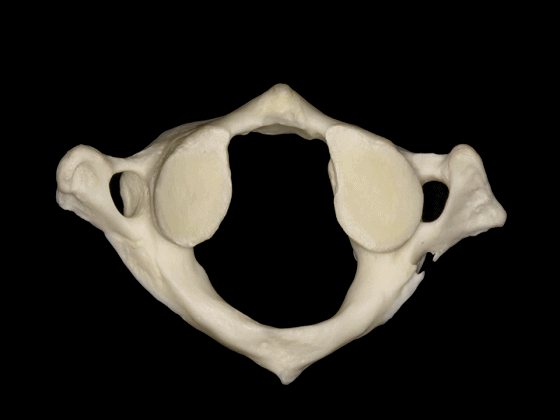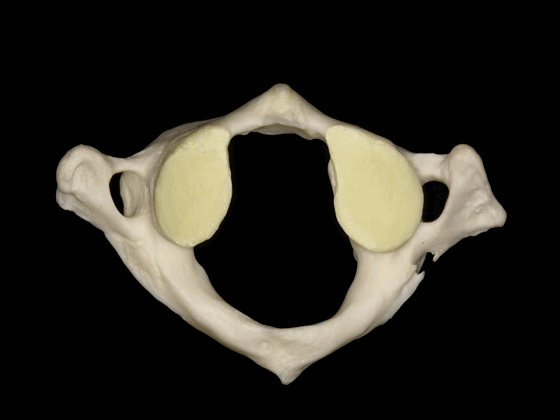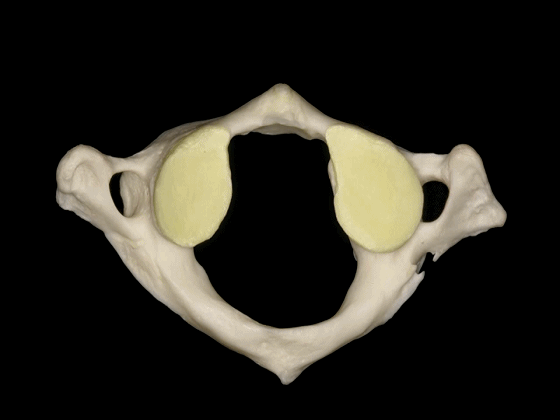
▼枢椎的椎体有一齿突、横突
And C2 has a body with an odontoid process, transverse process,
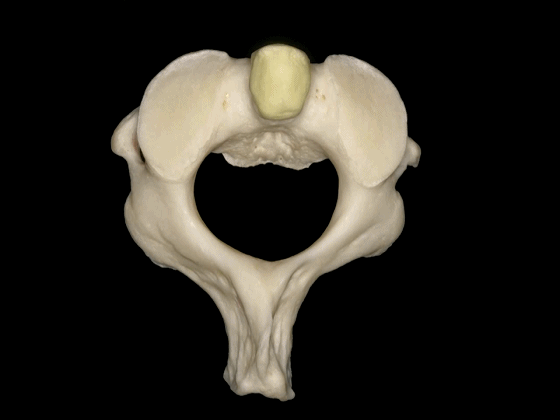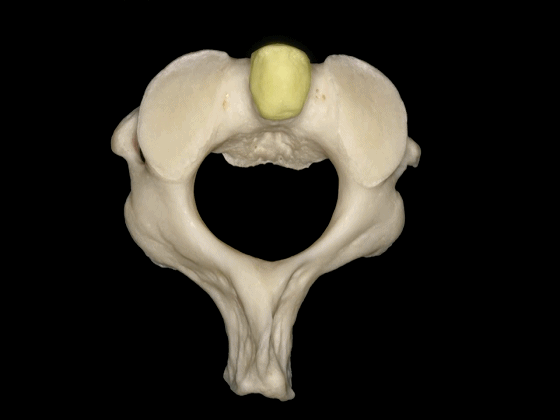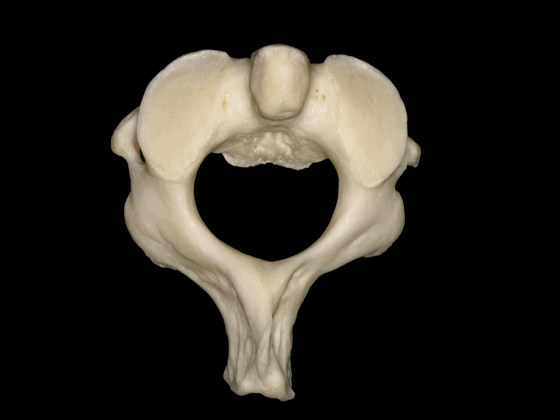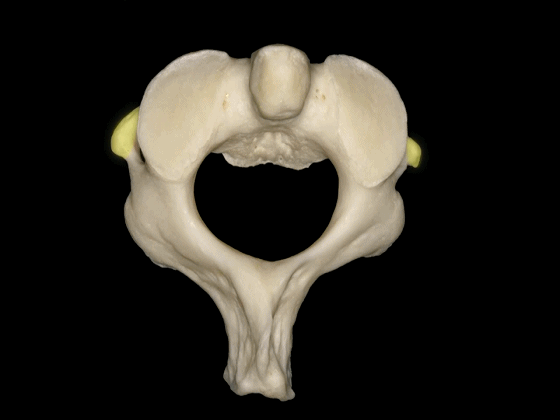
▼这是枢椎的上关节突、椎弓板、棘突。上关节突遮盖了横突。因此椎动脉由内向外进入寰椎横突孔。
lamina, spinous process, and superior articular processes which hide the transverse process. So the vertebral artery has to run from medial to lateral togo through the C1 transverse foramen.
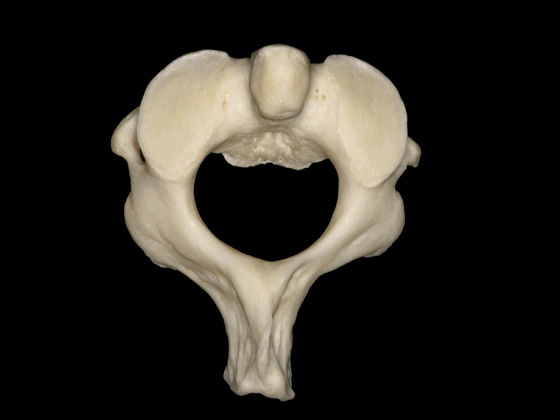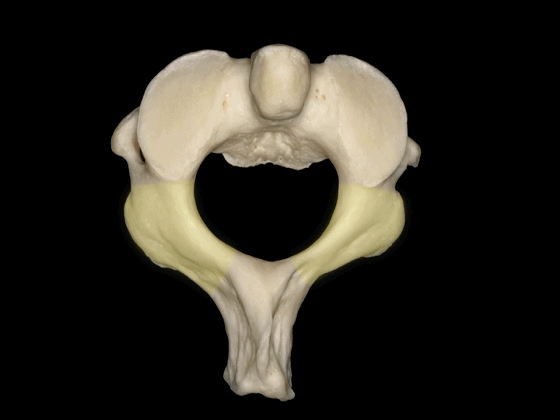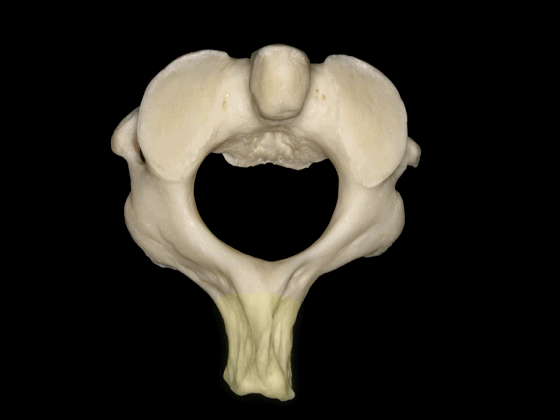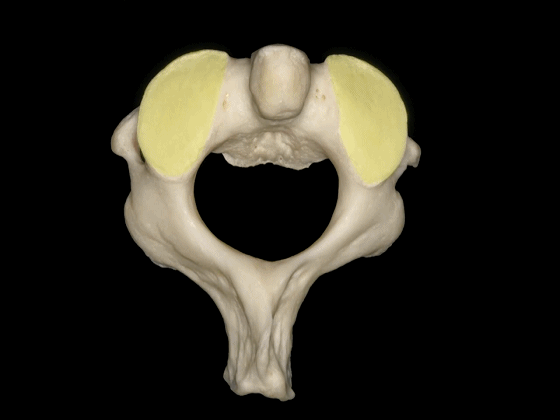
▼这是寰枢关节的上面观。可见寰椎横突孔(下图),但枢椎横突孔无法显示,这正是椎动脉V3段垂直部由内向外,上行于枢椎至寰椎横突孔之间的原因。
Here's a superior view of the atlanto-axial articulations in which we see the transverse foramen of C1, but we cannot see the transverse foramen of C2, which makes the vertical portion of V3 ascends superiorly and laterally to pass from the transverseforamen of C1 to C2.
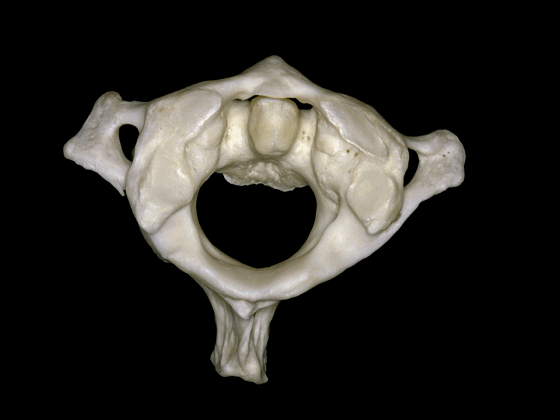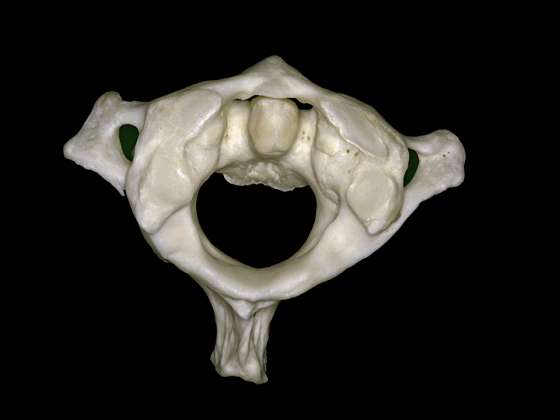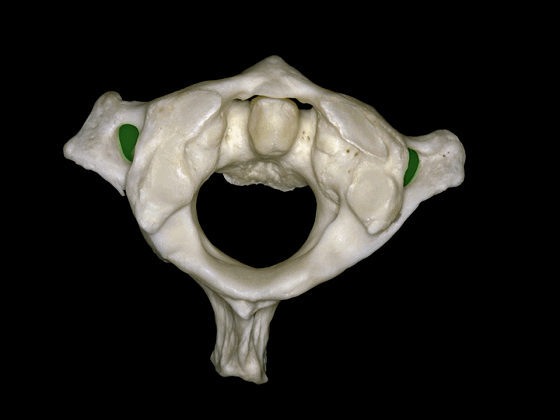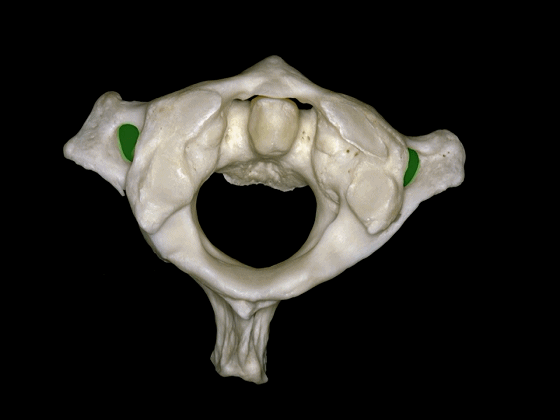
▼这是枢椎的下面观,可见其横突孔,枢椎的上关节突与横突孔几乎重叠,但与C3形成的下关节则位于横突孔后方。
In a view of C2 from below, it shows the transverse foramen here, and the superior articular process of C2 is located at the level of the transverse foramen, but the inferior articulations that articulate with C3 are behind the transverse foramen.
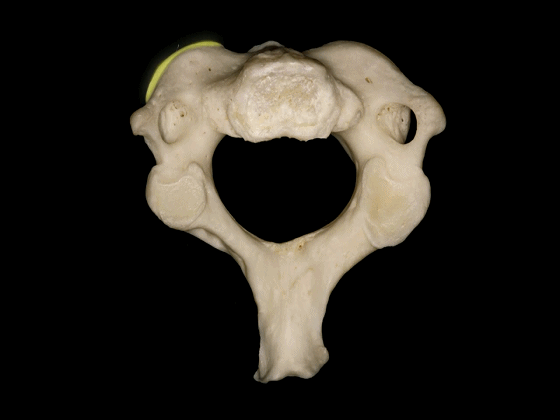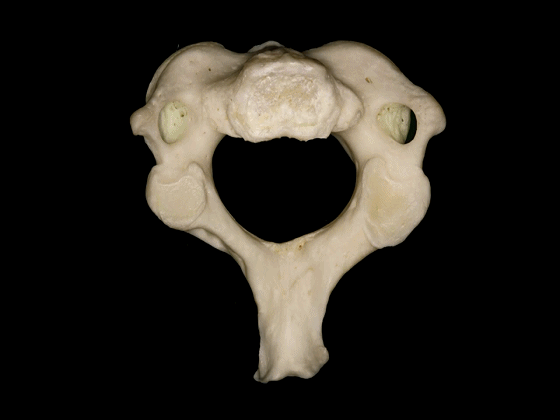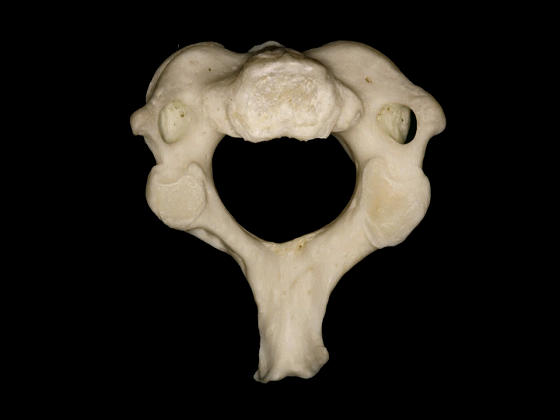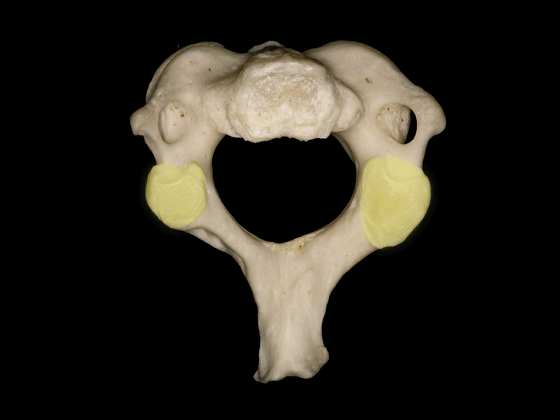
▼这是C3,其他的颈椎骨与C3形态相似。包括椎体,横突内有横突孔
The other cervical vertebrae...this is C3...are similar inconfiguration, with a body, a transverse foramen in the transverse process
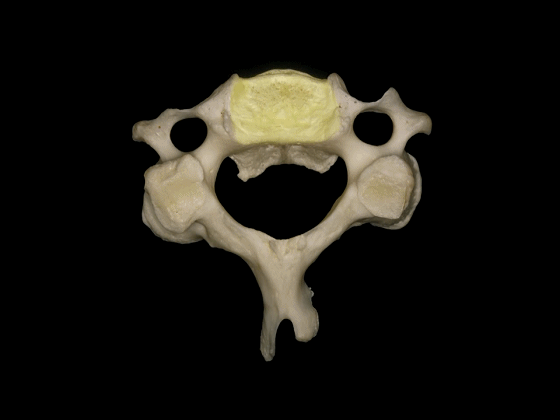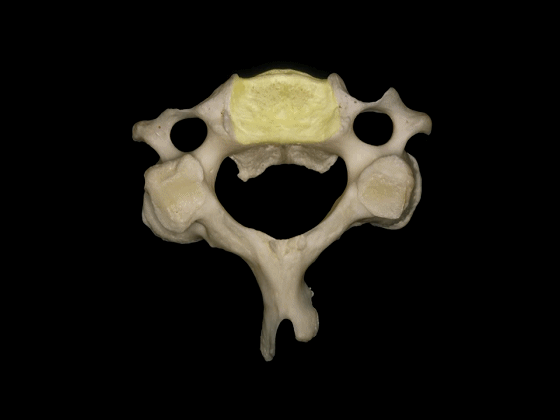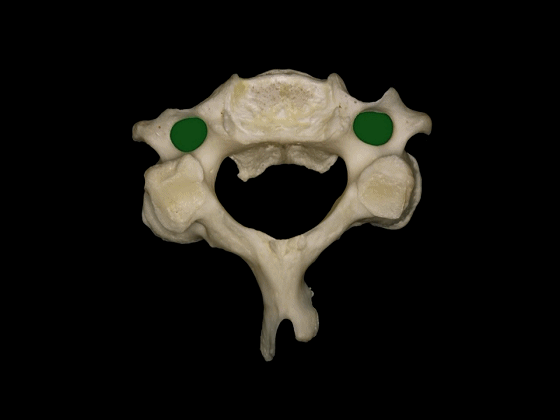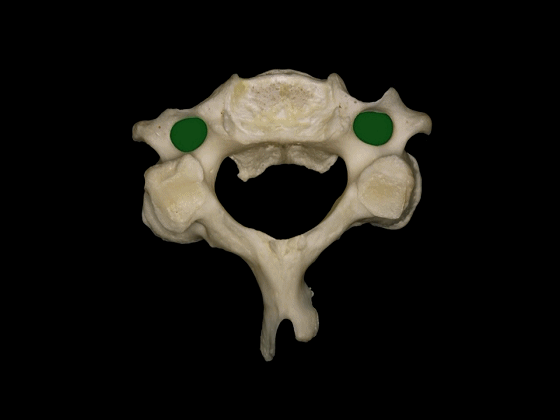
▼这是C3的关节突,椎弓板,棘突。
the articular processes, lamina, and spinous processes.
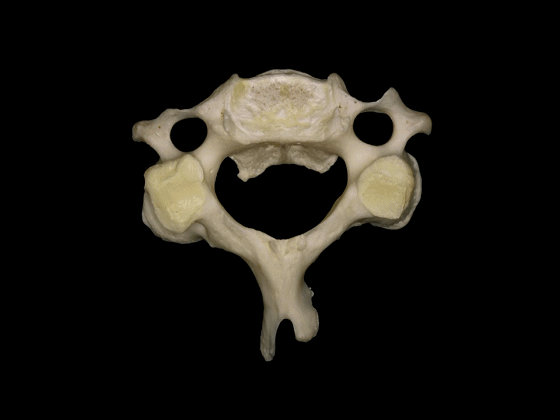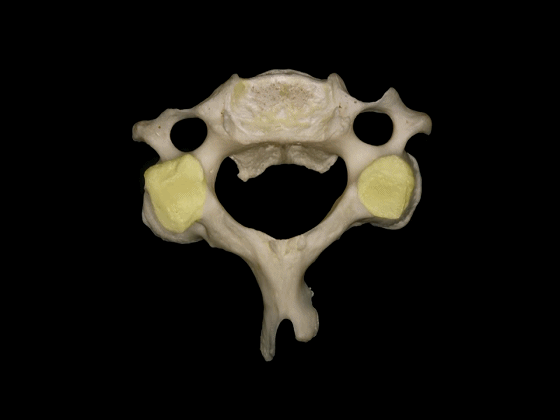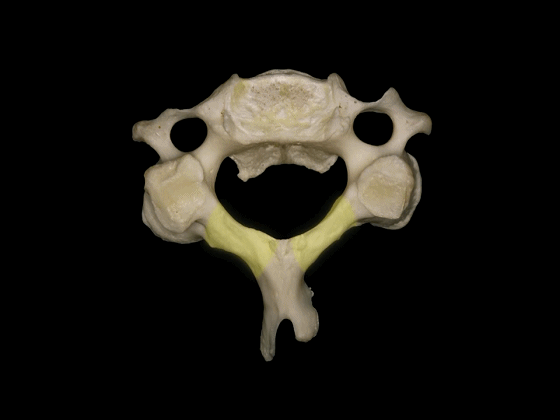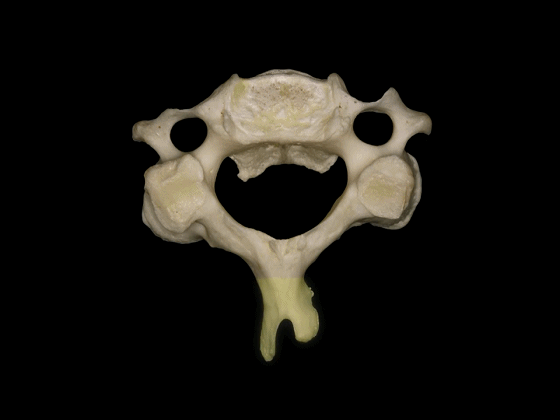
▼C3至C7椎体的后外侧唇向上突出形成钩突。
The posterolateral lips of the bodies of C3 to C7 project upwards forming the uncinate processes.
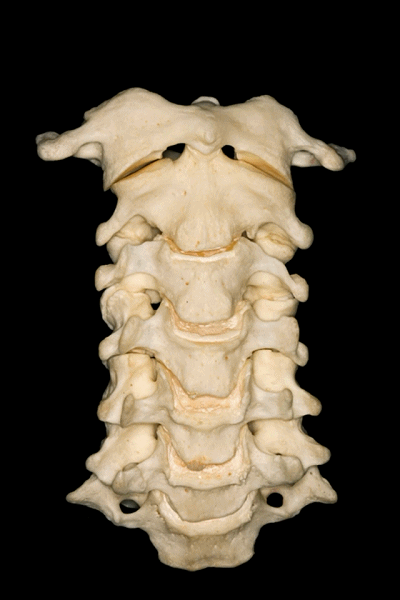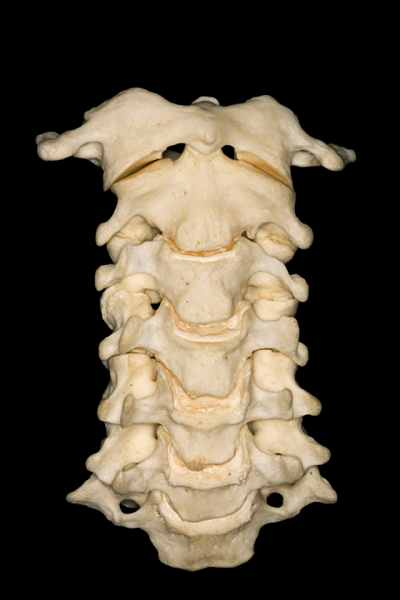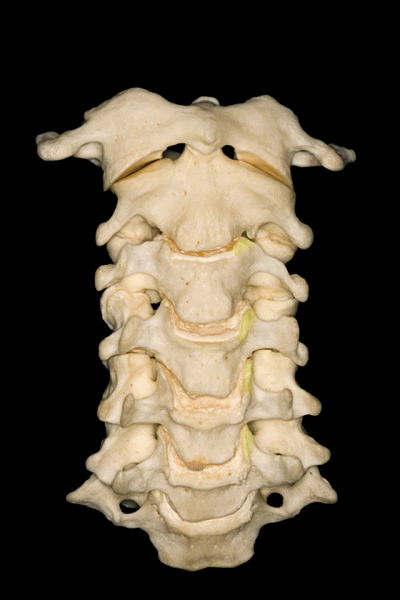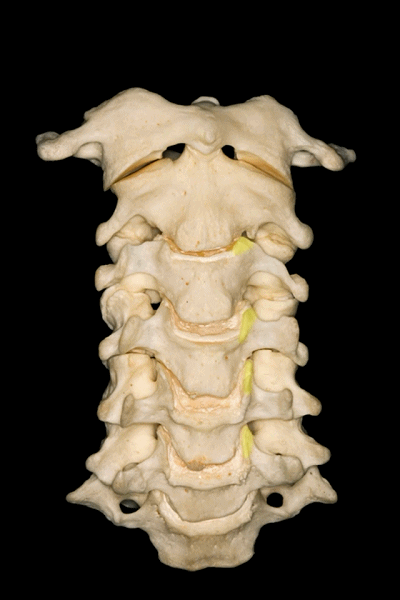
▼钩突的重要临床意义在于,其为椎间孔的前方毗邻。
This is important because the uncinate processes are relatedanteriorly to the intervertebral foramina.
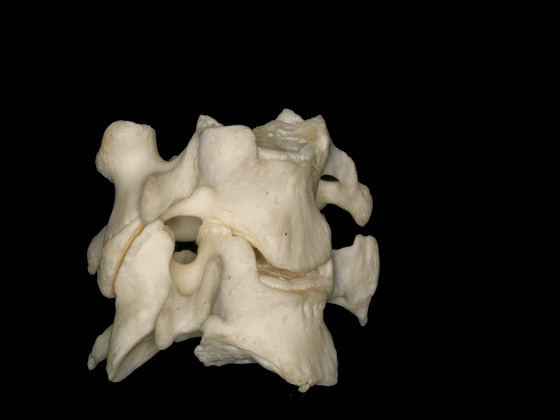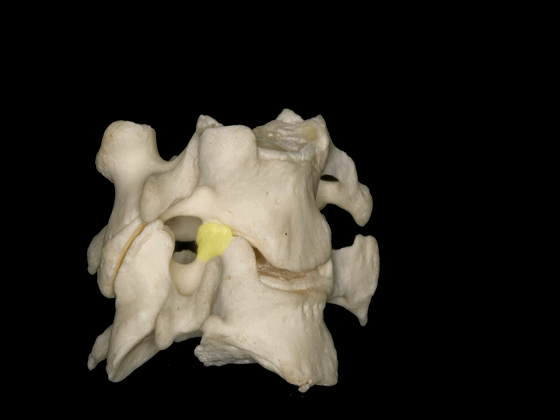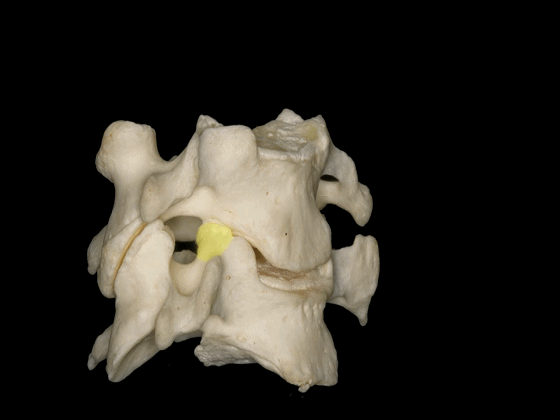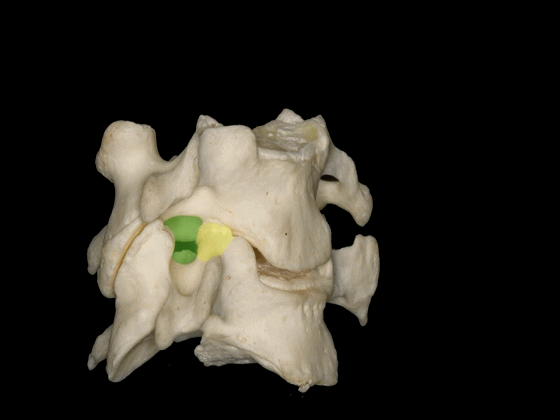
▼位于椎间孔内的结构有行于前部的椎动脉,以及位于后部的C3至C7的颈神经。
And the configuration of the structures in the intervertebralforamina are the vertebral artery run anteriorly, and the cervical nerves run posteriorly from C3 to C7.
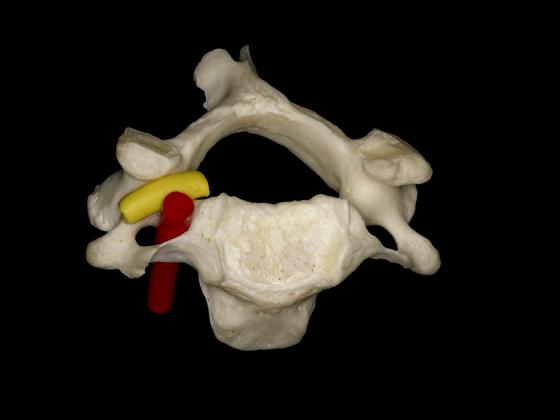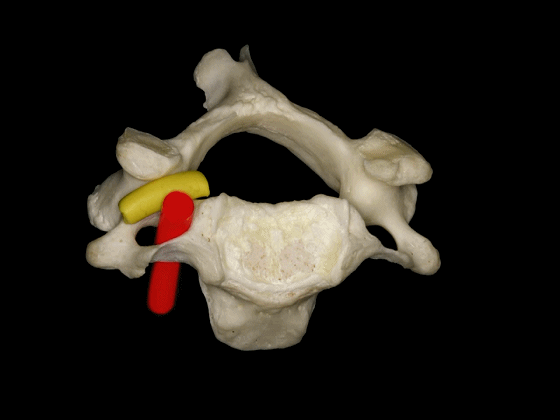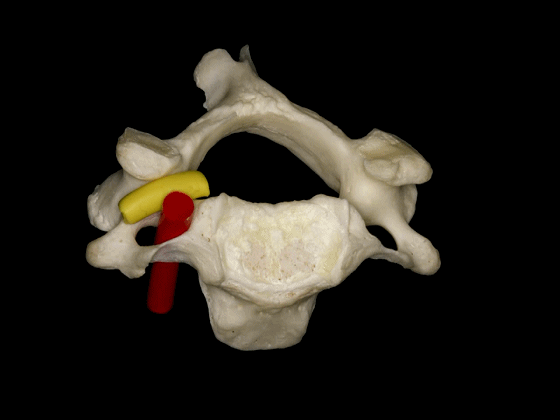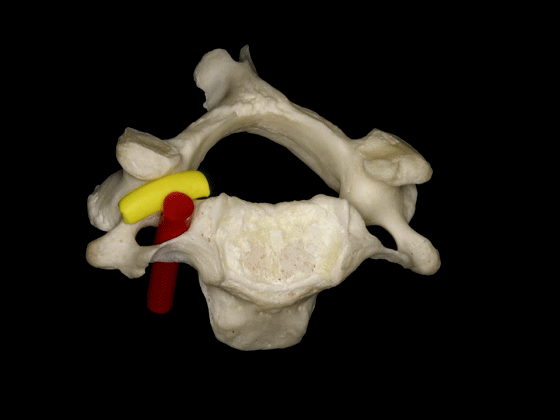
▼因此,椎动脉位于椎体侧方,C3至C7关节突的前方,寰枢关节的外侧。
So, the vertebral artery is lateral to the vertebral bodies, and anterior to the articular processes from C3 to C7, and lateral to the C1-C2 joint.
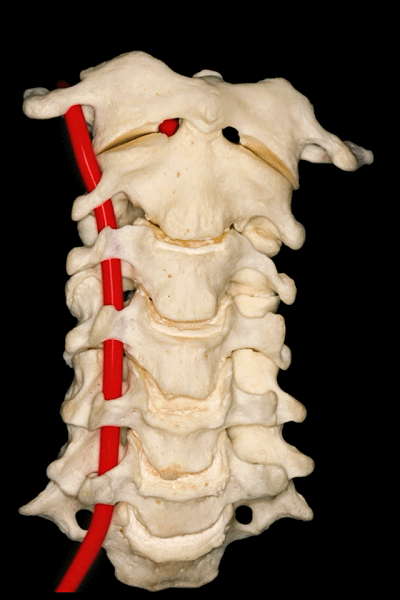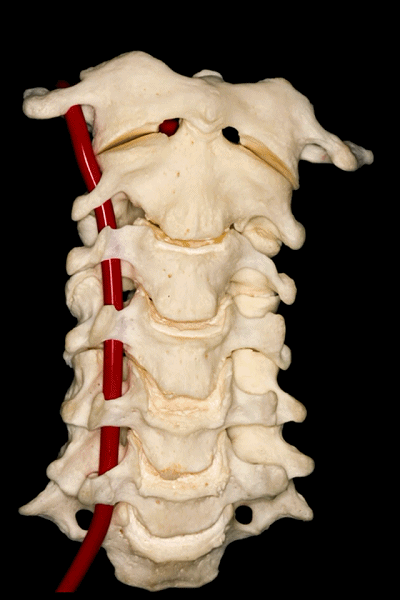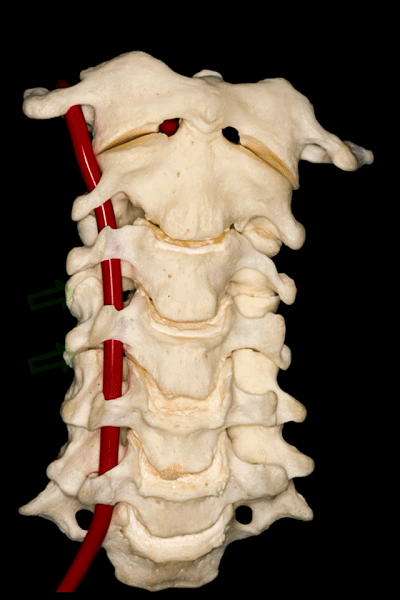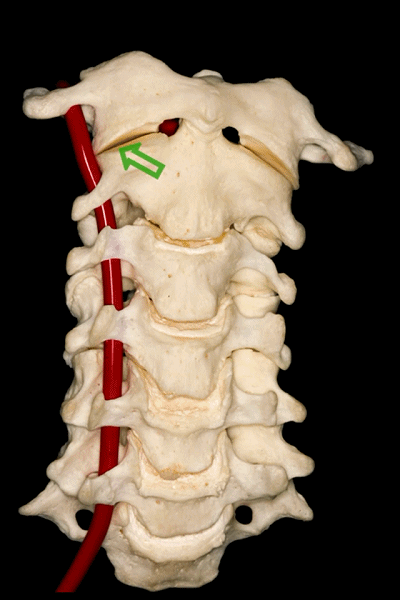
▼此图可以看出椎动脉位于C3-C7关节突的前方,以及寰椎关节的外侧。
This is a lateral image of the relationship of the vertebralartery anterior to the articular processes, and lateral to the atlanto-axial joint.
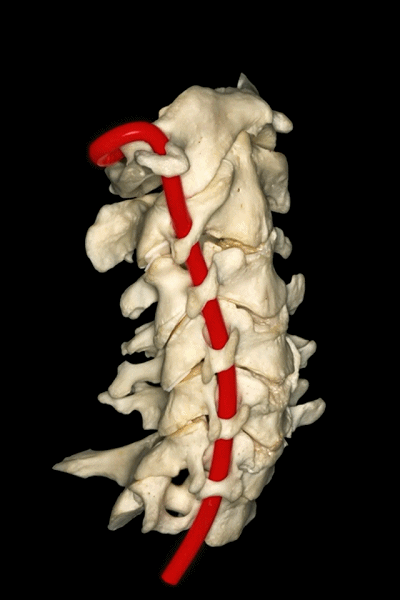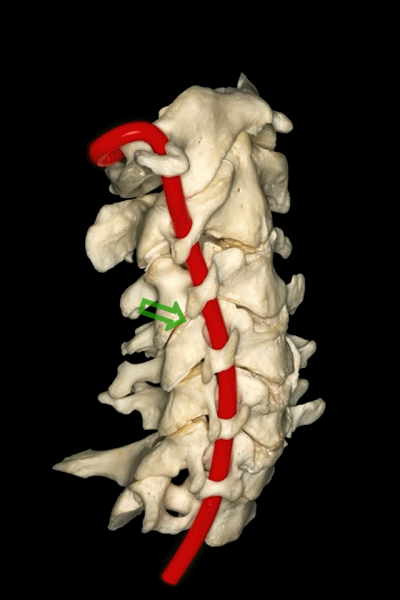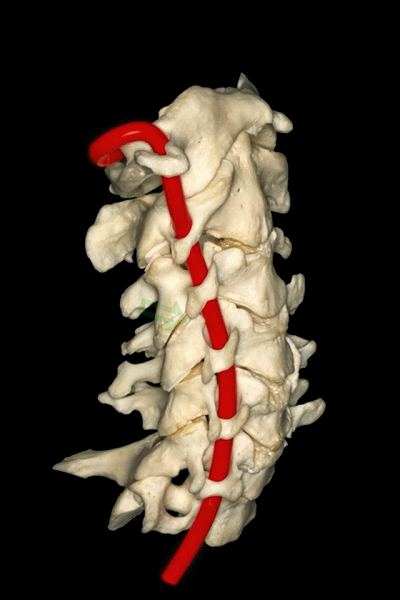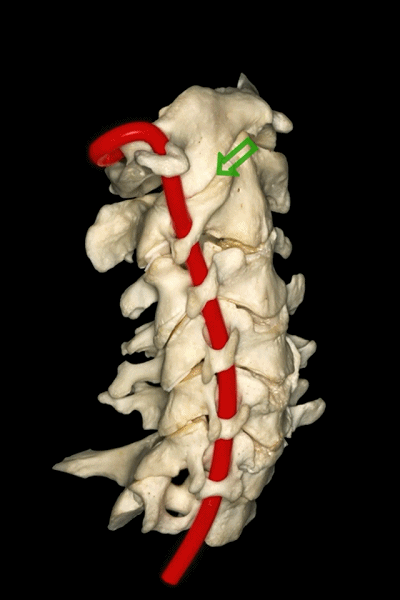
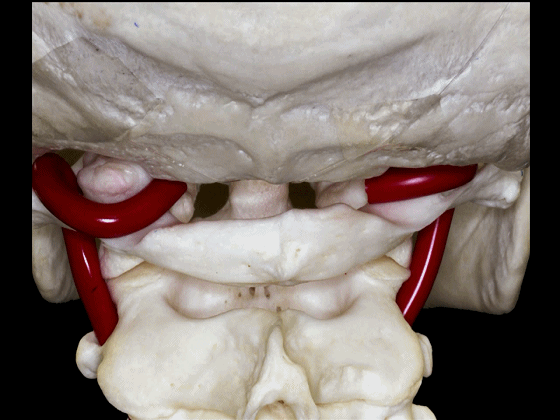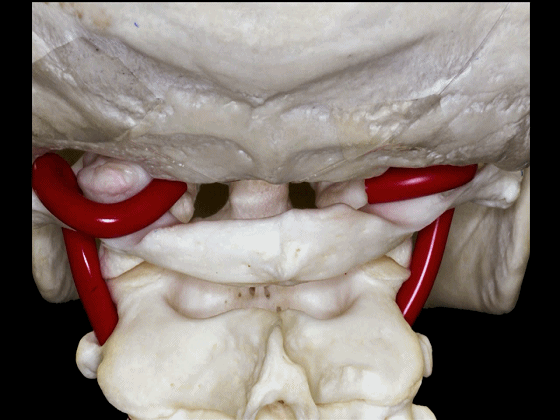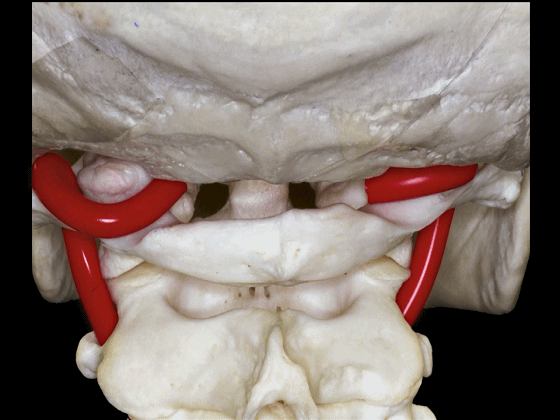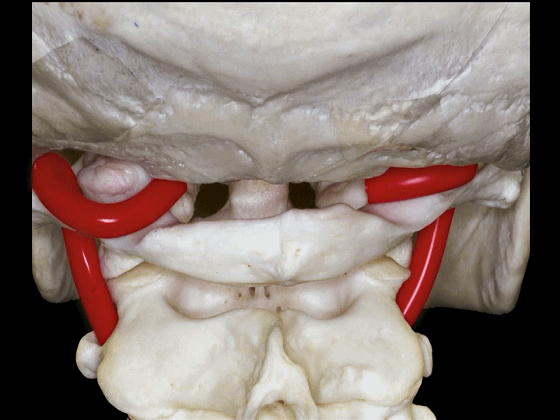
▼因此,经鼻或经口入路处理上段颈椎时,需深刻理解外侧的椎动脉,以及位于前内侧的颈动脉,以及颈静脉孔区的所有结构。
Transnasal or transoral approaches can access the uppercervical spine, and need to take into account the important relationships ofthe vertebral artery which is lateral, but also the relationships of the carotid which isanteromedial in this portion to the vertebral artery, and all the structures from the jugular foramen.
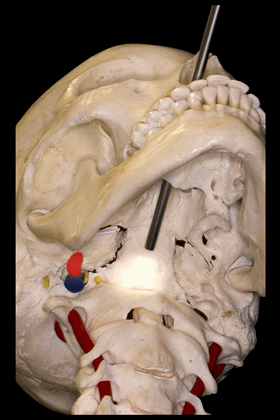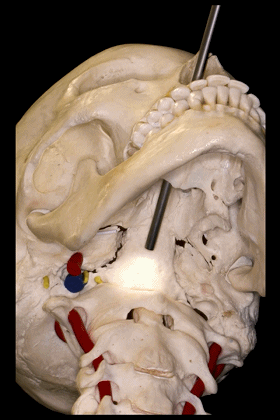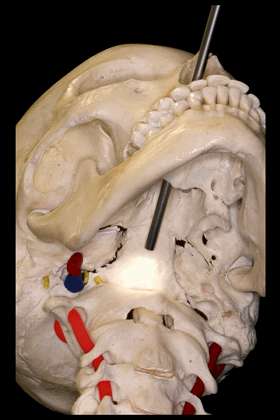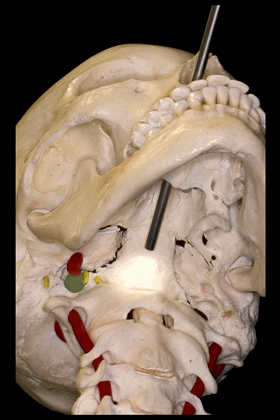
▼下面我们将讨论经口及经鼻至斜坡的相关入路。
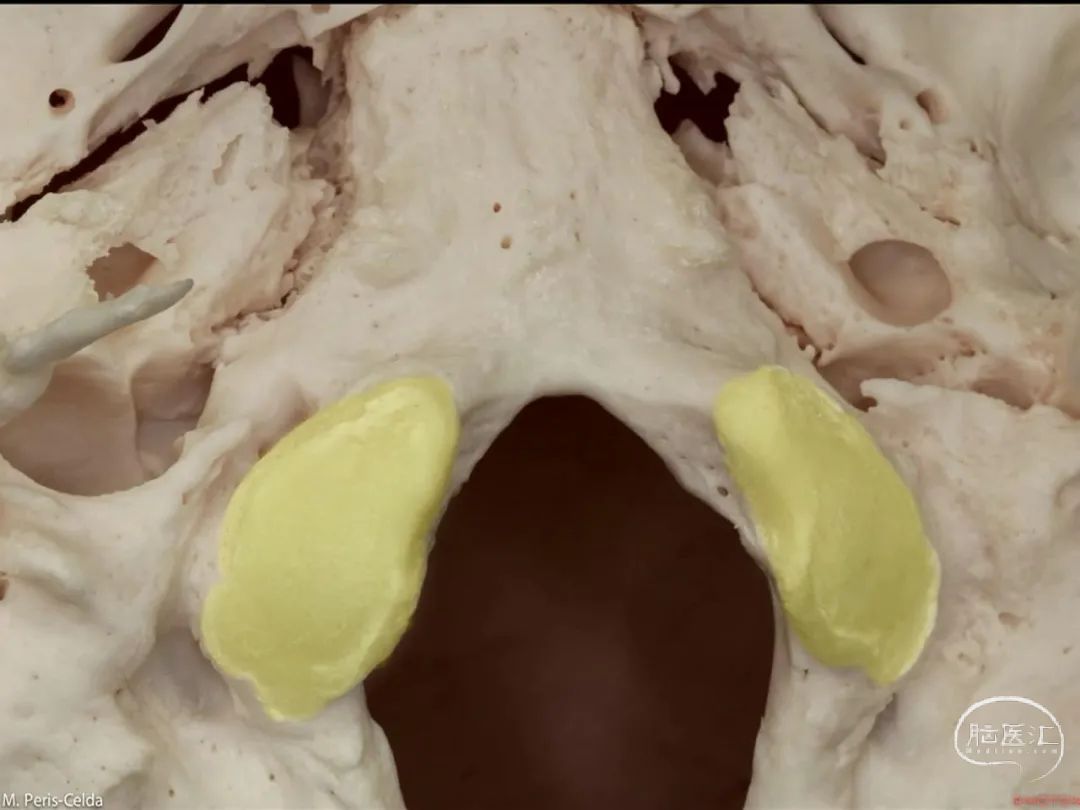
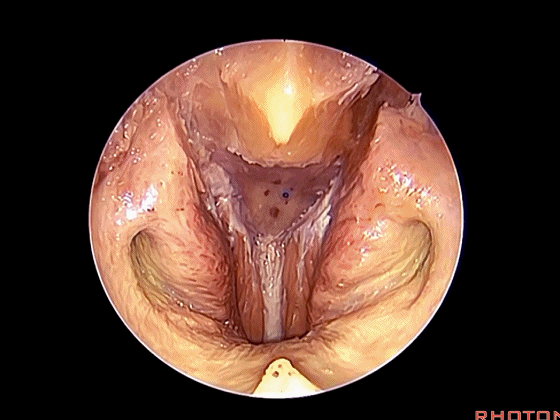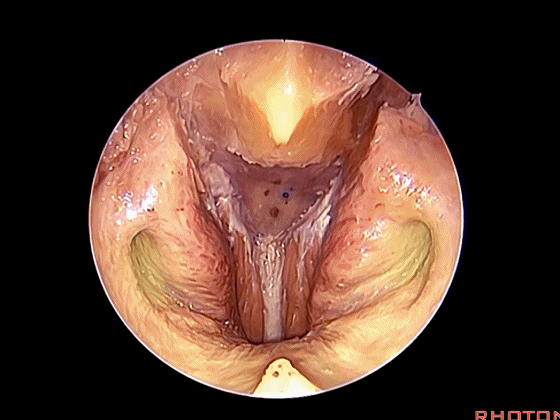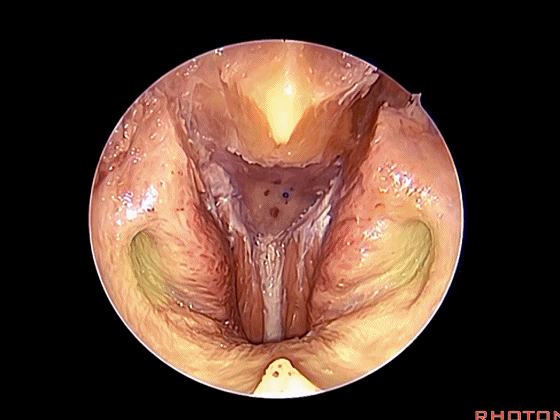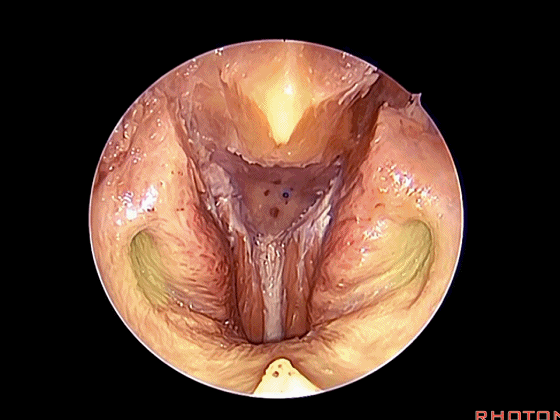
经鼻入路行齿状突切除术是常用的术式。从鼻腔内看,这是咽鼓管(下图)。
We'll do a quick look at transoral and transnasal exposures of clivus. And transnasal approaches for odontoidectomy are becoming more common. But here we look at nasal cavity. This is eustachian tube.
▼这是头长肌
What muscle? Longus capitis.
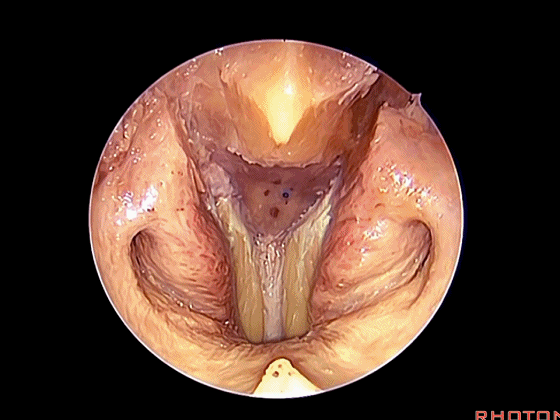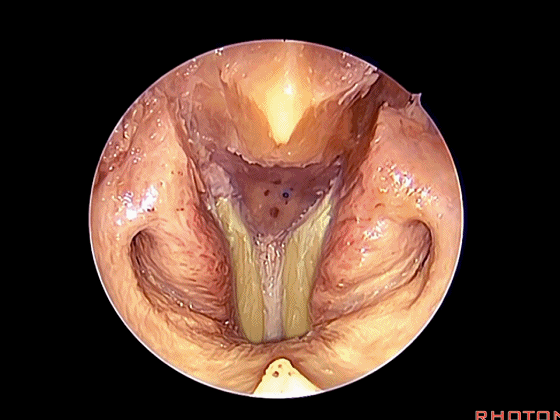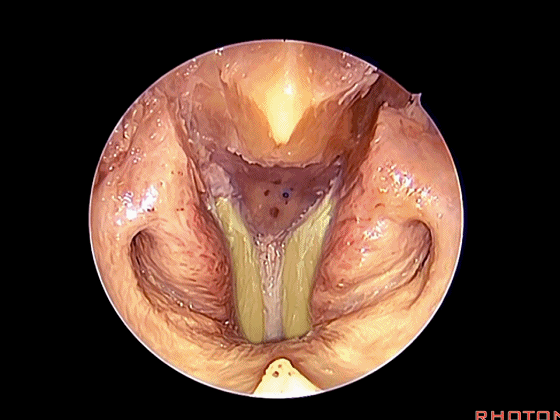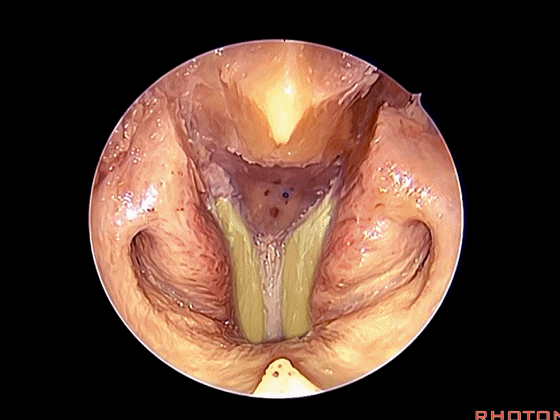
▼斜坡就在正前方
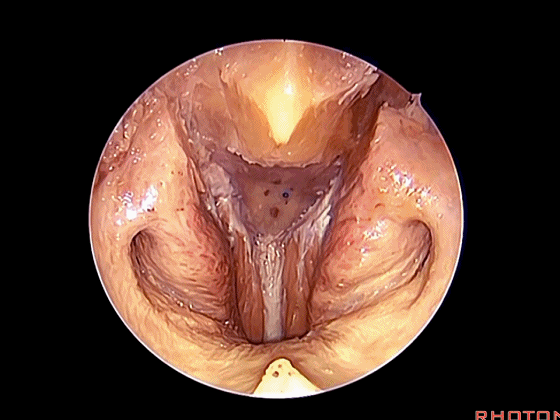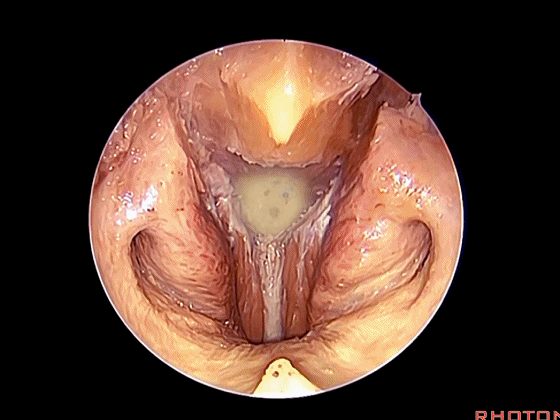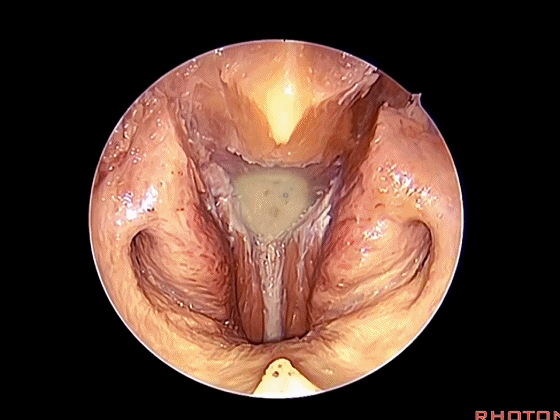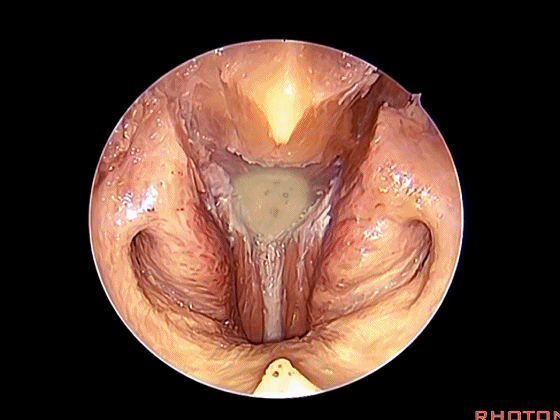
▼在这经鼻入路中。将头长肌(下图)牵向外侧,即可见头前直肌。这是45°成角内镜向外所见的术野。
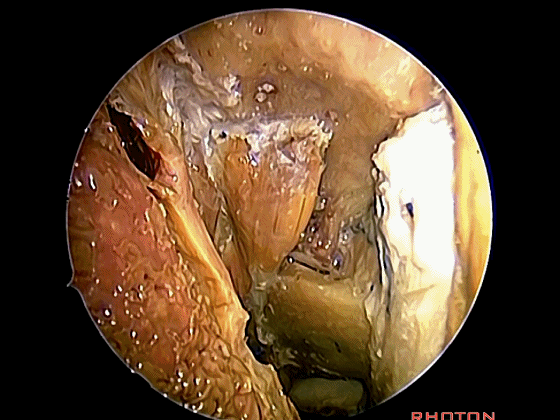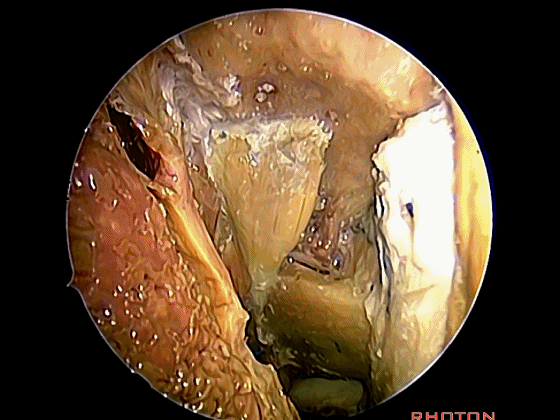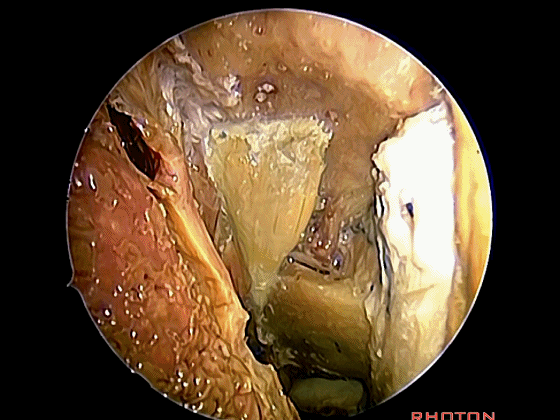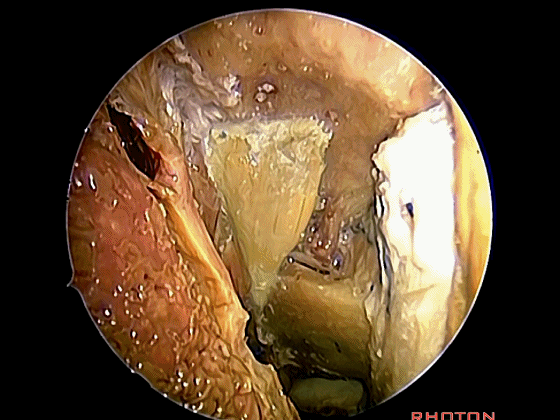
in the transnasal approach. Here we pull the longuscapitis laterally,and we see rectus capitis anterior. We're looking laterally withthe 45 degree endoscope.

▼这是头前直肌
声明:脑医汇旗下神外资讯、神介资讯、脑医咨询、AiBrain所发表内容之知识产权为脑医汇及主办方、原作者等相关权利人所有。未经许可,禁止进行转载、摘编、复制、裁切、录制等。经许可授权使用,亦须注明来源。欢迎转发、分享。









































