![]()
本篇为The Rhoton Collection解剖视频中《Preserving the Frontalis Muscle(额肌保护)》,这一章节实际讲解的是筋膜间-骨膜下入路保护面神经颞支技术。从基层医院的颅骨修补术,到比较复杂的额眶颧入路,都涉及到这一技术。为了便于初学者理解,笔者于正文开始前简要介绍颞肌筋膜解剖。为了更加直观的介绍筋膜间入路,本文选取精彩手术视频,在文末以动图的形式呈现。
笔者水平所限,错误之处请批评指正!

颞肌筋膜解剖
颞部皮肤大致分为3层:皮肤-颞浅筋膜层、颞肌筋膜浅层、颞肌筋膜深层;
额部皮肤大致分为2层:皮肤-帽状腱膜层、骨膜层。(额肌位于帽状腱膜层)
额颞部皮肤之间的关系大概为:皮肤-帽状腱膜层与皮肤-颞浅筋膜层相互延续,额部骨膜层在颞上线与颞肌筋膜浅层相互延续。
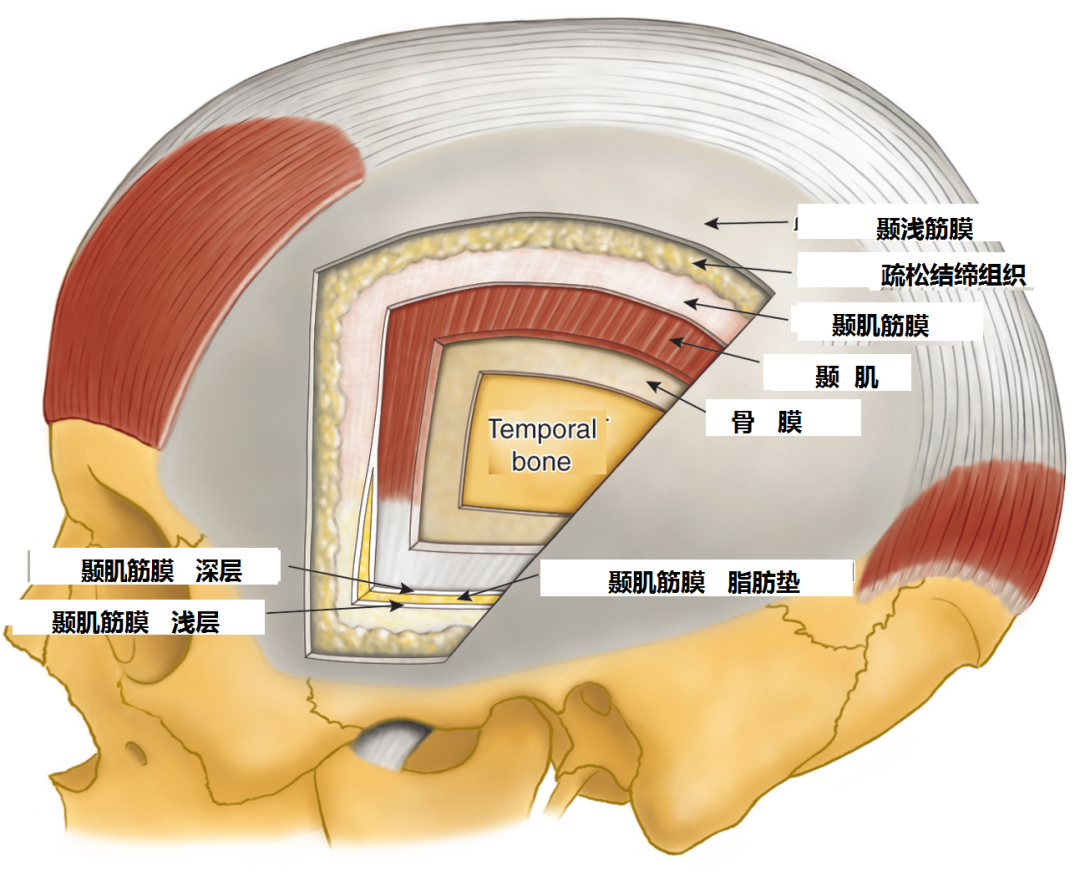
颞前区存在3层脂肪垫(下图):
第1层脂肪垫在颞浅筋膜与颞肌筋膜浅层之间,颞浅动静脉、面神经颞支均在其间走形。
第2层脂肪垫在颞肌筋膜浅层与颞肌筋膜深层之间。颞肌筋膜在眶上缘水平分裂为浅层和深层,容纳5~6mm厚镰刀状的脂肪垫(上图)。
第3层脂肪垫位于颞肌筋膜深层与颞肌之间,筋膜下入路时可涉及。

筋膜间-骨膜下入路
Interfascial-Subpericranial Approach
We want to talk about spanserving the frontalis muscle, which if lost can cause a significant cosmetic deficit.

我觉得这个话题很有必要性,因为在很多培训班上,大家很多的疑问都集中在如何在翻开额颞瓣时能够正确地保护好额肌。其中一种技术称为筋膜间入路。
The reason that I became interested in this project is that at many courses for trainees, there was considerable confusion about how we go about each step along the way of spanserving the frontalis muscle when we return a frontotemporal flap. One of the techniques that is used is called interfascial.

然而此技术仅仅强调了颞肌部分的暴露,即所谓的筋膜间入路。然而,想要真正有效地保护面神经全程,我们需掌握的不仅仅是颞区的筋膜间技术,还需要了解颞上线以内的骨膜下技术。
But that technique deals only with the part of the exposure over the temporalis muscle, which we describe as interfascial. While, to really save those nerves along their full course, we have to think not only interfascial exposure over the temporalis muscle, but we need to think about extending that exposure subpericranial medial to the superior temporal line.

还有一种技术也常用来保护支配额肌的神经,即所谓的筋膜下入路。
The other commonly used exposure to spanserve the nerves to the frontalis muscle is called subfascial exposure.

但同样地,筋膜下入路关注的也仅仅是颞区的暴露,而忽略了上述的骨膜下暴露技术,以及在颞上线处保护神经完整的重要性。
But again, subfascial deals only with the exposure over the temporalis muscle and doesn't fully explain the technique that also has to be subpericranial with maintenance of the continuity of the nerves across the superior temporal line.

来看看额肌(下图),其位于帽状腱膜层内。
So, the frontalis muscle we see here is embedded in the galea.

支配额肌的神经是面神经的颞支,文献中对其命名容易引起混淆,如所谓的额-颞神经、额颞神经、颞额神经等。我们采用大多数神经外科文献的命名方法,将其称为颞支。
And it's supplied by the temporal branches of the facial nerve, which if you look at various literature, are described as frontal-temporal, frontotemporal, temporofrontal nerves. We call them, we refer to them as in some of the papers in the neurosurgical literature, as temporal nerves.

面神经颞支从颞肌筋膜上方走行,随后支配额肌
And those nerves cross the temporalis fascia, and then, supply the frontalis muscle

面神经颞支进入额肌的位置通常位于眶上缘上方2cm内。
that is innervated by these branches of the facial nerve that enter the muscle usually within 2 cm above the superior orbital rim.

随后,神经末梢向后分布于肌肉内。
And then the nerve supply sspanads posteriorly in the muscle.

因此某些情况下,横切额肌中部,将造成切口以上的上部肌肉失支配。
So if for some reason, an incision extends across the mid part of the muscle, then the innervation to the upper part of the muscle is going to be lost.

来看下面这幅图,我们必须保护面神经全程,其出于茎乳孔,随后在腮腺内通常发出三支分支。
And in looking at this, we want to spanserve the nerve all the way from the stylomastoid foramen, where in the paroid gland it gives rise to usually three branches to the frontalis and the orbicularis oculi.

面神经颞支 支配额肌以及眼轮匝肌。
it gives rise to usually three branches to the frontalis and the orbicularis oculi.

因此通常有三支颞支跨过颧弓。在到达额肌时,这些分支进一步分为至少五支,均极其纤细而难以在显微镜下分辨。
Usually there are three branches, three temporal branches coursing the zygomatic arch. By the time they reach the frontalis muscle, they split up into five branches at least that are very tiny almost imperceptible and difficult to see even with a surgical microscope.

来看耳屏前方,在跨越颧弓时,主要有三支颞支。
So, if you look here in front of the tragus, as these nerves cross the zygomatic arch, there're commonly three temporal branches.

下图示三支颞支

最后方的一支,主要支配耳肌,该肌肉位于耳上方的帽状腱膜层内。
The most posterior one goes spandominantly to the auricularis, a muscle embedded in the galea above the ear.

下图示眶上区域。外侧是颞肌筋膜。
And here we see the supraorbital area. And here we have temporal fascia laterally.

在颞上线以内(下图),这些神经分支行于骨膜的浅面。
And then at the superior temporal line, the branches run on the outer surface of the pericranium here

下图示额部骨膜层

面神经颞支从额肌外侧缘的下方进入并向后方支配肌肉。
and then pass under the lateral edge of the frontalis muscle, and then sspanad posteriorly.

在肌肉的浅面,可见眼神经发出的眶上支,其为额神经的分支。
On the surface of the muscle, on the superficial side, you see the supraorbital branches of V1, branches of the frontal nerve.

因此,想要保护支配额肌的神经,需保留神经于颞肌筋膜的外表面,随后是其跨越颞上线处,然后向内保留于骨膜的外表面,在此处,神经从深面进入额肌的外侧缘。
So that, to spanserve the nerve supply to the frontalis muscle, we need to spanserve it on the outer surface of the temporal fascia, and then as it crosses the superior temporal line, and then medially on the outer surface of the pericranium, where it dives under the lateral edge of the frontalis muscle.

这里我们暴露了颞上线以内和以外的区域。下图示颞上线。
Here we've done an exposure both lateral to the superior temporal line and medial.

下图示切除了一小块颞肌筋膜浅层。
We've opened a window here in the superficial layer of temporal fascia.

在颞肌筋膜浅层的深面即可见筋膜间脂肪垫
And we see deep to the superficial layer of temporal fascia, the interfascial fat pad

在脂肪垫深面则是位于颞肌外表面的颞肌筋膜深层。
and then deep to it the deep temporal fascia on the outer surface of the muscle.

面神经颞支跨越颞上线,其为颞肌筋膜浅层和深层的共同附着线。
And then the nerves cross the superior temporal line, where both the superficial and deep layers of temporal fascia are attached to the line.

我们同时切开了一小块骨膜,其位于进入额肌的颞支神经丝的深面。
And then we've opened the window in the pericranium that is deep to these fine filaments of temporal nerves that pass to the muscle.

去除骨膜后,即可显露神经是如何从肌肉的外侧进入其下方的。
And we've removed the pericranium,and we see these branches then passing under the lateral side of the muscle.

由此可见,要想保护好颞支从茎乳孔至额肌的全程,需关注的不仅是颞上线以外的颞肌筋膜区域,还应注意颞上线以内的区域,用到的技术即骨膜下分离技术。这部分我反复强调的目的在于,大部分文献都只关注了筋膜下或筋膜间技术,而对于颞支跨越颞上线及走行于骨膜表面的部分极少述及。而保护神经的关键在于切勿暴露神经所在的层次。
So to spanserve the branches from stylomastoid foramen to the frontalis muscle, we must 、spanserve not only in the area of the temporal fascia lateral to the superior temporal line, but also medial to the superior temporal line where the dissection is subpericranial. And I emphasize that because a number of the papers describing the technique describe only the subfascial or the interfascial part of the procedure and then no mention is made of the nerves crossing the superior temporal line or crossing the outer surface of the pericranium. And the key to spanserving these nerves is not opening the layers between which they are sandwiched.

接下来让我们具体看一下这里的层次。下图示颞上线。
So that, now we take a look at the layers here.

颞上线以外,筋膜间脂肪垫(下图)显露。
Now, lateral to the superior temporal line,

这里我们已将帽状腱膜(在颞区又称为颞浅筋膜或颞顶筋膜)翻开,即进行的是帽状腱膜下暴露。
once we get to the interfascial fat pad...we've turned up galea, this is subgaleal.

贴着帽状腱膜的层次是疏松结缔组织,神经即走行于此层中。
And then the next layer is loose areolar tissue through which the nerves pass.

现在来看颞上线以外的区域,接下来的第一层是颞肌筋膜的浅层。
And then lateral to the superior temporal line,the first layer is superficial layer of temporal fascia.

接下来是筋膜间脂肪垫。
And then it's the interfascial fat pad.

再接下来是颞肌筋膜的深层。
And then, the next layer is...that's the deep fascia.

再往下就是颞肌。
And then the next layer is the temporal muscle.

最后一层是骨膜层,其位于颞肌的深面。
And the last layer is...well, it's pericranium or you can call it periosteum,it's attached to the muscle on the deep surface.

接下来是筋膜间脂肪垫。
And then it's the interfascial fat pad.

再接下来是颞肌筋膜的深层。
And then, the next layer is...that's the deep fascia.

再往下就是颞肌。
And then the next layer is the temporal muscle.

最后一层是骨膜层,其位于颞肌的深面。
And the last layer is...well, it's pericranium or you can call it periosteum,it's attached to the muscle on the deep surface.

在英文中,为了区分颞上线内外的骨膜层,两者有不同的拼写。
We call it periosteum to differentiate it from this layer medial to the superior temporal line that we call pericranium.

这是所谓的筋膜间-骨膜下入路,其筋膜间技术是由Yasargil教授提出的。
So we call one approach interfascial-subpericranial, and Yasargil gave us the interfascial approach.

另外的即筋膜下-骨膜下入路(下图),则由Barrow中心所倡导,最早是由Spetzler教授提出的。
The other approach is subfascial-subpericranial,and the subfascial approach, that term was called a the Barrow, and one of the early papers on that was with Spetzler.

综上,颞上线外侧分五层,内侧为一层。
So, there're five layers lateral,one layer medial.

因此,在起始阶段,我们都是在帽状腱膜下分离的,随后,在皮瓣的上部,分离也始终在,外侧来说是帽状腱膜和颞肌筋膜之间,内侧来说是帽状腱膜和骨膜之间,即沿着帽状腱膜下疏松结缔组织这一层进行分离。
And then we start the dissection subgaleal, and then, and up in this higher part of the flap, the dissection is between the galeal and the temporalis fascia laterally, and the pericranium medially, and that dissection is through the loose areolar tissue.

然而一旦显露出筋膜间脂肪垫的上缘
But once we reach the upper margin of the fat pad,

另外的即筋膜下-骨膜下入路(下图),则由Barrow中心所倡导,最早是由Spetzler教授提出的。
The other approach is subfascial-subpericranial,and the subfascial approach, that term was called a the Barrow, and one of the early papers on that was with Spetzler.

综上,颞上线外侧分五层,内侧为一层。
So, there're five layers lateral,one layer medial.

因此,在起始阶段,我们都是在帽状腱膜下分离的,随后,在皮瓣的上部,分离也始终在,外侧来说是帽状腱膜和颞肌筋膜之间,内侧来说是帽状腱膜和骨膜之间,即沿着帽状腱膜下疏松结缔组织这一层进行分离。
And then we start the dissection subgaleal, and then, and up in this higher part of the flap, the dissection is between the galeal and the temporalis fascia laterally, and the pericranium medially, and that dissection is through the loose areolar tissue.

另外的即筋膜下-骨膜下入路(下图),则由Barrow中心所倡导,最早是由Spetzler教授提出的。
The other approach is subfascial-subpericranial,and the subfascial approach, that term was called a the Barrow, and one of the early papers on that was with Spetzler.

综上,颞上线外侧分五层,内侧为一层。
So, there're five layers lateral,one layer medial.

因此,在起始阶段,我们都是在帽状腱膜下分离的,随后,在皮瓣的上部,分离也始终在,外侧来说是帽状腱膜和颞肌筋膜之间,内侧来说是帽状腱膜和骨膜之间,即沿着帽状腱膜下疏松结缔组织这一层进行分离。
And then we start the dissection subgaleal, and then, and up in this higher part of the flap, the dissection is between the galeal and the temporalis fascia laterally, and the pericranium medially, and that dissection is through the loose areolar tissue.

然而一旦显露出筋膜间脂肪垫的上缘
But once we reach the upper margin of the fat pad,

我们需离开位于外侧的颞肌筋膜的上方及内侧的骨膜上方疏松结缔组织层,切勿继续分离此层。
then, we wanna stay out of that loose areolar layer between the temporalis fascia and pericranium,not to open that layer.

而是经筋膜间或筋膜下分离颞上线外侧区域,
So we go interfascial or subfascial lateral to the superior temporal line,

然而一旦显露出筋膜间脂肪垫的上缘
But once we reach the upper margin of the fat pad,

我们需离开位于外侧的颞肌筋膜的上方及内侧的骨膜上方疏松结缔组织层,切勿继续分离此层。
then, we wanna stay out of that loose areolar layer between the temporalis fascia and pericranium,not to open that layer.

而是经筋膜间或筋膜下分离颞上线外侧区域,
So we go interfascial or subfascial lateral to the superior temporal line,

以及经骨膜下分离颞上线内侧区域。
and then, subpericranial medial to the line.

这就是外侧的五层,这是颞上线,这是内侧的单层。
Here we see the five layers lateral to the superior temporal line, the single pericranial layer medial.

切勿沿着位于外侧的颞肌筋膜、内侧的骨膜与浅表的帽状腱膜之间的疏松结缔组织层继续分离。
And we want to stay out of the loose areolar tissue between the temporal fascia and pericranium and the galea then more superficially.

另一个在培训班上出现的问题是,在做筋膜间入路时,多数人倾向于在此处作一切口,恰位于颞上线,以便游离颞肌。但若在颞上线处作此切口离断这些层次,那么极有可能将跨过此线经骨膜层以浅进入额肌的面神经颞支一起切断。因此,切勿在颞上线处作此纵向切口
Once we do the interfascial approach, I've noticed at courses,that there's a tendency of trainees to want to make a cut through this layer, right at the superior temporal line so you can free up the temporalis muscle. But if there's a cut through these layers at the line then commonly the nerves are cut before they cross the pericranium to reach the frontalis muscle. So that, instead of cutting vertically along the superior temporal line,

而是应该平行且位于颞肌筋膜浅层及筋膜间脂肪垫的深面。这才能保留颞肌筋膜浅层与骨膜层的延续性。
we wanna make a cut here that this cut is at level deep to the superficial layer of temporal fascia and the fat pad. And it leaves the superficial layer of temporal fascia connected to the pericranium.

切勿将这两者离断。
We don't want to separate those two layers.

因此这一切口需位于筋膜间脂肪层。切口的方向需与颅骨表面相平行。
We do an incision then deep to the interfascial fat pad to connect it. And that cut or the dissection is parallel to the outer surface of the skull.

因此,我们需确保颞肌筋膜浅层连接于额部的骨膜层。这里我们无需纵向切口也可以继续翻开皮瓣,只需将颞肌筋膜连同骨膜层一起剥离,方法是在颞上线处平行于颅骨表面进行分离。
So you wanna leave the superficial layer of fascia intact with the frontal pericranium. You don't wanna cut into this area, but still to turn the flap forward, you have to separate the temporal fascia and the attachment of the pericranium across the superior temporal line with a cut that is roughly paralell to the surface of the skull.

这就是分离后的情形。我们经筋膜间-骨膜下入路翻开了皮瓣,确保了颞肌筋膜浅层和额部骨膜层在颞上线内外的延续性。
So, here is what it looks like.We've elevated an interfascial-subpericranial flap maintaining the continuity of the temporal fascia and the pericranium across the superior temporal line.

接下来可以向任意方向翻开颞肌了。
And now we can fold the temporalis muscle in any direction that we want to.

现在来看具体的筋膜间-骨膜下入路的步骤。首先在颞上线外侧将帽状腱膜剥离于颞肌筋膜。
Now, this is the way we usually complete the interfascial-subpericranial approach. We start lateral to the superior temporal line elevating galea from temporal fascia.

至颞上线内侧,则将骨膜层连同帽状腱膜一起剥离于颅骨。即在形成上方皮瓣的时候,我们就已经避开了颞上线以内的疏松结缔组织层了。
And then medially to the superior temporal line, we leave the pericranium attached to the under surface of the galea. So we don't enter that loose areolar tissue medially in the upper part of the flap.

继续翻开皮瓣,在筋膜间脂肪垫的上缘,我们即在外侧采用筋膜间,在内侧继续骨膜下技术。
But as we elevate the flap then, here at the upper edge of the interfascial fat pad, we go interfascial lateral to the superior temporal line, and subpericranial medial.

由此确保避免进入有神经走行的疏松结缔组织层,其位于颞肌筋膜浅层与帽状腱膜之间。
So that we do not enter the loose areolar layer with the nerves in it, the loose areolar layer located between the superficial layer of temporal fascia and the galea.

再次强调培训班所见的错误,即作一切口以离断颞肌筋膜浅层与骨膜层,这会损伤走行于疏松结缔组织层内的面神经。
And, often at courses again I see individuals wanting to cut down and separate the superficial fascia from the pericranium, and it's in that layer here of loose areolar tissue that the nerves run.

因此,翻开皮瓣时,须保留该层次间的延续性,平行于颅骨切开,将颞肌筋膜浅层与骨膜层一起从颞上线处剥离。剥离后,方可继续翻开皮瓣。
So as you fold the flap forward, you want to maintain this continuity, and use a cut parallel to the surface of the skull, separating the superficial layer of temporal fascia and pericranium from the superior temporal line.Unless you separate that, you can't fold the flap forward.

该示意图上,错误的是颞肌筋膜浅层与骨膜层之间的纵向切口。正确的是在颞上线处沿着该层下方切开,从而保留这一层次的延续性。神经则位于这一层次的浅面。
And, so you don't wanna do a cut that separates superficial temporal fascia from pericranium. You want to under cut it along the line and maintain the continuity across these layers. The nerves are on the outer surface.

这就是经筋膜间-骨膜下入路最终形成的皮瓣。
And, here's the interfascial-subpericranial flap.

随后可将肌肉翻向任意方向。
And you can fold the muscle in any direction.

另一种做法是,在形成上部皮瓣时,颞上线以外部分经颞肌筋膜下分离,即在颞肌筋膜深层与颞肌之间进行。这就是所谓的筋膜下入路。
Now, the other approach is at the upper margin of the exposure laterally to go under the temporalis fascia between the temporalis fascia and the temporalis muscle.We call this subfascial approach.

而颞肌筋膜连同骨膜一起翻开,这是在翻开上部皮瓣时就开始的。
And then, we keep that temporalis fascia in continuity with the pericranium by elevating pericranium starting at the upper margin of the exposure.

这里,我们切开了颞肌筋膜深层,可见筋膜间脂肪垫位于颞肌筋膜浅层与深层之间。
And, here we've just opened the deep layer of temporal fascia to just take a look at the interfascial fat pad here between the superficial and deep layer of temporal fascia.

随后,上述两种入路中,(这里展示的是筋膜下入路)当颞肌筋膜连同骨膜层一起从颞上线处剥离后,都需要沿着颞上线预留一条肌筋膜条索,以便在关颅时缝合颞肌。
But then, in each of these approaches after we've elevated the temporalis fascia, here subfascial and the pericranium, maintaining their continuity across the superior temporal line, we then leave a musculofascial cuff along the line to use in closing the temporalis muscle laterally.

今天讨论上述内容的原因是由于大量文献仅针对外侧的颞肌部分,却忽略了保护面神经颞支的其他重要环节,即不管是筋膜下还是筋膜间入路,均需注意颞上线处神经完整性的保护,以及额部骨膜下分离技术的应用。
One reason that we describe this is that there are excellent descriptions of the lateral part of the approach over the temporalis muscle, but there's really minimal reflection of or discussion of spanserving the nerves,once you do the subfascial or interfascial approach,maintaining the continuity of the nerves across the superior temporal line and then on the outer surface of the pericranium.

再来看看颞浅动脉
The superficial temporal artery usually runs in the subcutaneous tissue superficial to the galea,

颞浅动脉走行于帽状腱膜以浅的皮下组织内,因此,通常作额颞瓣时无法显露该动脉的走行,除非在搭桥手术中的特意分离。
so that commonly we don't see that artery in a frontotemporal flap,unless we are going to harvest it for a bypass.

这是颞浅动脉的分叉部,可位于颧弓上下或同一水平。
We see the bifurcation, it can be above the zygomatic arch, at the level, or below.

若颞浅动脉的分叉部位于颧弓层面以上,面神经颞支通常向前行于颞浅动脉额支的下方。
But if the bifurcation is above the arch,usually the temporal branches pass forward below the frontal branch of the superficial temporal artery.

若颞浅动脉是低位分叉,面神经颞支则可能与颞浅动脉相缠绕或行于其深面。
But if the bifurcation is low, you may see the nerves intertwined or just deep to the branches of the superficial temporal artery.

扩大中颅窝入路 Extended middle fossa approach
下面笔者以“额颞断颧弓扩大中颅窝(Extended middle fossa approach)”手术入路为例,简要示范筋膜间骨膜下入路。
扩大中颅窝入路是翼点入路的改良术式,将额颞切口的耳前切口延长到颧弓以下1cm,切断颧弓,解除颧弓对颞叶底部暴露的影响。Kawase于1985年首次采用扩大颅中窝入路处理基底动脉中段动脉瘤,同时保留听力;并于1991年用于切除岩斜坡区脑膜瘤。术中切除Kawase三角骨质,向下达内听道和岩部颈内动脉,但保留了膝状神经节下方和内听道上外侧的骨质。
体位:患者仰卧,患侧肩下垫小枕,向对侧旋转30°~40°,头架固定,使 颧弓位于最高点。
切口:起自耳屏前方1cm,面神经颞支位于颞浅动脉前方约1cm处,故皮瓣切口应该尽量设计在颞浅动脉后方。皮瓣需要到达颧弓下缘(为了避免损伤面神经分支、腮腺导管等切口不应超过颧弓下缘1cm)。
切口应与骨窗的位置一致。如果骨窗靠近蝶骨大翼,切口弧形向前。如骨窗靠近颞骨鳞部,切口弧形向后。目前临床上多采用靠后的弧形切口,用来切除中颅底病变。向前的弧形切口多用在翼点入路或经侧裂-岛叶手术。

切口一般从额部开始,第一刀不要太深,切至额部骨膜上、颞肌筋膜浅层上方。

如果层次不容易分清,可用组织剪顺着帽状腱膜与骨膜之间的间隙进行分离。

耳屏前方的皮下筋膜层较复杂,需仔细分离,可以完美暴露出第1层脂肪垫中的颞浅动脉,再向前方顺着脂肪垫层继续分离少许距离。
颞浅动脉、面神经颞支位于第1层脂肪垫中,注意保护。

即使不需要搭桥,也应尽量保护好颞浅动脉STA主干。对于搭桥的病人,需要术前超声描记,从远端向近段游离,备用。

在额部 骨膜层下方钝性剥离,在颞部 将头皮与帽状腱膜层一起翻起,即沿着帽状腱膜下疏松结缔组织这一层进行分离。

采用钝性分离的方法,一直分离到额颧缝与耳屏的假想线附近,仔细辨认位于下方的第2层黄色脂肪垫。

沿上图中假想线,用手术刀在颞肌筋膜浅、深层之间分离出第二层脂肪垫,此时进入“筋膜间操作”。继续筋膜间分离,直至暴露出眶上外侧角(额骨颧突)。

这就是所谓的筋膜间-骨膜下入路。

下图示第2层脂肪垫,颞肌筋膜深层,颞肌筋膜浅层。

笔者更推荐下图中 使用组织剪 在颞肌筋膜浅、深层之间分离出第二层脂肪垫。
因为每个人第2层脂肪垫的厚度不一,用手术刀无法掌握深度,可能会损伤颞肌。

另有术者采用下图方法行筋膜间分离。利用的原理就是额部骨膜层 与 颞肌筋膜浅层 相互延续。

继续用剥离子 在骨膜下 钝性剥离额骨颧突,确保额部骨膜层和颞肌筋膜浅层在颞上线内外的延续性。

采用单极继续往下在筋膜间暴露出整个颧弓。

从颧弓上缘将颞肌筋膜浅层剥离

于颧弓上进行"V"形截骨术。为方便颧弓的复位重建,取下的颧弓应呈"V"形。游离的颧弓保留在附着于其下缘的咬肌上。

颧弓的切断范围不能太小,否则达不到满意的效果。前端到颧骨颞突的根部,以眶外侧缘为解剖标志,后端到颧骨颧突根部,以耳前结节为解剖标志。

在颞上线下方保留部分肌筋膜附着点,以备关颅时缝合颞肌之用。

沿额骨颧突紧贴 颞肌骨膜层 剥离颞肌。

此时,将颞肌及颧弓 经颧弓去除后的间隙向下翻转、牵拉。
颧弓切断 使 颞肌得以最大限度地向下牵拉,从而增加暴露的角度。

取下骨瓣后,可根据手术需要用磨钻或咬骨钳咬除颞骨鳞部,扩大骨窗范围,以便充分显露颞极和颞前部,甚至达中颅窝底。
将蝶骨嵴尽可能磨平达到与眶后壁平齐的程度,以充分显露外侧裂。

离断颧弓可以在无须牵拉颞叶的基础上,获得平齐中颅底的极佳显露。

![]()



