以下内容转载自“危重症医学系CMU”公众号
The Antiedematous Effect of Exogenous Lactate Therapy in Traumatic Brain Injury: A Physiological and Mechanistic Approach
David Emmanuel Duhaut, Catherine Heurteaux, Carine Gandin, Carole Ichai and Hervé Quintard
Neurocrit Care 2021 Apr 20.
doi: 10.1007/s12028-021-01219-y.
Background
Sodium lactate (SL) has been described as an efficient therapy in treating raised intracranial pressure (ICP). However, the precise mechanism by which SL reduces intracranial hypertension is not well defined. An antiedematous effect has been proposed but never demonstrated. In this context, the involvement of chloride channels, aquaporins, or K-Cl cotransporters has also been suggested, but these mechanisms have never been assessed when using SL.
背景
乳酸钠被认为是治疗颅内压增高的有效方法。然而,乳酸钠降低颅内高压的机制尚不明确。既往已经提出乳酸钠有抗水肿作用,但尚未得到证实。在这种背景下,也提出了有氯离子通道、水通道蛋白或钾氯协同转运蛋白的参与,但在使用乳酸钠时尚未对这些机制进行评估。
Methods
In a rat model of traumatic brain injury (TBI), we compared the effect of SL versus mannitol 20% on ICP, cerebral tissue oxygen pressure, and brain water content. We attempted to clarify the involvement of chloride channels in the antiedematous effects associated with lactate therapy in TBI.
方法
在大鼠创伤性脑损伤(TBI)模型中,我们比较了乳酸钠和甘露醇对颅内压、脑组织氧分压及脑含水量的影响。我们试图阐明在TBI患者应用乳酸钠进行抗水肿治疗的过程中有氯离子通道的参与。

Results
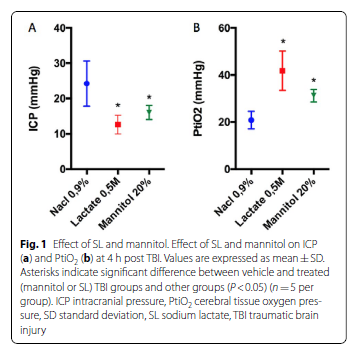
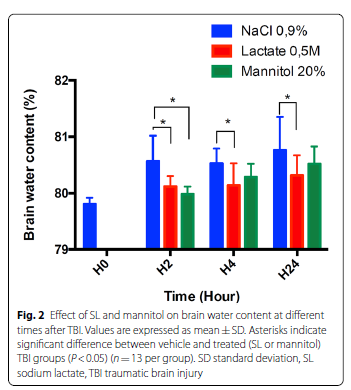
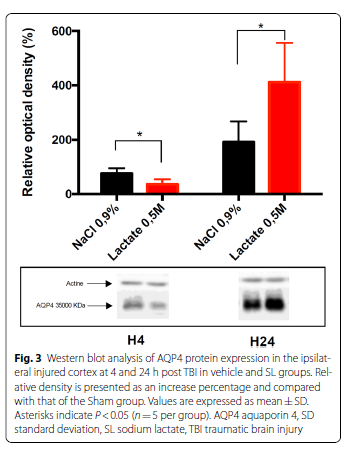
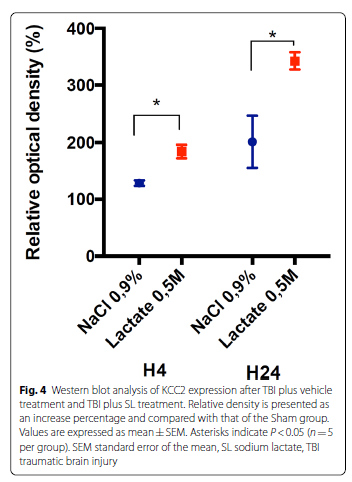
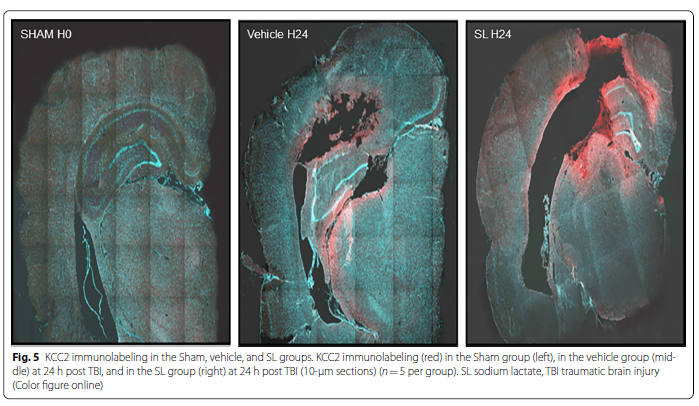
An equimolar single bolus of SL and mannitol significantly reduced brain water content and ICP and improved cerebral tissue oxygen pressure 4 h after severe TBI. The effect of SL on brain water content was much longer than that of mannitol and persisted at 24 h post TBI. Western blot and immunofluorescence staining analyses performed 24 h after TBI revealed that SL infusion is associated with an upregulation of aquaporin 4 and K-Cl cotransporter 2.
结果
重度TBI后4 h,等摩尔量单次推注乳酸钠和甘露醇可显著降低脑组织含水量及颅内压,并改善脑组织氧分压。乳酸钠降低脑组织含水量的作用持续时间长于甘露醇,可持续至TBI后24h。TBI后24小时进行的蛋白印迹和免疫荧光染色分析显示,输注乳酸钠与水通道蛋白4和钾氯协同转运蛋白2的上调有关。
Conclusions
SL is an effective therapy for treating brain edema after TBI. This study suggests, for the first time, the potential role of chloride channels in the antiedematous effect induced by exogenous SL.
结论
乳酸钠是治疗TBI后脑水肿的有效疗法。本研究首次表明氯离子通道在外源性乳酸钠诱导的抗水肿效应中的潜在作用。
首都医科大附属北京天坛医院 苗明月 译
【危重症医学系CMU】公众号简介
首都医科大学危重症医学系官方公众号,定期发布最新专业资讯和学系动态、分享危重症相关领域的经典文献和权威指南。




