本篇为The Rhoton Collection解剖视频中《Far Lateral Approach and the Jugular Foramen 远外侧入路与颈静脉孔区》一章,笔者进行了重新编排。其中颈静脉孔区解剖相对比较复杂,希望读者对不熟悉的解剖结构自行扩展学习。

本文共139张图片。错误之处,请批评指正!
![]()
远外侧入路与颈静脉孔区解剖
Far Lateral Approach and the Jugular Foramen
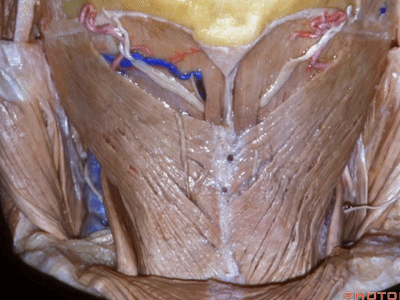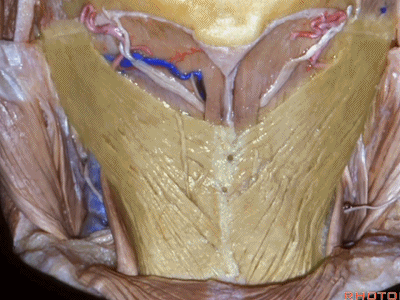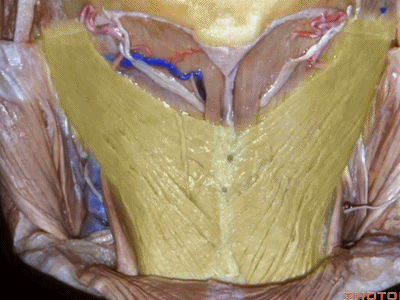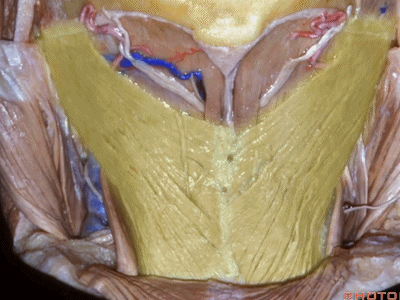
▼今天的话题先从颈后肌群肌肉看起,这是斜方肌(trapezius[trə'pi:zɪəs])
So that we're working in this corner of the skull base. And,Help us with these muscles on the back of the neck. What is this?Trapezius
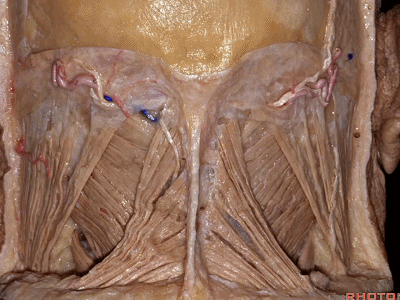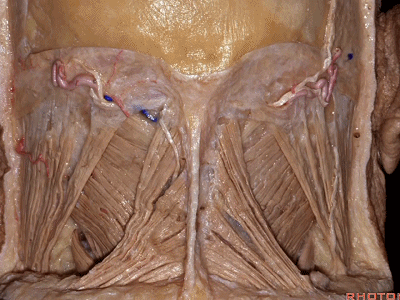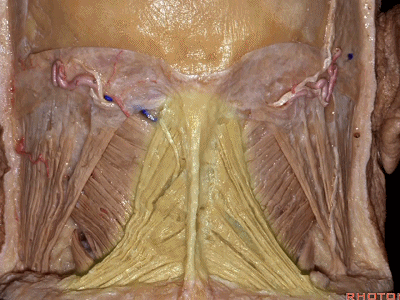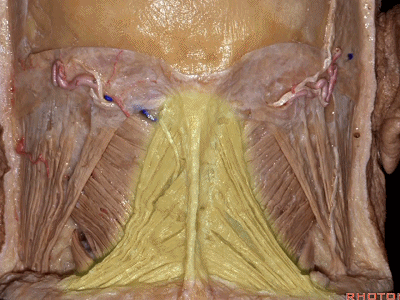
▼这是胸锁乳突肌(sternocleidomastoid ['stərnɒ'klɪdmas'tɔɪd])
▼这是头夹肌 (splenius ['spli:nɪəs])
this is splenius (capitus)
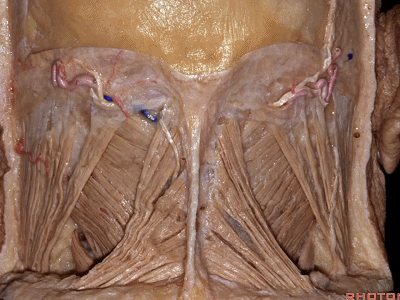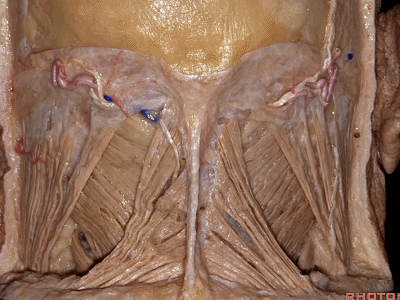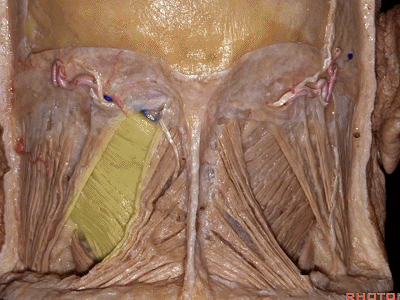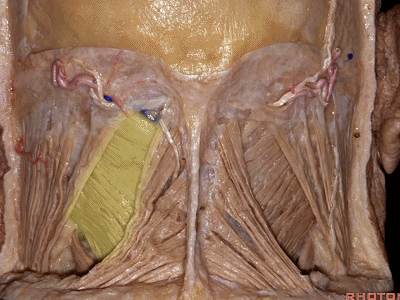
▼位于胸锁乳突肌和斜方肌之间的三角是 颈后三角(Posterior triangle)。
And we call this area between the sternocleidomastoid and the trapezius, that's the...what triangle of the neck?Posterior triangle.
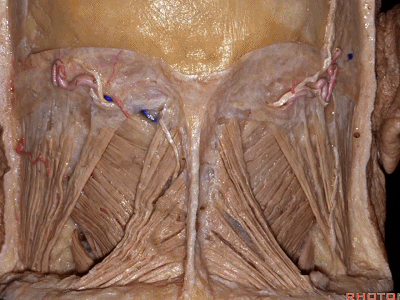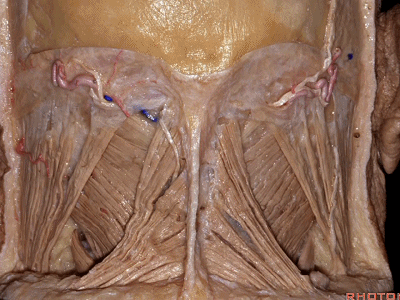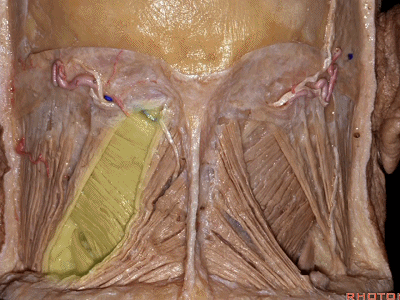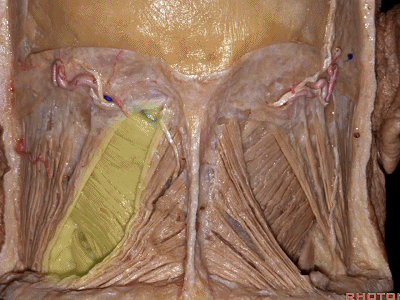
▼将胸锁乳突肌翻向前,斜方肌翻向下。
Now we folded the sternocleidomastoid forward,the trapezius downward,
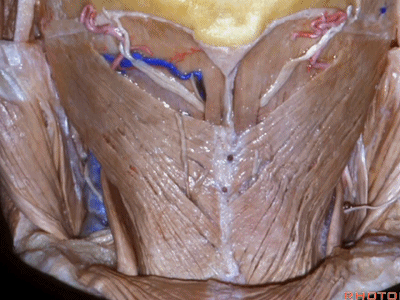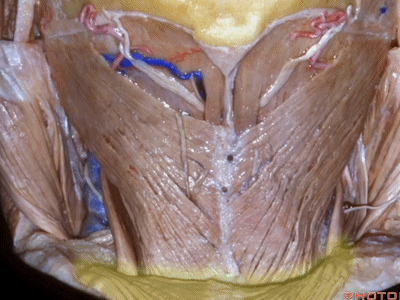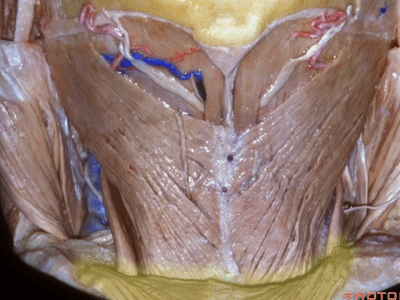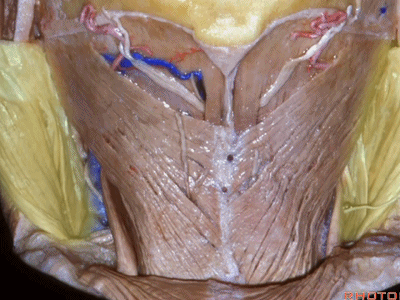
▼露出的是头夹肌
and we're looking at splenius
▼这是头半棘肌(semispinalis capitus)['semɪspaɪ'nælɪs]
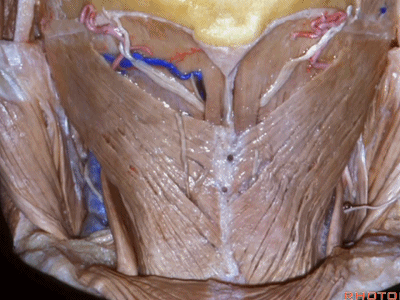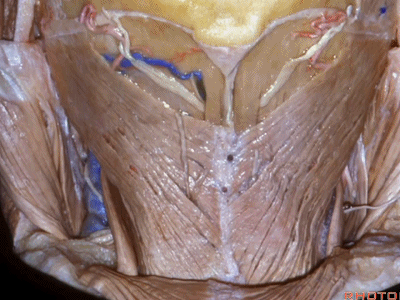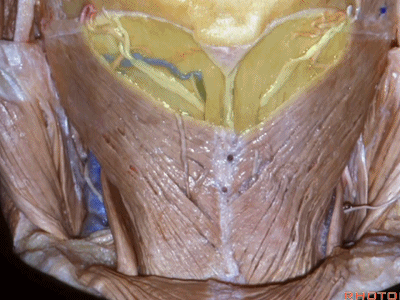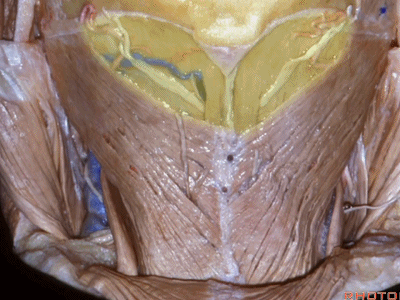
▼继续向下翻开头夹肌
And we reflect the splenius
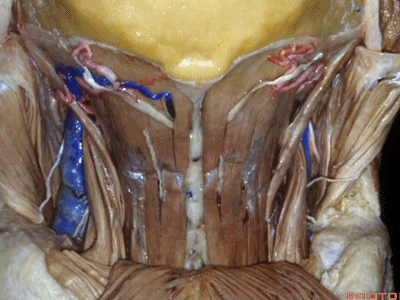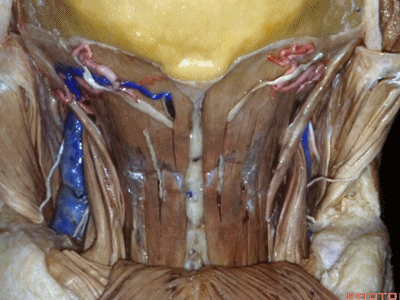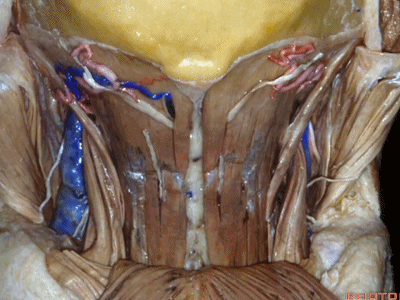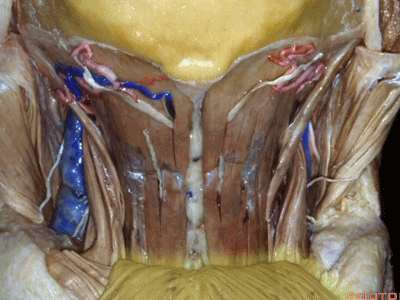
▼下方是头最长肌(longissimus capitus)[lɒn'ɡɪsɪməs]
under it, we see what muscle?This is longissimus capitus.
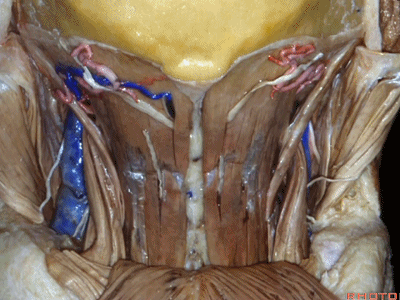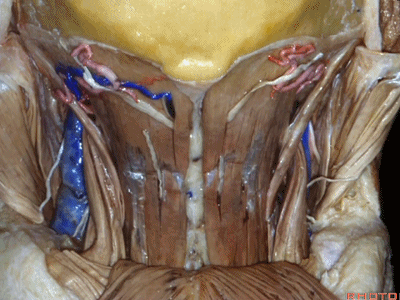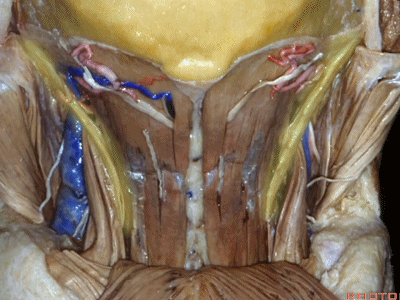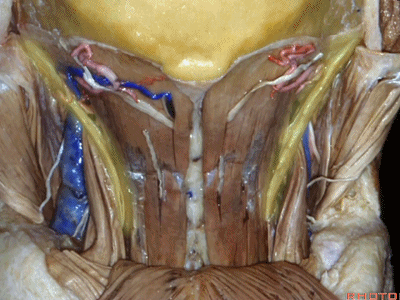
▼在搭桥手术中寻找的枕动脉,可出现在头最长肌的深层或浅层。
And the occipital artery, if you're doing bypasses,can either pass deep or superficial to the longissimus capitus.
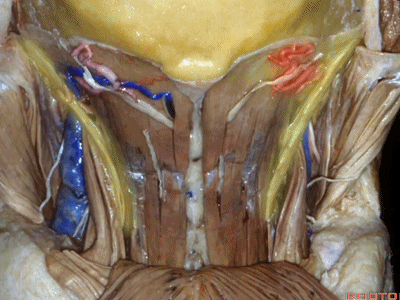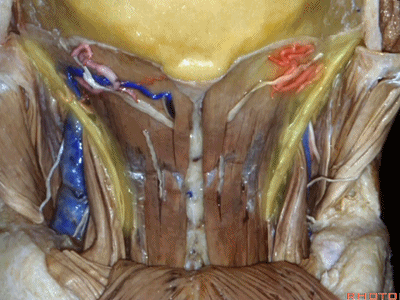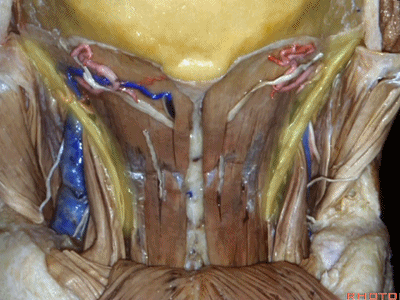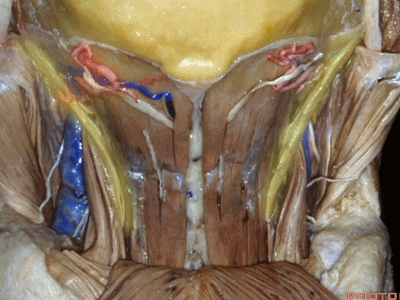
▼翻开半棘肌 即可暴露 枕下三角(suboccipital triangle)。
And then you reflect the semispinalis capitus and you see the suboccipital triangle.
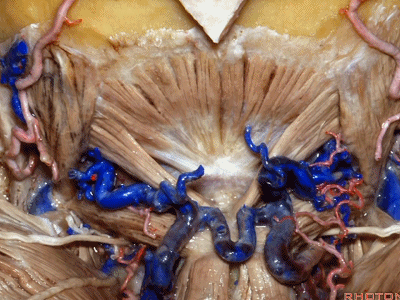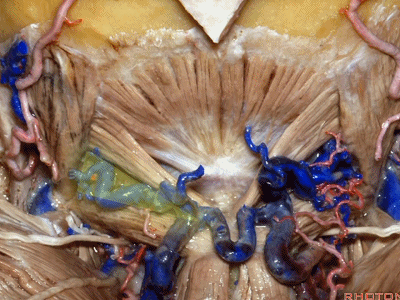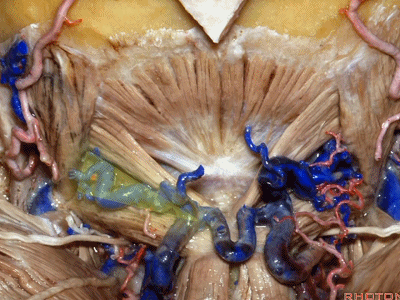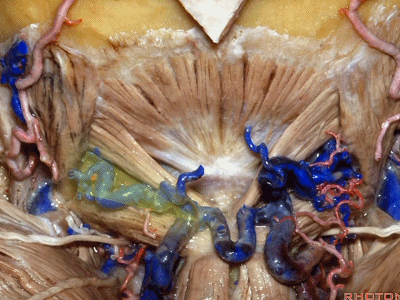
我刚开始做远外侧入路时,或进行经髁扩展入路时,我逐块分离肌肉,然后就发现很难缝合,且伴有很高的假性脑膜膨出和伤口裂开的发生率。因此开颅时可作一完整的肌皮瓣,这样也容易缝合。
When I first started doing far lateral approaches, or transcondylar,I turned these muscles as individual layers,and I found that it was very difficult to close and with a high rate of pseudomeningoceles and wound dehiscences.So we turn all of these muscles down with the scalp flap as a single layer.It's just so much easier to close.
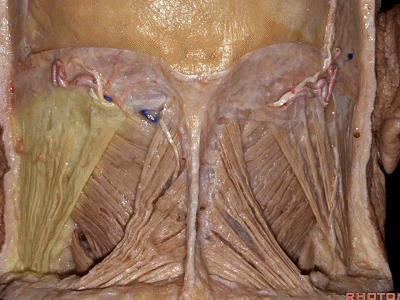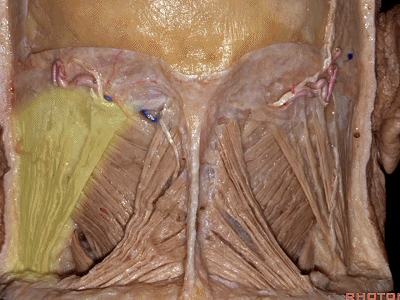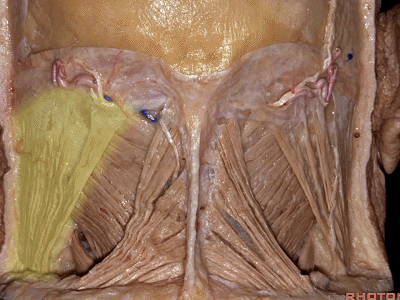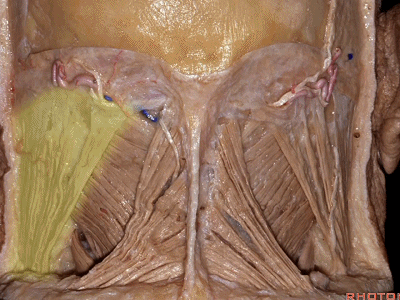
▼来看看构成枕下三角的肌肉,这是上斜肌(superior oblique)[əˈbliːk] ,起自枕骨,止于寰椎横突。
These muscles form the border of the suboccipital triangle.So this is superior oblique. It runs from occipital bone to transverse process of C1.
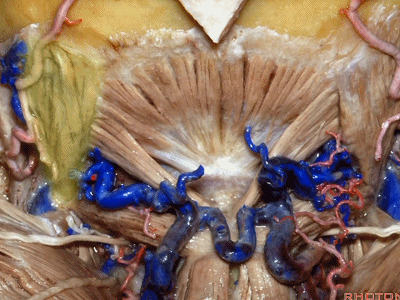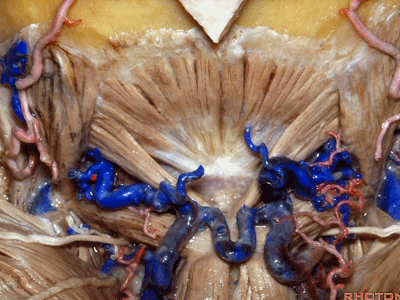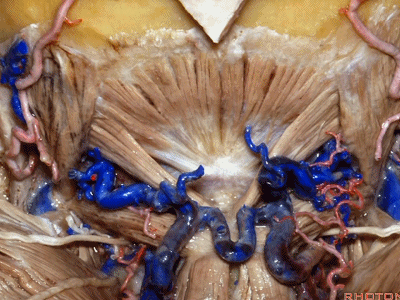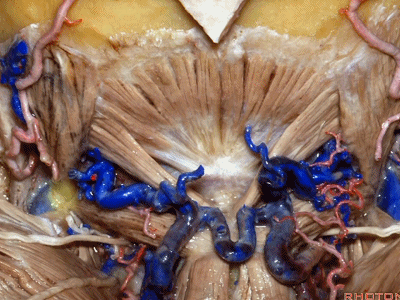
▼这是 下斜肌(inferior oblique),起自寰椎横突,止于枢椎棘突。
Anyone...this is inferior oblique that runs from transverse process of C1 to spine of C2.
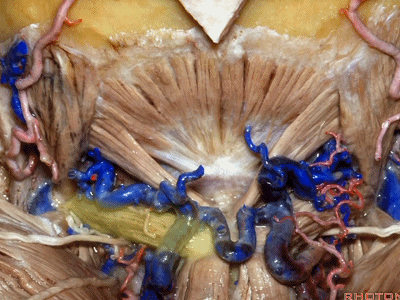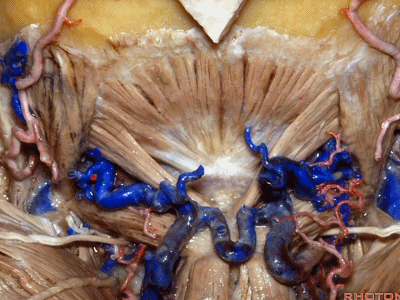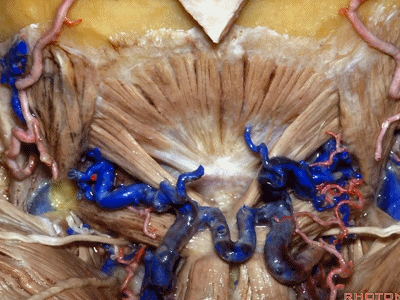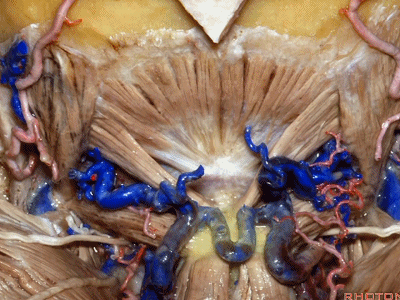
▼这是头后大直肌(rectus capitus posterior major)。起自枢椎棘突,止于枕骨。
And then from spine of C2 to occipital bone is rectus capitus posterior major.
rectus ['rektəs] 直肌
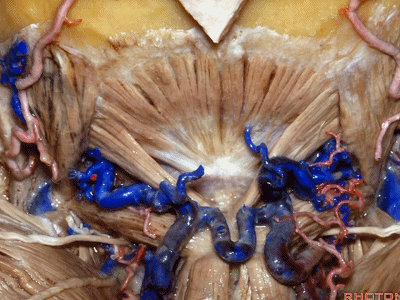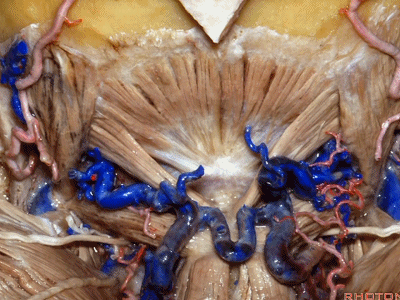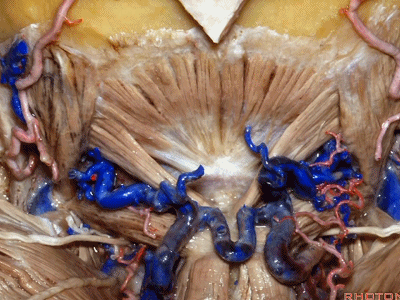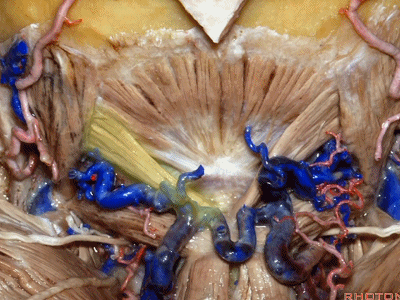
▼枕骨至寰椎的这块肌肉是 头后小直肌 (Rectus capitus posterior minor)
What muscle is this that runs from occipital bone to C1?Rectus capitus posterior minor.
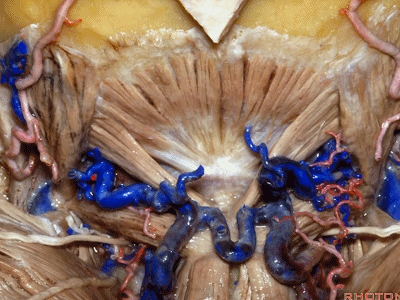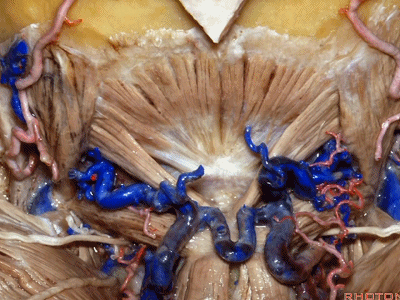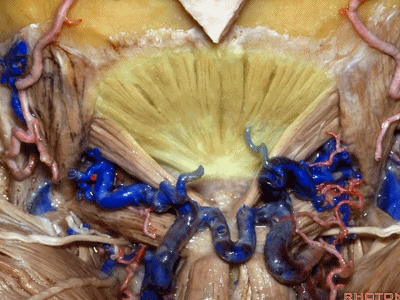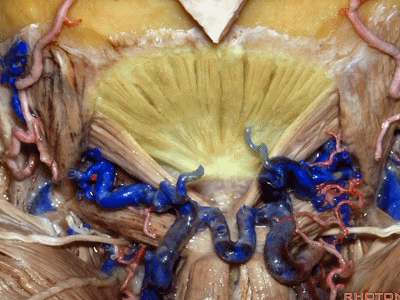
▼枕下三角 由上述三块肌肉(上斜肌、下斜肌、头后大直肌)围成,
The suboccipital triangle is between these three muscles,
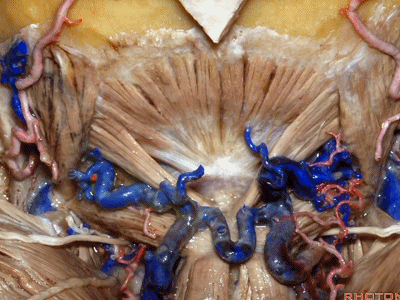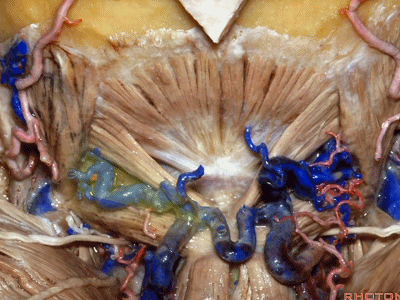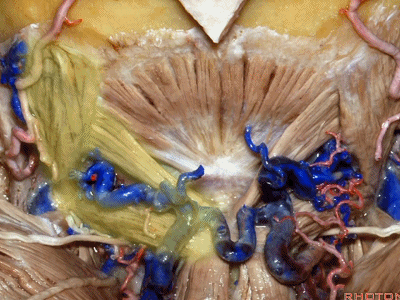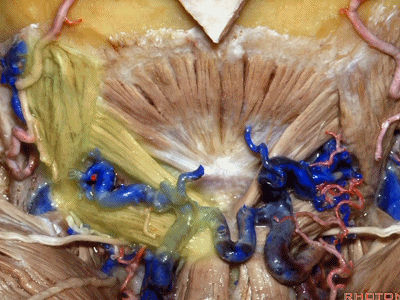
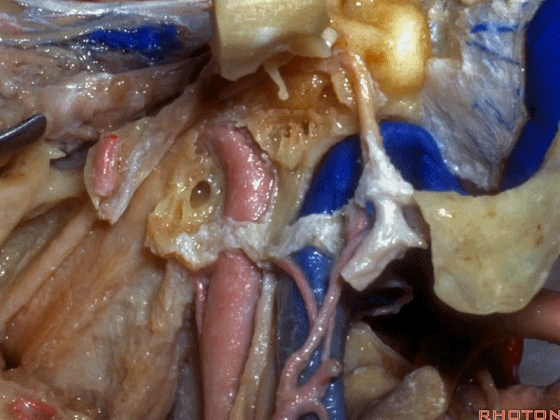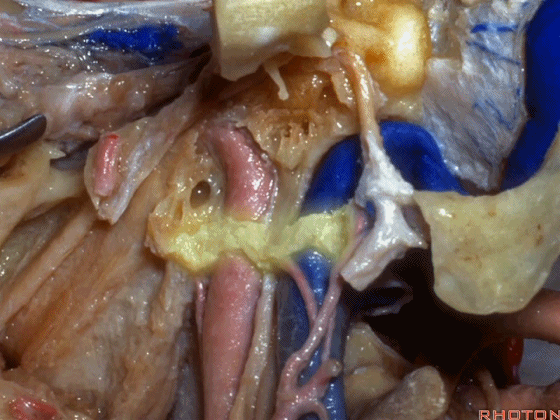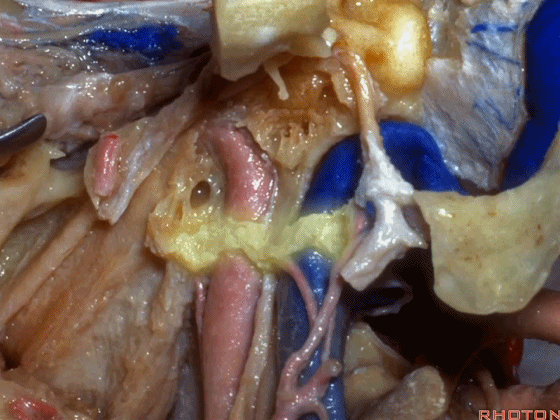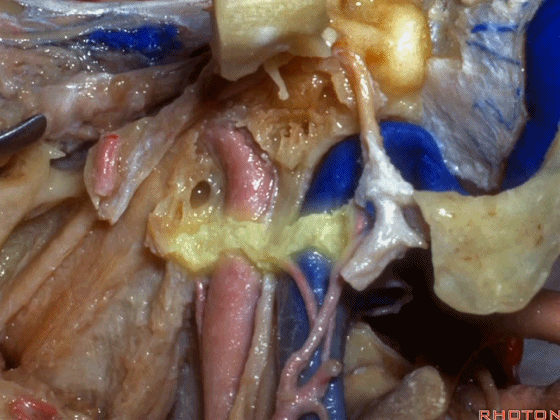
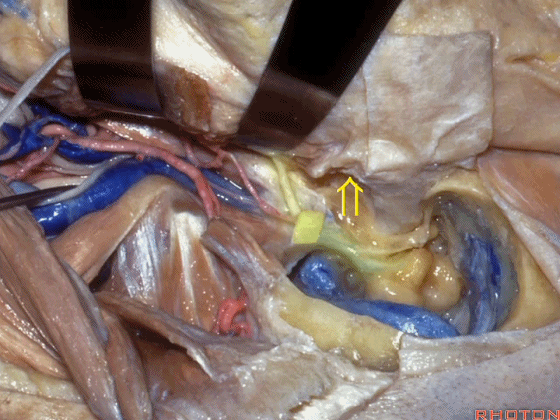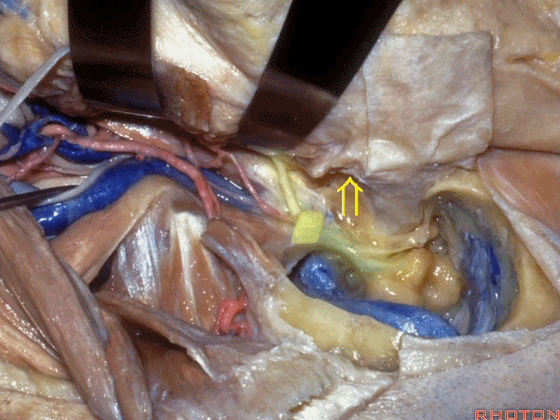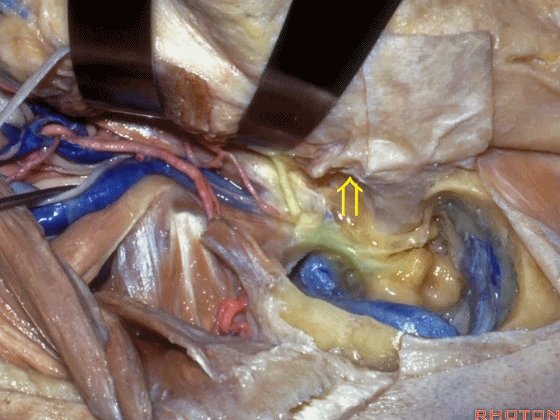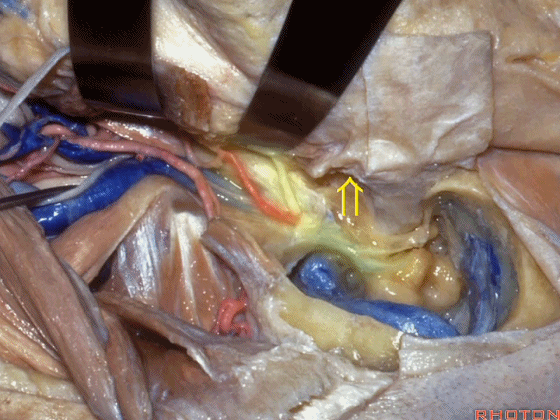
▼其重要性在于,椎动脉越过寰椎髁,即进入该三角内,其周围常有静脉丛附着,Ossama Al-Mefty称之为 第二海绵窦。
and the importance of that is the vertebral artery as it passes behind the atlantal condyle, is in the depths of this triangle, often embedded in this venous plexus that Ossama Al-Mefty calls the second cavernous sinus.
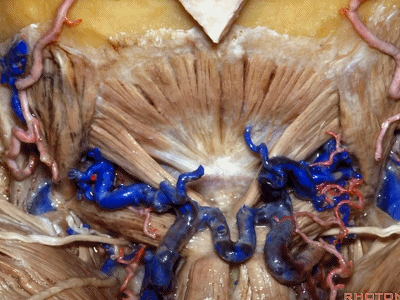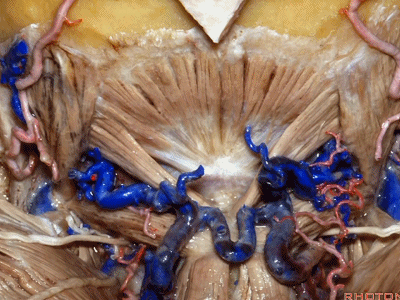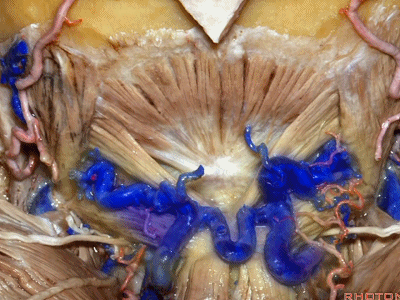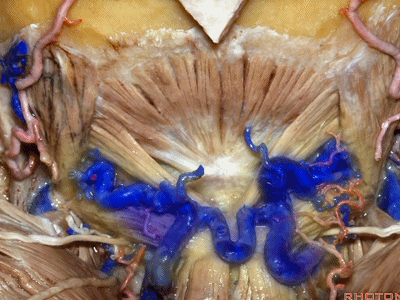
▼这里我们翻开了上斜肌(下图),这是下斜肌、头后大直肌(下图)。
So, here we've reflected the superior oblique,the inferior oblique,the rectus capitus.
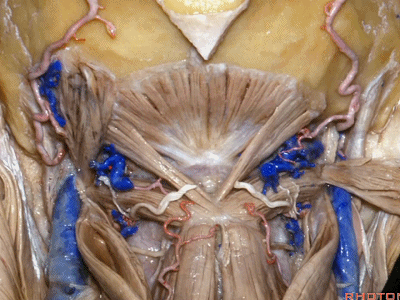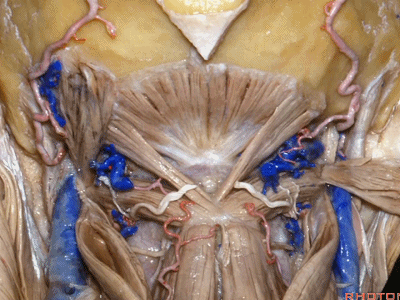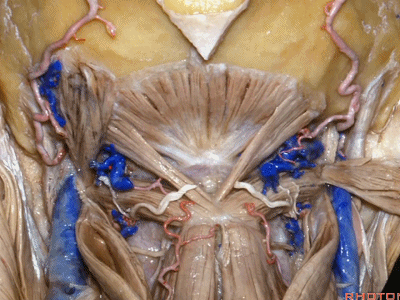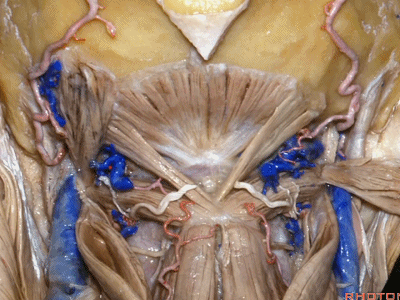
▼继续翻开这些肌肉,即可见椎动脉向上穿过寰椎横突,走行于寰椎髁后方。
And when we reflect those muscles, we see the vertebral artery ascending through the transverse process of C1,usually passing behind the atlantal condyle.

▼下图示寰椎横突

▼下图示寰椎髁
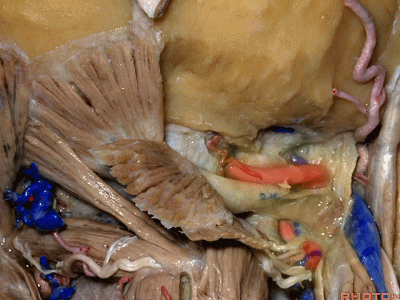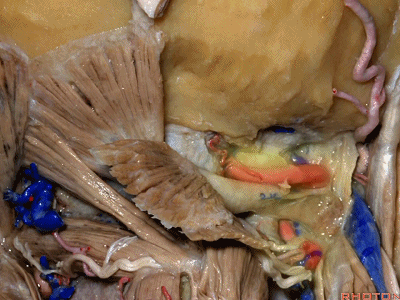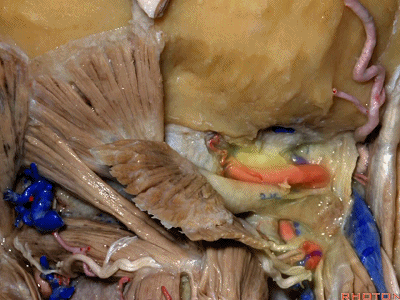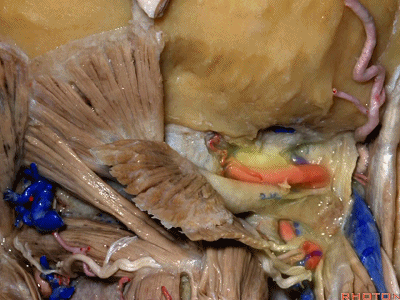
▼但当椎动脉迂曲时,其位置可高至枕髁后方(下图),甚至可达枕骨,这种情况下极易在乙状窦后开颅时误伤。
But if the artery is tortuous,the vertebral artery can pass higher behind the occpital condyle, or even wraps against the occipital bone where it could be very easy to damage it in a retrosigmoid craniotomy.

▼椎动脉在穿入硬膜前,常发出一支粗大的脑膜后动脉(下图),此动脉可牺牲,但切勿将硬膜外起源的小脑后下动脉 与之相混淆,这种情况可见于10%的病例。
And the artery just before it enters the dura here,usually gives off a big posterior meningeal branch that you usually sacrifice,but you don't want to confuse this with an extradural origin of the PICA,that occurs in about 10% of cases.
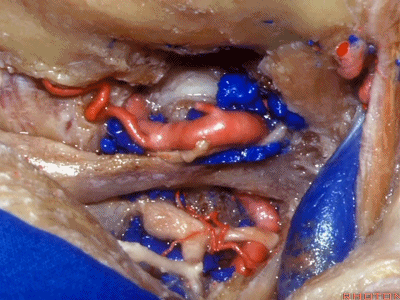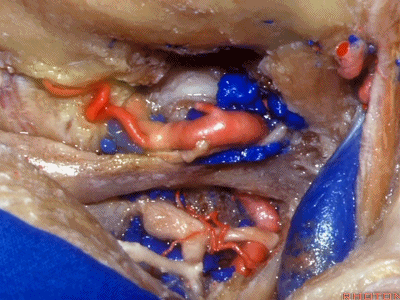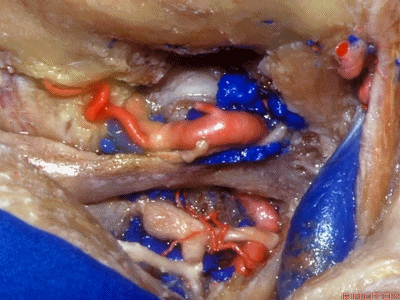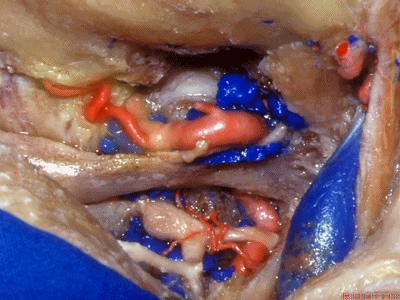
▼下图下方是寰椎髁( atlantal condyle),上方是枕髁(occipital condyle)。
Here we see the atlantal condyle,here below the occipital condyle.
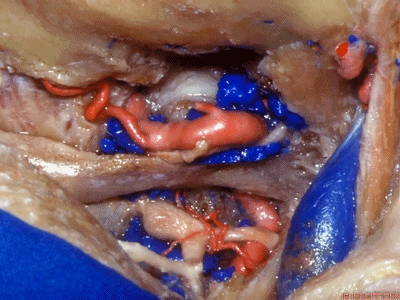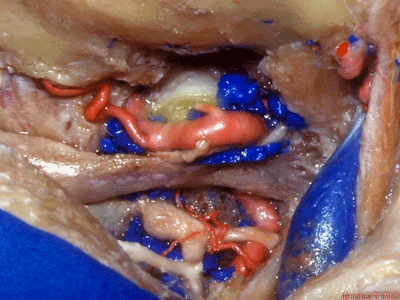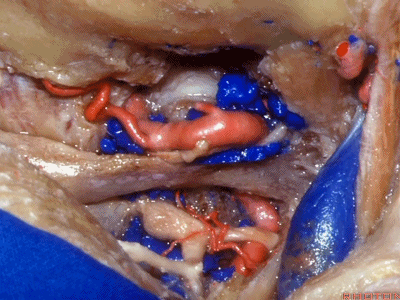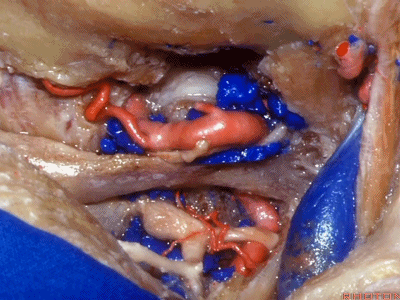
▼然后,我们将颅骨切开。
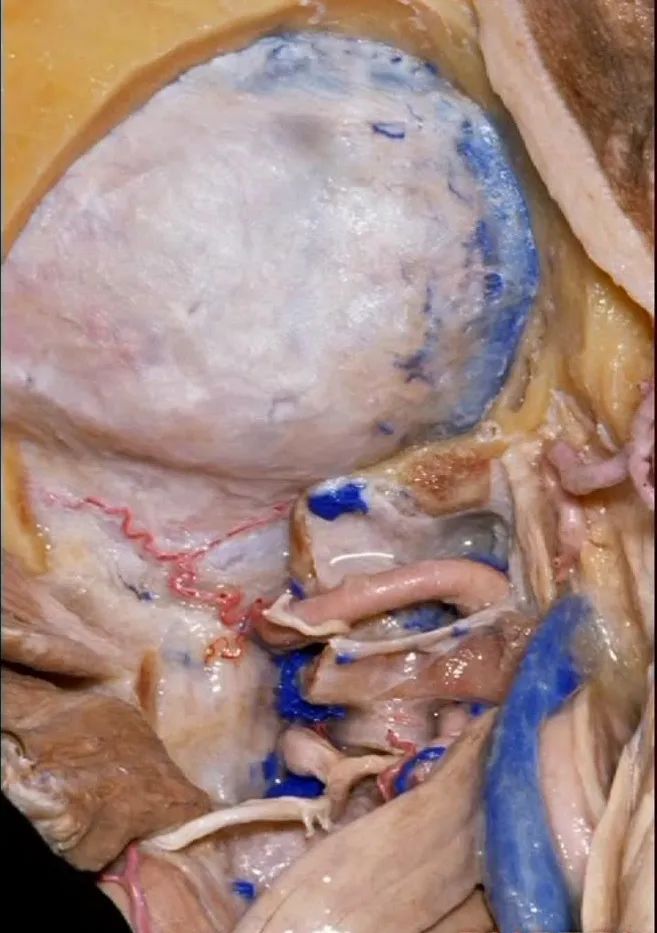
▼将硬膜向下切开。
And we can open this dura down.
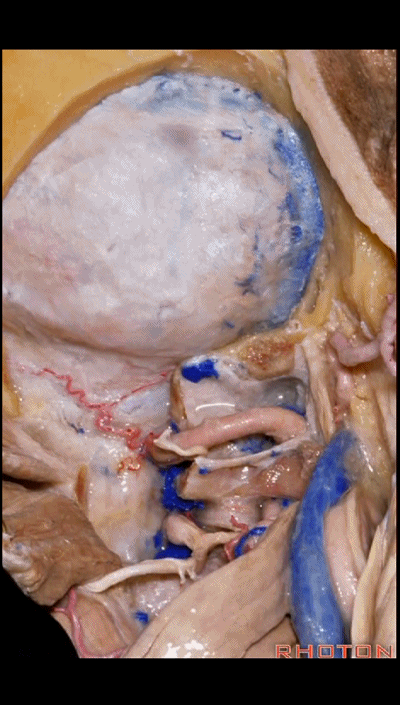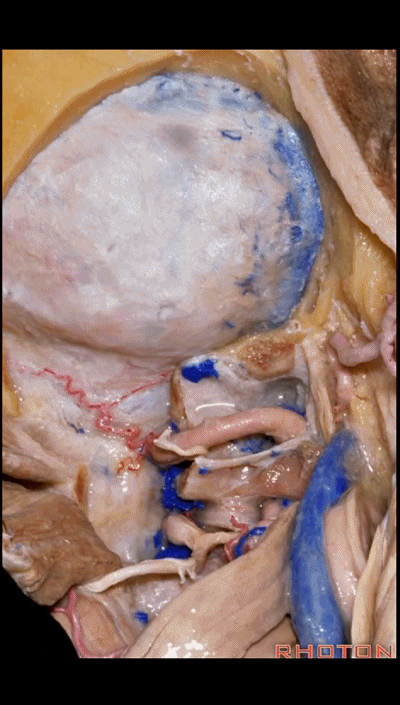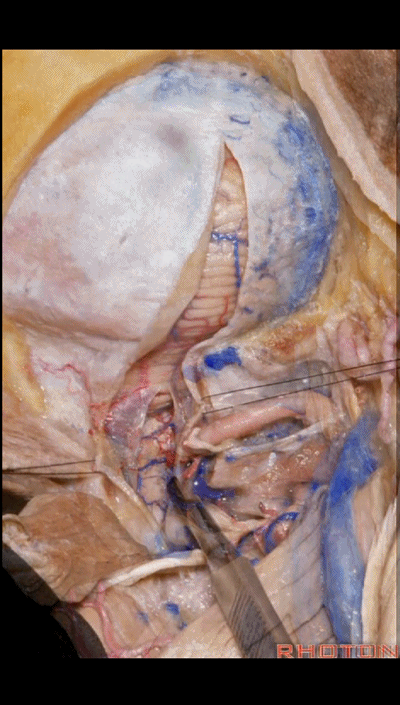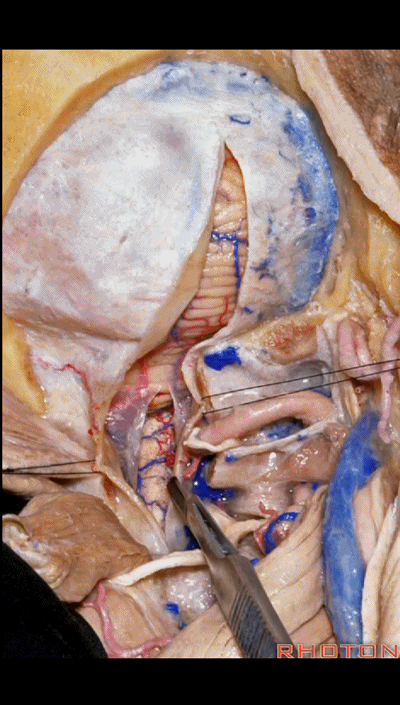
▼对于血管性病变,一般仅需切除同侧半的寰椎后弓即可。
For vascular pathology,you can often do a removal of the ipsilateral half of the posterior arch of C1.
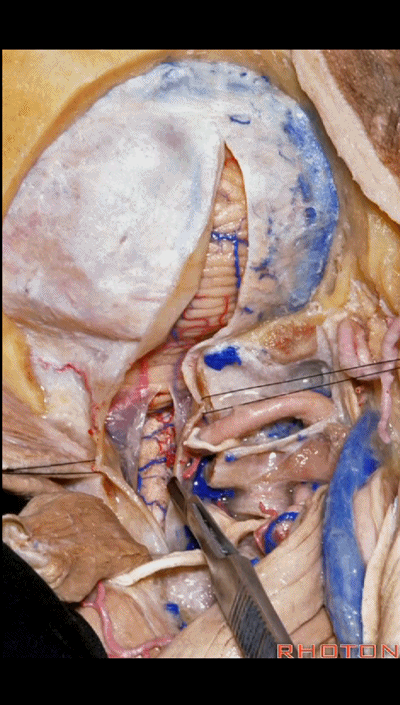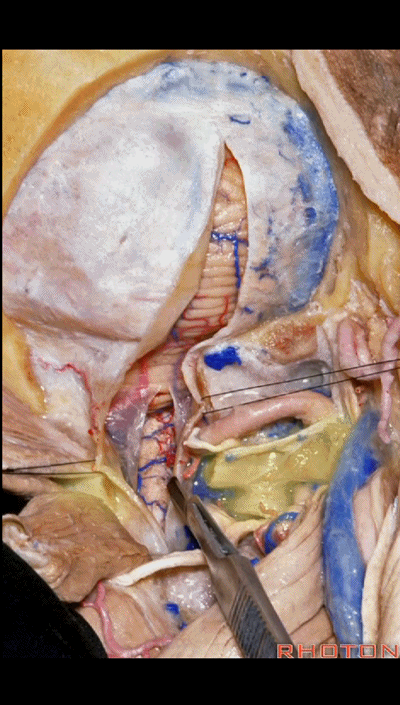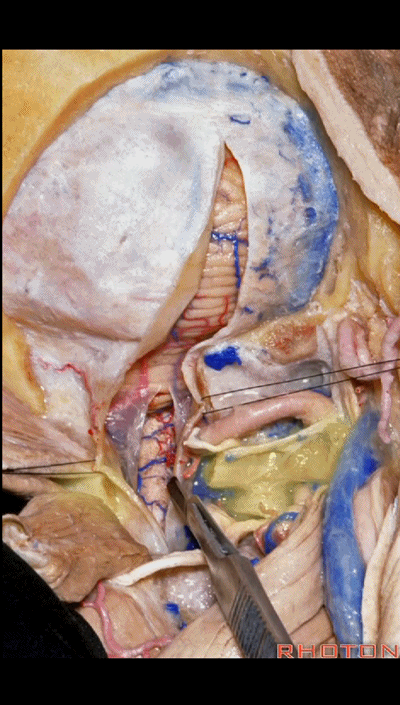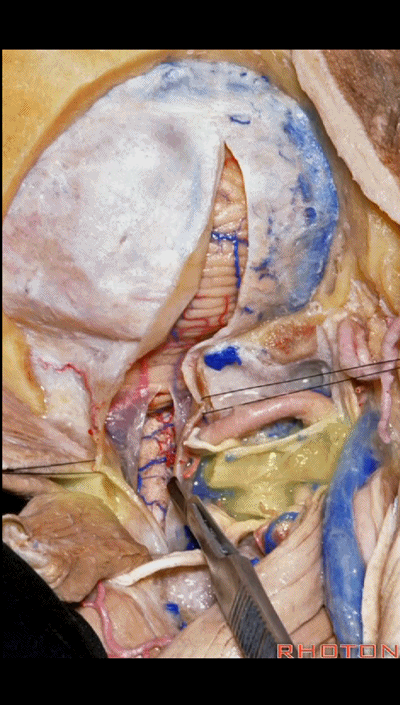
▼但对于肿瘤性病变,我们通常需要更大的切口,需打开枕骨大孔及枢椎。在这种情况下,我们常使用马蹄形切口并翻向下方。
But for tumor pathology, we often need a wider opening here at the foramen magnum and C2.And in that case, we would use a horseshoe type of flap and flap that downward.
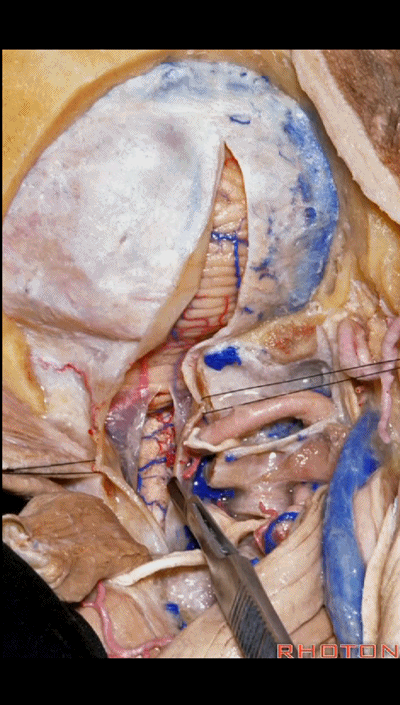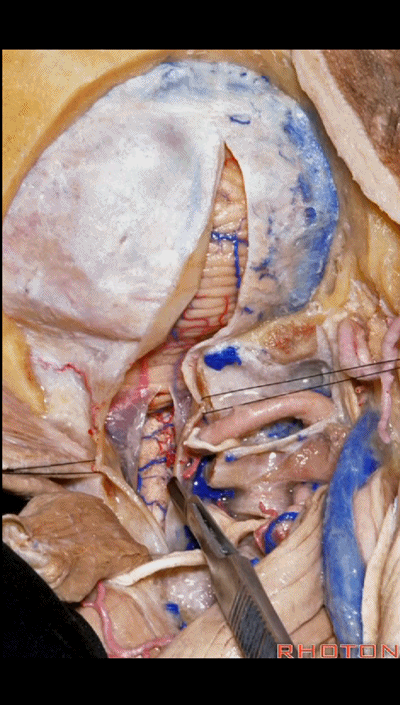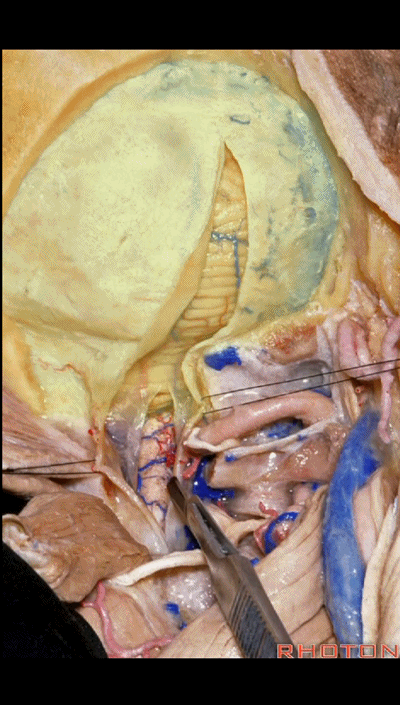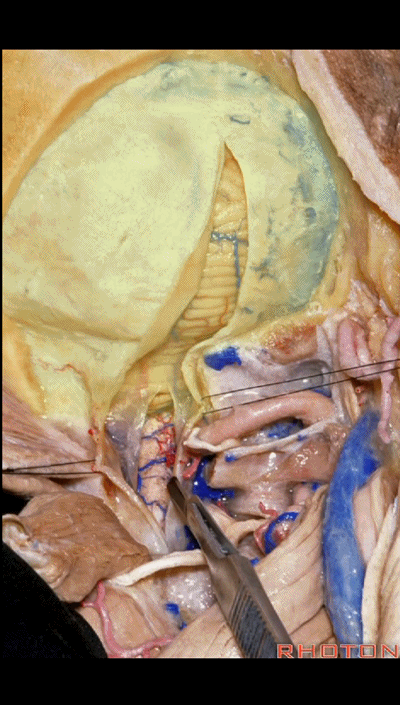
▼如果病变仅位于椎动脉入硬膜处,例如起源于小脑后下动脉的动脉瘤,则不需要那么广泛的椎体切开术,作一个曲棍球棍样切口的远外侧入路即可。
If you're just dealing with pathology right here at the dural entrance, an aneurysm arising from the PICA, then you don't need a wide laminectomy and you can do a hockey stick incision to complete the far lateral approach.
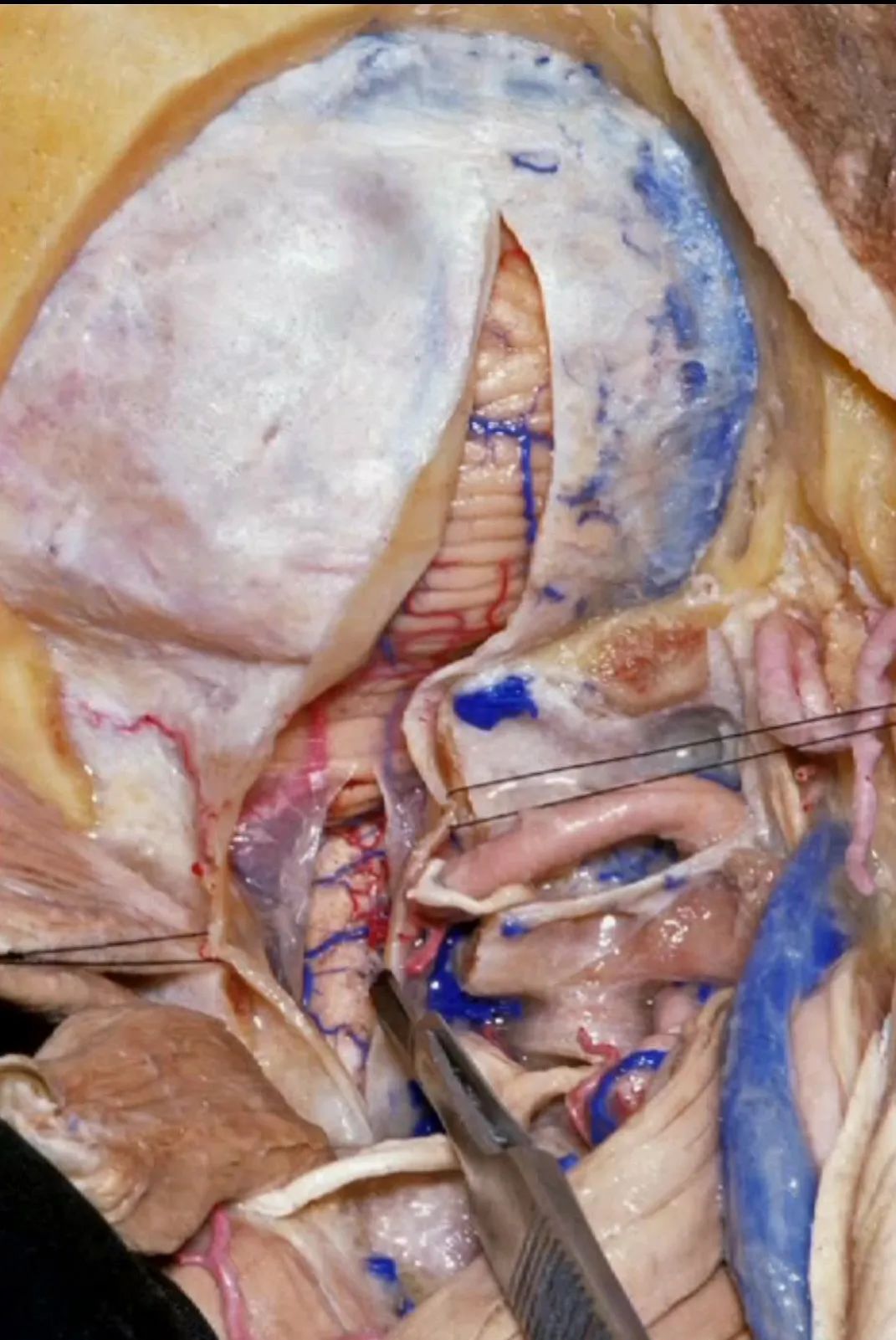
▼下图展示的是保留寰枕关节的髁上暴露。这是我们磨除了部分枕髁(下图)。
And here we drill supracondylar. We preserve the joint.This is...we've drilled off some of the occipital condyle.
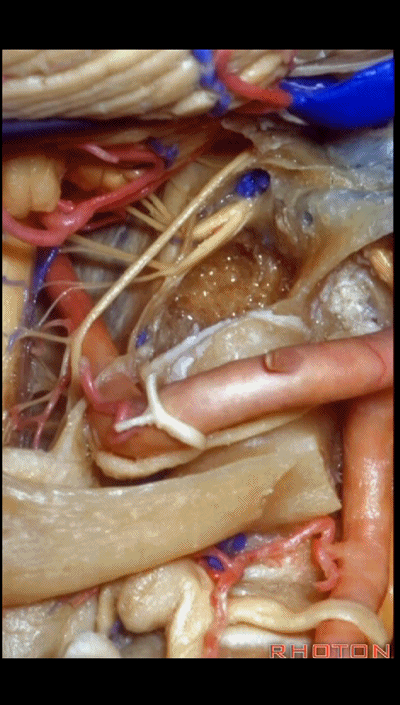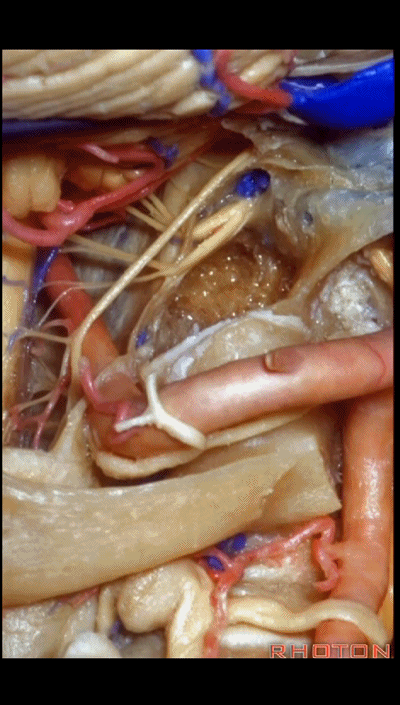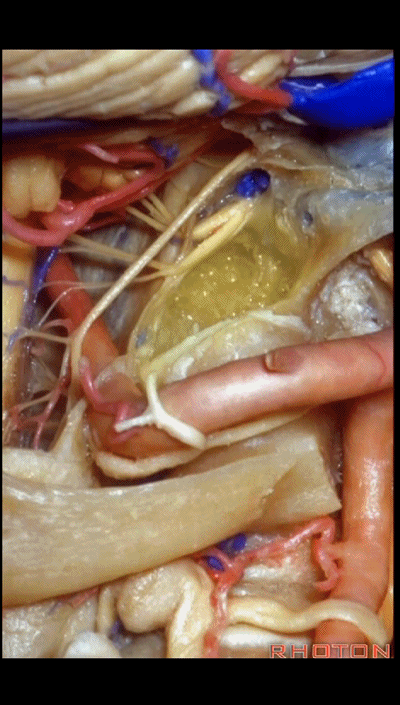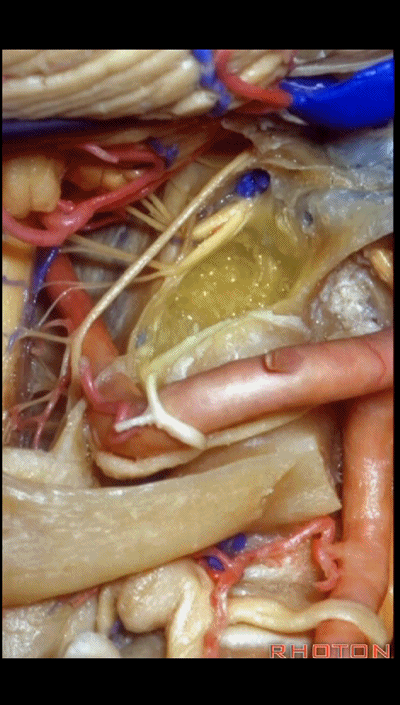
▼可见舌下神经从髁上方穿过,此为髁上入路(supracondylar approach)。
And here you see the hypoglossal nerve passing above the condyle in a supracondylar approach.
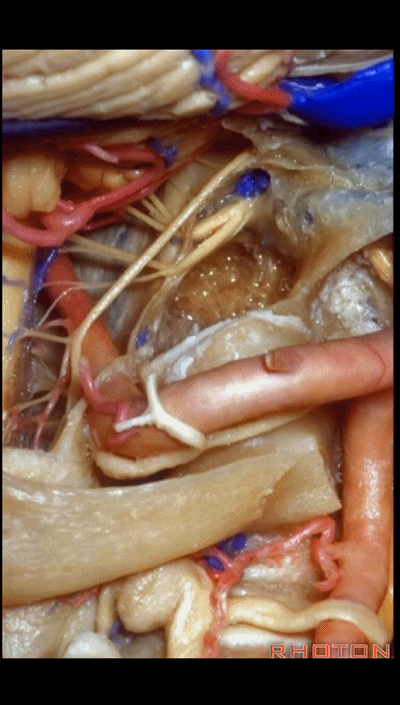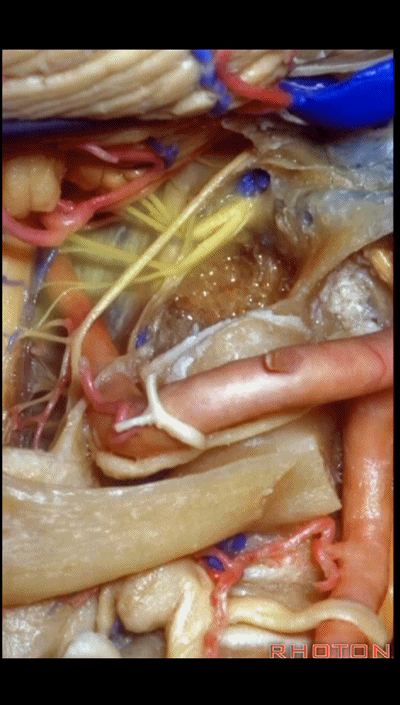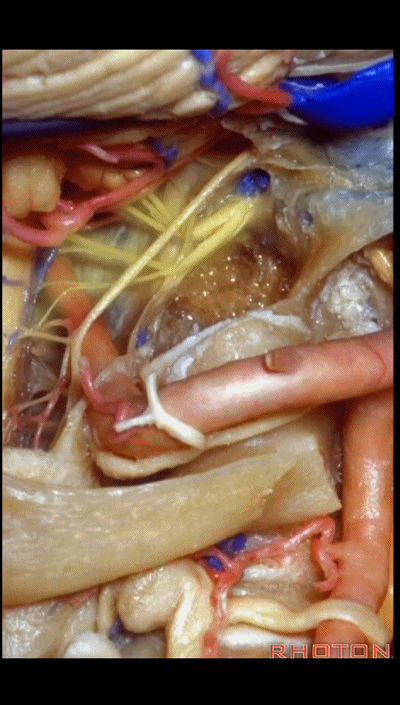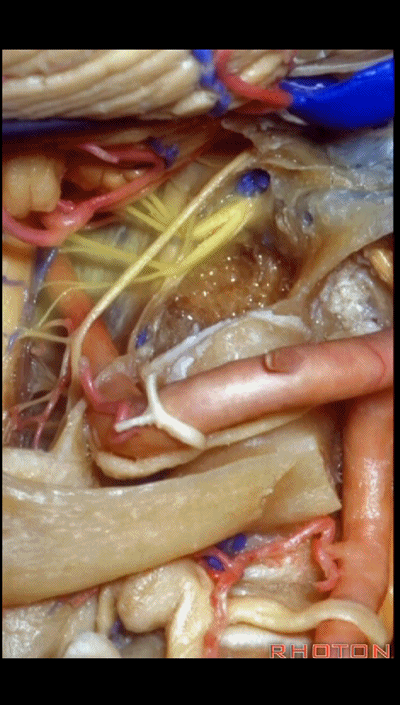
磨除枕髁后,即可显露下斜坡。我常利用该入路切除脊索瘤,尤其当其侵入髁部,就可使用该髁上入路。
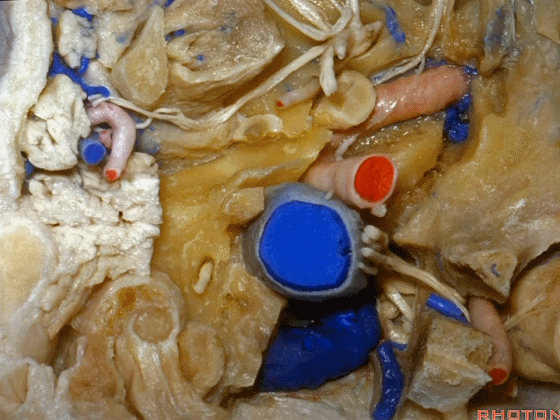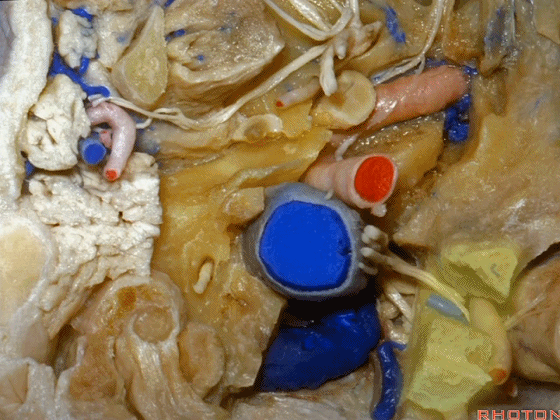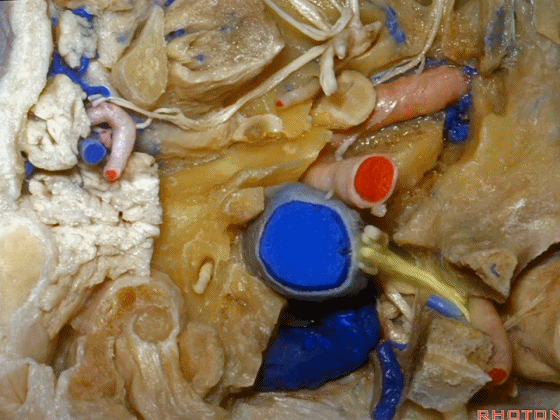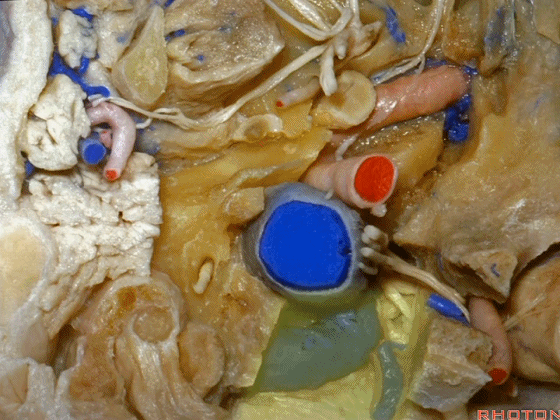
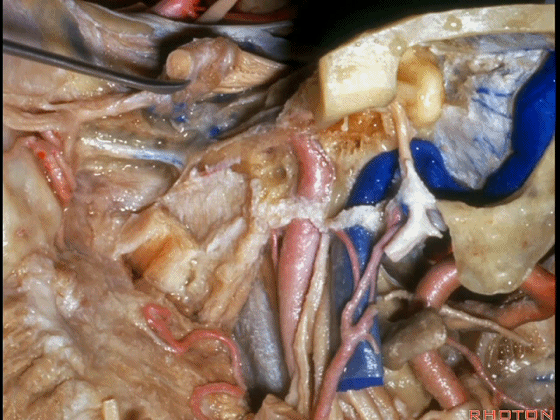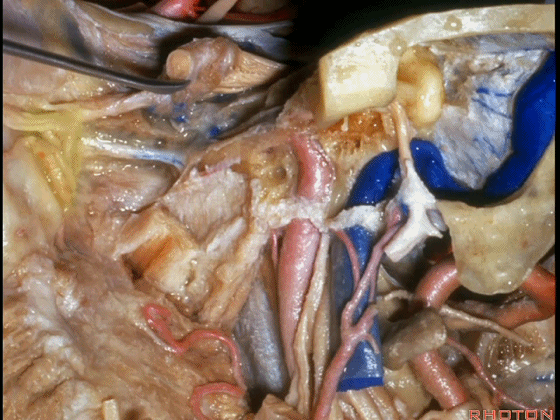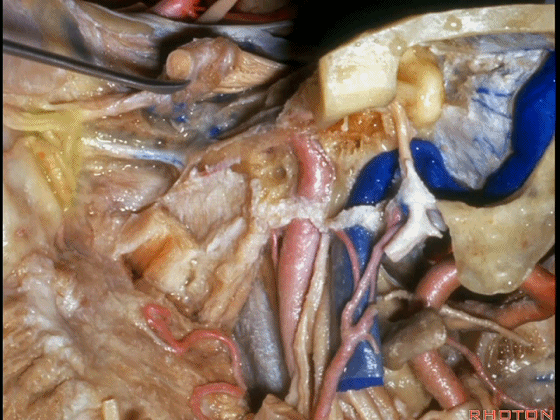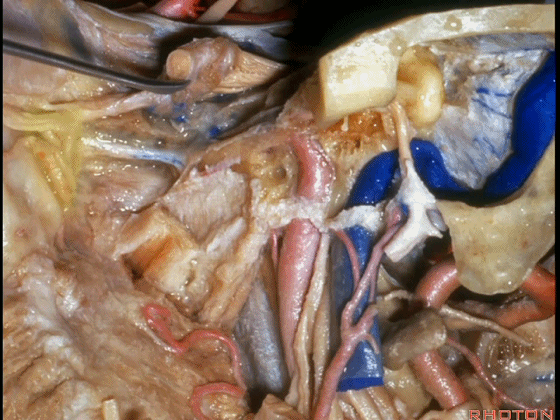
▼这里我们切开椎动脉周围的袖套结构,从而将其移位。
Here we've opened a cuff of dura around the vertebral artery so it can be mobilized.
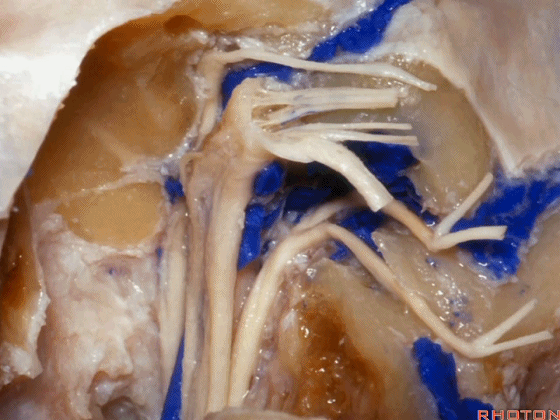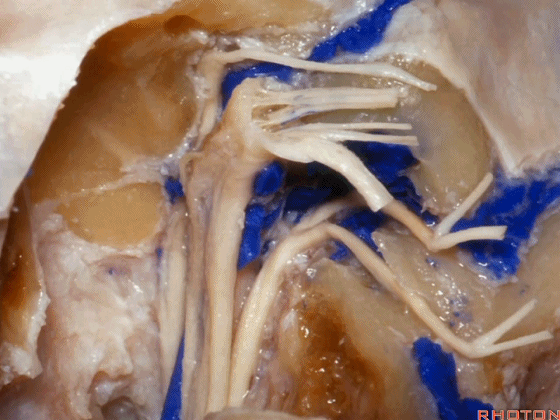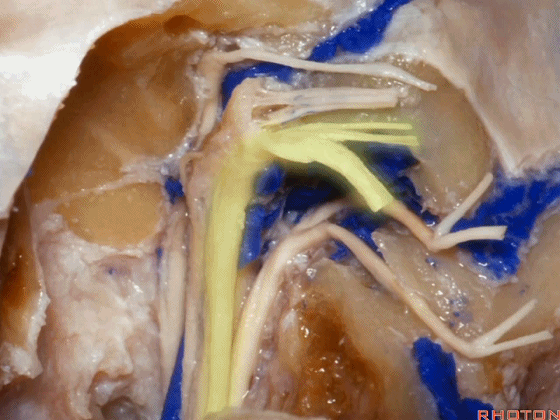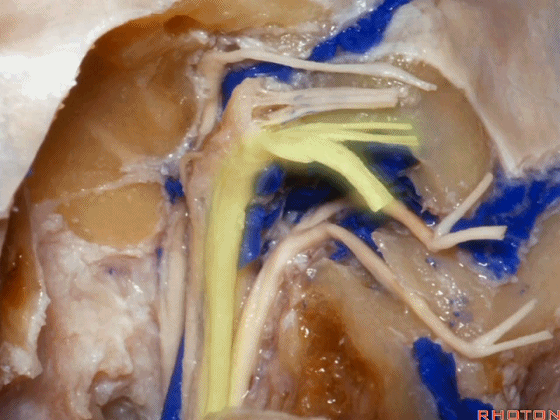
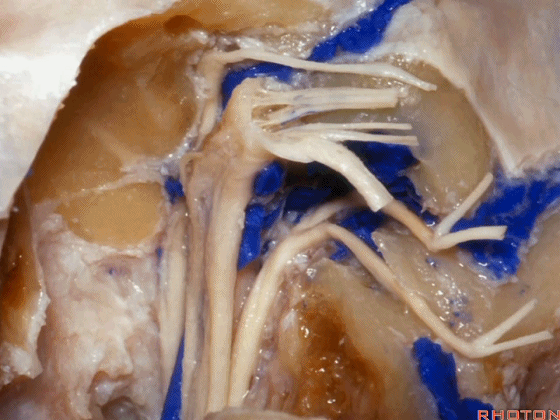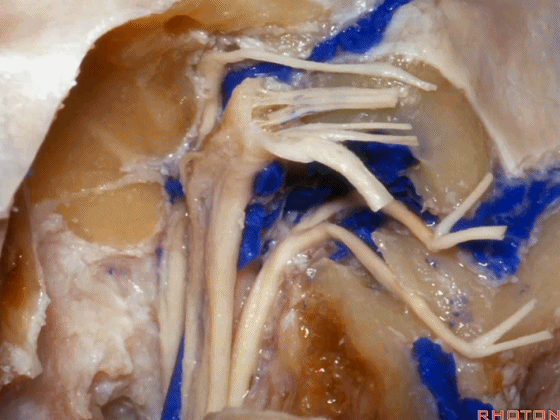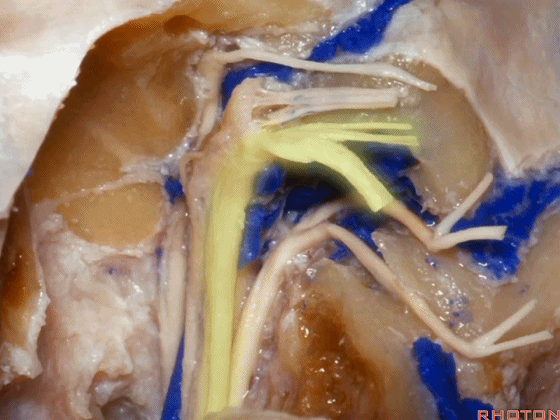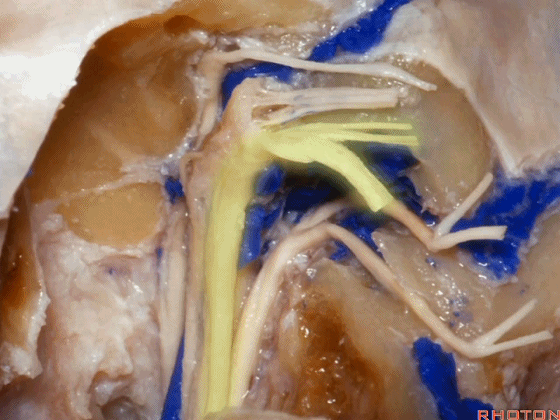
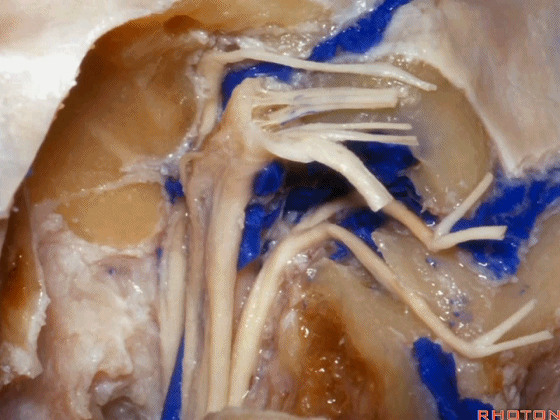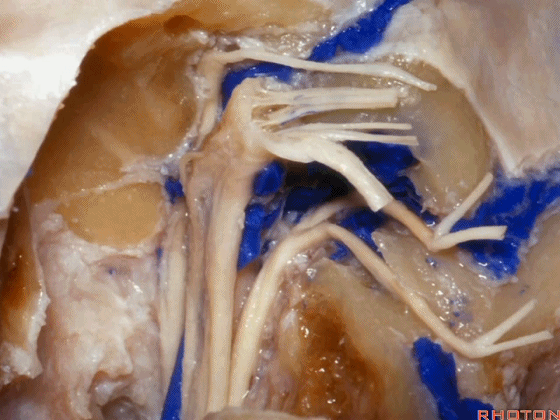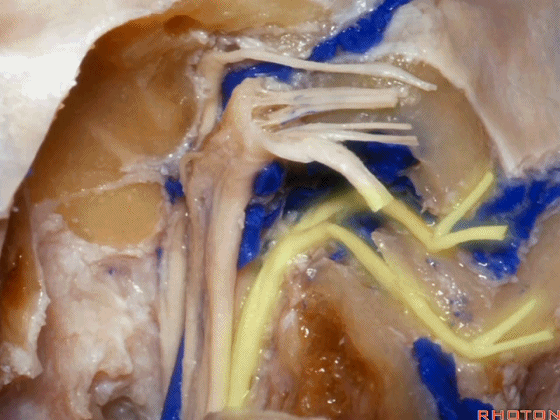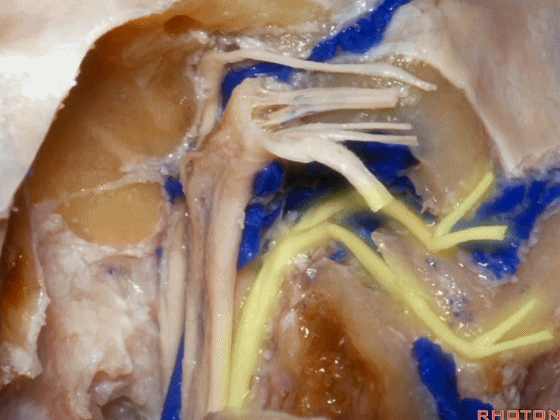
▼可见舌下神经管内的舌下神经
We see the hypoglossal nerve in the hypoglossal canal,and IX, X, XIentering the jugular foramen above.
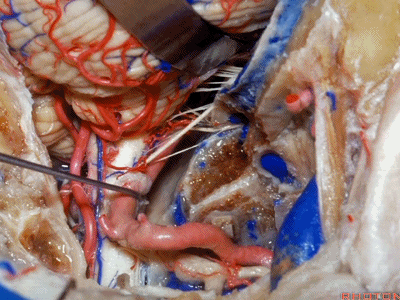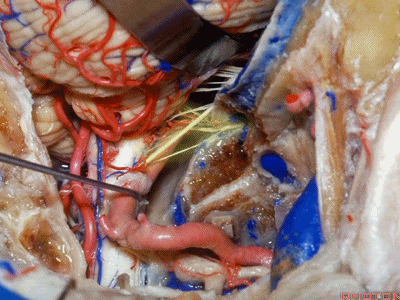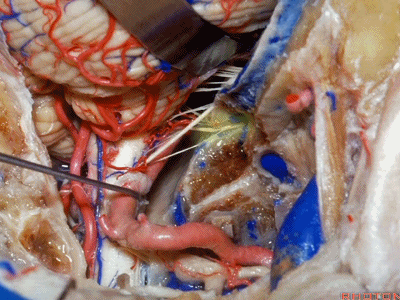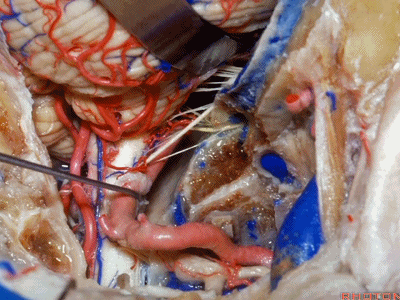
▼下图示舌咽神经
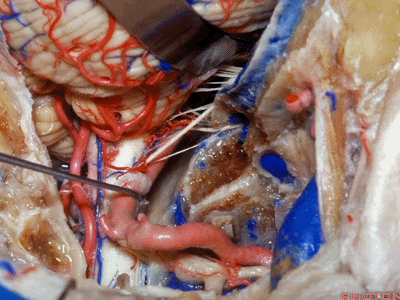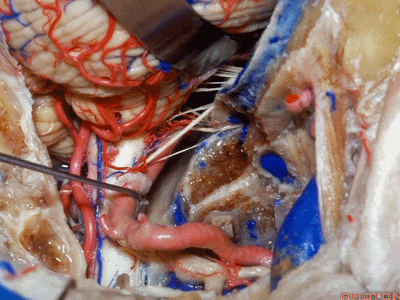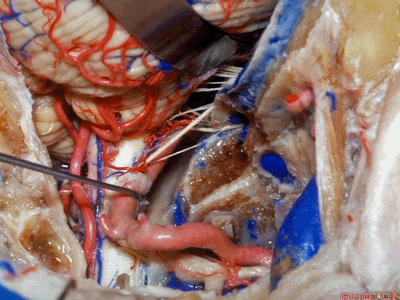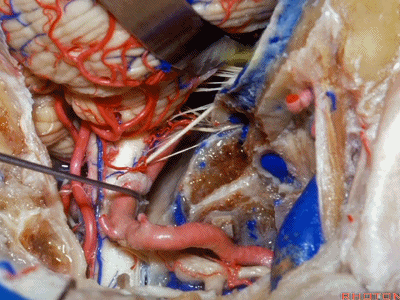
▼下图示迷走神经
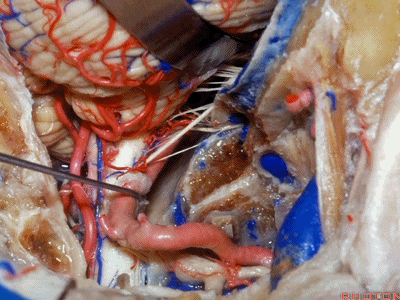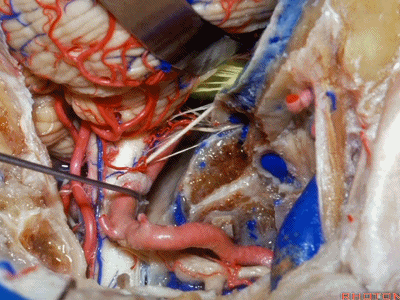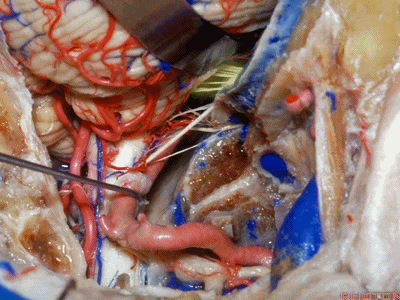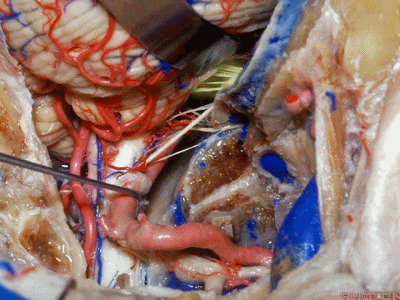
▼下图示副神经
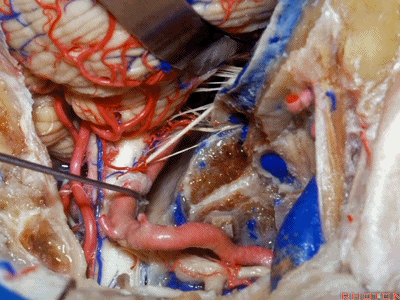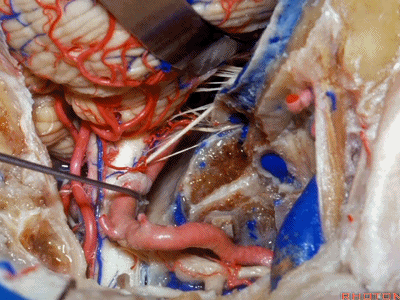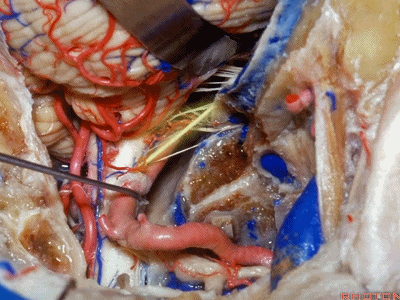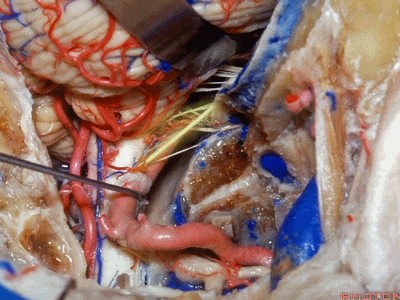
▼舌咽神经IX、迷走神经X,、副神经XI进入上方的颈静脉孔。
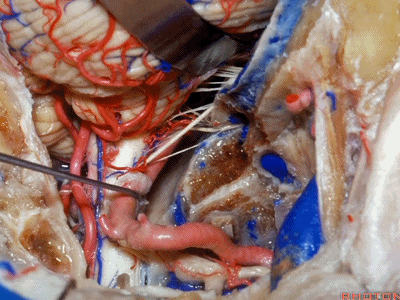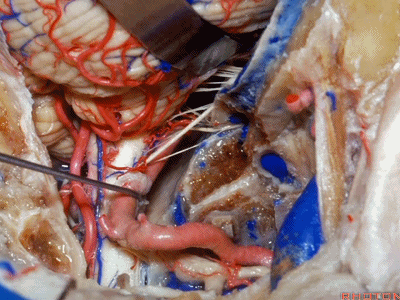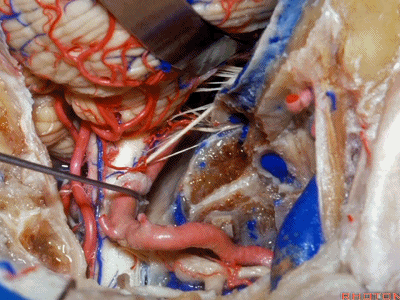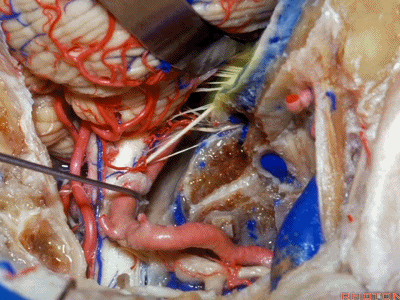
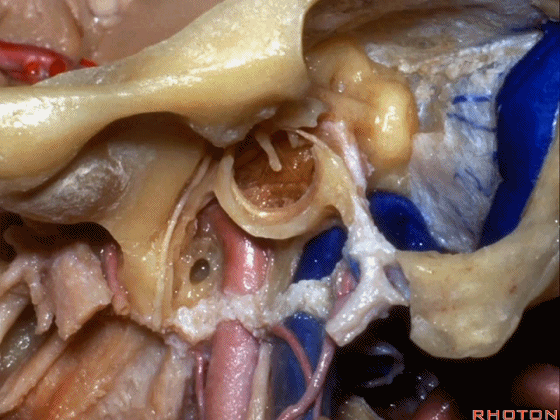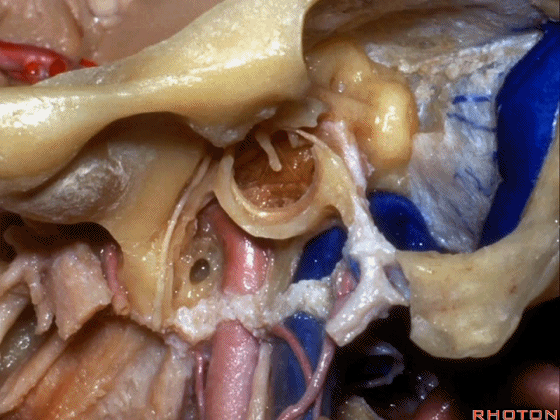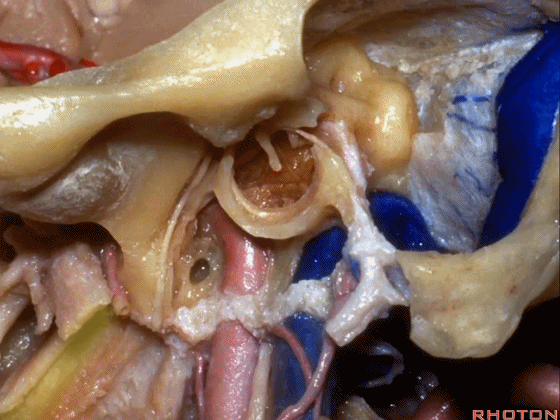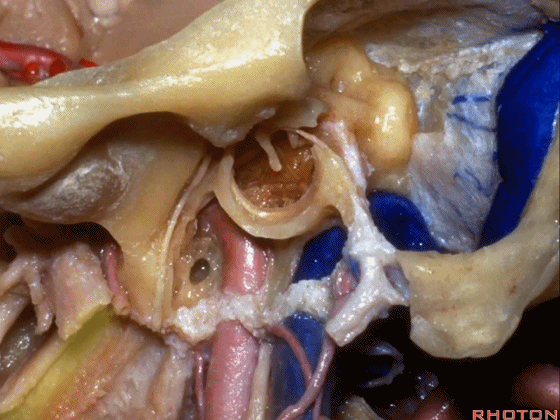
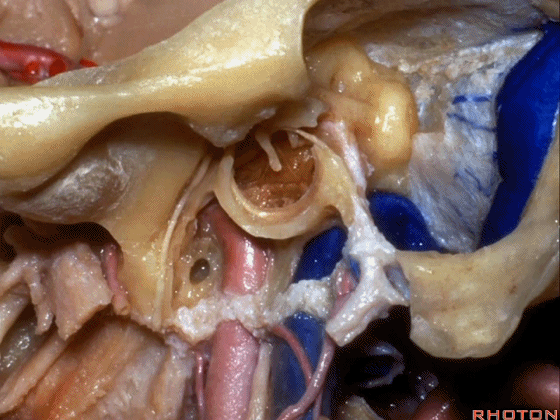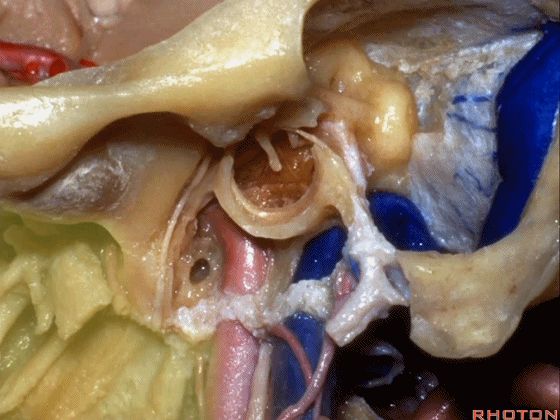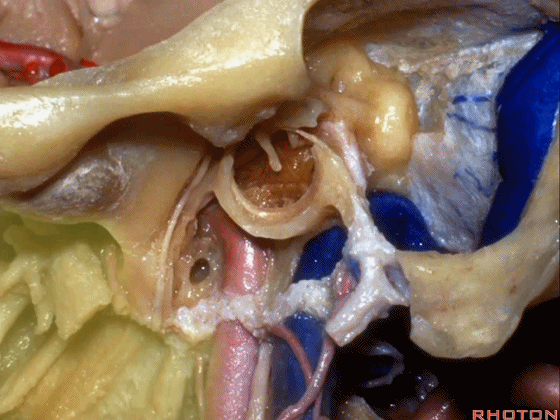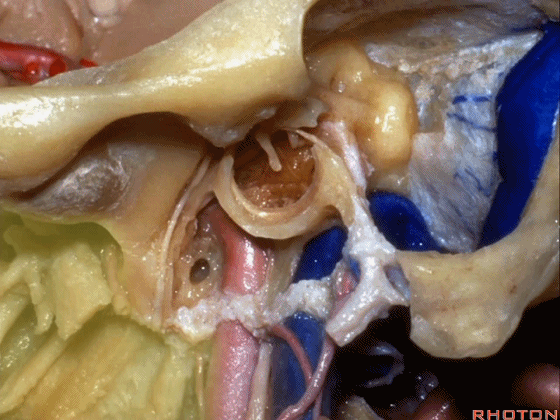
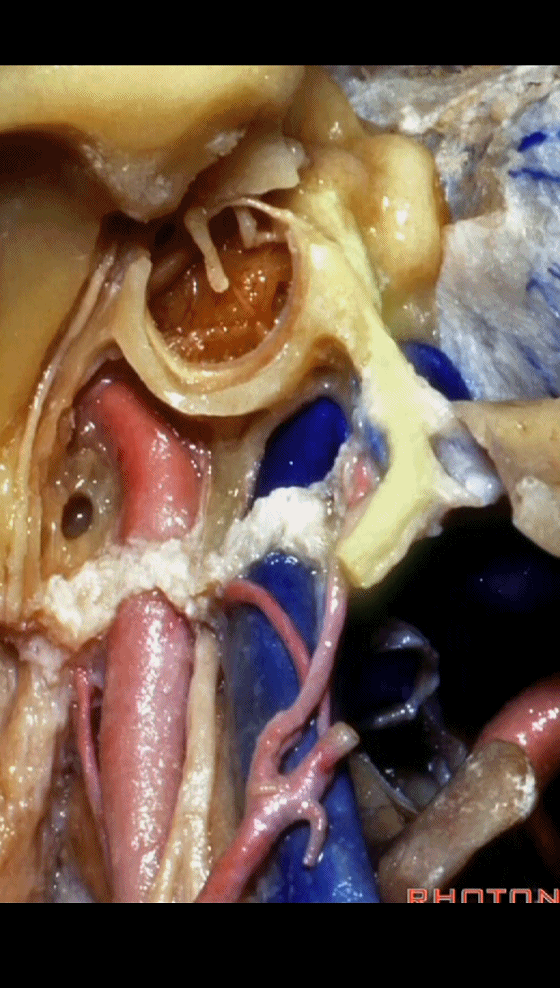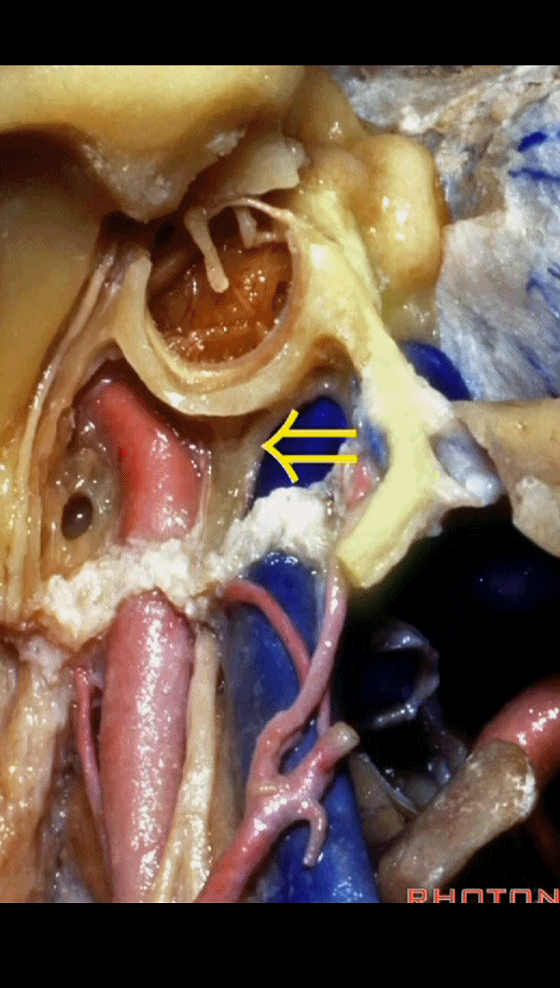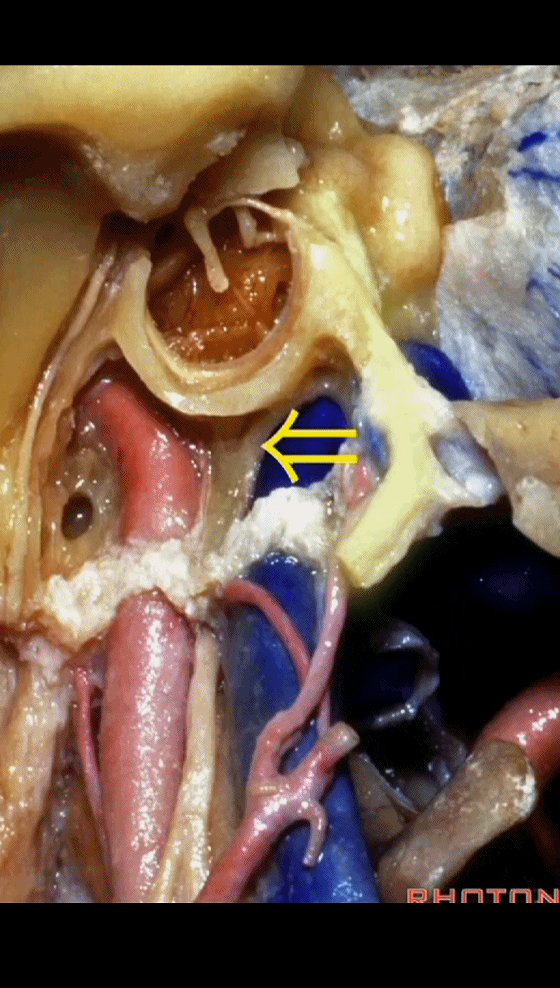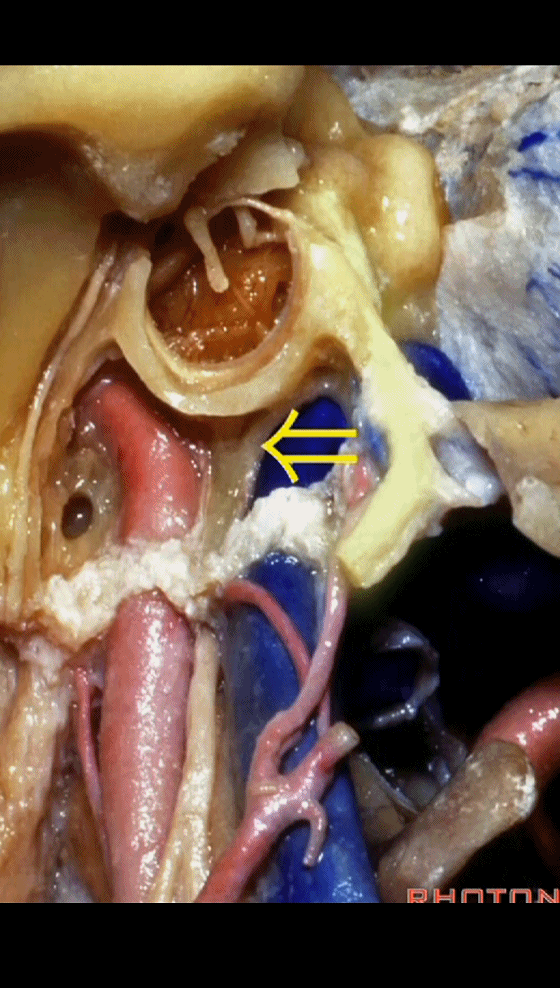
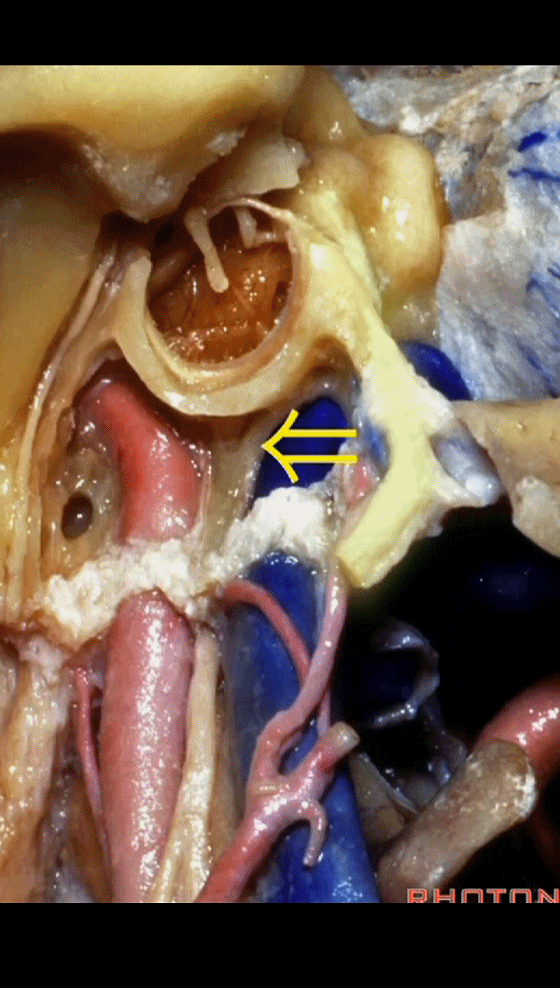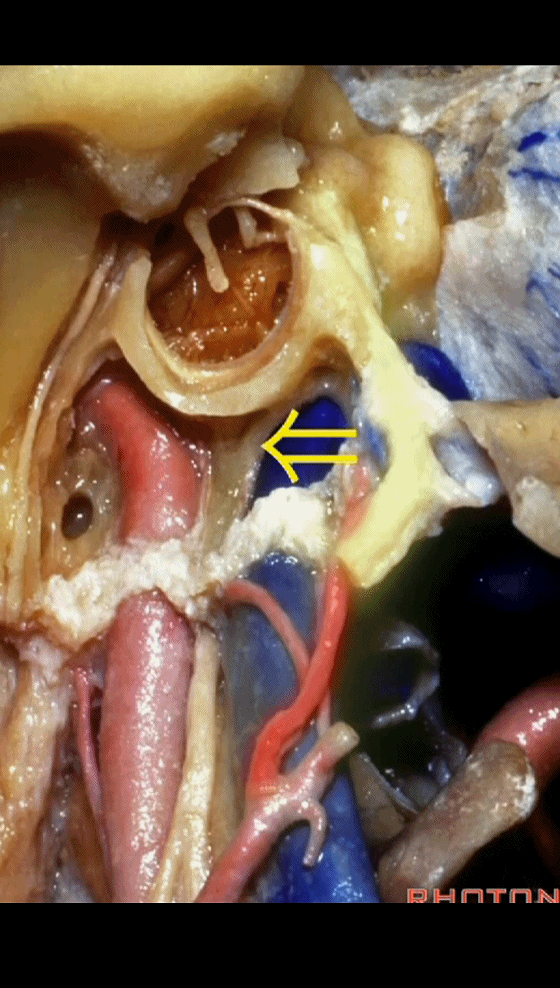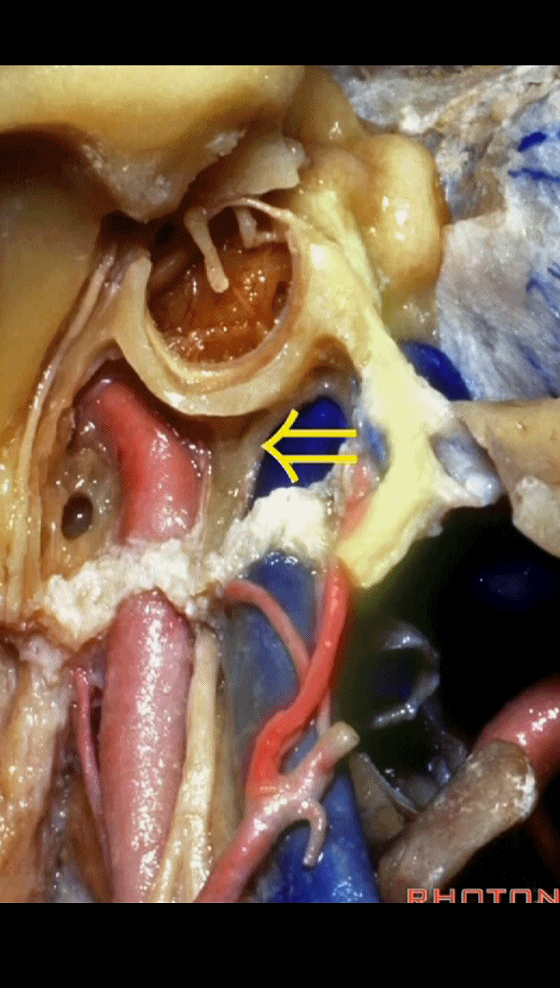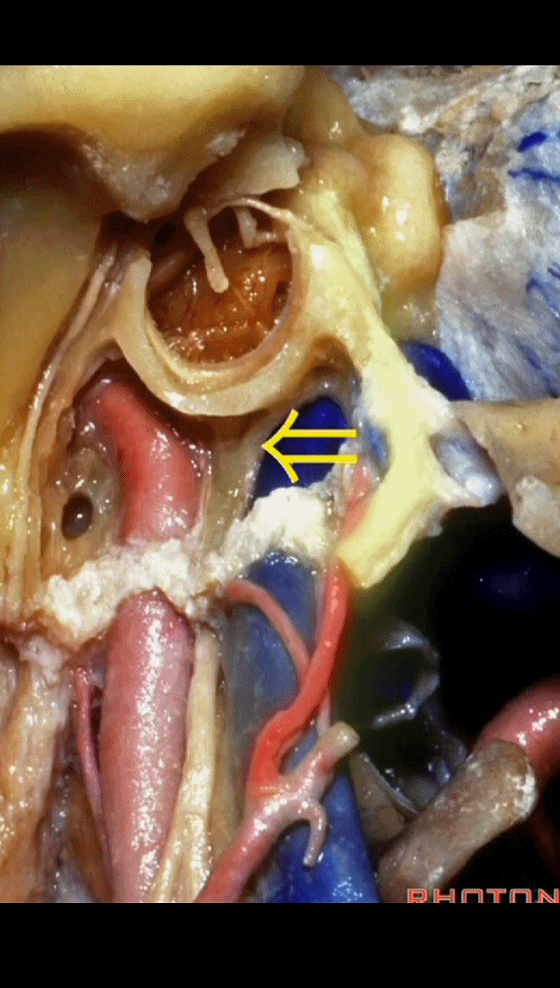
▼该处即为颈静脉孔(jugular foramen 下图),位于枕骨髁旁部的前方。
Over in this area we have jugular foramen here in front of this paracondylar part of the occipital bone.
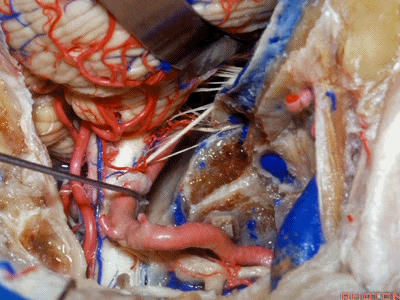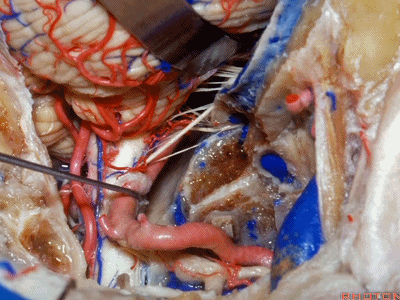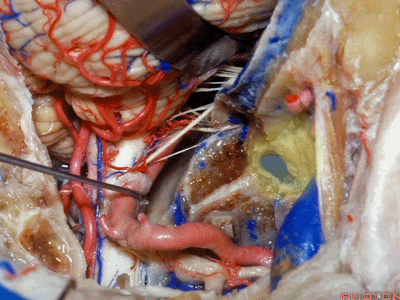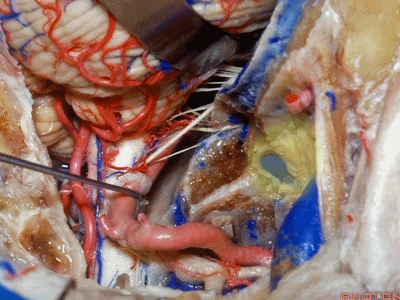
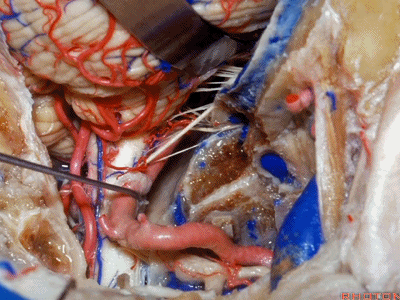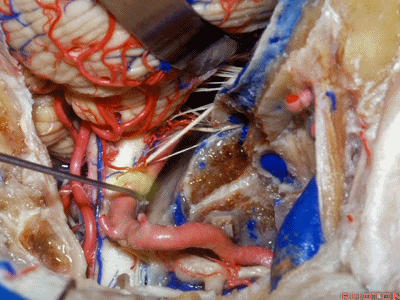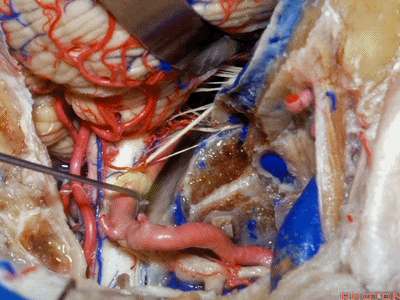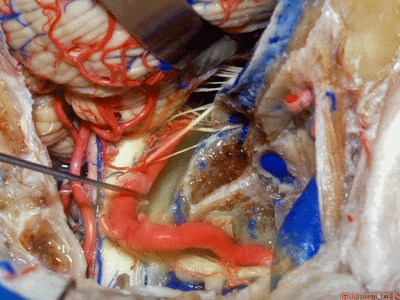
▼接下来,我们移开椎动脉,
And now,here we mobilize the vertebral and this is a...what is that...
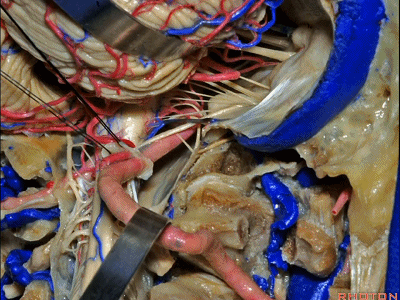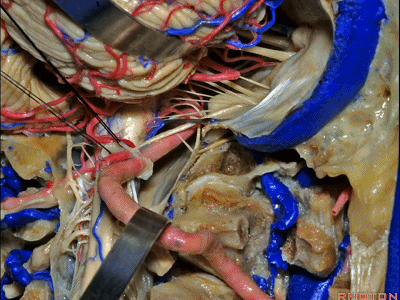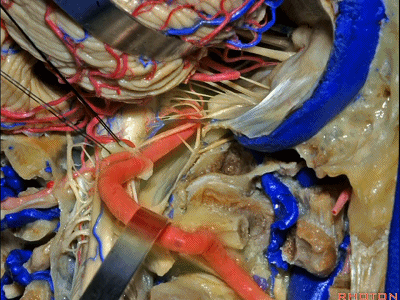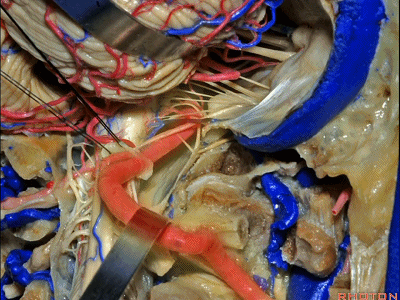
▼这是硬膜外起源的小脑后下动脉 。因此,切勿在硬膜外损伤该血管。
that's an extradural origin of the PICA. So,you want to be very careful and not occlude that artery extradurally.
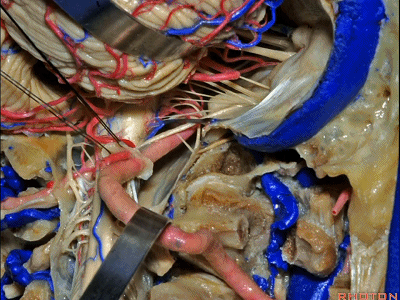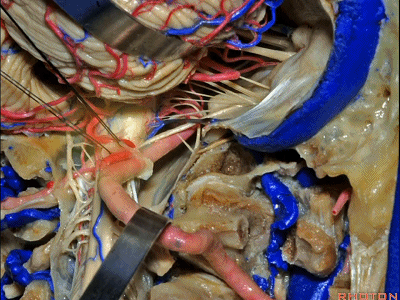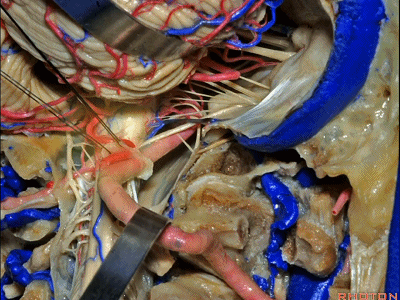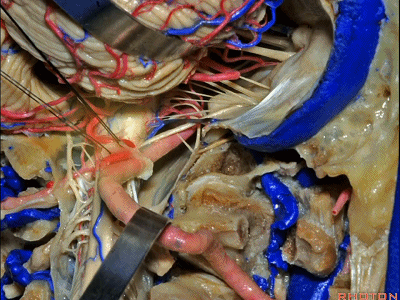
▼同时我们作了髁旁扩展,以暴露颈静脉孔后方。从后方入路暴露颈静脉孔。
Here we've also drilled out paracondylar to expose the back side of the jugular foramen, a posterior approach to the foramen.
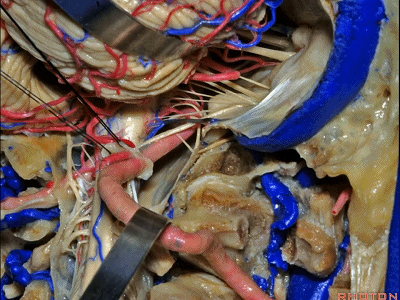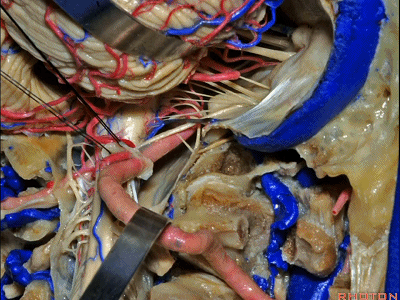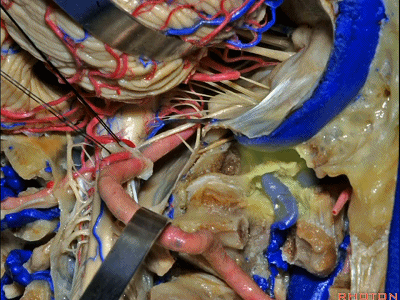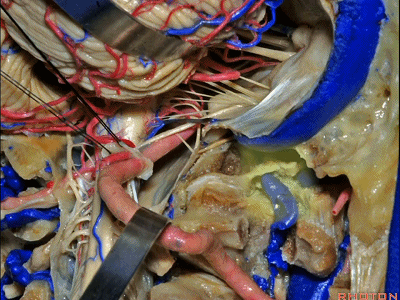
▼再让我们对比一下常规的远外侧入路(下图右侧)与经髁扩展(下图左侧)。
But this just compares far lateral approach with a transcondylar approach.
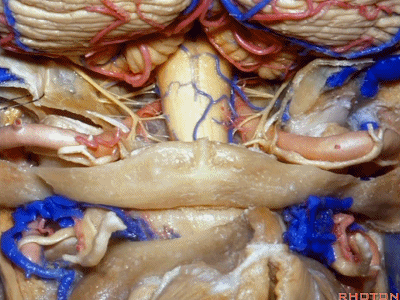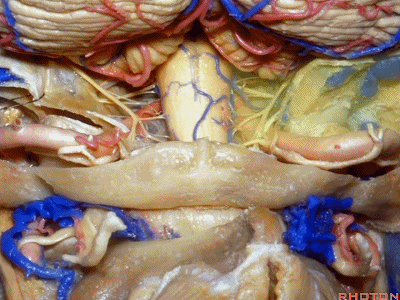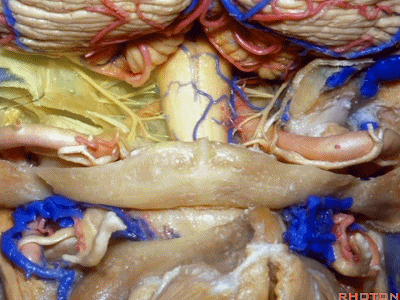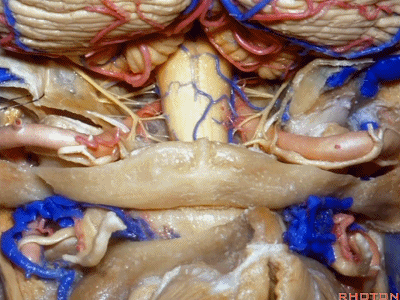
▼你会发现尽管枕髁位于前外侧(下图),但它们仍然阻挡了通向脑干前方的视线。
And you see even though the condyles are anterolateral, they still can block access to the front of the brainstem.
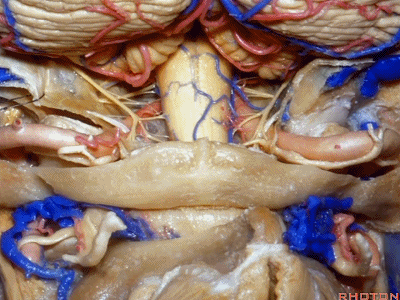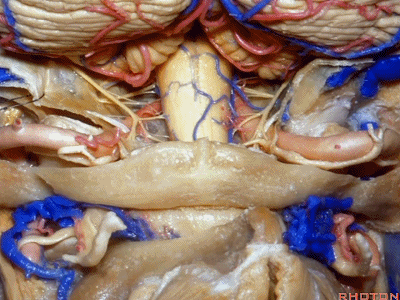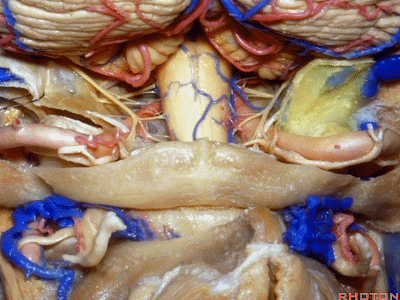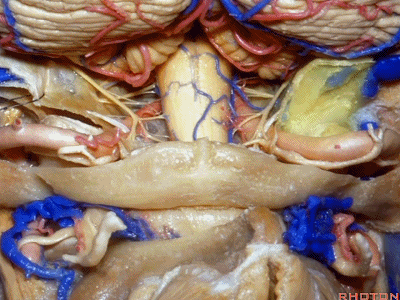
▼而下图左侧我们磨除了枕髁,你可以感受下这一角度向前方扩展了多少。
And here's the approach drilling out the occipital condyle. You see how much further forward that angle is.
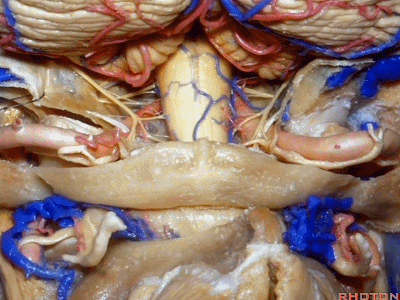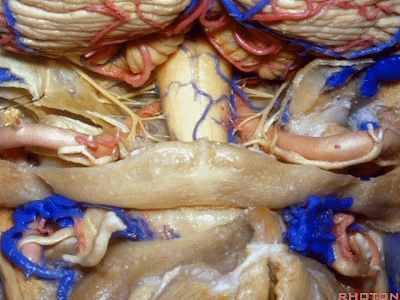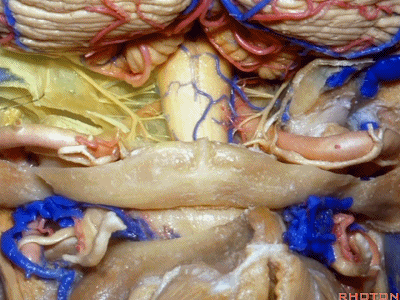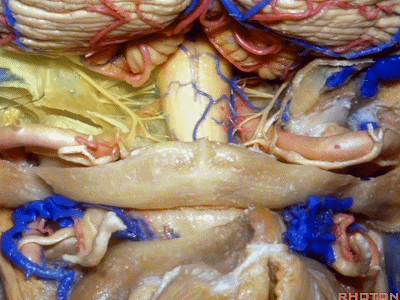
▼将硬膜向后翻开,磨除枕髁,即为经髁入路。
And if you pull this dura backwards,you can drill out the condyle, then in a transcondylar approach.
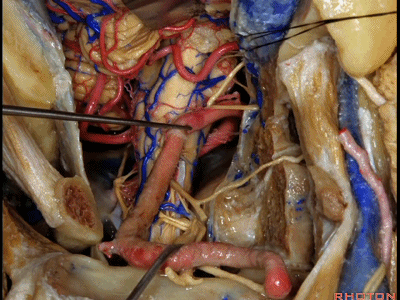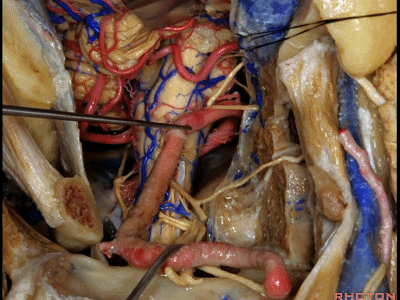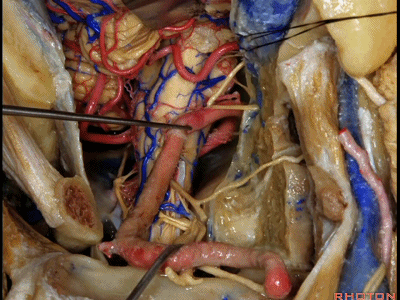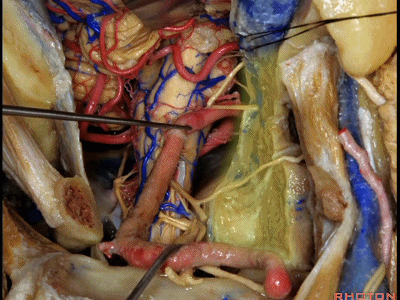
▼现在可以越过延髓前方,暴露至对侧椎动脉。
You can actually look across in front of the medulla to the contralateral vertebral artery.
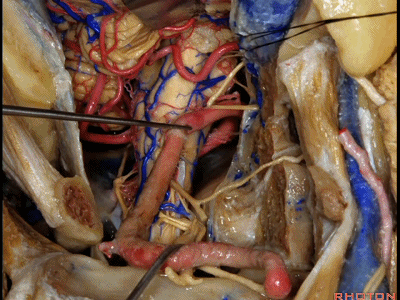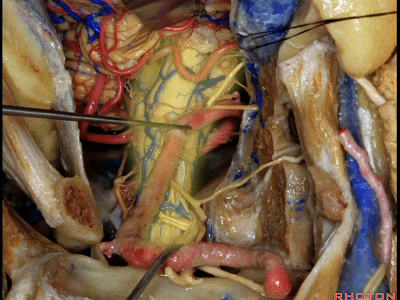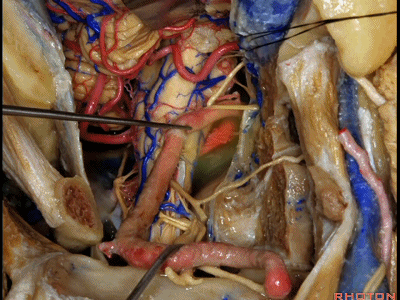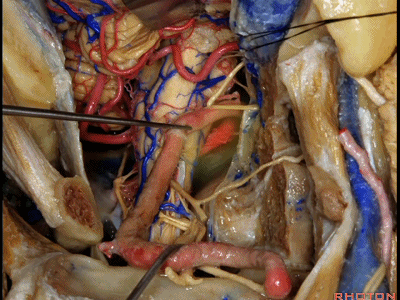
▼我们可从舌下神经下方,进入下斜坡,切除下斜坡脊索瘤,直至对侧的舌下神经管。因此,通过该入路也可暴露下斜坡,而不需要经过口腔或鼻腔。
You can actually look across in front of the medulla to the contralateral vertebral artery.We're looking under the hypoglossal nerve. You can get into the lower clivus, and take out chordoma in the lower clivus, all the way across to the contralateral hypoglossal canal. So, this is a route you can take to the lower half of clivus without coming through the oral cavity or through the nasal cavity.
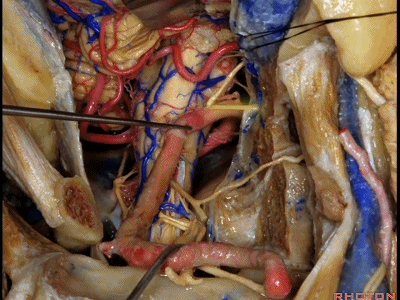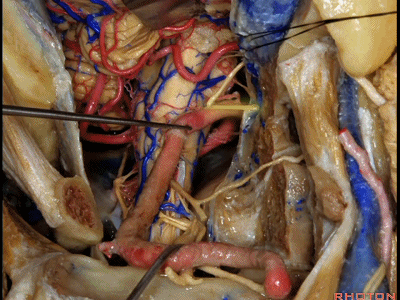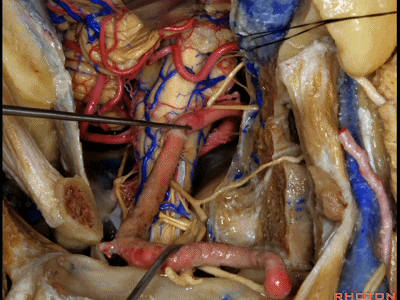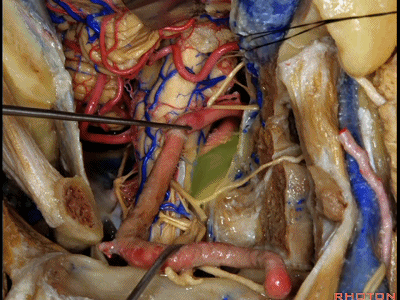
▼这里我们分离头外侧直肌,进行髁旁暴露(下图)。
Now here we've detached the rectus capitus lateralis, and have done a paracondylar exposure.
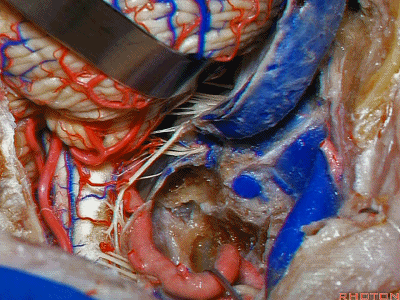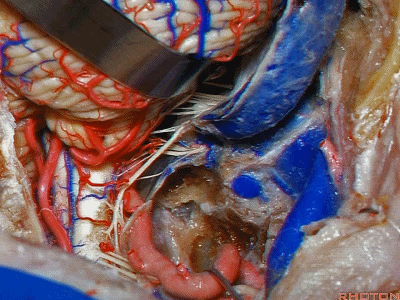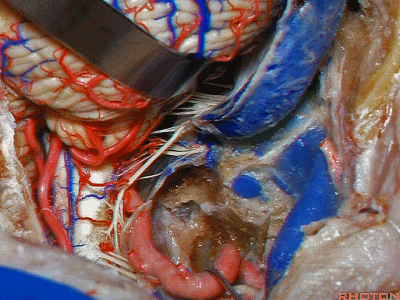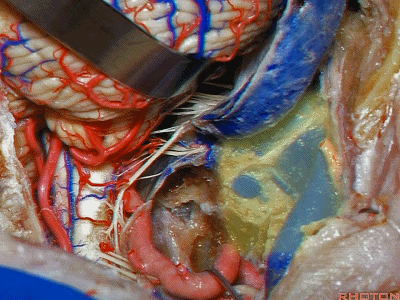
▼倘若病变已侵犯颈静脉球,则可结扎乙状窦和颈内静脉(下图)。在移位椎动脉之后,从后方切除这一段乙状窦。
And here, if the pathology blocks off the jugular bulb, then you can ligate the sigmoid and the internal jugular vein.And you can resect this segment of the sigmoid from the back, after you mobilize the vertebral artery.
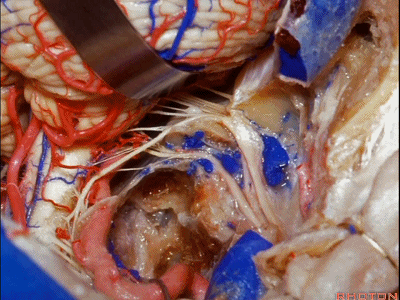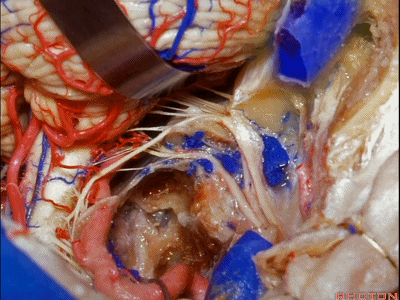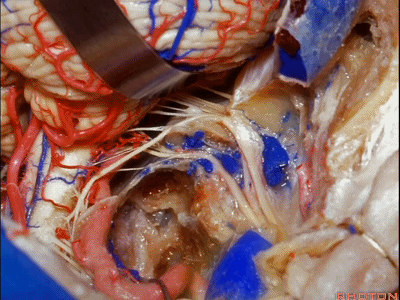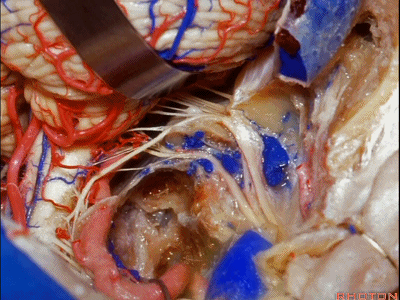
▼但是这一后方入路对于更为前方的暴露有限,例如当颈静脉孔区病变向前侵犯至咽鼓管或颞下窝的时候。
But this posterior approach will not get you forward to much of the pathology in the jugular foramen that extends forward down the eustachian tube or into the infratemporal fossa.
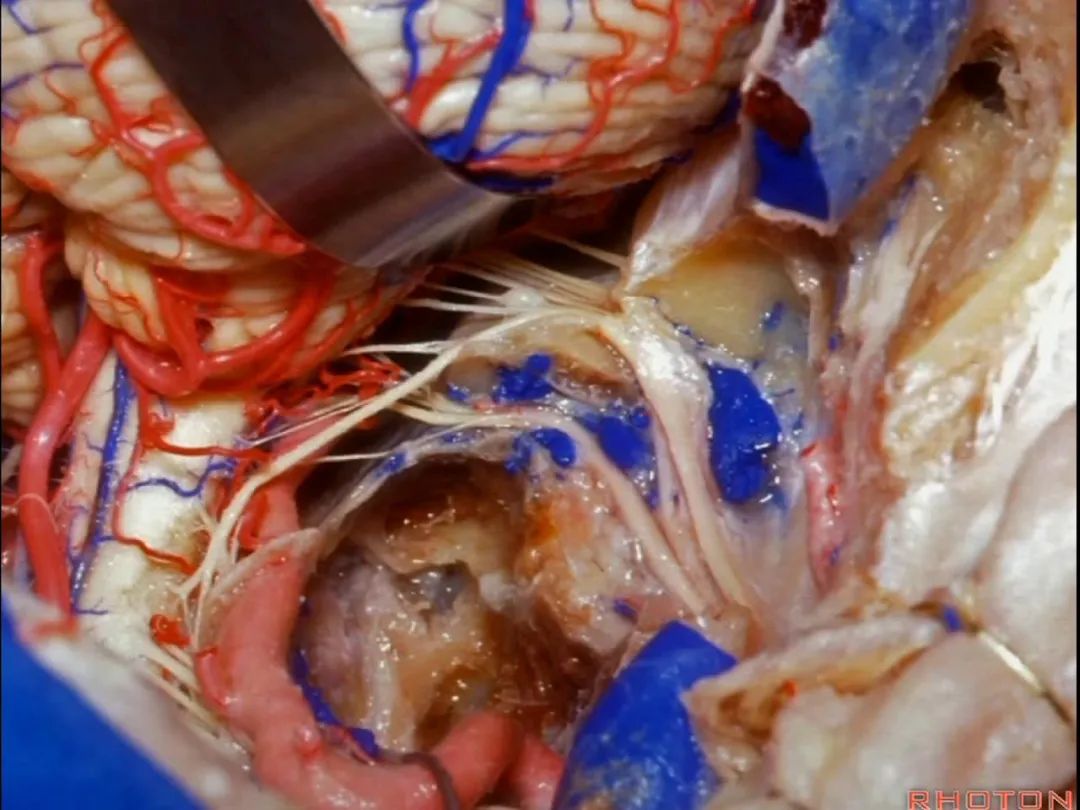
▼再看看后方暴露的颅神经(右侧)。下图示舌咽神经 IX
And here's just the exposure of the nerve from the back,and we see IX,
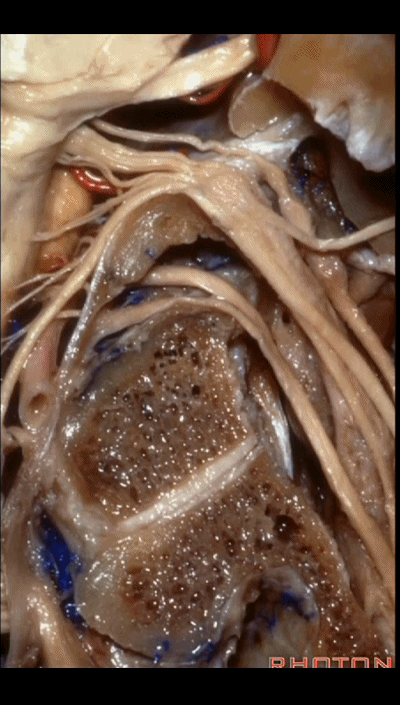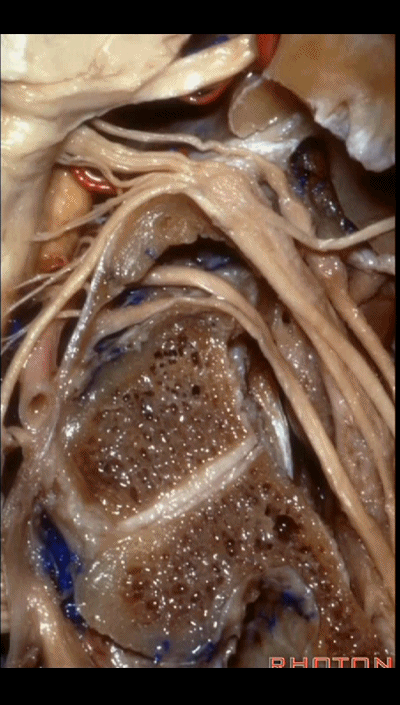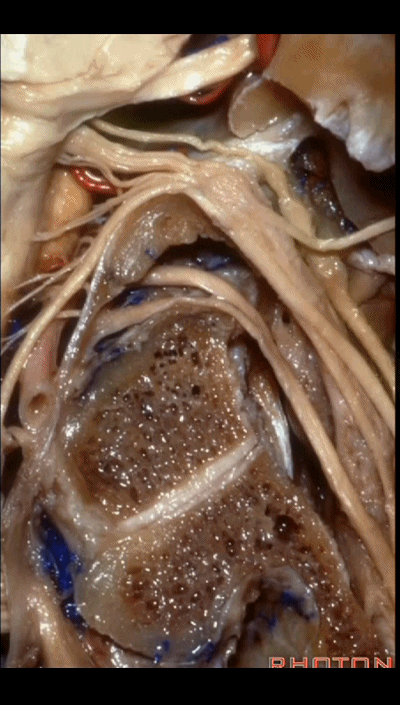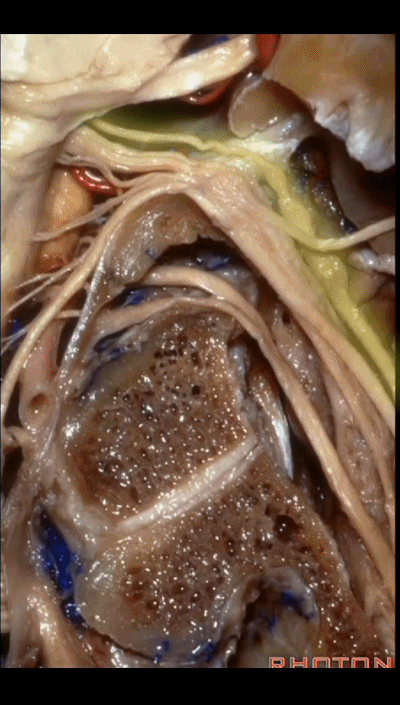
▼下图示 迷走神经 X
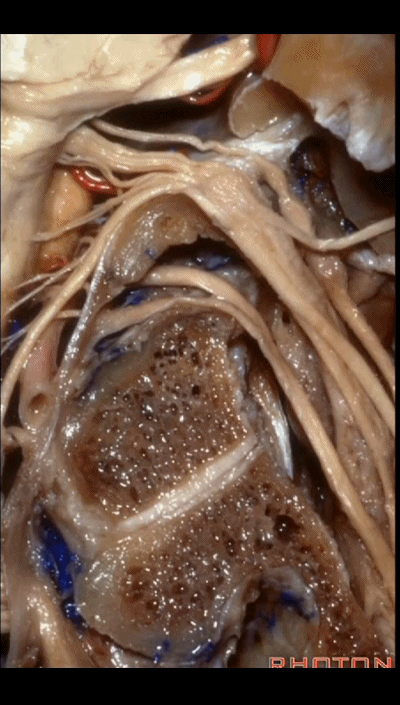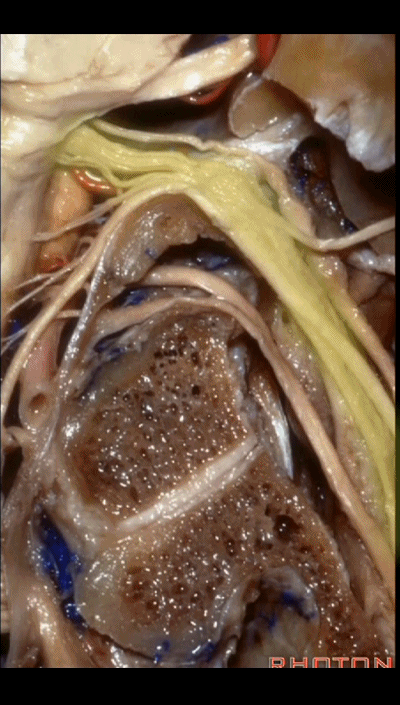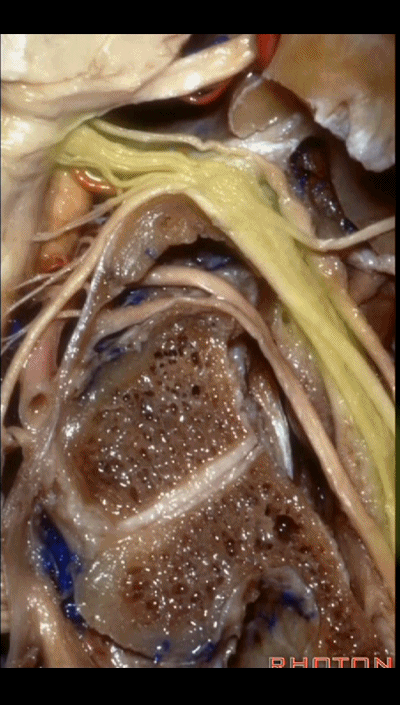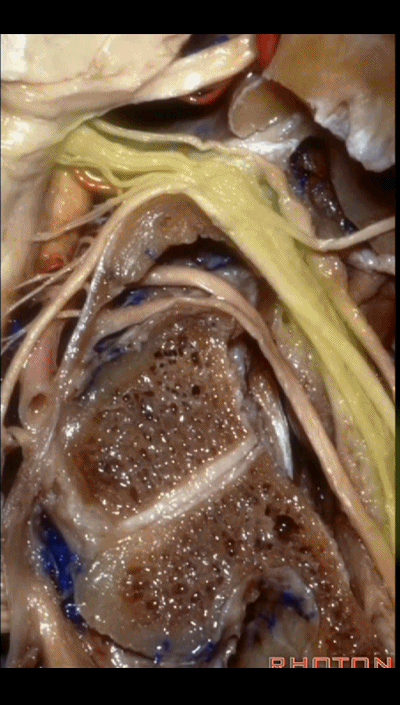
▼下图示副神经 XI
and this is the XI here
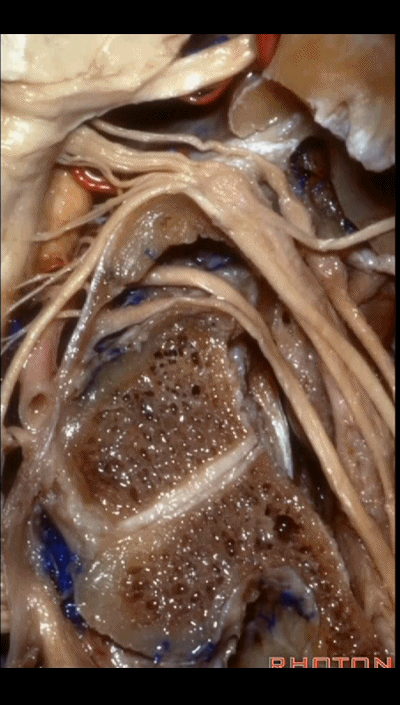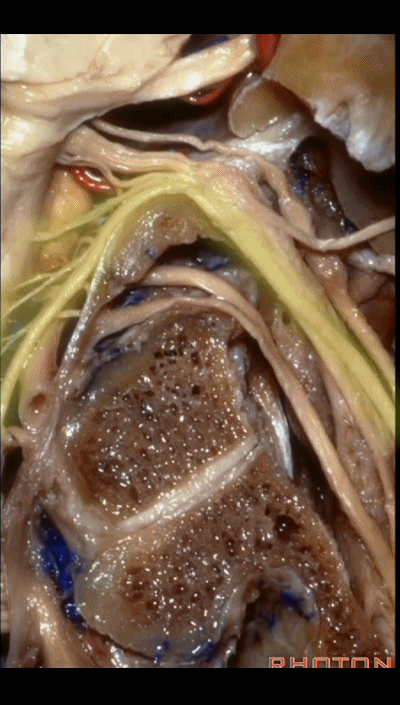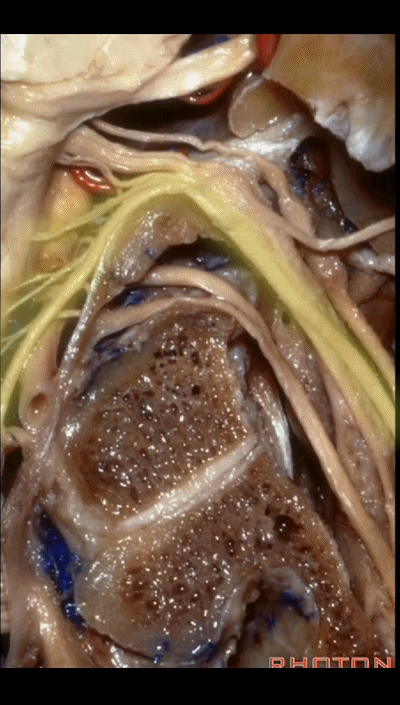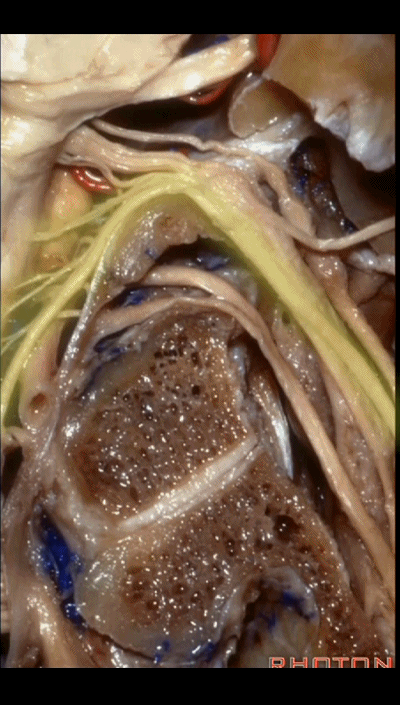
▼下图示 舌下神经(hypoglossal nerve)
and this is the hypoglossal nerve coming through the hypoglossal canal.
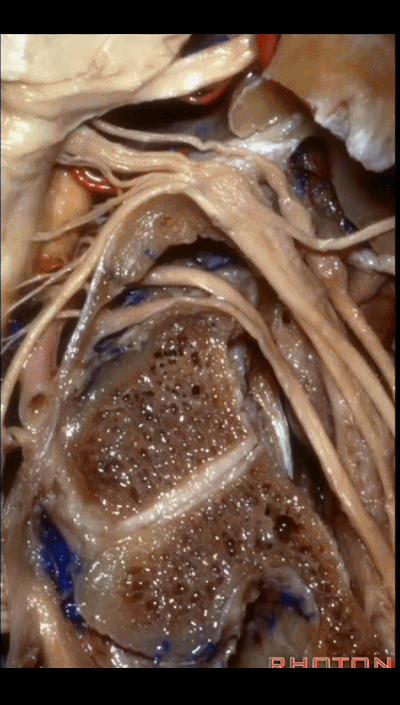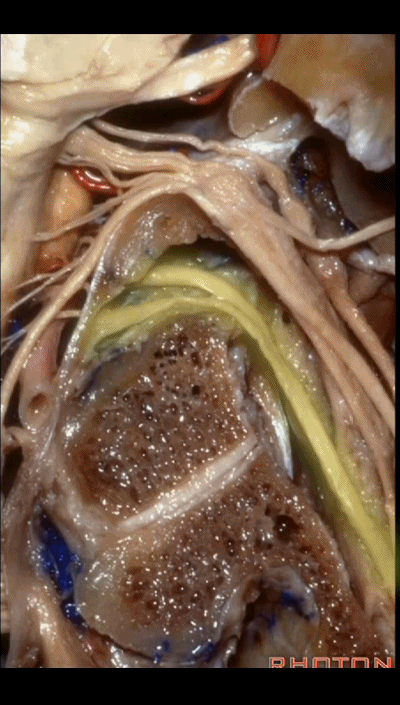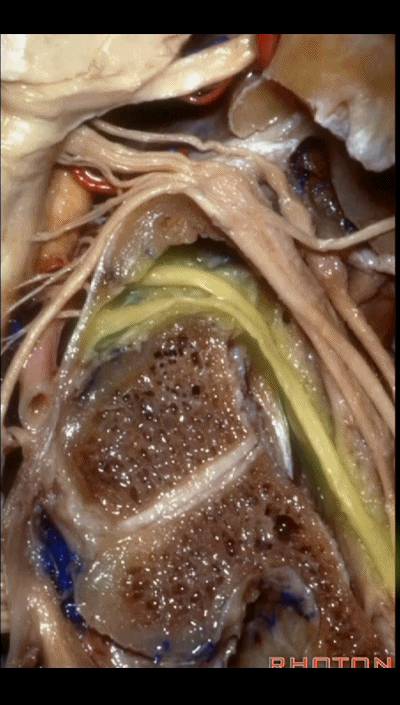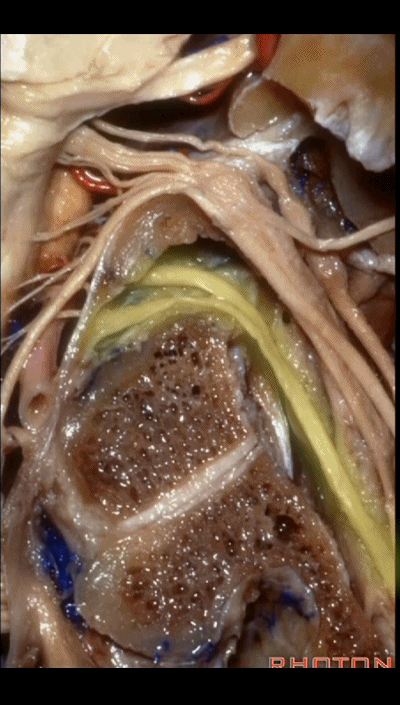
▼下图示 舌下神经管(hypoglossal canal)
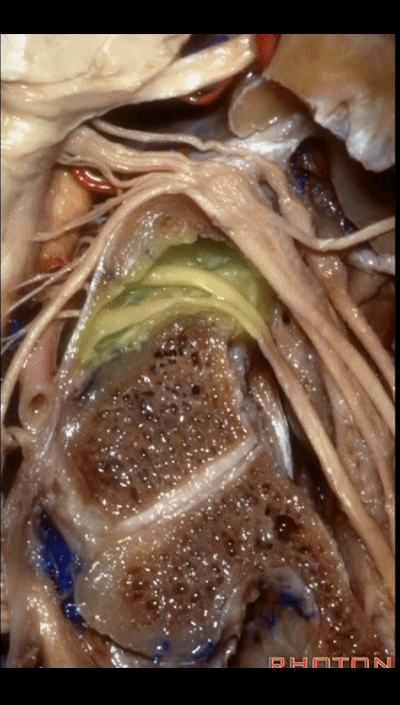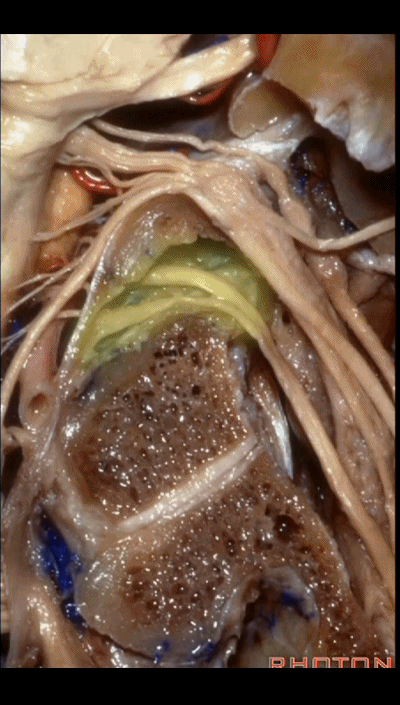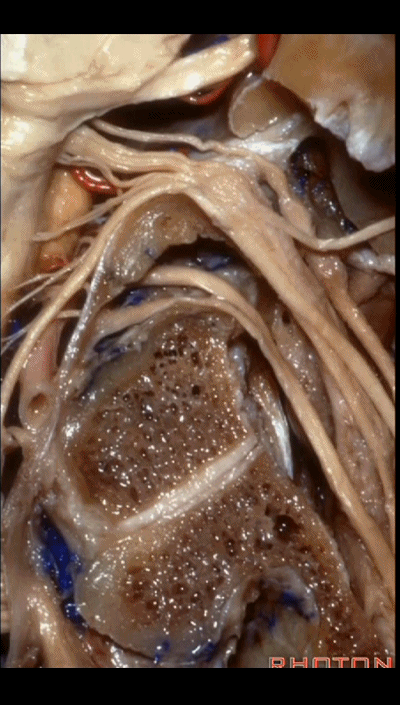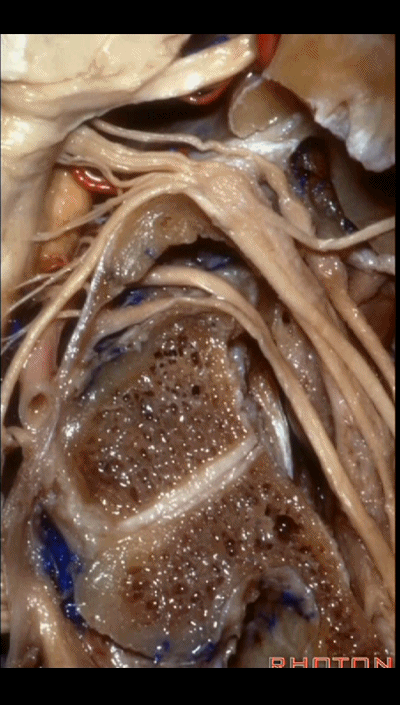
这四条神经随即与颈内动静脉伴行,从颈静脉孔下方即进入颈动脉鞘的上部。
But you see four nerves join the internal jugular vein and carotid just below the jugular foramen in the upper part of the carotid sheath.
▼下图中发自舌咽神经的是 Jacobson's神经(舌咽神经的鼓室支),Jacobson's神经越过岬部即移行为岩小神经,其进入耳神经节,并最终支配腮腺。
And arising right here is what nerve? What arises from IX here? Jacobson's nerve (the tympanic branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve). What does this Jacobson's nerve eventually become?Jacobson's nerve crosses the promontory and it becomes the Lesser petrosal which ends up going through what ganglion? Otic, and ends up innervating parotid gland.
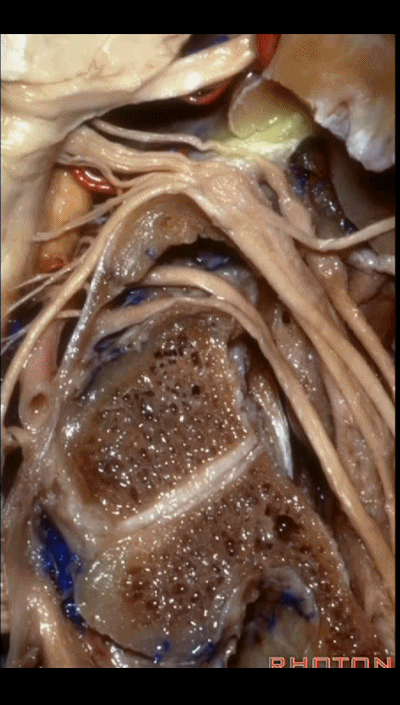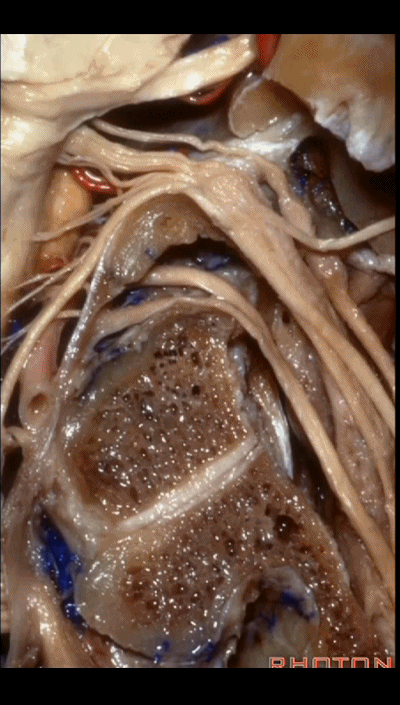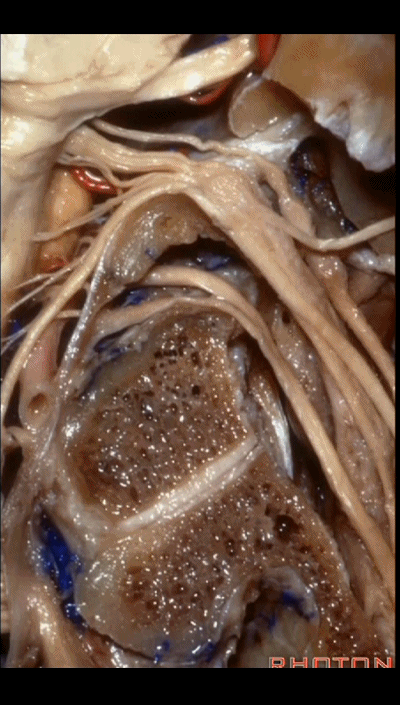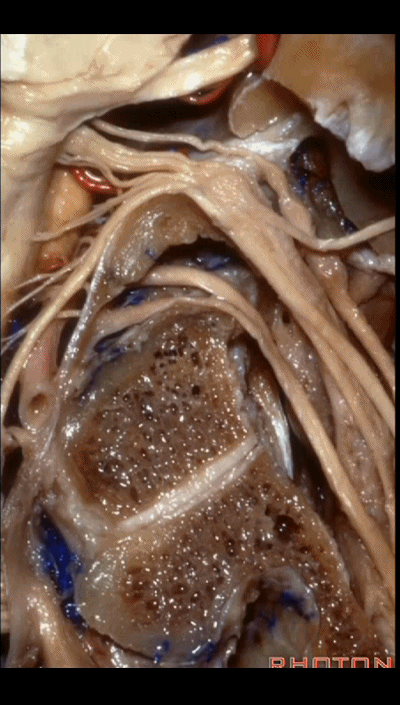
▼这根沿着颈静脉球前壁、颈静脉窝走行的神经是 Arnold's神经(迷走神经的耳支)。Arnold's神经接受外耳道皮肤的一般躯体感觉传入。
Now, what nerve is this that passes along the anterior wall of the jugular bulb, the jugular fossa?Arnold's nerve (the auricular branch of the vagus nerve).What is Arnold's nerve? where does it end up?It ends up in the skin around the external canal.
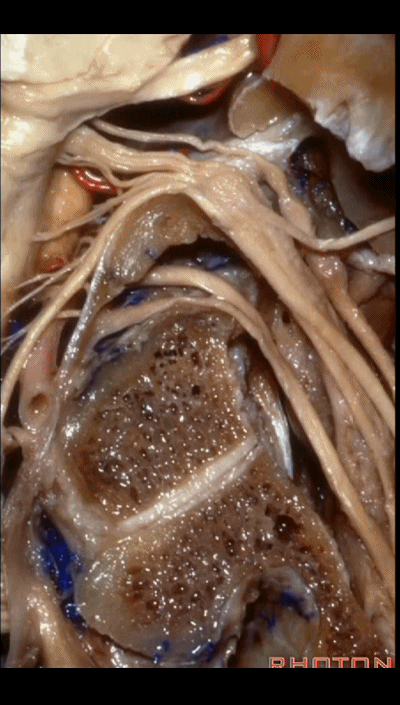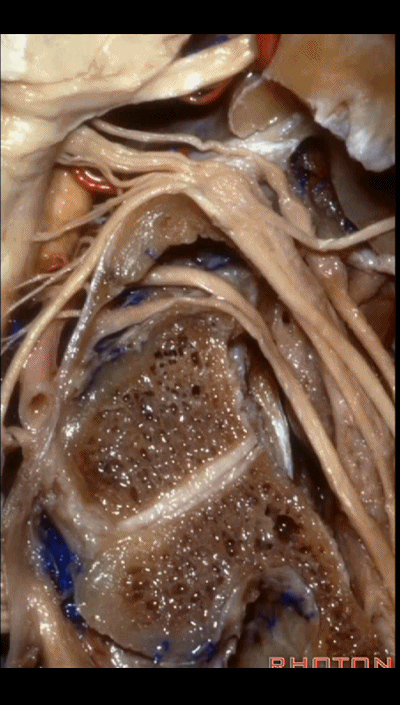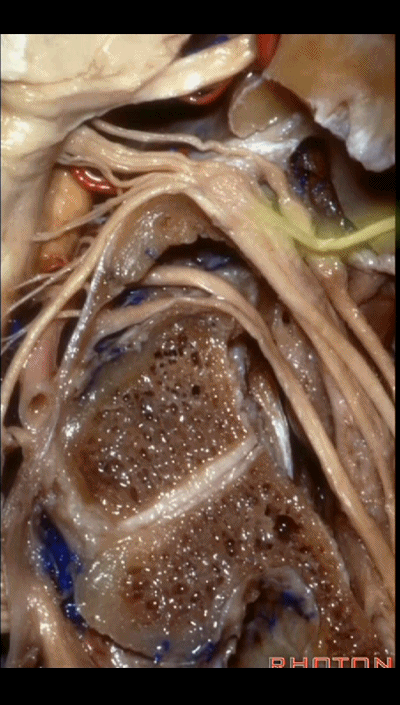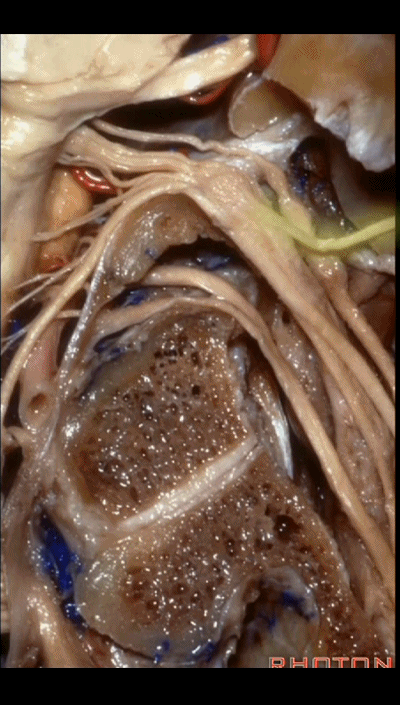
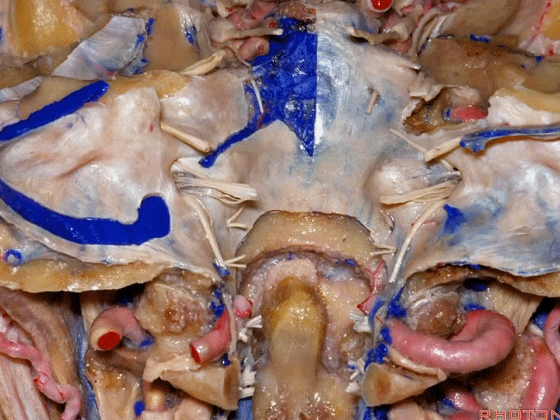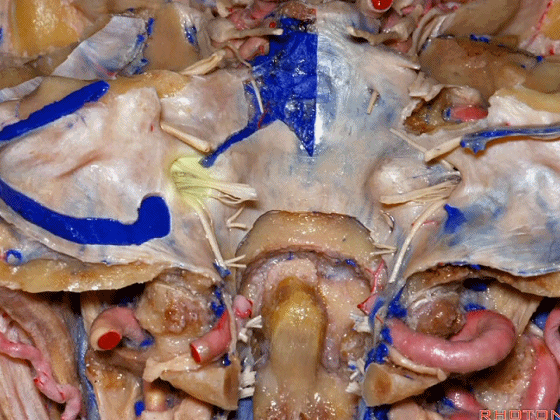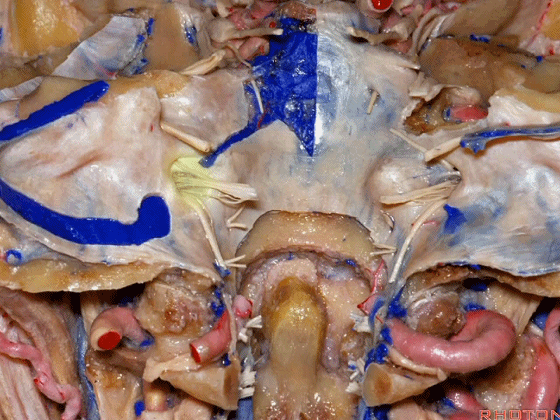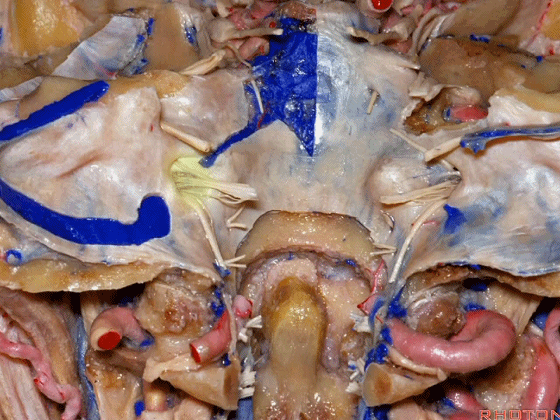
▼下面我们讲解从颈静脉孔向下至寰枕髁区域。在颈静脉孔内下方的结构是颈静脉结节。下图示颈静脉孔(jugular foramen)。
So we move from this area down to the jugular foramen,down to the area along the occipital and atlantal condyle.And in this area just below and medial to the jugular foramen we have the jugular tubercle that.
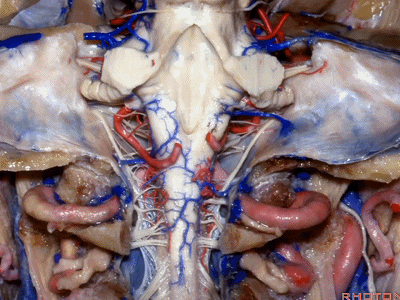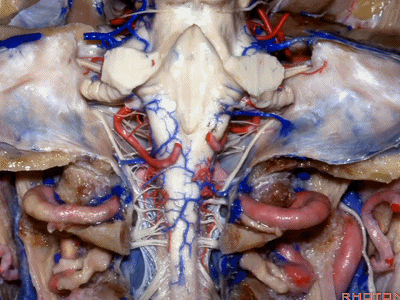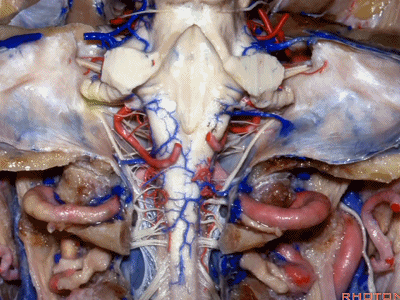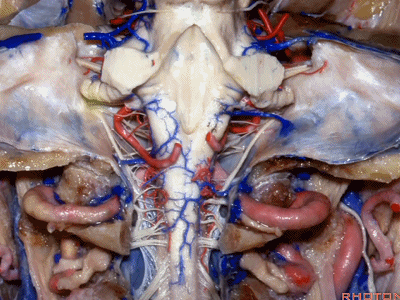
▼下图示颈静脉结节(jugular tubercle)。我们抬起小脑后会发现,其阻碍了至脑干前方的视线。
If you're lifting cerebellum, jugular tubercle that blocks access to the front of the brainstem.
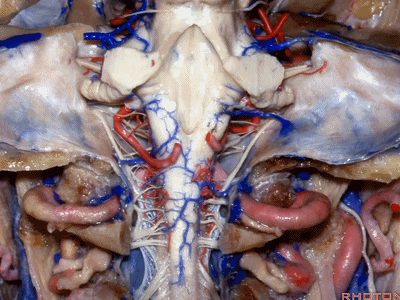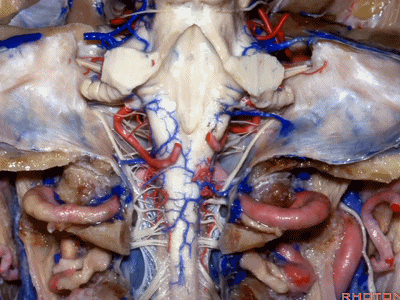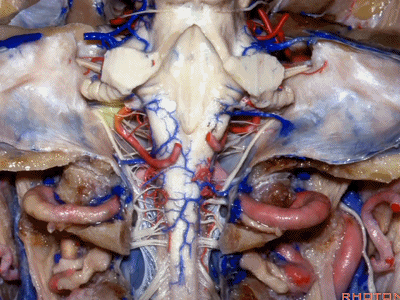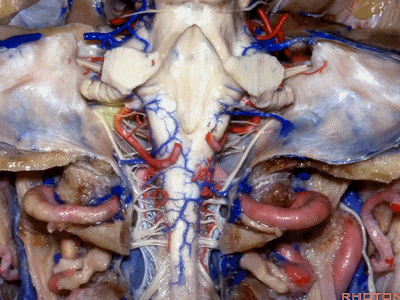
▼这是舌下神经(下图)、枕髁(下图)。从后向前观察枕髁,可见舌下神经穿过枕髁的中部。
here's 12th nerve and it comes through...this is occipital condyle...it comes through the bone just above the midportion...if you look at occipital condyle from back to front,it passes above the midportion of the occipital condyle.
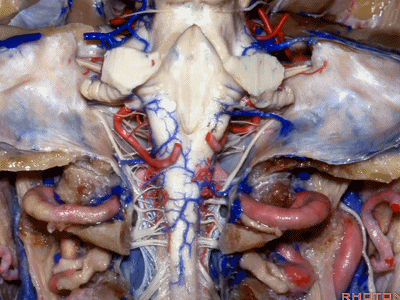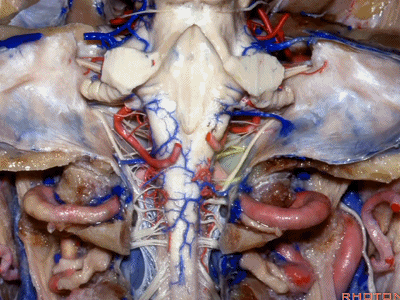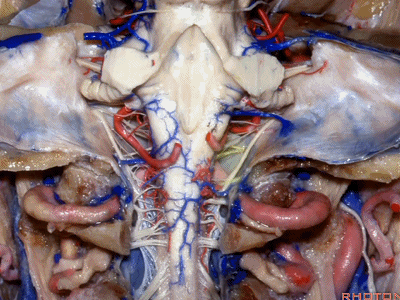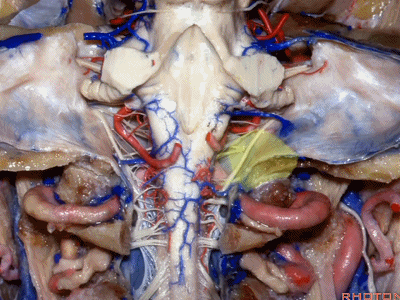
▼当磨至枕髁时,可暴露位于髁旁的颈静脉孔后部(下图)。
If you drill off to the side of the condyle,then in this area, you drill paracondylar, you expose the back of the jugular foramen in this paracondylar location.
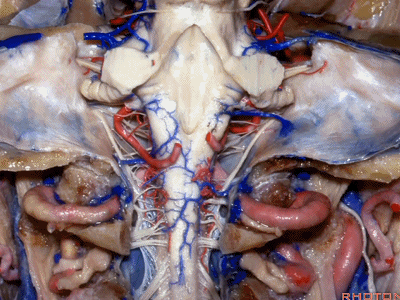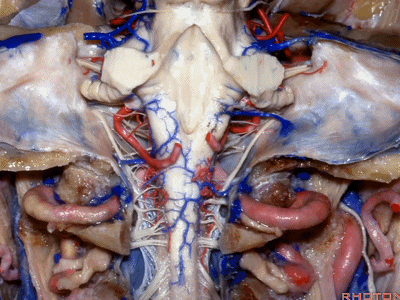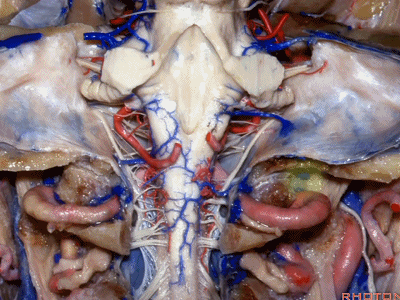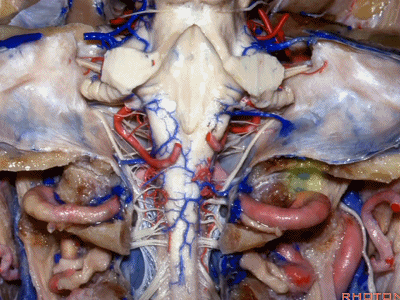
▼下图示去除脑组织,保留椎基底动脉。
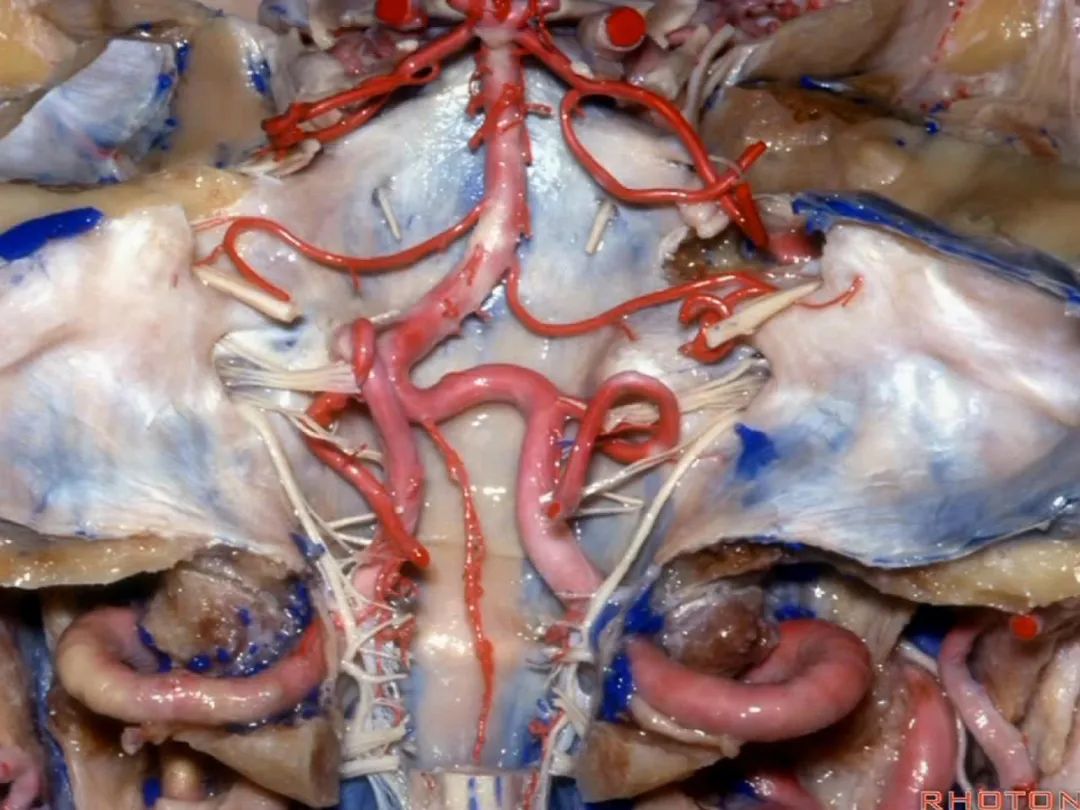
▼下图示去除椎基底动脉,颈静脉孔区(左侧)
So, here we see jugular foramen.
▼岩下窦穿入颈静脉孔的岩部。
The inferior petrosal sinus passes through the petrosal part.
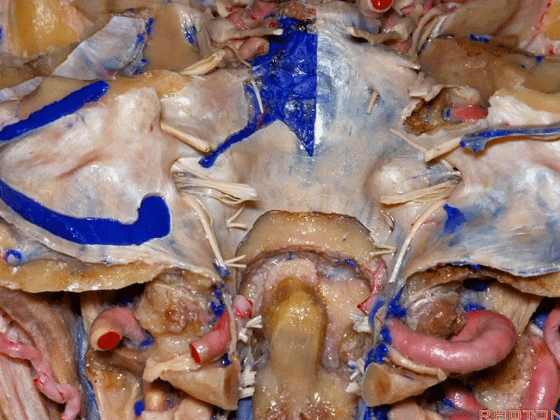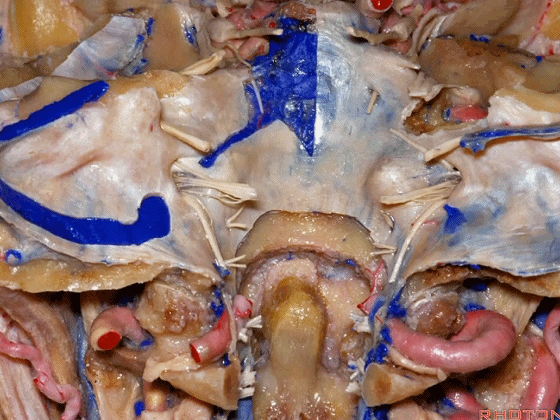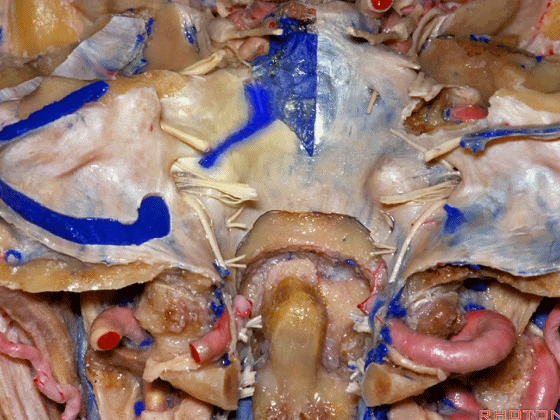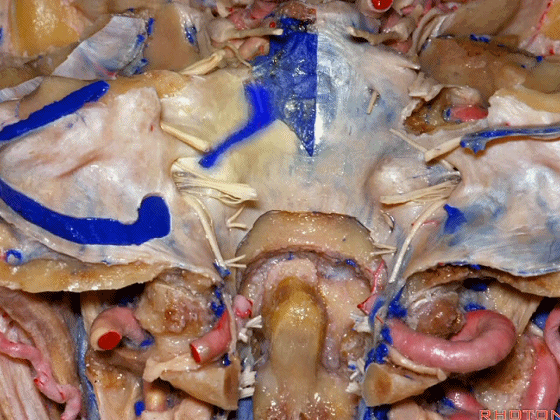
▼乙状窦穿入较大的颈静脉孔的乙状部。
Sigmoid passes through the larger sigmoid part.
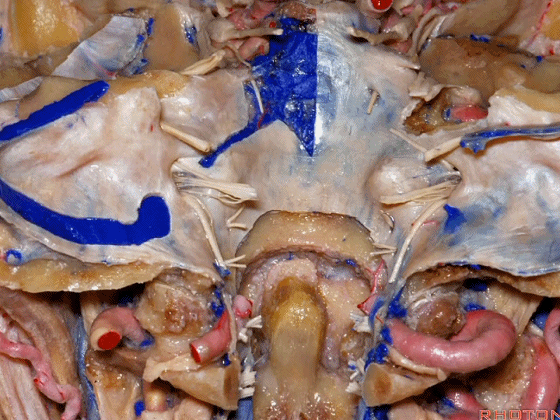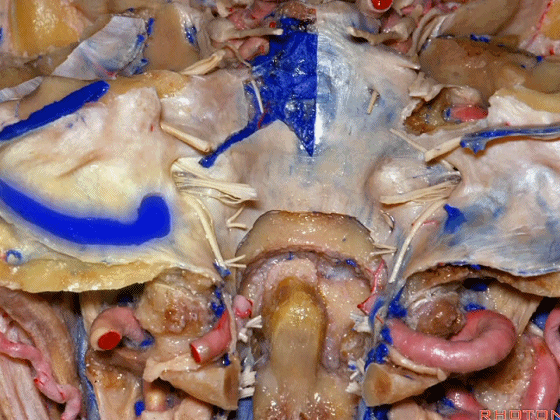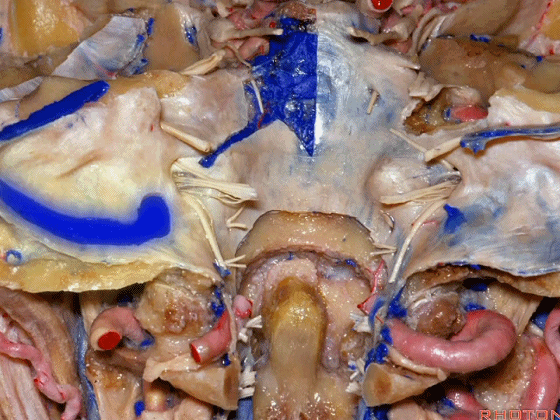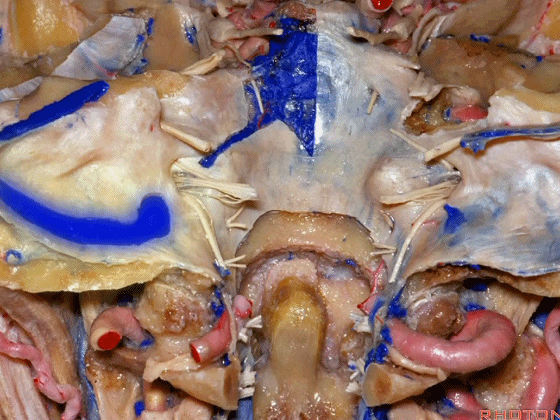
▼再来看看左侧颈静脉孔,这是其顶壁 和 舌咽神经。
Here's the roof of the jugular foramen.
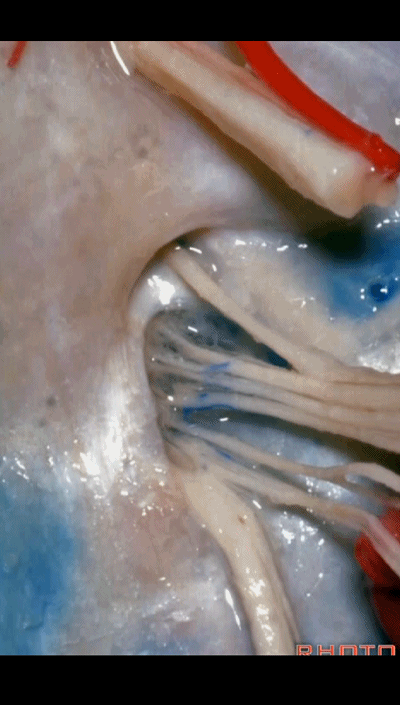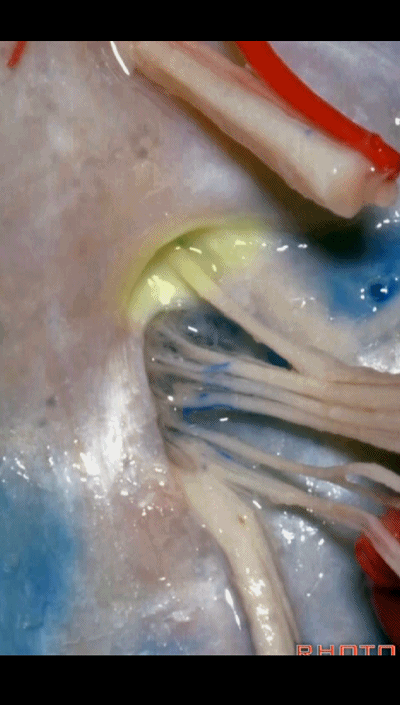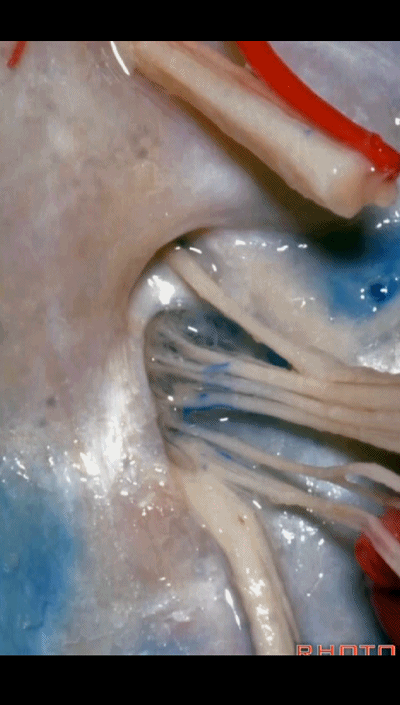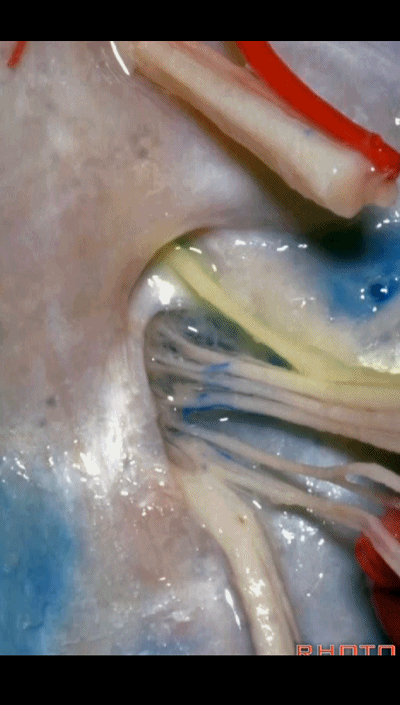
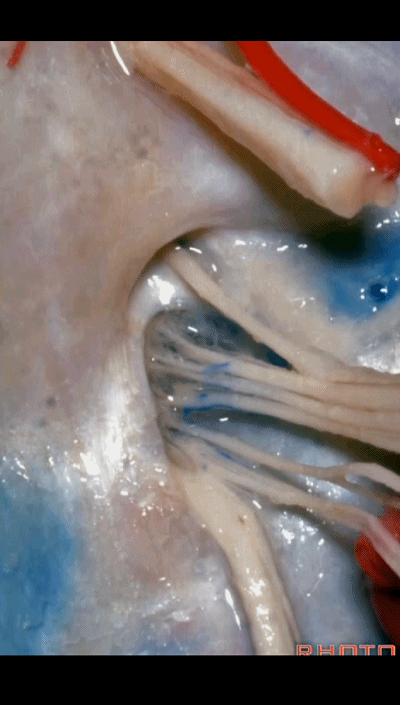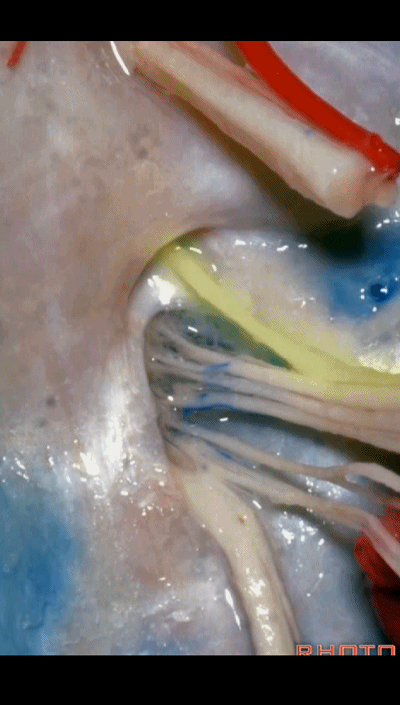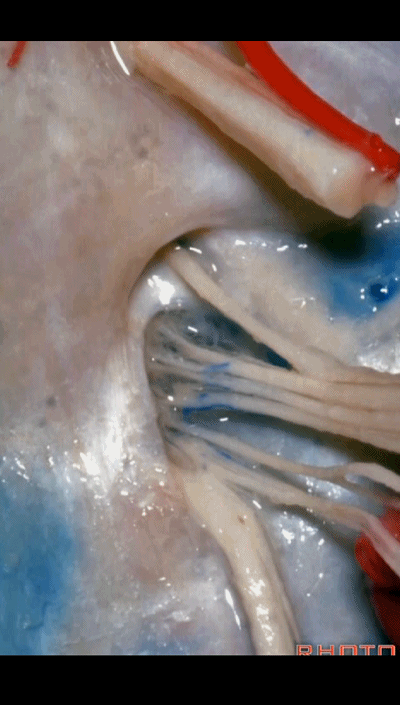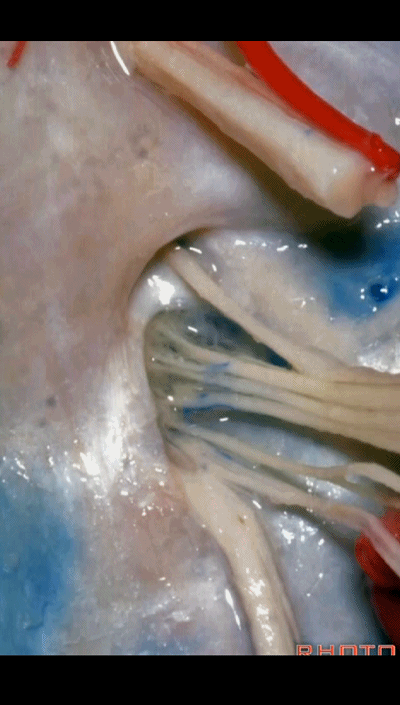
▼在脑池内,舌咽神经贴着迷走神经,很难分辨两者。
And,in the cistern, IX is often adhere to X.You can't tell IX from X.
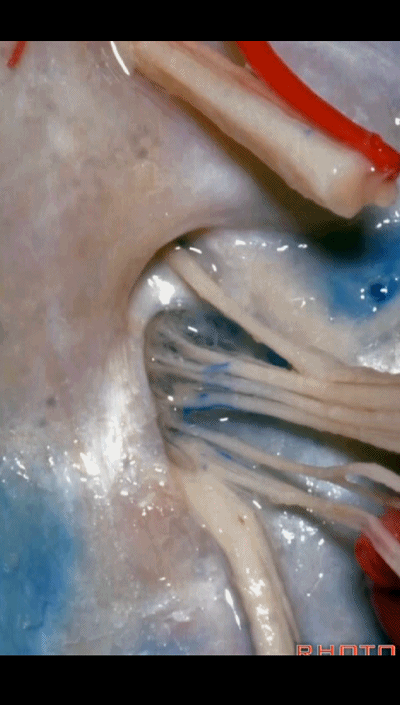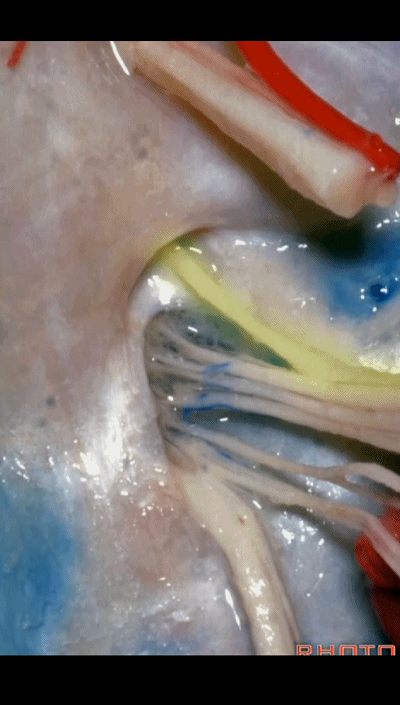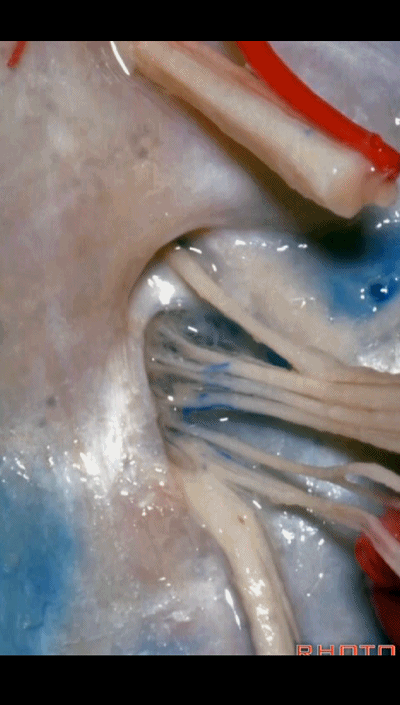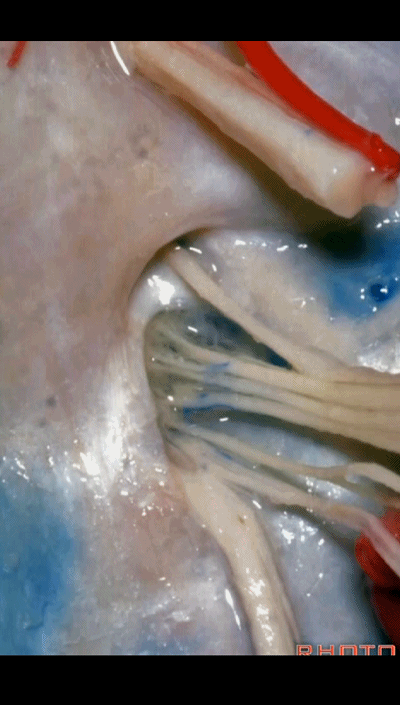
▼但在颈静脉孔的顶壁,有一硬膜分隔(下图)将舌咽神经和迷走神经分开,
But always in the roof of the jugular foramen,there's a dural septum between IX and X,
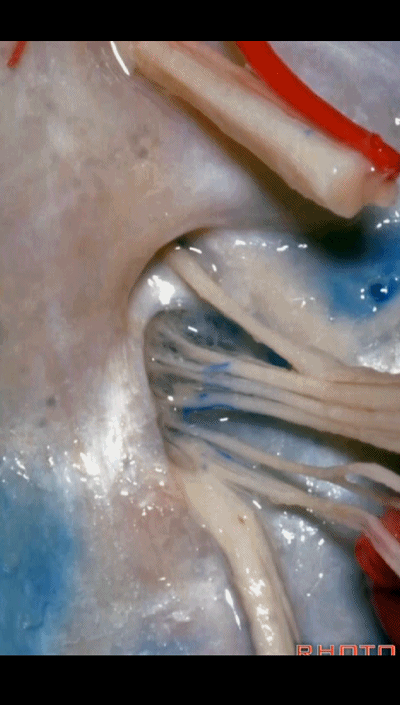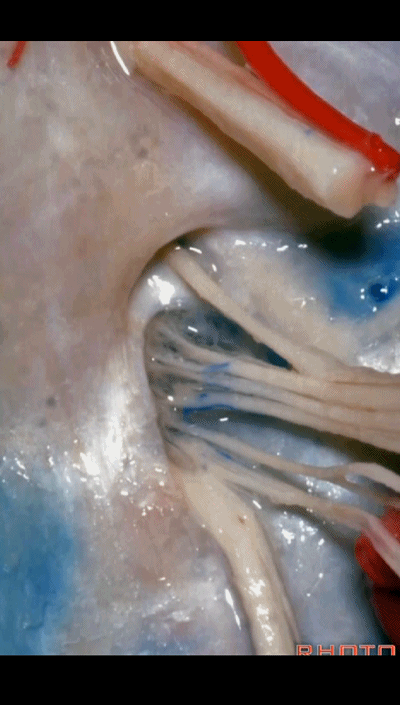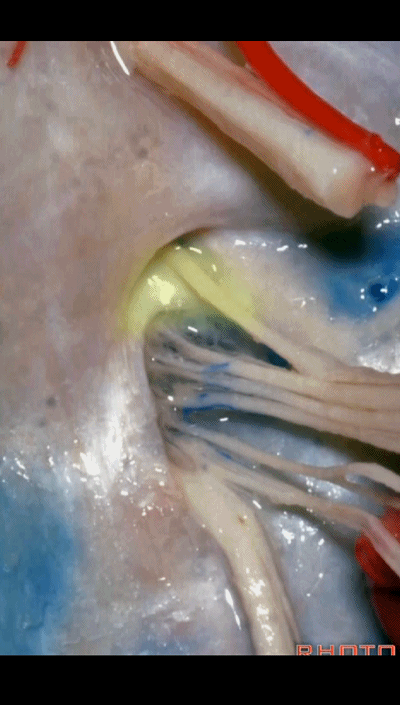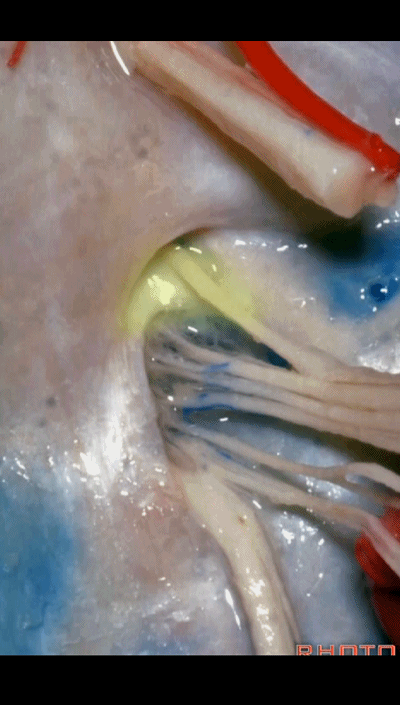
▼在脑池内,舌咽神经贴着迷走神经,很难分辨两者。
And,in the cistern, IX is often adhere to X.You can't tell IX from X.
▼但在颈静脉孔的顶壁,有一硬膜分隔(下图)将舌咽神经和迷走神经分开,
But always in the roof of the jugular foramen,there's a dural septum between IX and X,
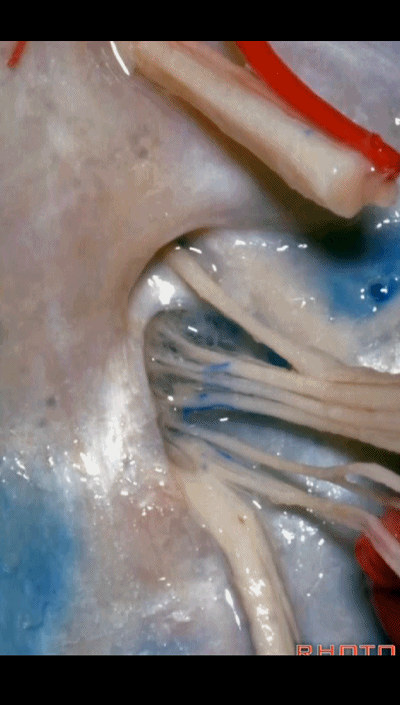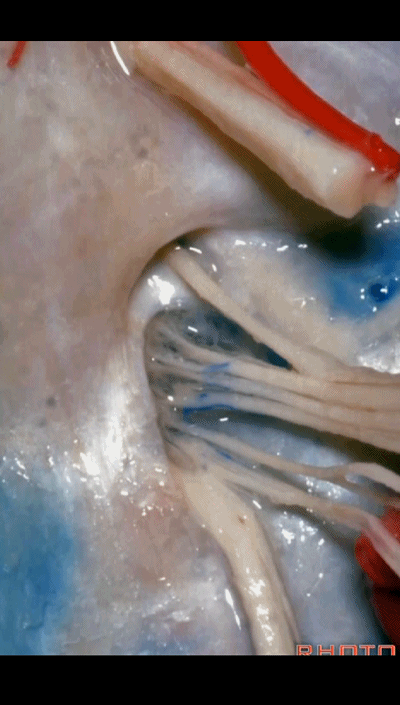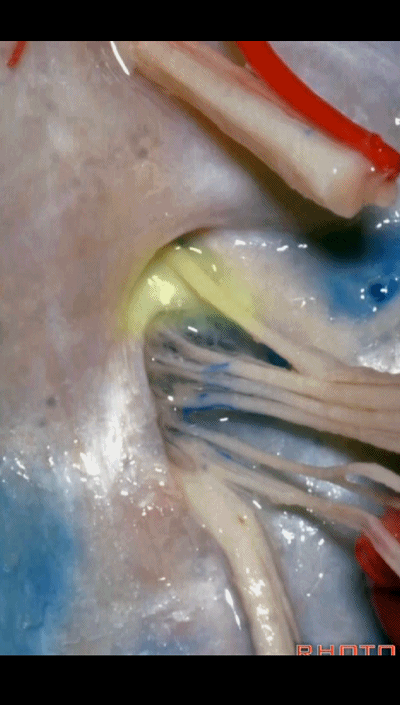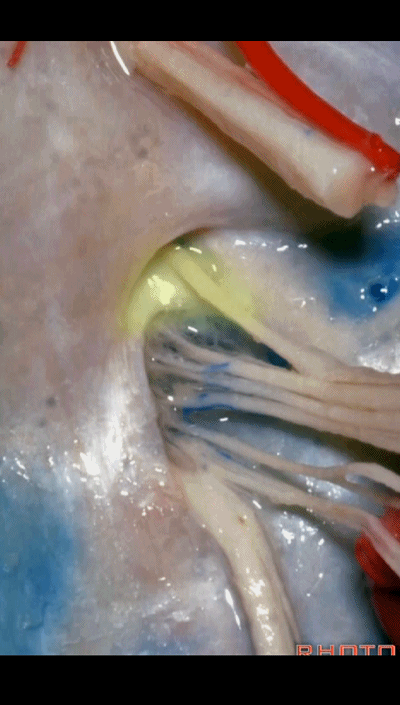
▼我们称下图这个结构为 舌咽道(glossopharyngeal meatus),舌咽神经穿行其中。
and we call this the glossopharyngeal meatus, a little cave that IX enters,
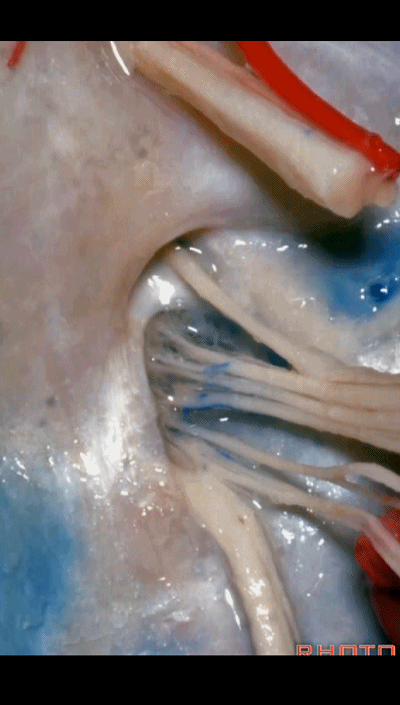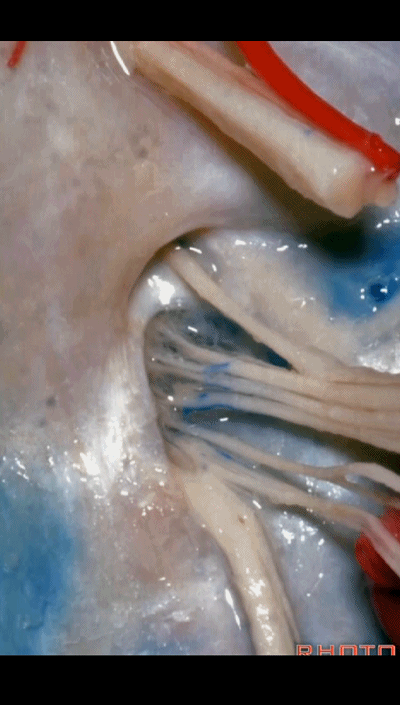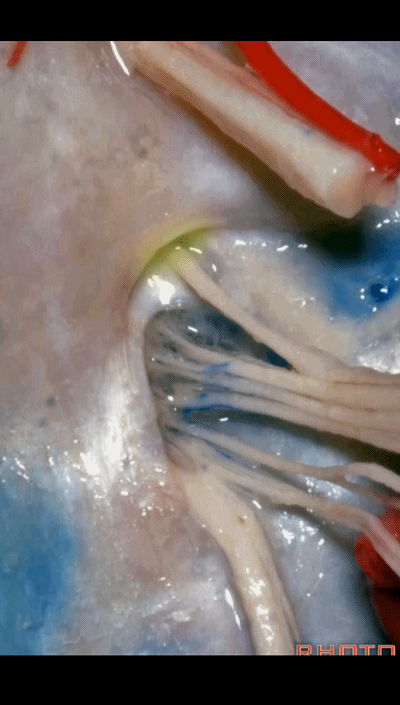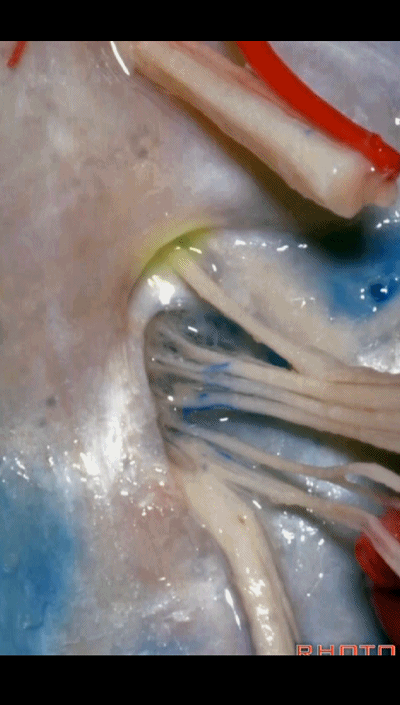
▼下图为迷走道,内有 迷走 和 副神经 穿行。
and this is the vagal meatus that X and XI pass through the dural roof of the foramen.
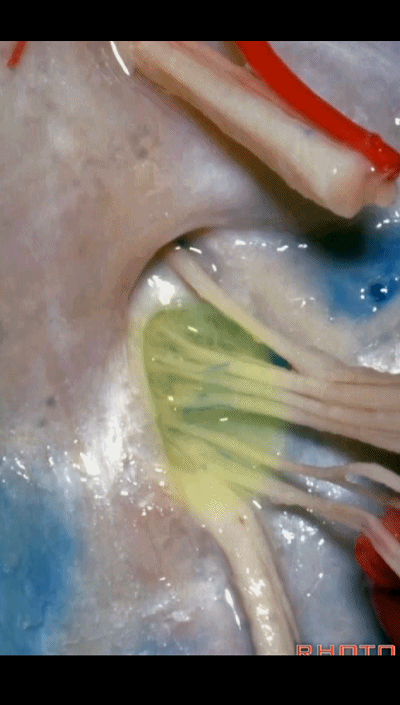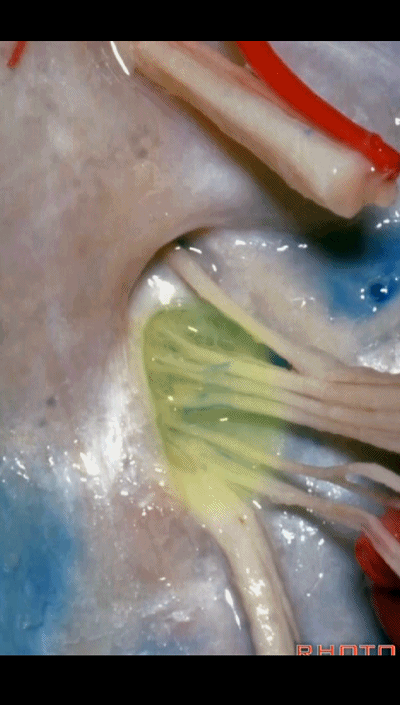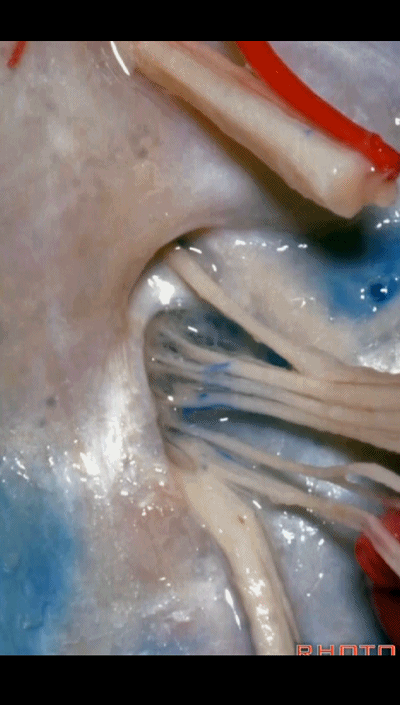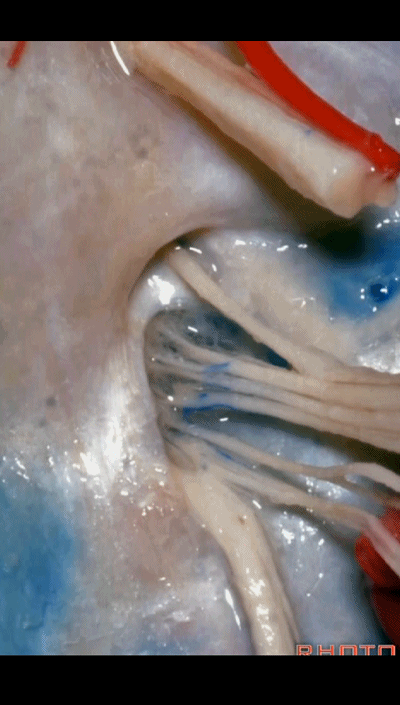
▼下图示放大观。颈静脉孔的岩部、乙状部。
And we blow this up, petrosal part, sigmoid part,
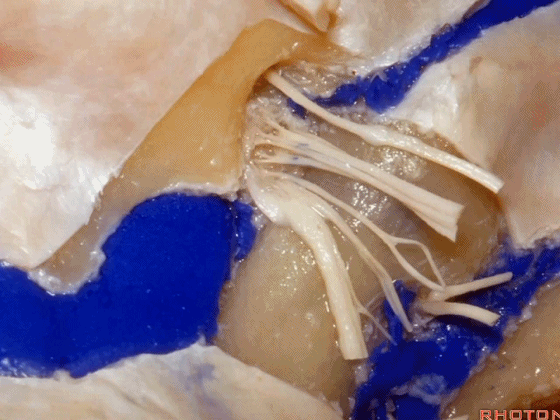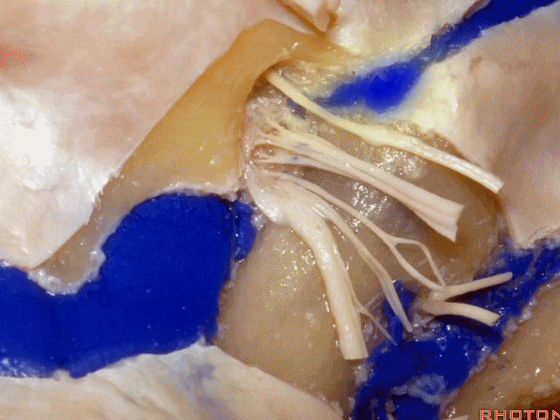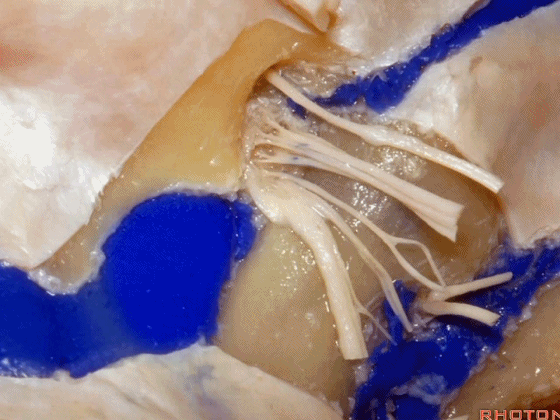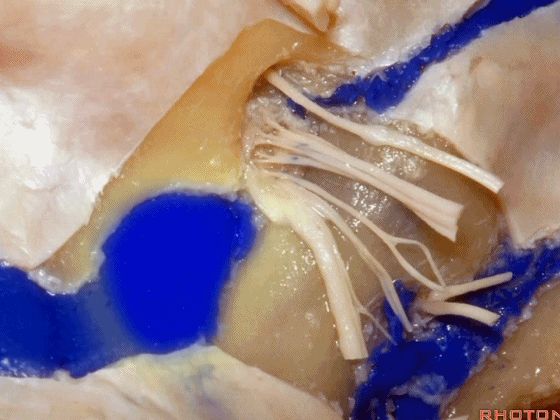
▼颈静脉孔的 中间部(intrajugular part)
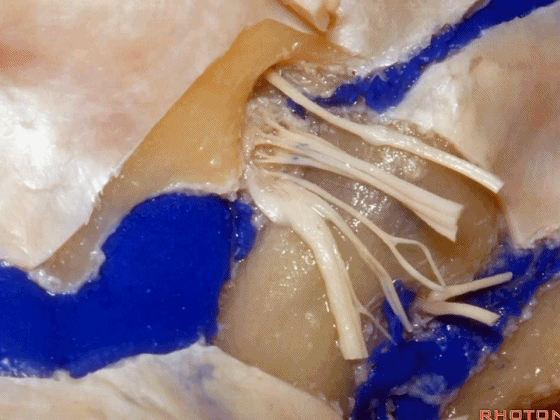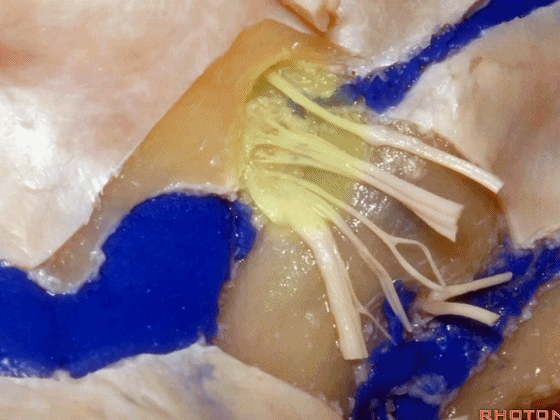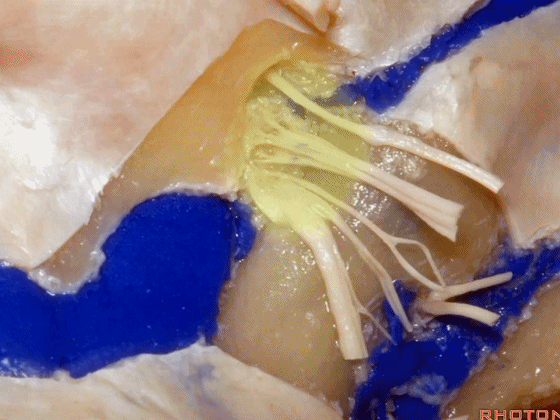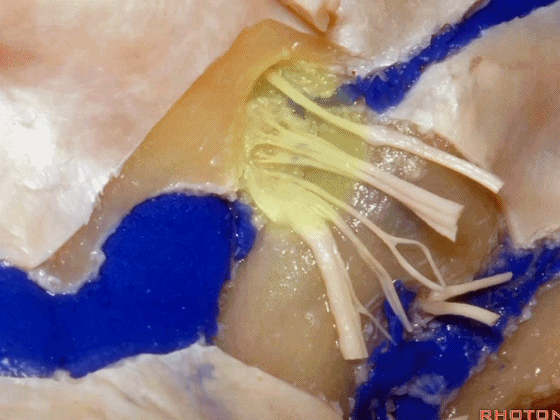
▼颈静脉中间部,其内有舌咽神经、迷走神经、副神经。
下图示舌咽神经
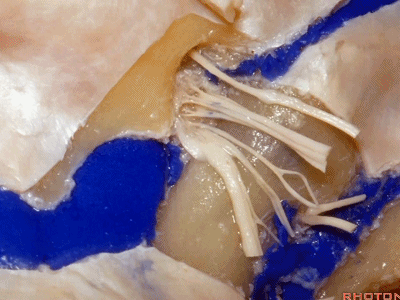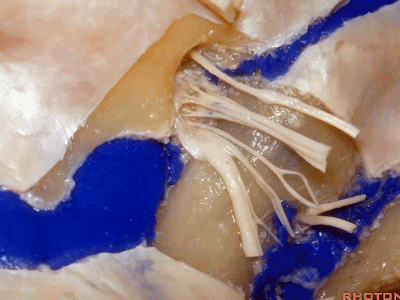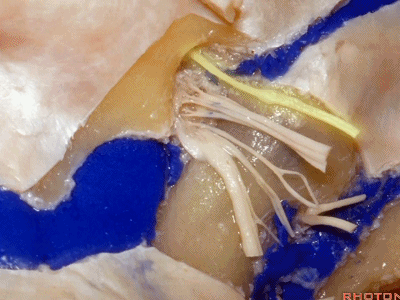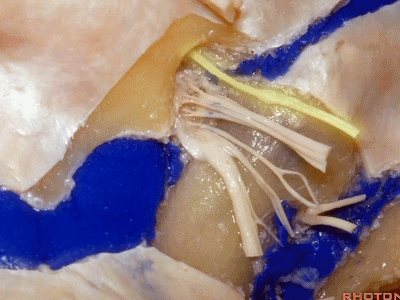
▼下图示迷走神经
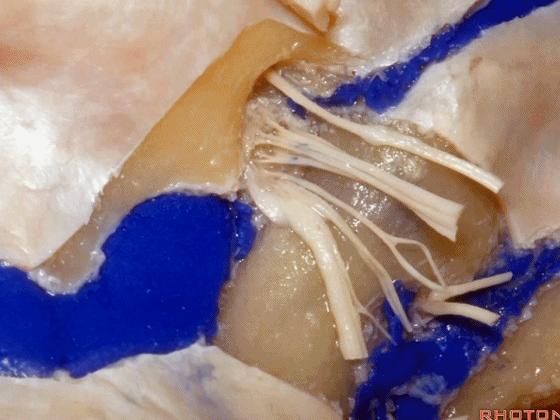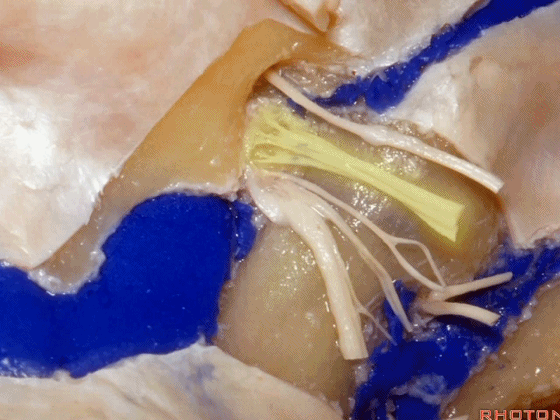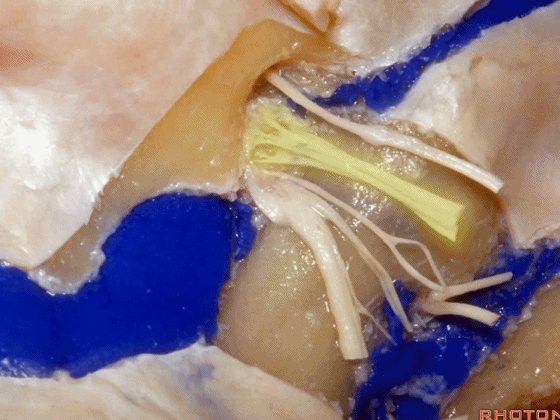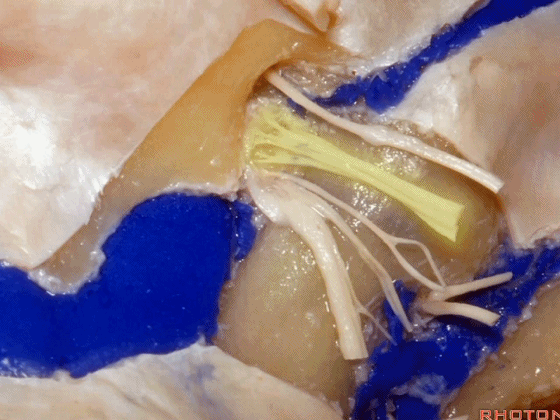
▼下图示副神经
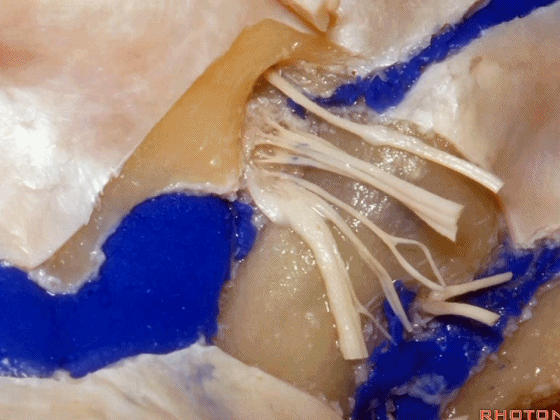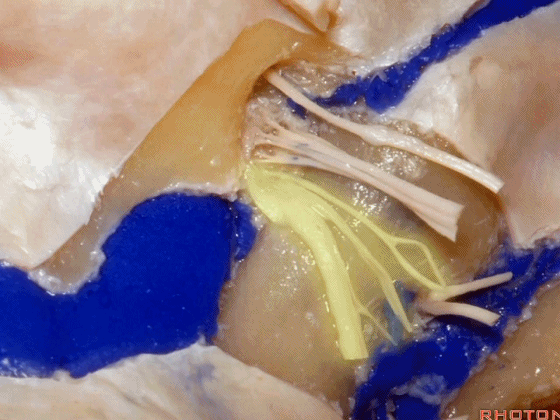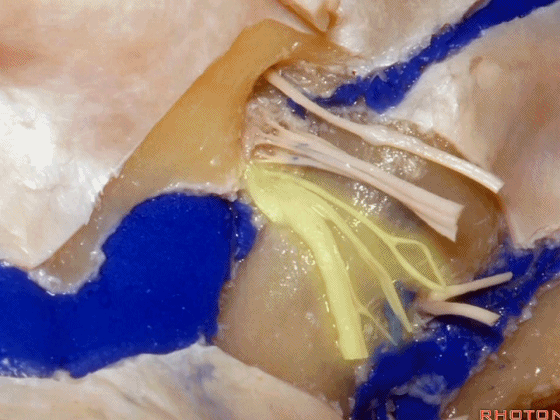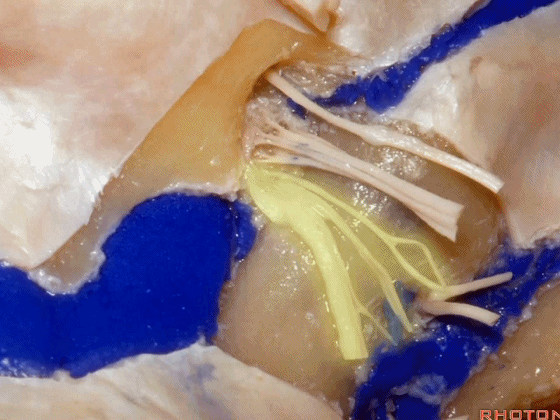
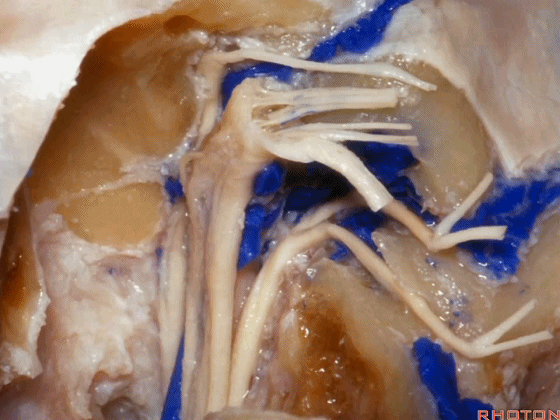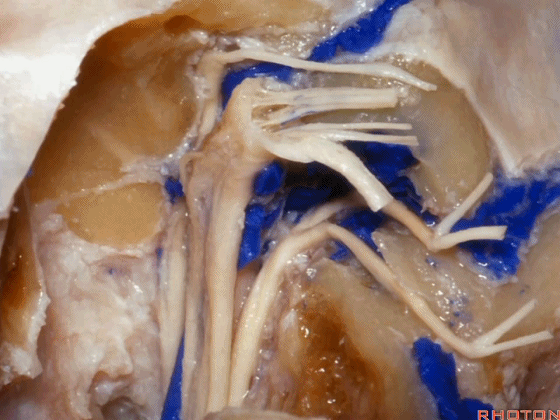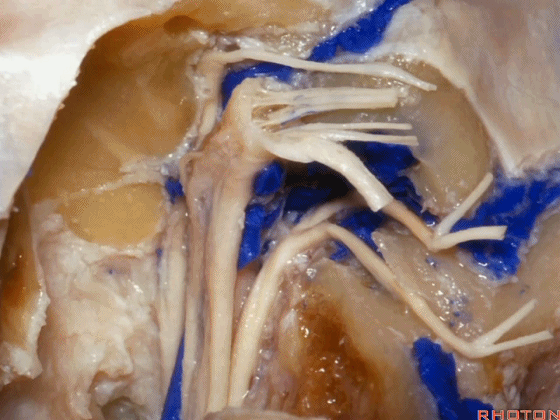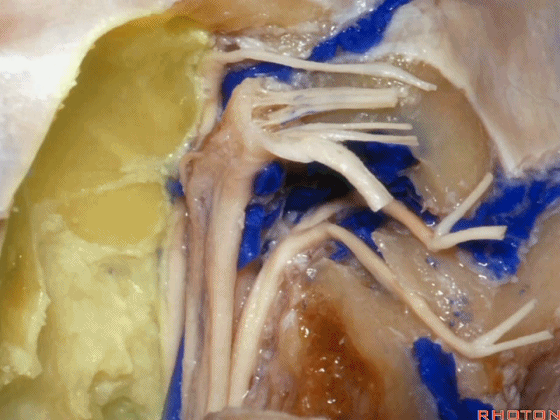
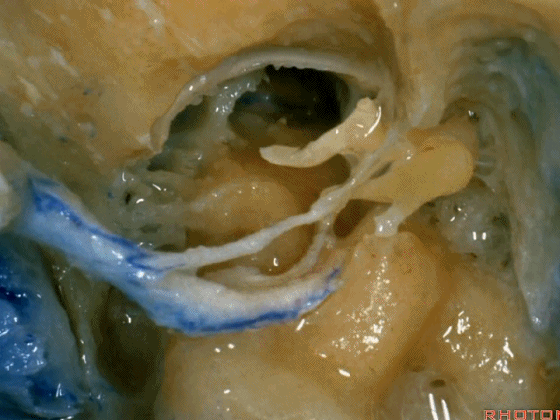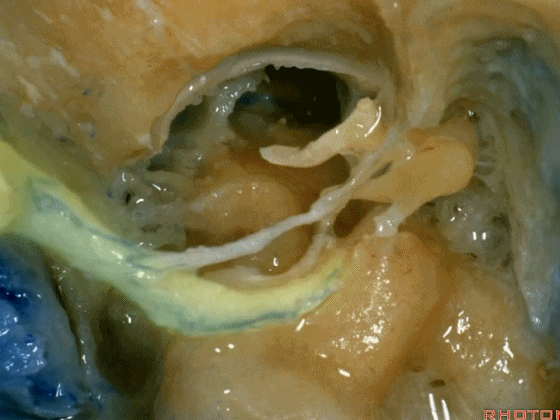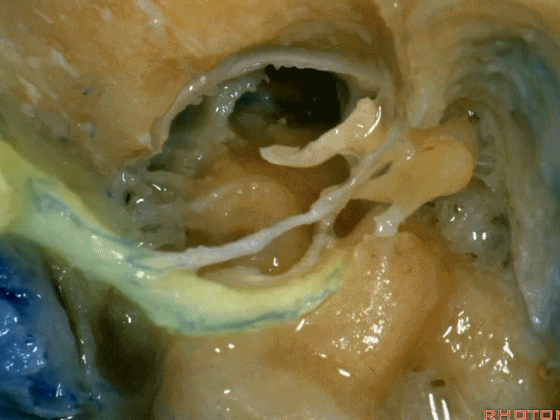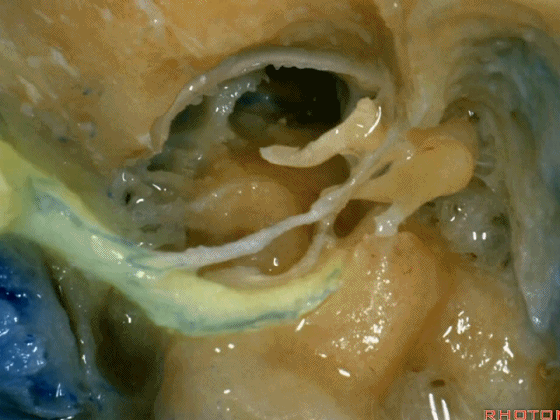
▼这是舌下神经,其进入分为两裂的舌下神经管。通常情况下,舌下神经的两束神经根在出舌下神经管的颅外口前汇合。
And these are...what is that nerve?That's XII,and it enters a bifid hypoglossal canal when you see that usually the two bundles of rootlets join before they reach the extracranial end of the hypoglossal canal.
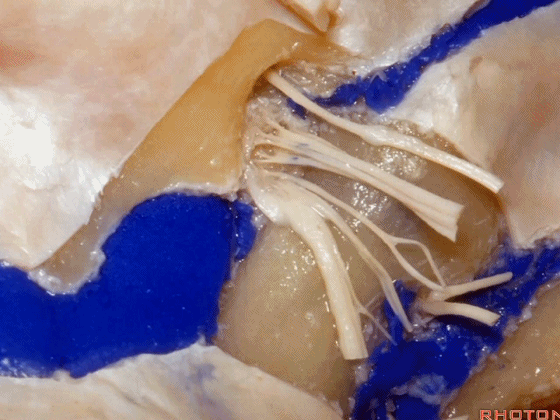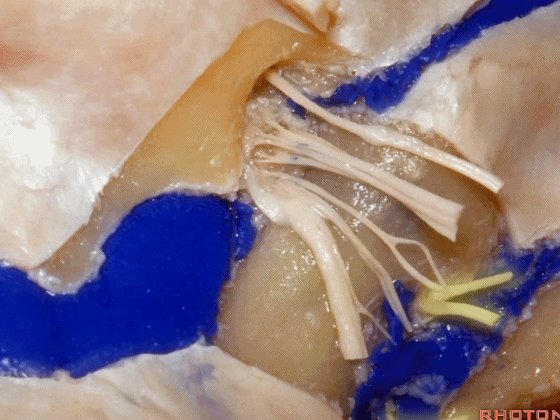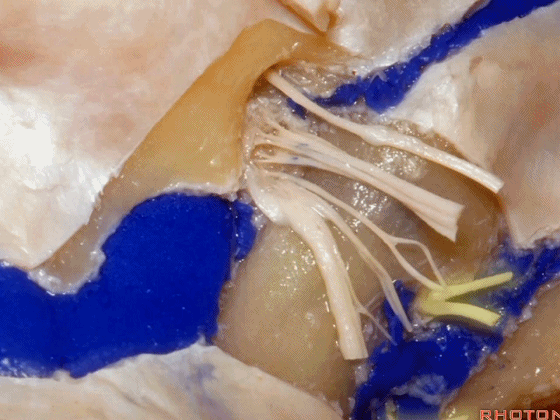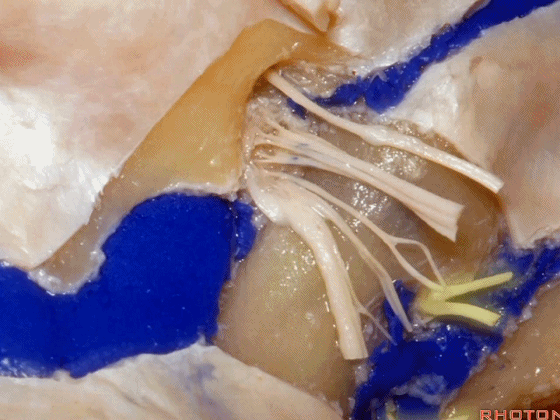
▼接下来把颈静脉球从颈静脉窝内移除。下图示颈静脉窝
And then you can remove the jugular bulb from the jugular fossa.
▼这是舌咽神经
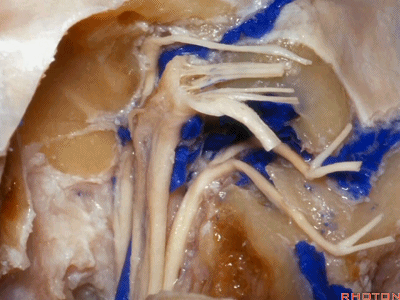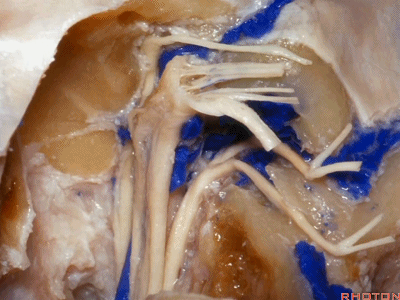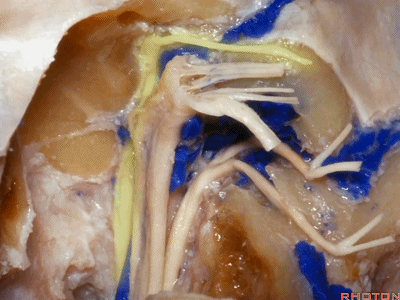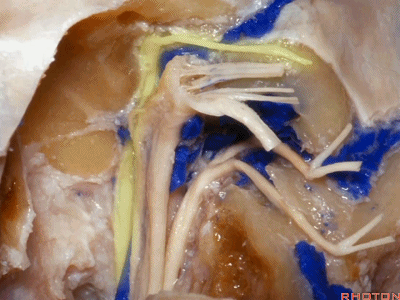
▼这是Jacobson's神经起源处
origin of Jacobson's here,
▼这是迷走神经
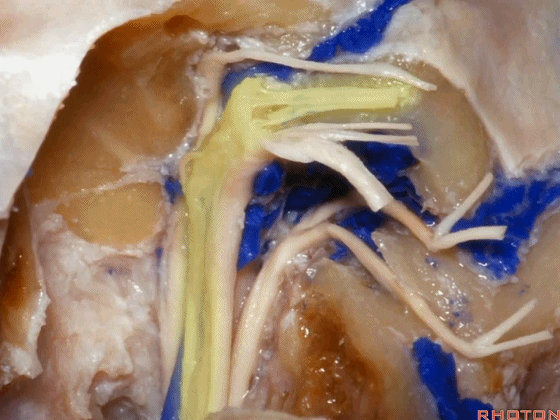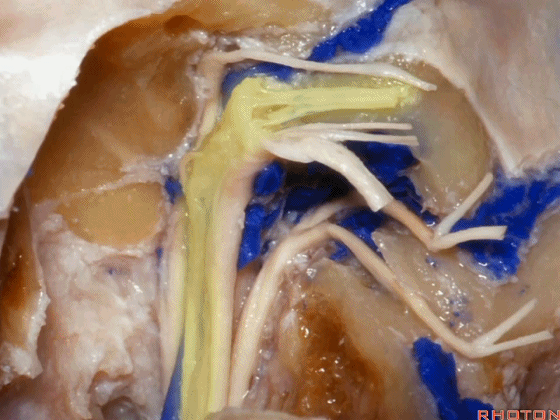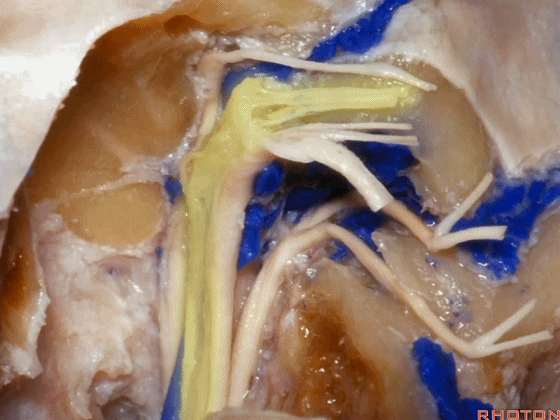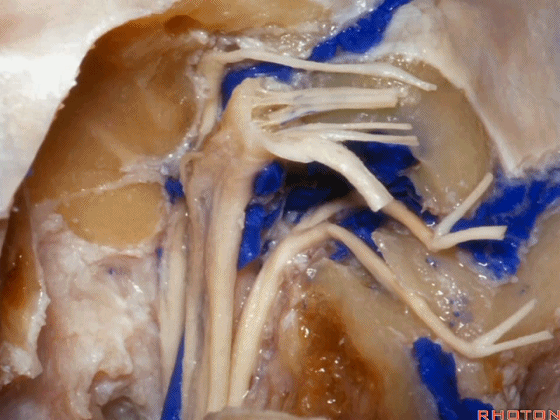
▼这是Arnold's神经
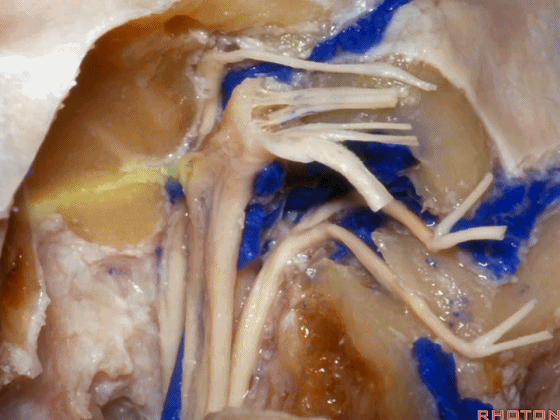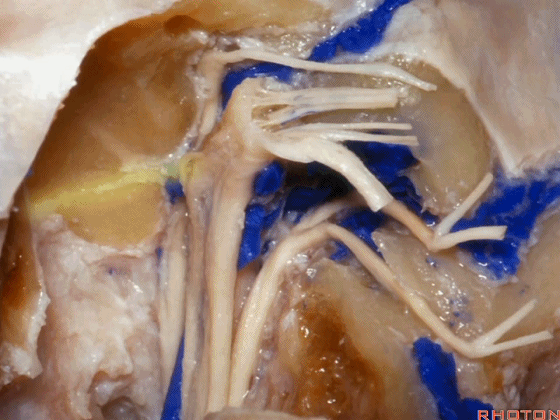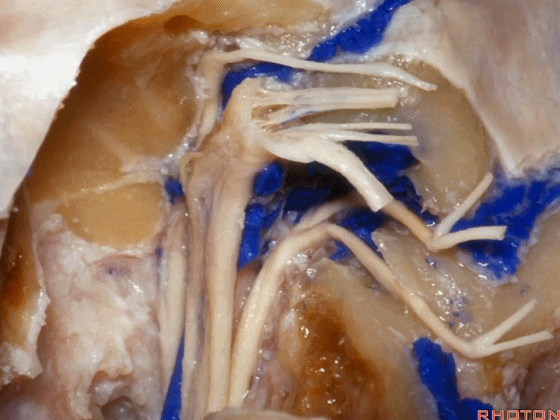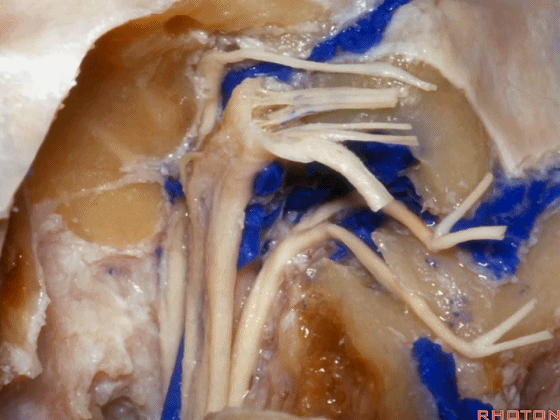
▼这是副神经的颅根和脊髓根
cranial and spinal of XI,
▼这是舌下神经,穿行于舌下神经管,其位于髁上区域。
here's XII passing through the hypoglossal canal in a supracondylar location
上述神经在颈静脉孔下方即加入颈动脉鞘内。
and they all join in the carotid sheath just below the foramen.
▼这是从后方暴露的术野,也同时展示了髁旁暴露。我们常需保护这些神经表面的静脉壁,这样的操作更利于神经的保护。
So you can get an exposure like this from the back.And here's just...you can look in paracondylar.We usually save some of that venous wall over these nerves. And,if you can do that, then you preserve usually preserve these nerves.
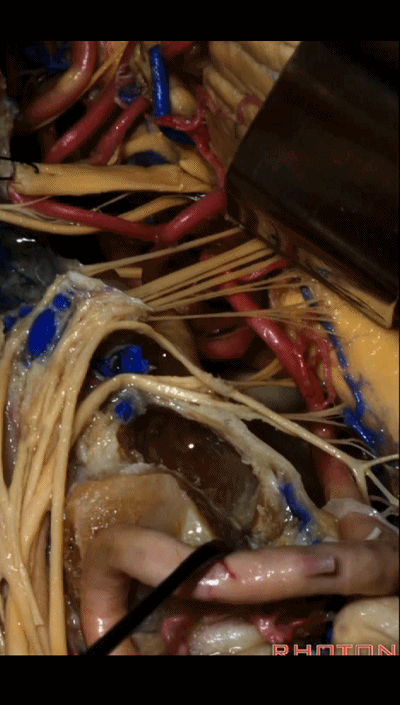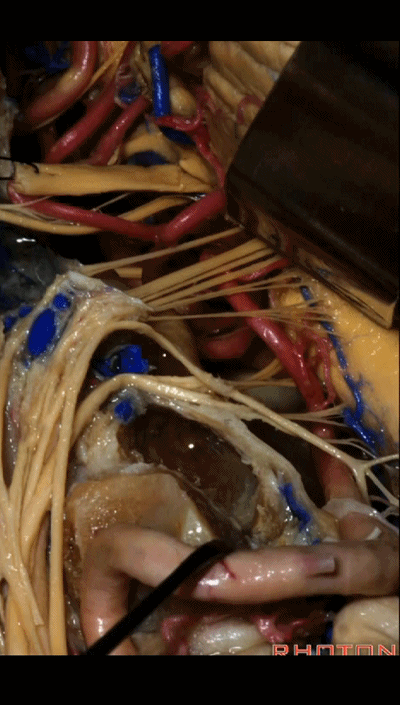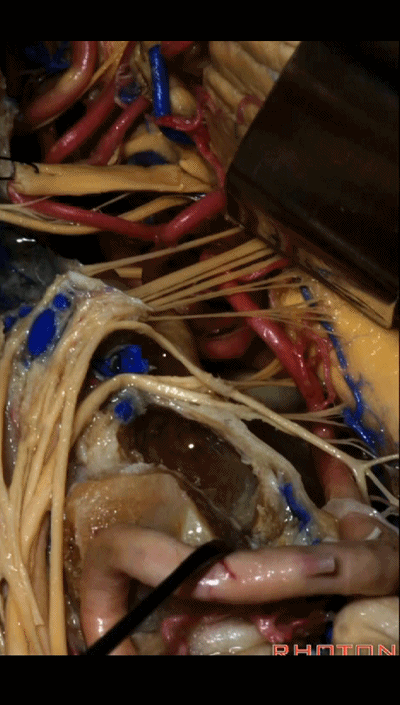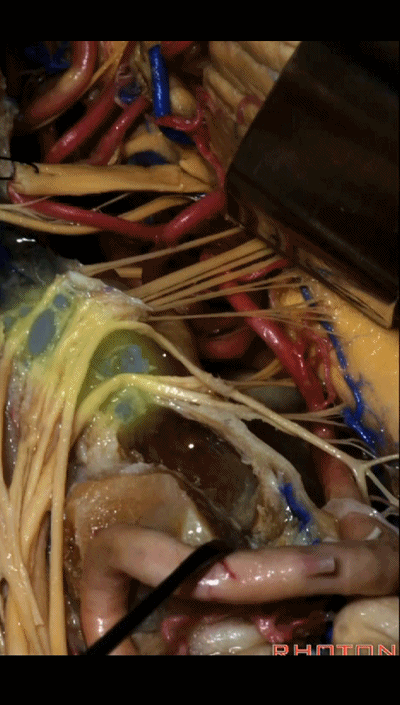
▼下面我们讲解颅底颈静脉孔区和枕骨大孔区。颈静脉孔位于枕髁前部的外侧。
So, we're moving into this area of posterolateral skull base.We see the jugular foramen lateral to the anterior half of the occipital condyles.
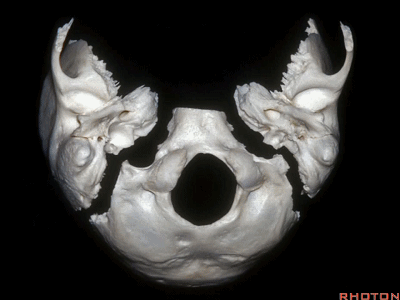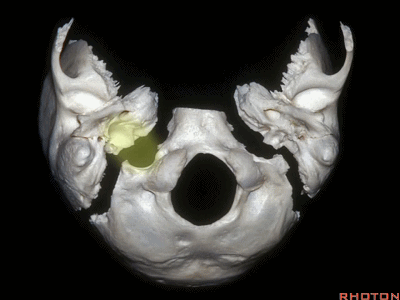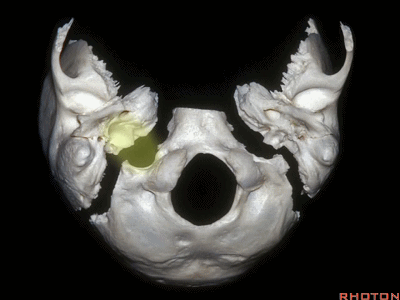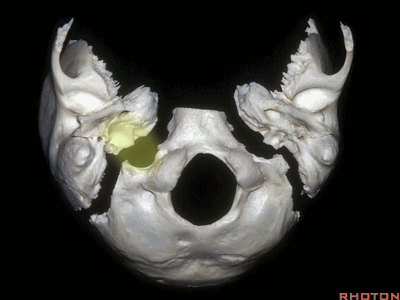
▼颈静脉窝位于颅底的下表面。乙状窦沟、颈静脉孔沿下图方向在颞骨下方前行。右侧的颈静脉孔通常较大。
And you see the jugular fossa on the lower surface, but the temporal bone,the sigmoid, the foramen is directed forward under the temporal bone.And it's larger on the right side usually.
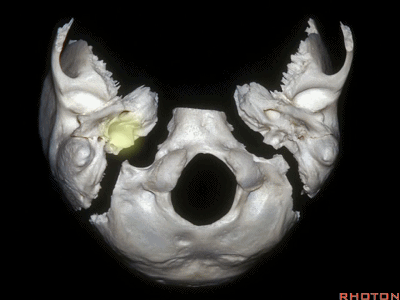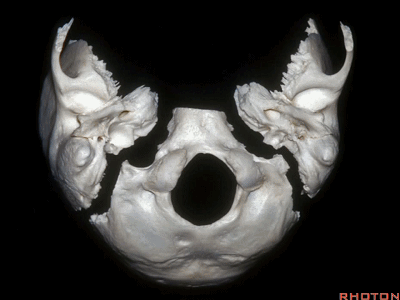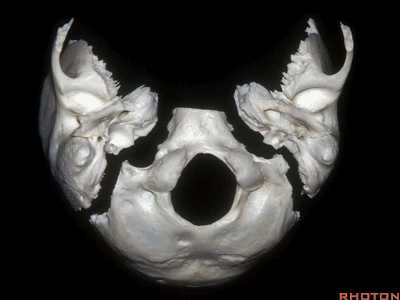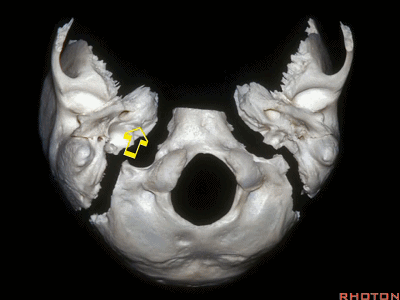
▼枕髁位于枕骨大孔的前外侧。
The condyles are anterolateral to the foramen magnum from 1 to 3, and 9 to 11 o'clock.
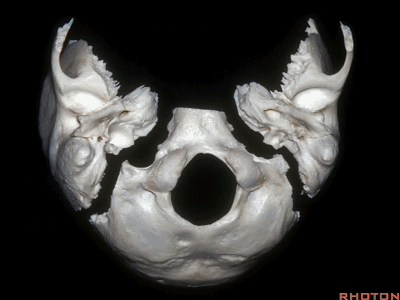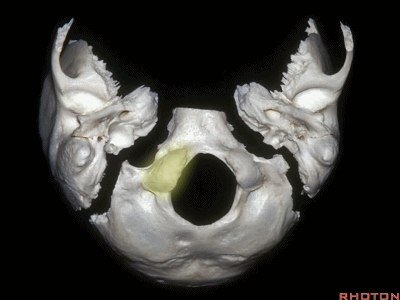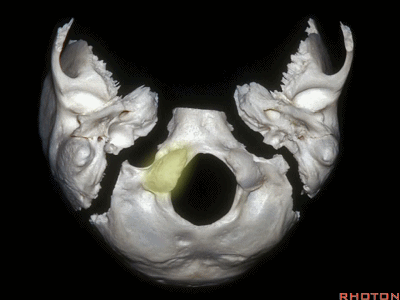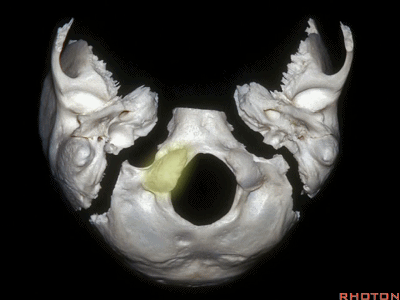
▼枕髁分别位于枕骨大孔1~3、9~11点钟方向。
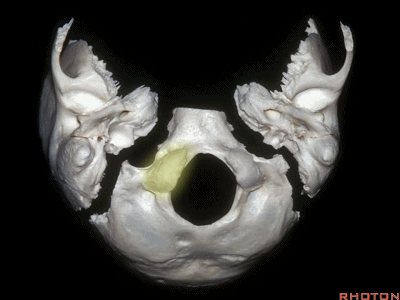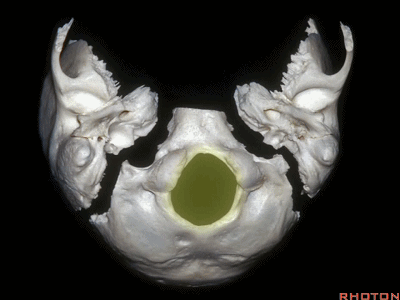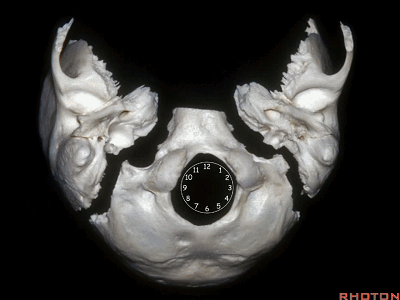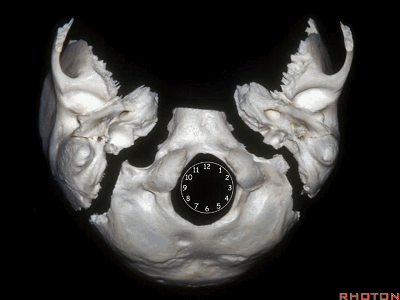
▼现在我们从下方观察(右侧),这是颈内静脉
So that, if we look from below now, internal jugular vein,
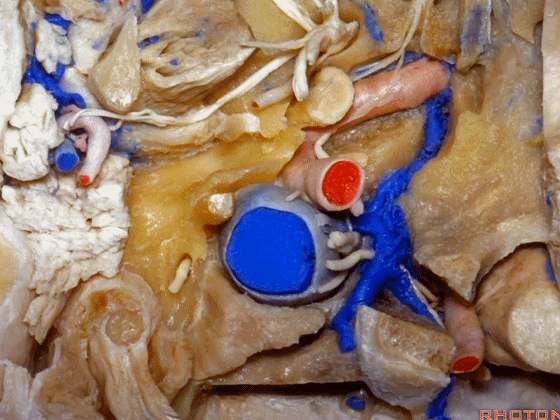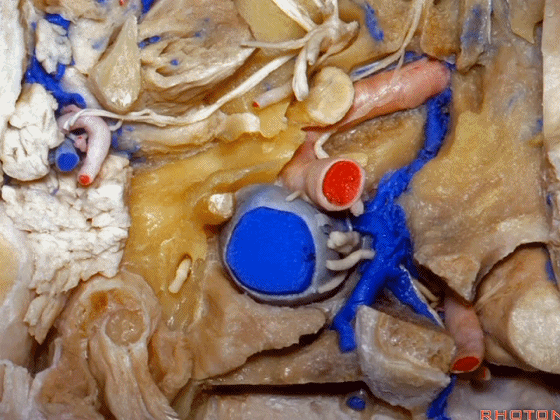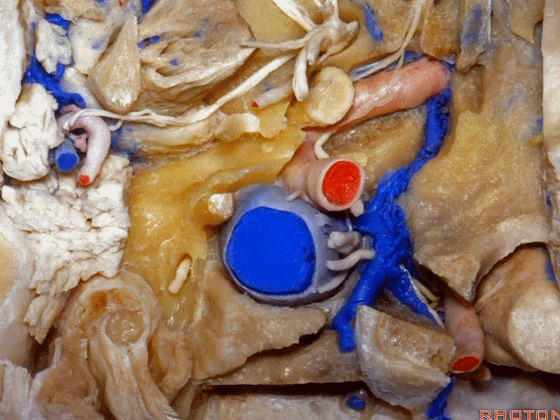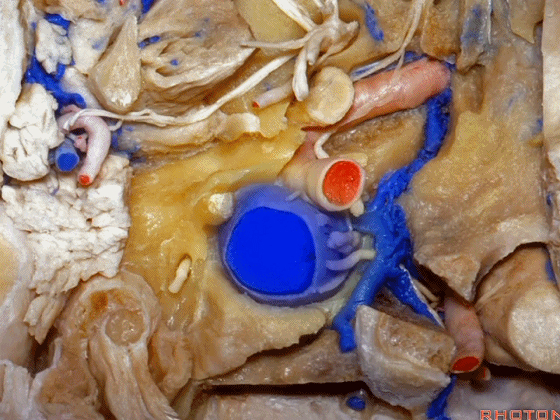
▼在颈内静脉前方有颈内动脉,颅外病变可沿颈内动脉蔓延。
some of the relationships on the front you have the carotid artery and, pathology out of the bone can follow the carotid.
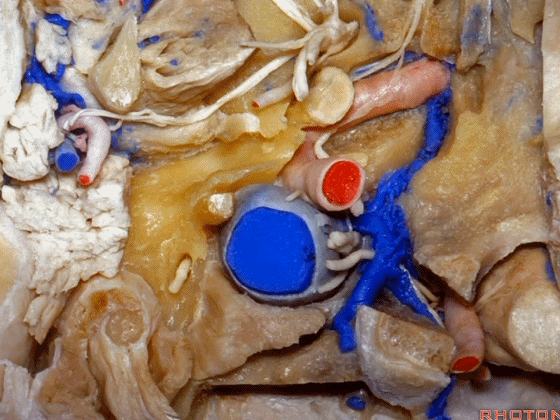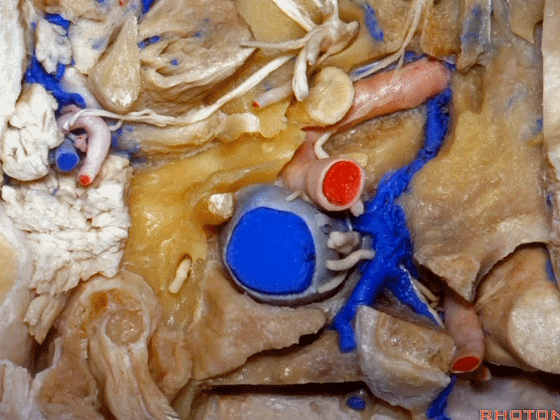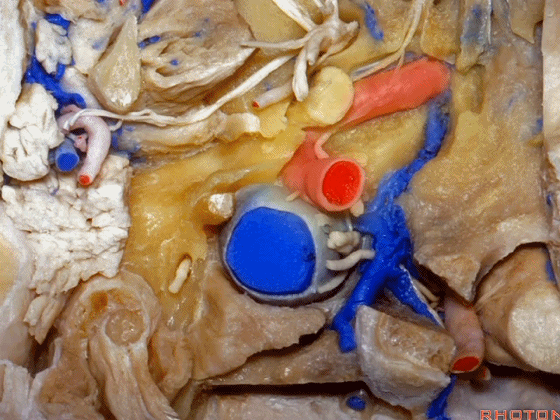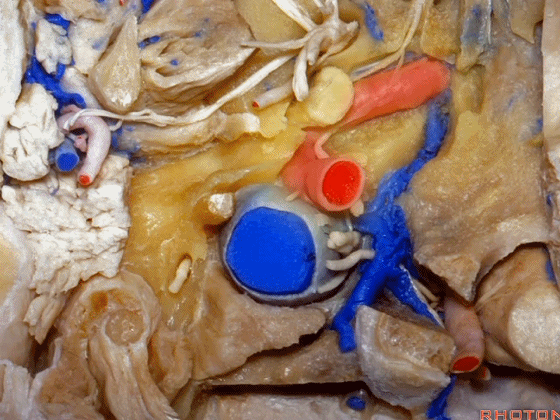
▼这是咽鼓管(eustachian tube),颈静脉球区病变可沿着它向前蔓延。
Here's the eustachian tube and, pathology in the jugular bulb can follow the eustachian tube forward.
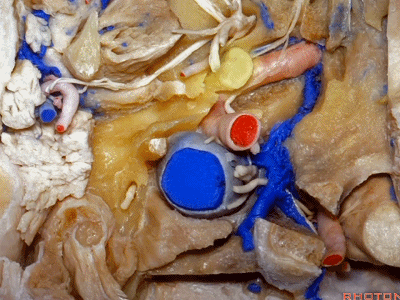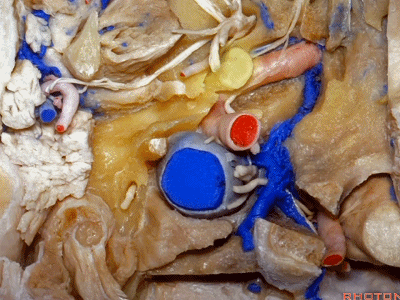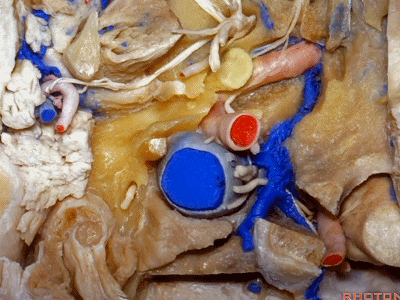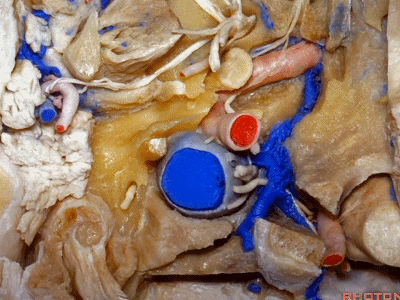
▼在外侧,是面神经
Laterally here we have the...what is that...facial nerve
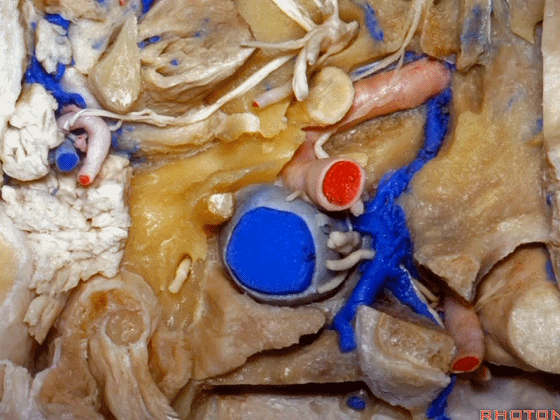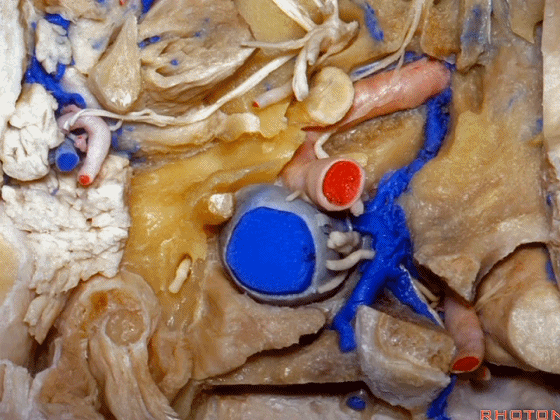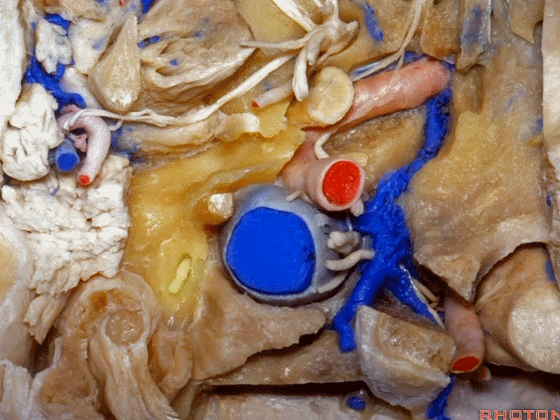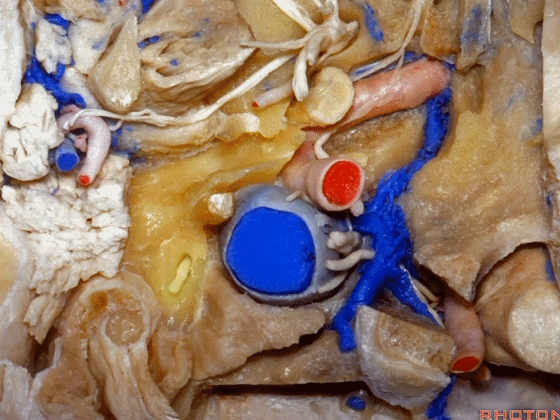
▼这是茎突(styloid)
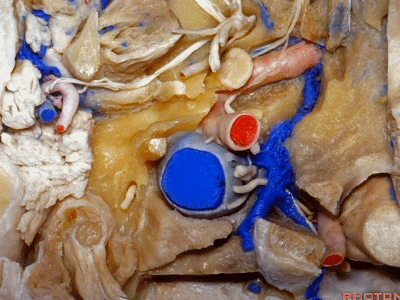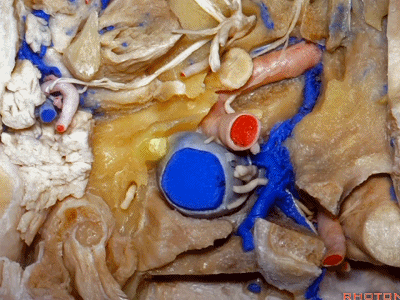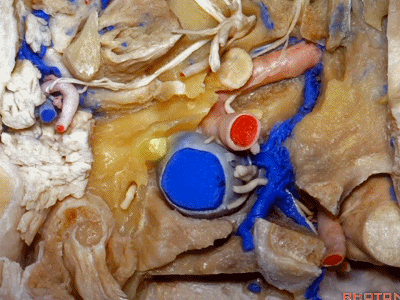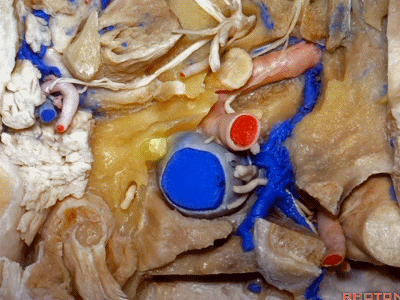
▼下图可见舌下神经在枕髁上方走行并加入颈动脉鞘内的其余神经。
Here we see XII coming above the condyle and joining the nerves in the carotid sheath.
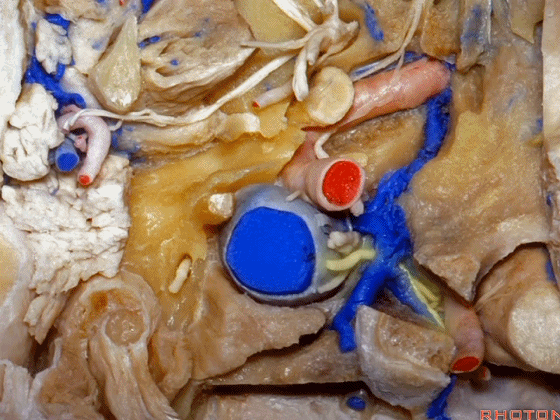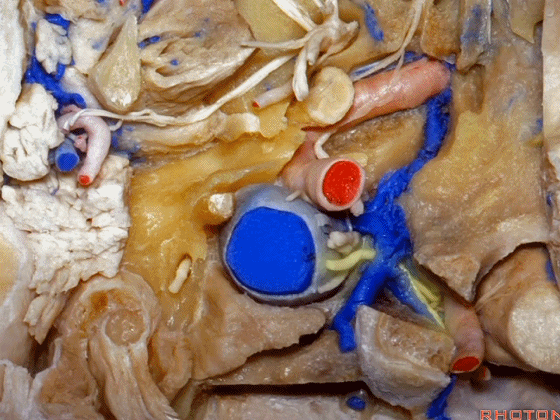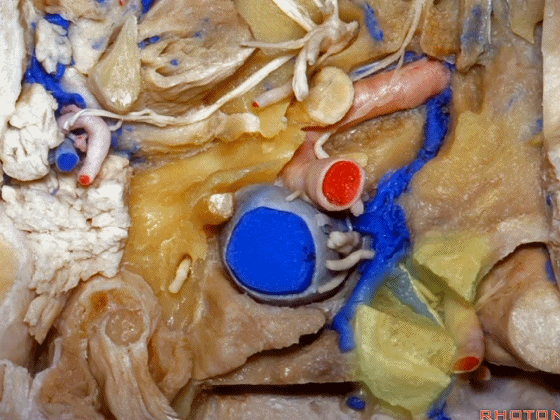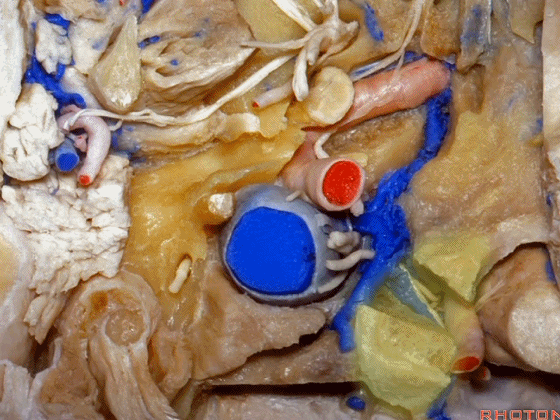
▼这是附着在颅底的头外侧直肌。
And what muscle is this? Rectus capitus lateralis that attaches to the skull base.
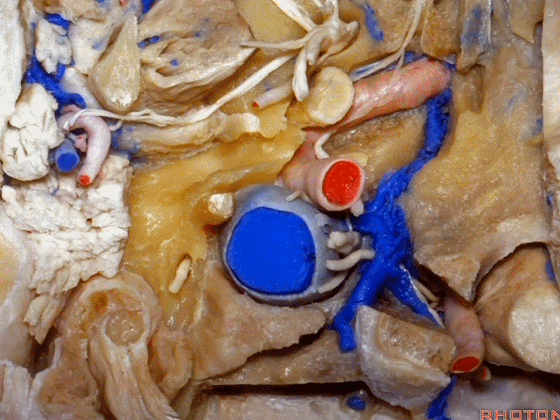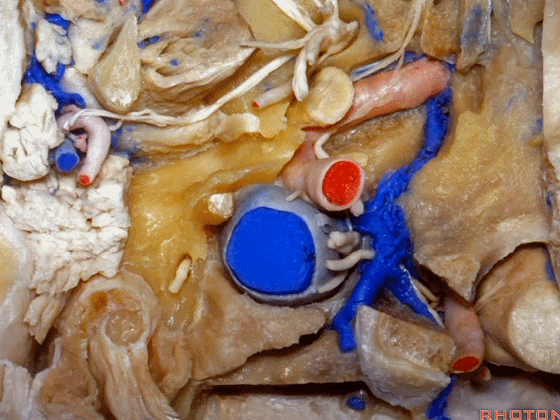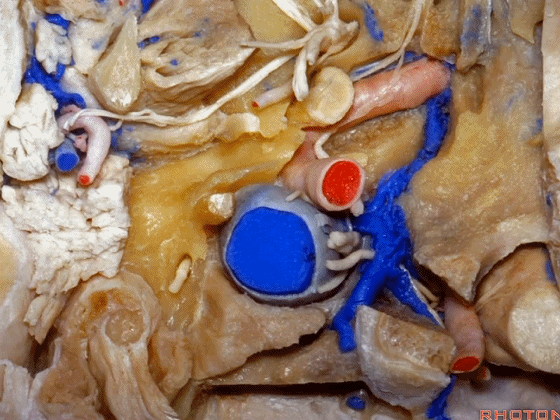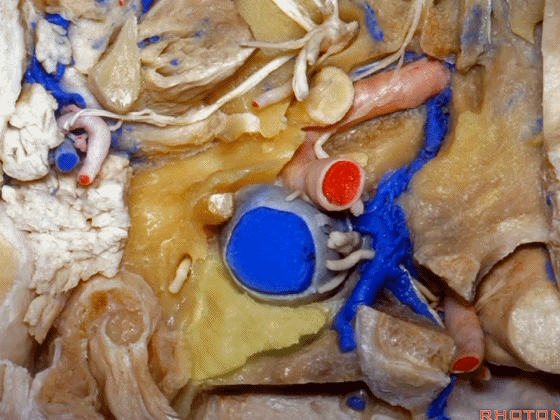
▼我们进一步磨除枕骨,保留部分枕髁,可见舌下神经。这里看到的即为髁旁入路时磨除的范围,以此从后方暴露颈静脉孔。
And here we detach that muscle. We drilled out the occipital bone,condyle, part of it still here,hypoglossal nerve.We've drilled it out in a paracondylar approach to expose the back of the jugular foramen.
▼然而大多数颈静脉孔的病变可沿着咽鼓管向前,沿着颈内动脉、鼓索蔓延并进入颞下窝。下图示(左侧)咽鼓管。
But we said most pathology in the jugular fossa extends forward down the eustachian tube,along the carotid,follows the chorda tympani,gets into the infratemporal fossa.
▼下图示颈内动脉。
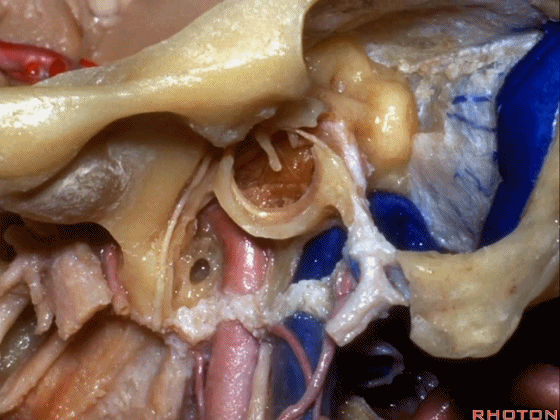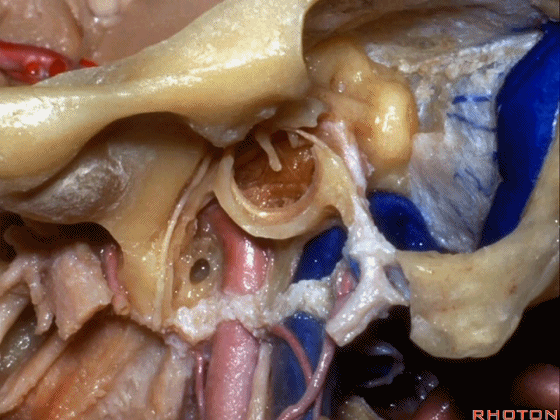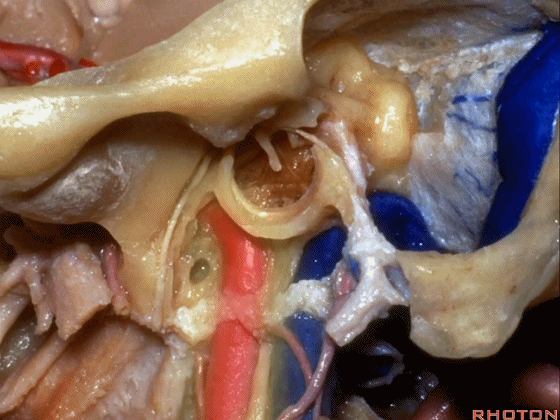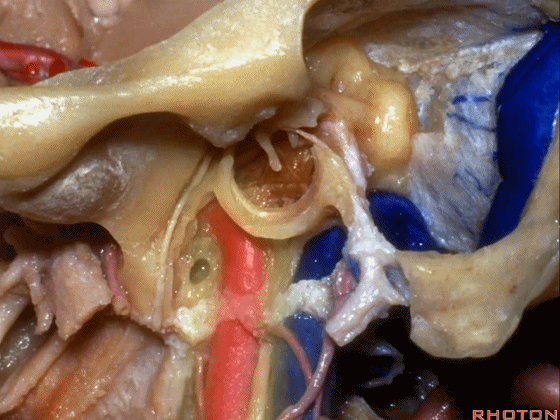
▼下图示鼓索
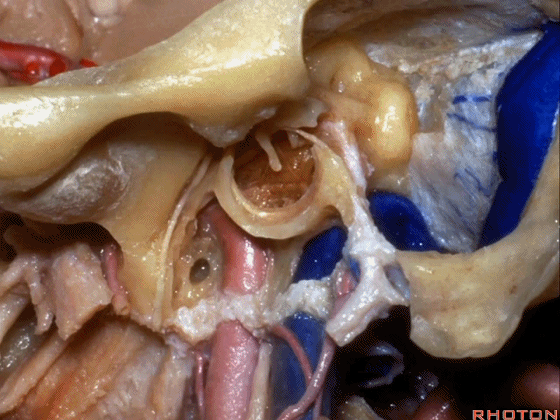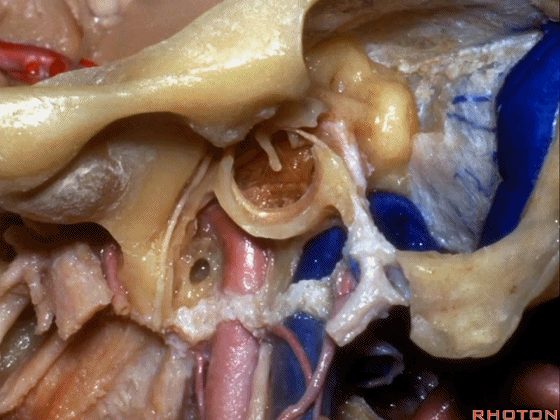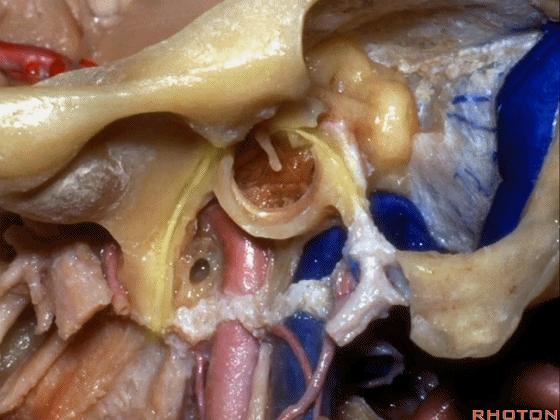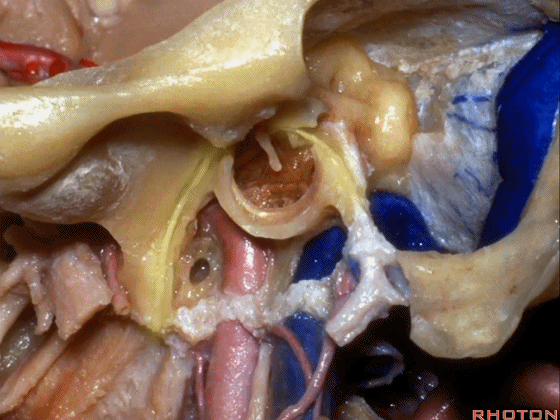
▼下图示颞下窝
▼面神经恰位于颈静脉外侧。因此,针对这样的病变我们选用耳后切口,将皮瓣翻向前从而向前方暴露病变。
And you have the facial nerve directly lateral.So, for this we use a postauricular incision that you can fold this flap forward and follow the pathology anteriorly.
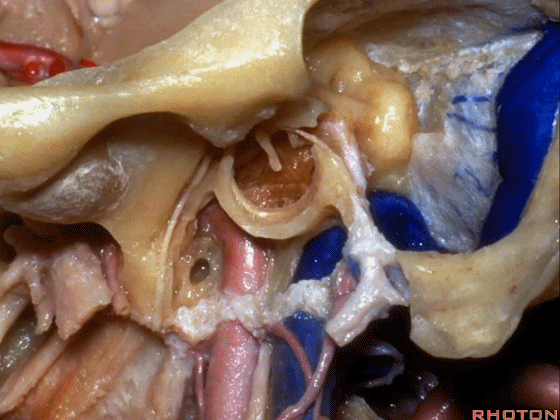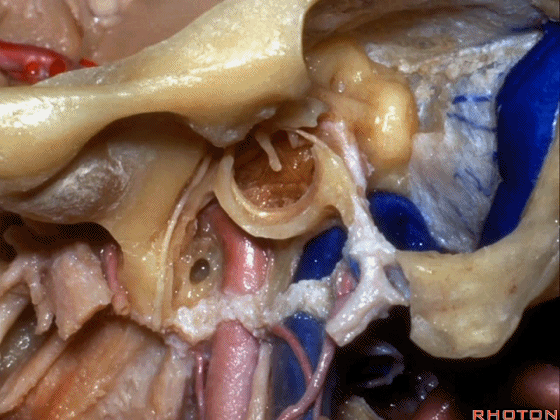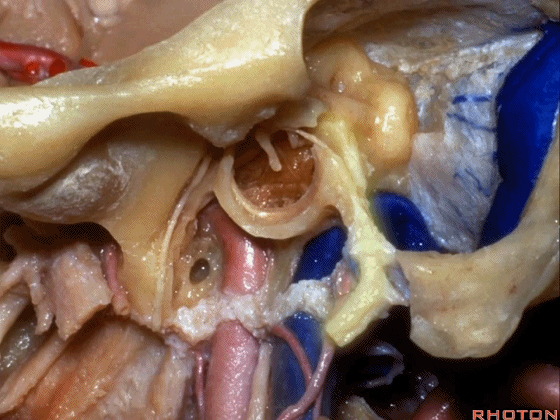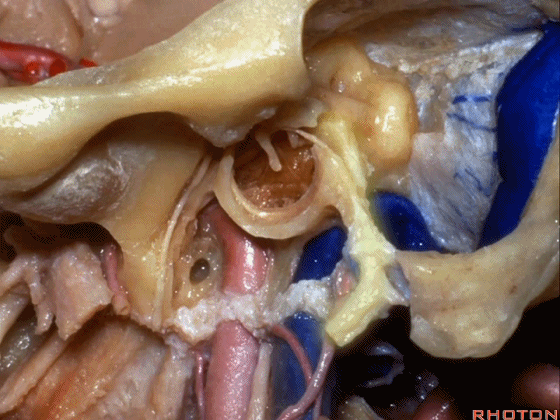
▼下图示颈动脉鞘(carotid sheath)
▼该部位的病变常向前侵犯,而我们也向前暴露。下图示进入中颅窝的颈内动脉。
So that, often this pathology will extend forward, you can follow it forward. Carotid going to middle fossa.
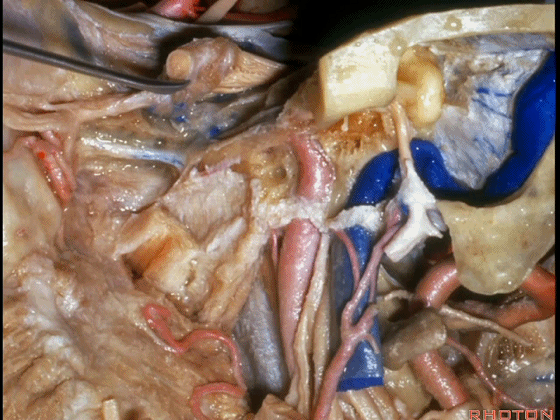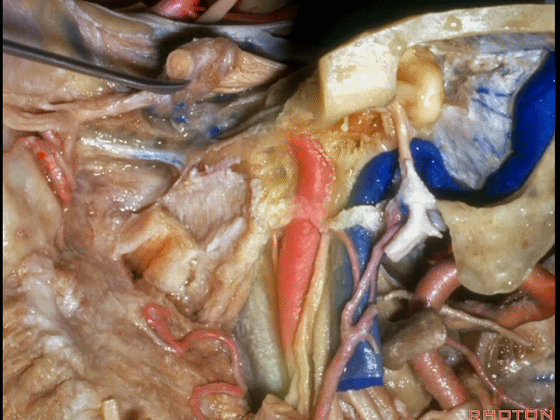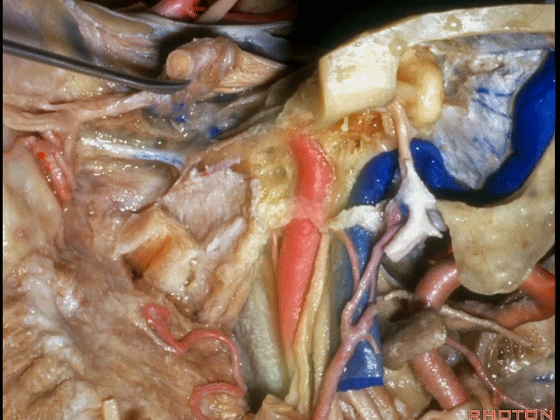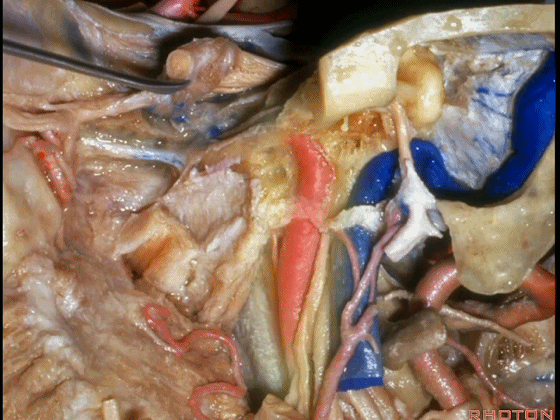
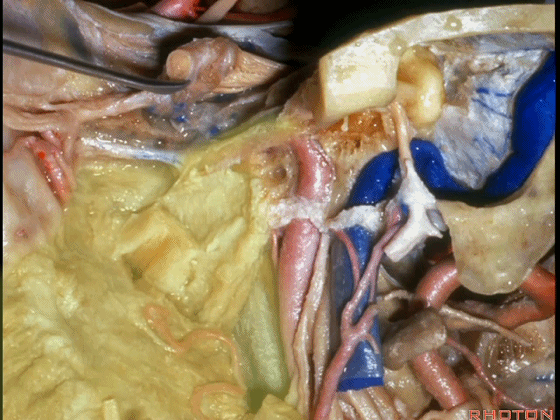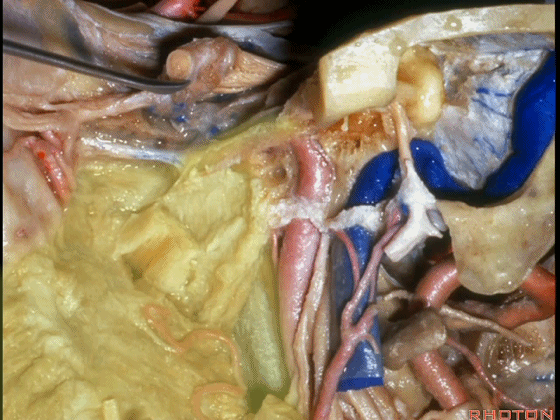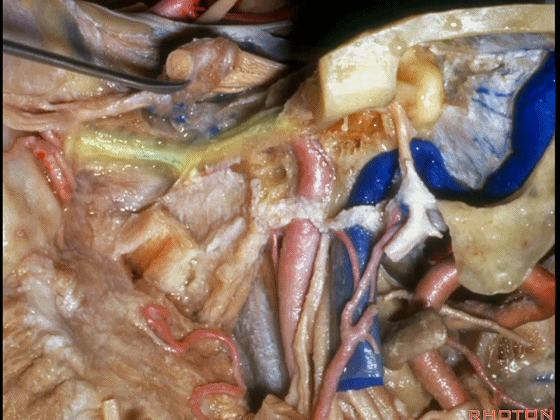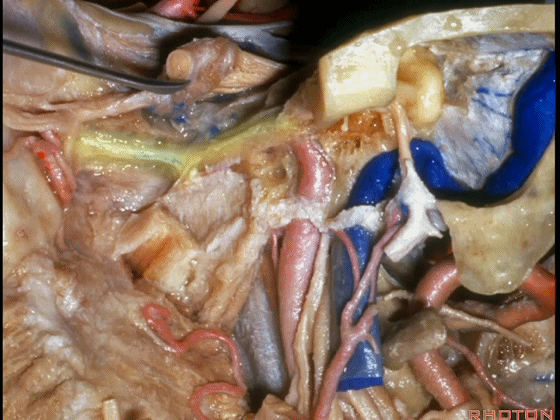
▼这根神经是岩浅大神经,在颈内动脉岩骨段上方走行。
What nerve is that...that runs on the upper surface of the petrous carotid?GSPN.
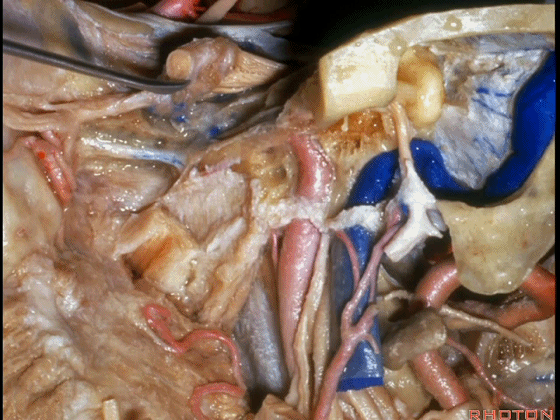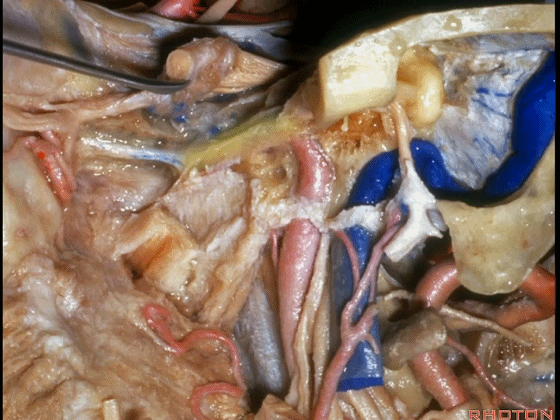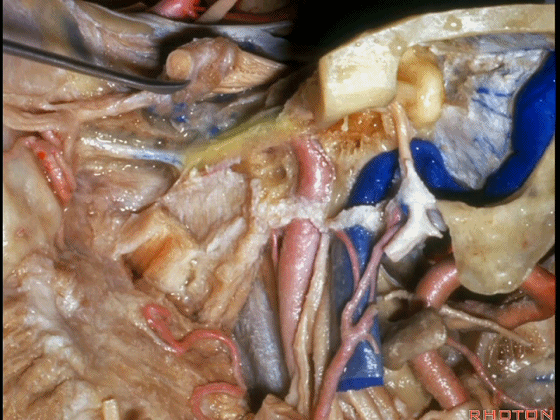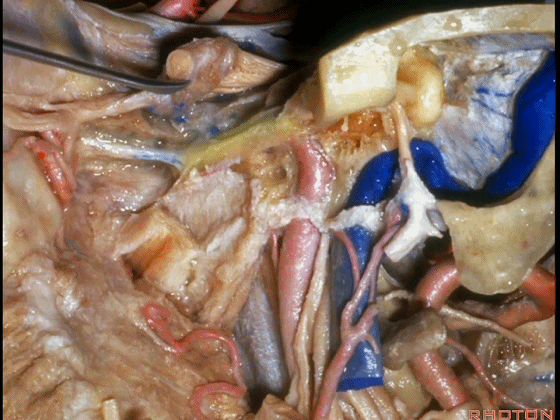
▼岩浅大神经进入颞下窝(下图),并继续向前移行为翼管神经。
And where infratemporal fossa and from there it runs forward in the...
▼翼管神经进入翼腭窝(下图)。
that it's toward the pterygopalatine fossa that we talked about yesterday.
▼这是另一个视野,颈内动脉位于颈动脉鞘内。面神经在外侧下行。在这些入路中,我们将面神经向前移位(下图)。
So, and just another view of this, the carotid inside the carotid sheath,facial nerve descending laterally.For these approaches we move the facial nerve forward,
▼需保护茎乳动脉(下图),其供应面神经的血供。
and we wanna preserve the stylomastoid artery that supplies the facial nerve.
▼这是术中的耳后切口(左侧)。
So we do a postauricular incision.
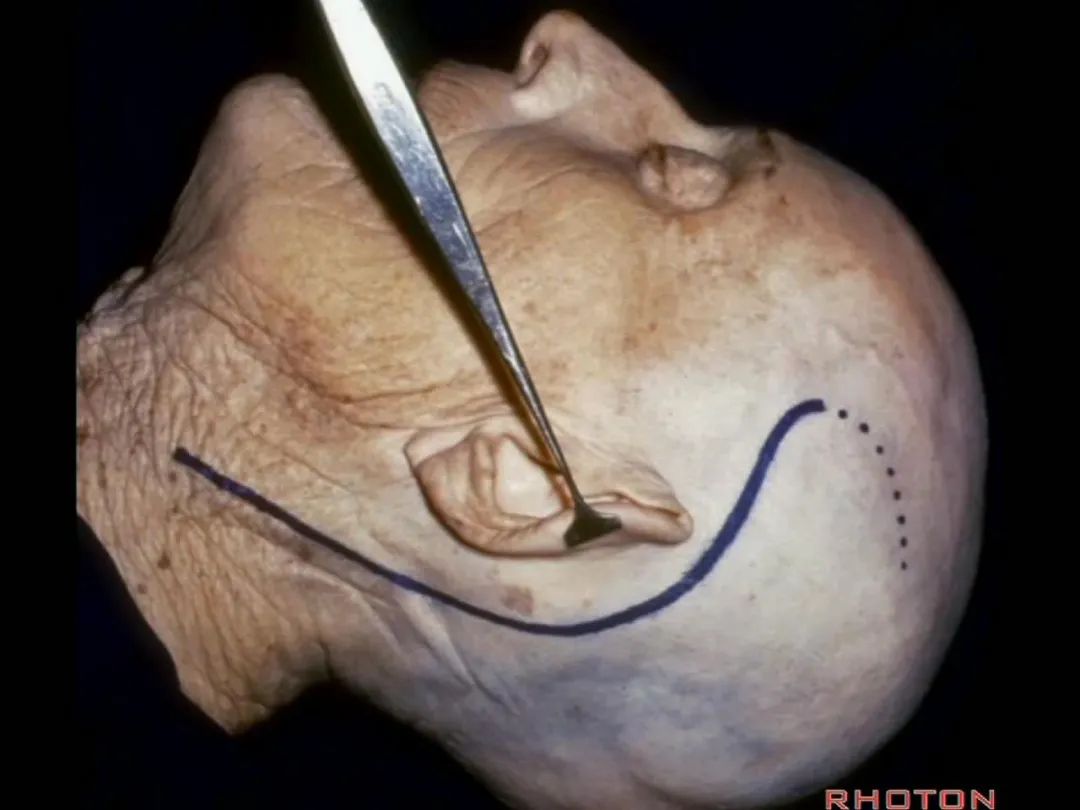
▼我们同时进行乳突和颈部的解剖,下图示乳突部。
We expose the mastoid and do a neck dissection.
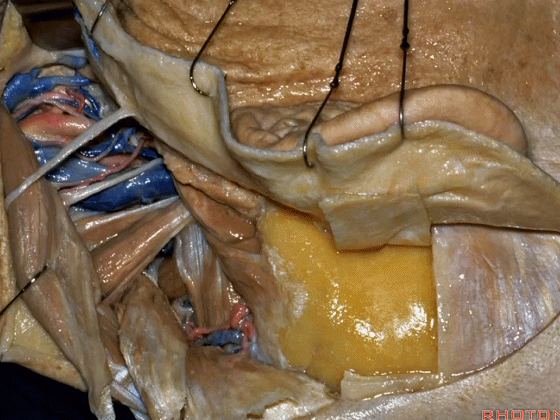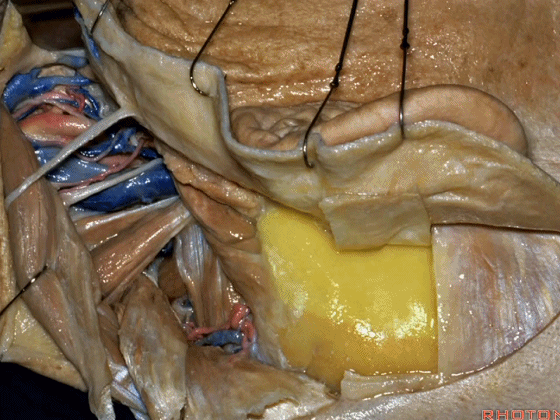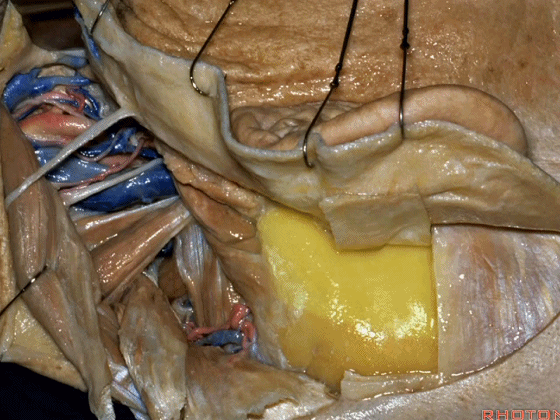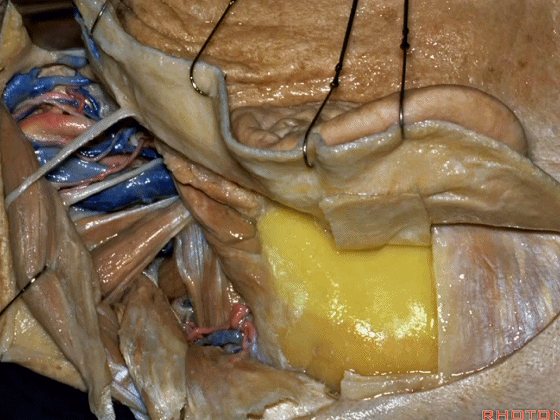
▼结合上两部分操作,我们通常至少须切除外耳道的后半(下图)。这块翻起的筋膜(下图)用于最后对外耳道分修补。
And here we turned up a little flap of fascia to use in closing the canal.Combined the two, we often have to resect at least posterior half of the external auditory canal.
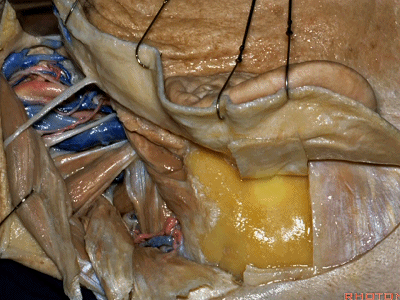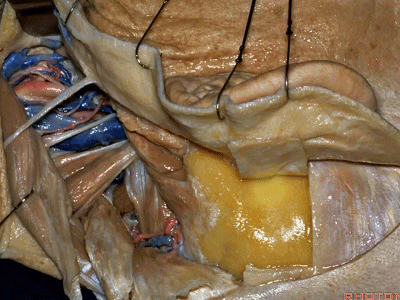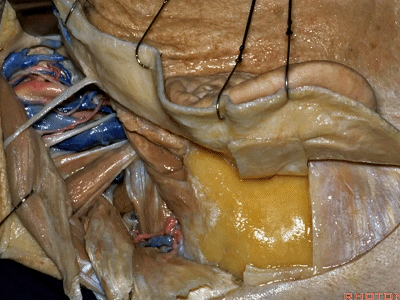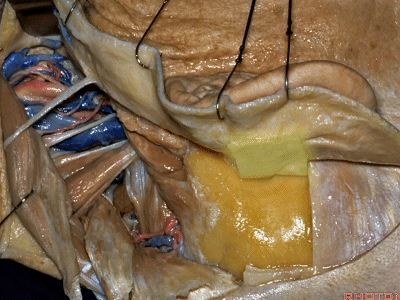
▼随后进行乳突切除术。
And then we drill out the mastoidectomy that you've already done.
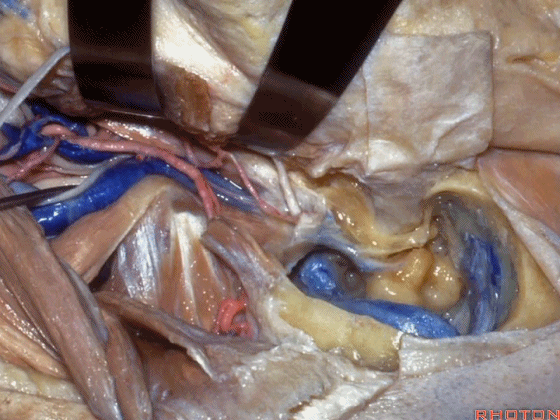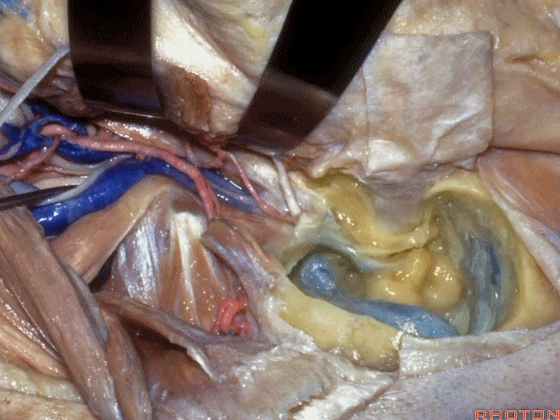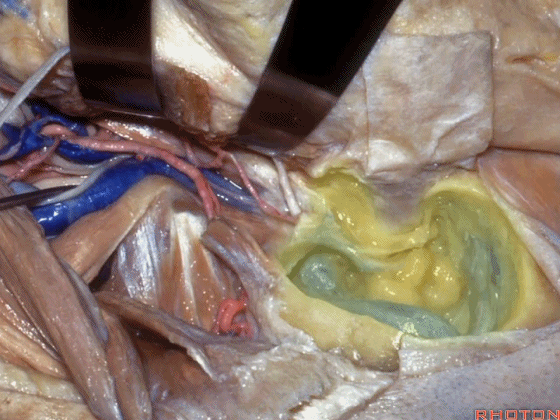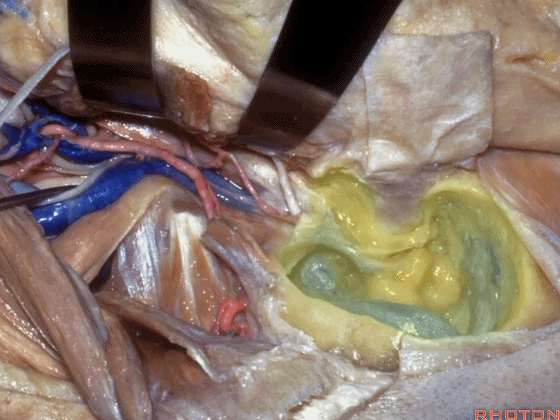
▼可见面神经(下图),在颈静脉孔的外侧下行,位于迷路下方。
And, we have facial nerve descending lateral to the jugular bulb here it descends lateral to the jugular bulb that's in an infralabyrinthine position.
▼这是面神经
Here's facial nerve
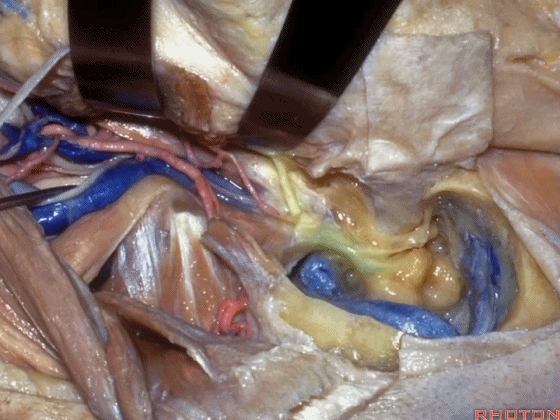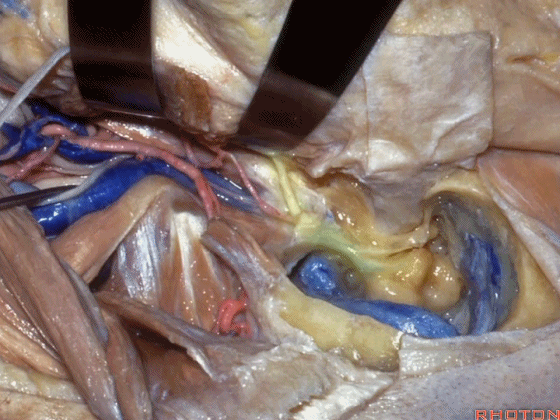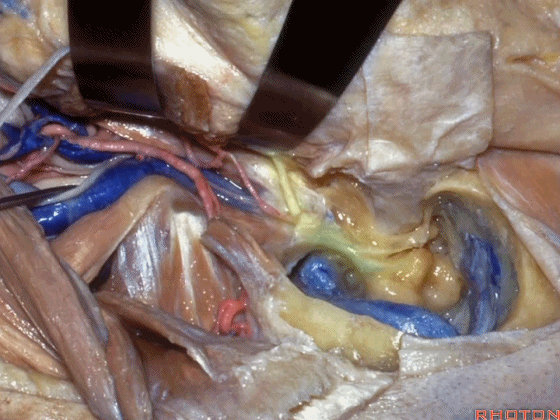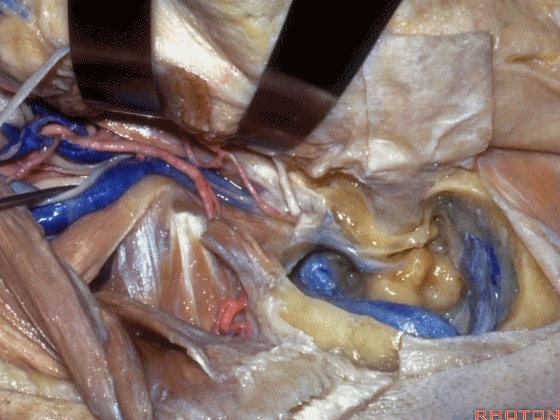
▼这是 鼓索。
This is chorda tympani.
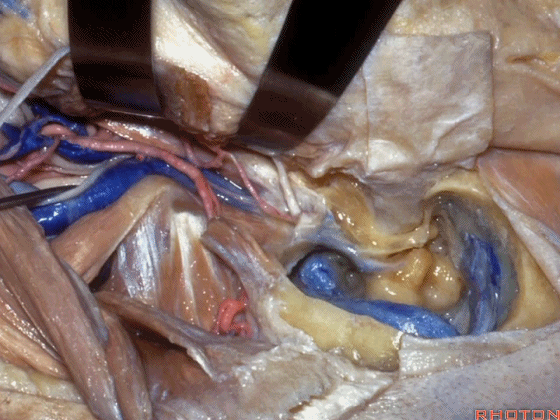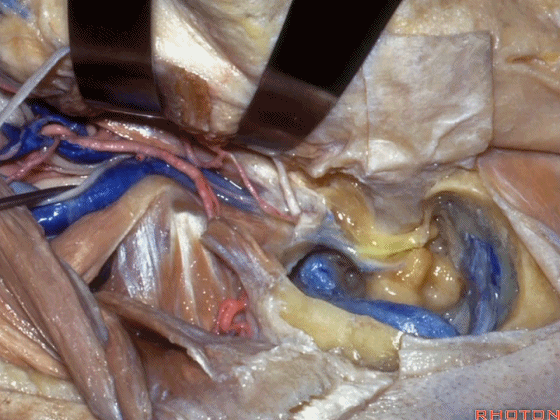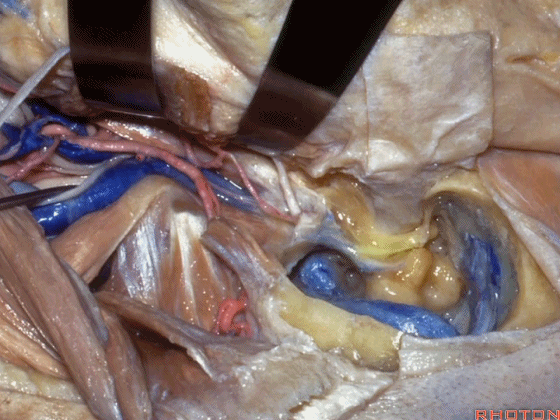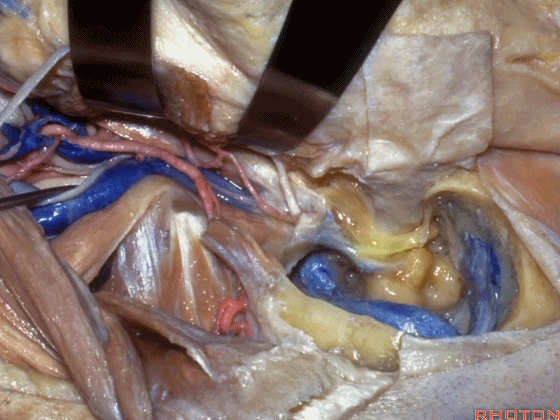
▼下图示外侧半规管、后半规管。
What canal? Lateral,posterior.
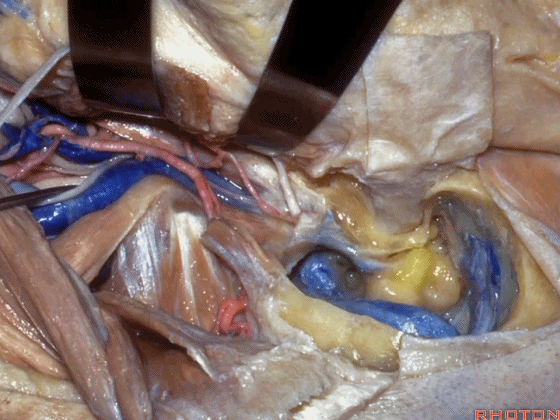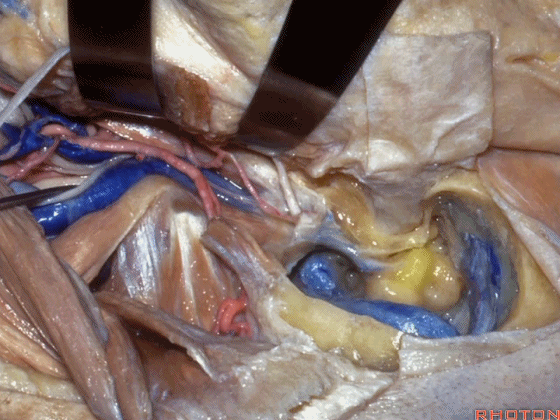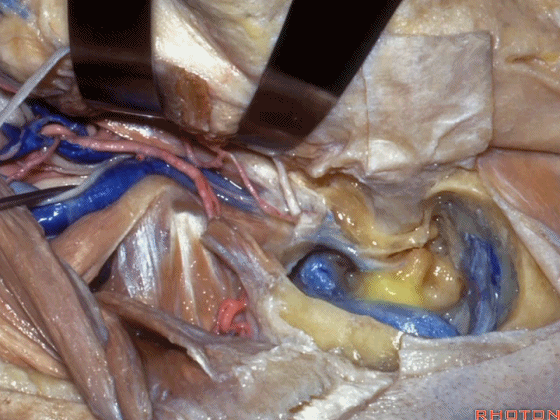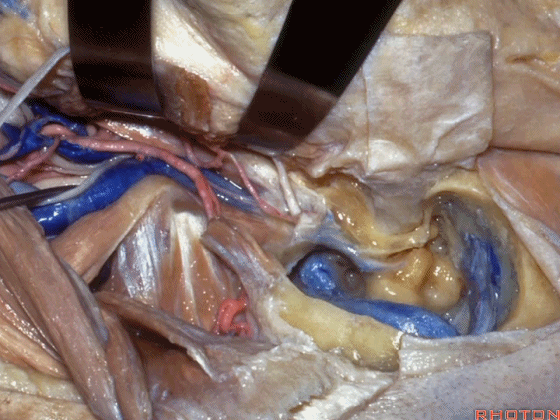
▼至此该入路已完成了一半。然而,想要充分暴露颈静脉球,必须将面神经向前移位。
So you've already done part of this approach. But often, to get into the jugular bulb, you have to move this facial nerve forward. It's an anterior transposition.
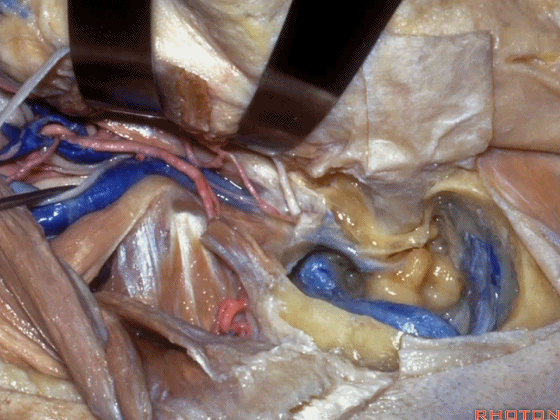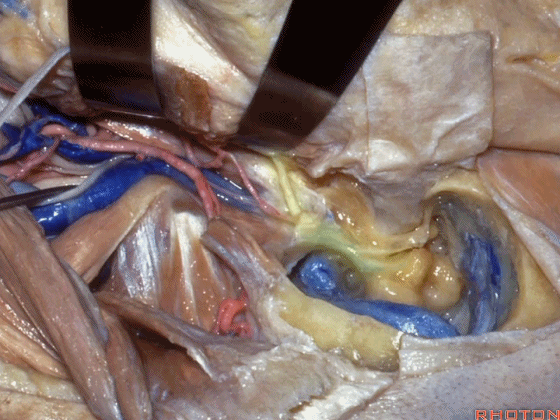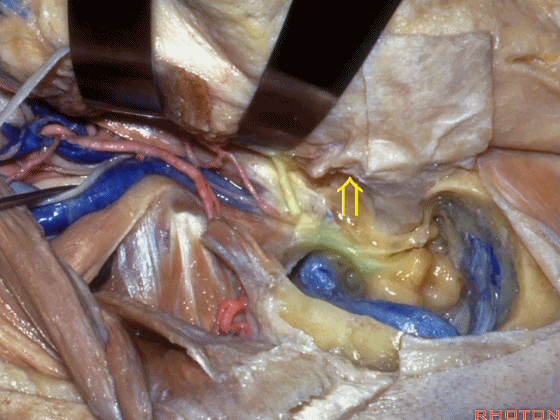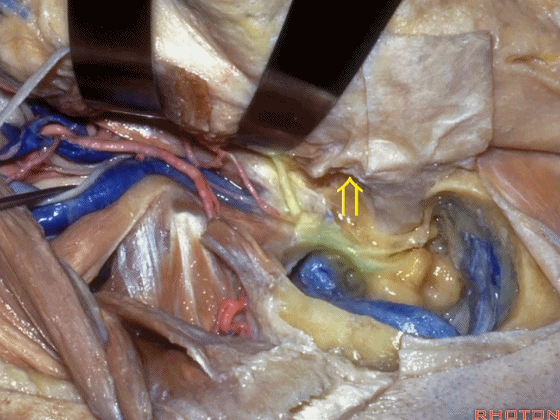
▼此时如果能对茎乳孔口的袖套样组织(下图)进行保留,并保护茎乳动脉(下图),则一般可避免术后面瘫。
If you save a cuff of tissue at the stylomastoid foramen and preserve this stylomastoid artery, usually you do this and there's no facial weakness.
Here, now we've freed up the facial nerve,lateral canal, and this is stapes here,
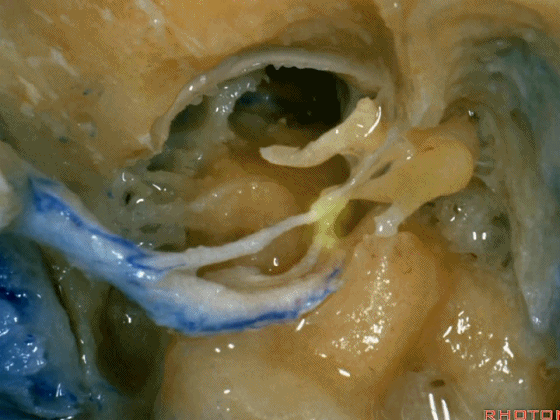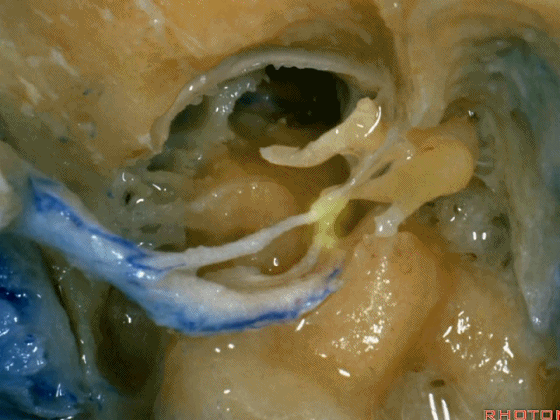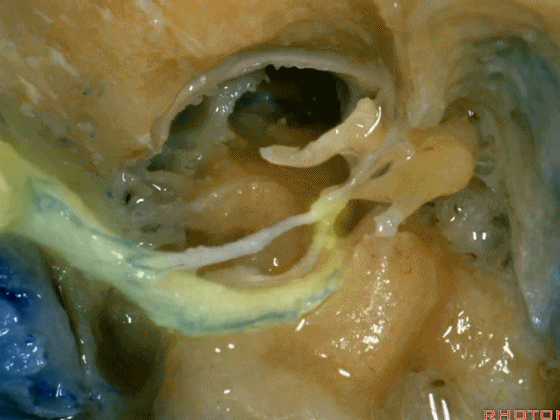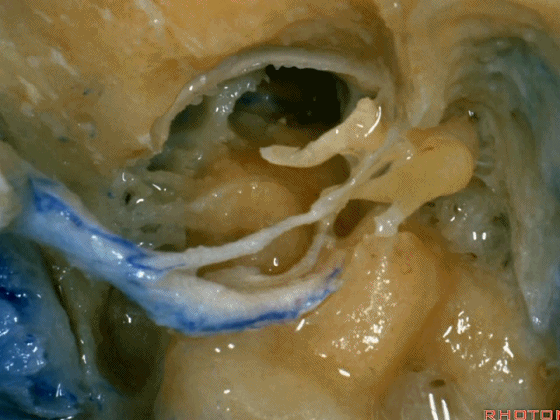
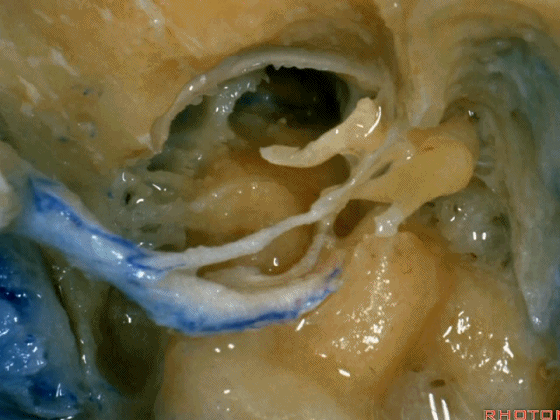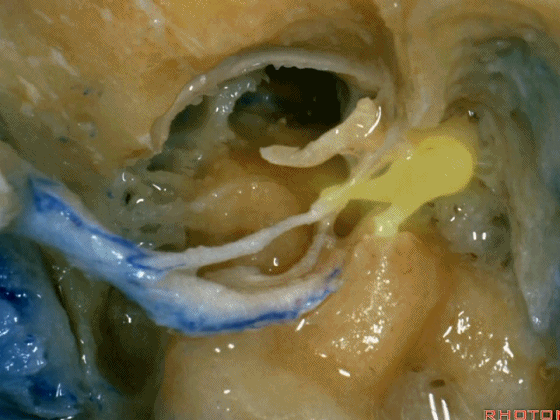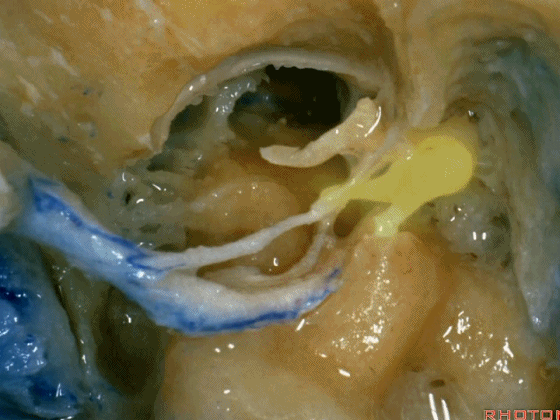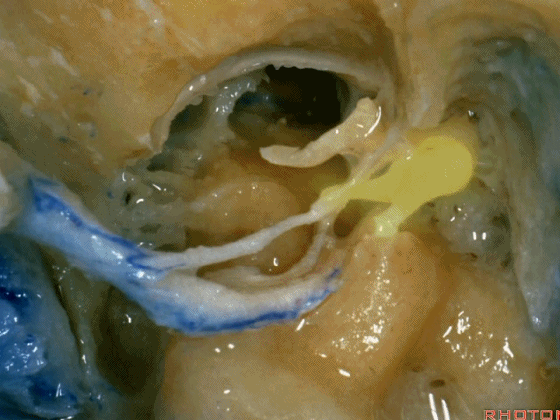
▼这是向前开口的咽鼓管。颈静脉窝病变可以侵犯中耳,沿咽鼓管蔓延。
What is this? Eustachian tube that opens forward. Jugular fossa pathology can get into the middle ear, run down the eustachian tube.
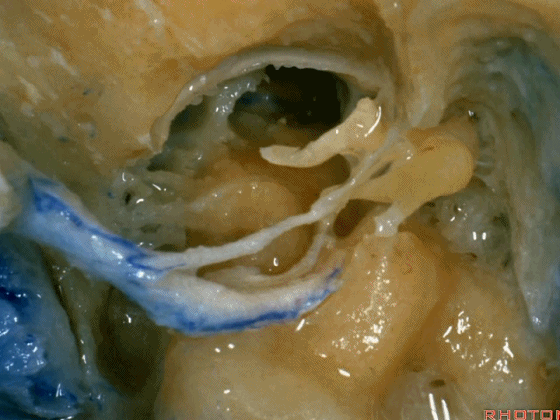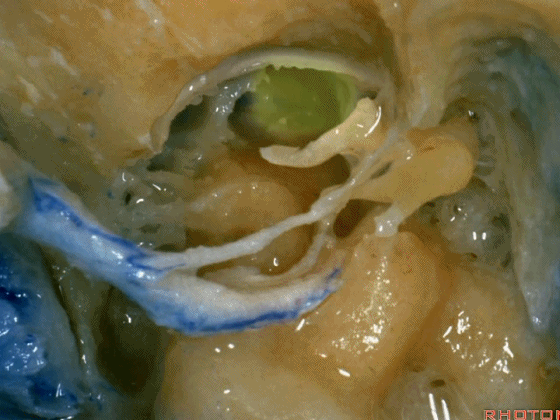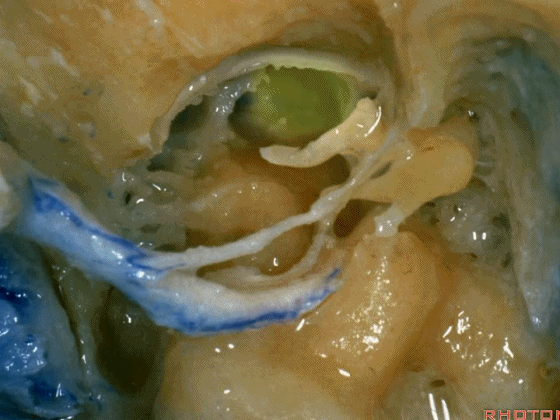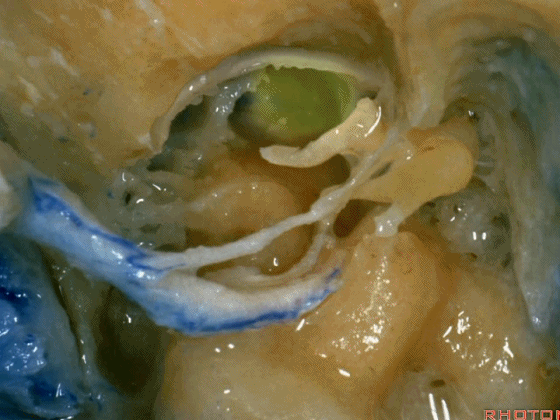
▼这里已经将外耳道的后半切除了,为了向前暴露颈静脉球,尤其当病变累及颈内动脉,我们必须切除外耳道,切除鼓膜(下图示鼓膜位置)。
And you usually...we've resected the posterior half of the external canal, but to get forward on the bulb,and especially if the carotid's involved,you often have to resect the external canal,remove the tympenic membrane.
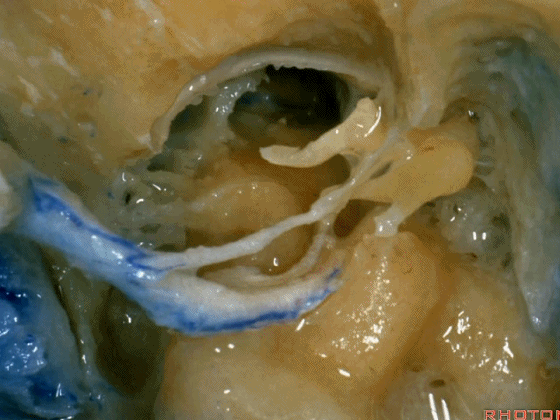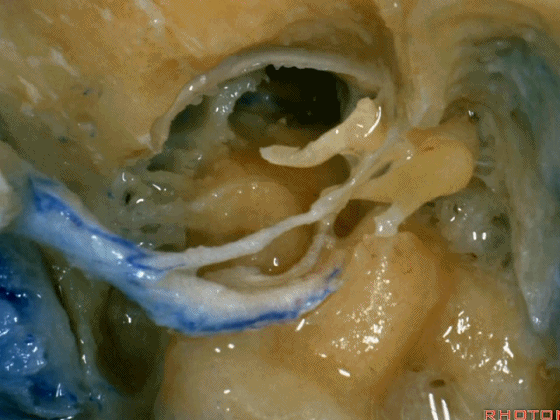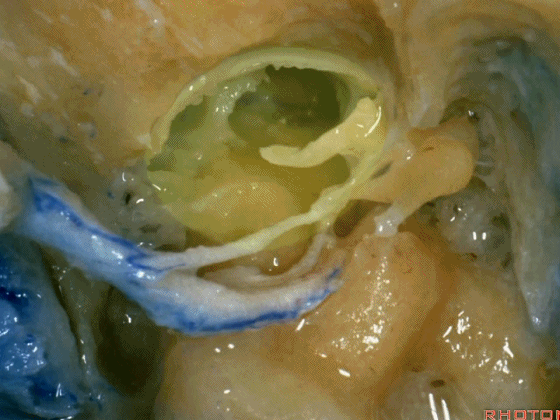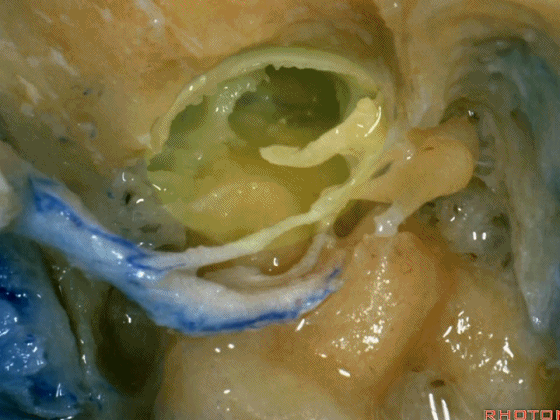
▼这是暴露后的术野,已显露颈静脉球。现将面神经向前移位(下图)。我们常须切除部分听小骨。若将镫骨(下图)保留于卵圆窗,则可保留部分听力。
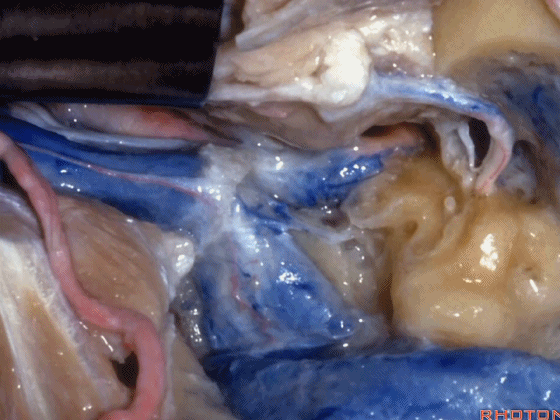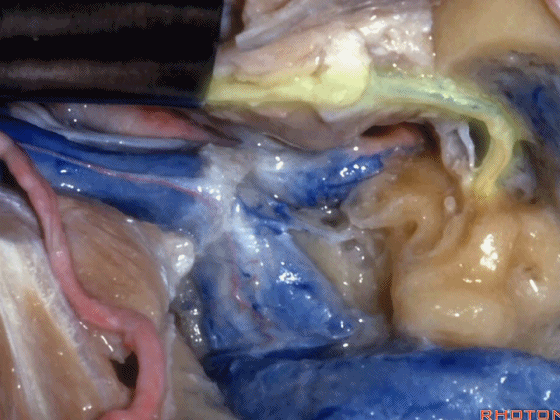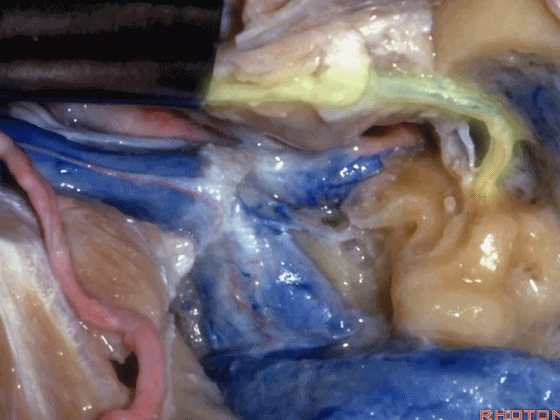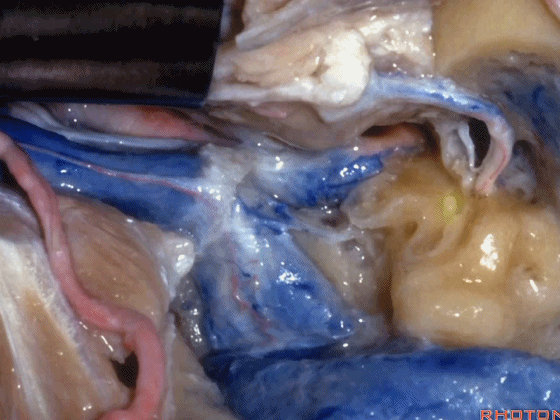
▼这是颈静脉孔的岩部
Here we see the petrosal part of the foramen,
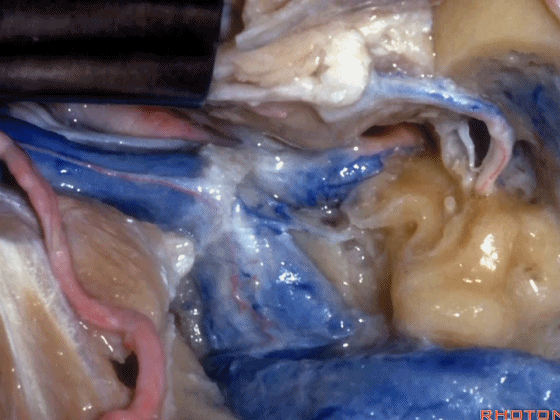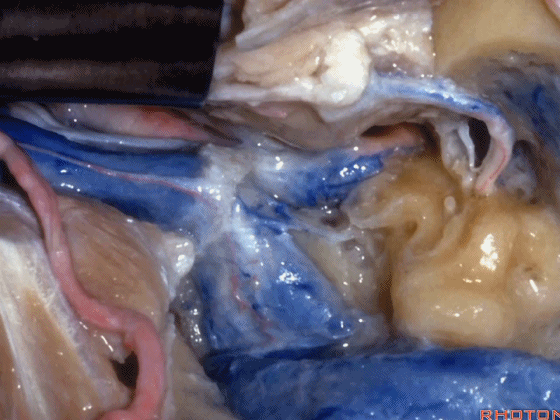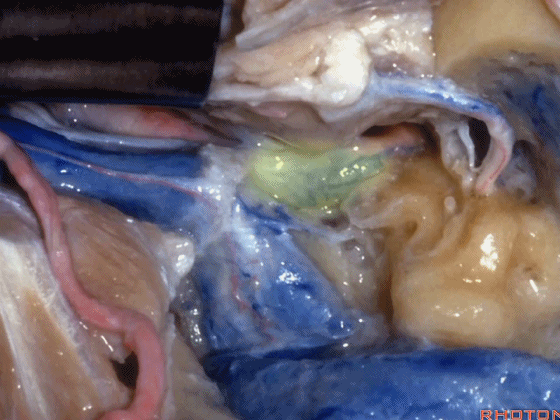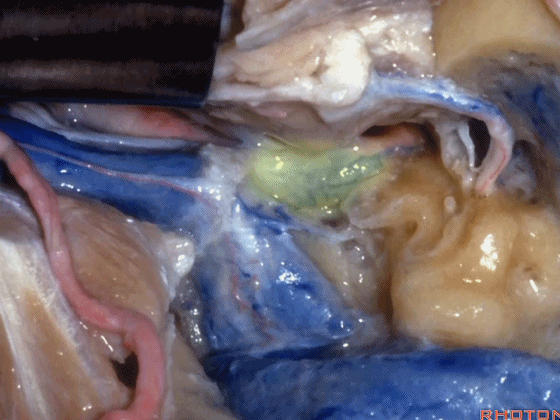
▼这是颈静脉孔的乙状部
here the sigmoid part of the foramen
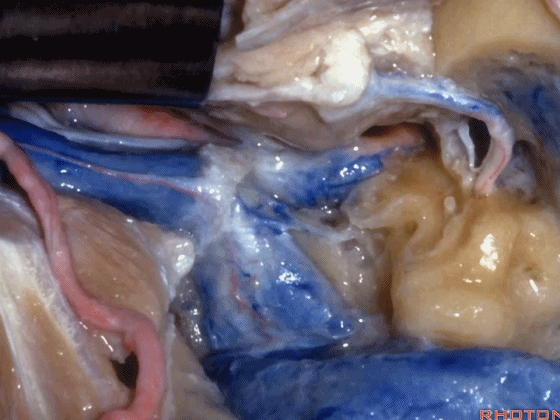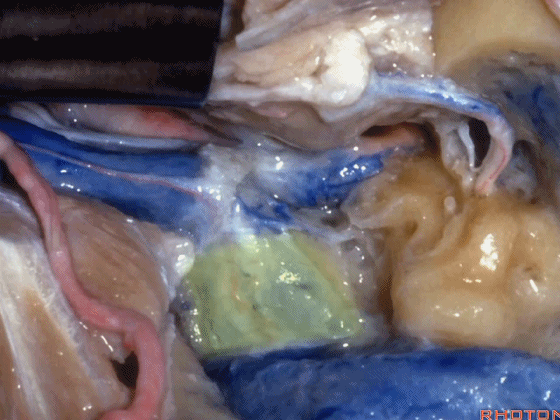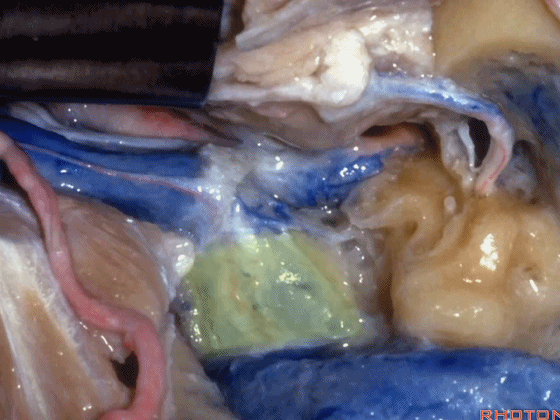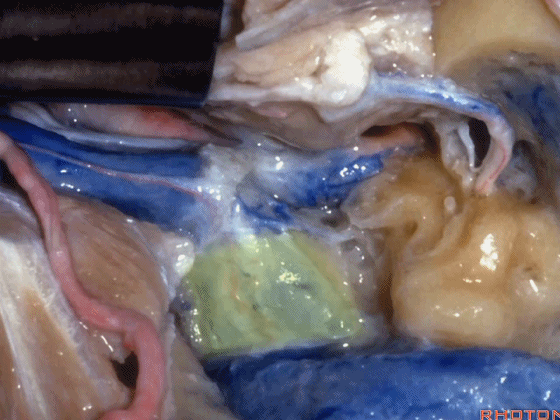
▼这是颈静脉孔的中间部,此处有神经穿行于岩部和乙状部之间。
and then in this notch, the intrajugular part, is where the nerves are going to pass through between the petrosal and sigmoid part of the foramen.
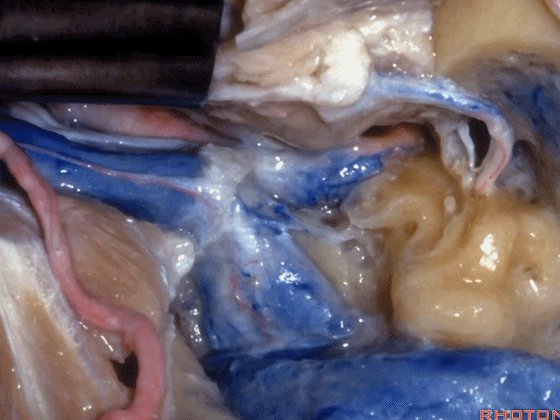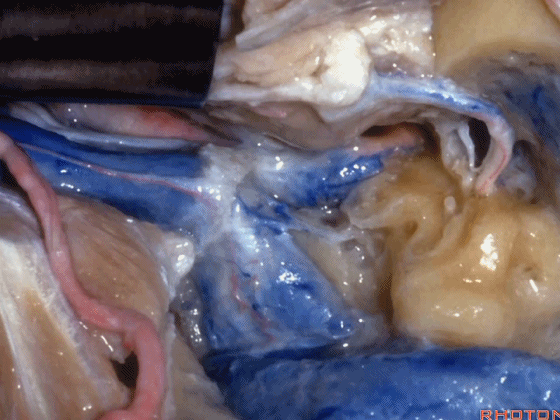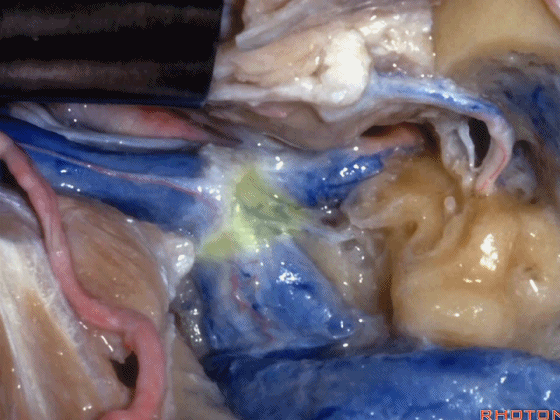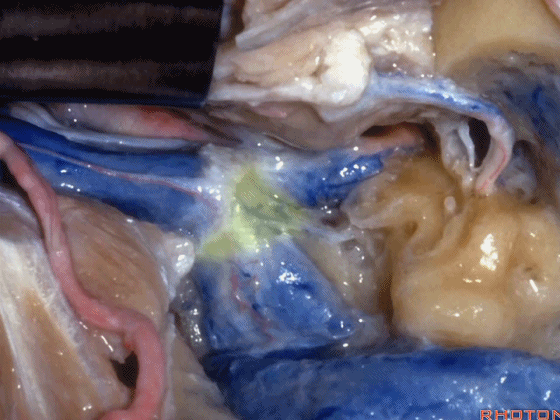
▼该部位的病变常常堵塞颈静脉球,因此术中可结扎乙状窦和颈内静脉。
And the pathology in this area usually occlude the jugular bulb,so that you can ligate the sigmoid and internal jugular vein.
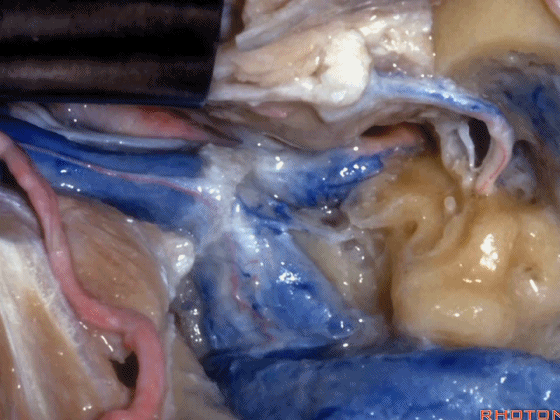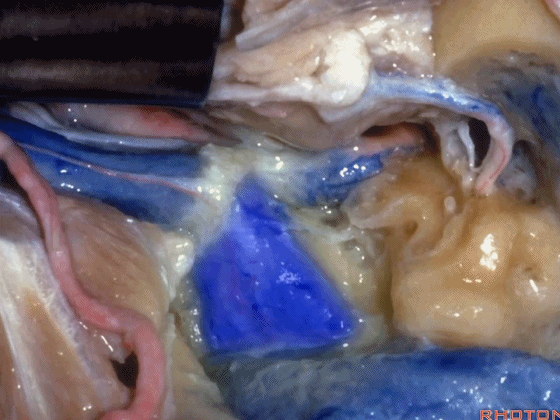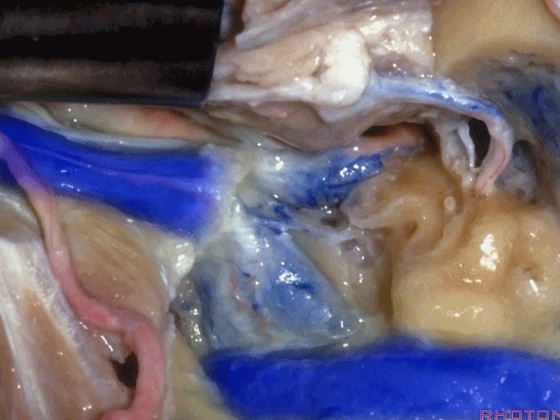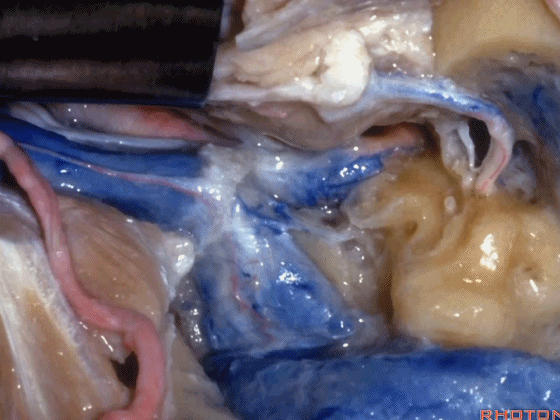
▼随后可经乙状窦后进行暴露。下图示乙状窦。
And you can look in behind the sigmoid and open retrosigmoid.
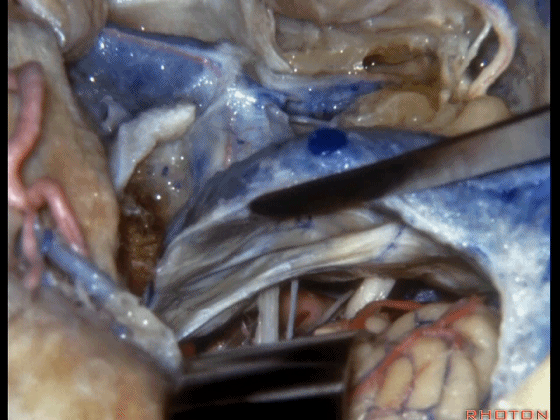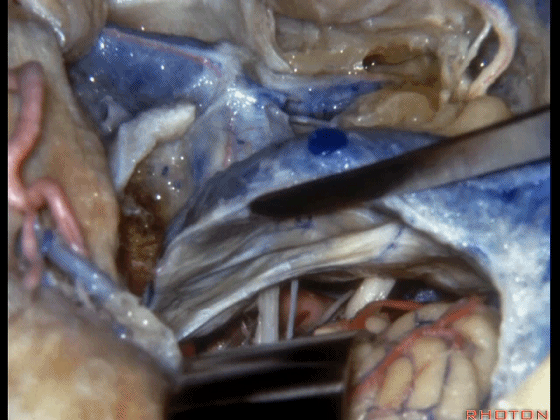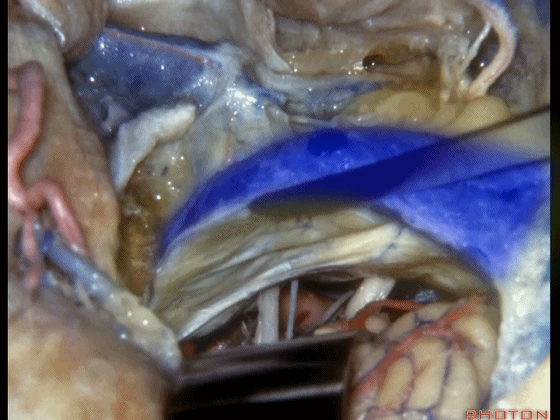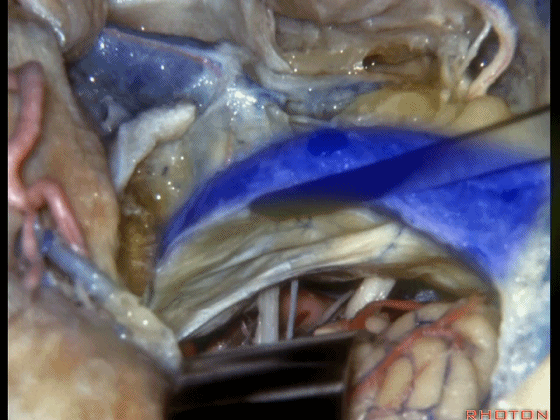
▼这是前庭蜗神经、舌咽、迷走神经。
Here we see VIII, IX, X.
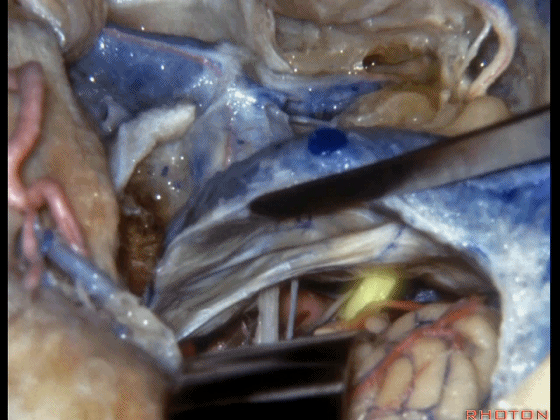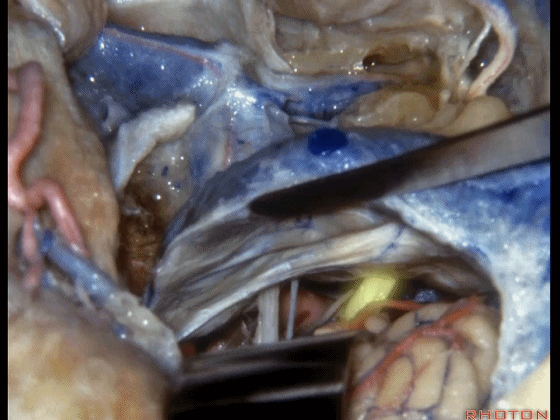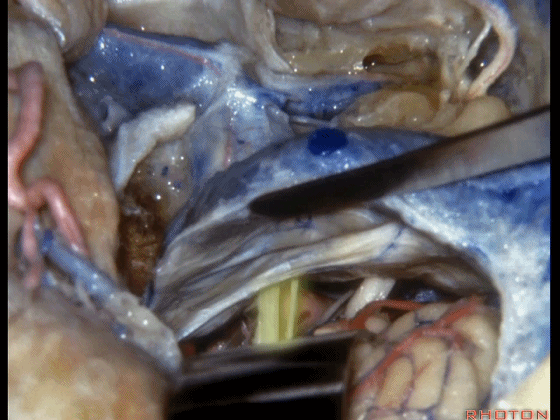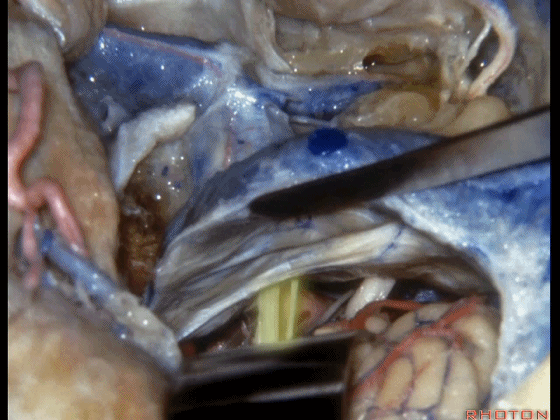
▼我们可结扎常已被堵塞了的乙状窦和颈静脉。
You can ligate the sigmoid and the jugular vein that are usually occluded.
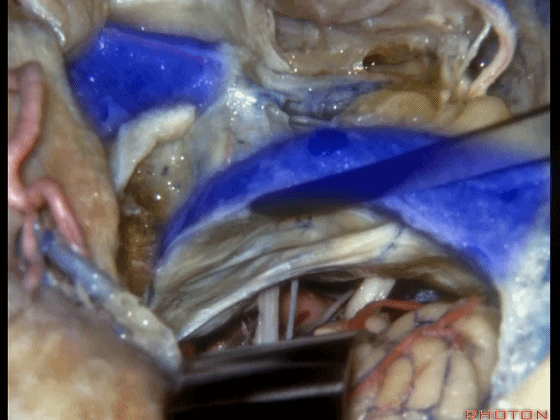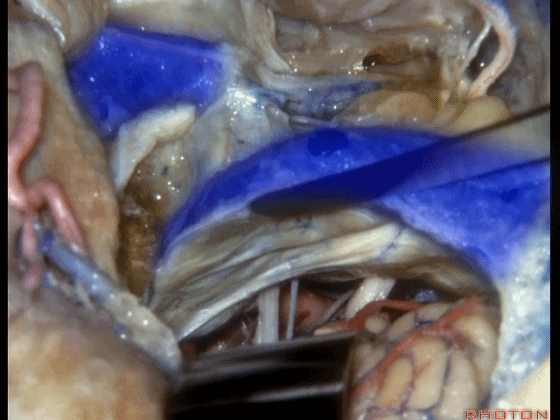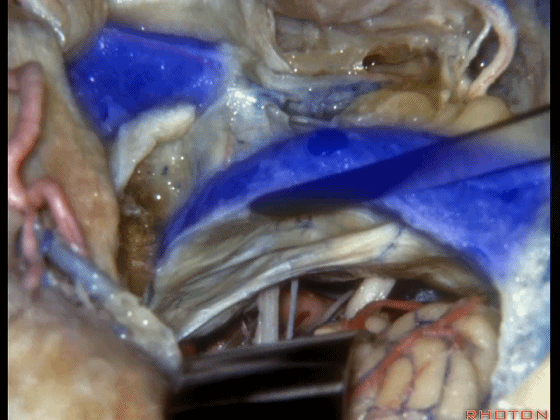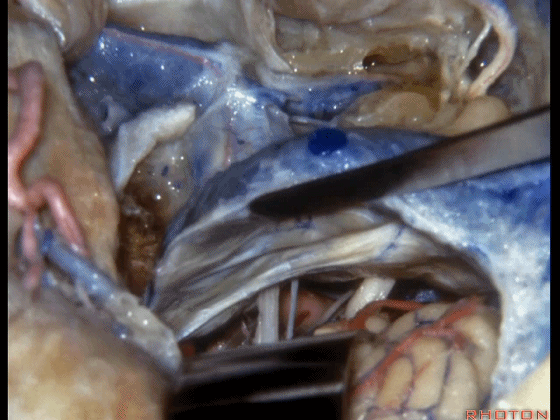
▼随后可进行切开。一旦结扎并切除这一静脉结构的外侧壁后,即可保护内侧壁
And you can open it.And if you...once you ligated and resected this lateral half of the veining,you can save the medial venous wall,
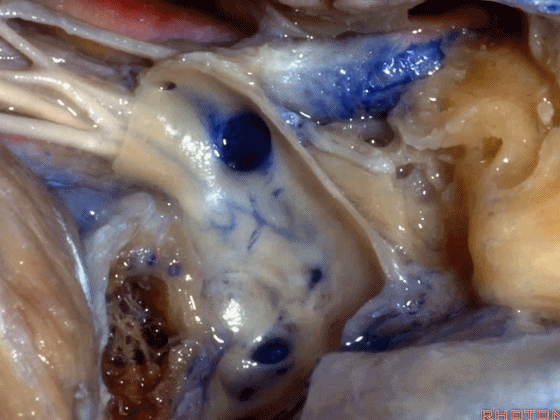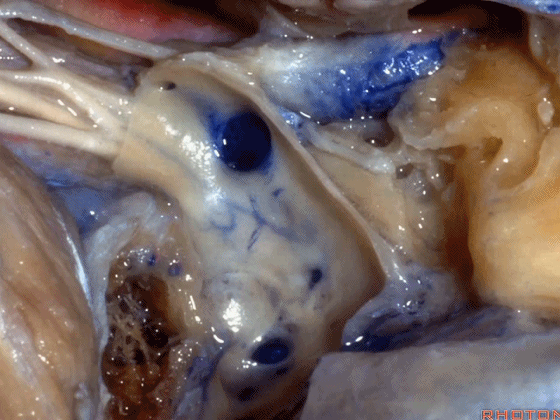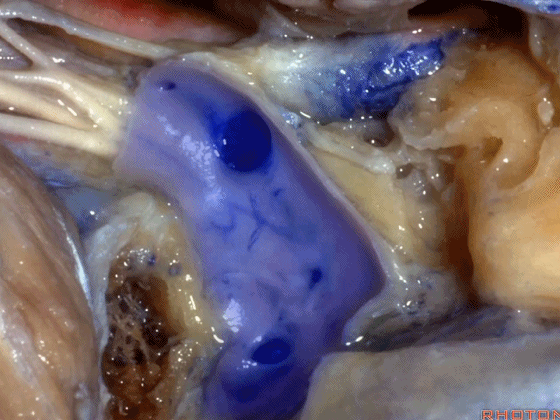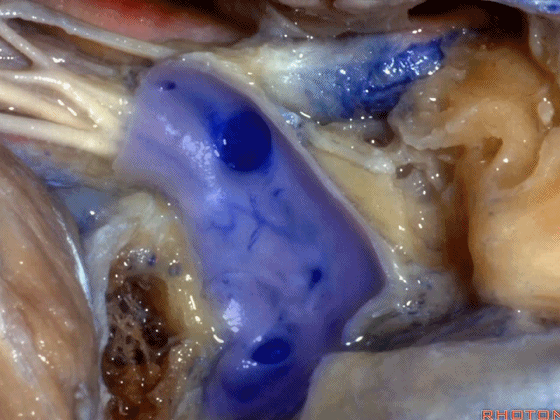
▼从而保护舌咽神经、迷走神经、副神经
then you can protect IX,X,XI,
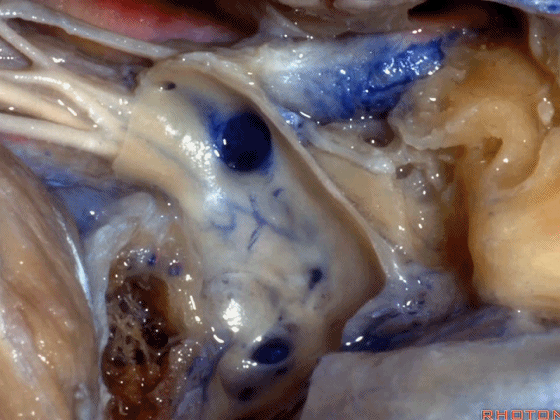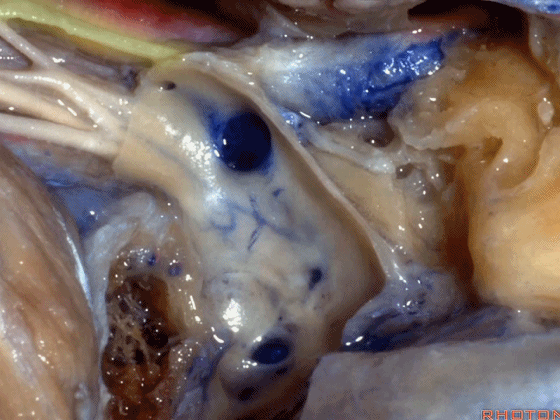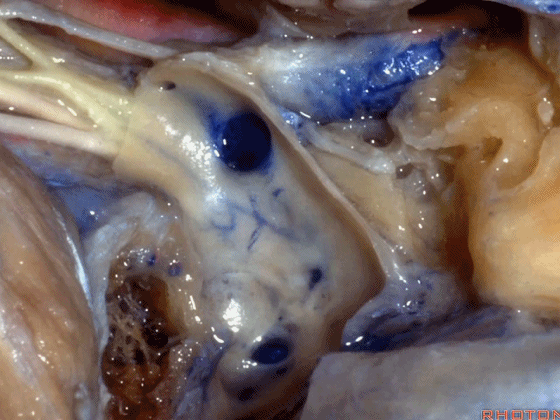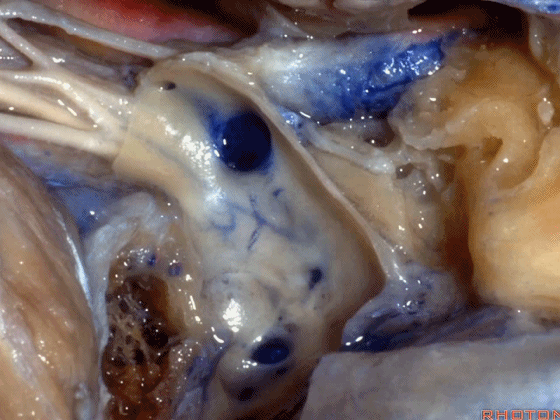
▼这是舌下神经,在迷走和副神经之间走行于后方。
what nerve is that...coming through between X and XI that's going backwards?That's...XII. It's gonna run forward to the tongue.
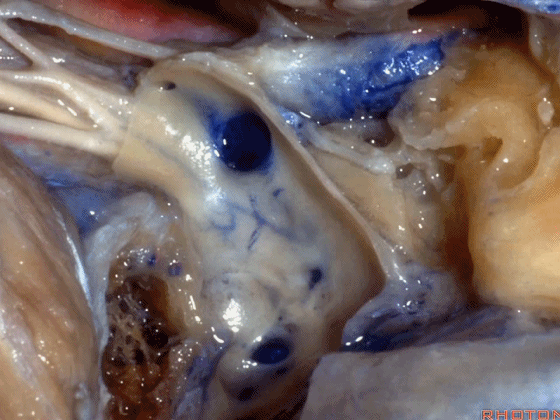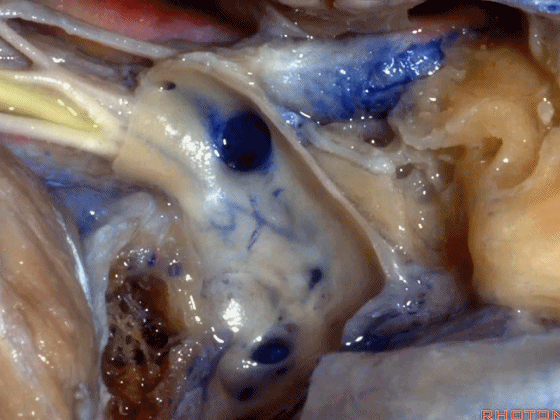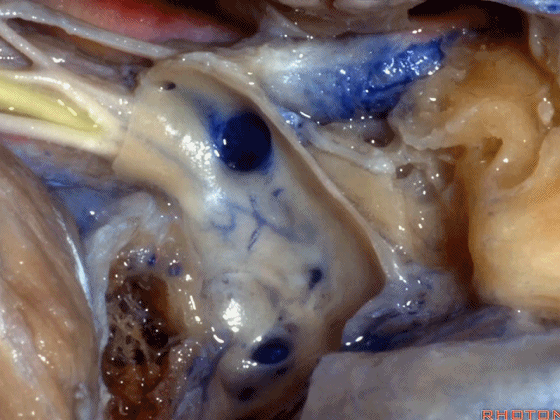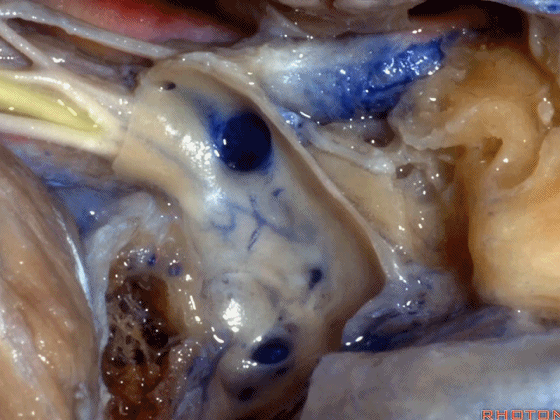
▼若保留静脉内侧壁,即可保护上述这些神经。这是颈静脉孔的岩部(下图)。
But if you preserve this medial venous wall, you can usually preserve all of those nerves.Here's the petrosal part of the foramen.
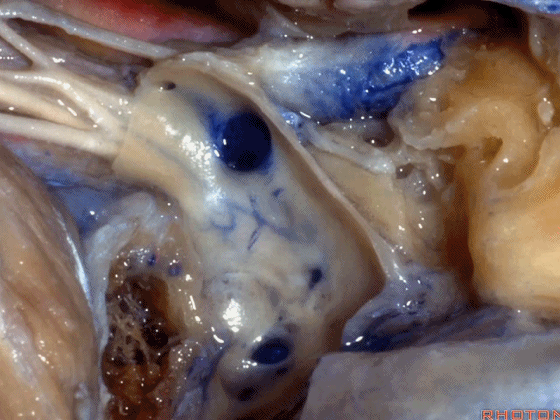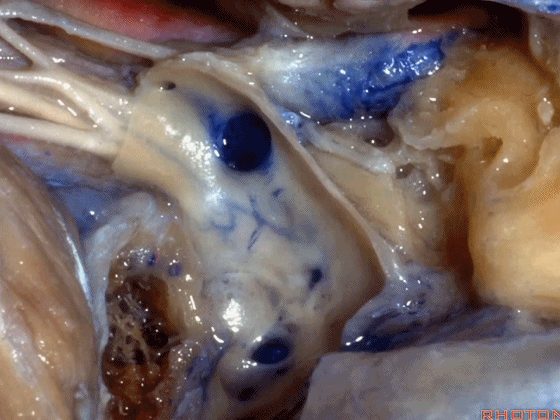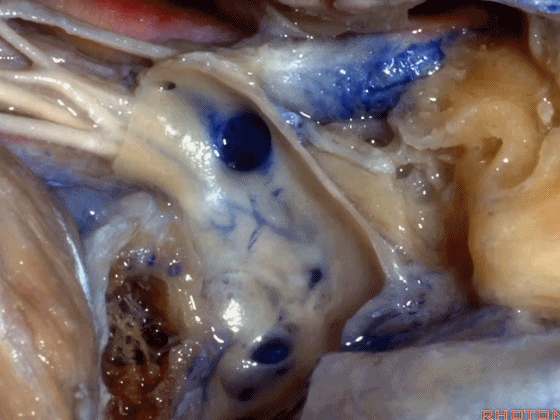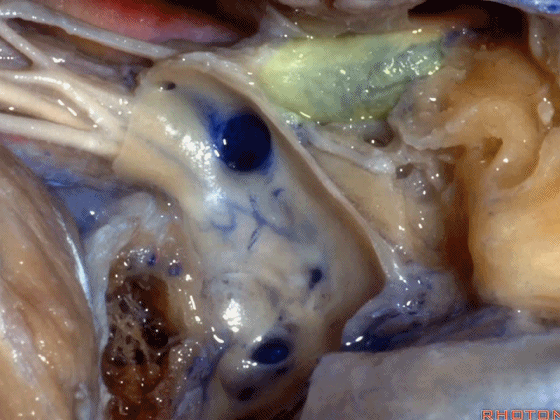
▼但如果术中不得不切除静脉内侧壁,从而直视神经表面,那么对于这些神经的保护则非常困难。总之,去除该静脉的内侧面,神经损伤的风险大大增加。
But if you have to resect that medial venous wall,and if you're wanting directly on the surface of nerves, then it's very hard to preserve these nerves then we could work at it. But,pull that medial venous wall comes up by the risk of the nerves greatly increases.
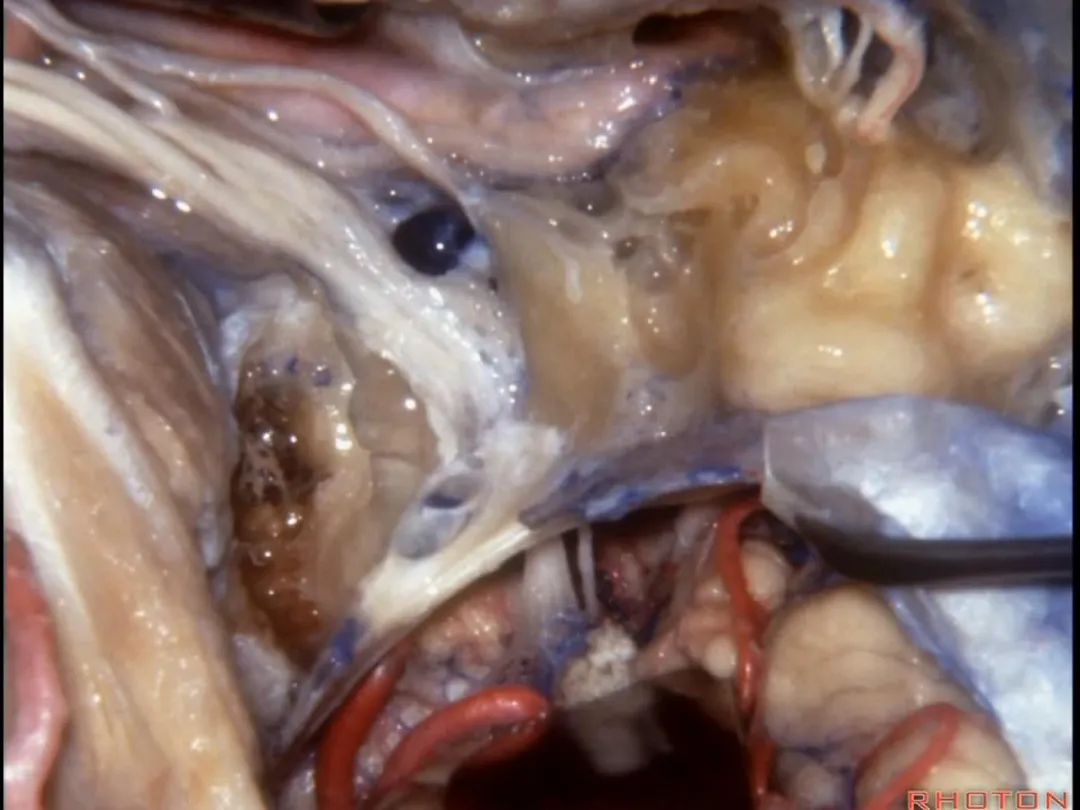
▼静脉壁已被去除。这是舌咽神经、其他后组颅神经
after the venous wall is elevated.Here's IX,the other nerves,
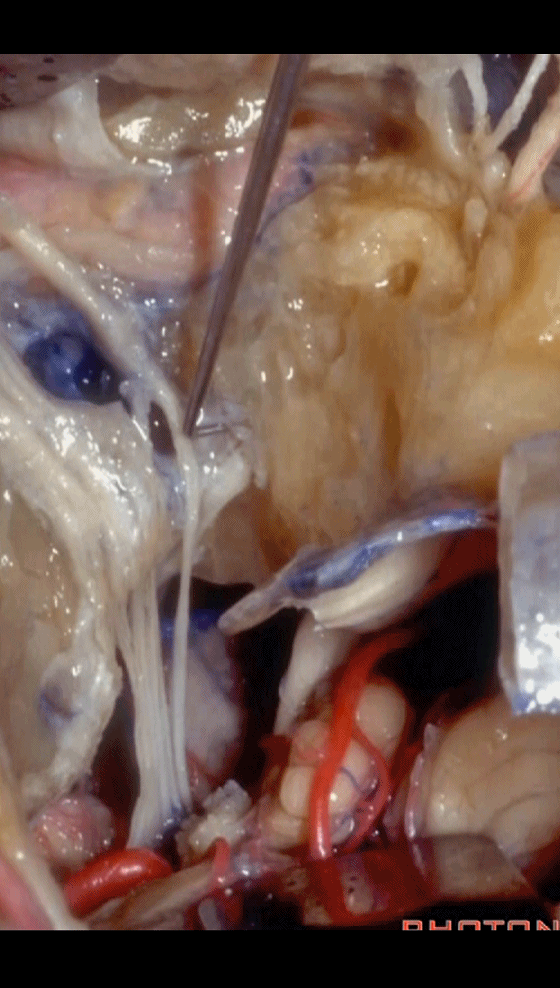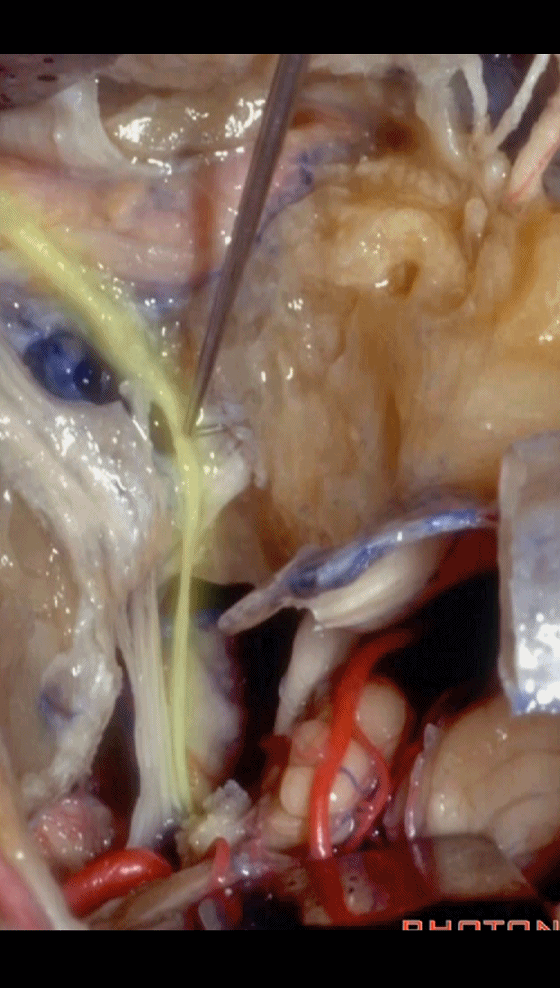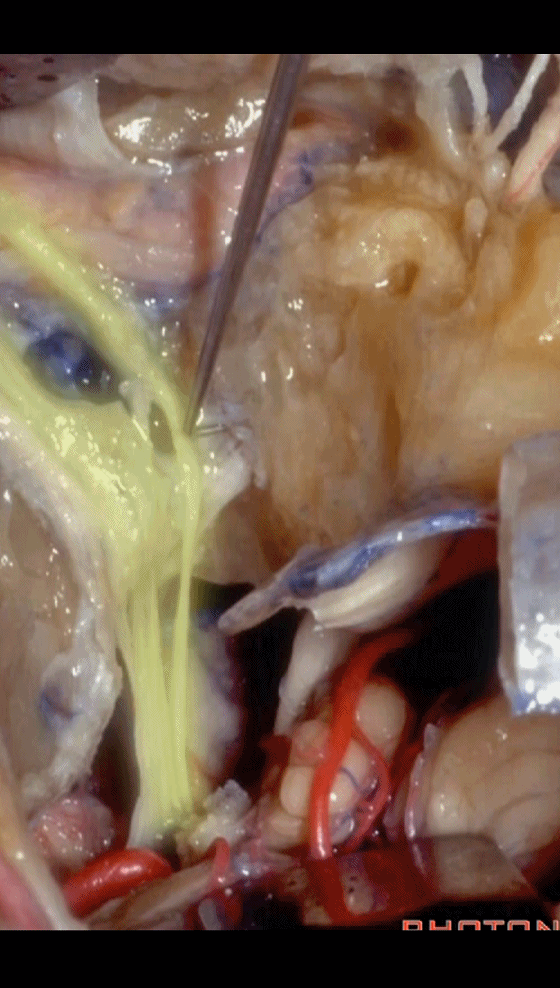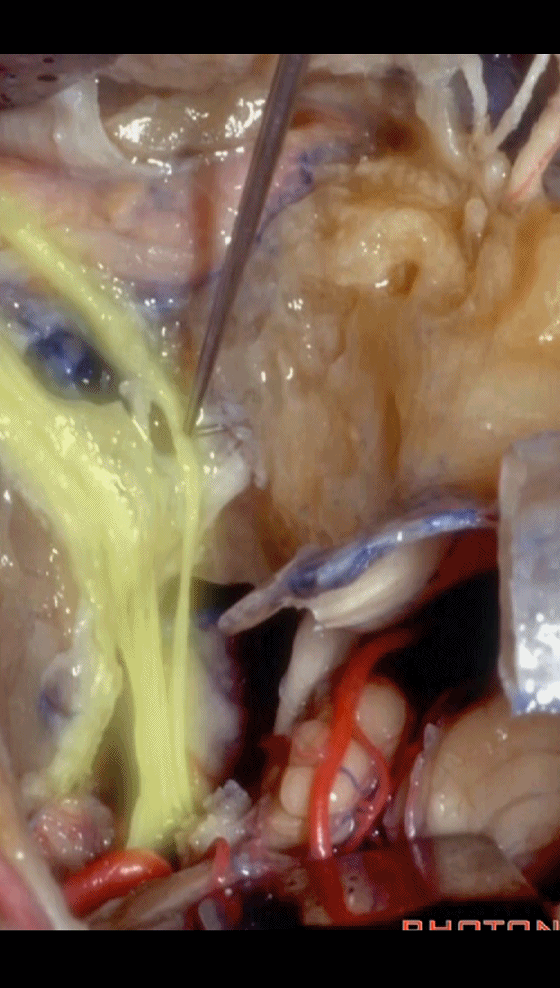
▼这是保留于卵圆孔内的镫骨,从而可保留听力。
Here's the stapes still in the oval window, so,hearing is preserved.
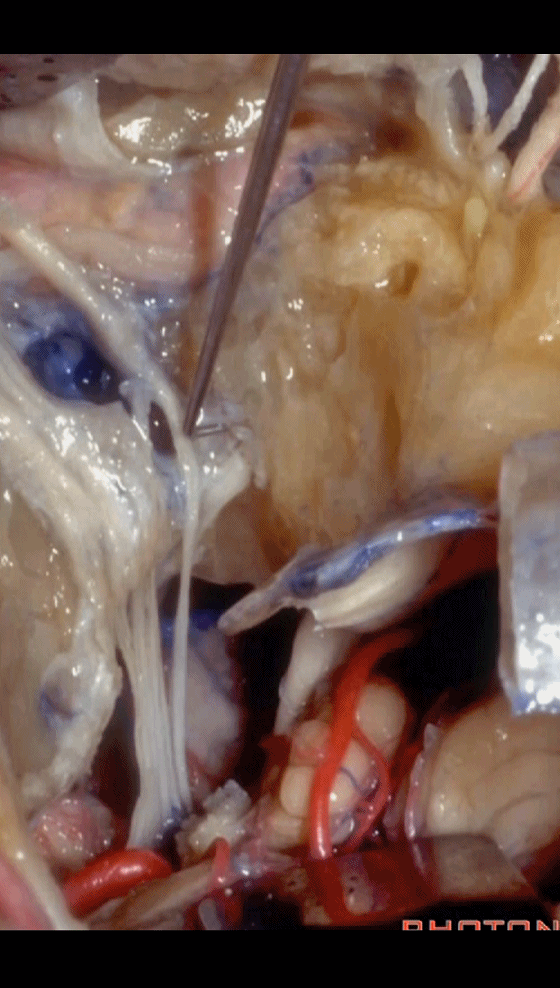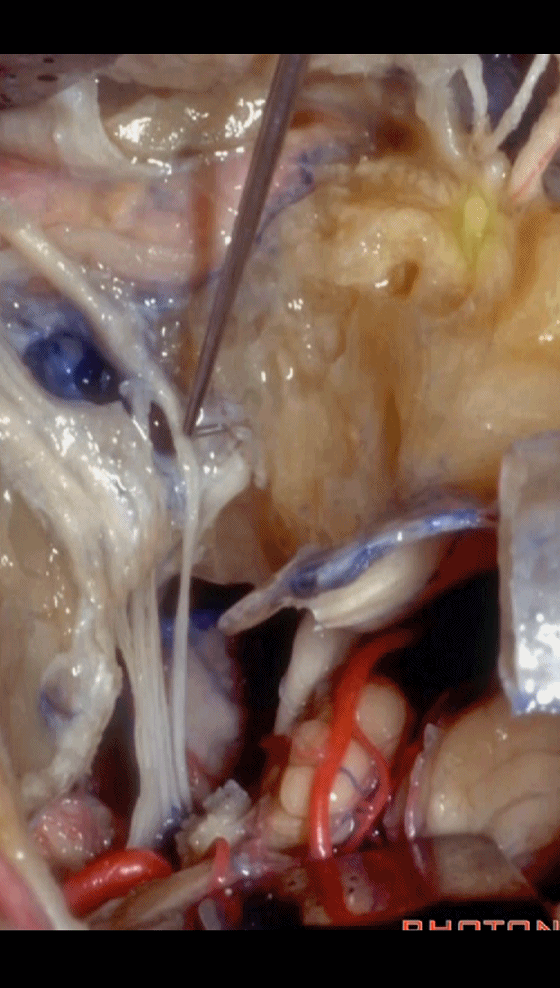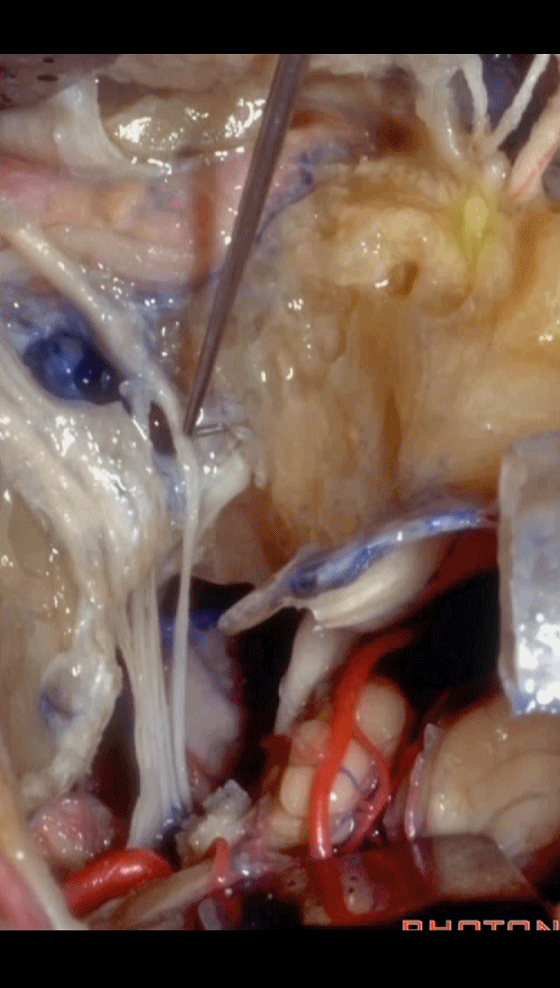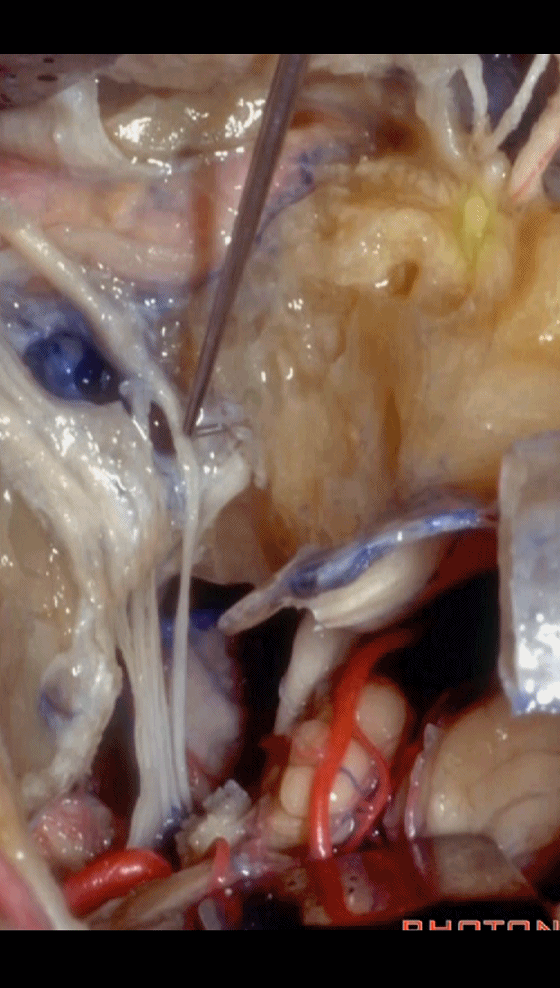
▼以上就是关于侧后颅底及远外侧入路的相关解剖及入路。

希望对大家有所帮助,更多往期内容请点击下方




