Our Case
History
• 53 y/o male,who suffered from mild headache after he was diagnosed with vascular malformation accidentally.
• PE: NS (-)
1
Preoperative
Part 1 Diagnosis
Figure 1A-C Brain MR T2WI images show the void signal (blue arrows) on the cerebellum and the abnormal dilated tentorial vessels (red arrows).
Part 2 DSA:Tentorial DAVF
Figure 2A-B Feeding artery 1 (RICA): The marginal tentorial branches of ICA, which is too tortuous to superselect.
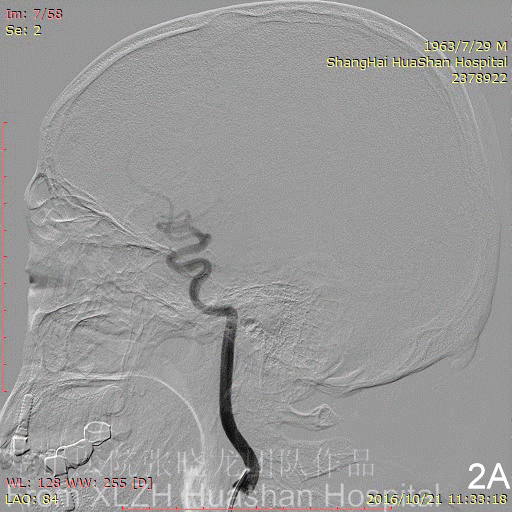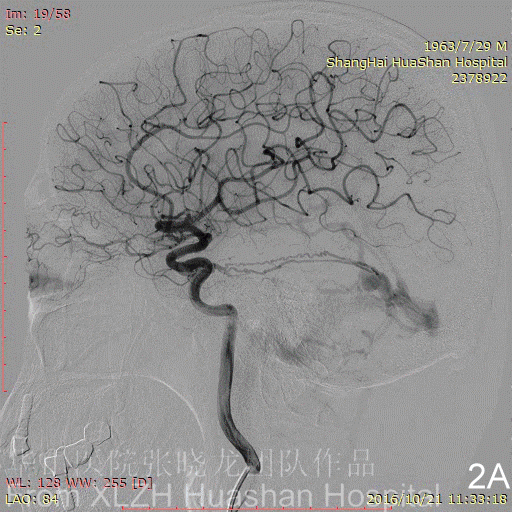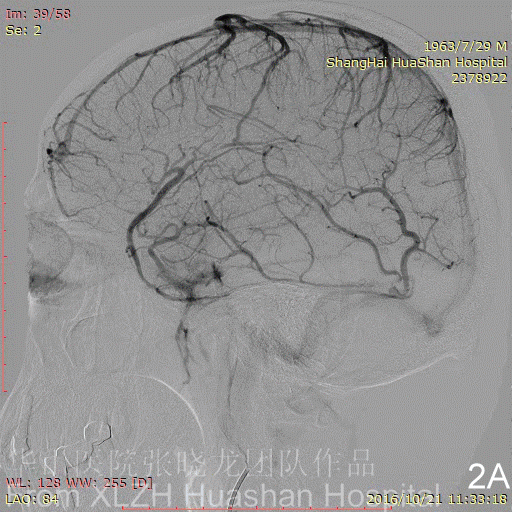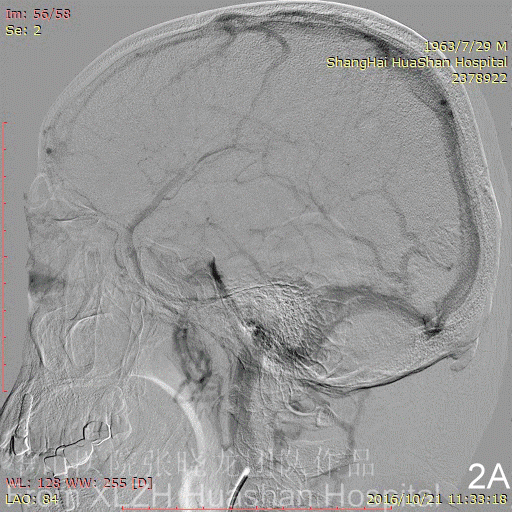

Figure 3A-B Feeding artery 2 (R-MMA): the Right MMA is also too tortuous and difficult for advancement.
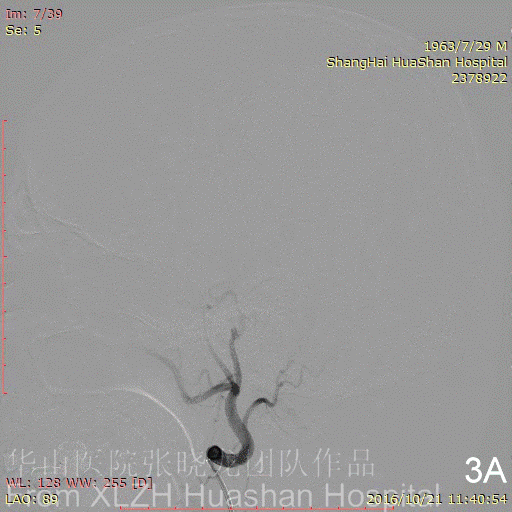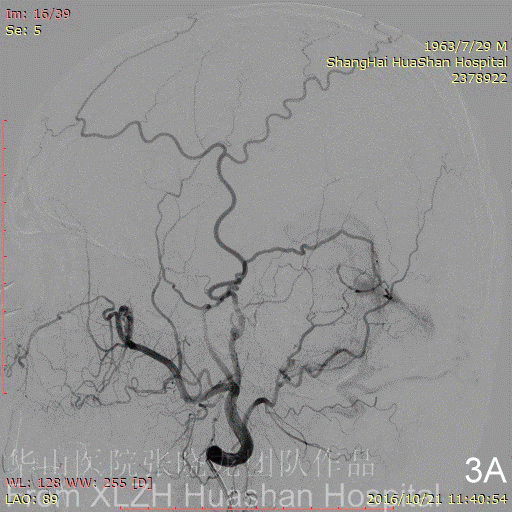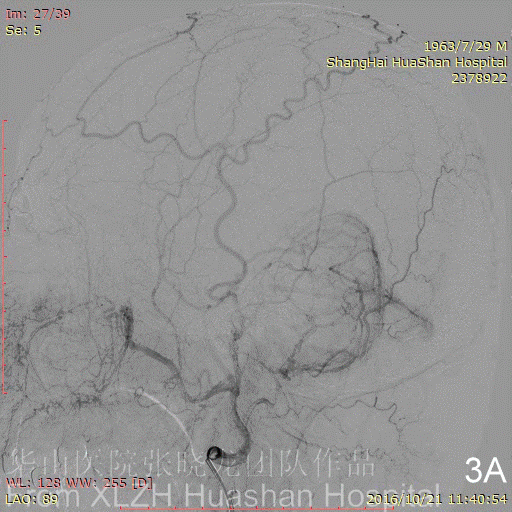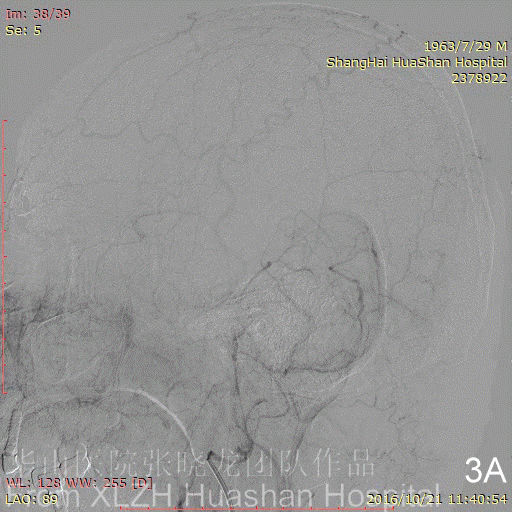
Figure 3C-D Feeding artery 3 (R-OcA): Meningeal branch arising from the proximal right occipital artery.
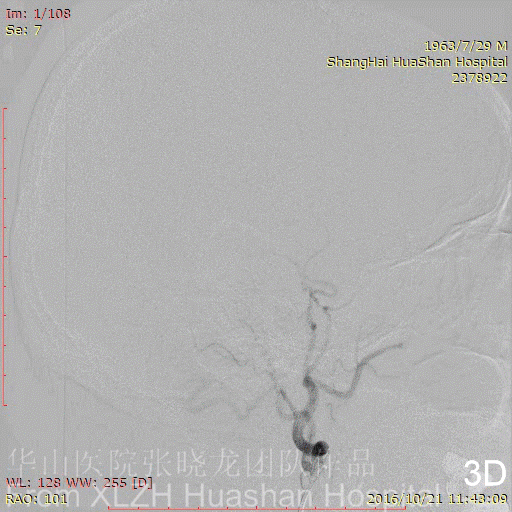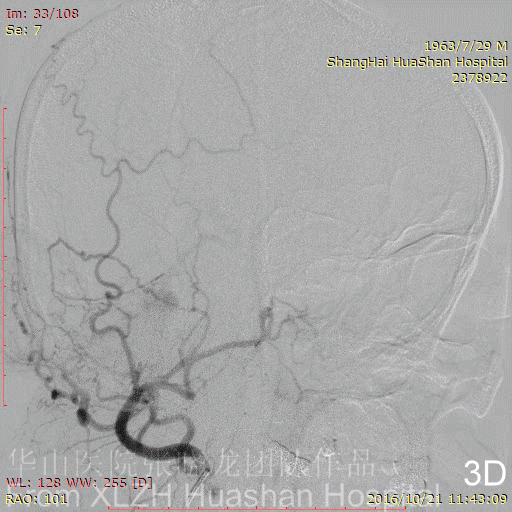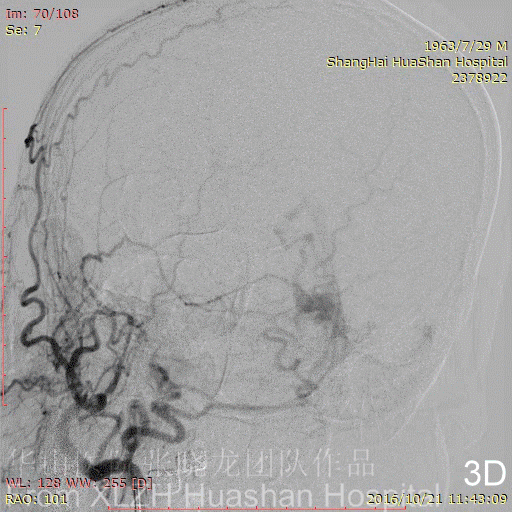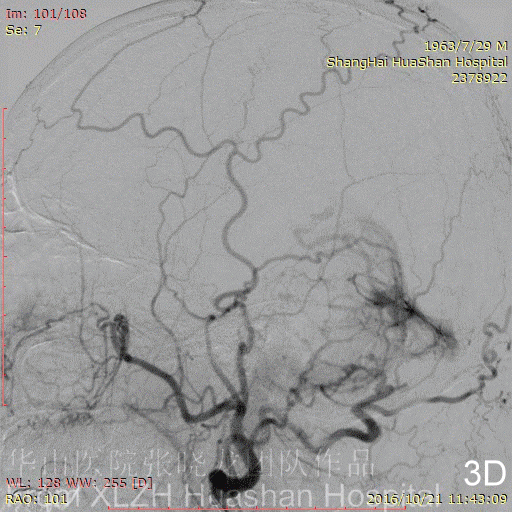
Figure 4A-C Feeding artery 4 (L-OcA): Left MMA is under-developed.


Figure 5A-E Feeing artery 5 (LVA): This case is a multiple tentorial DAVF. The major part is located along the straight sinus, and drained through the venous pouch.
And the other part which adjacent to the Galen's vein is fed by the meningeal branches arising from the superior cerebellar arteries or posterior cerebral artery.



Figure 6A-B Feeding artery 6: Left costocervical truck.
Figure 7 RICA is normal.
Part 3 DSA:Treatment Stretegy
• The ICA marginal tentorial branches and right MMA are too difficult for the microcatheter to navigate through.
◇ The right MMA is still our first choice, though this route is very tortuous.
• The meningeal branches arising from the superior cerebellar arteries or posterior cerebral artery are not suitable as the treatment route due to the risk of Onyx reflux.
◇ The meningeal branch arising from the proximal occipital artery also feeds the same shunt. Balloon assisted embolization can be chosen using this pathway.
◇ Scepter Balloon assisted technique can be used in a fistula which is fed by occipital branches.
2
Intraoperative
Part 1 Treatment
Figure 8A-E After embolization via RMMA (A-C, Onyx quickly refluxed), angiography shows the residue of the fistulas (D, E).
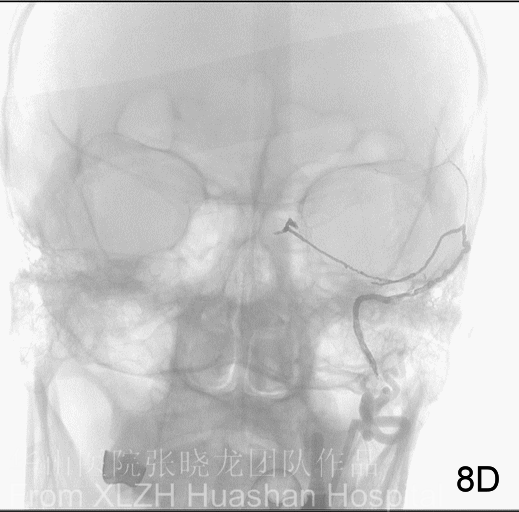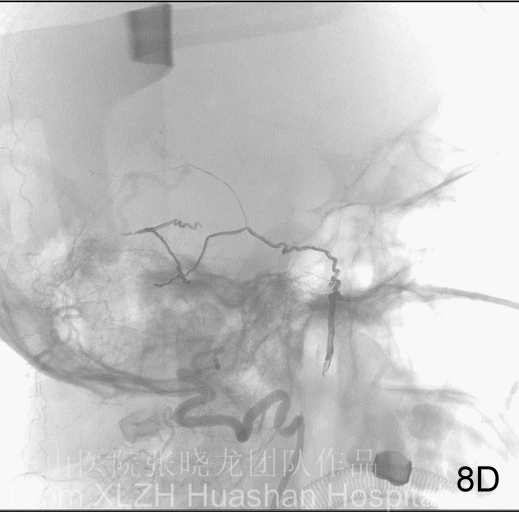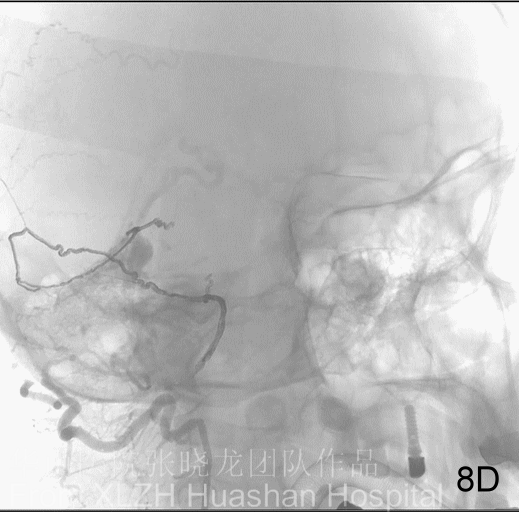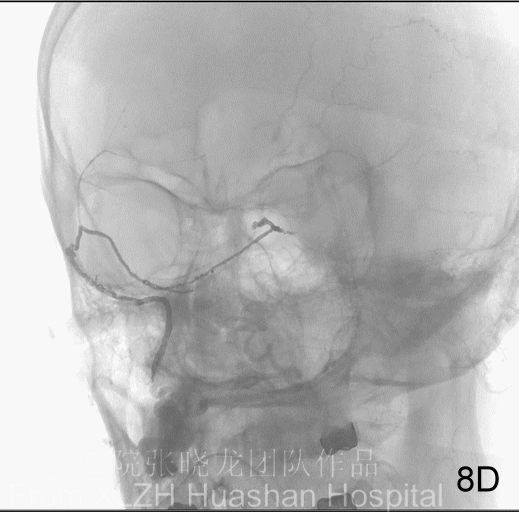

Figure 9A-B Embolization via ROcA (Scepter Balloon, mind the dangerous anstomosis).
Figure 9C-G Embolization via ROcA 1. The Onyx formed a plug at the initial part of the feeding artery first (C), meanwhile the Scepter balloon occluded the reflux route (D). Therefore, instead of reflux, Onyx flowed antegradely (E, F). The video shows the course of Onyx flow (G).

Figure 10A-B Embolization via ROcA 2. Be aware of the contrast draining into the occipital sinus via Anastomosis from the left costocervical trunk. The fistula fed by left costocervical truck (10A). The contrast in the PMA location during the Onyx flow (10B).

Figure 11A-E Embolization via ROcA 3(A). Onyx flowed into the venous pouch.


Figure 12 Onyx casting bilateral posterior meningeal arteries, tentorial fistula and the anastomosis with the left costocervical artery.

Figure 13 Onyx kept refluxing and penetrated behind the balloon, therefore we quit injection.
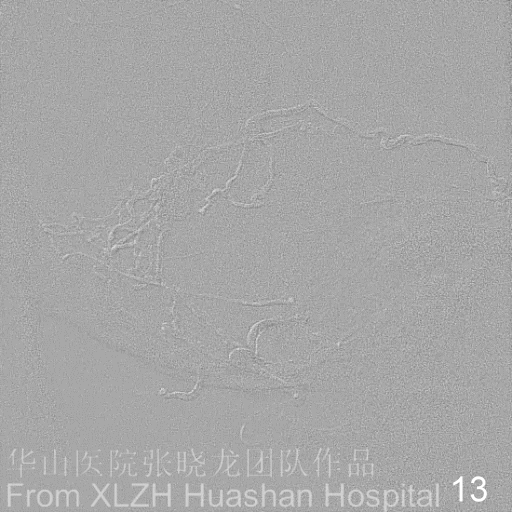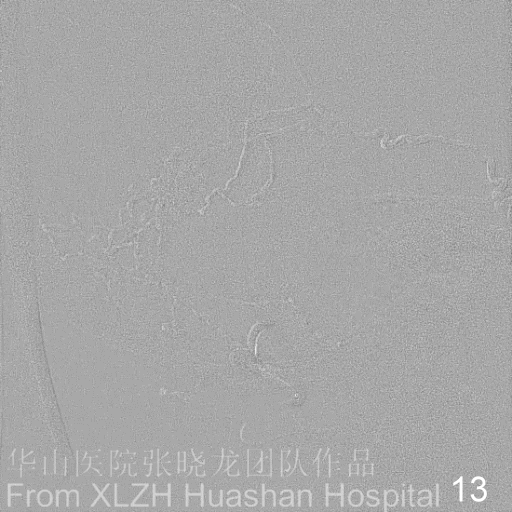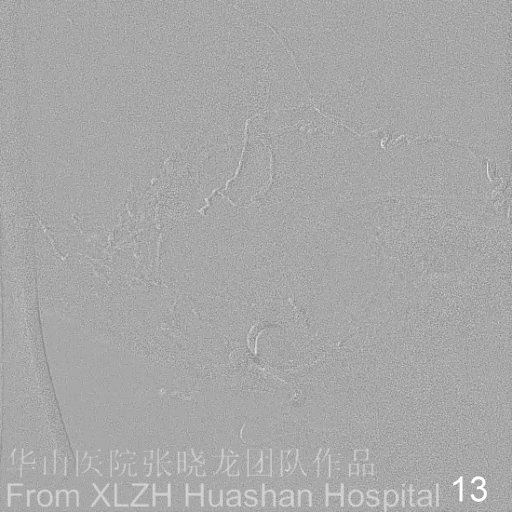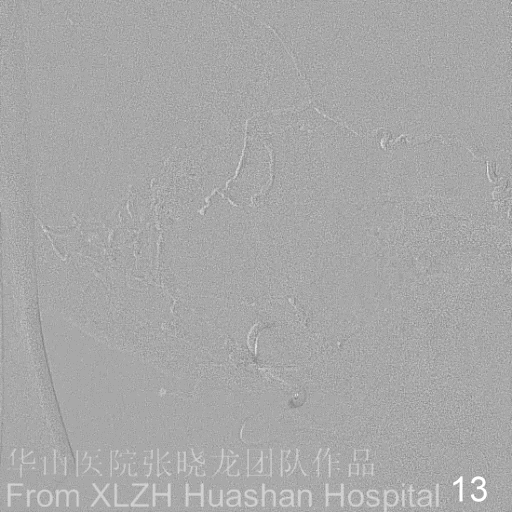
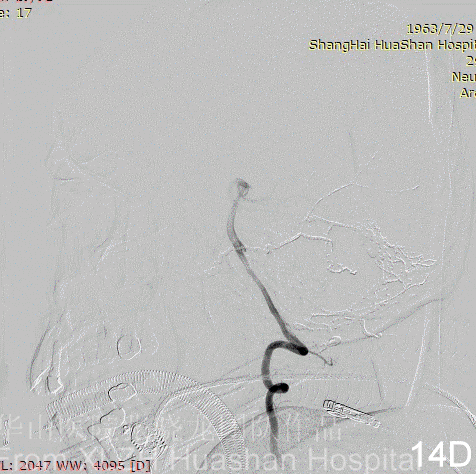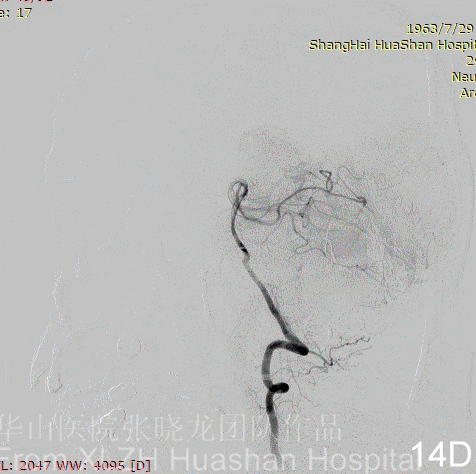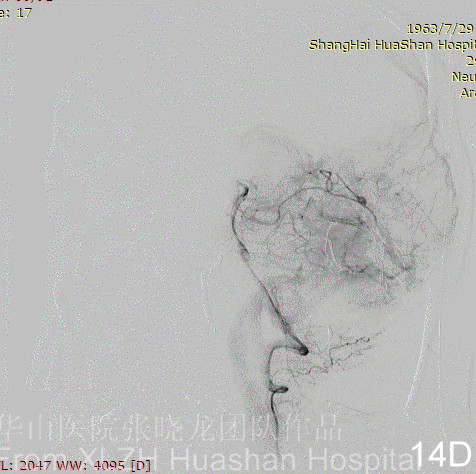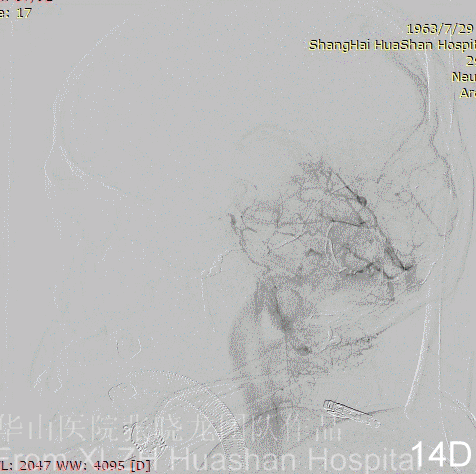
Figure 14A-D Postoperative angiography shows residual fistula with antegrade drainage.

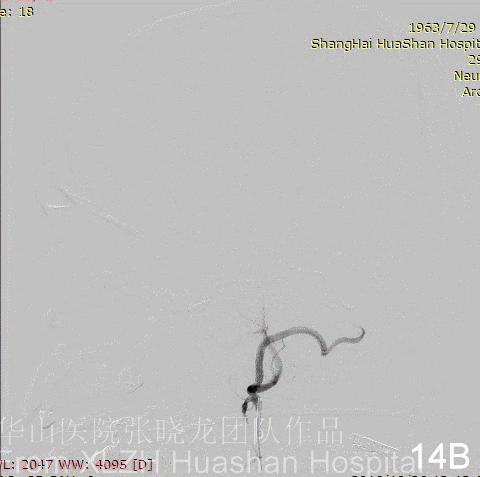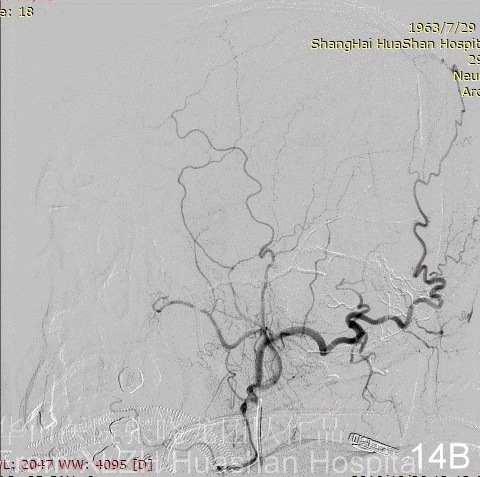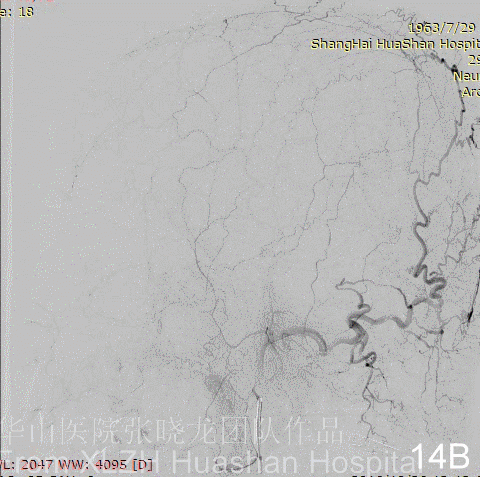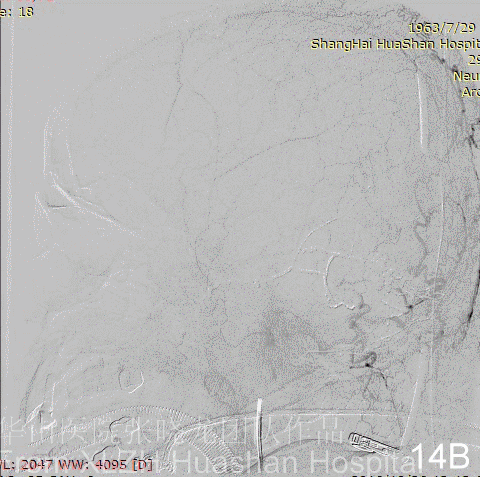

3
Postoperative
Part 1 Examination
Figure 15A-C Postoperative CT. No antiplatelet has been spanscribed.



Part 2 Four months follow-up
Figure 16A-E Follow up angiography.
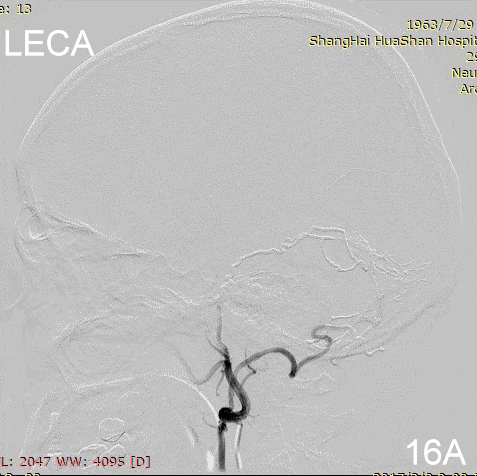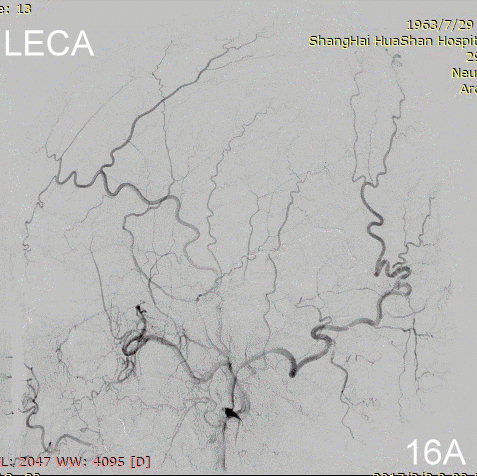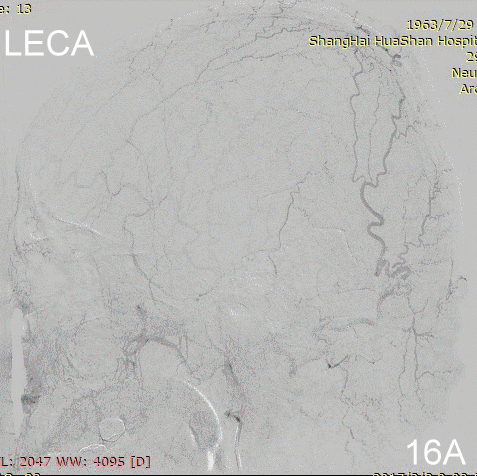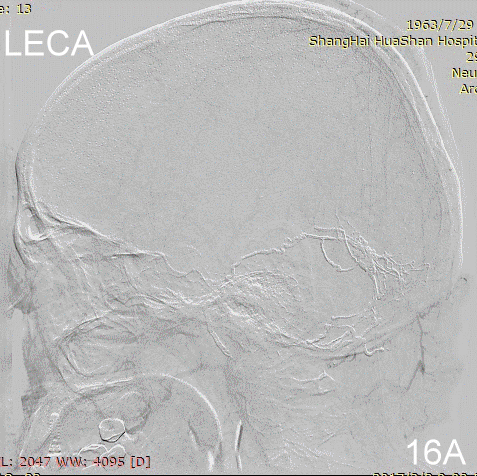
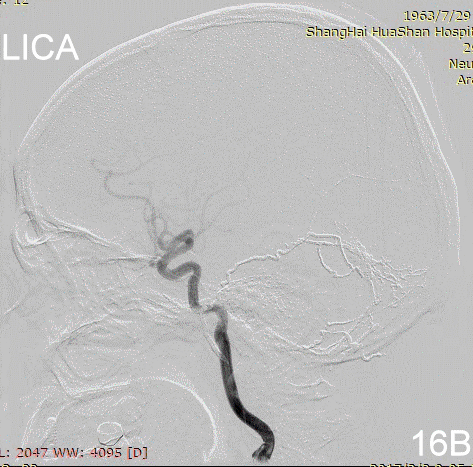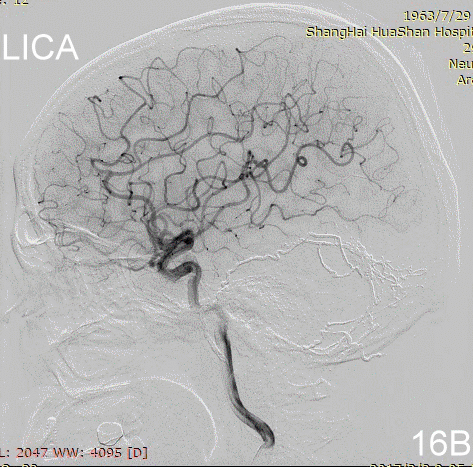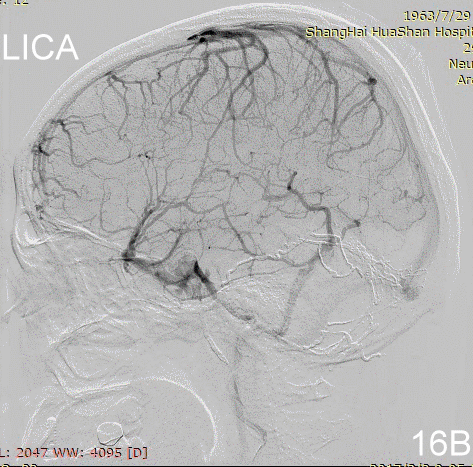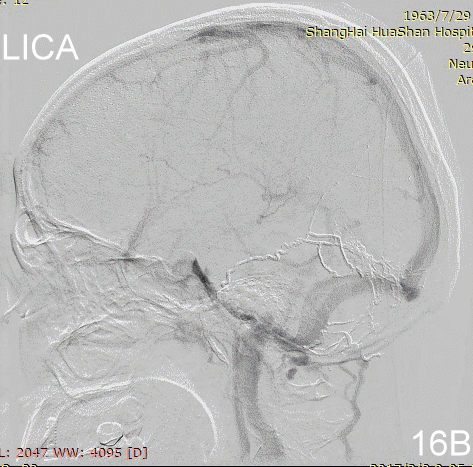
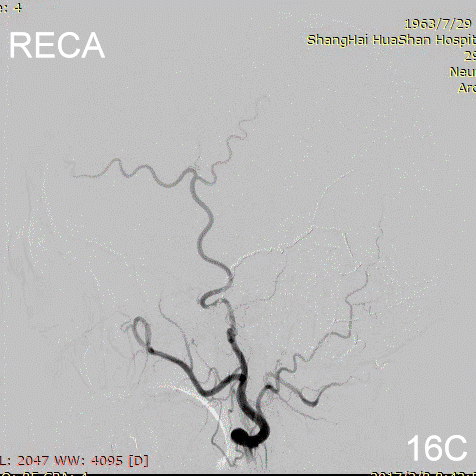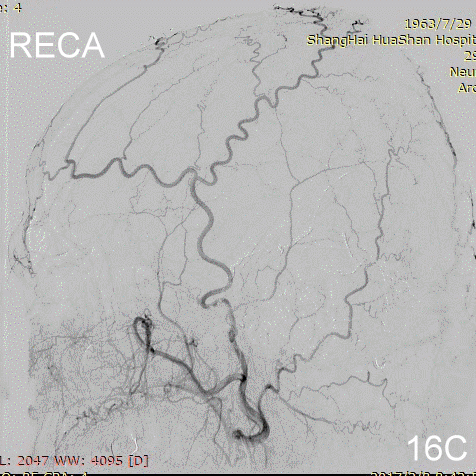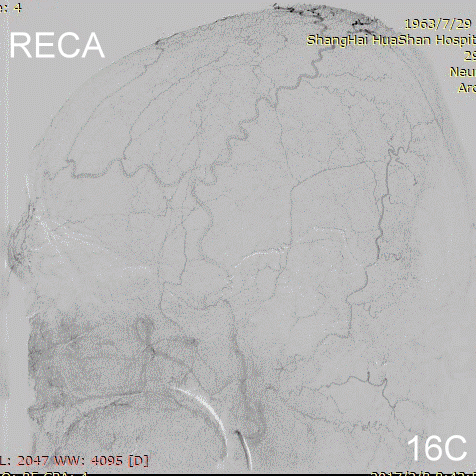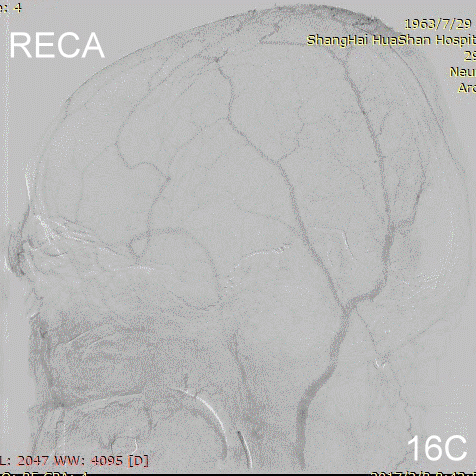
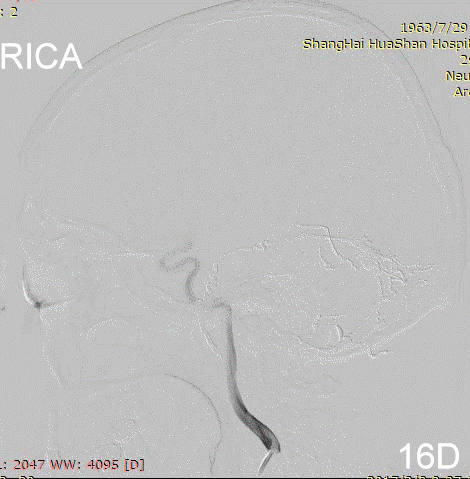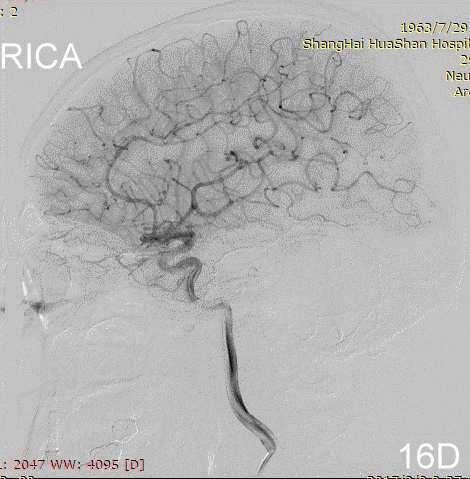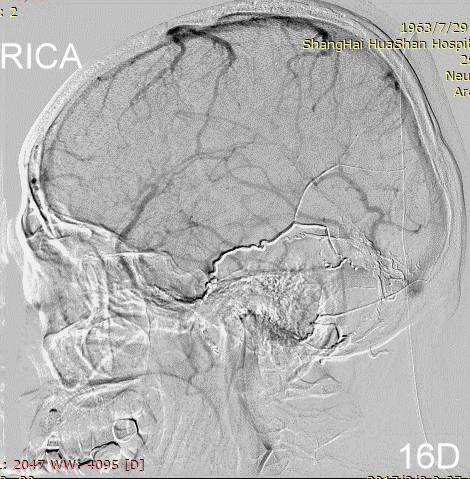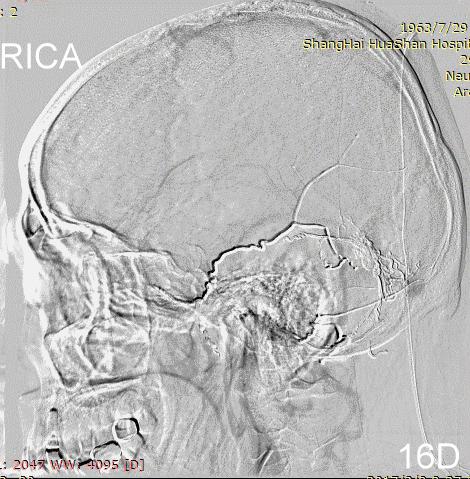

Figure 17A-B Contrast on residual fistula via postoperative and follow-up angiography.


3
Postoperative
Discussion on remnant fistula
• Preoperative image shows two seperate shunts, one was located adjacent to the Galen's vein, one was along the straight sinus. If the Onyx refluxed to the superior shunt, it can cure all the fistulas. But in this case the Onyx refluxed to the proximal side of the Scepter Balloon, therefore we stopped.
• The remnant fistula is fed by the right SCA, which has a benign behavior (Type I). Radiotherapy is another option for such case.
Discussion on treatment
1. Treatment route
• A smooth MMA is still the first choice to embolize the tentorial DAVF.
2. About balloon
• It is risky to inflate Scepter balloon in the proximal MMA.
• The inflation of Scepter balloon in the occipital artery is safer.
3. About dangerous anastomosis
• MMA and ECA are prone to have potential dangerous anastomosis with the intracranial arteries on the skull base.
• The dangerous anastomosis between the occipital artery and the posterior meningeal artery, vertebral artery and APA should be considered.
4. Experience on using Onyx from this case
• Onyx may plug in the proximal feeders first, then flow antegradely with the proximal balloon occlusion.
• Venous pouch was fully filled with Onyx could be an indication of the healing of the DAVF.






