如前所述,Rhoton教授将颞骨解剖分为三部分进行讲解:1.中颅窝部分;2.后颅窝部分;3.乳突部分。本篇为第三部分(乳突部分),主要讲解了乳突切开术及乙状窦前幕上下联合入路的相关解剖。本篇内容对于神经外科医生来说相对比较陌生,笔者将于近期撰文分步讲解乳突切开术、乙状窦前入路。
本文共111张图片。错误之处请批评指正。

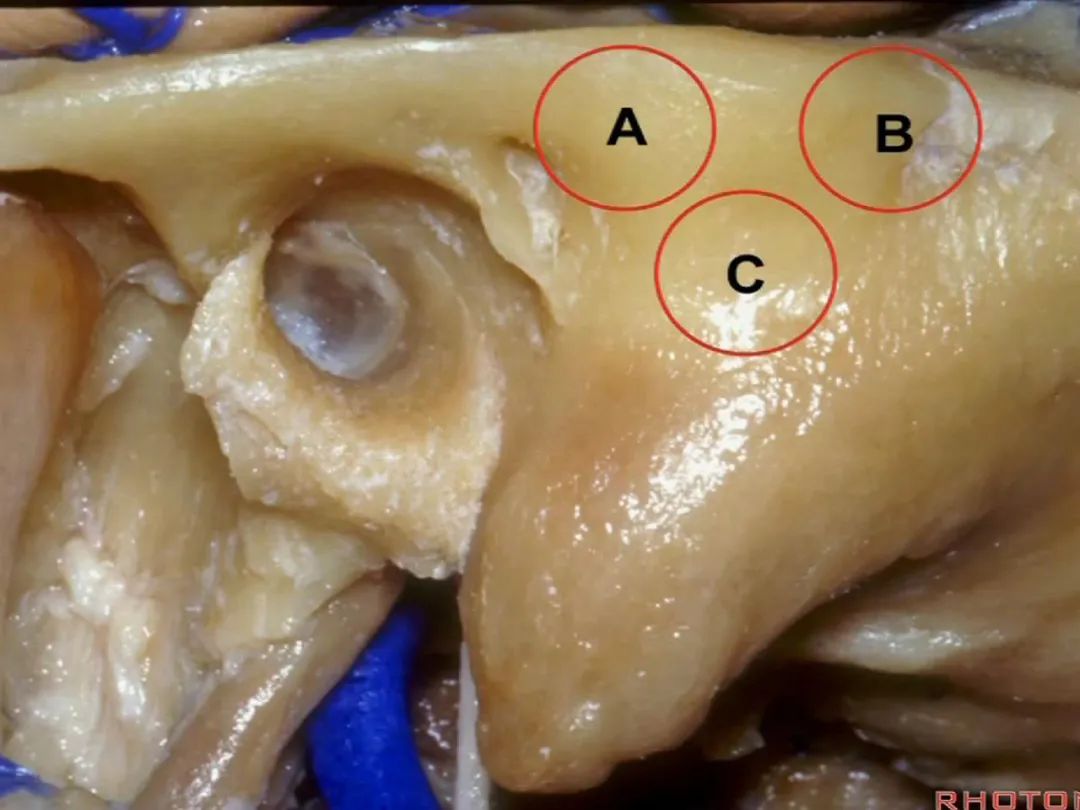
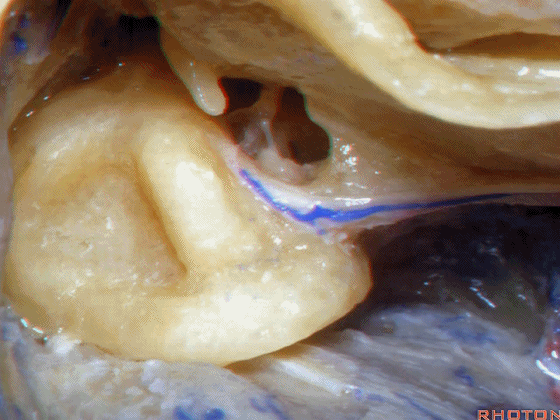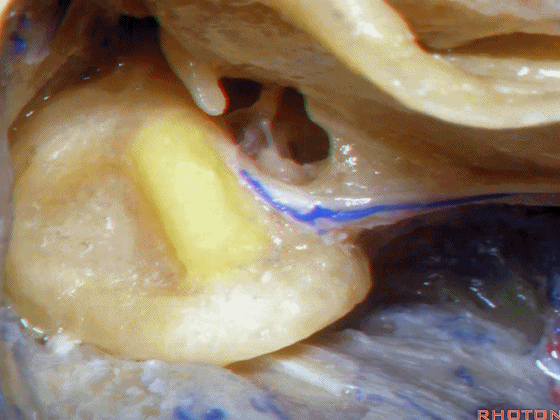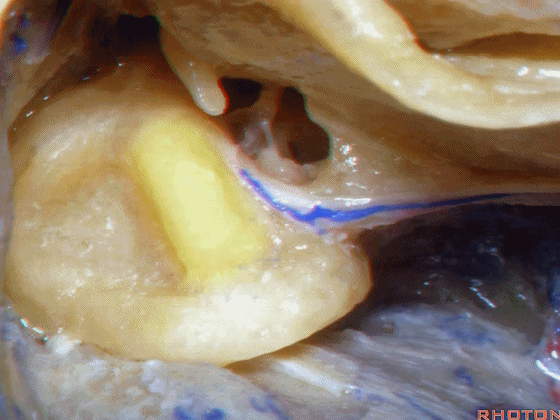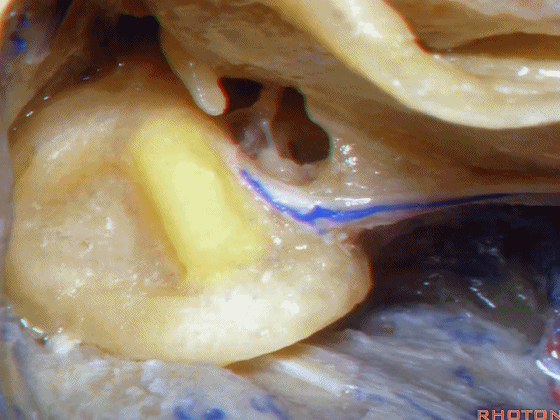
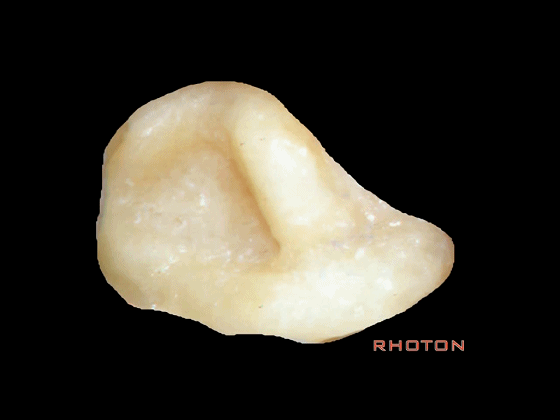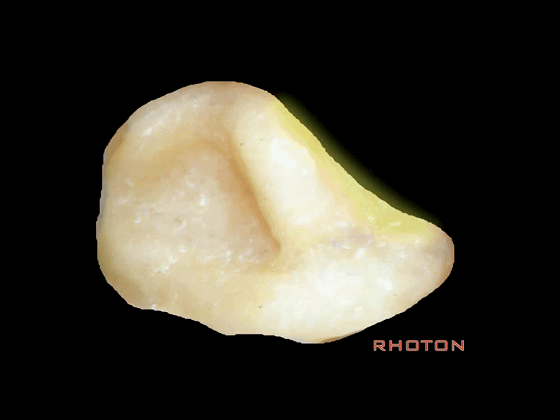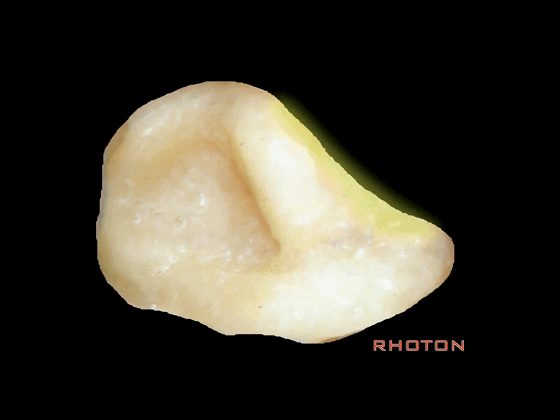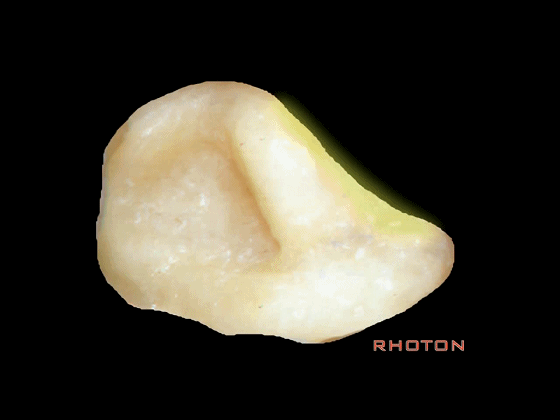
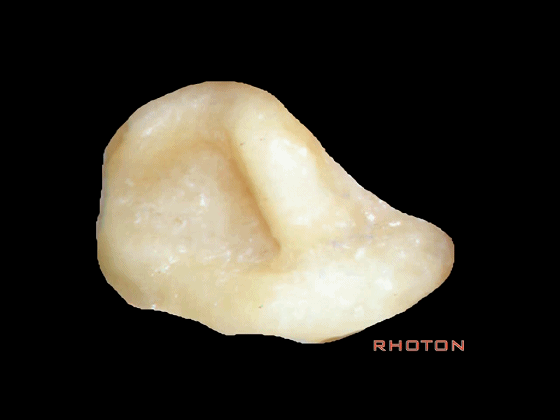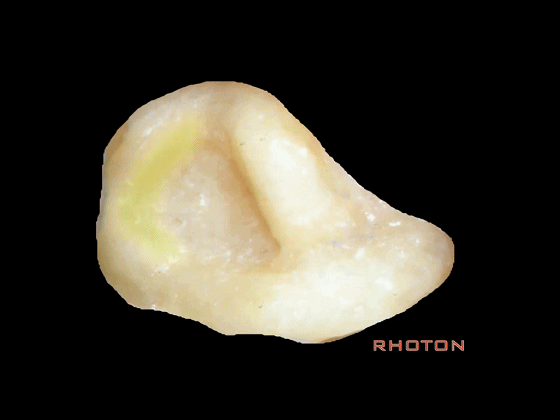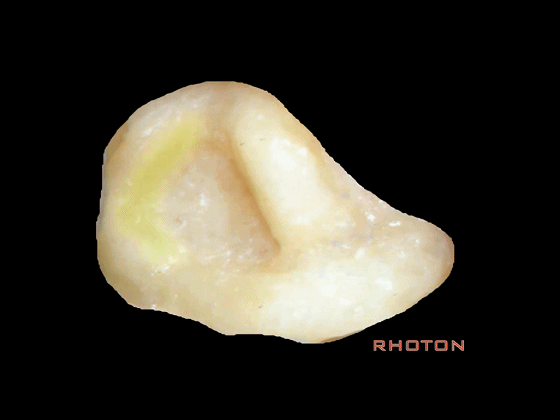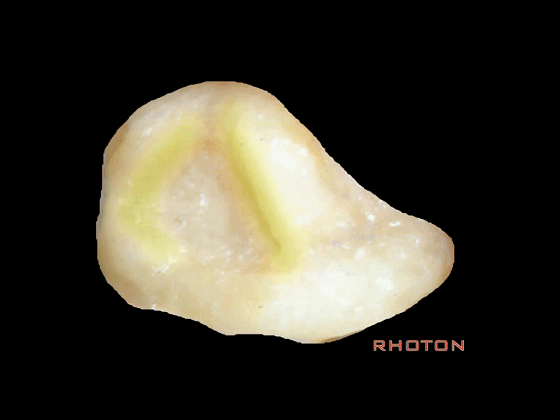
▼今天我们介绍侧方的经乳突入路。下图为左侧乳突,A线代表面神经走行,位于Henle棘的深面,下图示Henle棘(位于外耳道的后上缘)
And now, we'll review the approaches from laterally directed through the mastoid...So, everyone passes that course. Course of facial nerve? A, deep to the spine of Henle.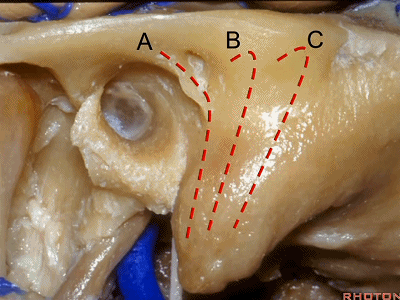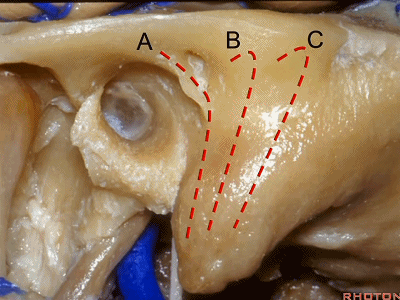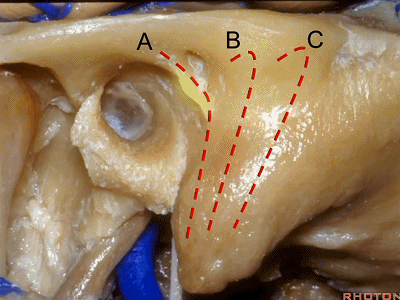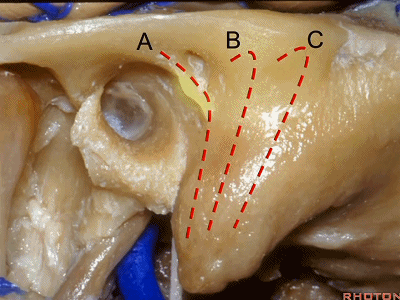
▼下图A点示鼓室窦的位置,位于迷路的浅层。
Mastoid antrum, that's lateral to the labyrinth that...at A.
▼下图为右侧乳突切开后,这里可见乙状窦(下图)
And, here we see sigmoid,
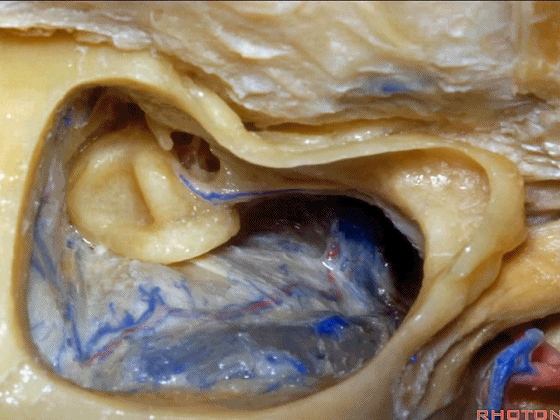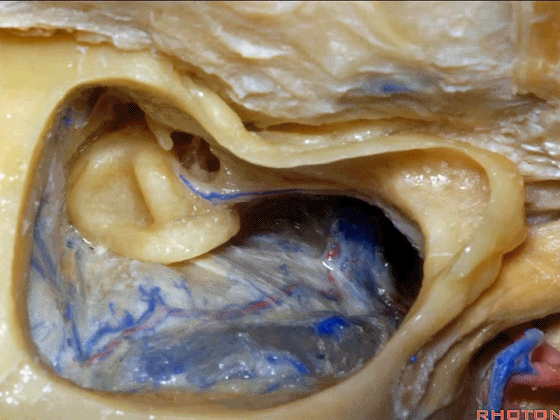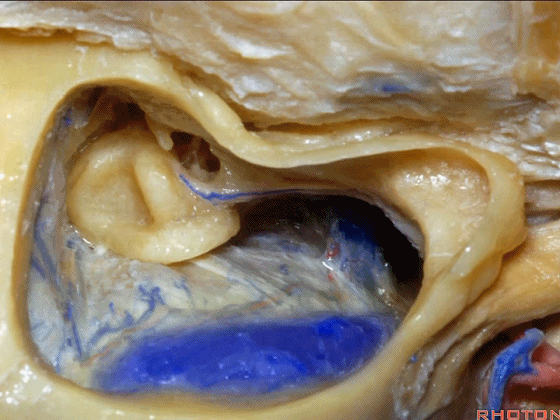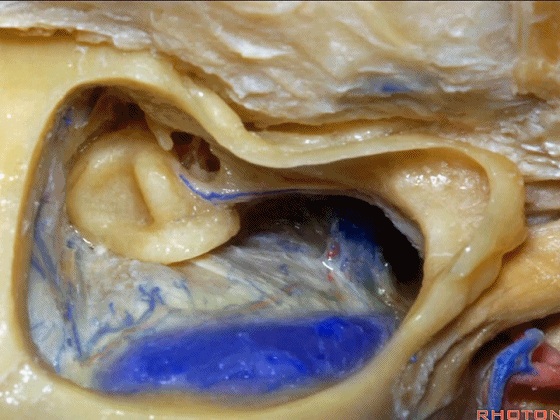
▼下图示颈静脉球,位于迷路下方。
jugular bulb, infralabyrinthine,
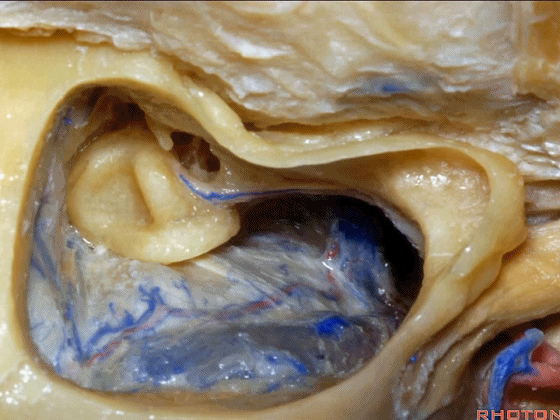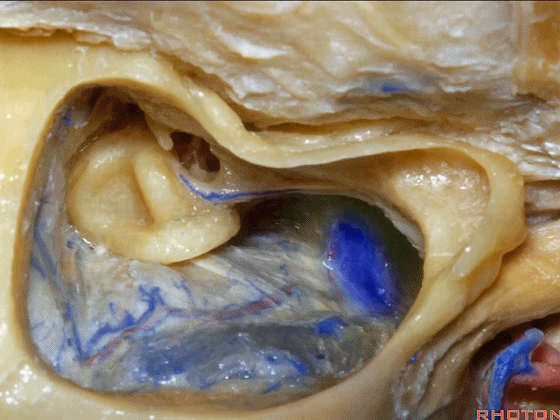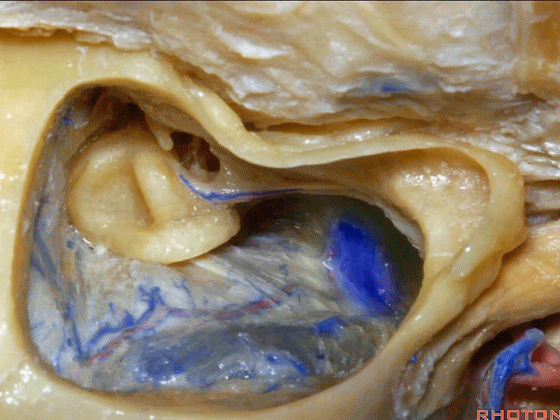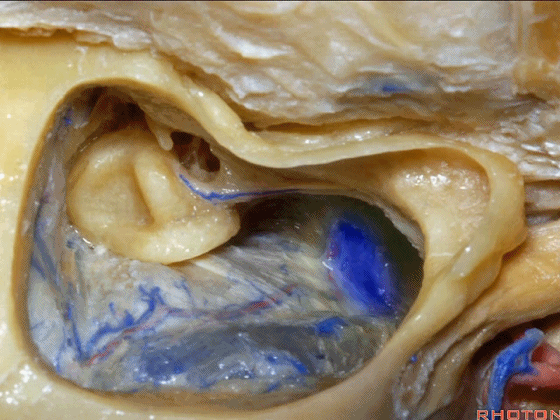
▼下图示颞底的硬膜
tegmen, middle fossa,
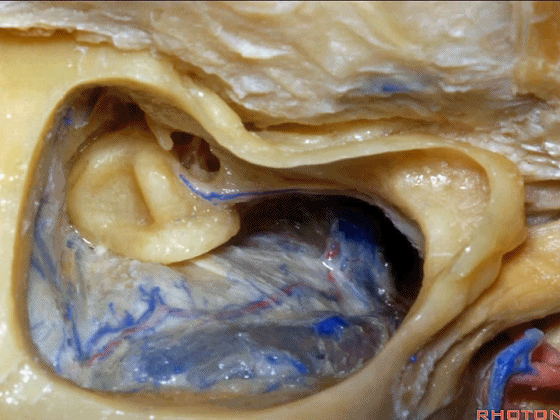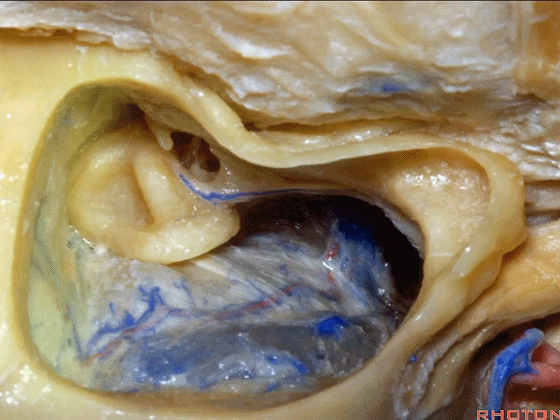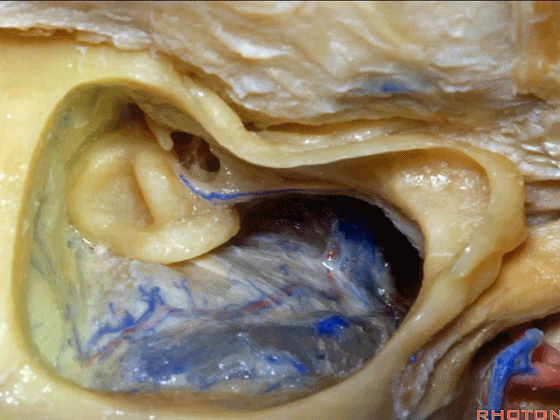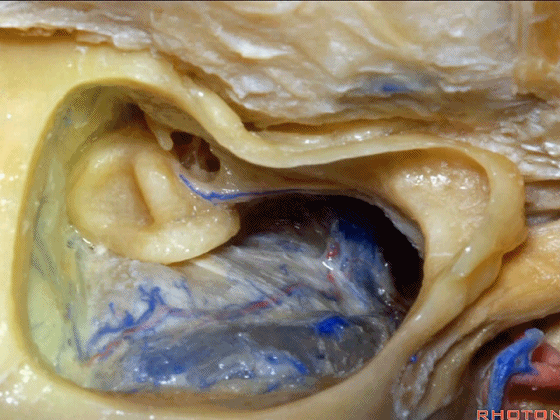
▼下图示岩上窦。
superior petrosal sinus.
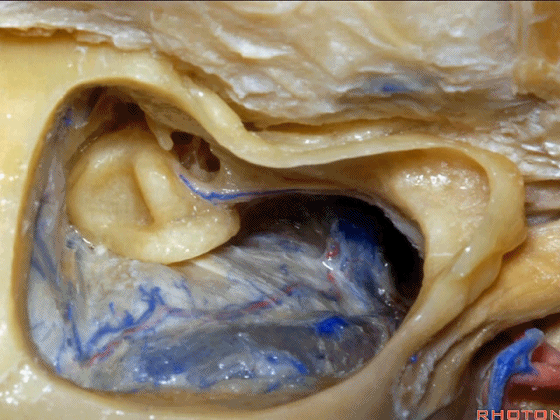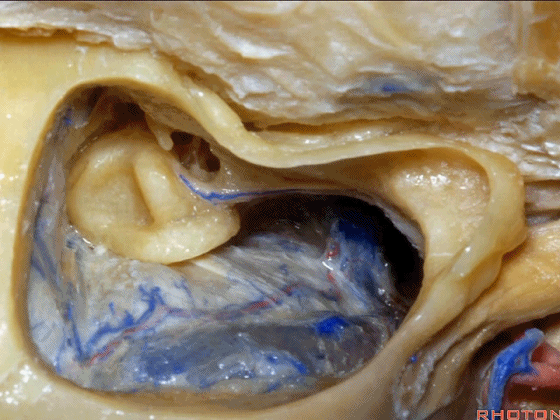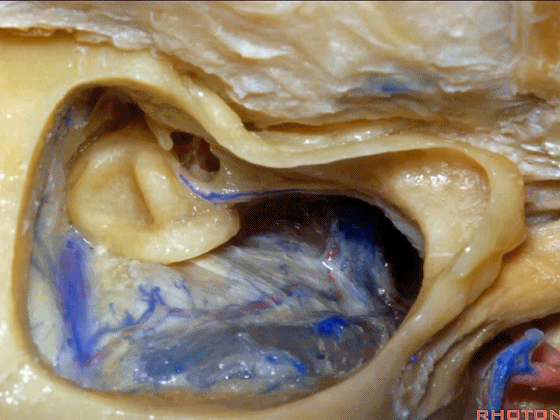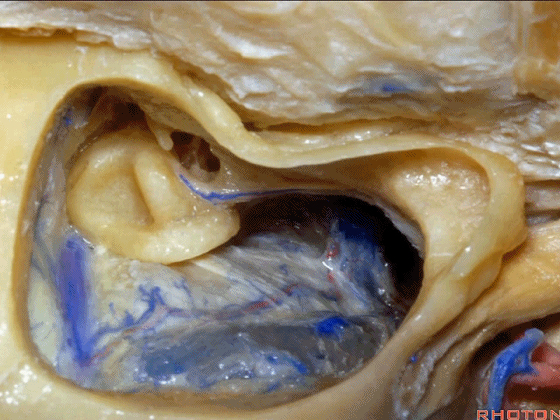
▼这个夹角是窦膜角(Citelli角,乙状窦的前缘与颞底硬膜之间的夹角)。
What do we call this angle here? Sinodural angle.
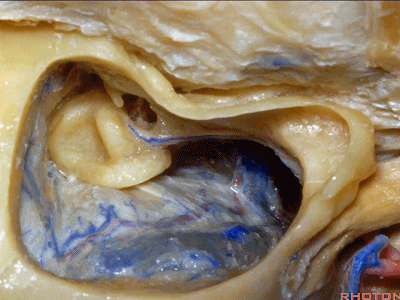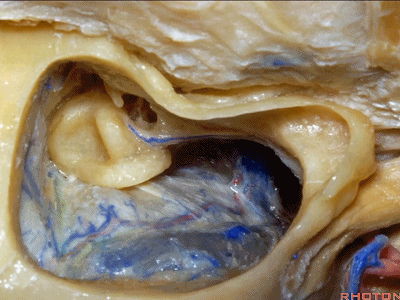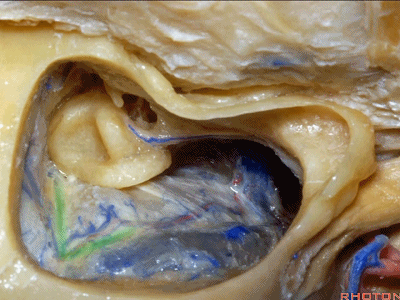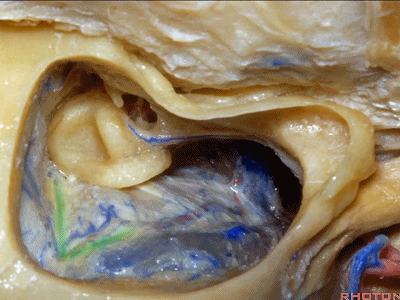
▼下图示迷路
labyrinth
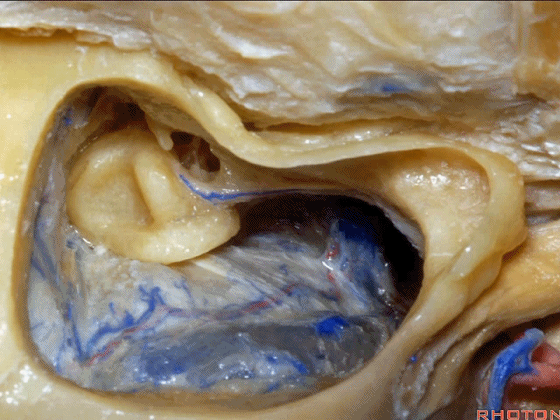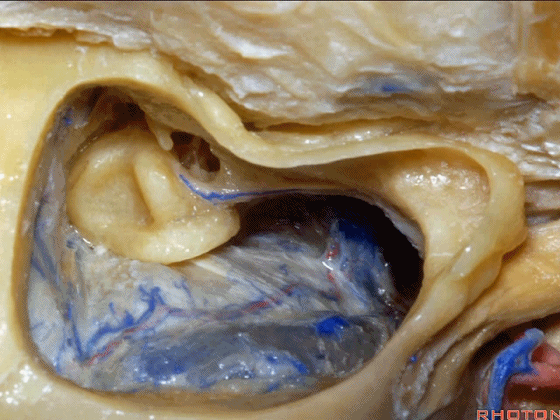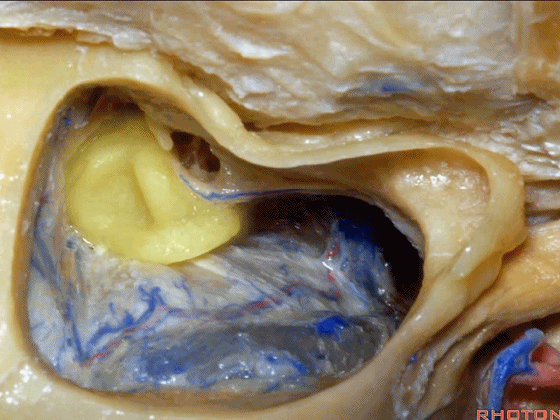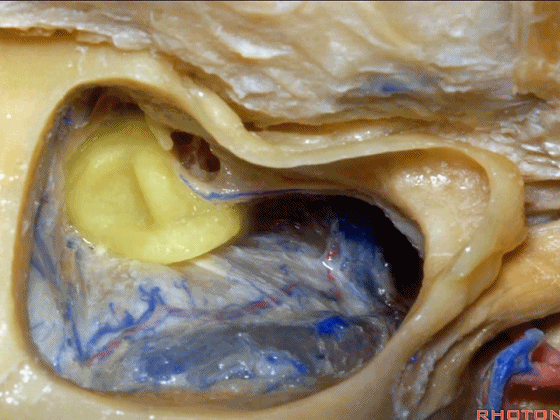
▼这是面神经隐窝
this is the facial recess
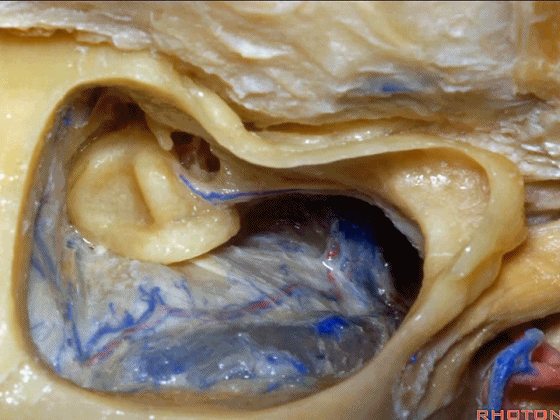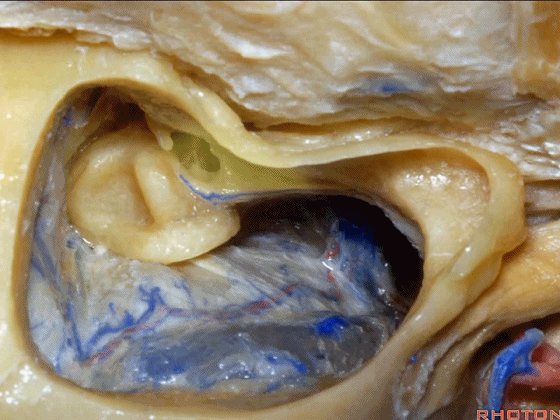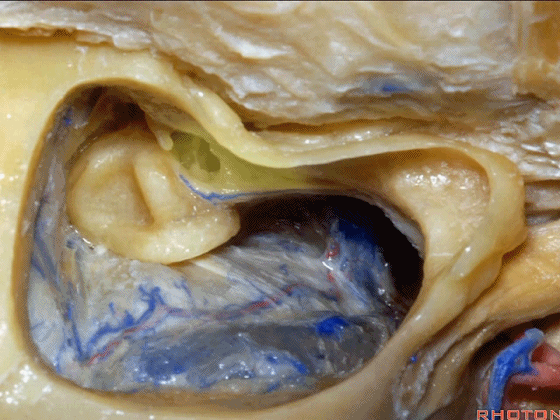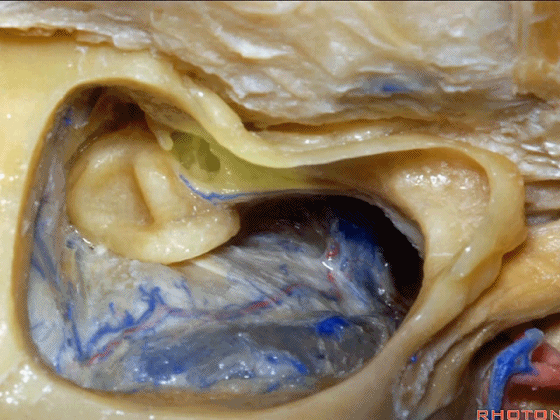
▼这上方的是砧骨窝。
and above is the fossa incudis.
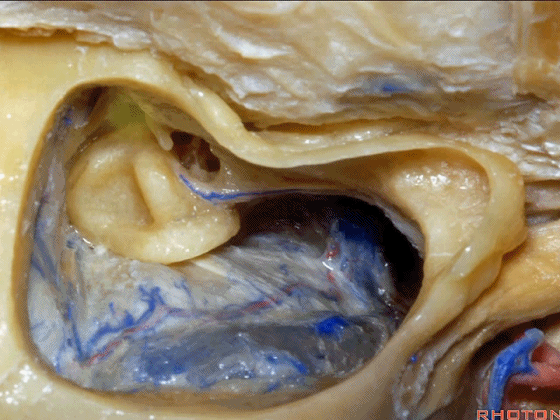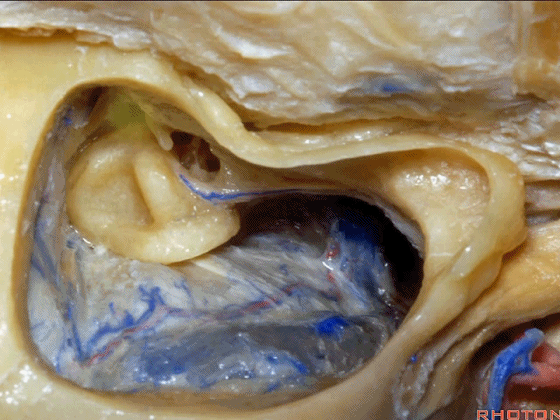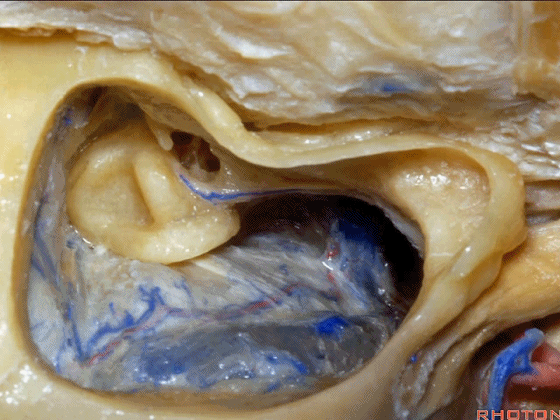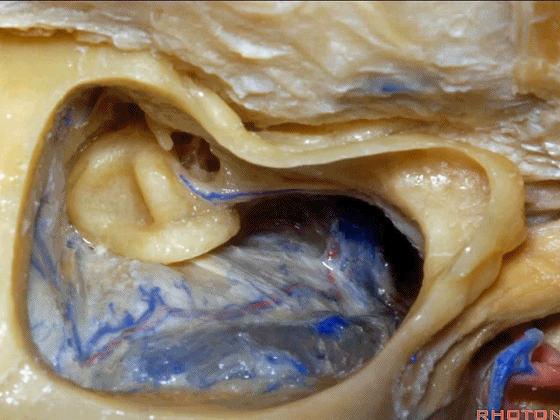
▼你总能发现砧骨的短突指向面神经鼓室段。下图示砧骨短突。
You always see the short process of the incus pointing toward the tympanic segment of the facial nerve,
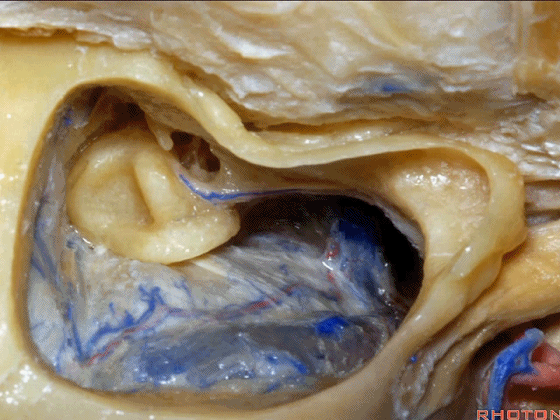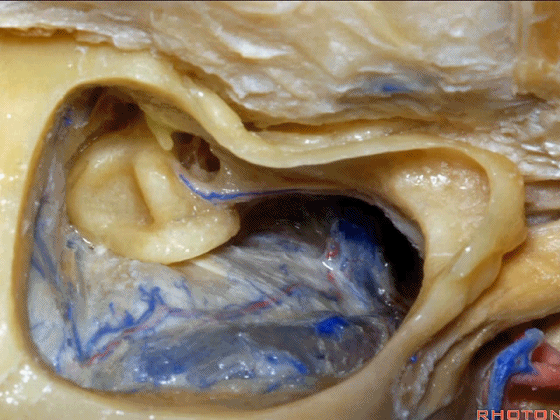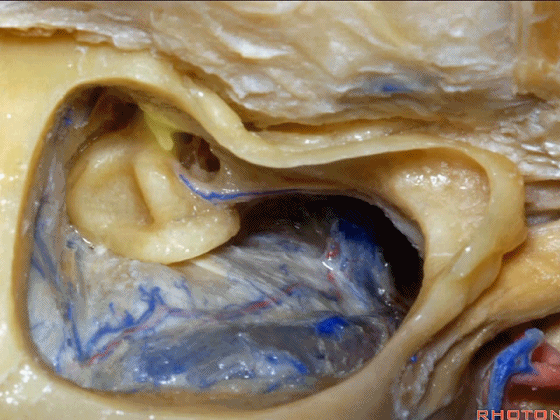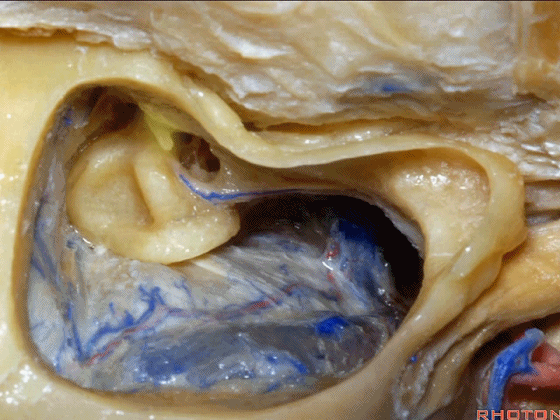
▼下图示面神经鼓室段
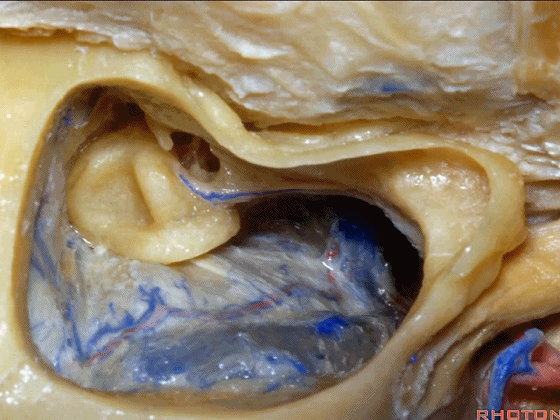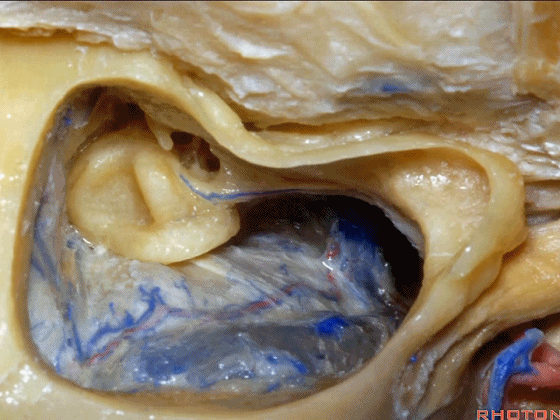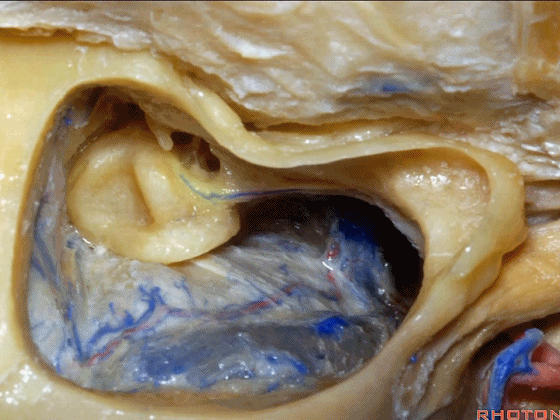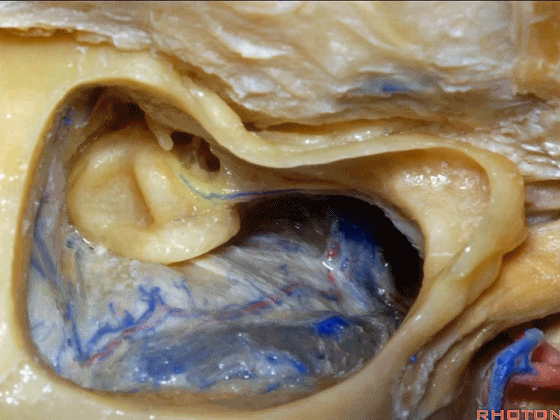
▼面神经在外侧半规管下方经过随后向下走行。
which passes below the lateral canal and then downward.
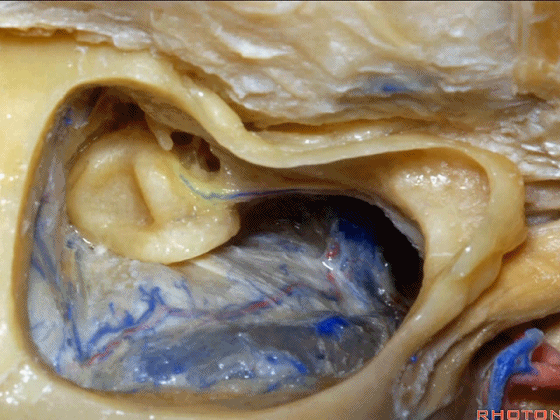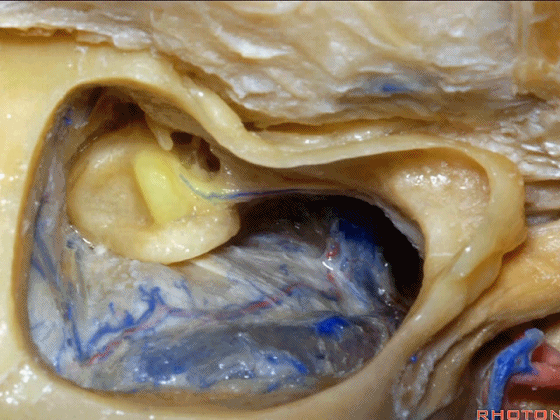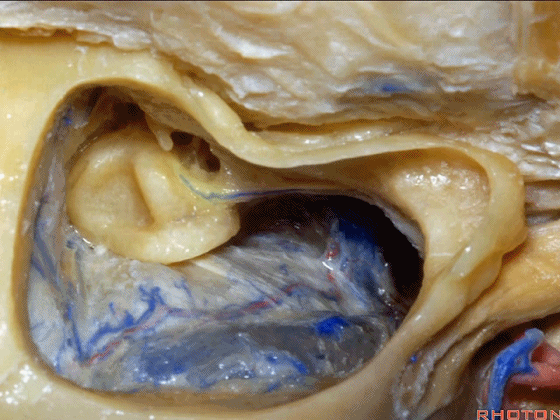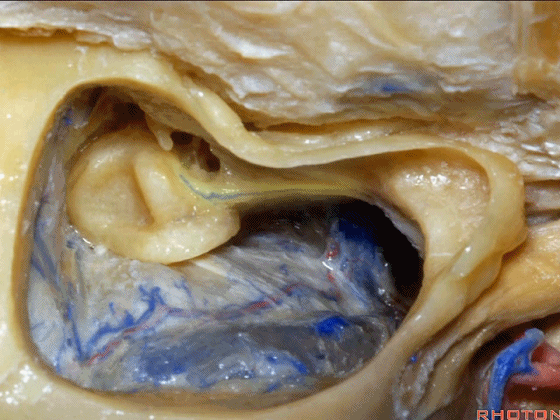
▼来看看迷路,这是上半规管。
So, the labyrinth, this is superior.
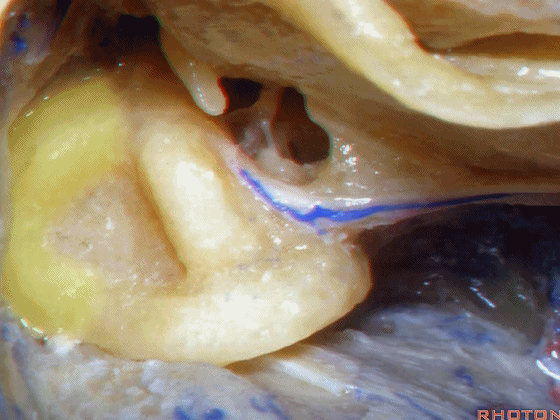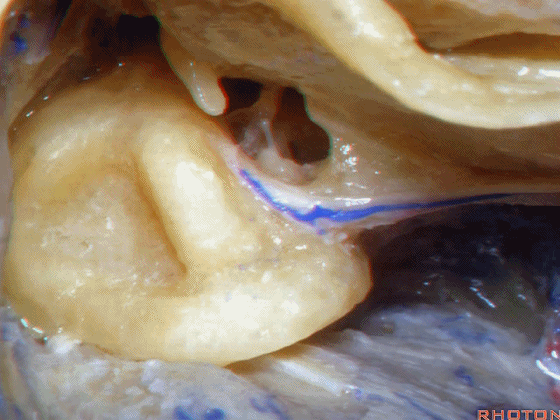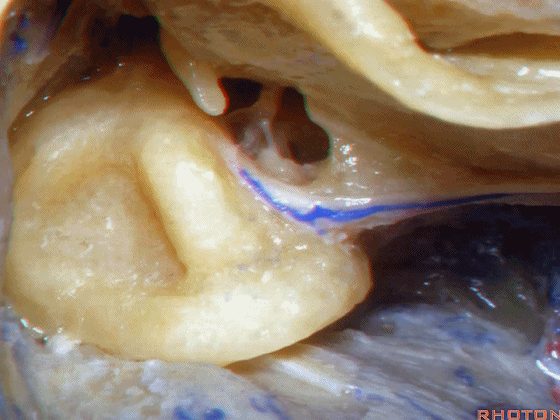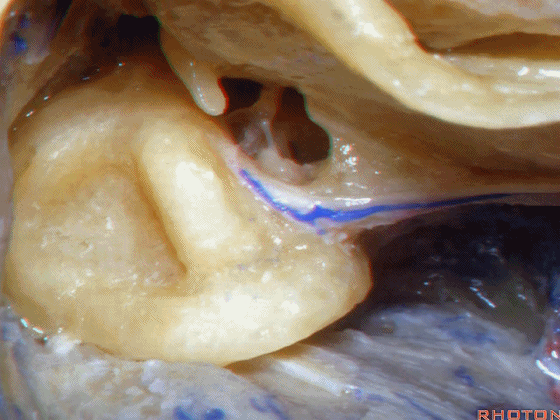
▼这是外侧半规管
▼在外侧半规管周围,有后半规管对其环绕,一半在下,一半在上。
And you see how this lateral canal, the posterior canal wraps around it, half is below, half above.

▼面神经沿外半规管下方走行。
And where is the facial nerve? Well, the answer is facial nerve along this area.
▼从侧方看,总骨脚在c点。位于上半规管的后端和后半规管的上端交汇处。
Where is the common crus when you look at it lateral? c,at the back end of the superior, up end of the posterior.
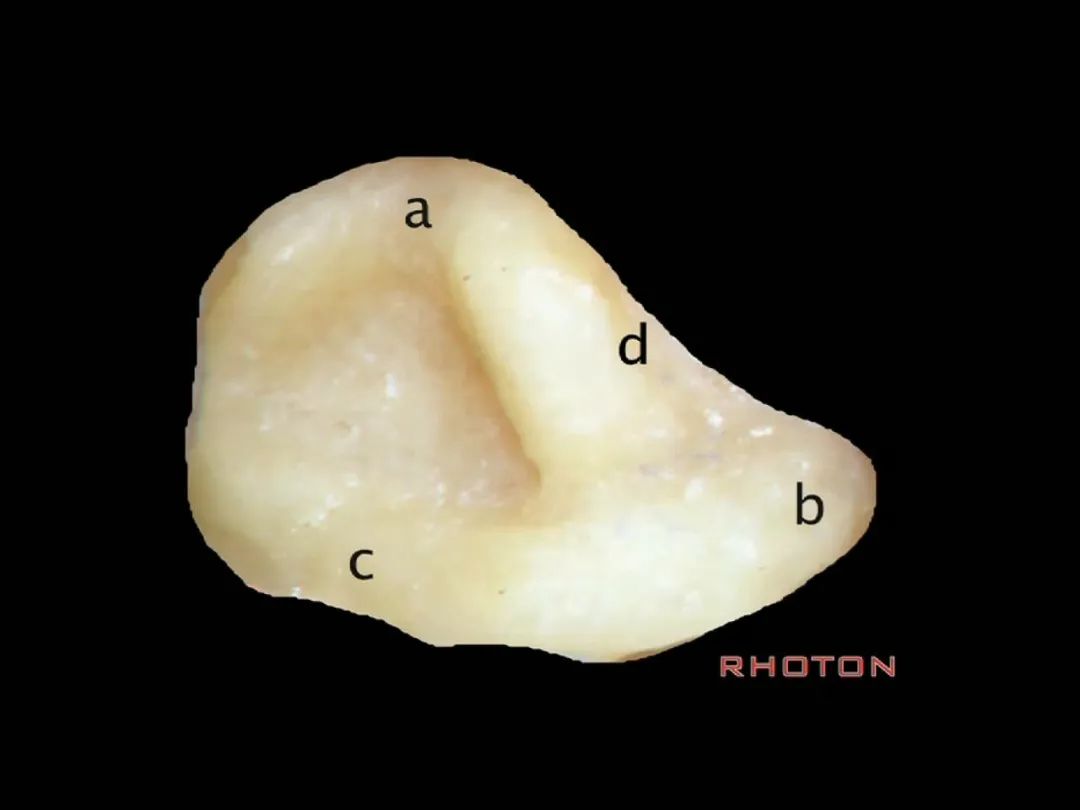
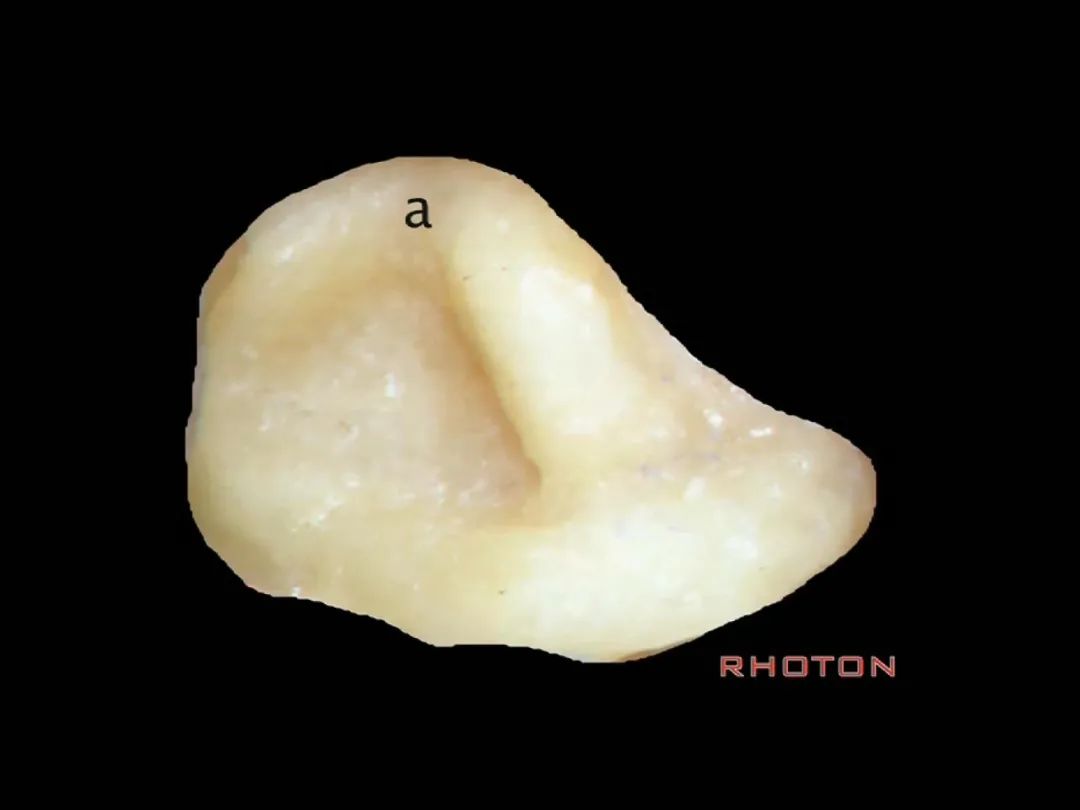
▼前庭上区,为上半规管和外侧半规管的前端所在,位于a点。
Superior vestibular area,at the anterior end of the superior and lateral canal, at a.
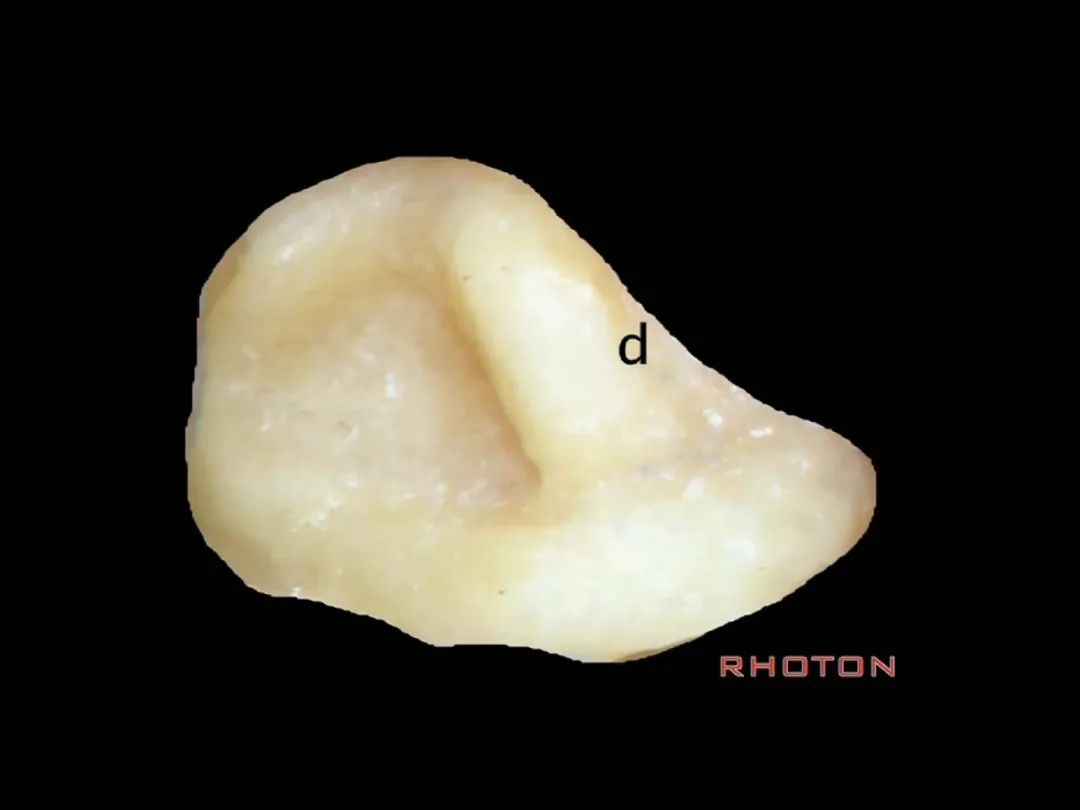
▼乳突切开术中易损伤面神经的部位,在d处。
Drill damage to facial nerve, at d.
▼在上半规管内上方操作时也能碰到面神经,膝状神经节也可能出现在该区域。因此我们通常先从上半规管的上方、外侧半规管的上方进行磨除(下图)。
You can also get it if you drill on the medial to the up side of the superior canal. You can beg the geniculate ganglion in that area. So we always drill lower side of superior canal, up side of lateral canal, first.
▼接下来再看一下听小骨。这是镫骨肌,其肌腱附着于镫骨。
just a view of the ossicles. This is...what is that?Well, that's stapedius muscle, the tendon attaches to the stapes.
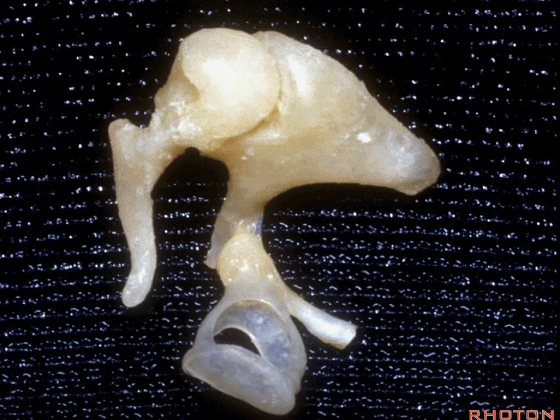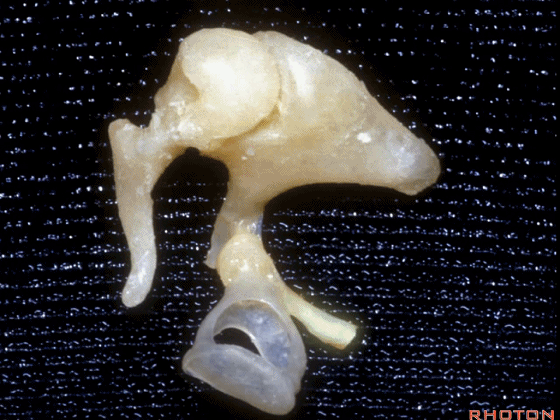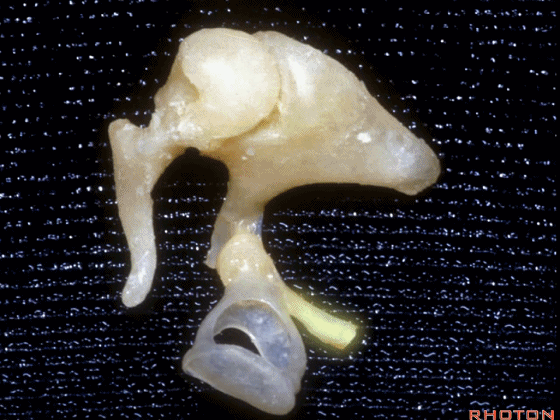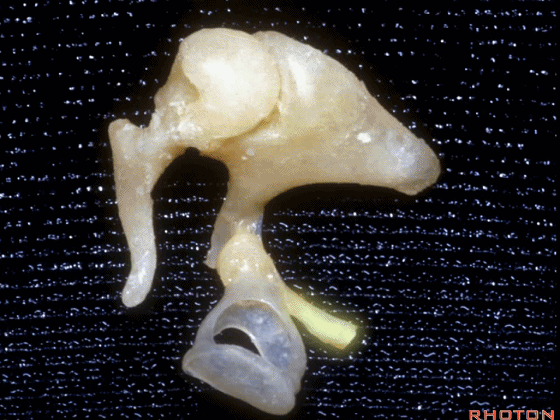
▼这是镫骨
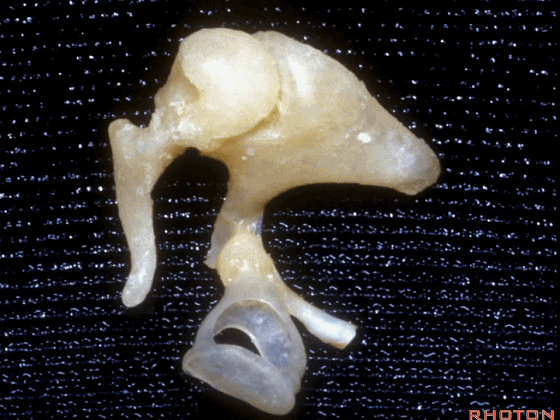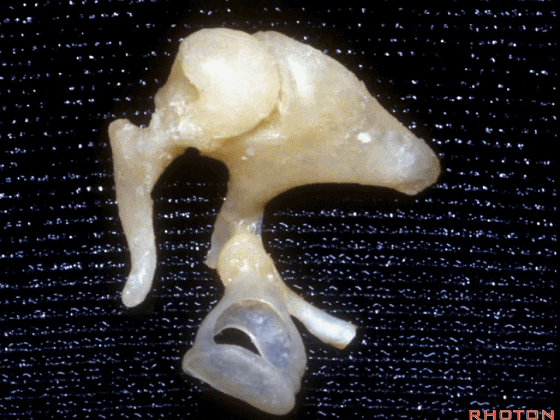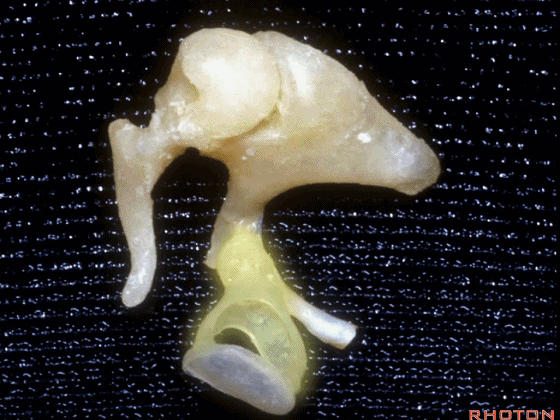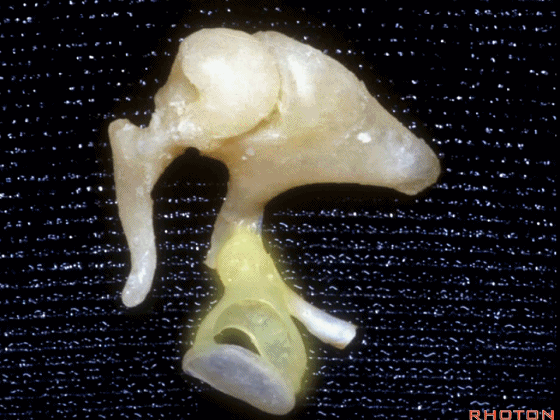
▼这里是 右侧前庭的内面观。我们将镫骨从卵圆窗内取出。
Now you're...you're sitting inside the vestibule.We pull the stapes out of the oval window.
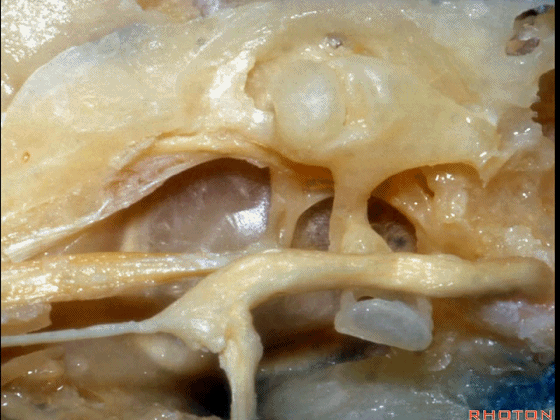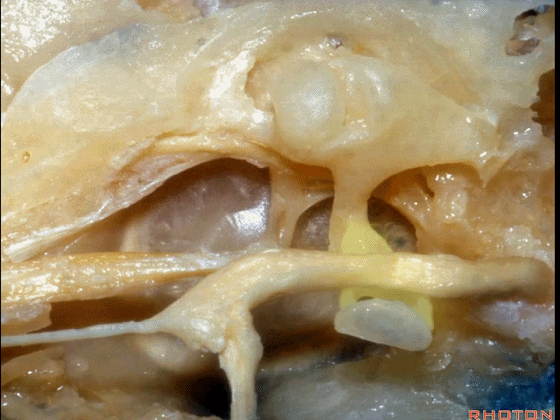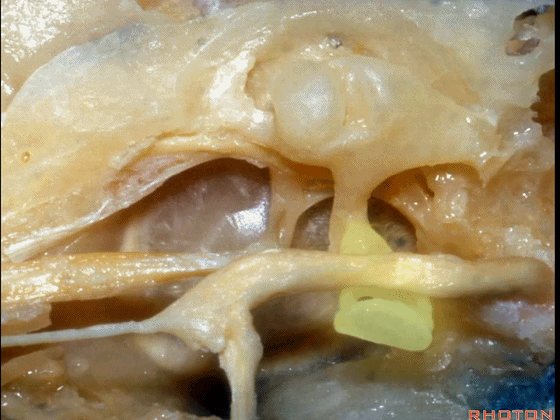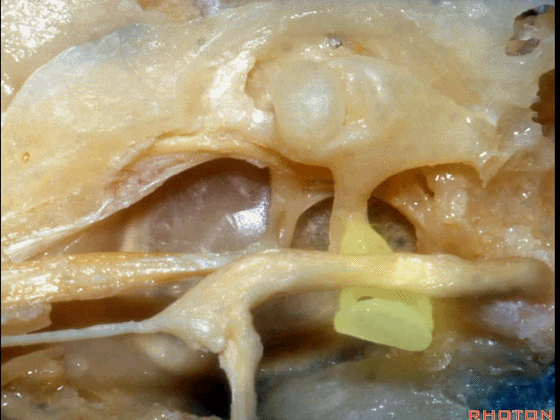
▼下图示鼓膜的内侧面。
You're looking out of the inside of the tympenic membrane.
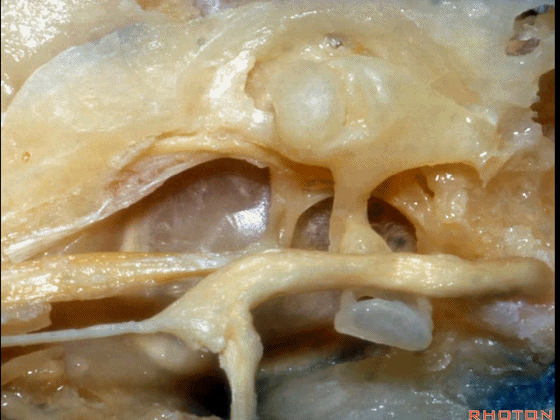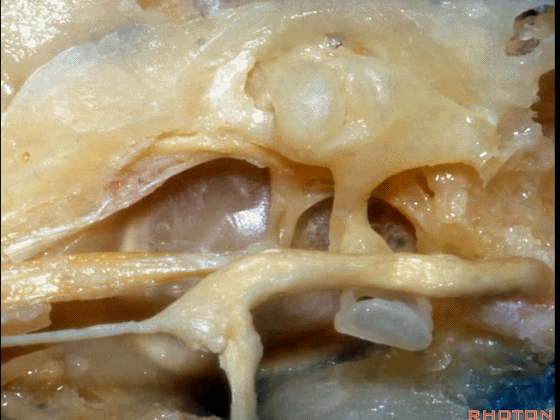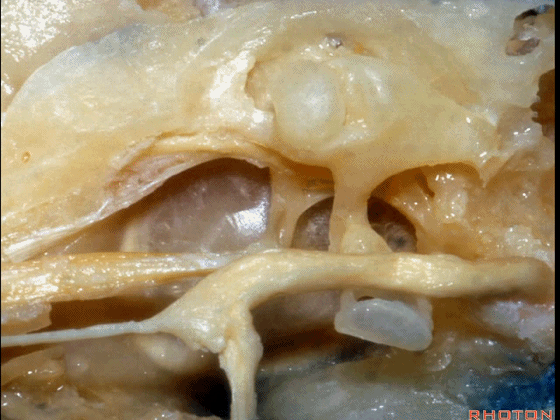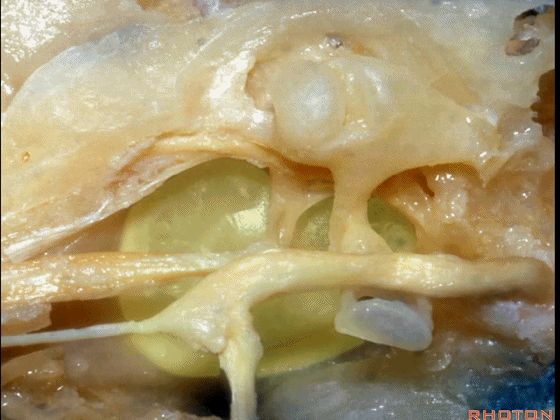
▼越过鼓膜内面走行的是鼓索。
And then crossing the inner surface of the tympenic membrane...chorda tympani.
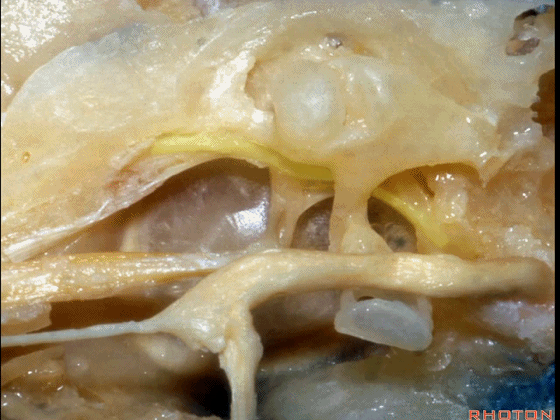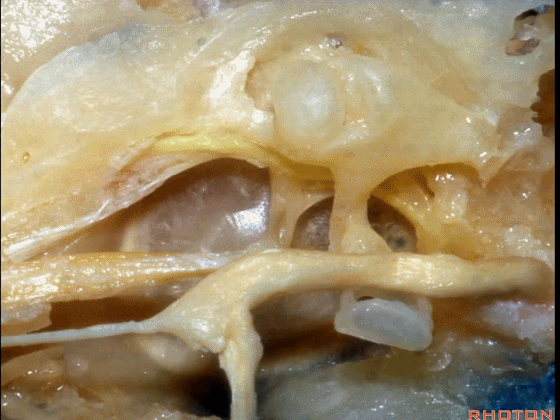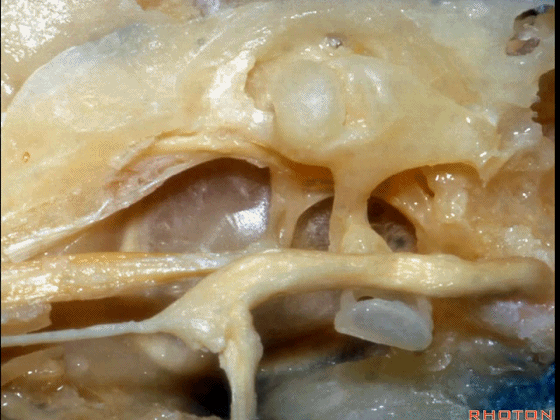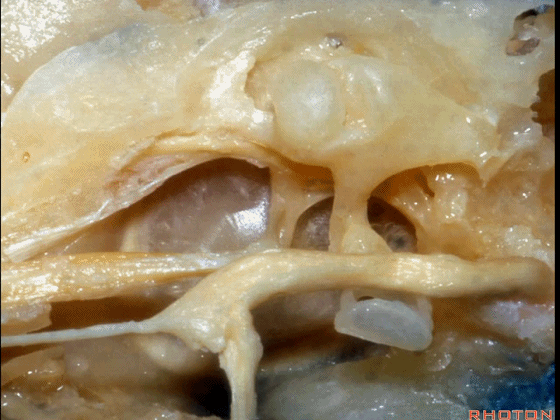
▼这是面神经
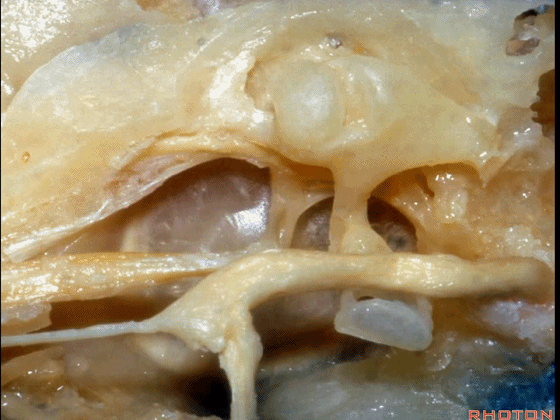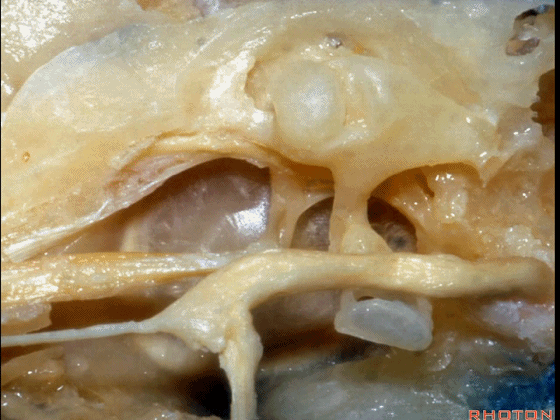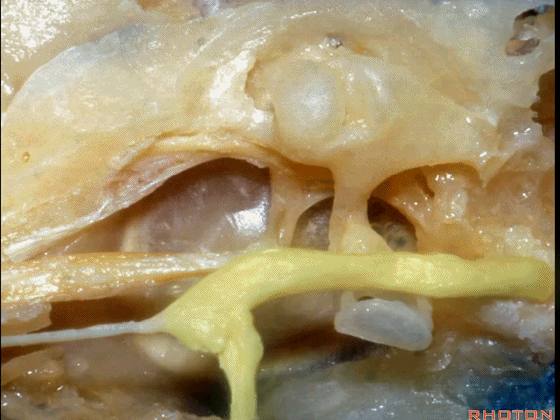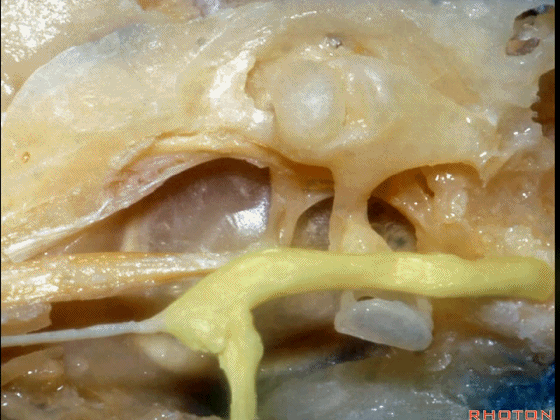
▼下图示面神经迷路段、膝状神经节、鼓室段、乳突段。
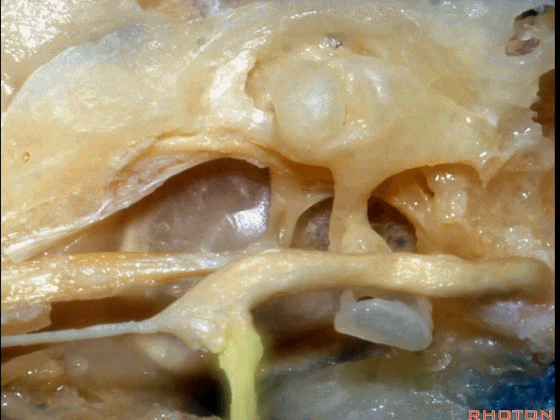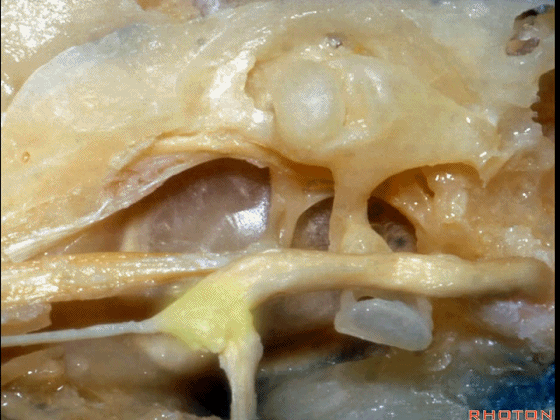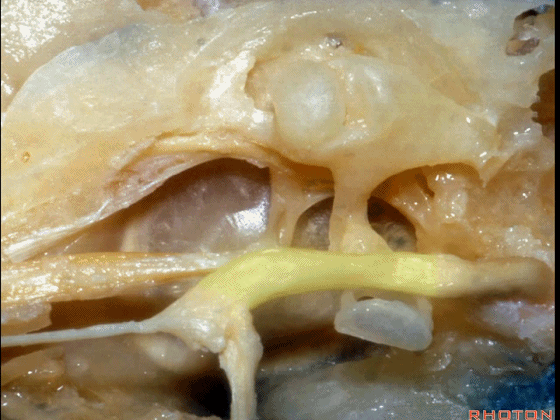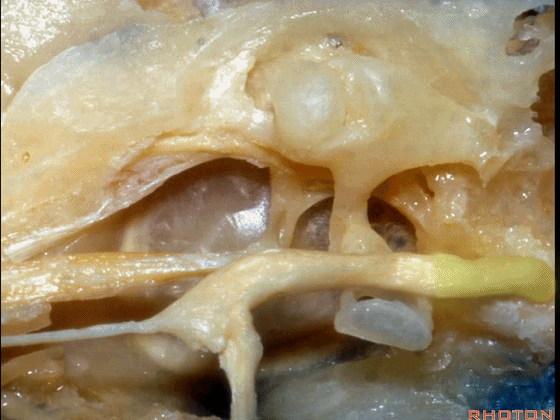
▼这是 鼓膜张肌
What is this? Tensor tympani,
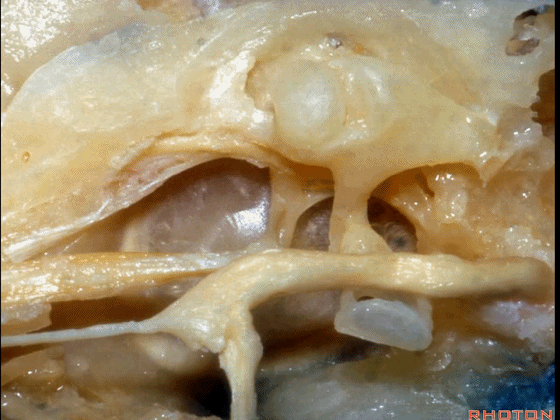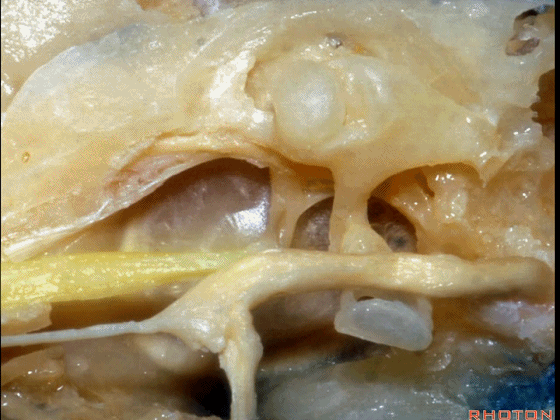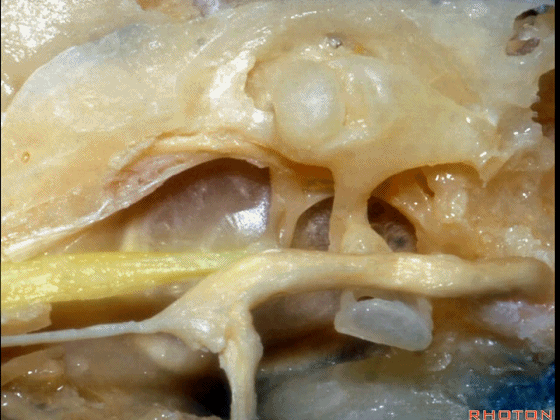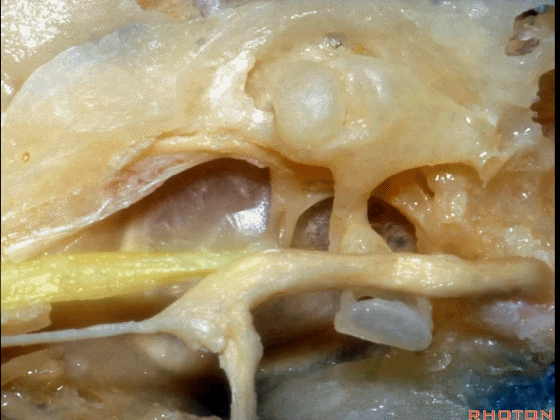
▼鼓膜张肌附着于锤骨(下图)。
it attaches to the malleus.
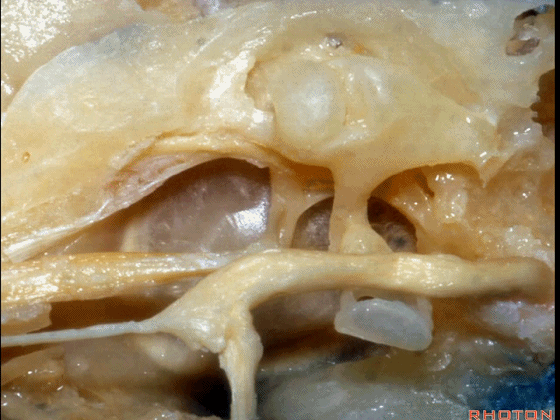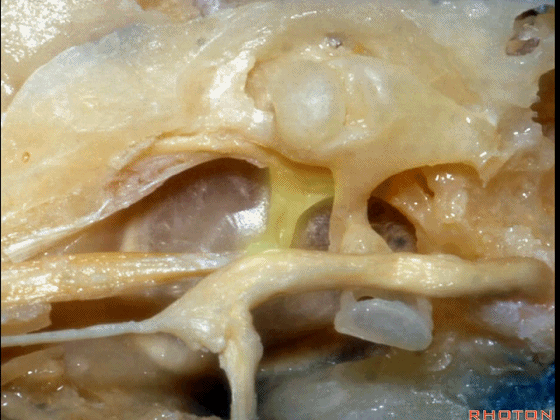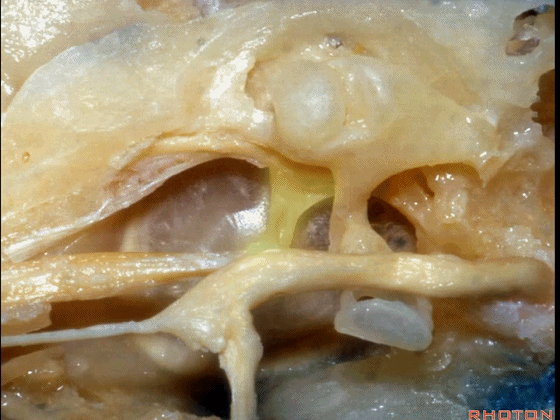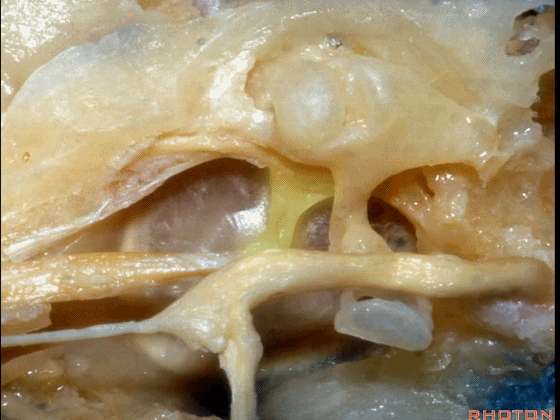
▼下图为左侧乳突,镫骨
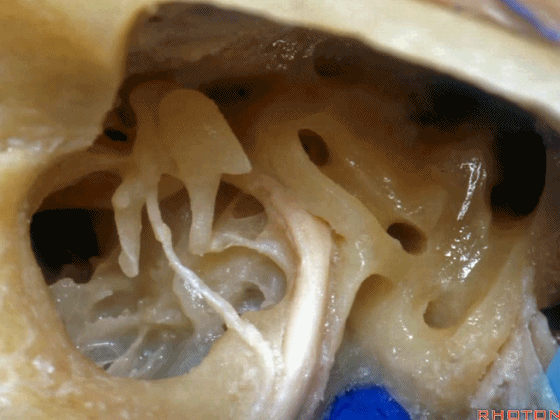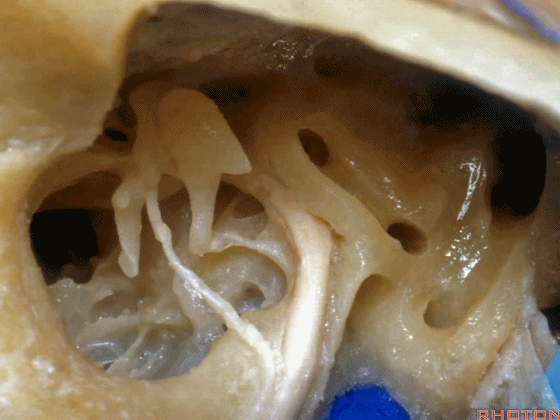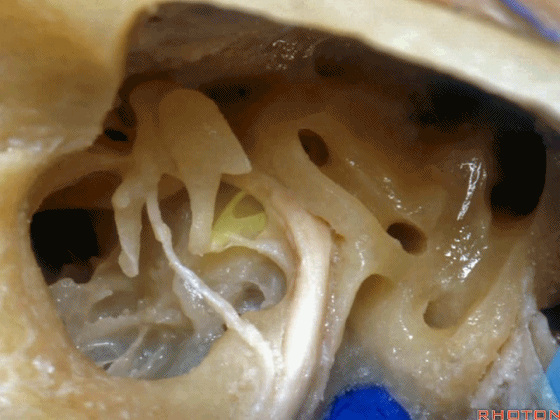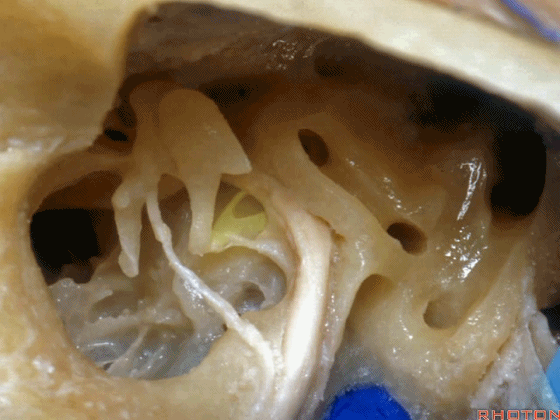
▼镫骨肌(下图)附着于镫骨颈。
Stapedial muscle attach to the neck of the stapes.
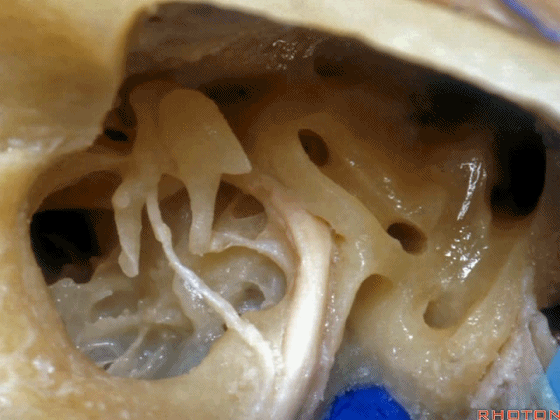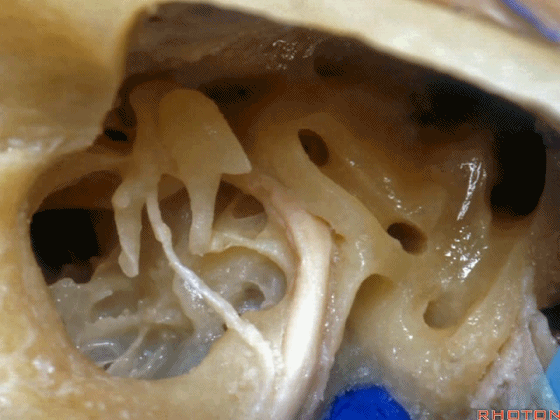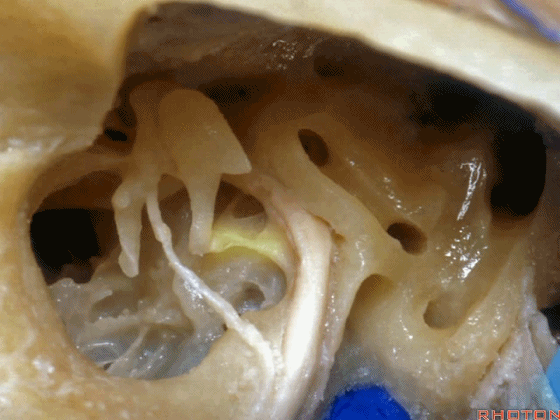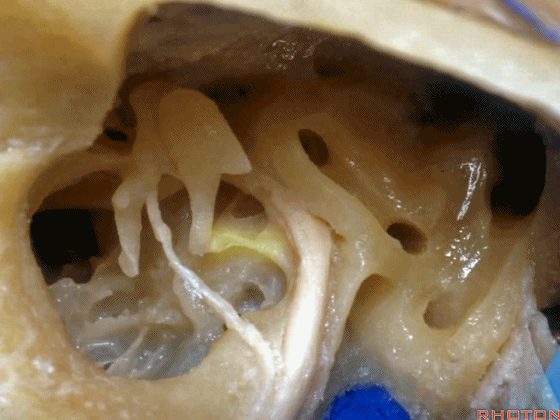
▼这是面神经隐窝
And this is what recess?facial,
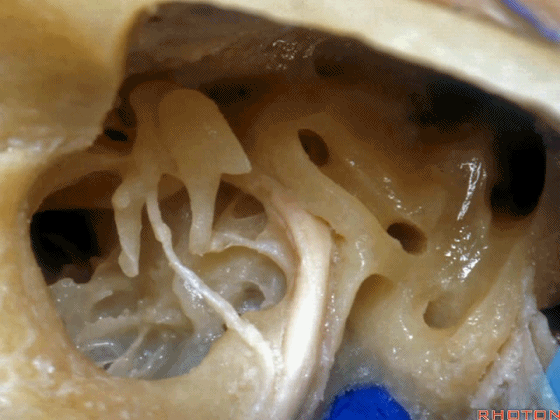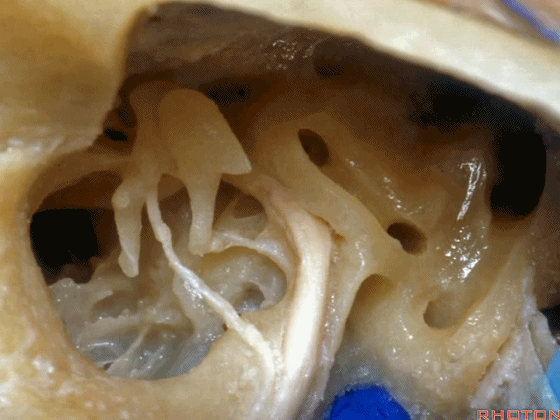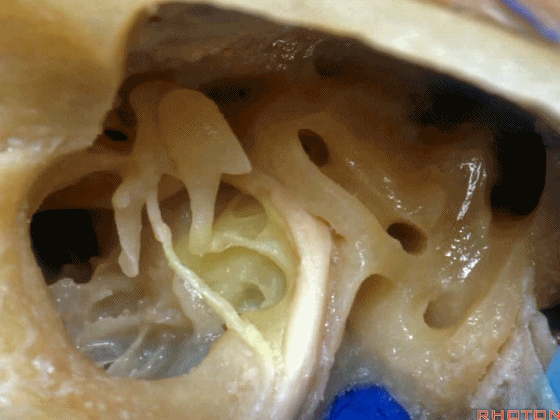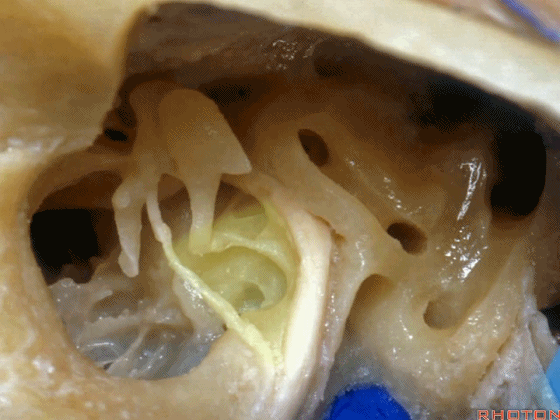
▼这是砧骨窝
and this is fossa incudis
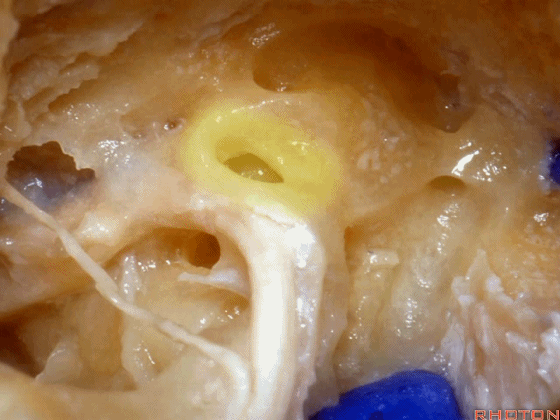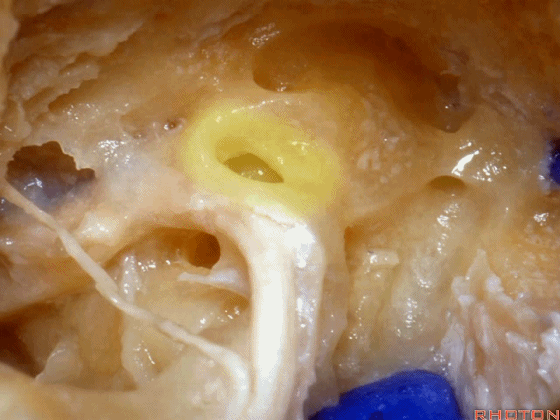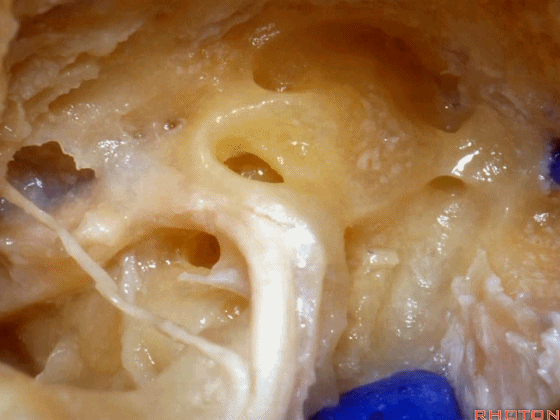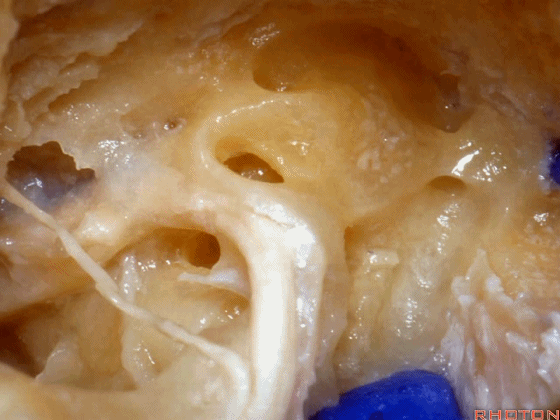
▼下图示卵圆窗
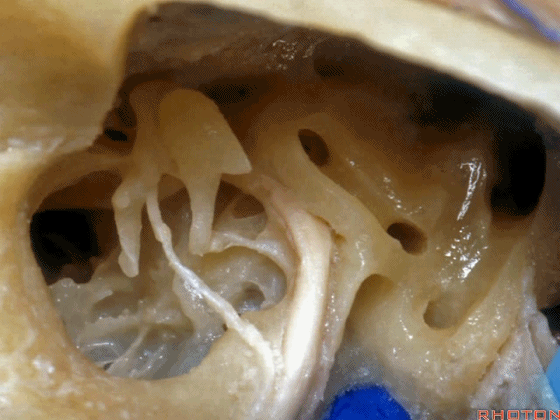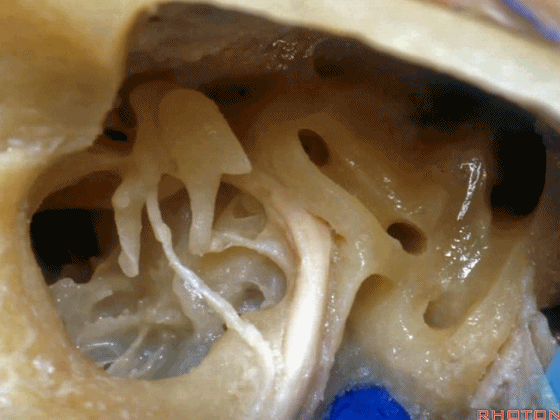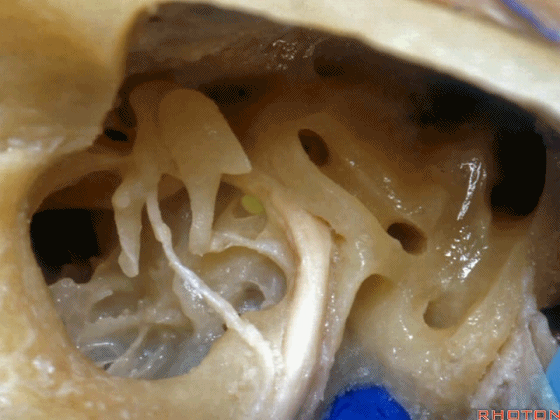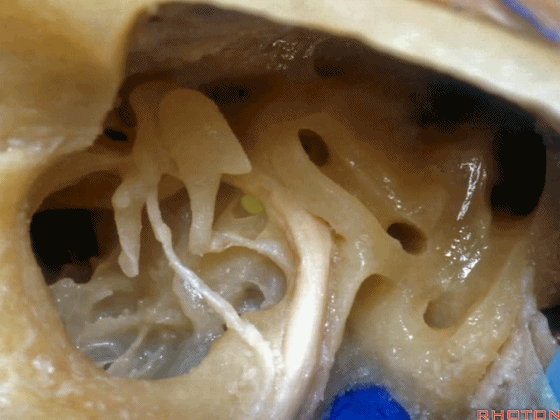
▼下图示耳蜗植入的位置。透过面神经隐窝,可暴露圆窗,并置入线路,这里就是耳蜗植入的位置。
Here's where you...it's where the cochlear implant. You work through the facial recess, you look through it, you see the round window and stick a little, wire up in there for a cochlear implant.
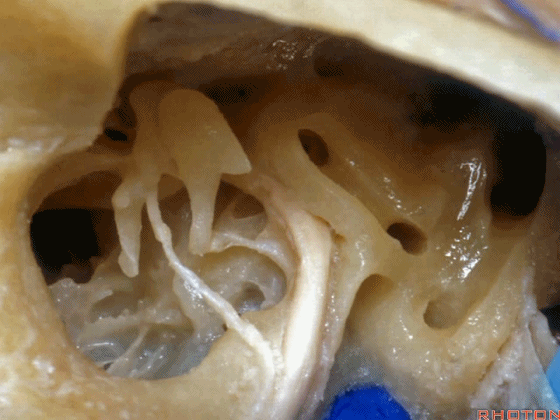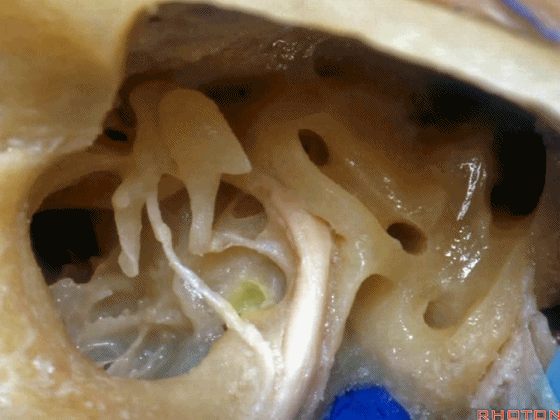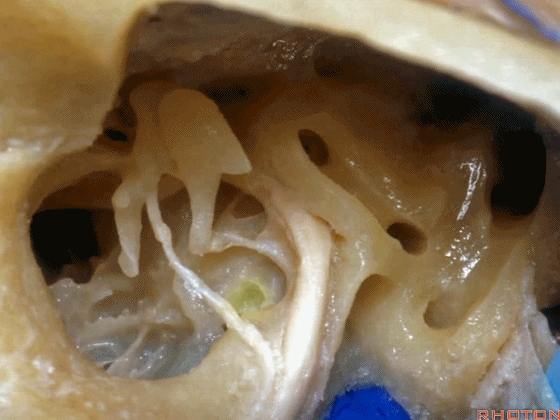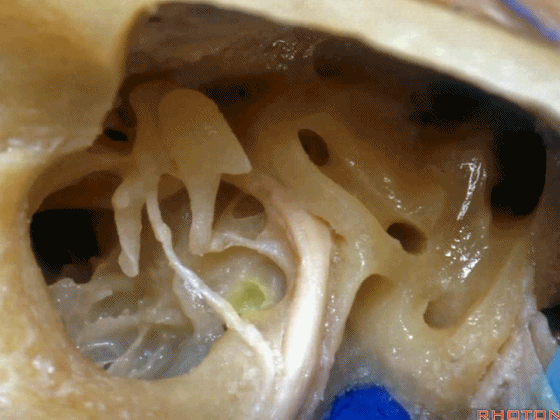
▼这是内淋巴囊
and this is the endolymphatic sac
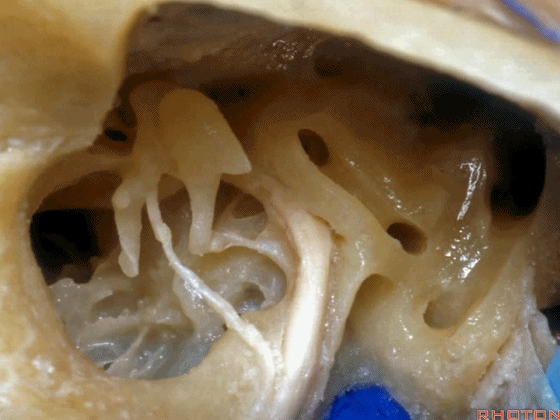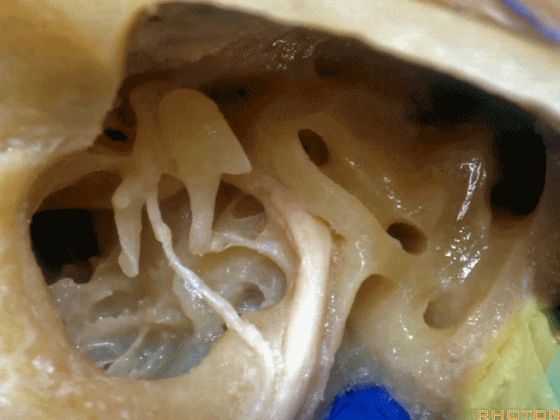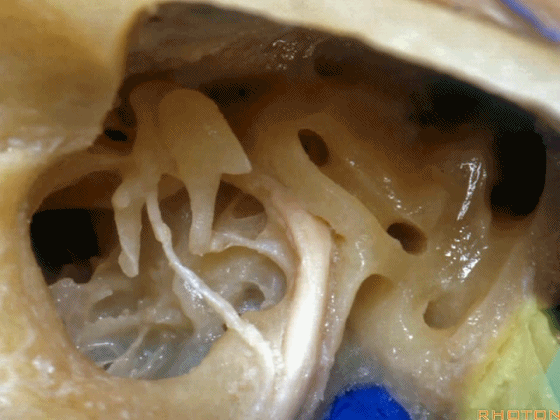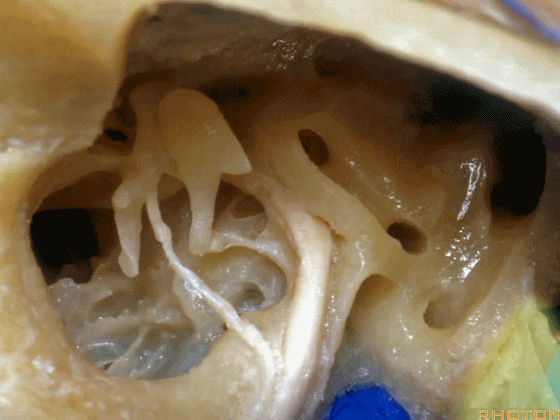

▼这是经乳突入路的暴露(左侧)
So, here is just...an approach through the mastoid then
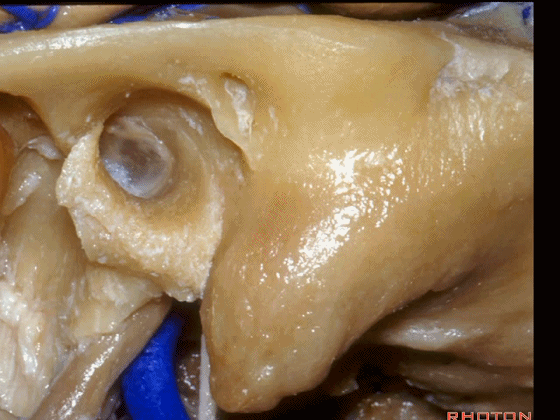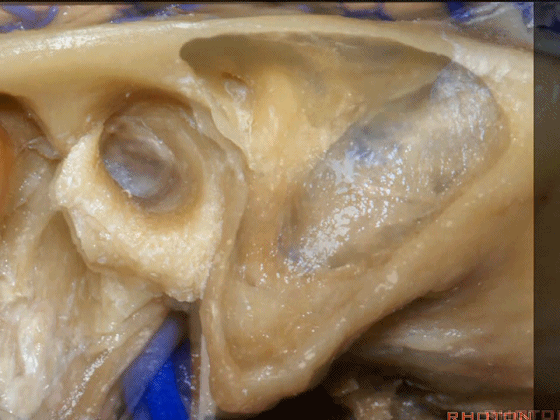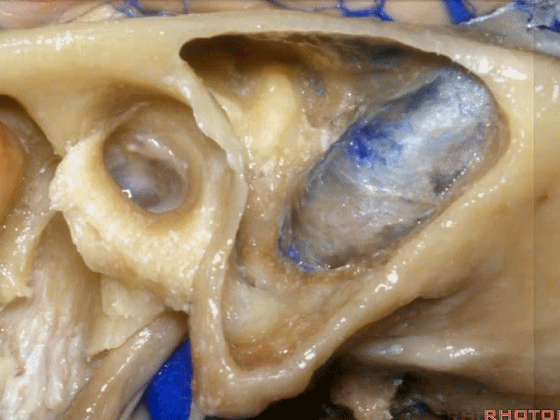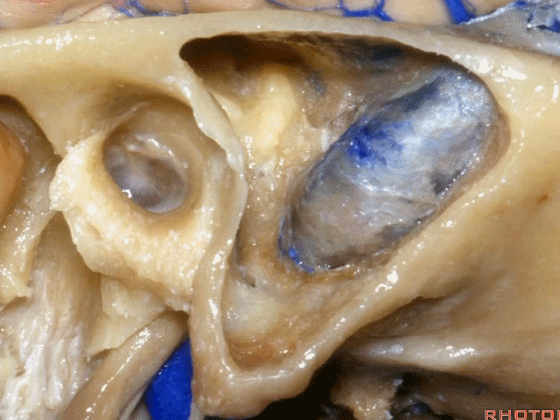
▼下图示 乙状窦、窦膜角、中颅窝底。
and,sigmoid, sinodural angle,middle fossa plate.sinodural angle,
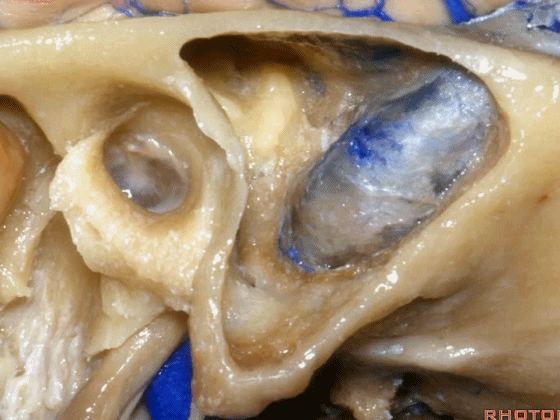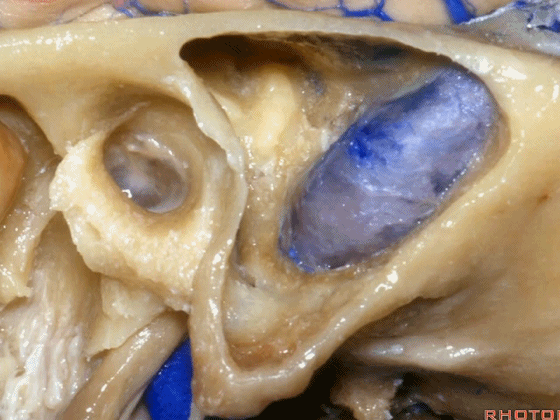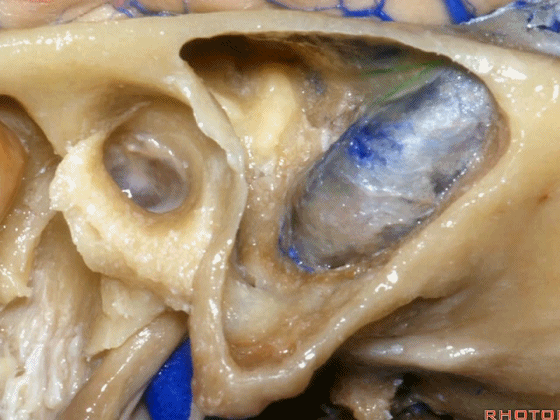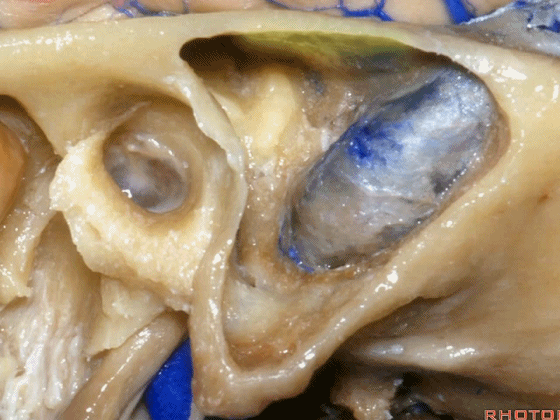
▼这是后半规管,其包绕外侧半规管的后部。
What canal? Posterior wrapping around the back part of the lateral canal.
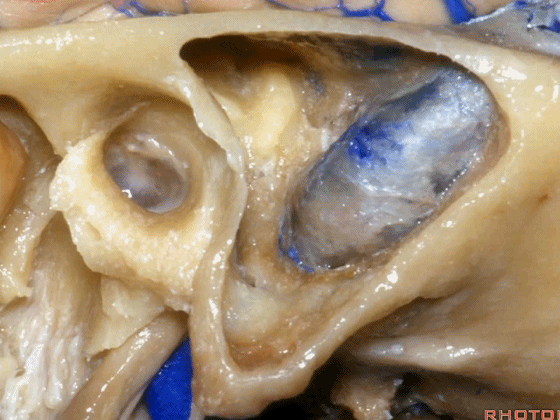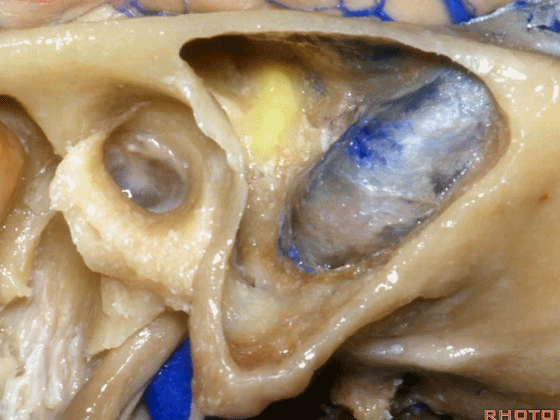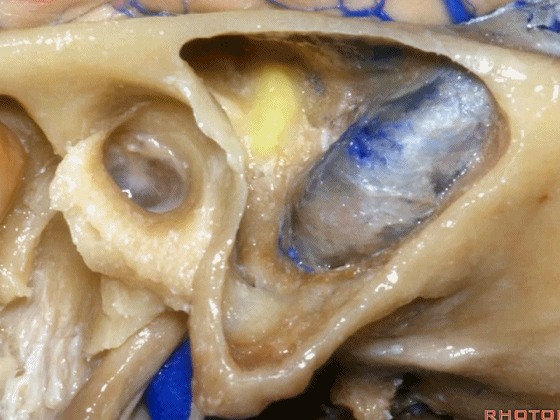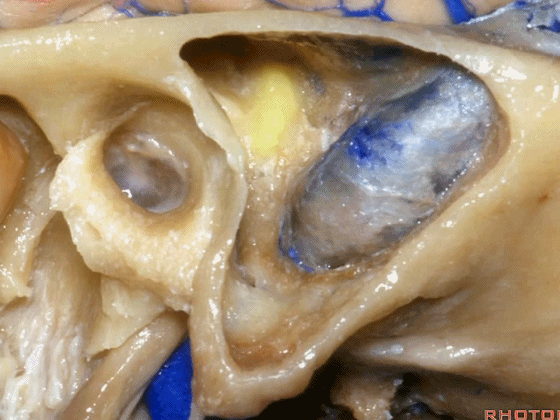
▼这是Henle棘
This is the spine of Henle.
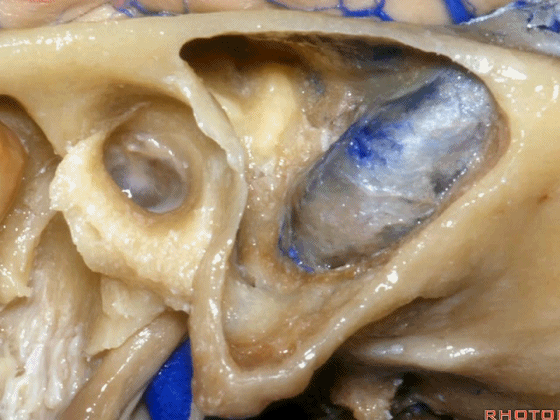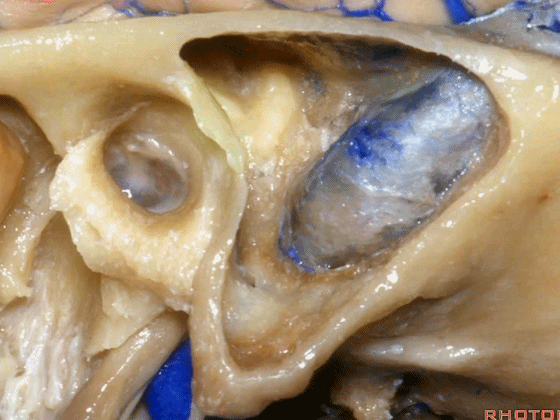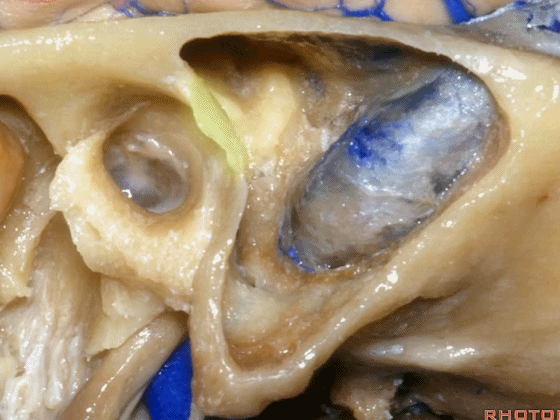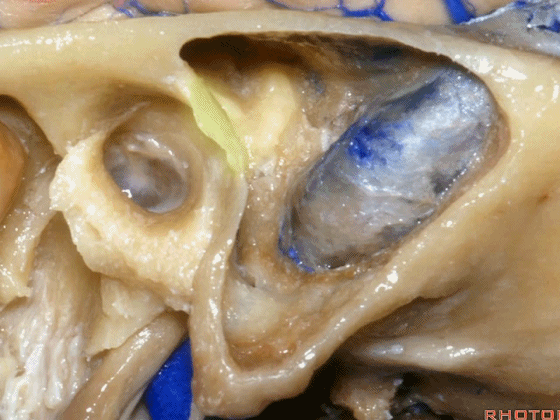
▼这是鼓室
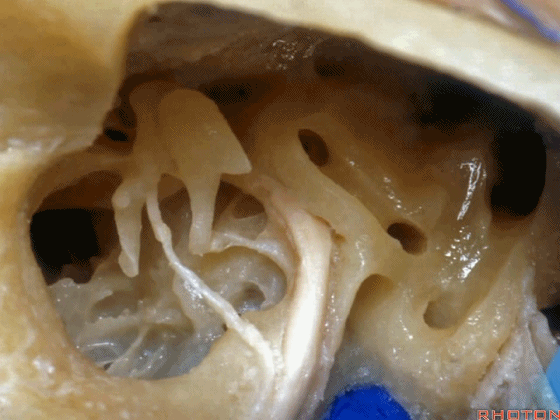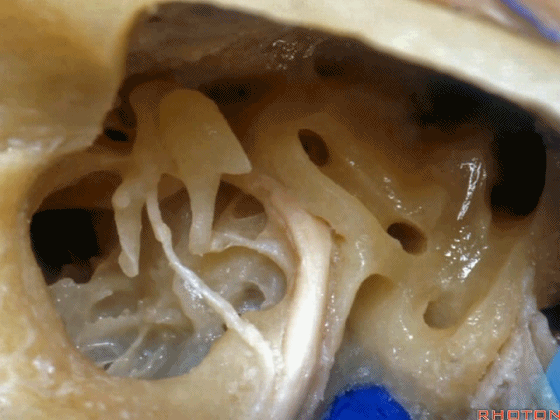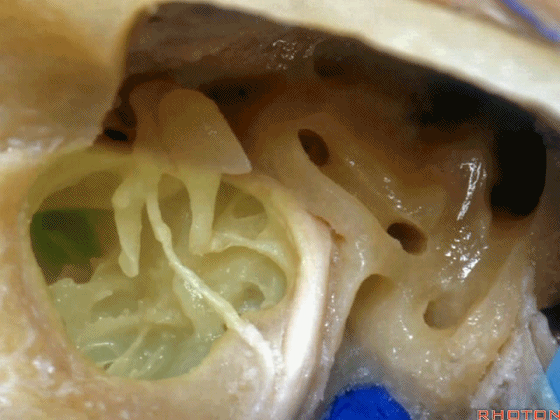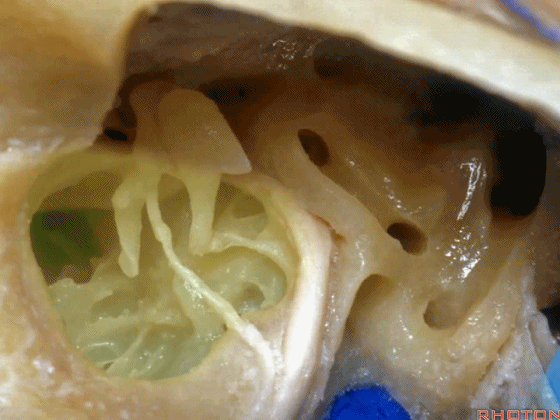
▼这是从鼓膜内面走行的鼓索。
chorda tympani crossing inner surface of tympenic membrane.
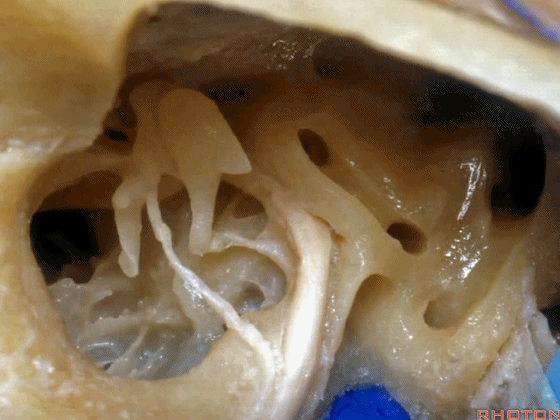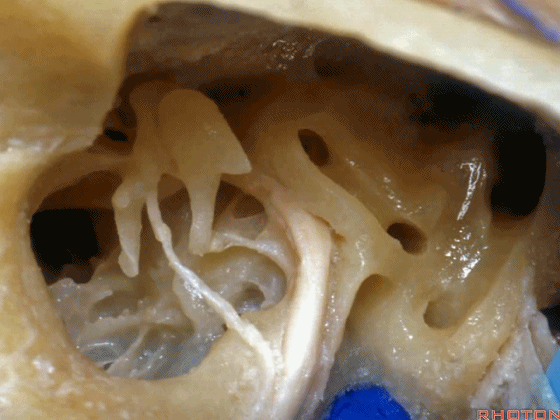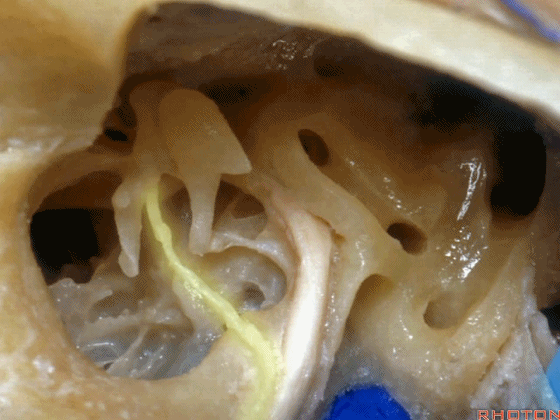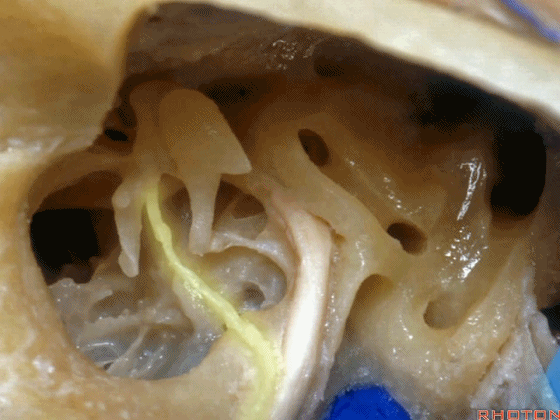
▼这是咽鼓管(下图)。经乳突或经迷路入路中,为防止脑脊液漏,需封闭咽鼓管,而上述情况下听力本来就无法保留了。
What is that... that dark hole? It's eustachian tube. So that, often when they drill out the mastoid or translabyrinthine, to prevent CSF leak, they'll plug the eustachian tube, ...since hearing has been lost.
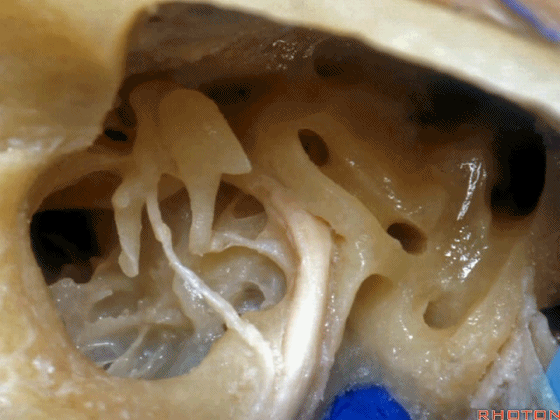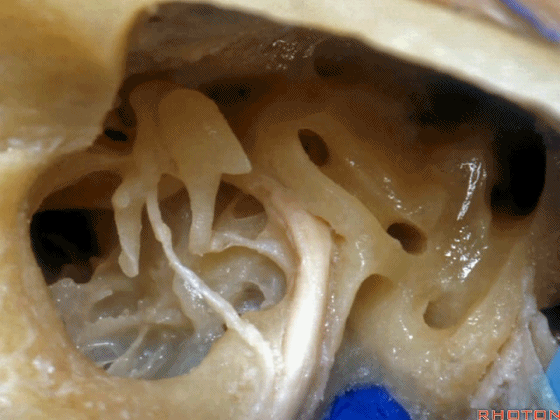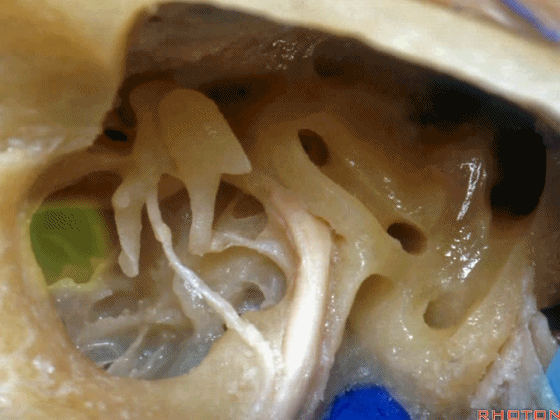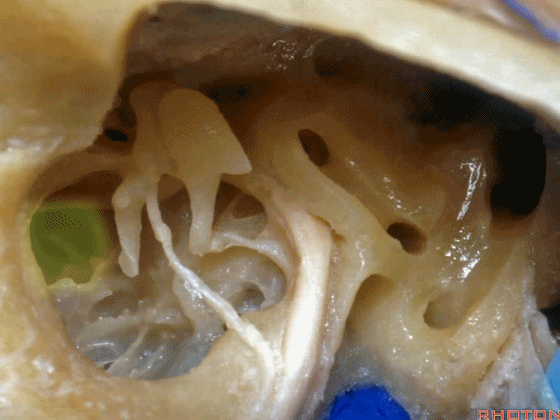
▼这是锤骨
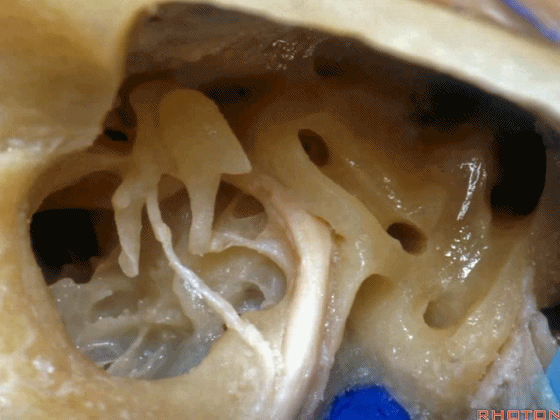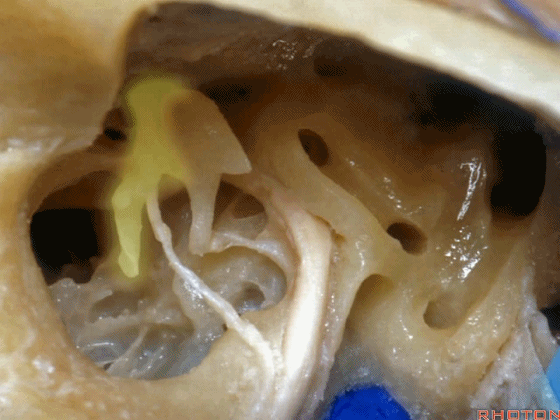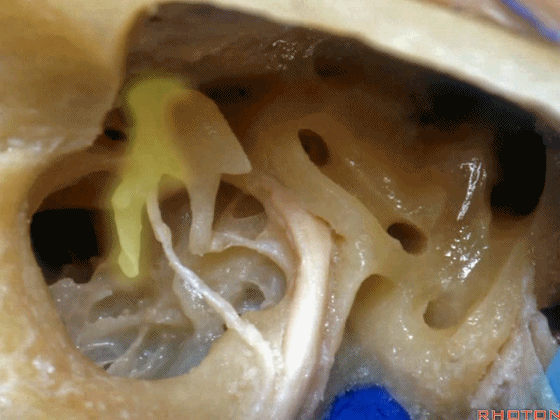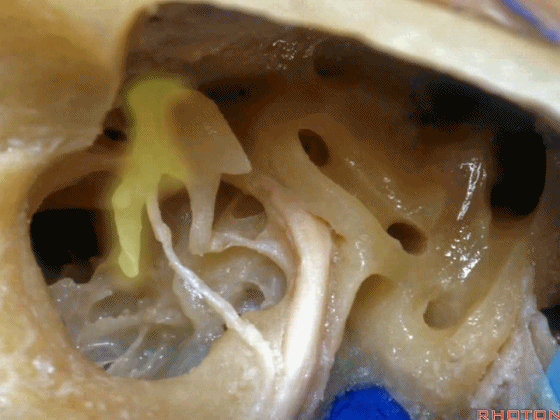
▼这是砧骨
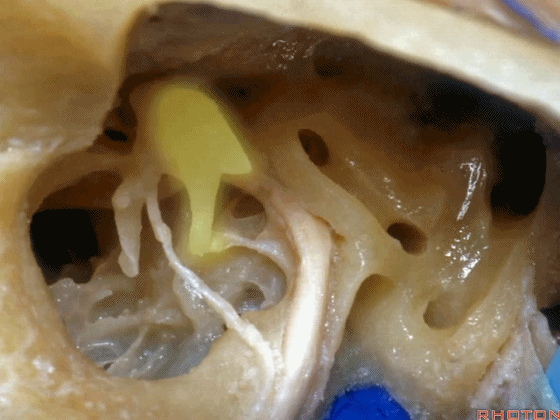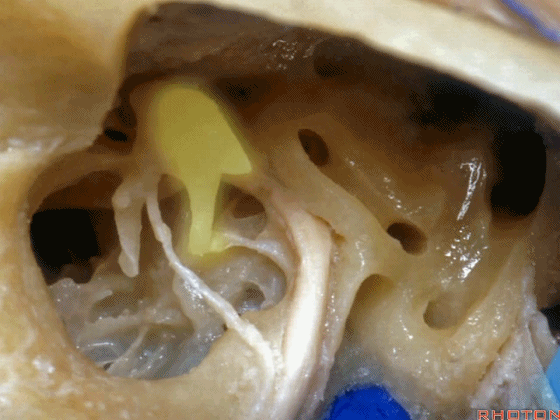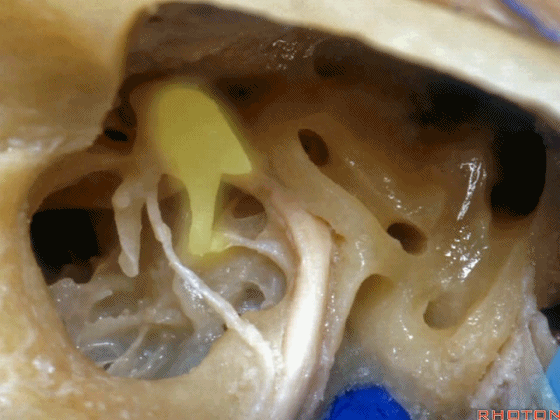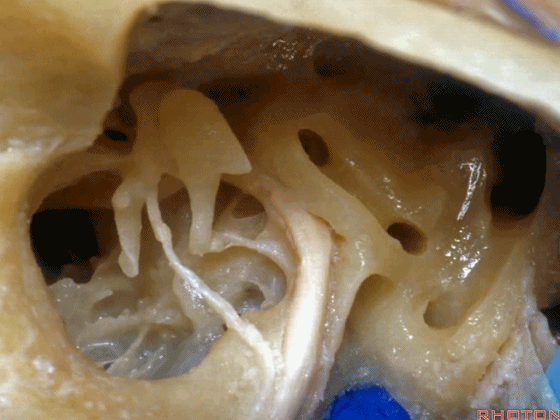
▼这是镫骨
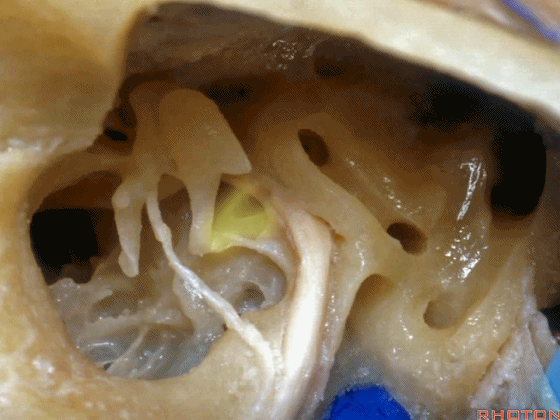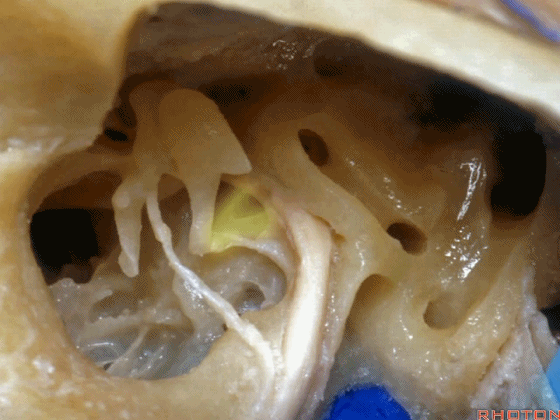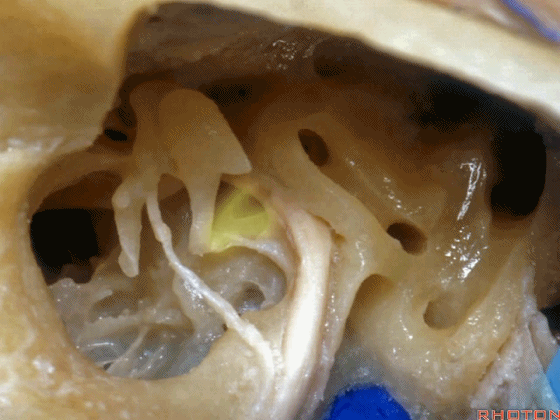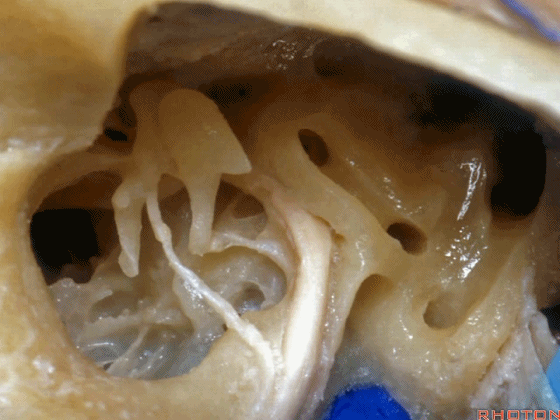
▼砧骨短突(下图)是术中的一个解剖标志。它常指向 面神经鼓室段
short process of incus, you can use it as a landmark. It always points to tympenic segment of facial nerve.
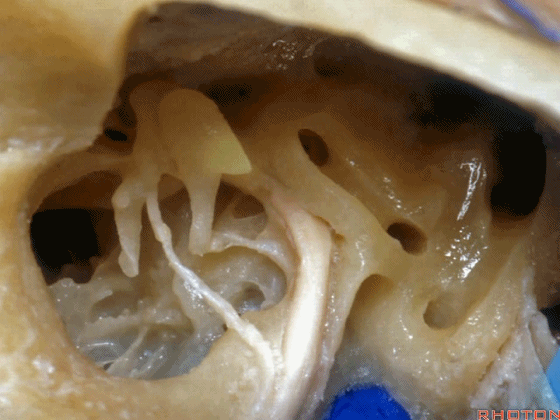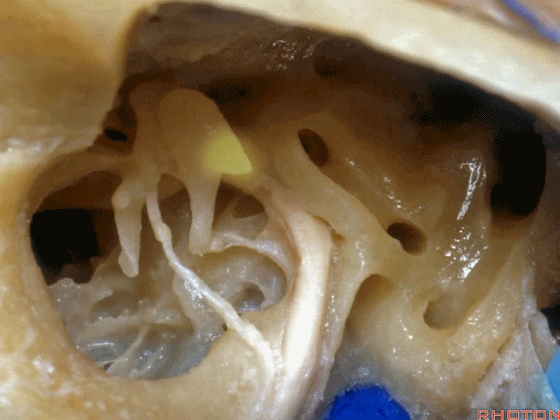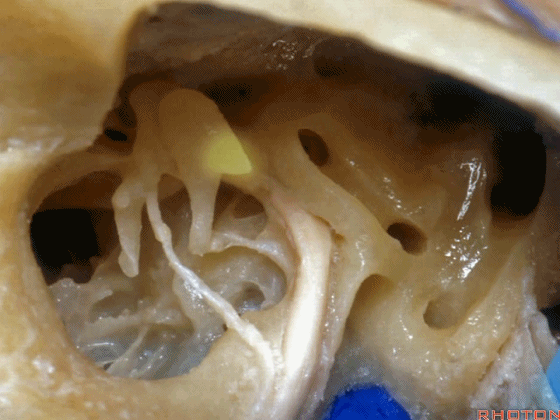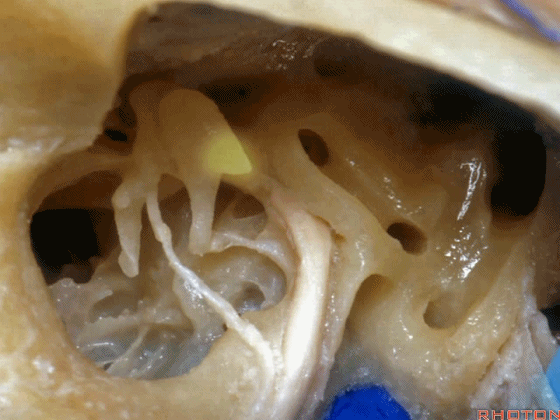
▼这是面神经鼓室段
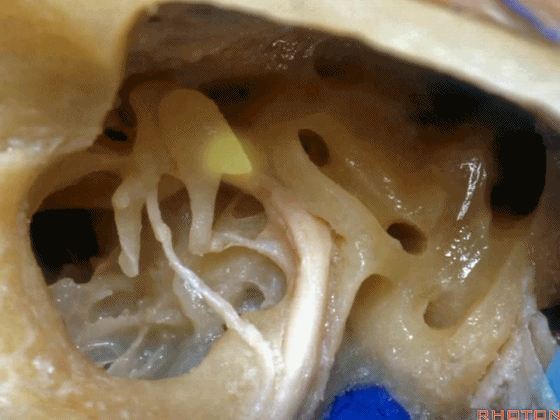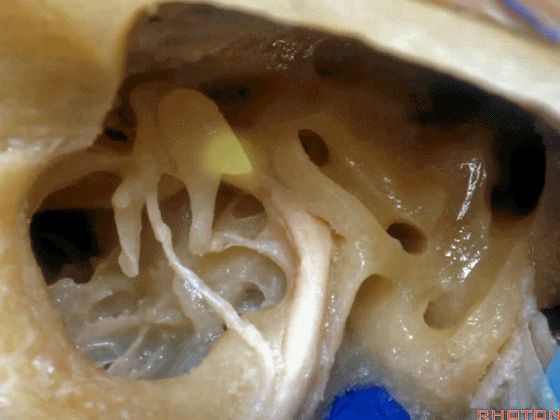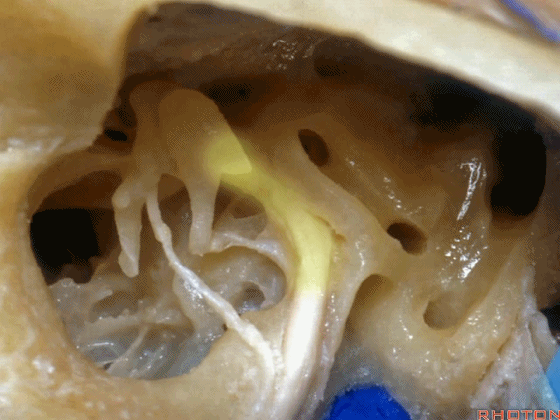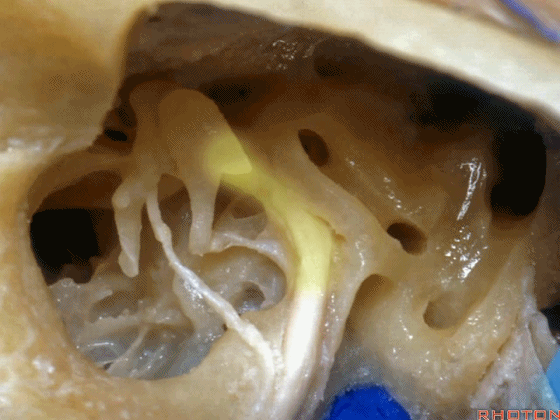
▼面神经鼓室段向下走行于外侧半规管的下方。
facial nerve that turns downward below which canal? That's lateral canal.
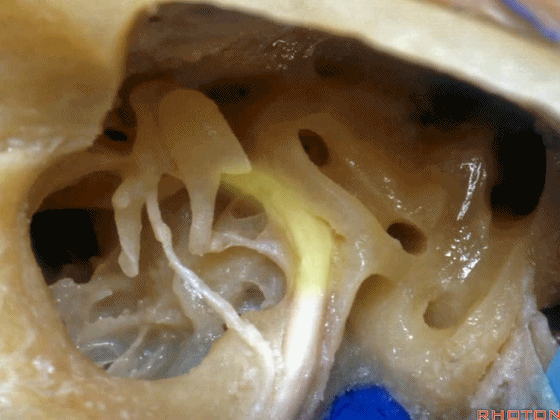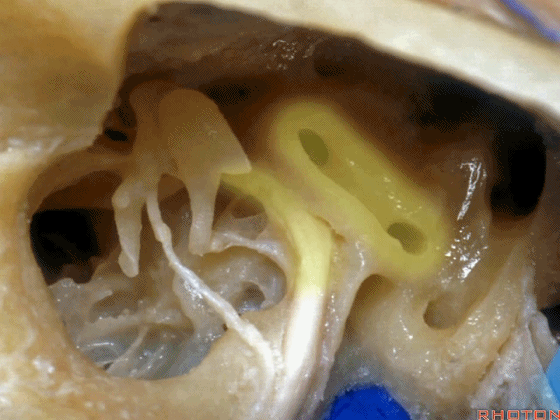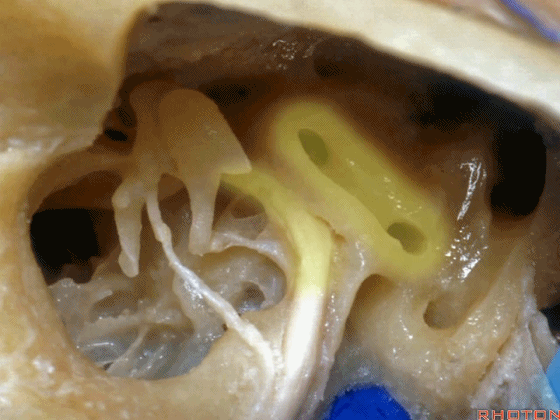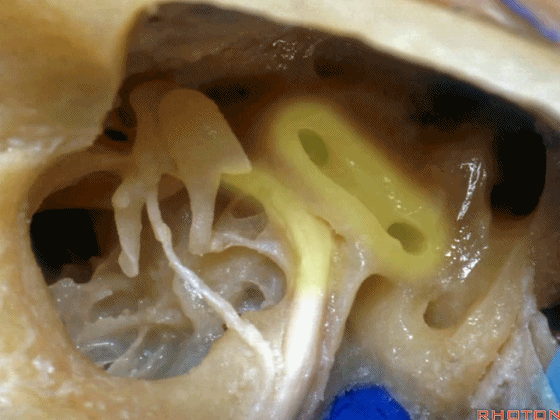
▼这是后半规管,暂时看不到上半规管,直至暴露外侧半规管顶的内侧方可显露。
This is the posterior, and then you don't see superior until you work medial over the top of the lateral canal.
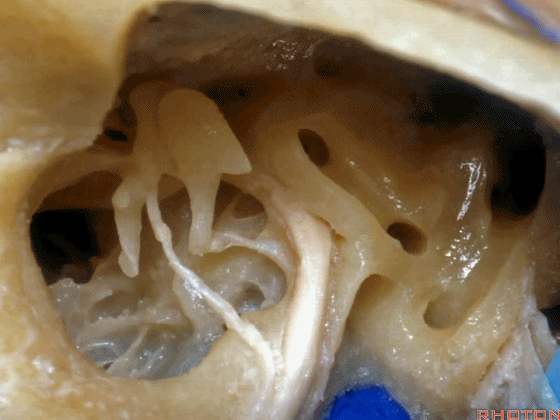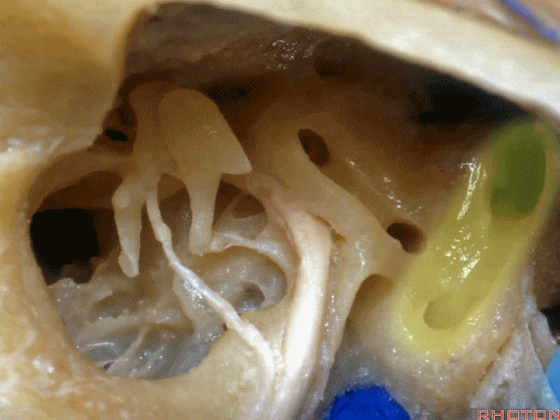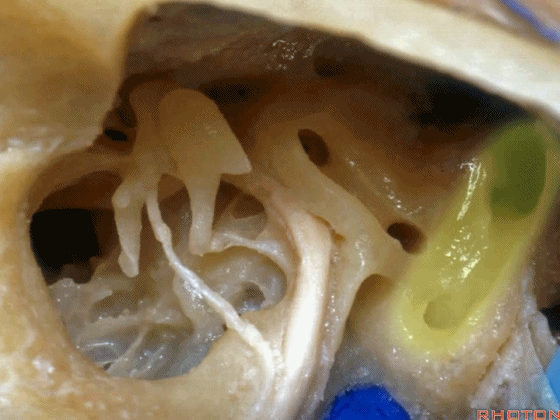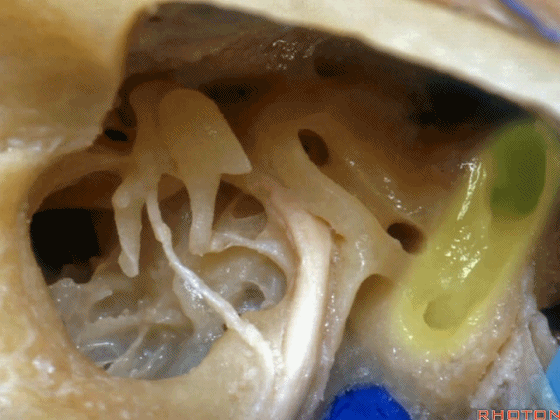
▼这里,我们看到外侧半规管 和 向下走行的面神经
So, here we just see lateral canal. This is facial nerve turning downward,
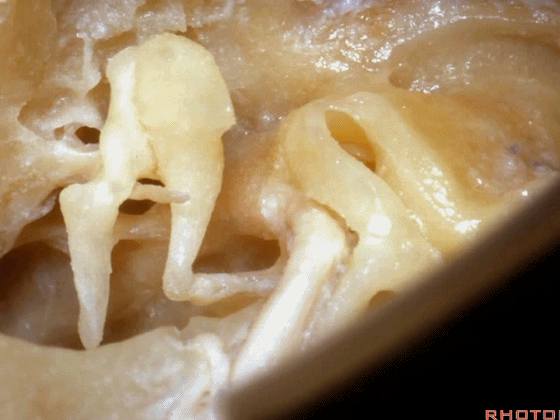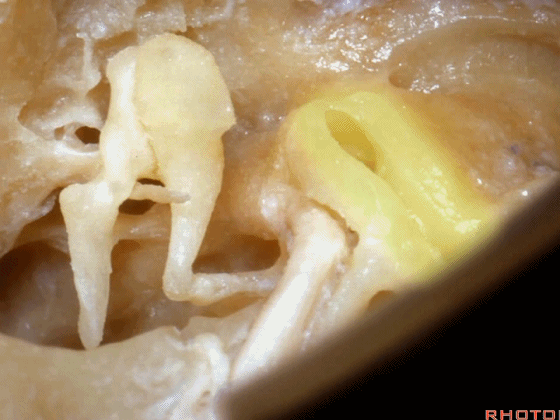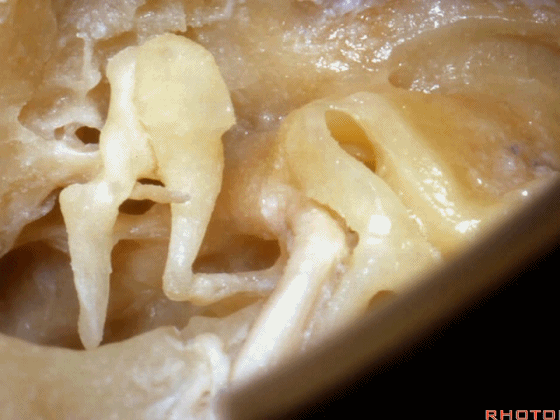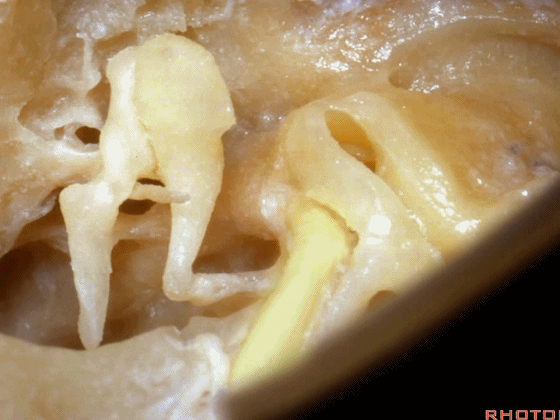
▼镫骨的短突 指向 面神经鼓室段
the short process of the incus pointing toward this tympenic segment of facial nerve,
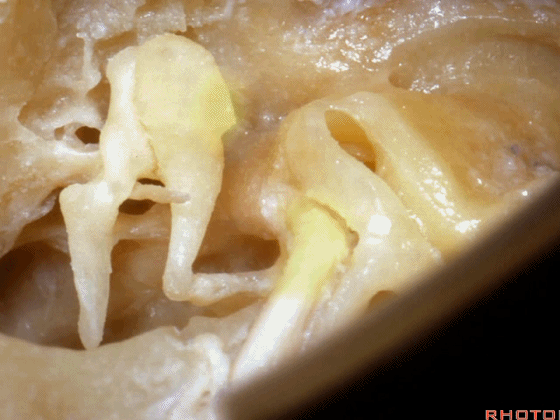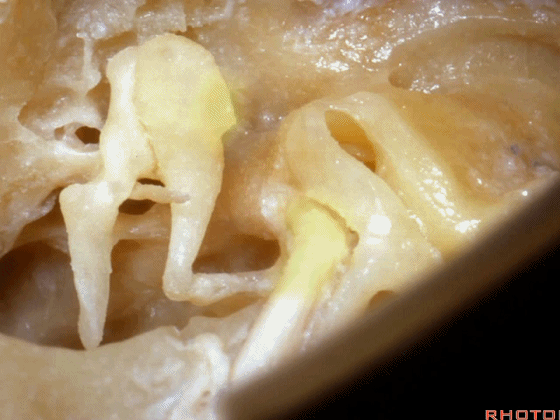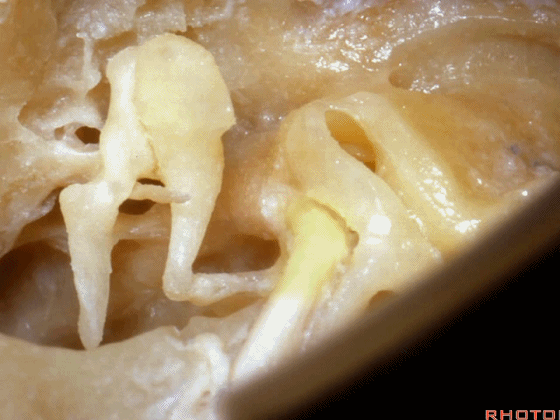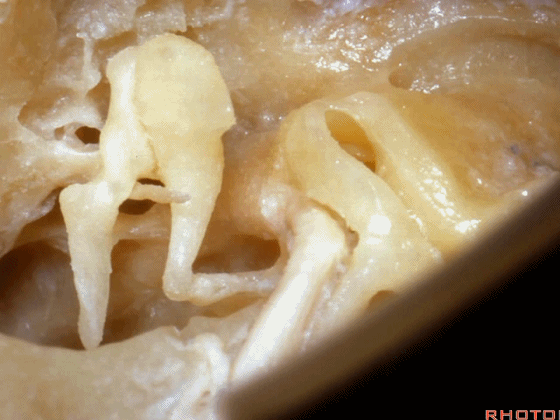
▼现在我们磨除了各半规管,仅保留外侧半规管前端的壶腹骨脚(下图)。
Here we've drilled out the canals. We've saved the anterior end, the ampullated end of the lateral canal.
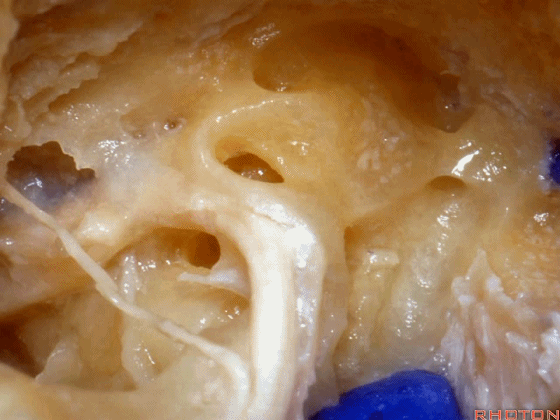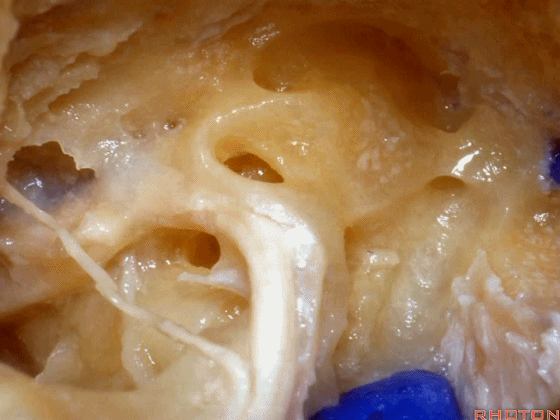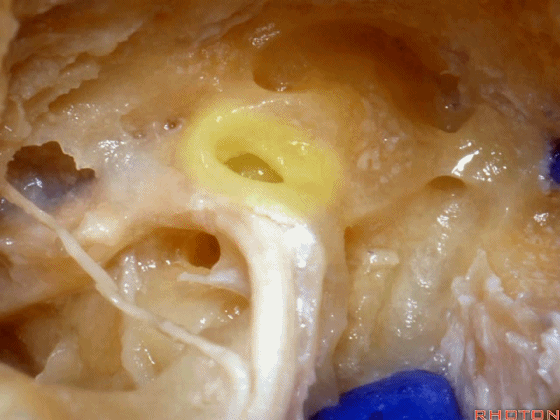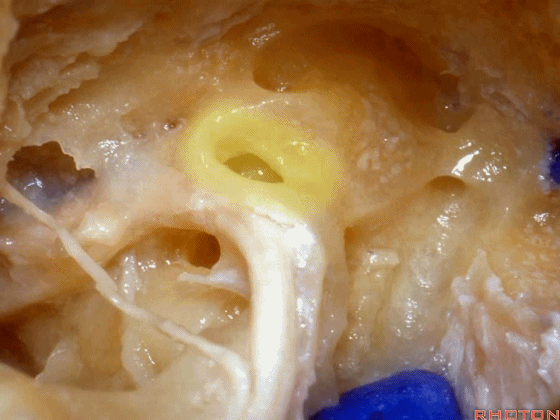
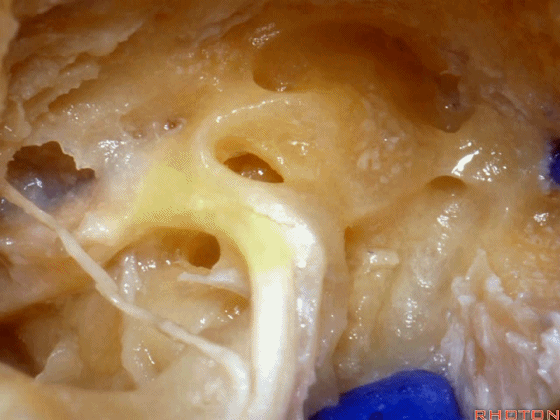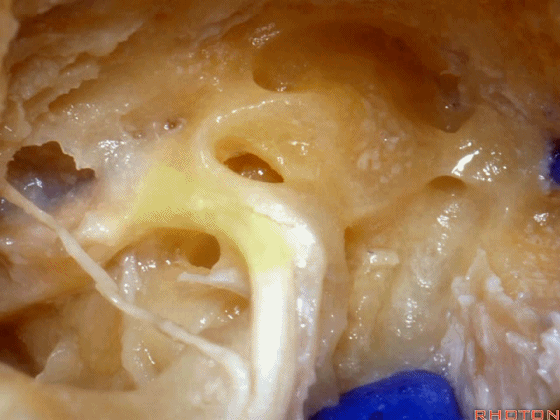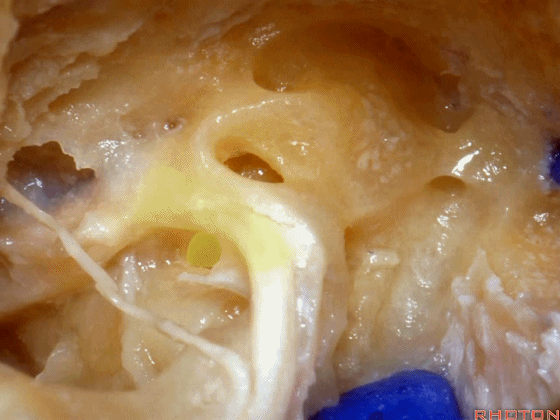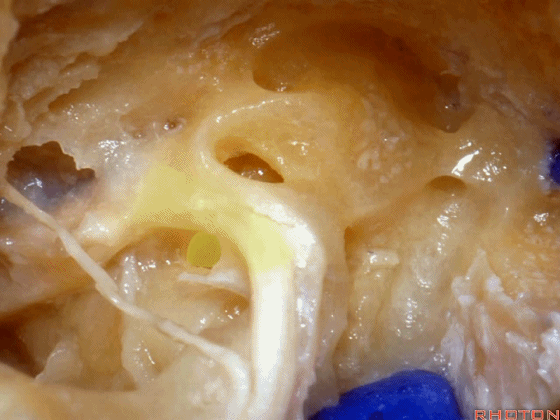
▼面神经鼓室段 行于 卵圆窗 内 镫骨 的下方。下图示卵圆窗
And the facial nerve, tympenic segment passes just above the stapes sitting in the oval window,
▼这是镫骨肌
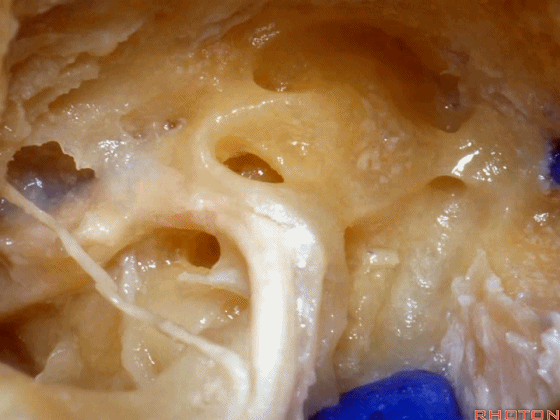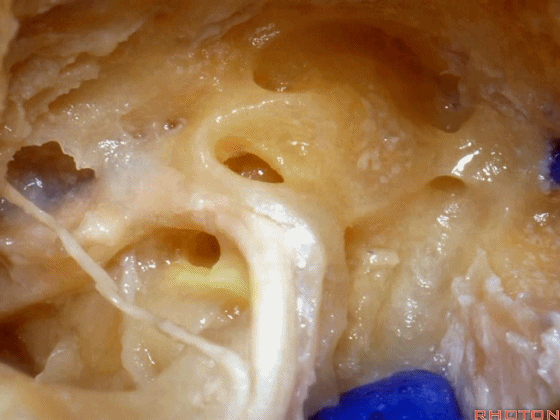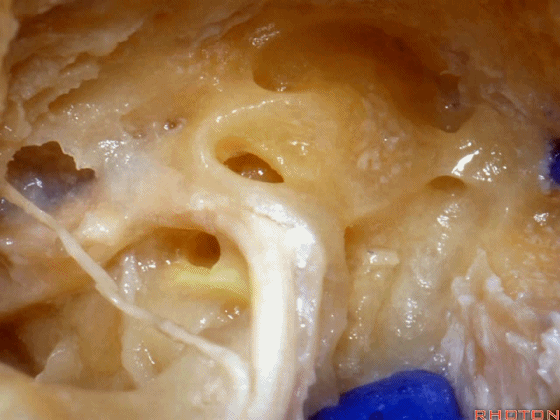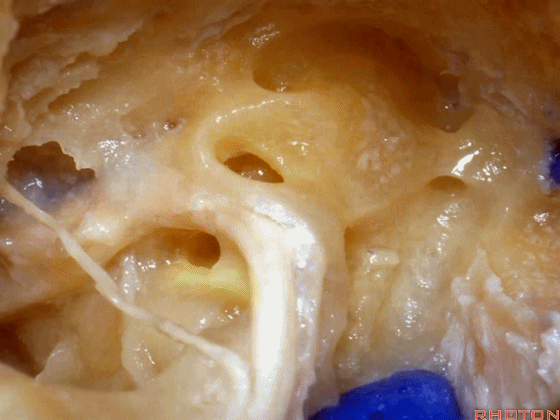
▼这是面神经上方的外侧半规管的壶腹。因此需首先从外侧半规管的上方开始磨除。
and then, here is that ampulla of the lateral canal above the facial nerve. So you wanna drill that up side of the lateral canal first.
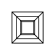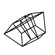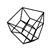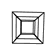
右侧经迷路入路、经耳蜗入路
▼现在是右侧乳突,这是Henle棘
So that, spine of Henle is here,
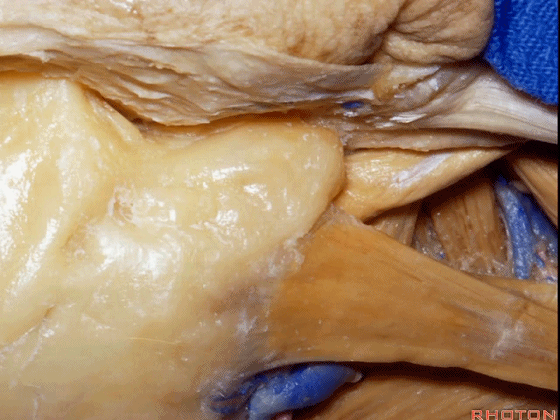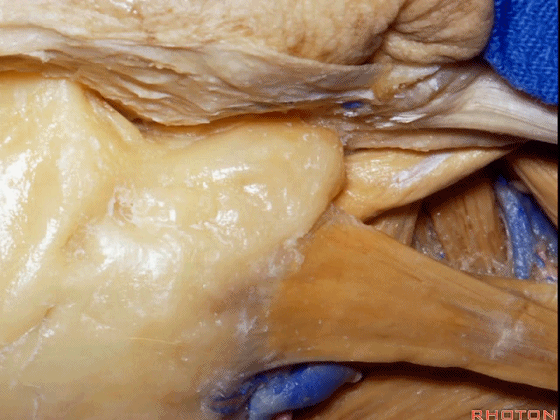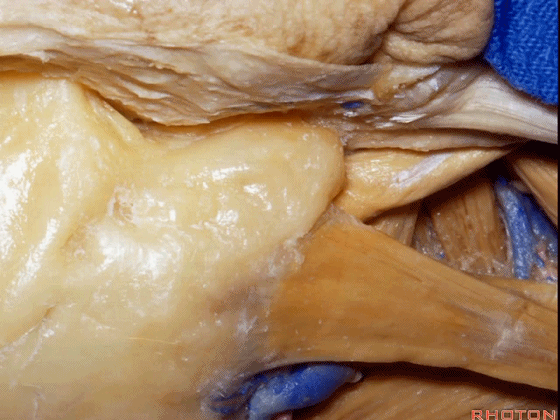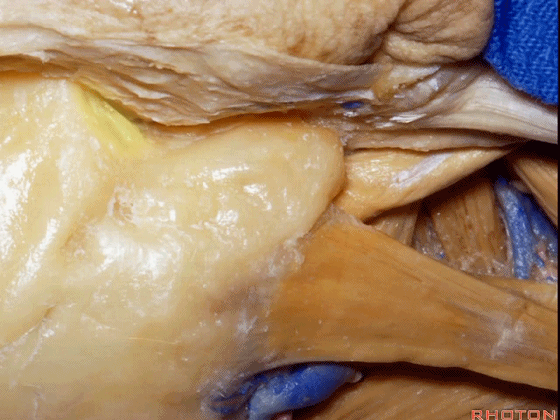
▼这是外耳道、乳突尖。
external canal、mastoid tip.
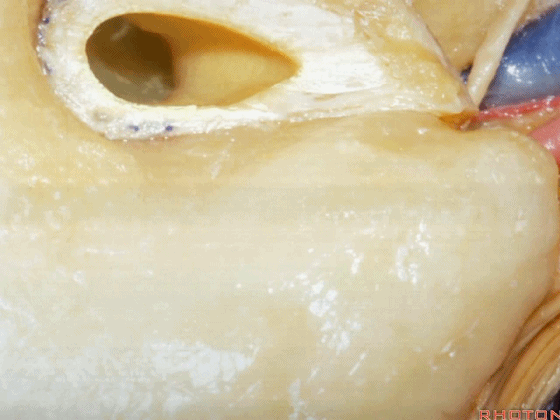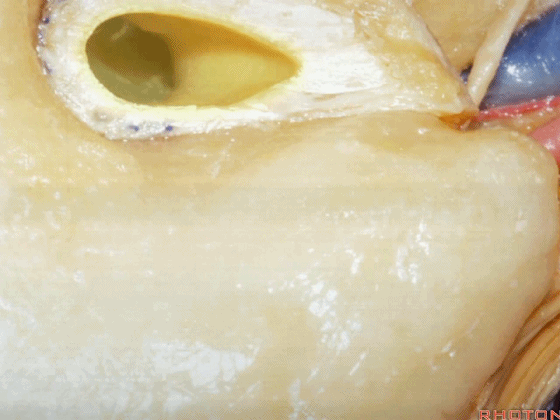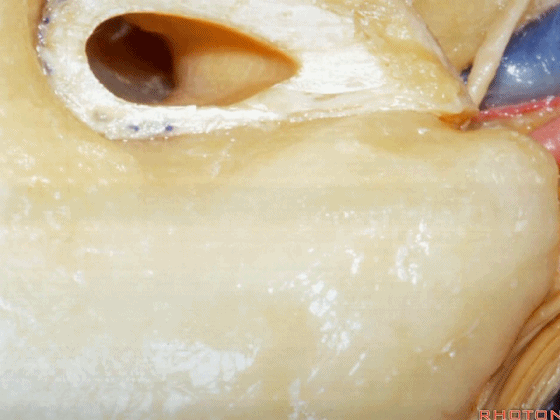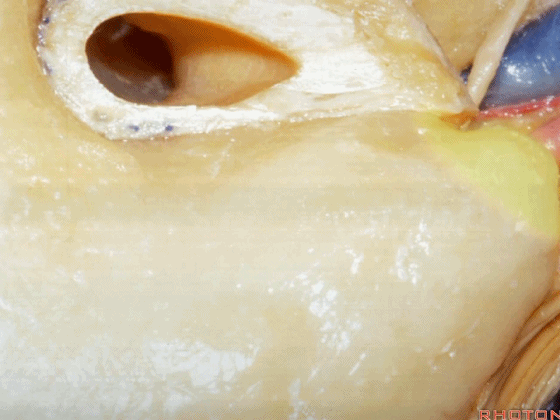
▼磨除这个区域,即可见鼓室窦。
You drill through this area and the mastoid antrum comes into view.
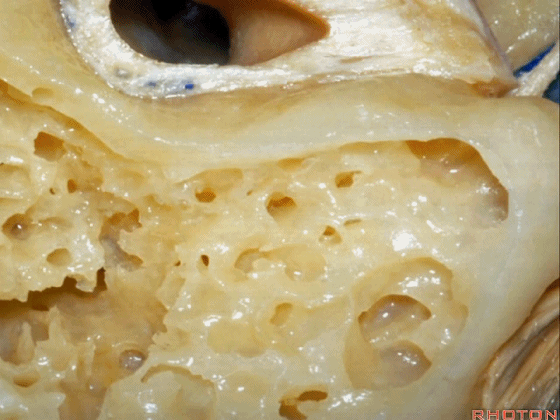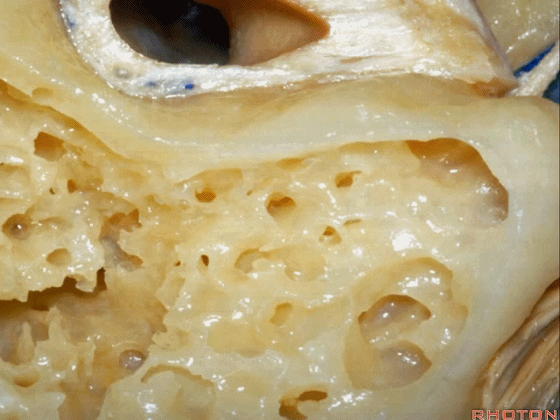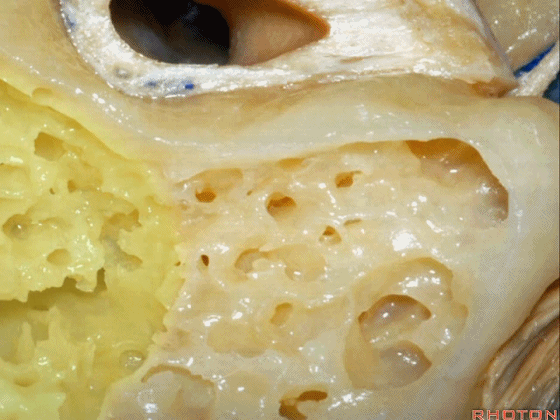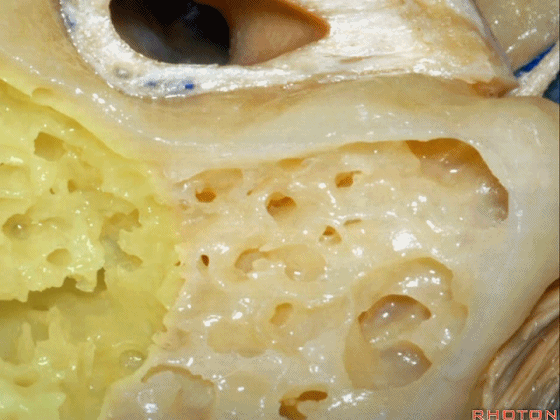
▼这是面神经
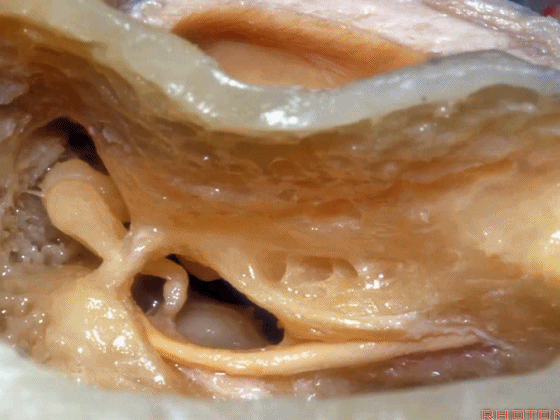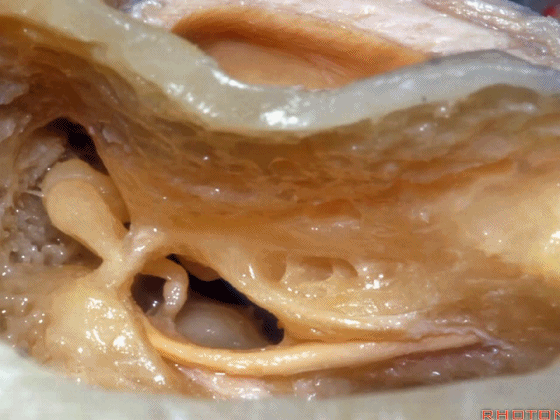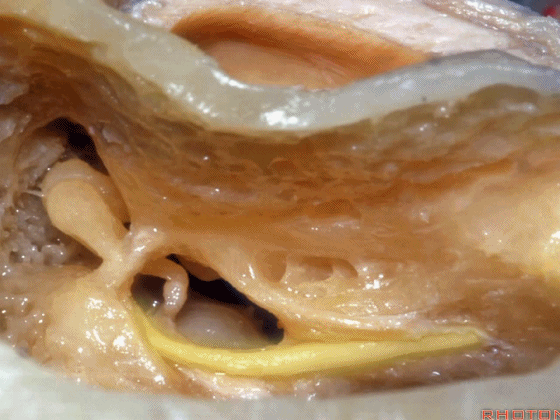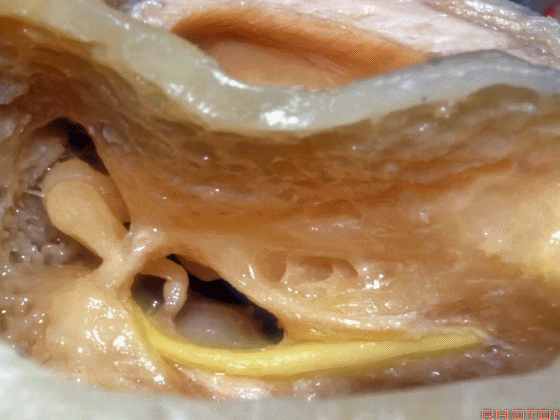
▼这是鼓索
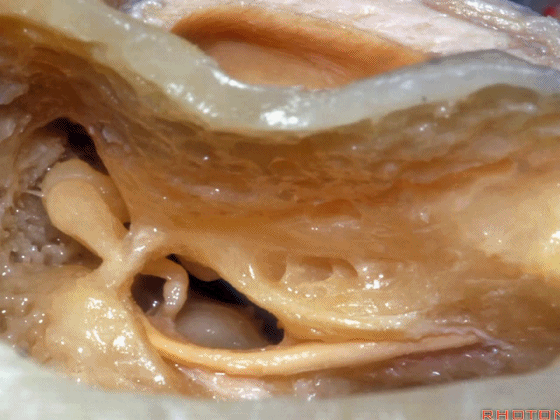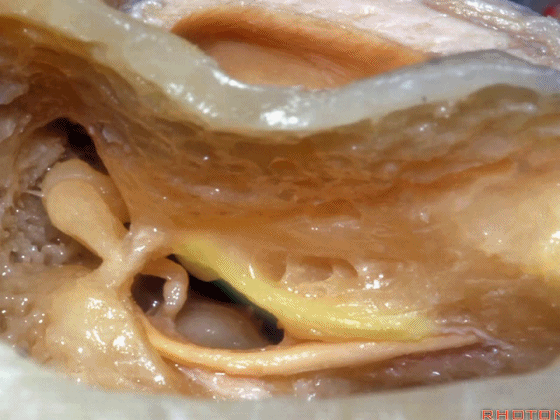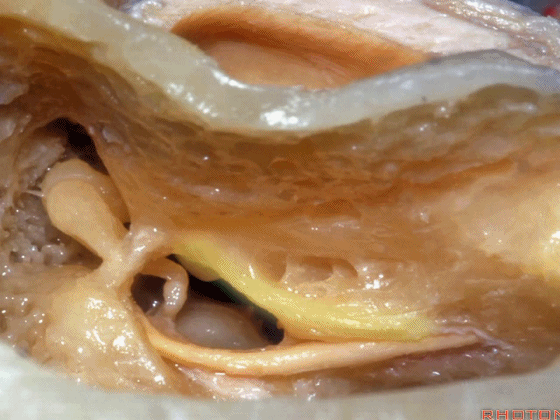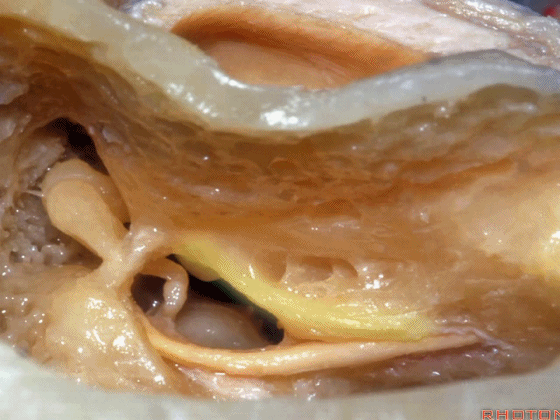
▼这是 面神经隐窝
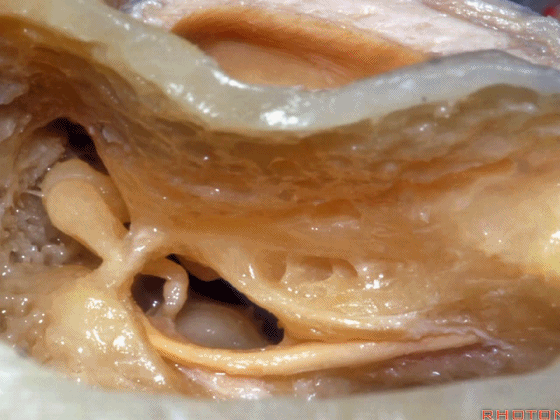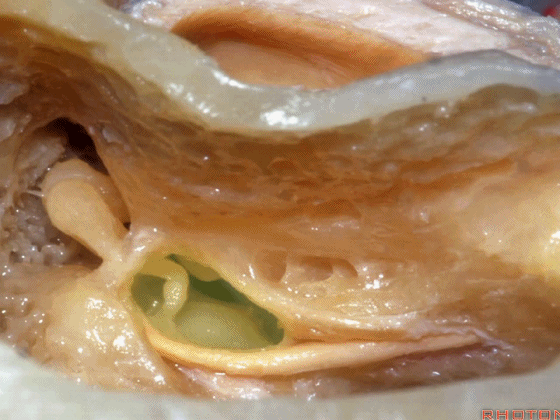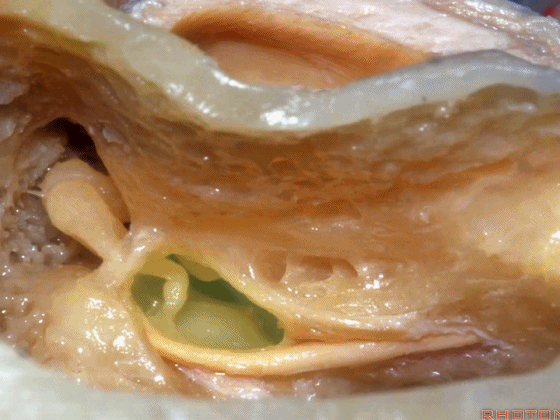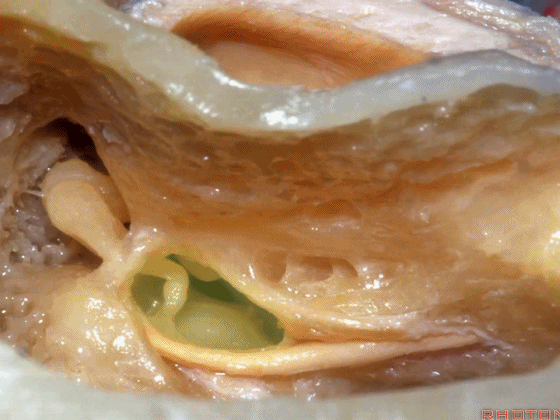
▼这是 砧骨窝
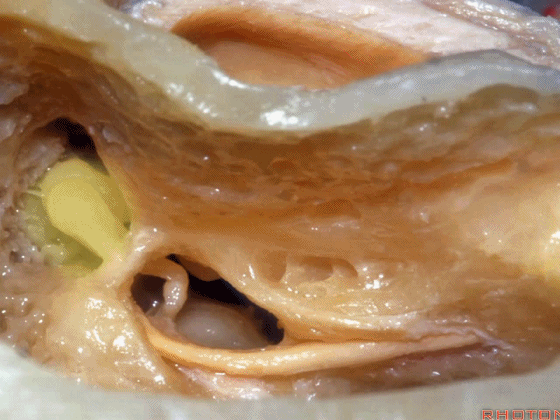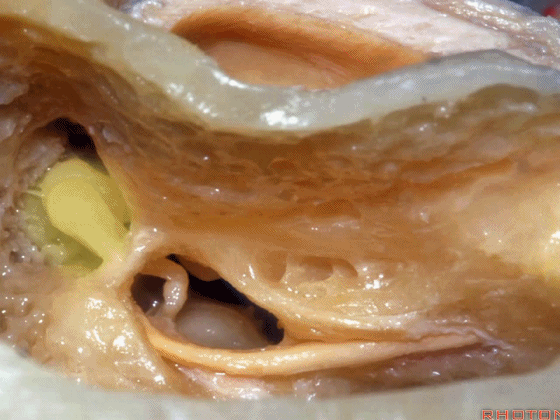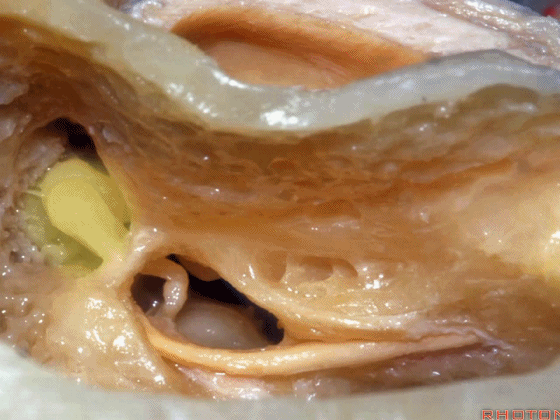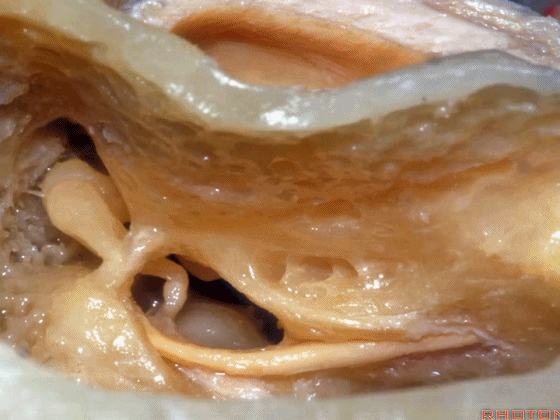
▼磨开后可见一微小的骨桥,称之为“buttress”。
So you drill this, commonly there's a little bridge of bone that's called the "buttress".
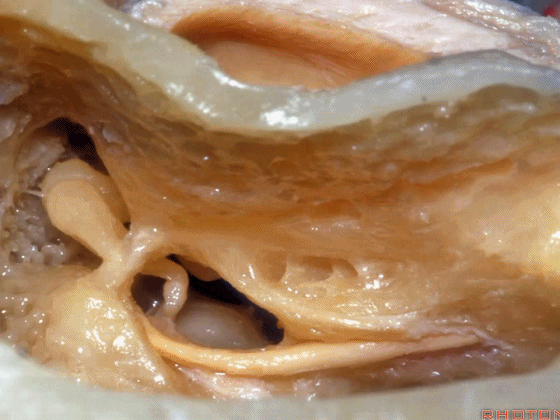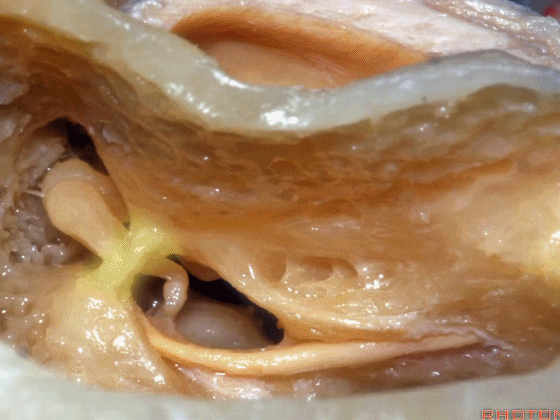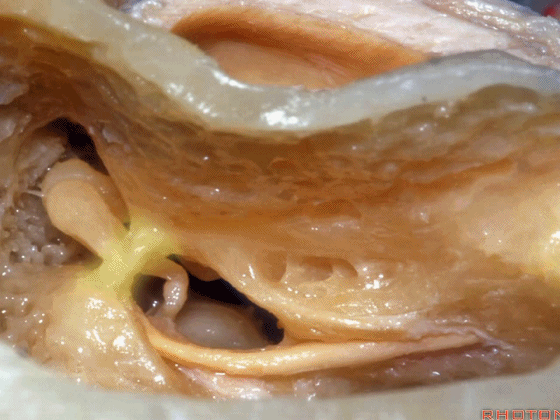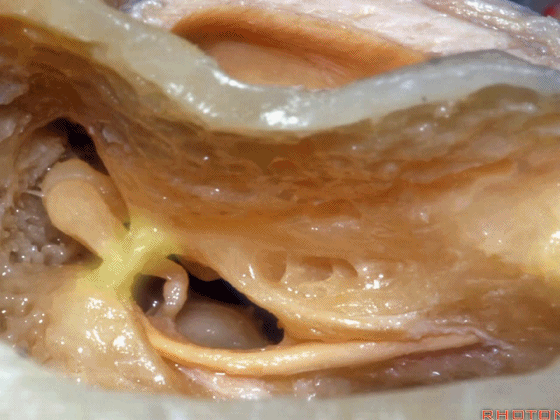
▼buttress连于外侧半规管的前界与外耳道后壁之间
from the anterior edge of the lateral canal across to the posterior canal wall,
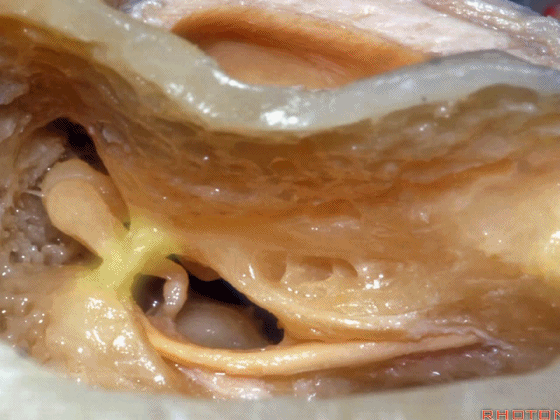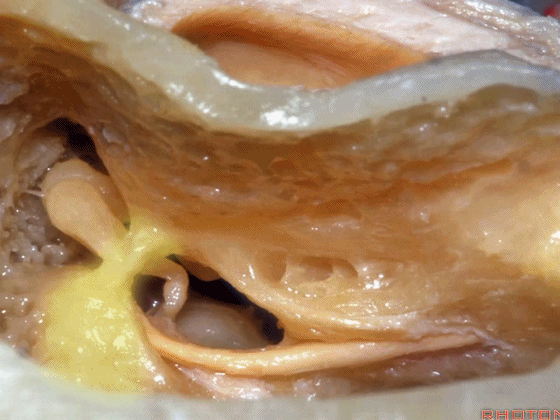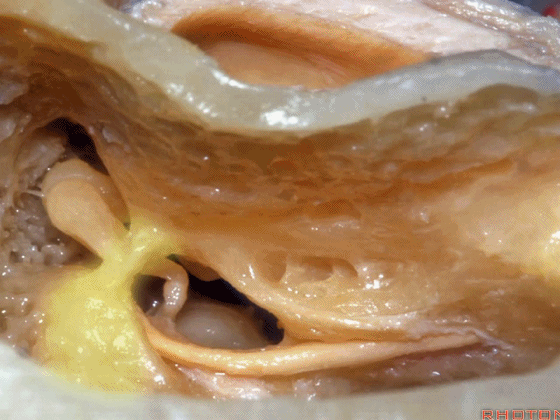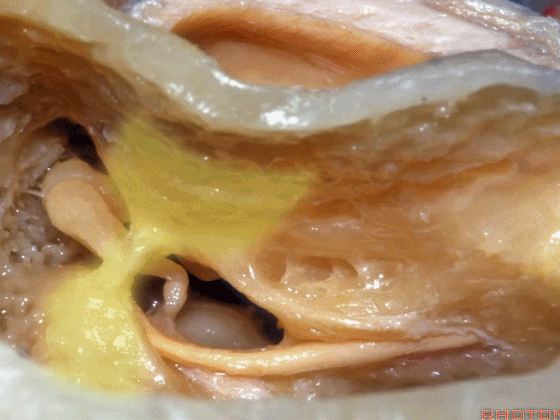
▼术中有时可以看到这个“buttress”,它需慢慢显露出来,可见其连接面神经隐窝和砧骨窝。
Some of you drill it and see the "buttress",and then that comes out last and it communicates the facial recess and the fossa incudis.
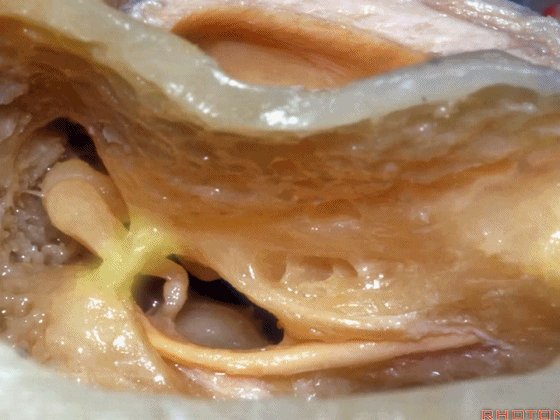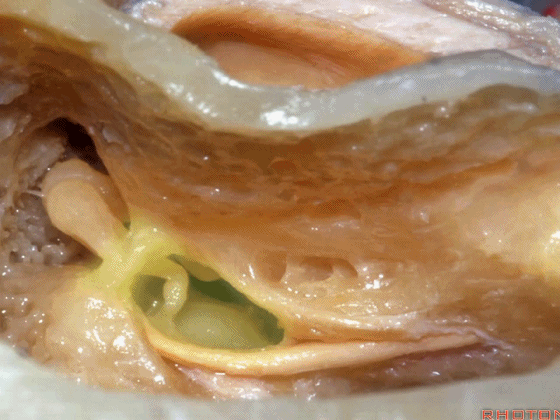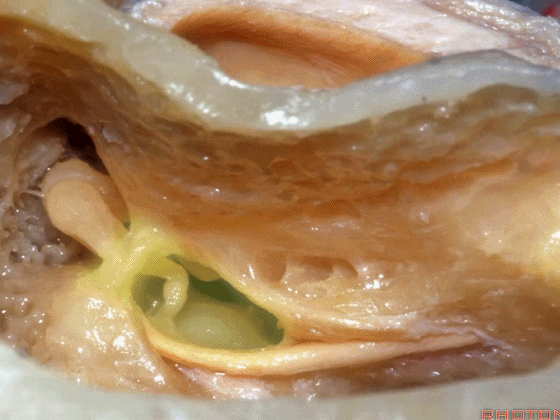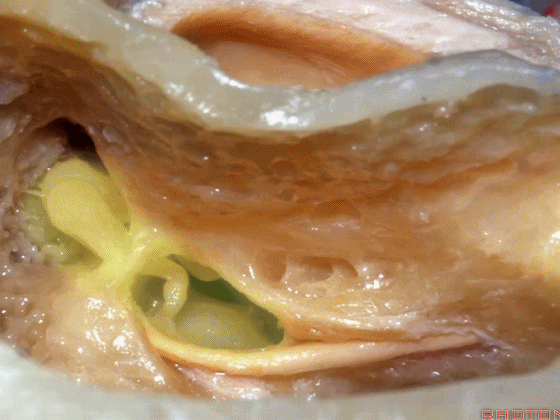
▼然后,上半规管位于最深面。
And then, the deepest canal is the superior.
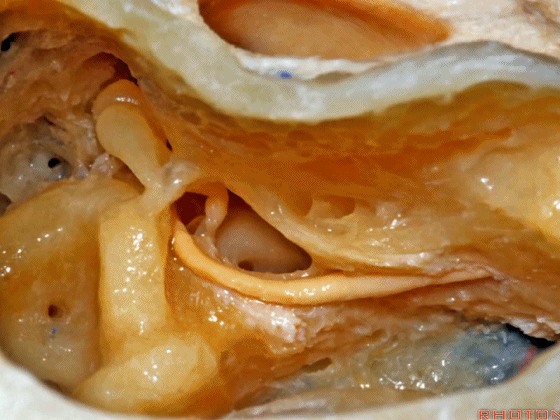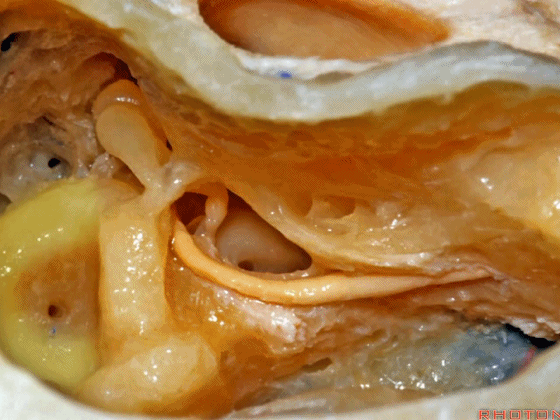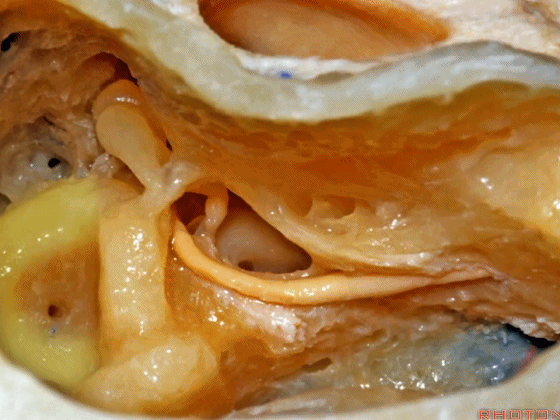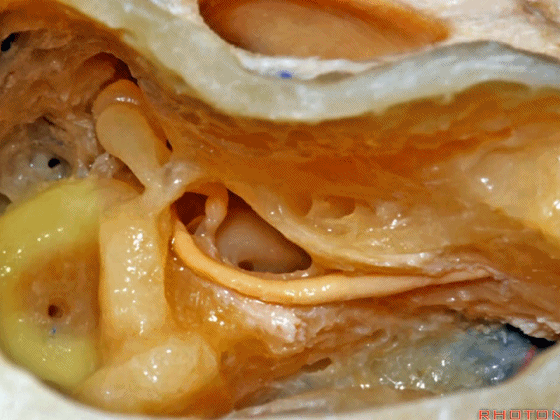
▼这是外侧半规管,其后部有后半规管环绕。
This is lateral canal, with the posterior canal wrapps around the back end of it.
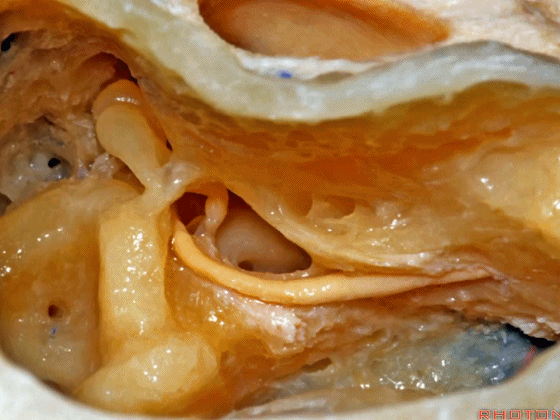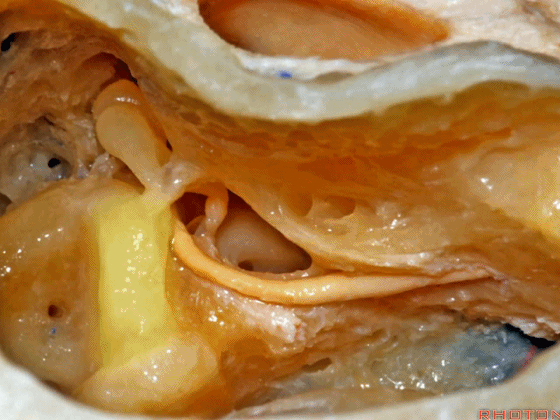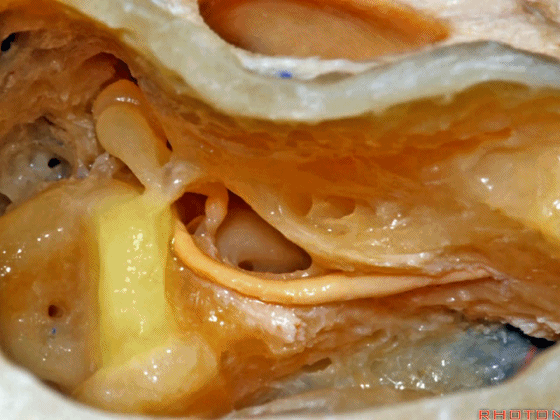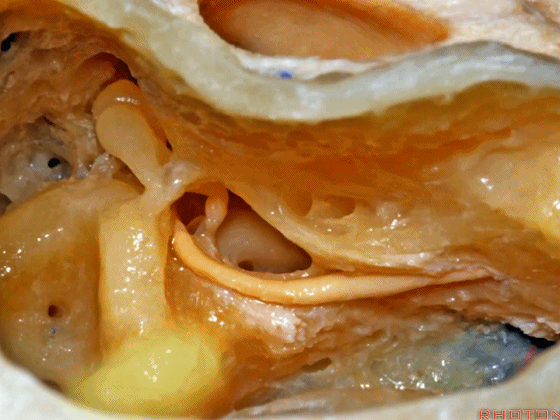
▼面神经下行于外侧半规管下方。
The facial nerve turning downward below the lateral canal.
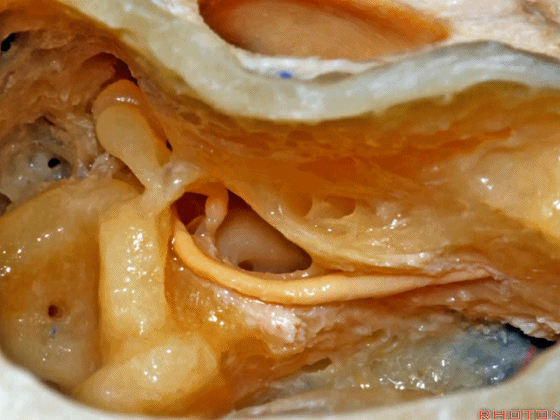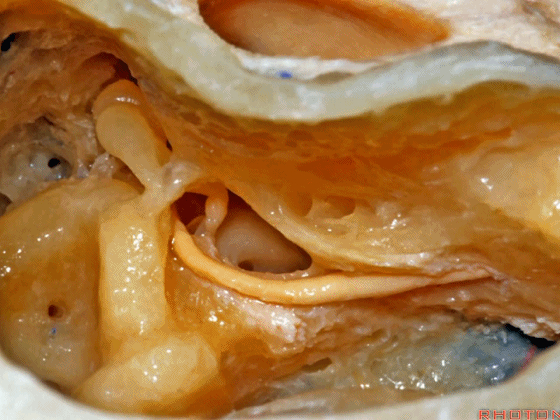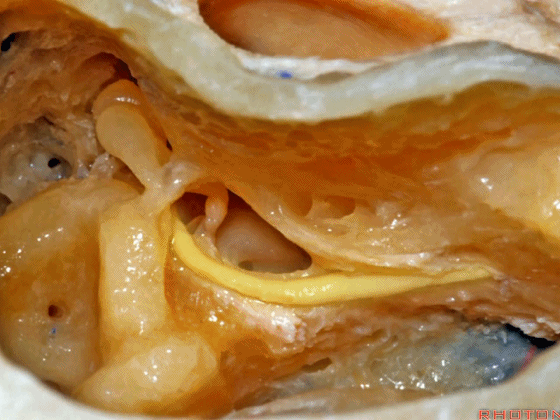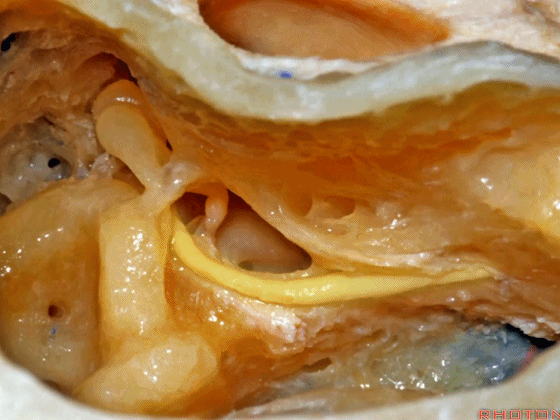
▼这里我们暴露了内淋巴囊,术中可经乙状窦后探入,或者也可以通过乙状窦前经迷路来暴露。
内淋巴囊是2014年公布的人体解剖学名词,是内淋巴管远侧端的膨大结构。位于颞骨岩部、靠近乙状窦处的硬膜下间隙内,对前庭功能和内淋巴的吸收有重要作用。
Here we've exposed the endolymphatic sac, and you can get into the sac retrosigmoid, or you can identify the sac presigmoid in this retrolabyrinthine exposure.
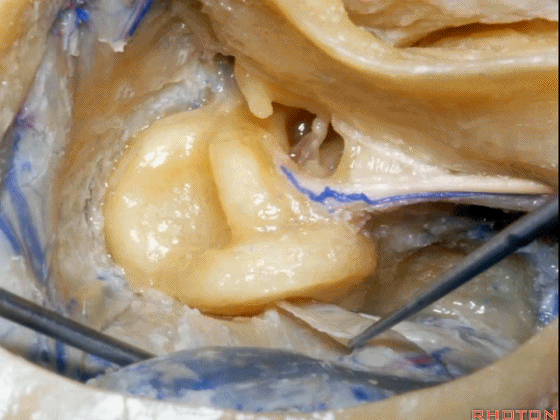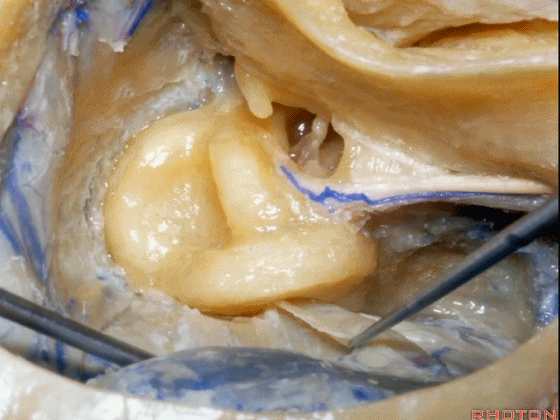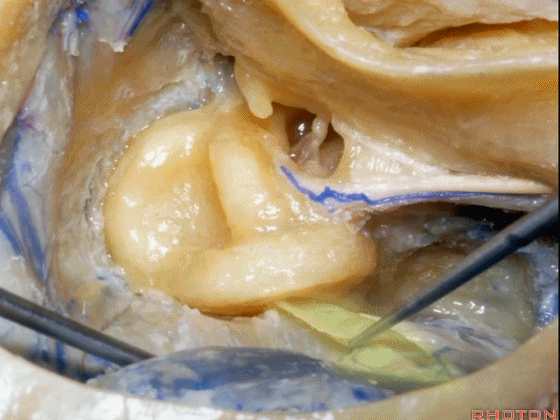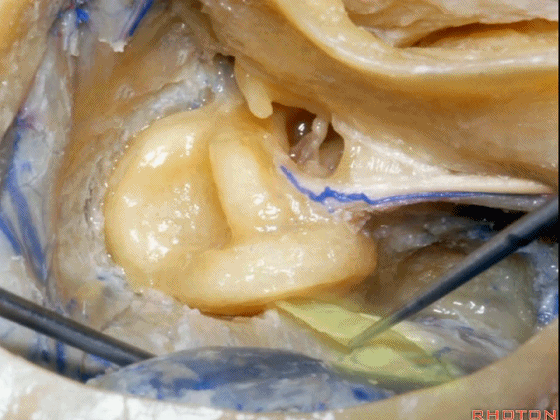
▼接下来,可作一个部分迷路切除术,切除上半规管以增加对中颅窝的暴露。
Now you can do a partial labyrinthectomy if you take out the superior canal, it increases the access to the middle fossa.
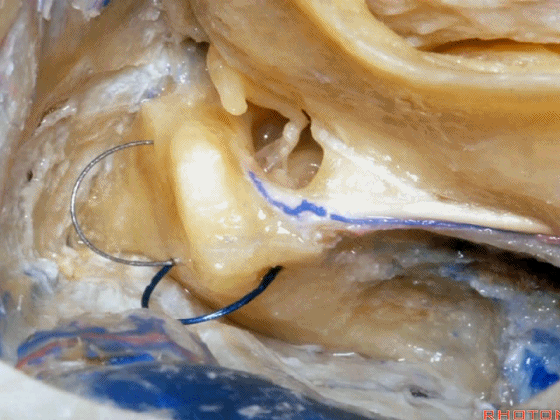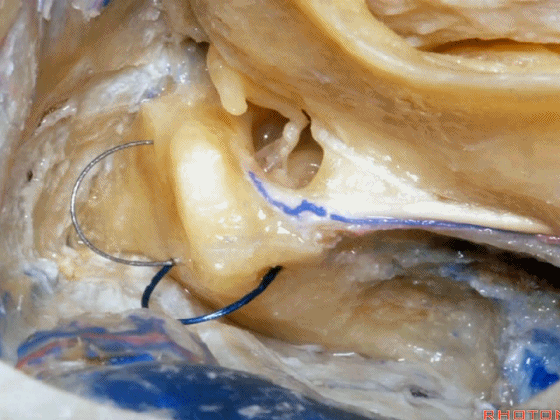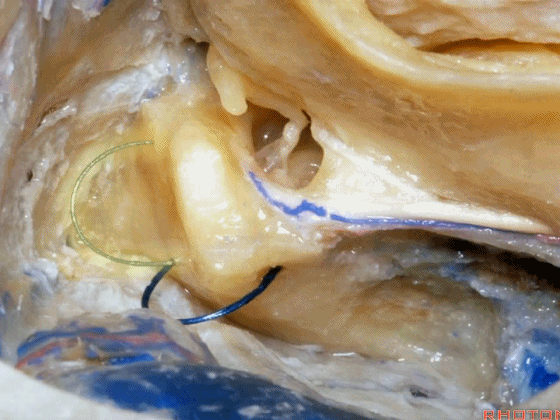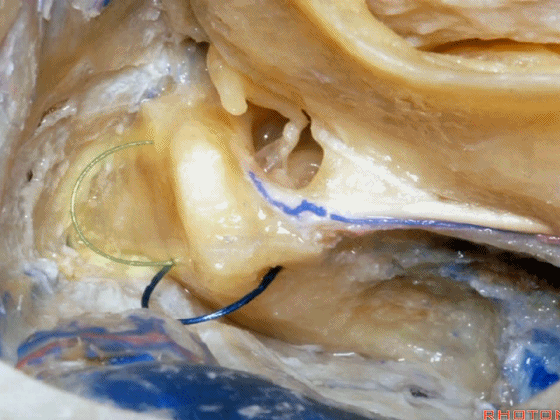
▼而切除后半规管则可扩展至后颅窝的视野。封堵这些开口,可保留约半数患者的听力。
And if you take off the posterior canal, it gives a little increased access to posterior fossa. If you plug these openings, you can save hearing in about half the cases.
▼如果打开了外侧半规管,则很难保住听力。
If you get into the lateral canal, it's hard to preserve hearing,
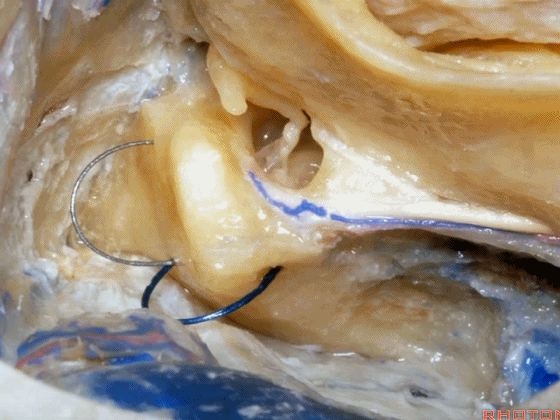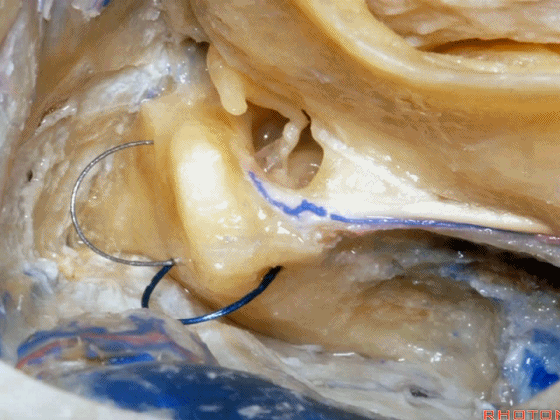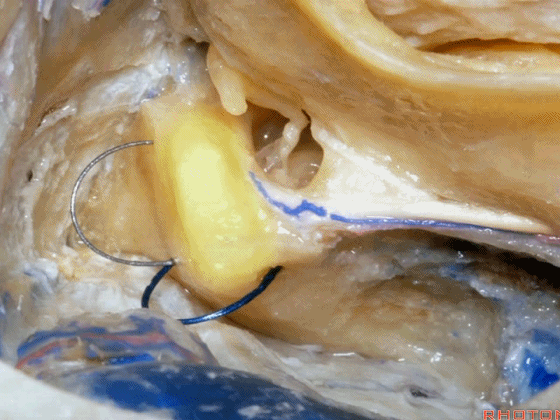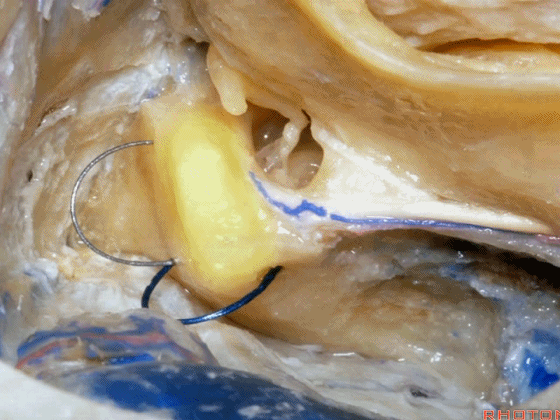
▼现在我们继续磨除上半规管,保留上半规管的壶腹骨脚(下图),保留其所在的前庭上区。
And here we've taken out the lateral canal. We still have the ampullated end of it here at the superior vestibular area preserved.
▼如果仅需暴露桥小脑角,可以单纯作迷路后入路,
但是想要暴露内听道的神经,必须切除整个迷路。
接下来,我们磨除整个迷路(经迷路入路),从而暴露内听道(下图)。
And then, you drill out the labyrinth, it gives you access to the internal acoustic meatus.If you need just CP angle here,you can do retrolabyrinthine, but to get the nerves in the meatus, you need to drill out the labyrinth.
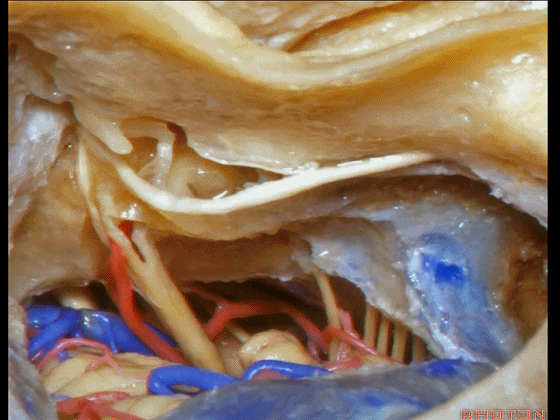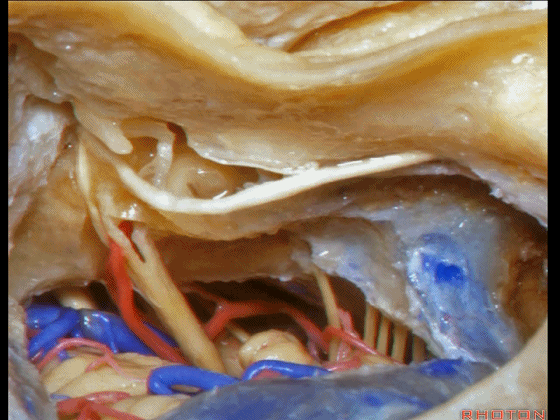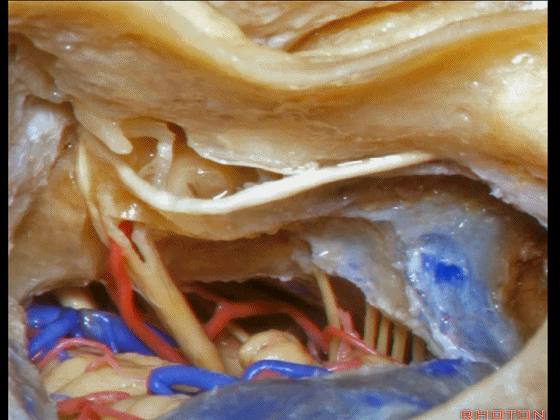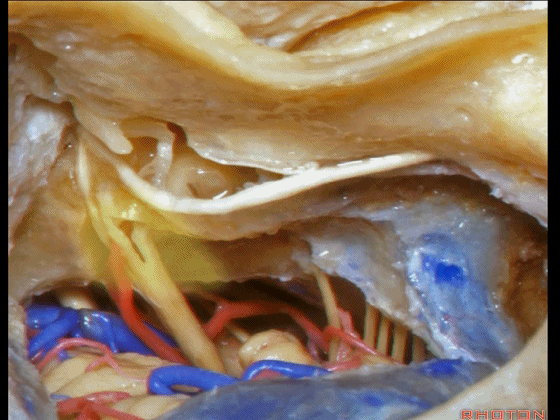
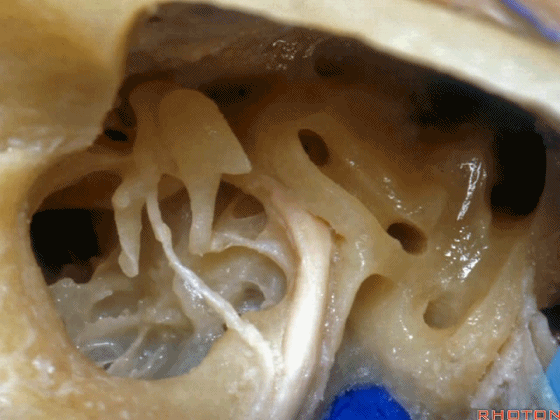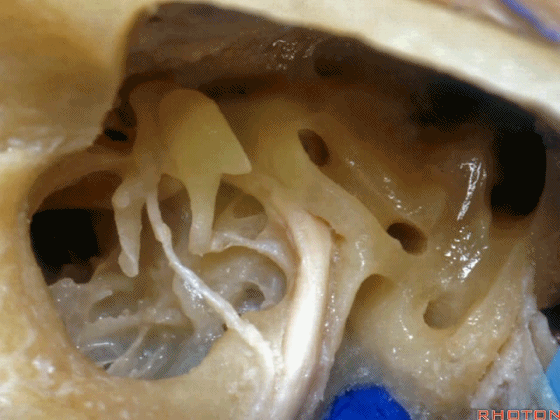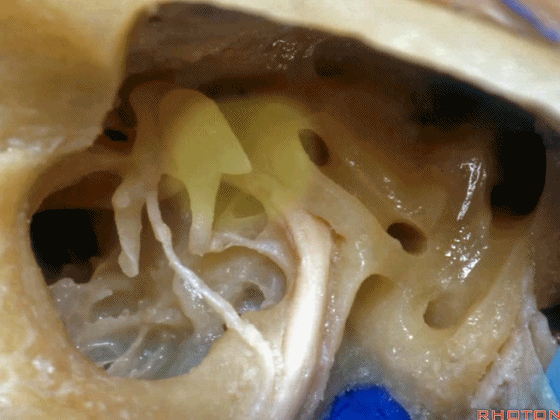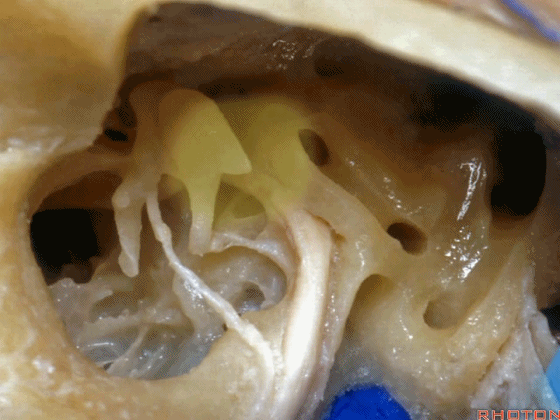
▼这是三叉神经
This is V
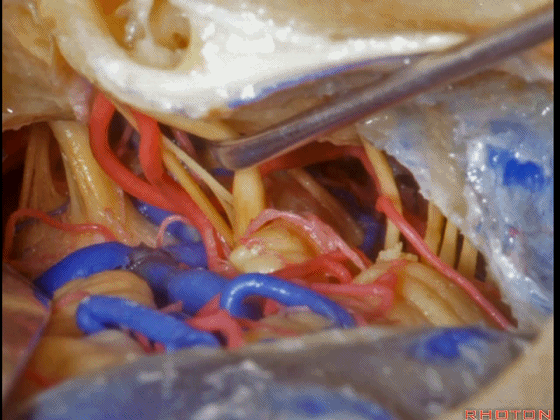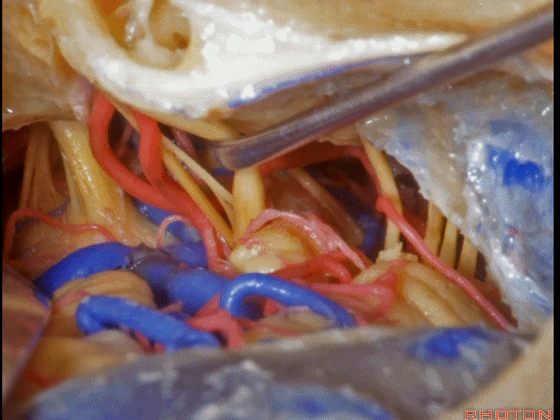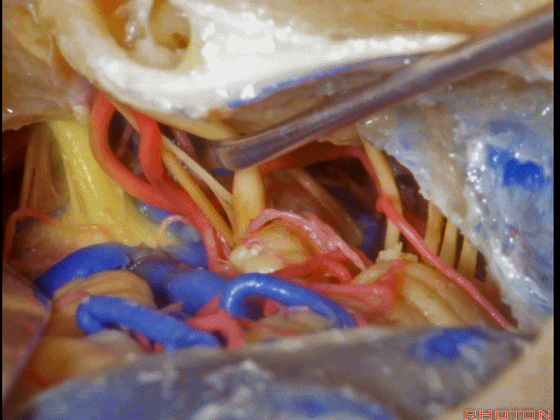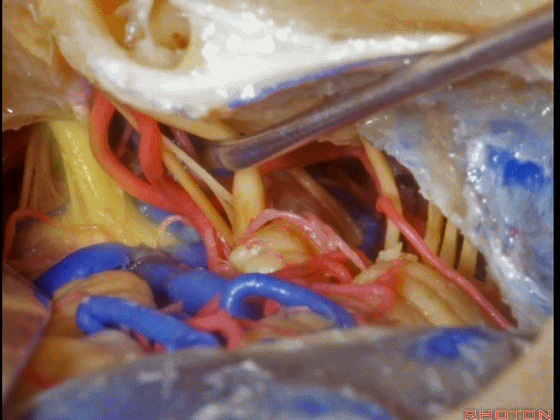
▼这是面神经全程
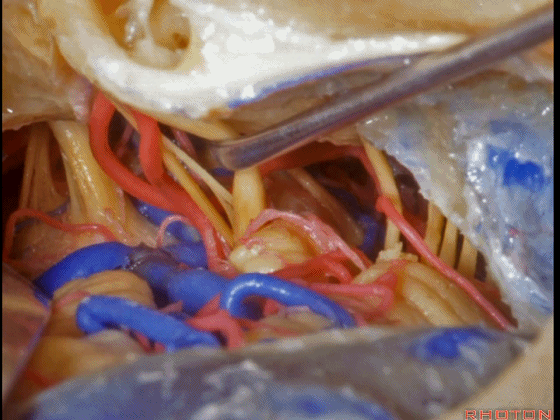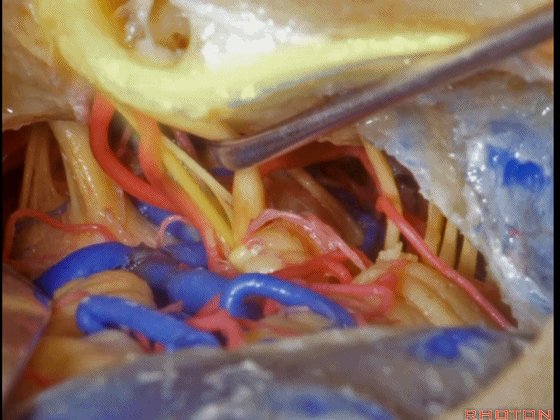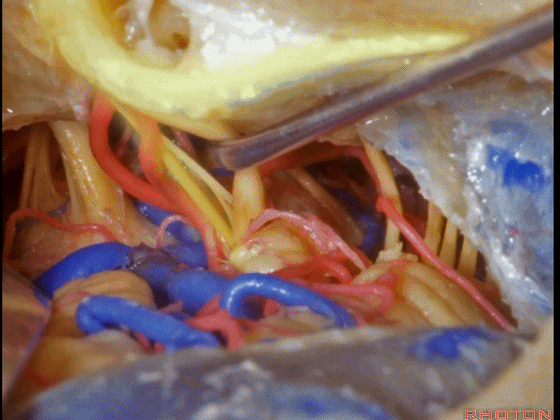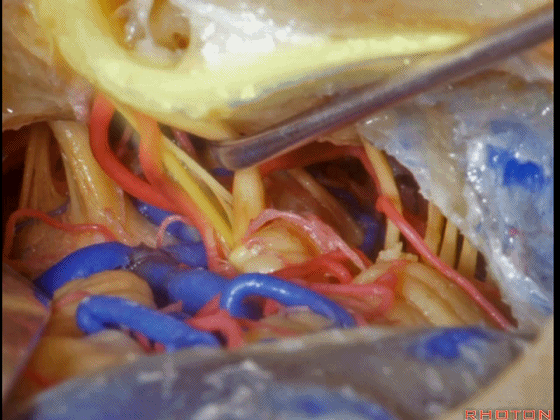
▼这是中间神经
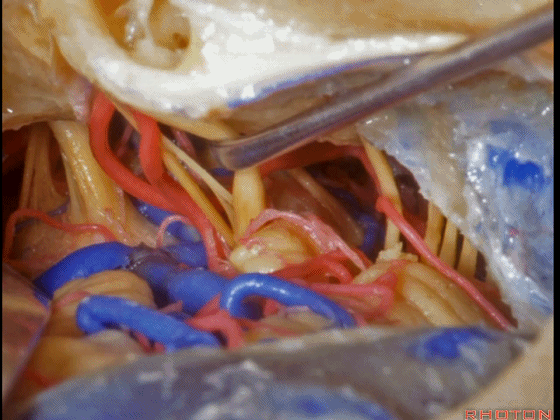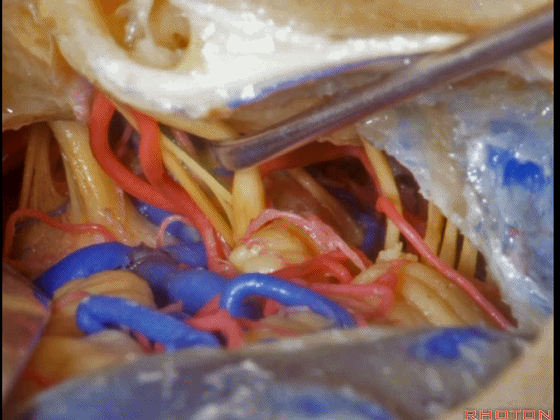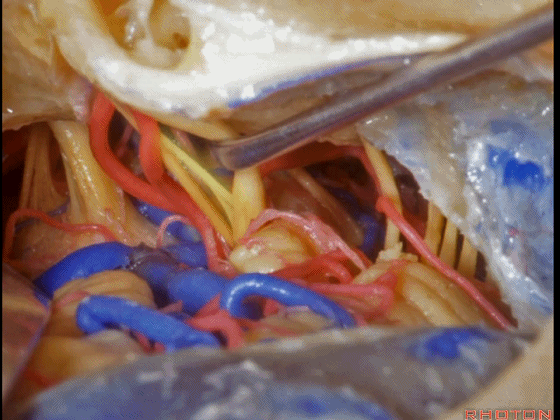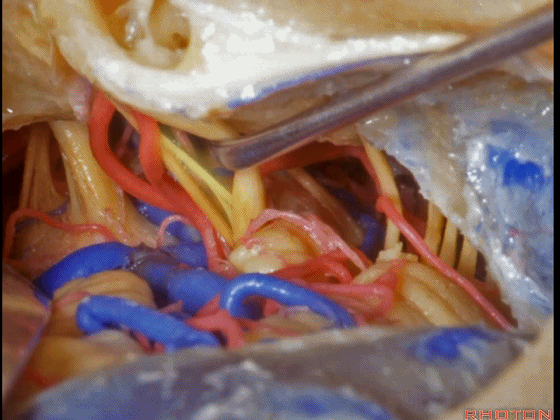
▼这是 前庭蜗神经
VIII,
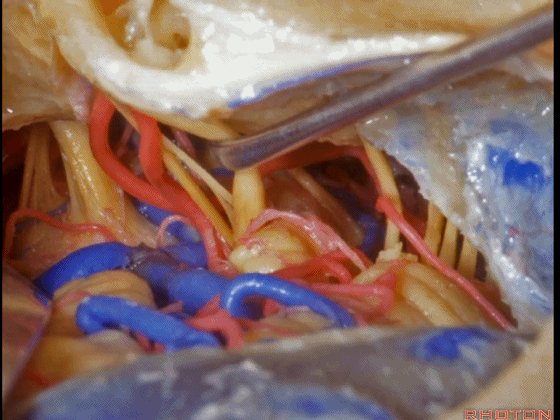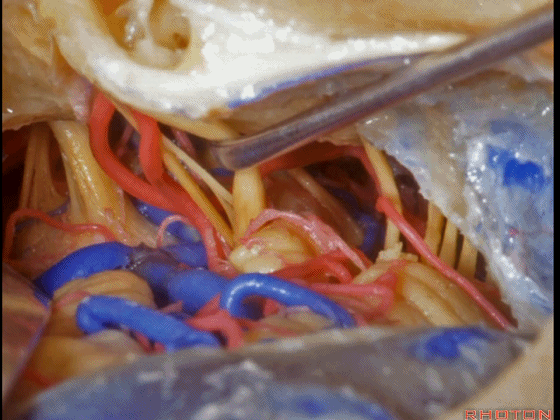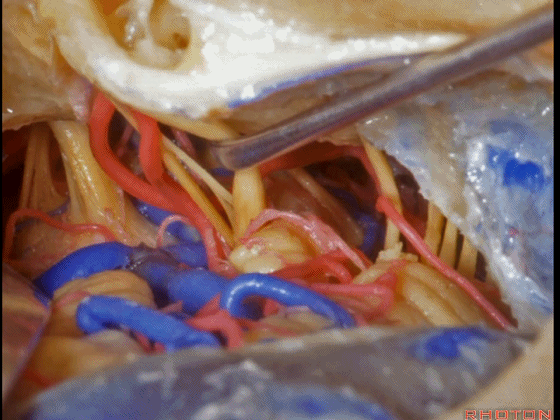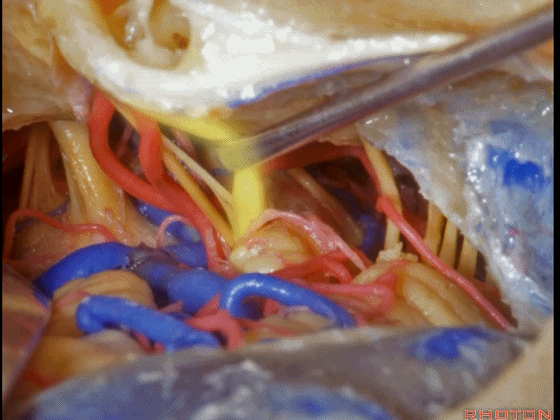
▼这是舌咽神经、迷走神经
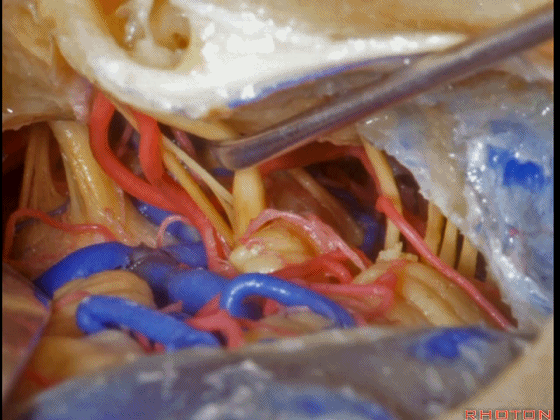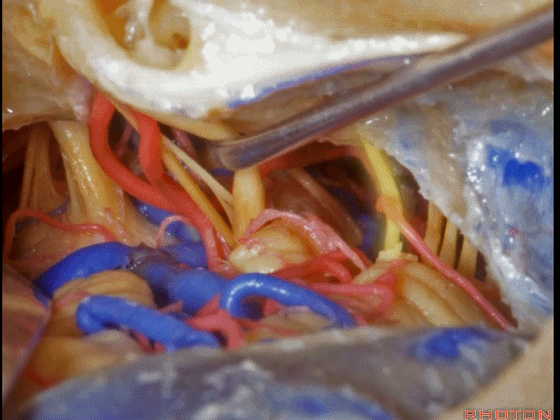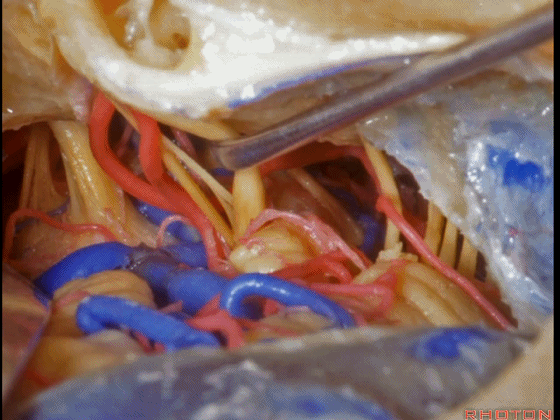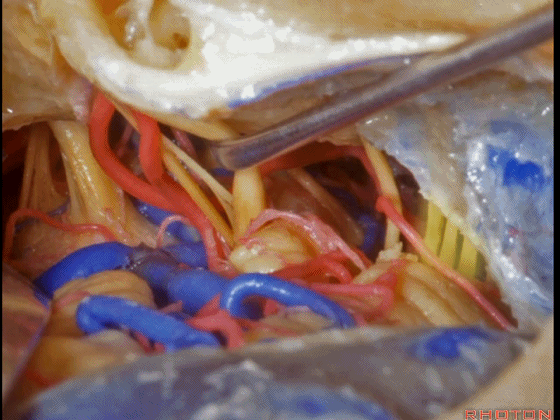
▼这是 外展神经
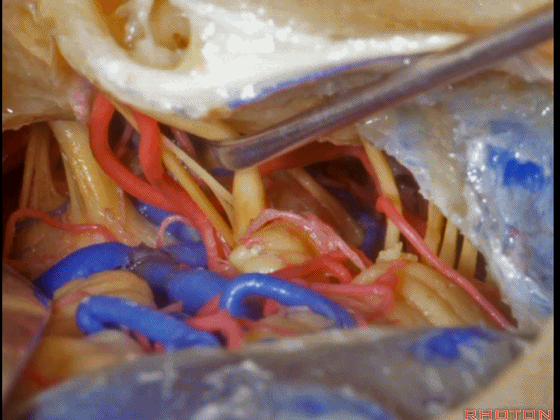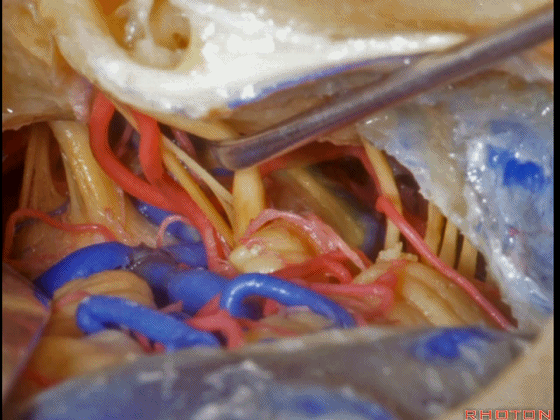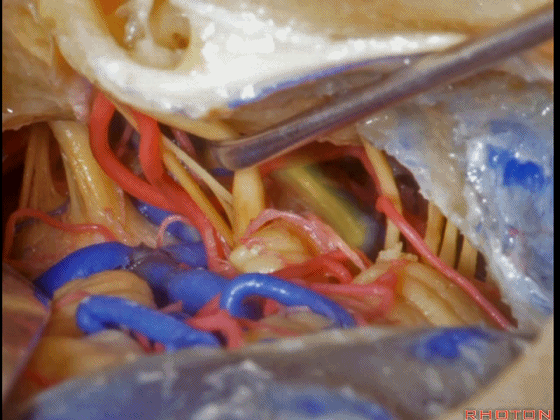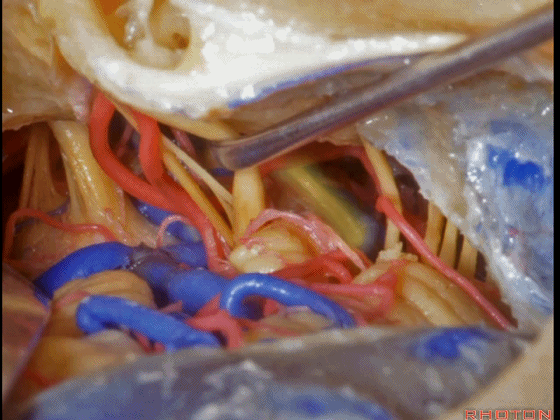
▼这是 三叉神经运动支,其发自感觉根的上内侧。
motor V that arises around the superomedial side of the sensory root.
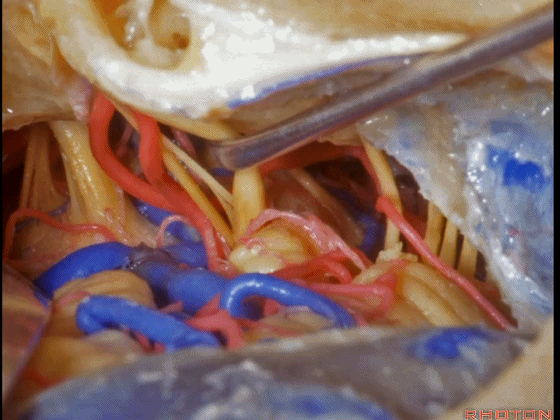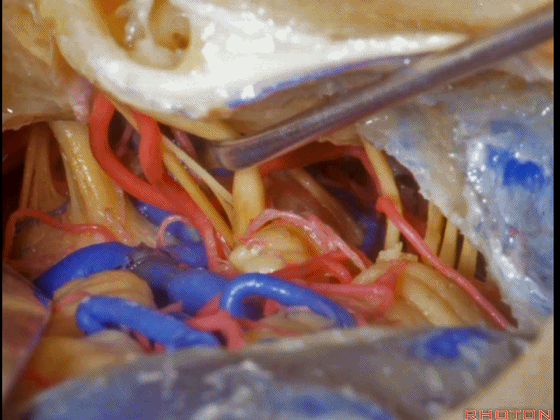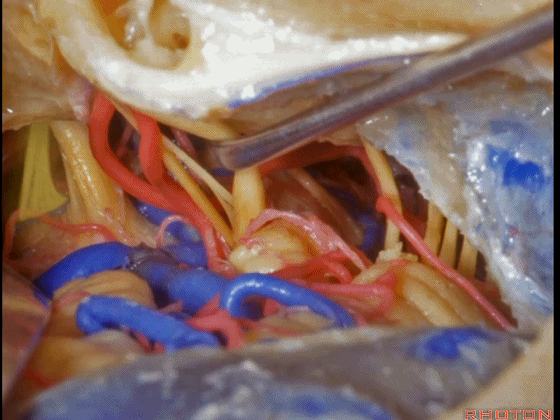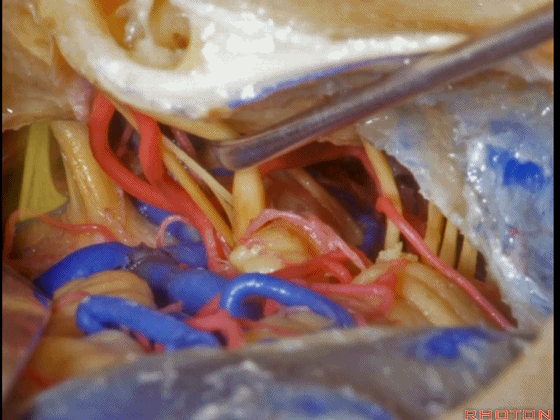
▼有时,可见5~7束运动根在感觉根上内侧进入脑干。
Sometimes, 5 or 6,7 rootlets come into the brainstem superomedial to the sensory root.
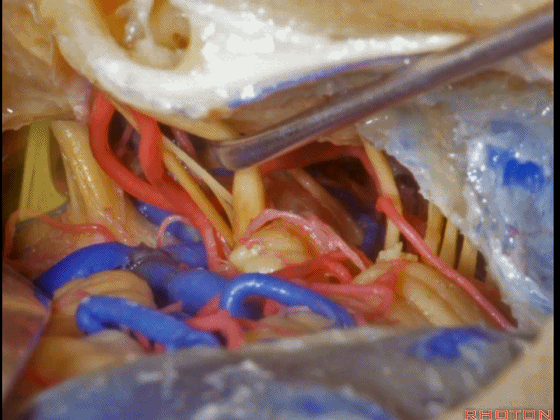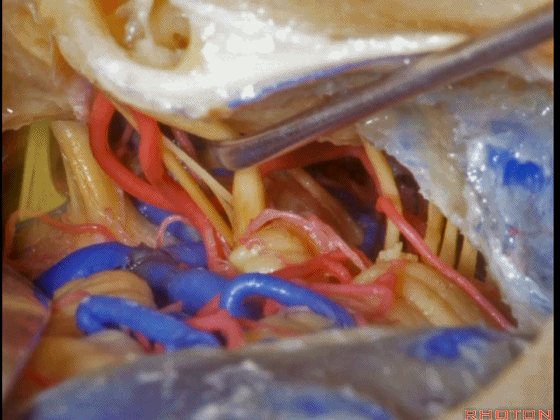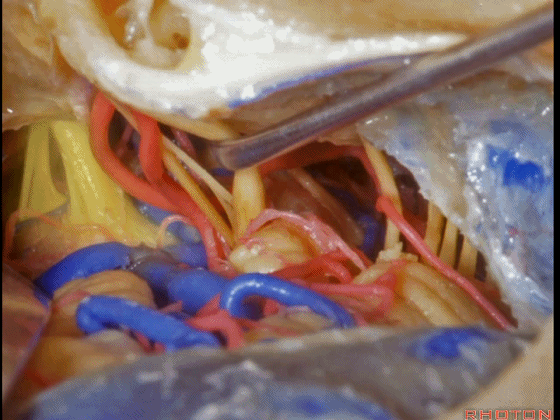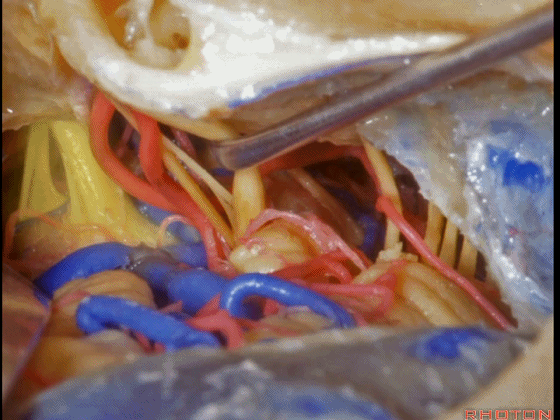
▼这是 鼓膜
And, here we just see the tympenic membrane,
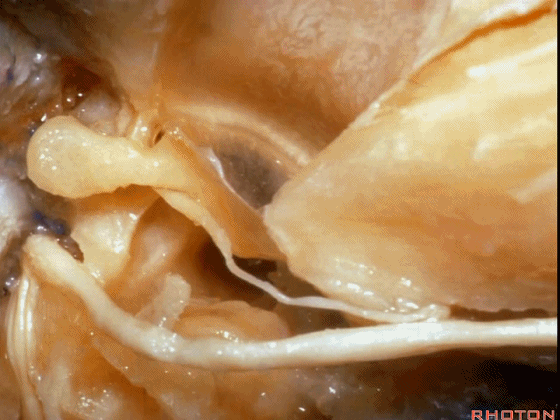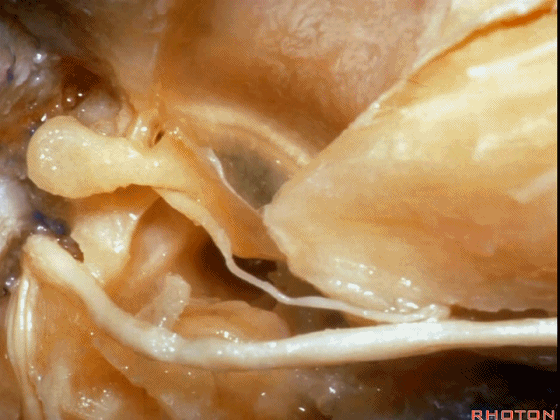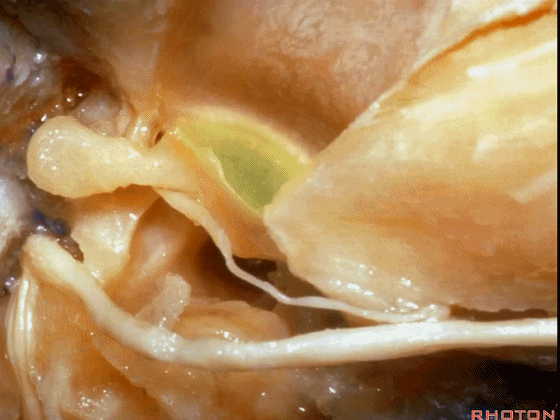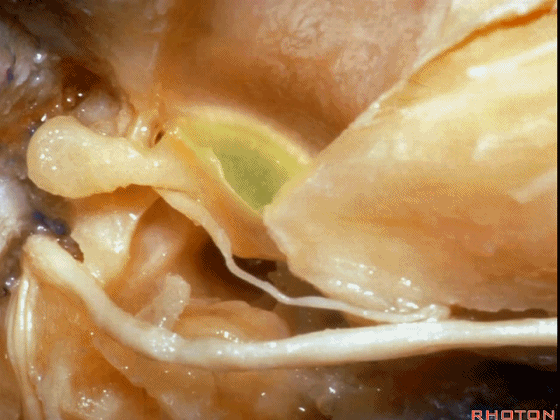
▼这是 鼓索
chorda tympani,
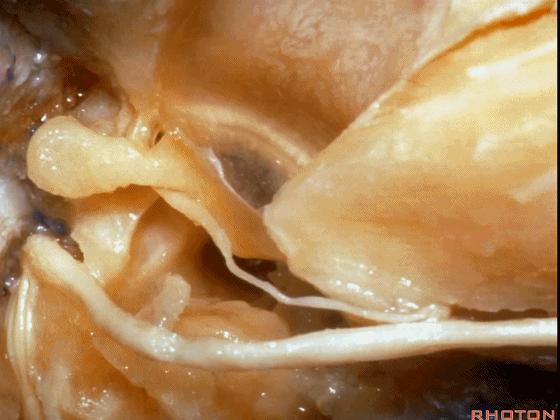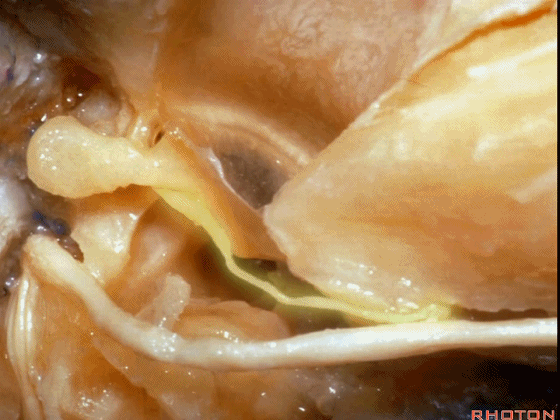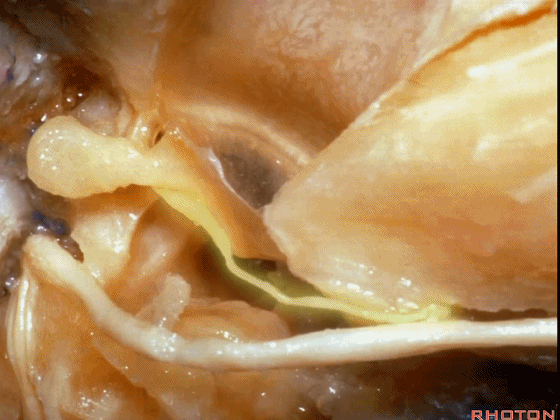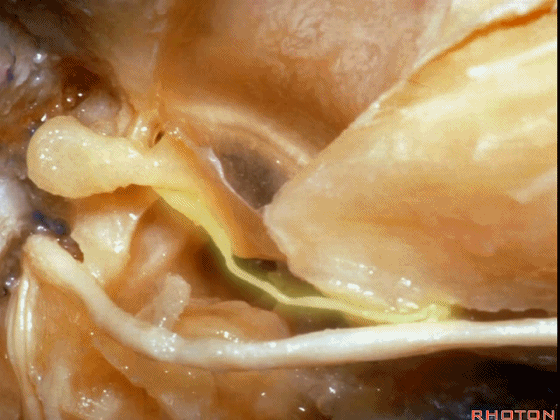
▼这是 面神经的乳突段。
what segment of facial...mastoid,
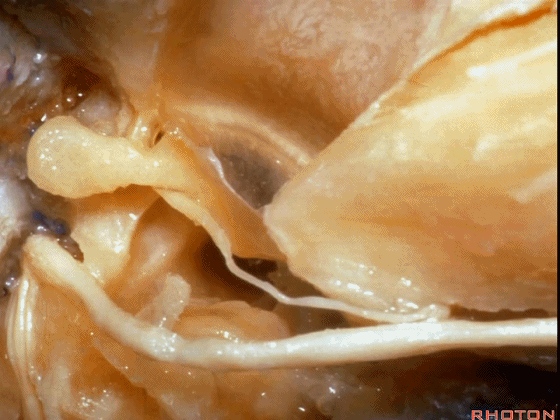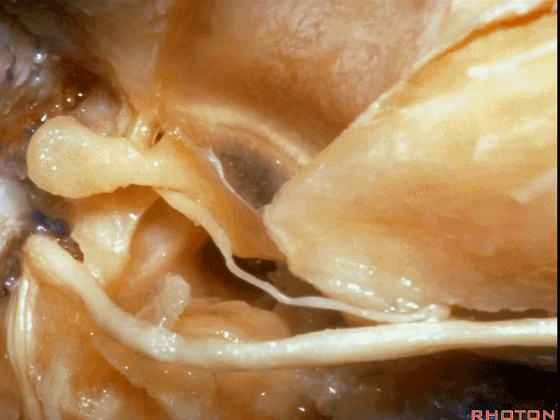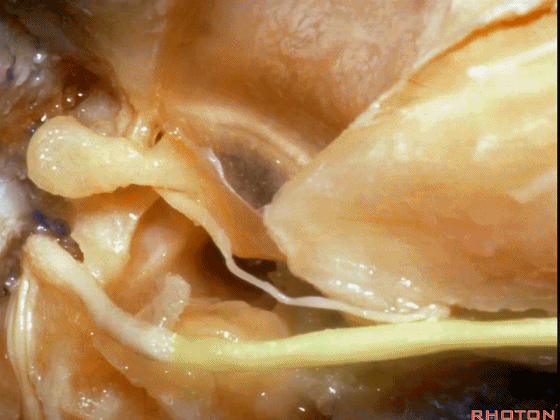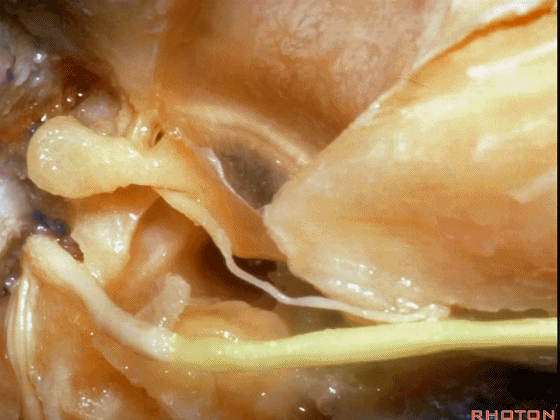
▼这是 面神经鼓室段
tympenic segment
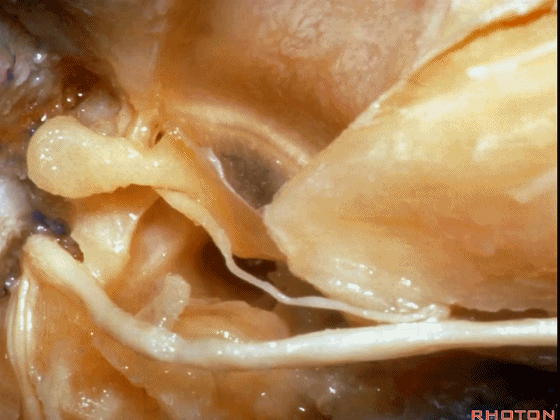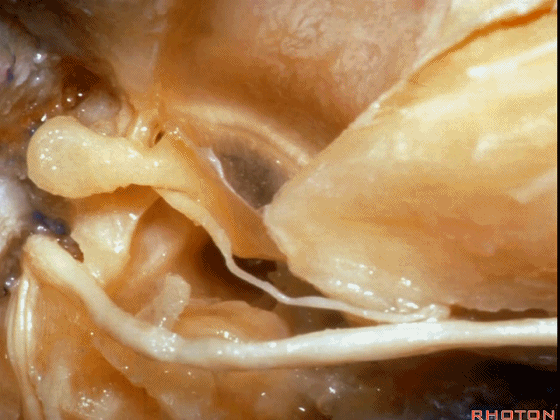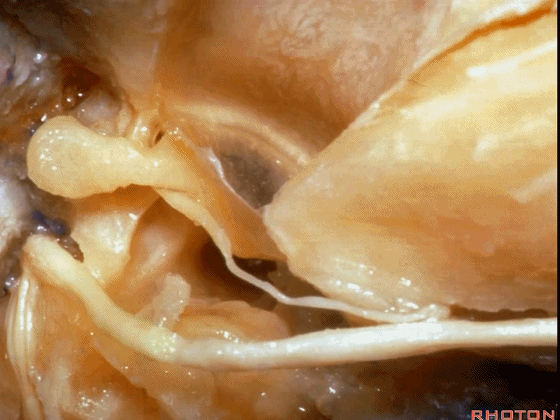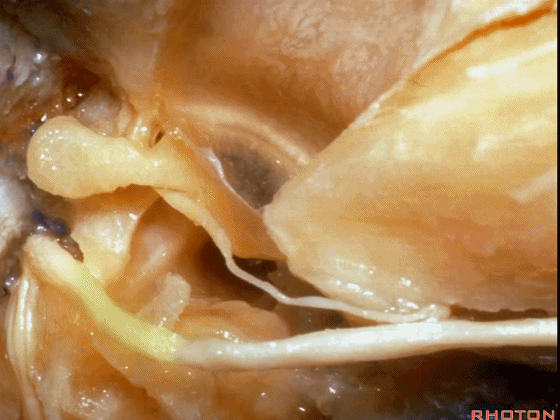
▼面神经鼓室段,走行于镫骨上方,镫骨连于卵圆窗。下图示镫骨
tympenic running above the stapes sitting in the oval window.
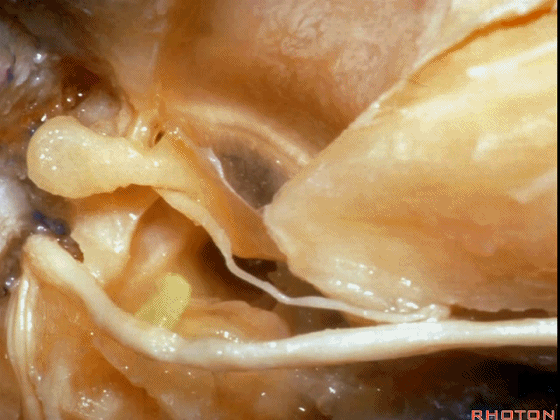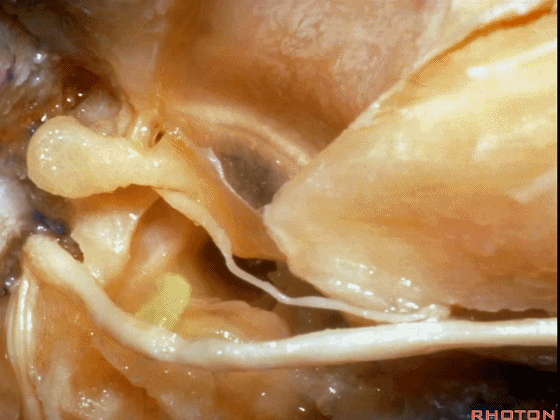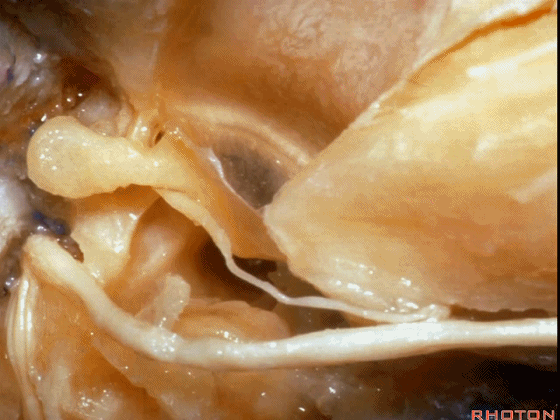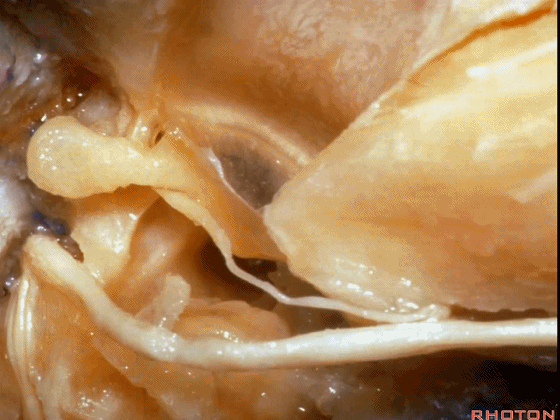
▼这是 膝状神经节
And here's the geniculate ganglion here.
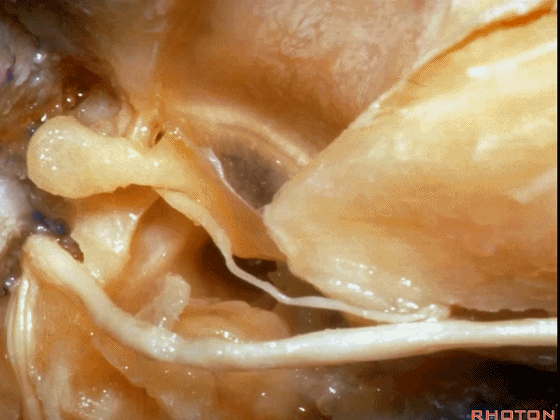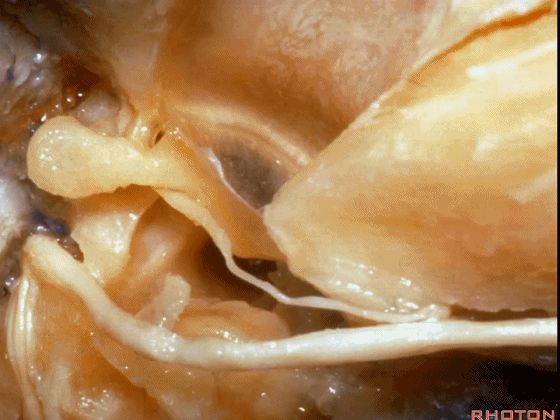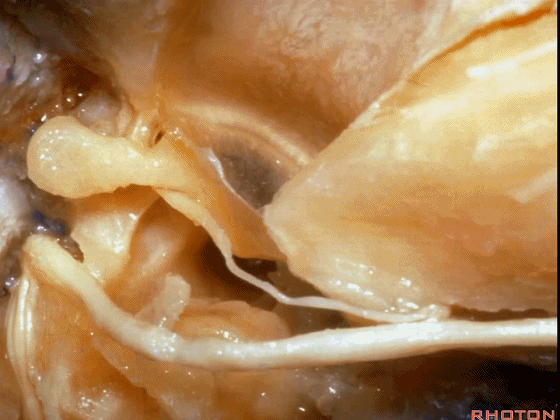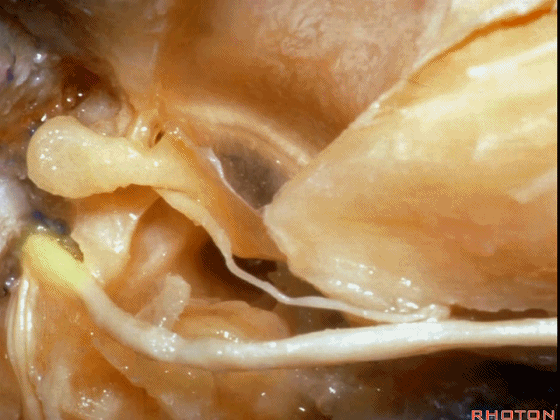
▼对面神经进行移位时,需处理起自该处的岩浅大神经(下图)
If you wanna move a facial nerve that right here where the greater petrosal nerve arises,
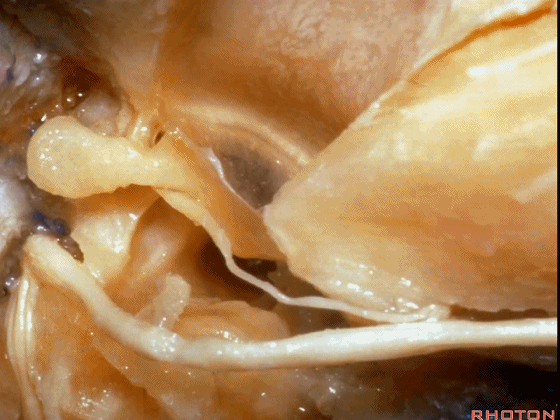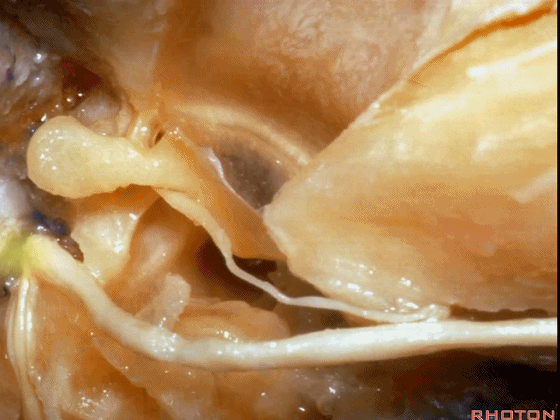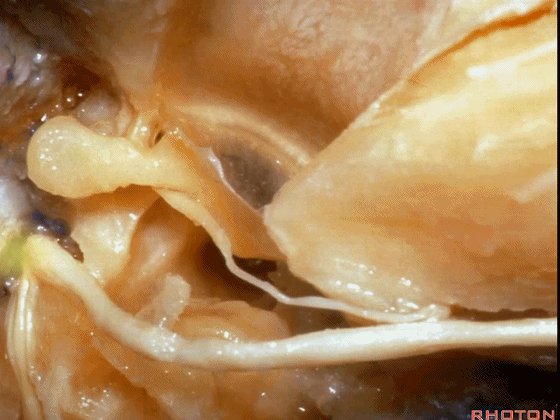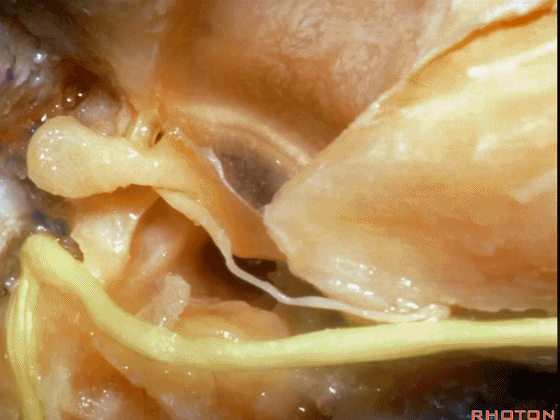
▼离断岩浅大神经后可移位面神经至后方,从而作一经耳蜗入路,但这常导致术后暂时性的完全性面瘫,其恢复程度也仅能达到患者闭眼。
if you divide that you can move the facial nerve posteriorly, like this, to get in for a transcochlear approach, but that always results in a temporary complete facial palsy that rarely or uncommonly recovers the better than a retrieve which some eye closure.
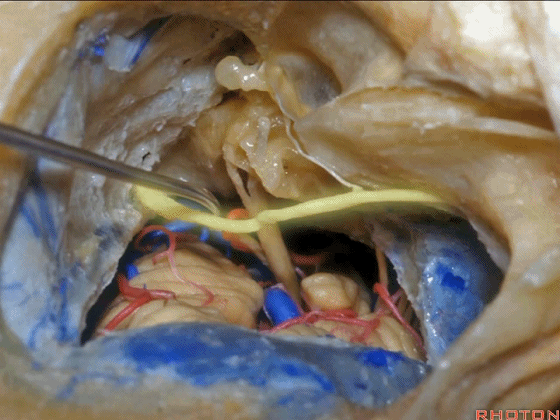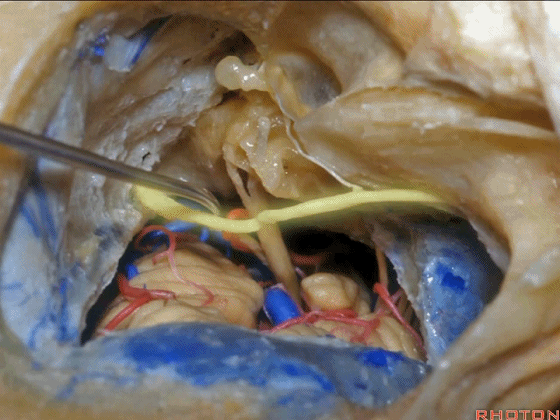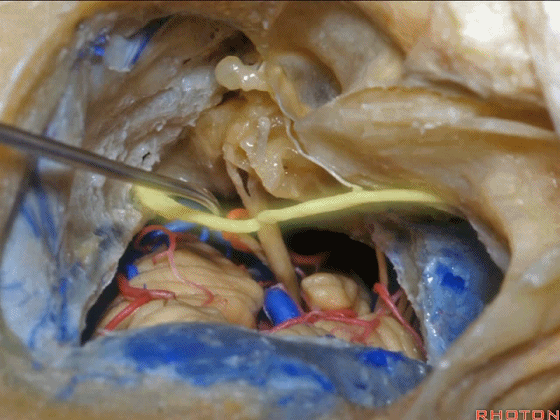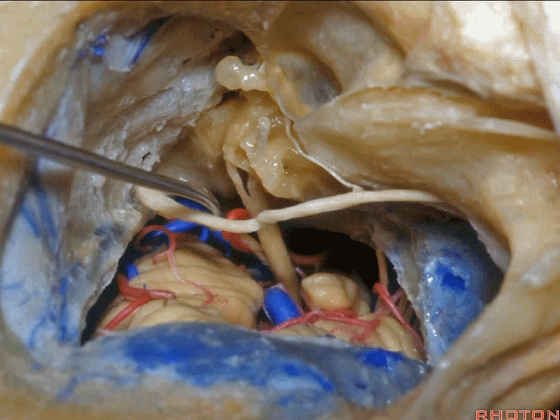
▼一旦进行面神经移位后,即可显露岩尖,将耳蜗磨除,即为 经耳蜗入路。
So, once you work around or move the facial nerve back, you can get into the petrous apex, into the cochlea, drill it out in a transcochlear approach,
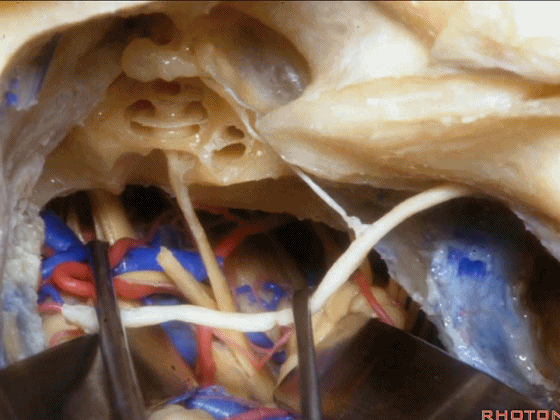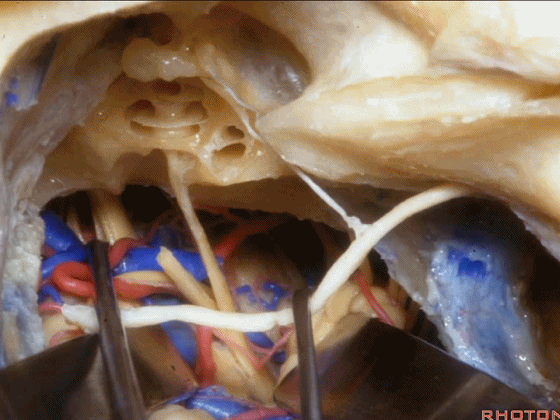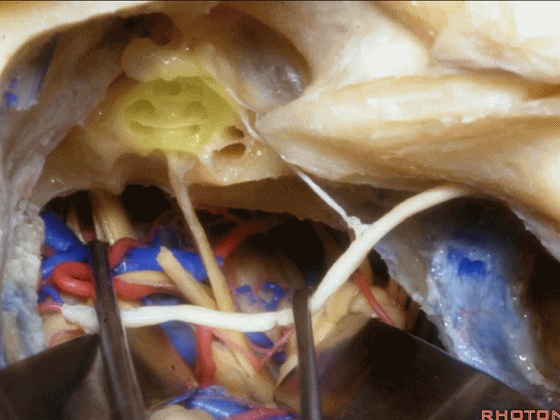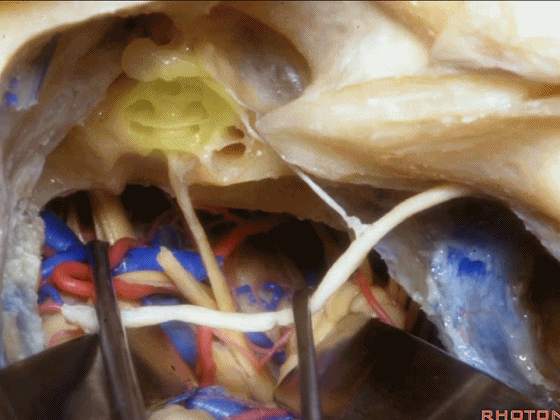
▼这一入路可暴露至岩尖,至三叉神经下方,至基底动脉侧方,外展神经旁。
and then, that delivers you through the petrous apex, below V, down to the side of the basilar, adjacent VI.
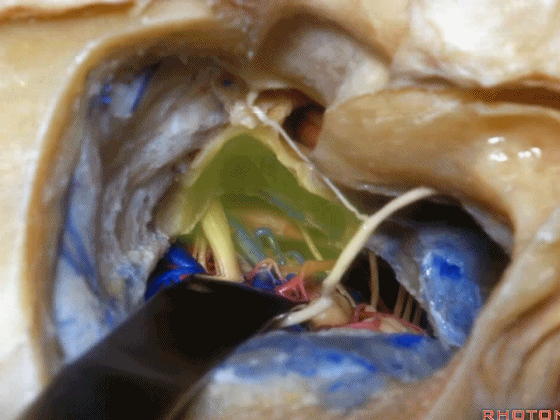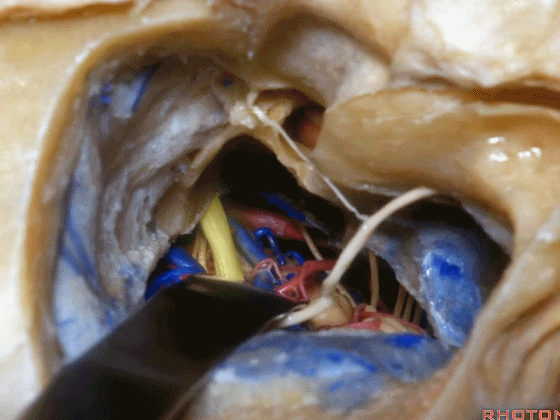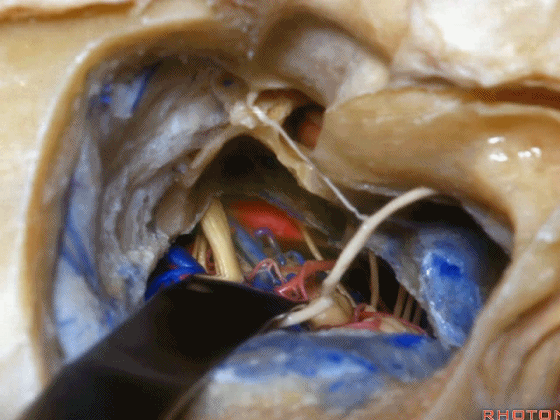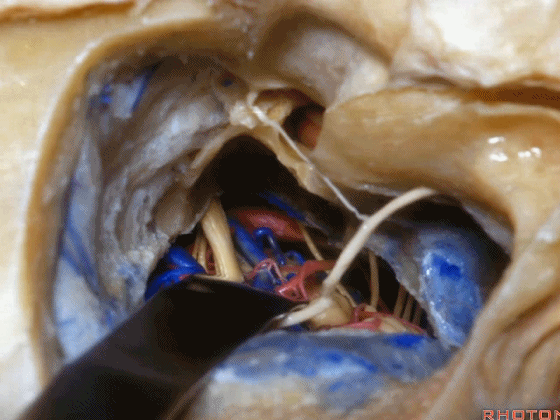
▼这就是暴露后的术野。斜坡侧方、岩下窦、外展神经
The exposure looks like this, side of clivus, inferior petrosal sinus.through the inferior petrosal sinus.
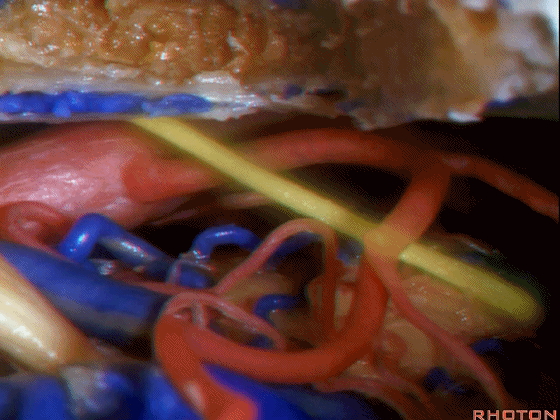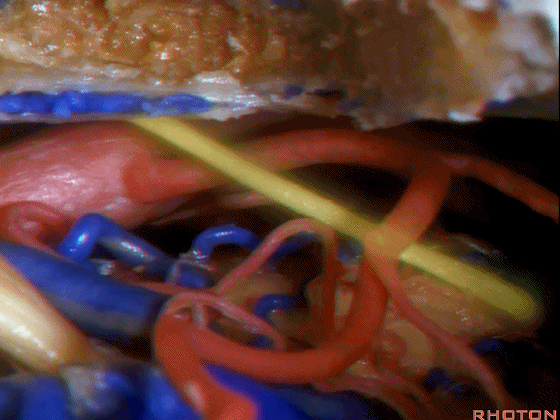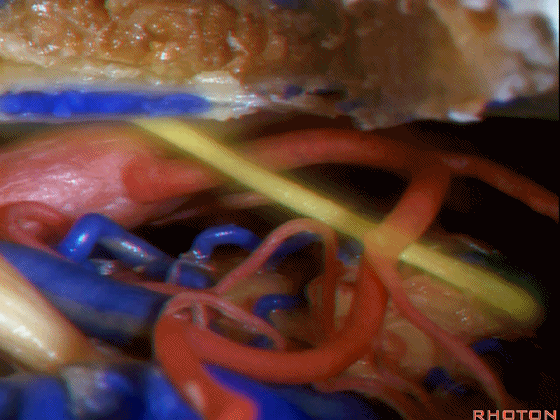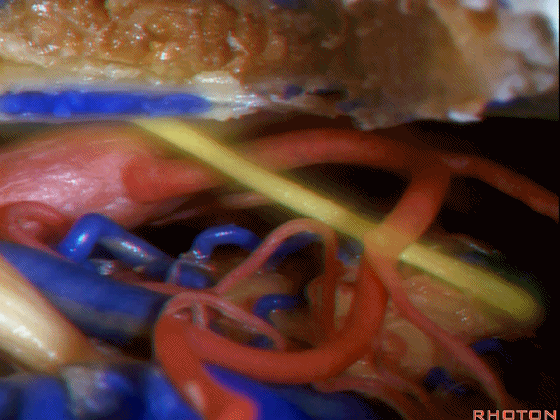
左侧乙状窦前幕上下联合入路
▼随后,我们可行颞枕部开颅(以左侧为例),作乙状窦前入路。这里我们已经磨至迷路(下图)
And then you can combine that in a presigmoid approaches with a temporal occipital craniotomy.Here we've drilled out the labyrinth
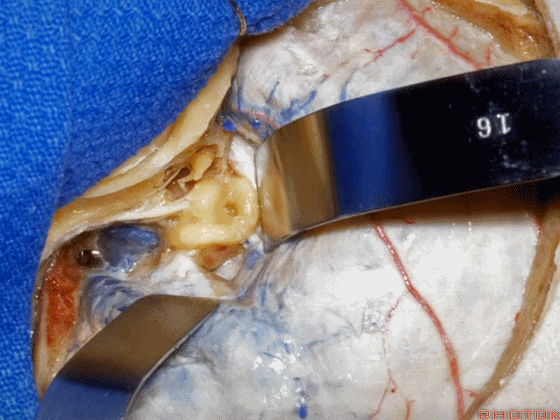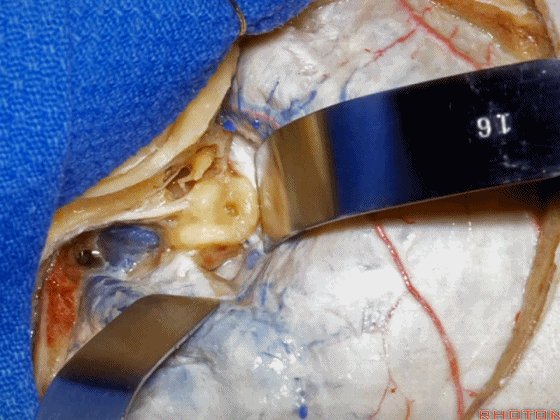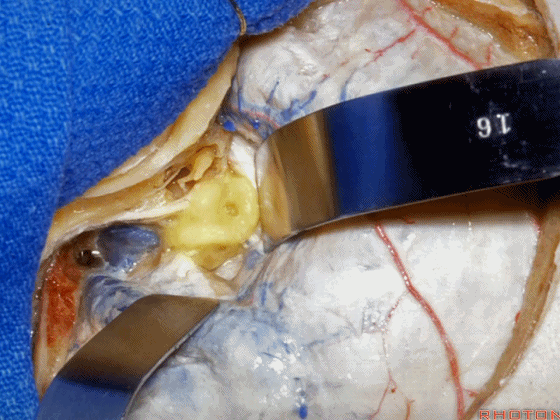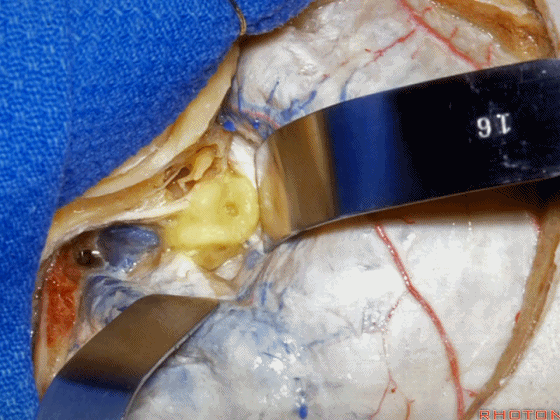
▼这是上半规管、后半规管、外侧半规管
we see...what canal...faces middle fossa, temporal lobe? Superior,lateral,posterior,
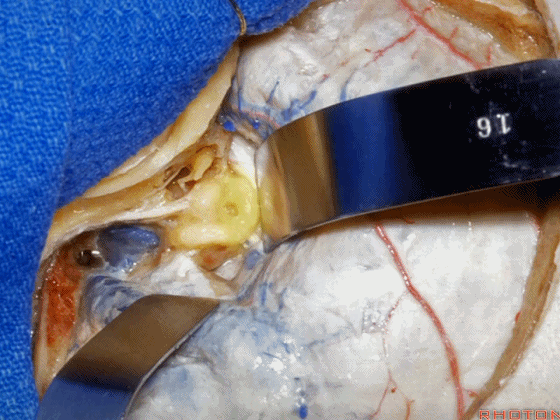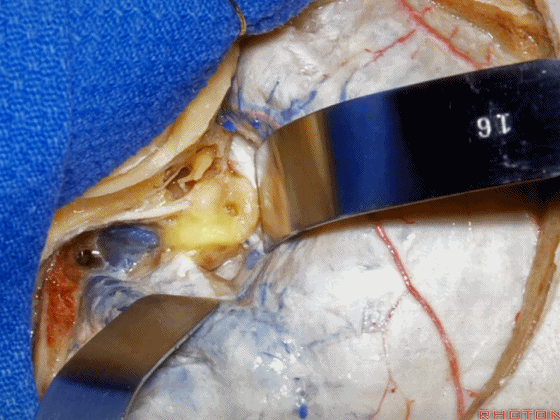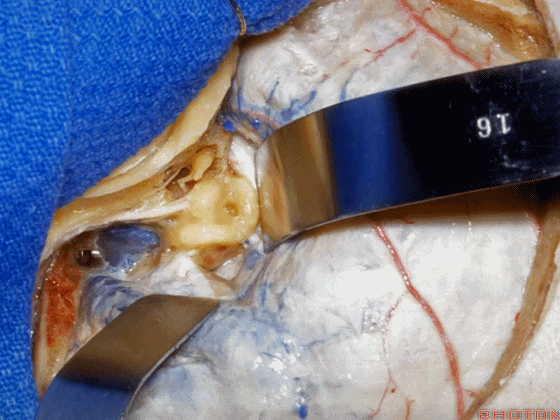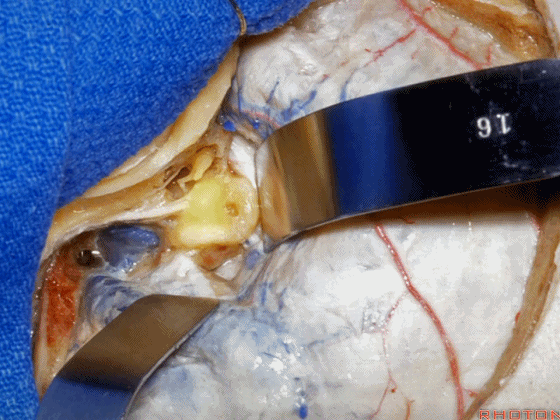
▼这是 内淋巴囊
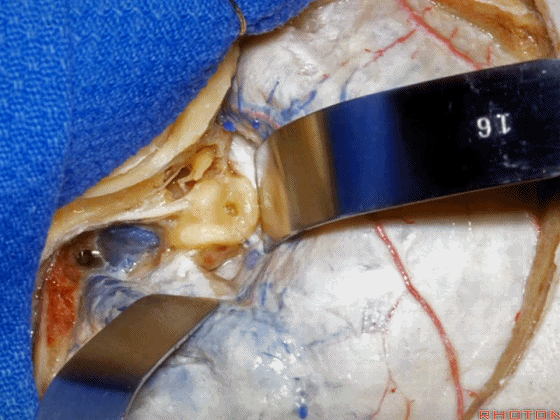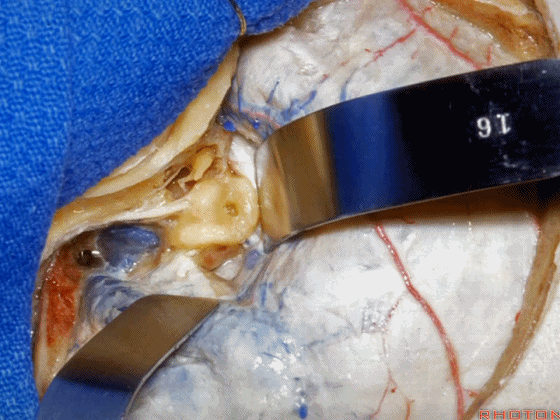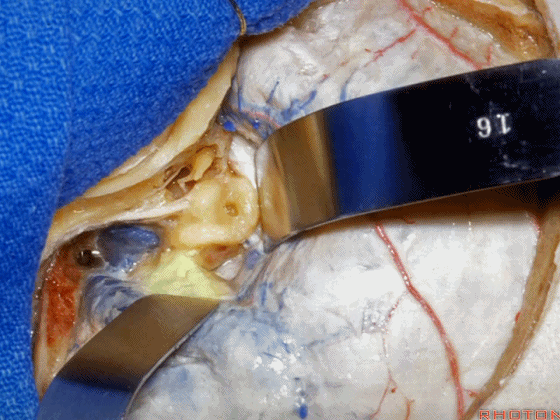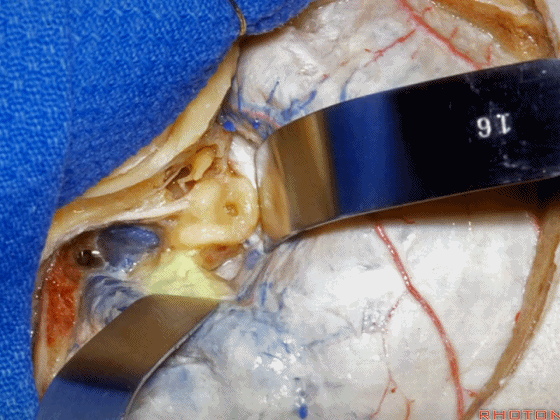
▼接下来,我们按下图打开颞叶硬膜,并切开岩上窦(下图)
And in this approach then, we open the temporal dura, divide across the superior petrosal sinus.
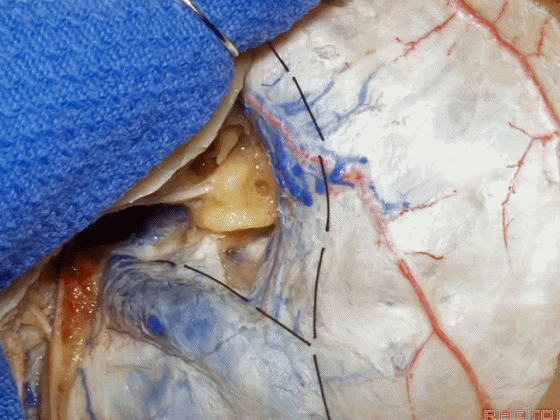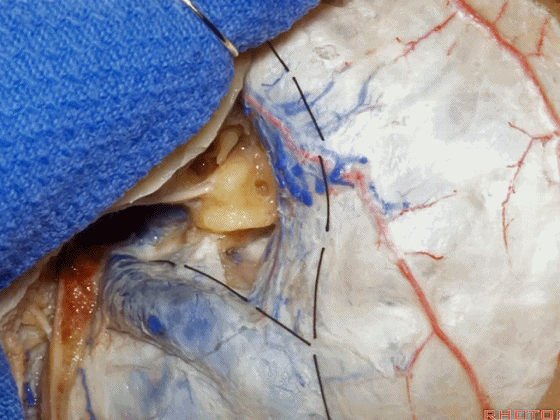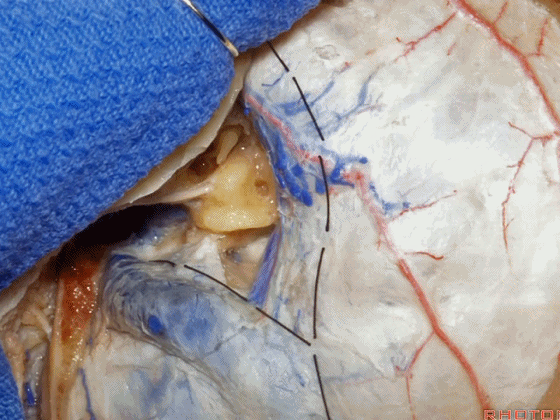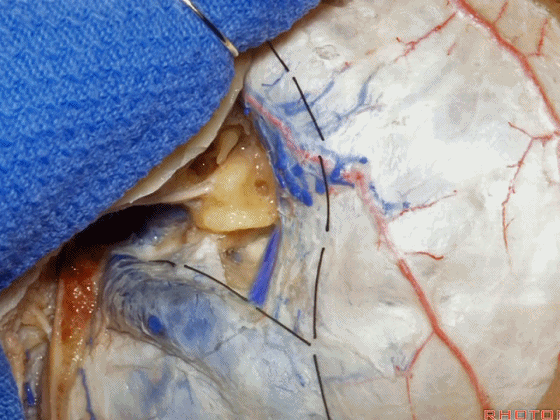
▼位于颞底硬膜、乙状窦、骨迷路之间的硬膜称之为 Trautmann's三角。
between the sigmoid and the labyrinth, we call Trautmann's triangle.
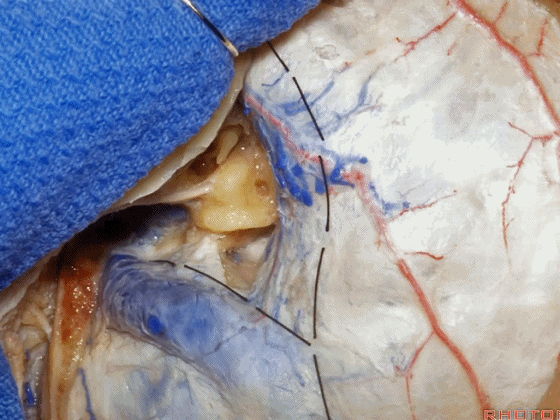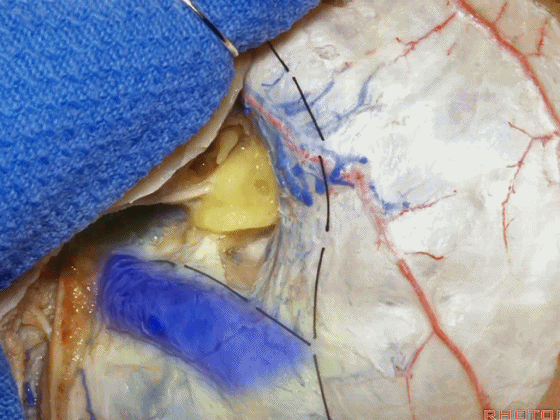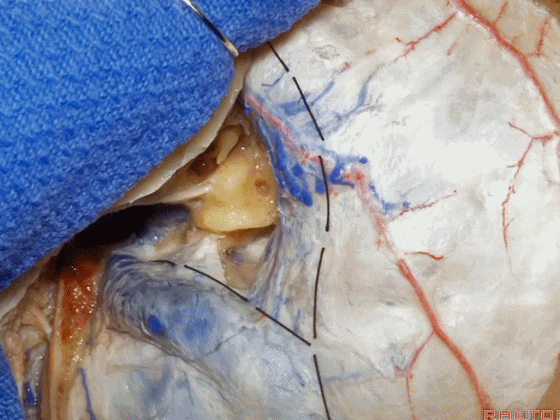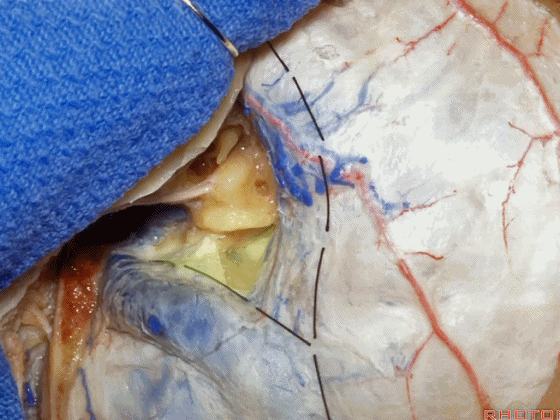
▼我们常同时切开内淋巴囊。这是暴露的后颅窝,面神经、前庭蜗神经、舌咽神经、迷走神经。
You usually divide through the endolymphatic sac. And this is the posterior fossa exposure, VII, VIII, IX, X.
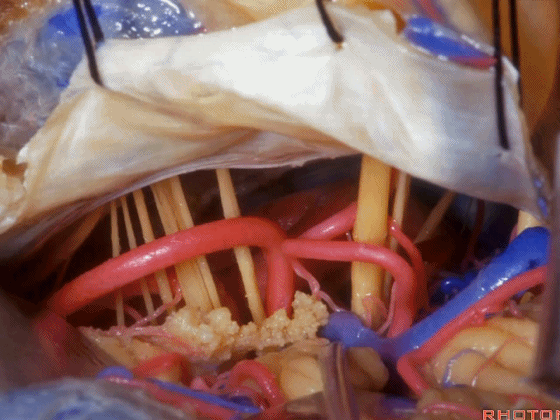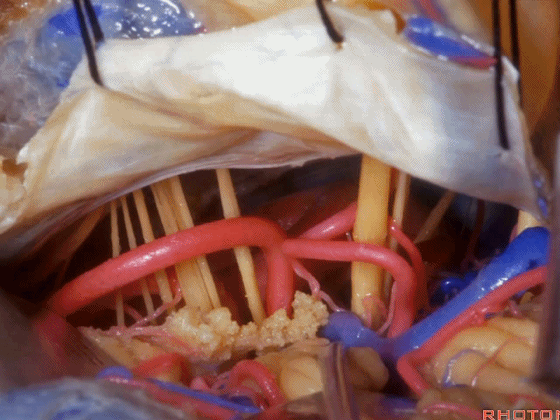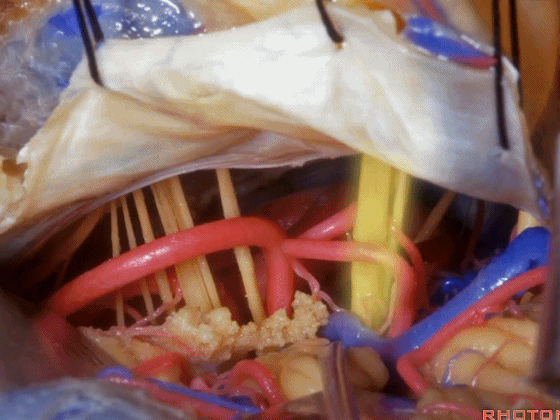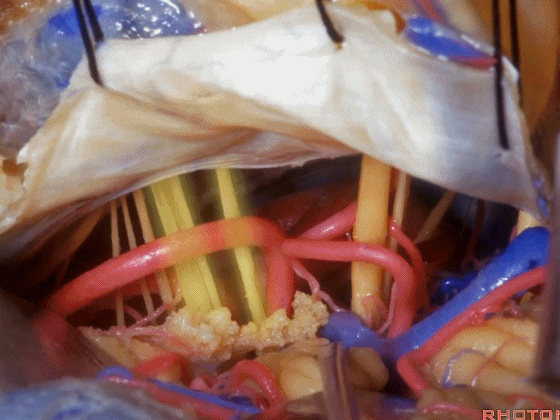
▼随后我们切开小脑幕
And then we divide the tent
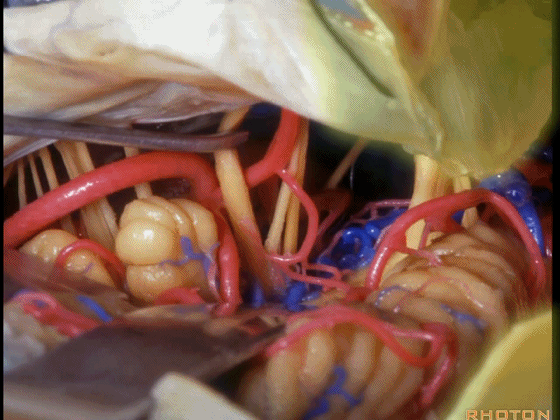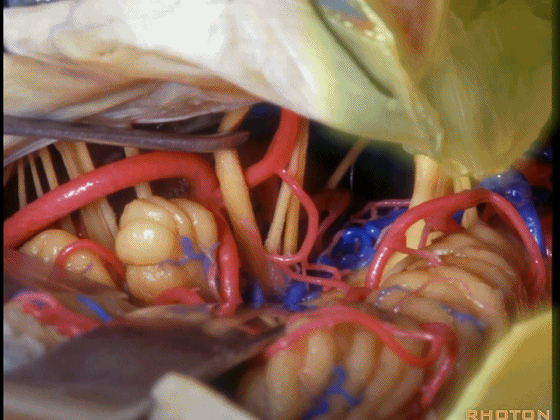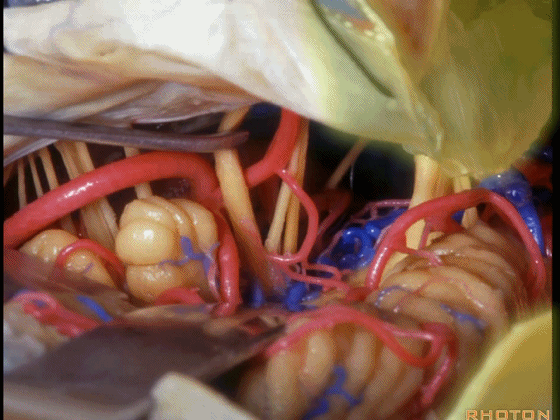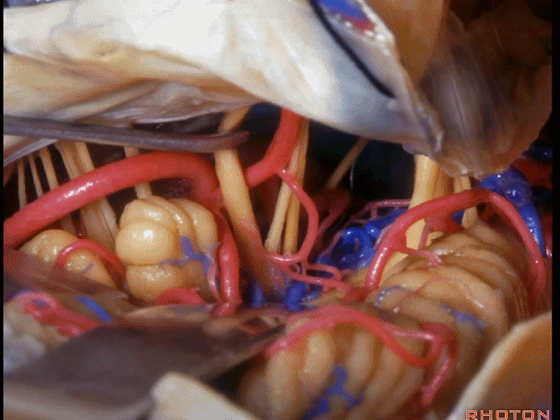
▼可见三叉神经及其运动根
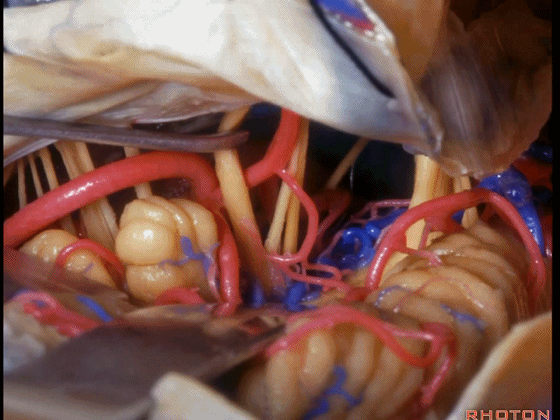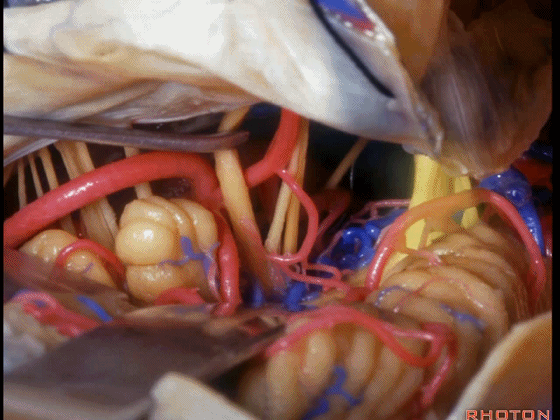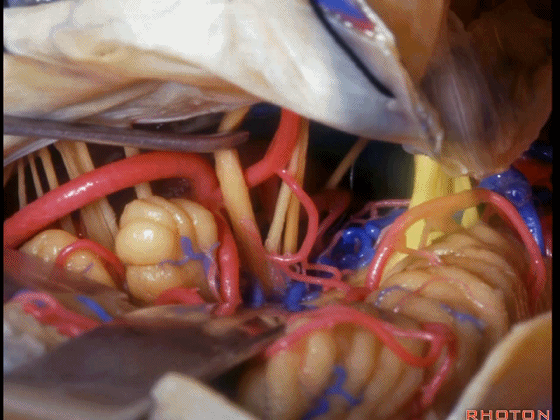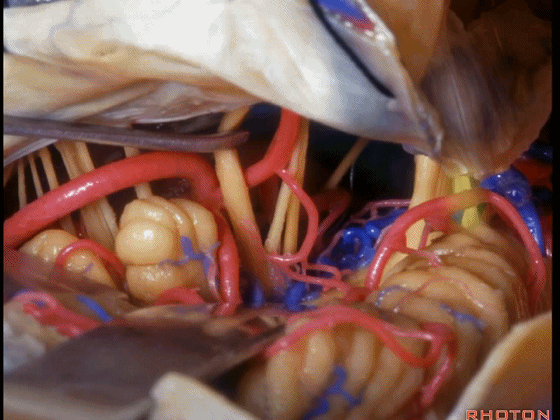
▼可见面神经、中间神经、前庭蜗神经。
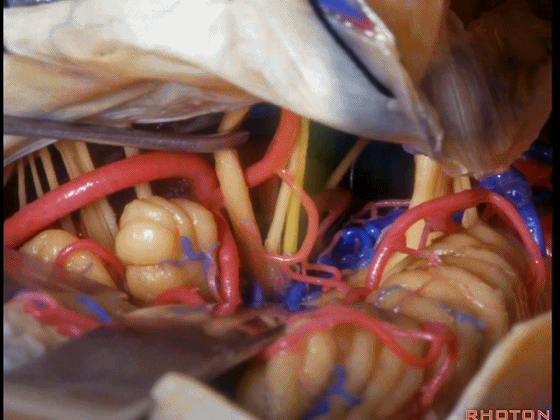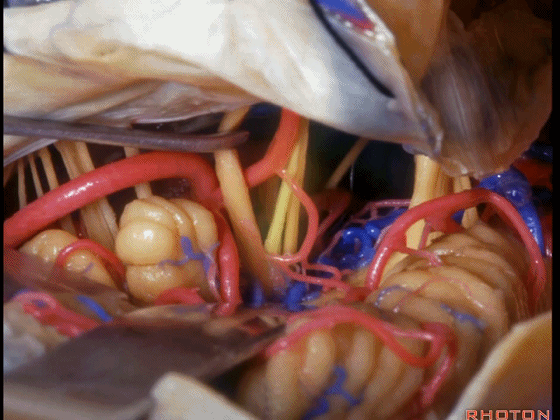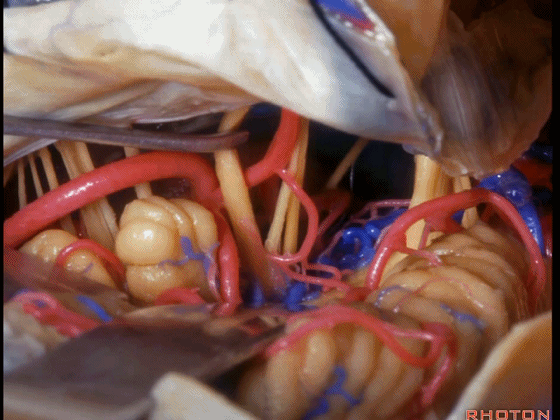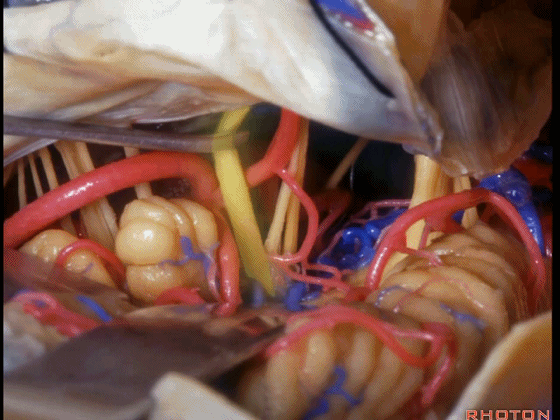
▼随后我们磨除迷路,即可暴露内听道(下图)。这就是 经迷路入路。
And then, you drill out the labyrinth, you have access to the meatus.This is a translabyrinthine exposure.
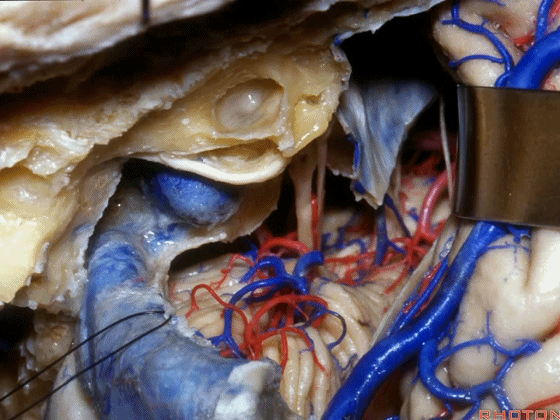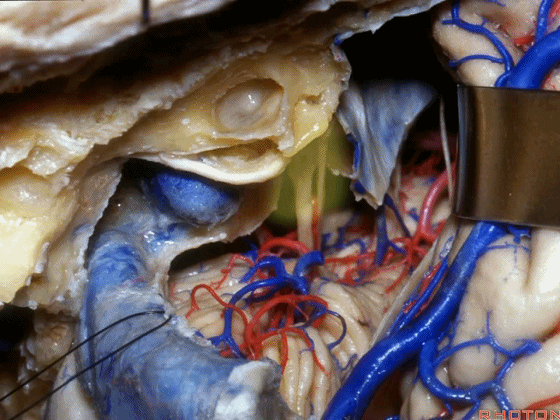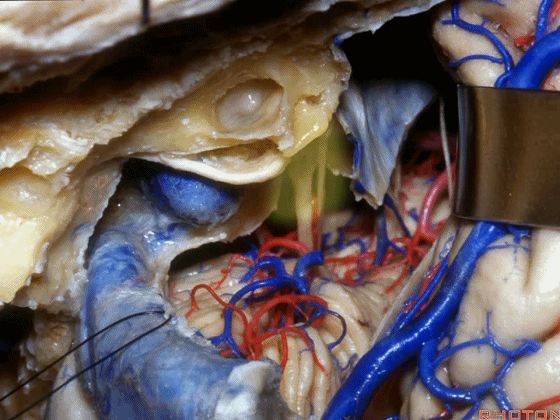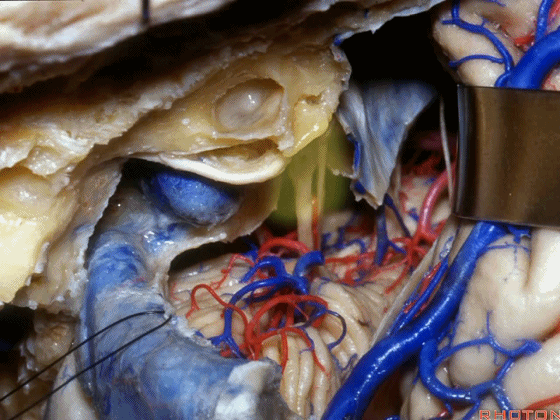
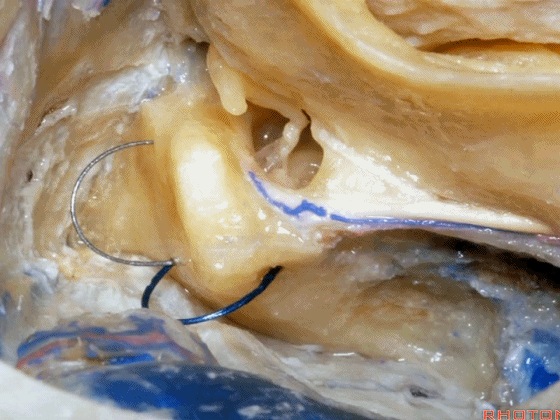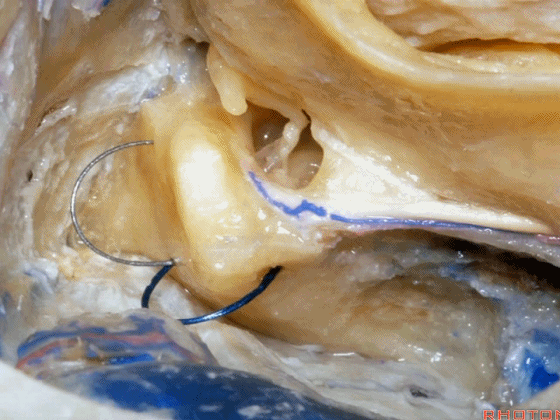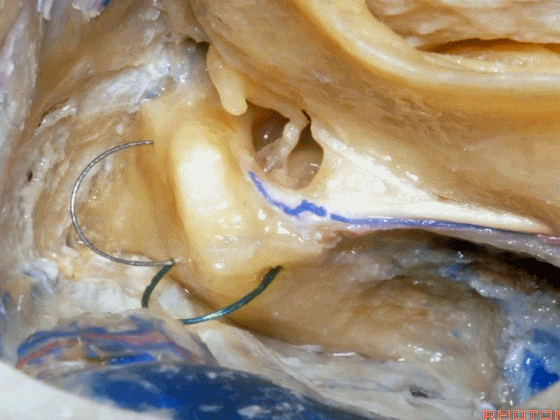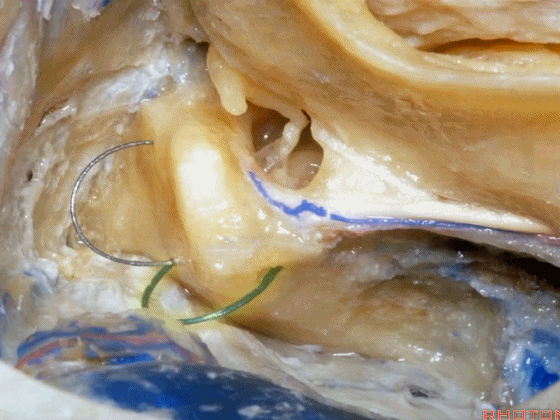
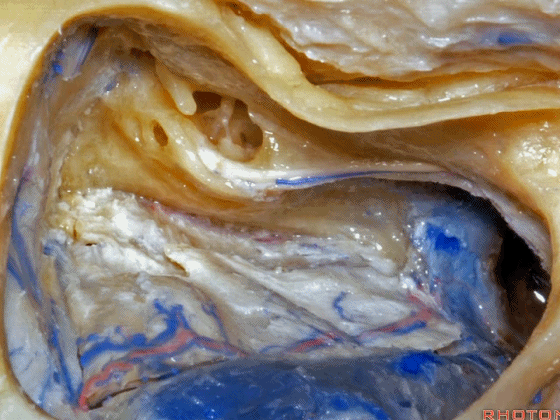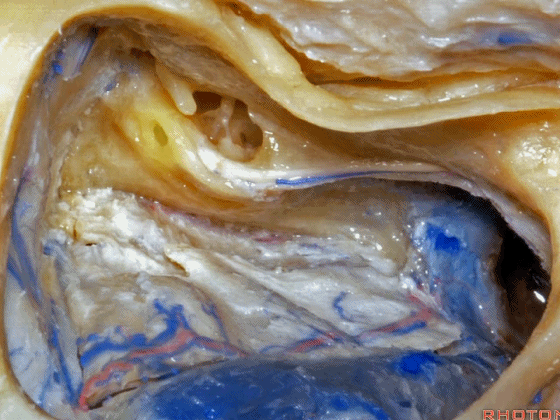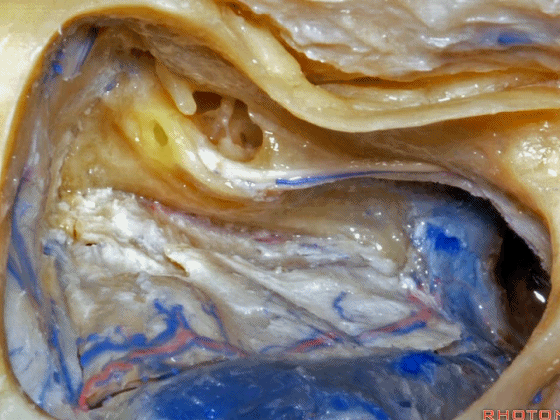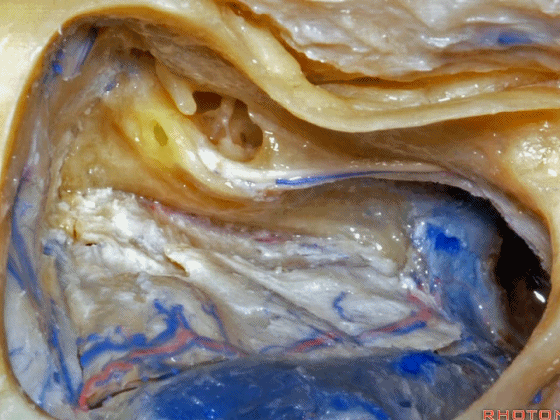
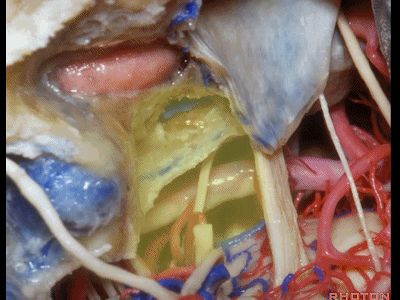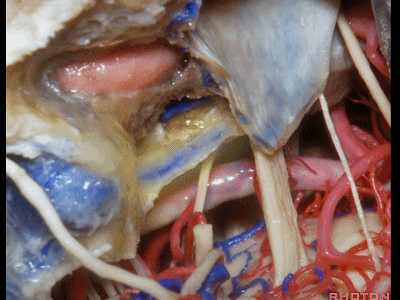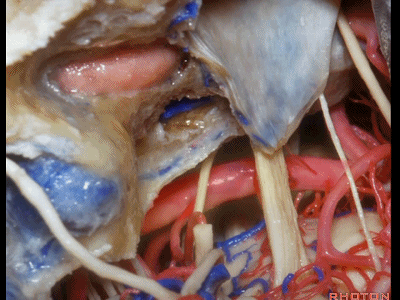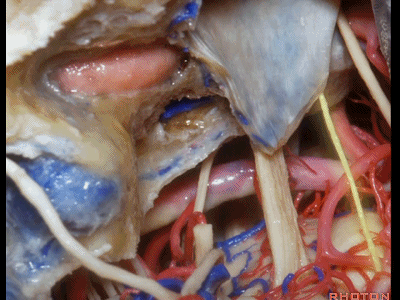
▼在切开小脑幕和颞叶硬膜时,我们需注意保护Labbe静脉(下图)。
Always when we divide the tent, we want to...at open the temporal dura, we want to preserve Labbe, it's an important consideration in planning these approaches.
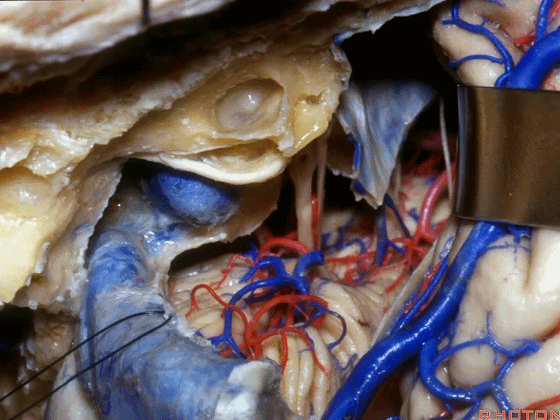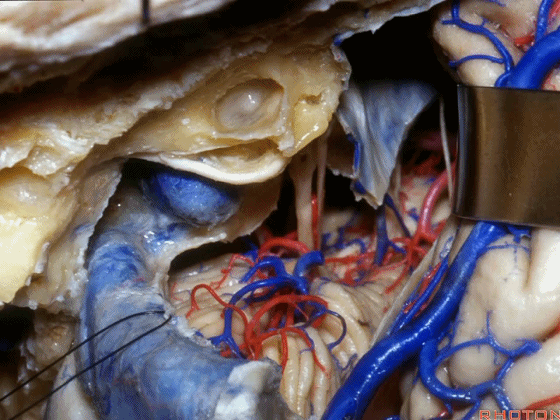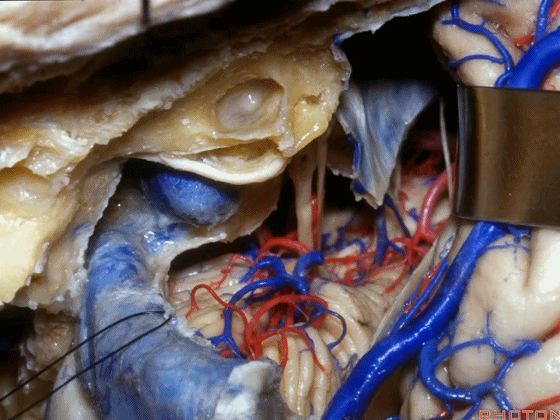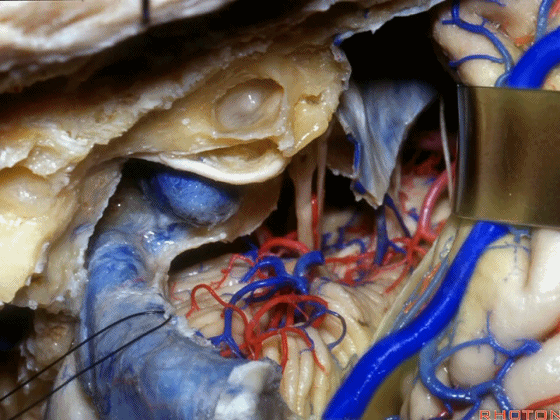
▼而在切开小脑幕时,我们需注意保护滑车神经(下图)。
And then in dividing the tent, we always wanna preserve 4th nerve.
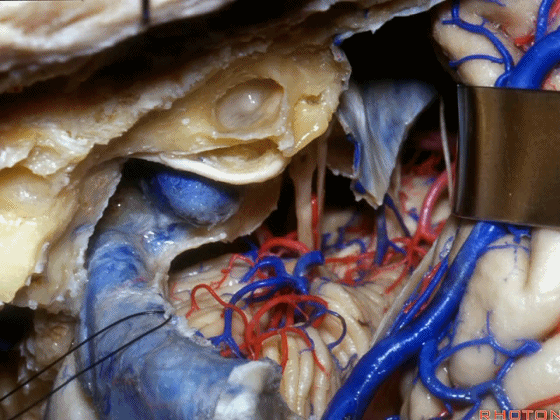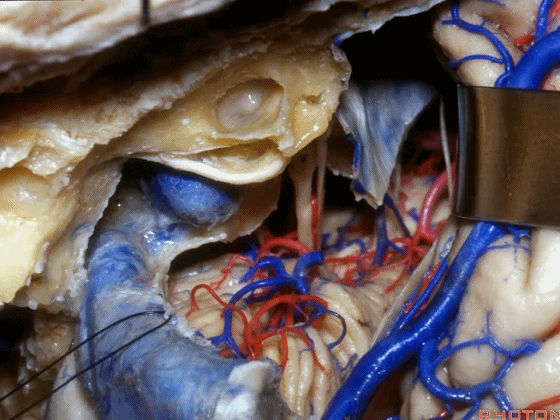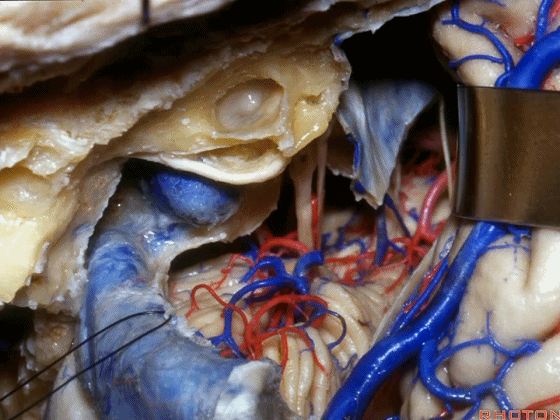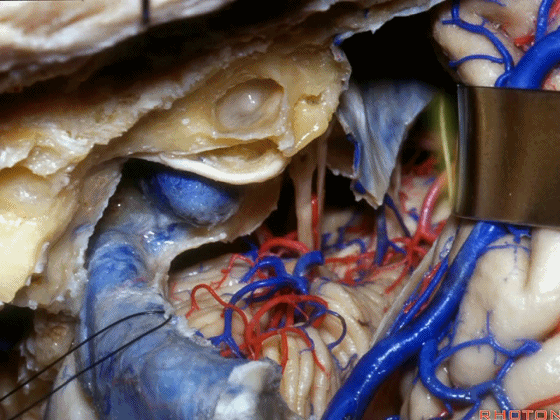
▼接下来可将面神经向后移位,磨除耳蜗,即为 经耳蜗入路。
And then you can move the facial nerve posteriorly,drill out the cochlea
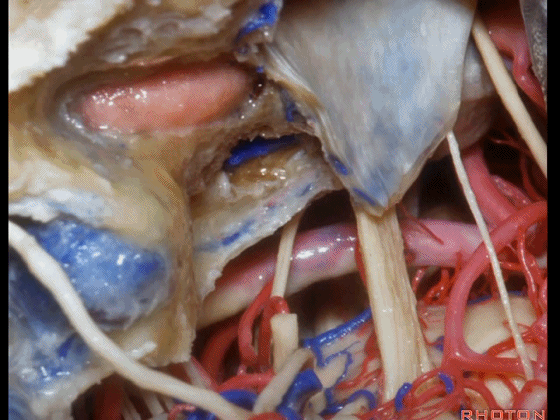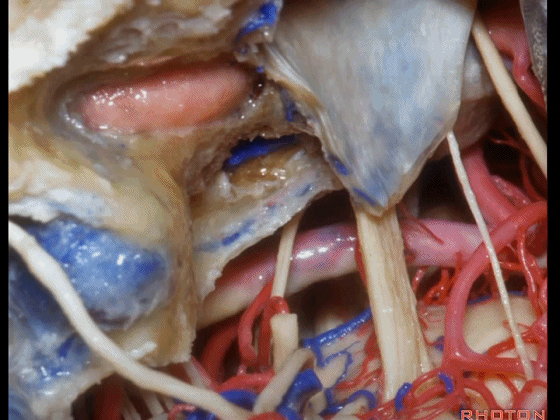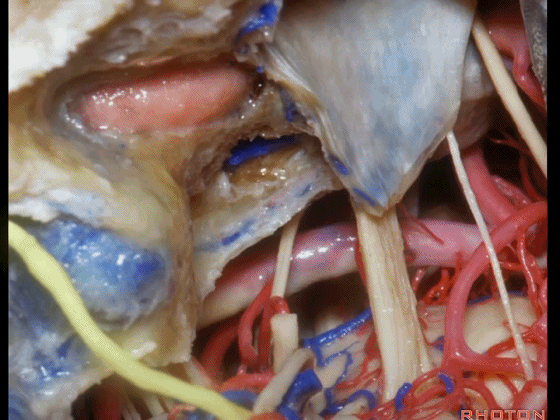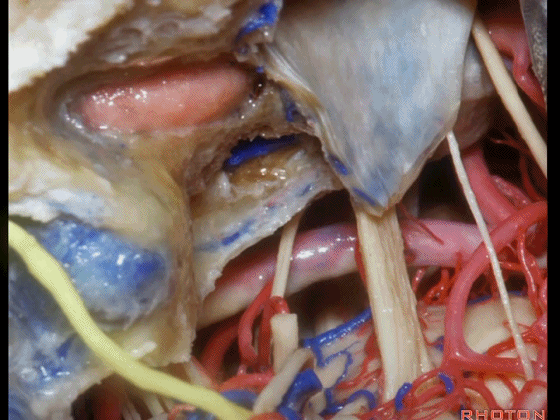
▼经耳蜗入路向下暴露至斜坡侧方、岩下窦、外展神经、基底动脉、滑车神经、动眼神经。
you down to the side of the clivus,the inferior petrosal sinus, 6th nerve, basilar artery, 4th nerve, 3rd nerve.
声明:脑医汇旗下神外资讯、神介资讯、脑医咨询所发表内容之知识产权为脑医汇及主办方、原作者等相关权利人所有。未经许可,禁止进行转载、摘编、复制、裁切、录制等。经许可授权使用,亦须注明来源。欢迎转发、分享。







































![]()