在The Rhoton Collection解剖视频中,Rhoton教授将颞骨解剖分为三部分进行讲解:1.中颅窝部分;2.后颅窝部分;3.乳突部分。本篇为第一部分(中颅窝部分)。由于笔者近日正在制作岩尖切除技术学习笔记,其中涉及的颞骨岩尖解剖部分,读者可以提前通过本篇文章进行复习。

本笔记按照常规的解剖顺序将原视频中部分段落重新编排,共128张图片。错误之处请批评指正。
颞骨解剖(中颅窝部分)
Navigating the Temporal Bone, Part 1
今天我们介绍颞骨相关的解剖入路,包括经中颅窝、后颅窝以及经乳突的入路。首先介绍经中颅窝的入路。
This lecture will review the approaches to the temporal bone as seen through the middle and posterior fossa and from laterally through the mastoid. We'll begin with the approaches through the middle fossa.
颞骨底面观。颞骨分为5部分,这是颞骨的鳞部(squamosal part [skwə'məʊsl] 下图)。其构成中颅窝底及外侧壁。
What part of temporal bone is this?forms floor of middle fossa, lateral wall of middle fossa? Anyone? Squamosal part.
后面的是乳突部(mastoid part ['mæstɔɪd] 下图)。
Posteriorly is mastoid part.
内侧为颞骨岩部(Petrous part ['petrəs] 下图)。
Petrous part, medially.

这是鼓室部 (tympanic [tɪm'pænɪk]),其构成了下颌窝的后壁,以及外耳道的前下缘。
Tympanic part here from the back wall of the condylar (mandibular) fossa, and the lower and anterior margin of the external canal.
这是下颌窝(mandibular fossa [mæn'dɪbjʊlə])
第5部分是茎突部(styloid part ['staɪlɔɪd])。
And the 5th part is the styloid part.

接下来,我们从后方观察颞骨,最前方这个压迹是三叉神经压迹(trigeminal despanssion)
So that, if we look from the back of this temporal bone, what is this despanssion?Trigeminal despanssion.

这是三叉神经突起 (trigeminal prominence)
and this is trigeminal prominence

这是内听道顶部的内听道压迹(meatal despanssion ['mi:tl])
This is meatal despanssion above the internal acoustic meatus. (meatus [mɪ'eɪtəs]道; 口; 管)
随后是 弓状隆起 (arcuate eminence )
and then... arcuate eminence, ['a:kjʊɪt] [ˈemɪnəns]
这块区域是 鼓室盖(tegment ['teɡment])。
and this area is... tegment.

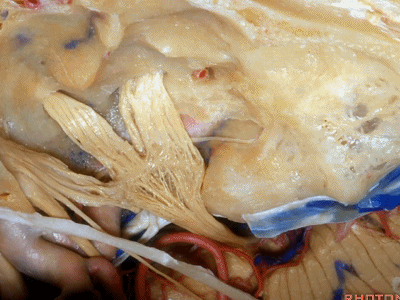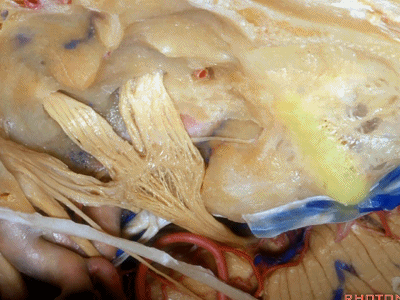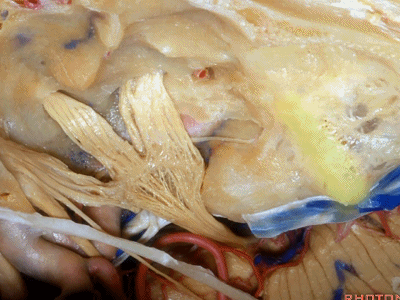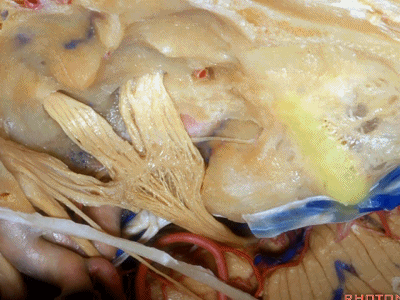
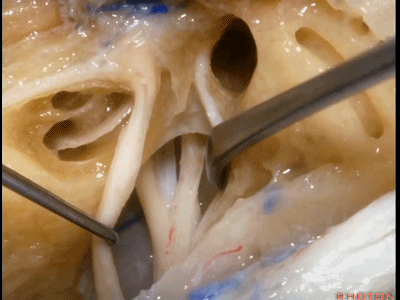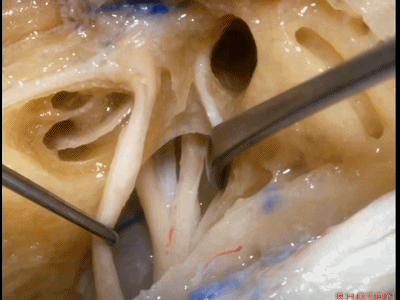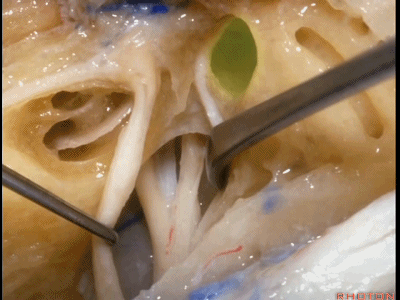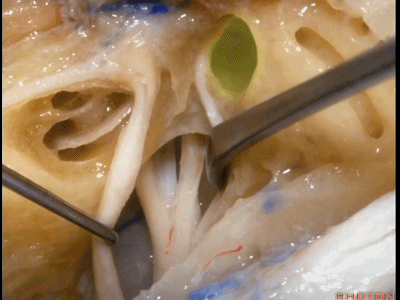
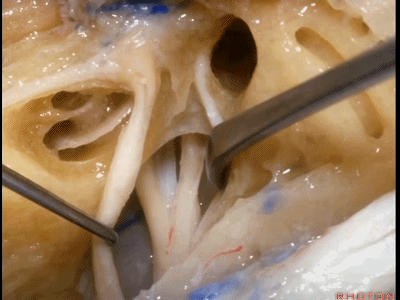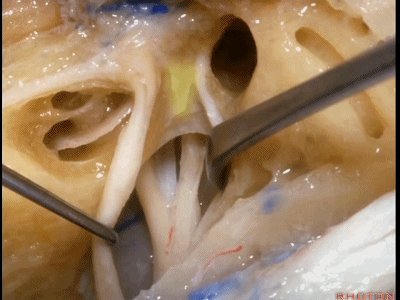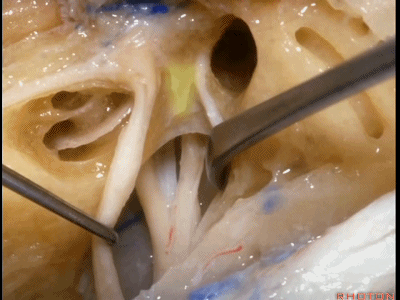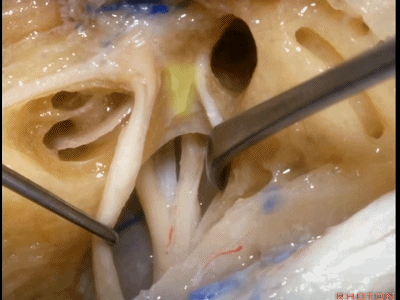
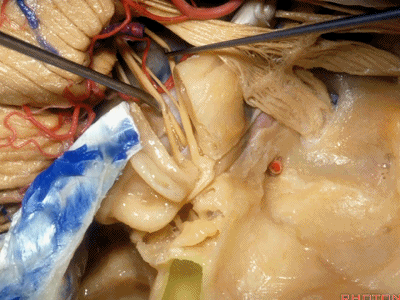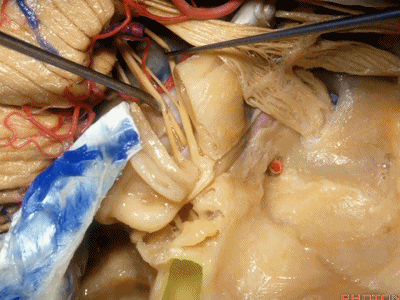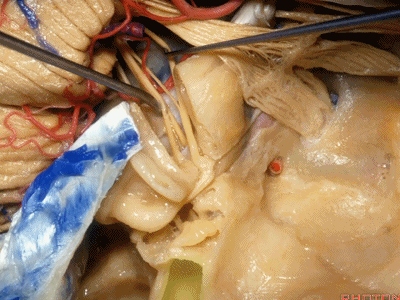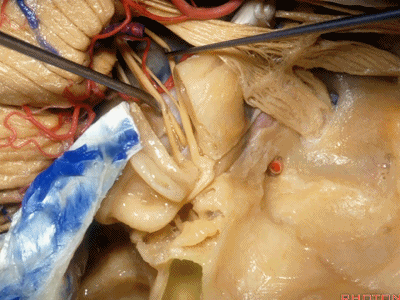
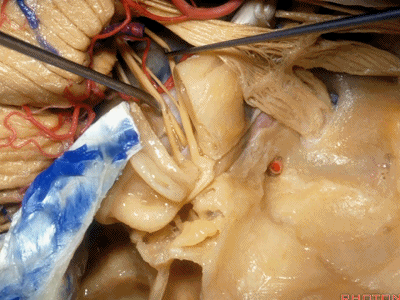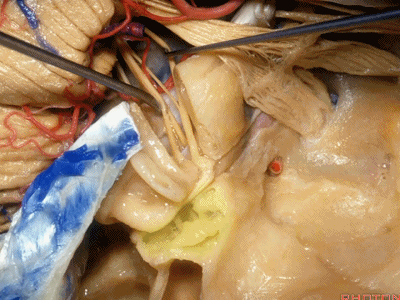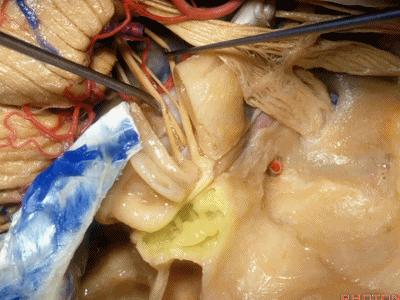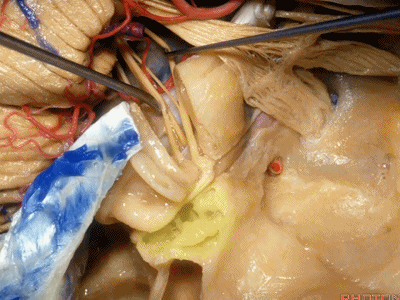
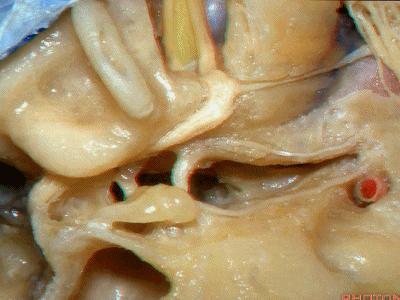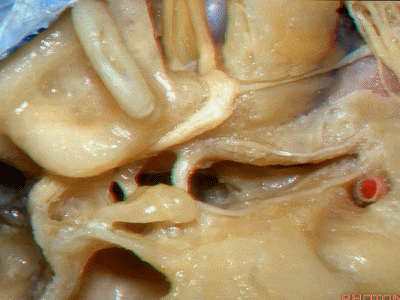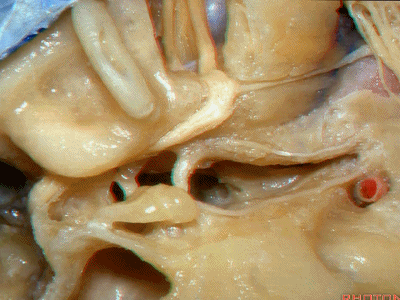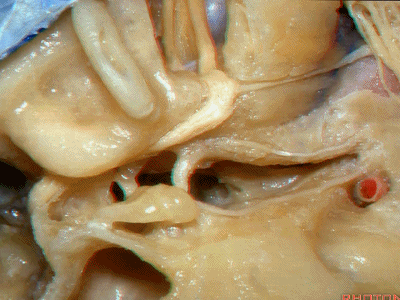
这是中颅窝底。我们将硬膜剥除至岩骨嵴( petrous ridge 下图)。
We're looking at floor of middle fossa. We peel the dura back to the petrous ridge.
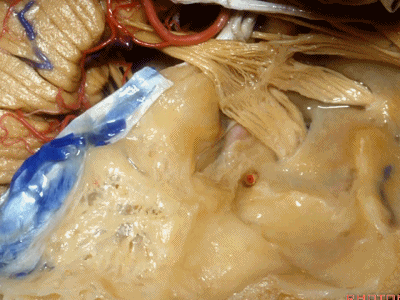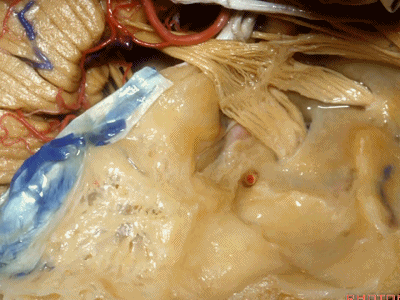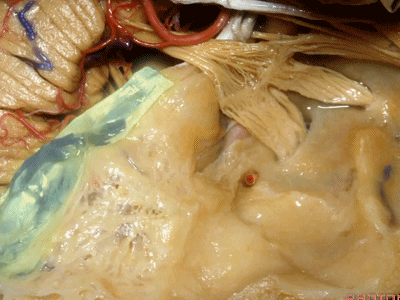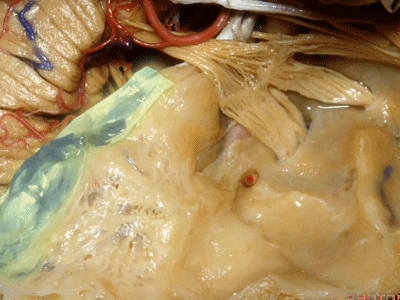
从内向外,依次有三叉神经压迹 (trigeminal imspanssion)
So, as we look at middle fossa,medially, you have trigeminal imspanssion
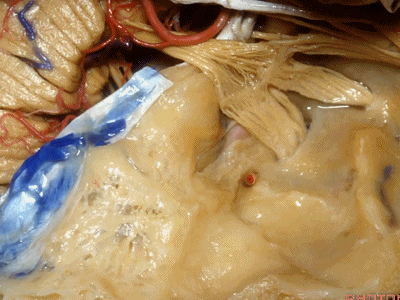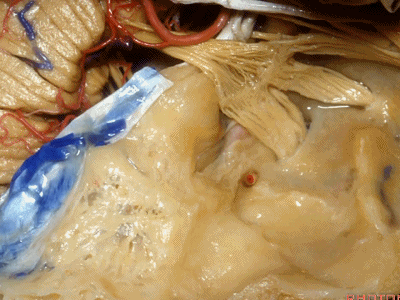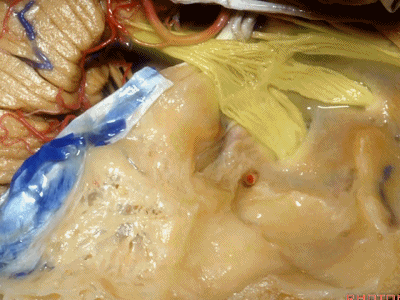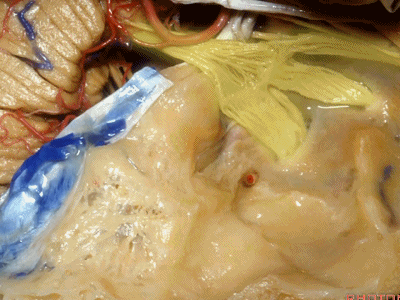
随后是下图的三叉神经突起(trigeminal prominence)
and then there rises up to a prominence that we call a trigeminal prominence
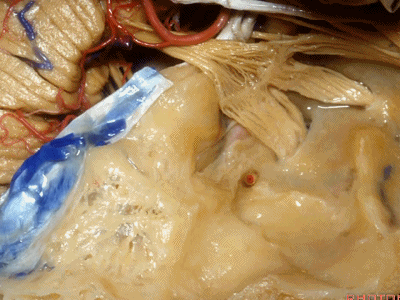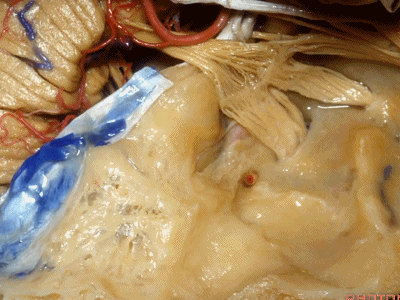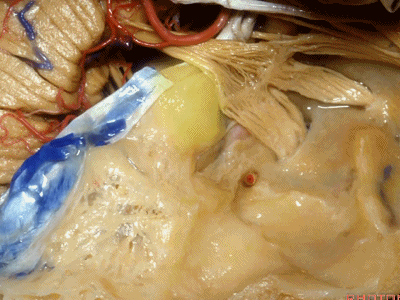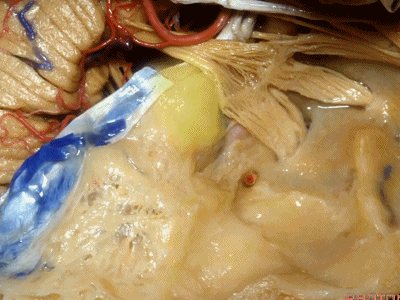
随后再次凹陷,恰位于内听道的上方,故称之为内听道压迹(meatus despanssion)。
and then it sinks down again into an imspanssion above the internal acoustic meatus. We call this the meatus despanssion

此后再次凸出形成弓状隆起(arcuate eminence)
And then it rises up back the arcuate eminence.

弓状隆起的外侧是一层菲薄的鼓室盖(tegment)。
And lateral to the arcuate eminence is this paper-thin bone,that we call it tegment.
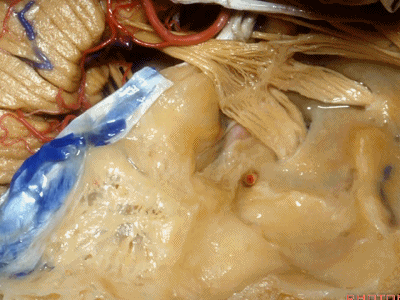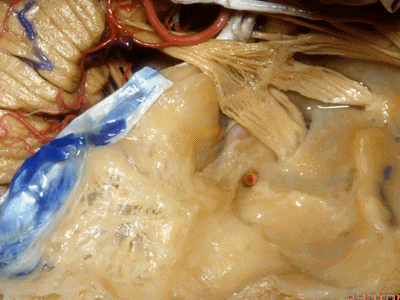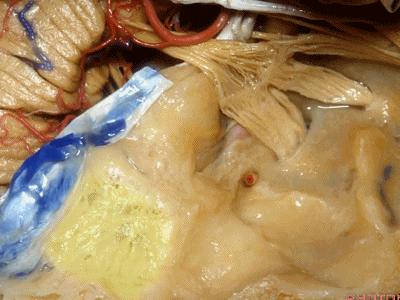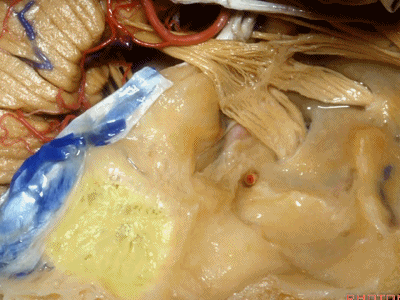
鼓室盖 构成外耳道、鼓室、乳突窦的顶壁。
下图示外耳道顶壁(external canal)
And it roofs the external canal, the tympanic cavity, and the mastoid antrum.

下图示鼓室顶壁(tympanic cavity)
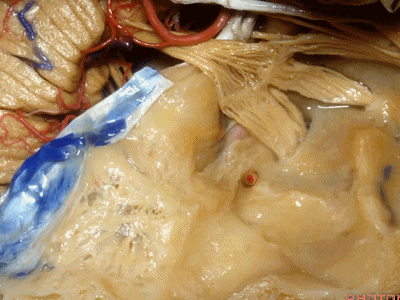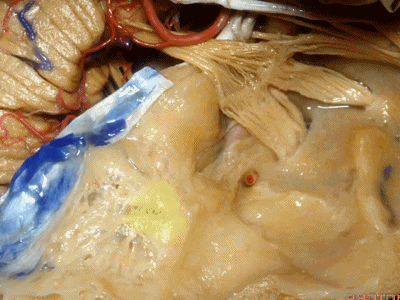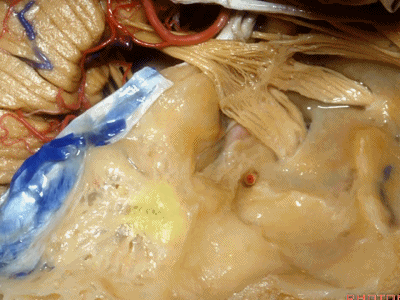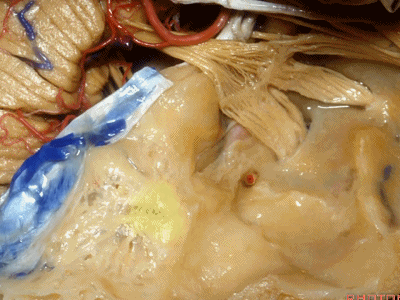
下图示乳突窦的顶壁(the mastoid antrum ['æntrəm] 窦)
外耳道、鼓室、乳突窦这些结构都位于这层薄薄的鼓室盖下方,该处为自发性或乳突术后脑脊液漏的最好发部位。
All sit below this paper-thin bone that is the most common site of spontaneous or postmastoid leaks into the middle ear.
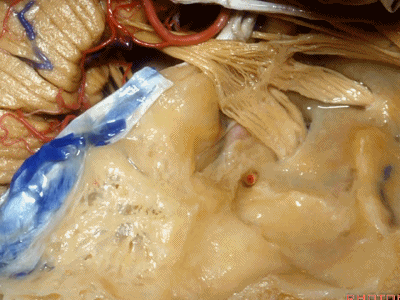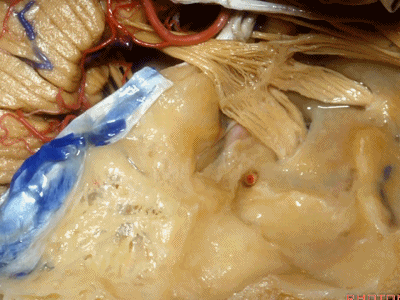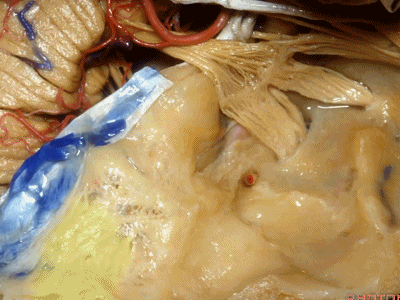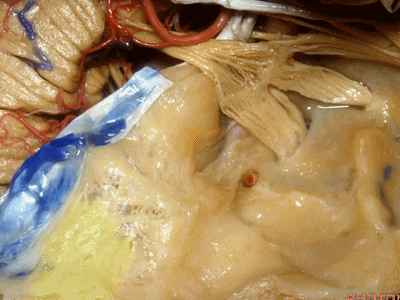
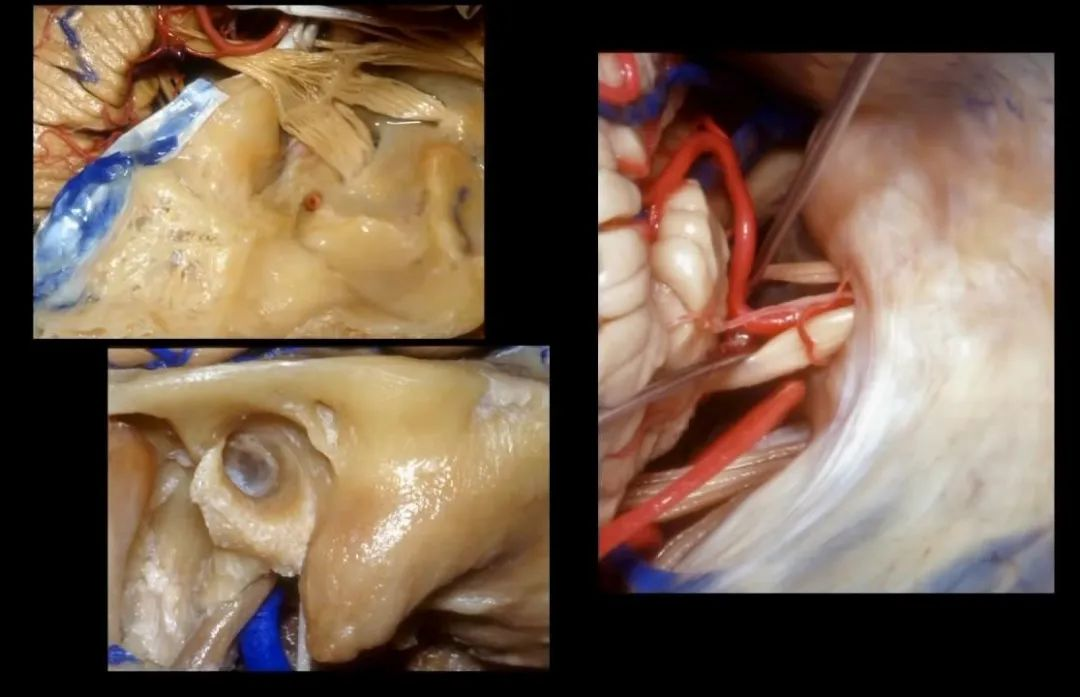
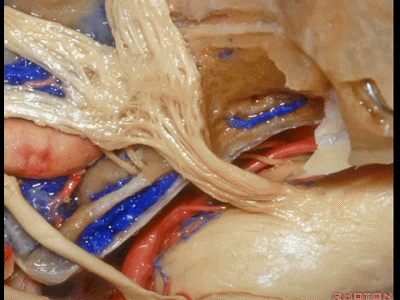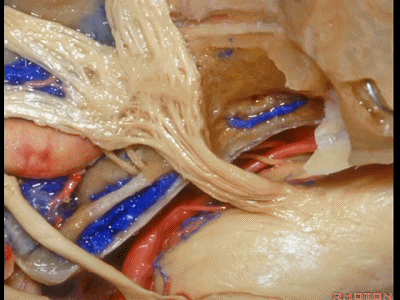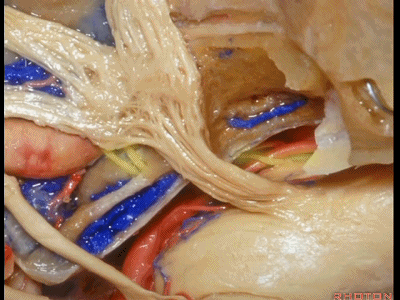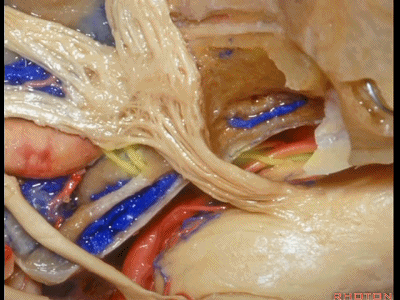
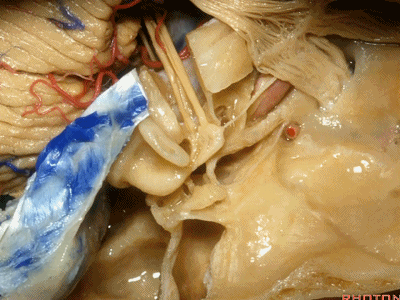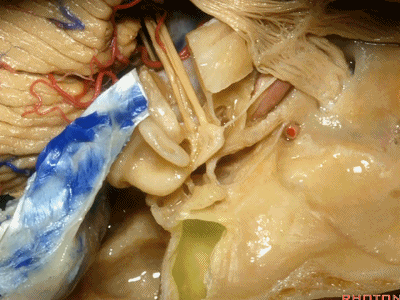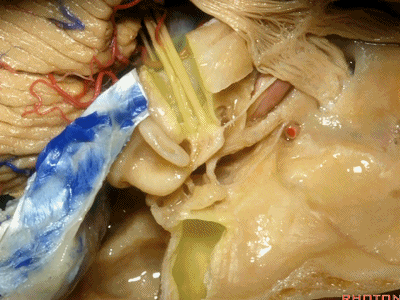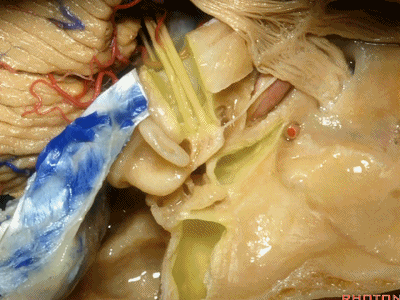
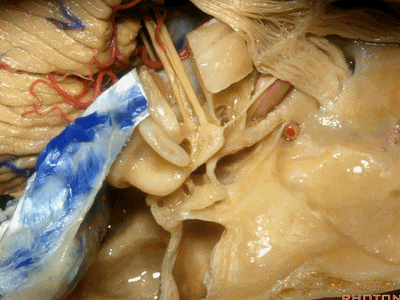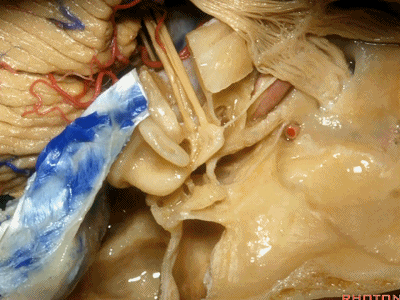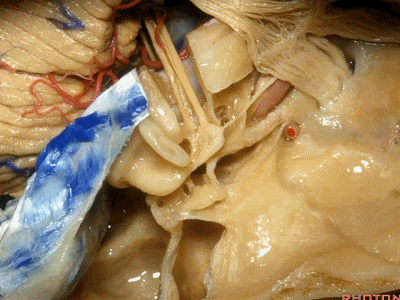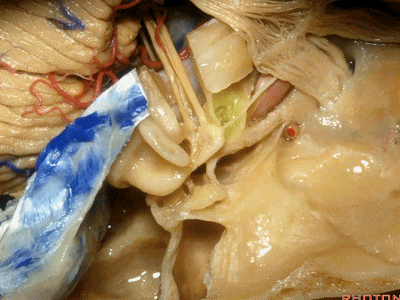
此处为岩浅大神经(GSPN greater superficial petrosal nerve)。其下方为 颈内动脉(carotid artery)。通常情况下,三叉神经外侧的颈内动脉管壁有骨质覆盖,然而在大约15%的病例中,位于三叉神经外侧、颈内动脉上方的骨质会呈开裂状。
And here we see the...greater petrosal nerve, and under it is the...carotid artery. Usually the carotid lateral to the trigeminal nerve is covered by bone,but in about 15 percent of cases, there'll be a dehiscent bone over the carotid artery lateral to the trigeminal nerve.
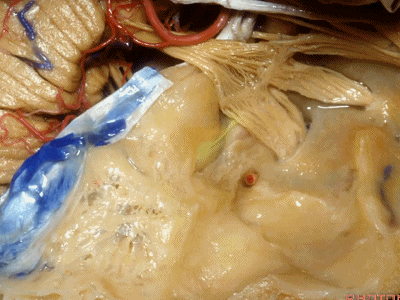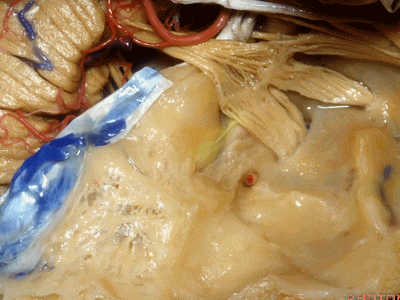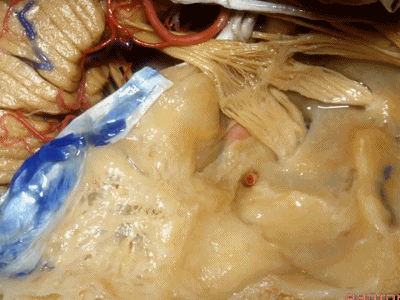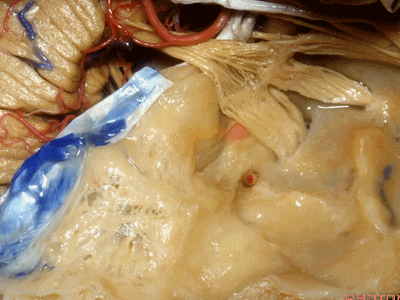
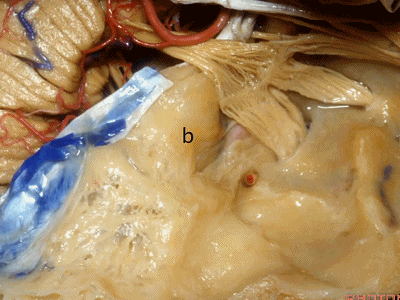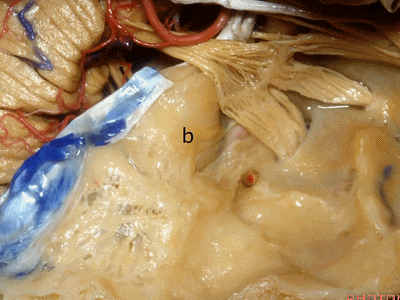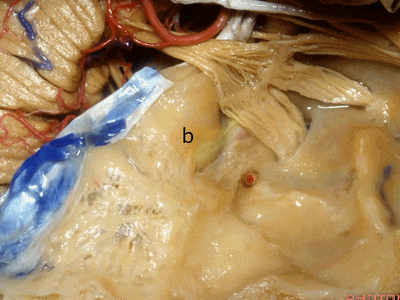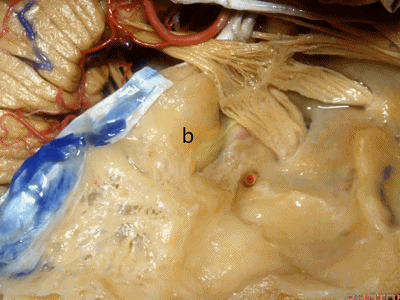
耳蜗(cochlea)在下图的b点
Where is the cochlea...everyone? At b here,

耳蜗在岩大神经离开膝状神经节(geniculate ganglion)的后方。
Cochlea is in back of the greater petrosal nerve just distal to where it exits the geniculate ganglion([dʒə'nɪkjʊlɪt] ['ɡæŋɡlɪrn]).
实际手术中,我们常抬起硬膜,从上往下看,这是岩浅大神经(greater petrous nerve)
So at surgery we're usually elevating this dura and looking at it up side down. And, there we see the greater petrous nerve
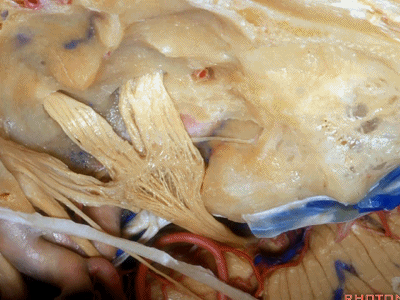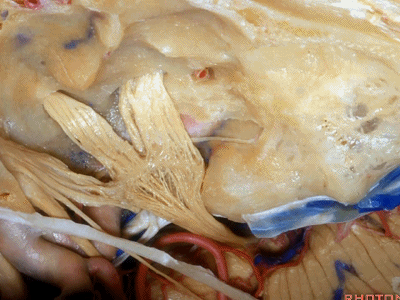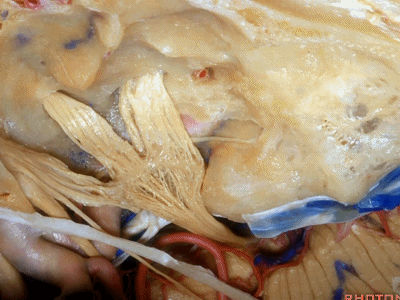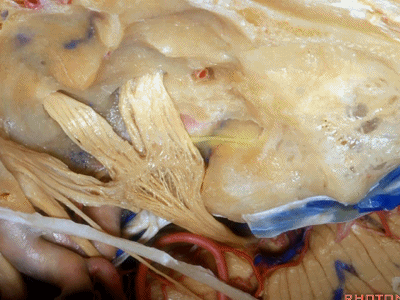
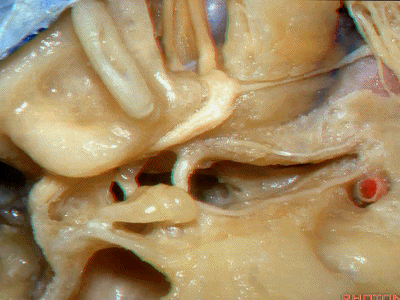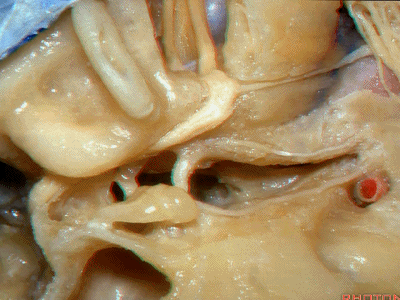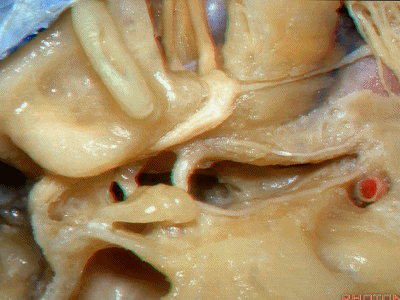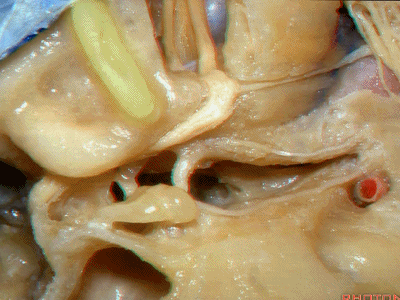
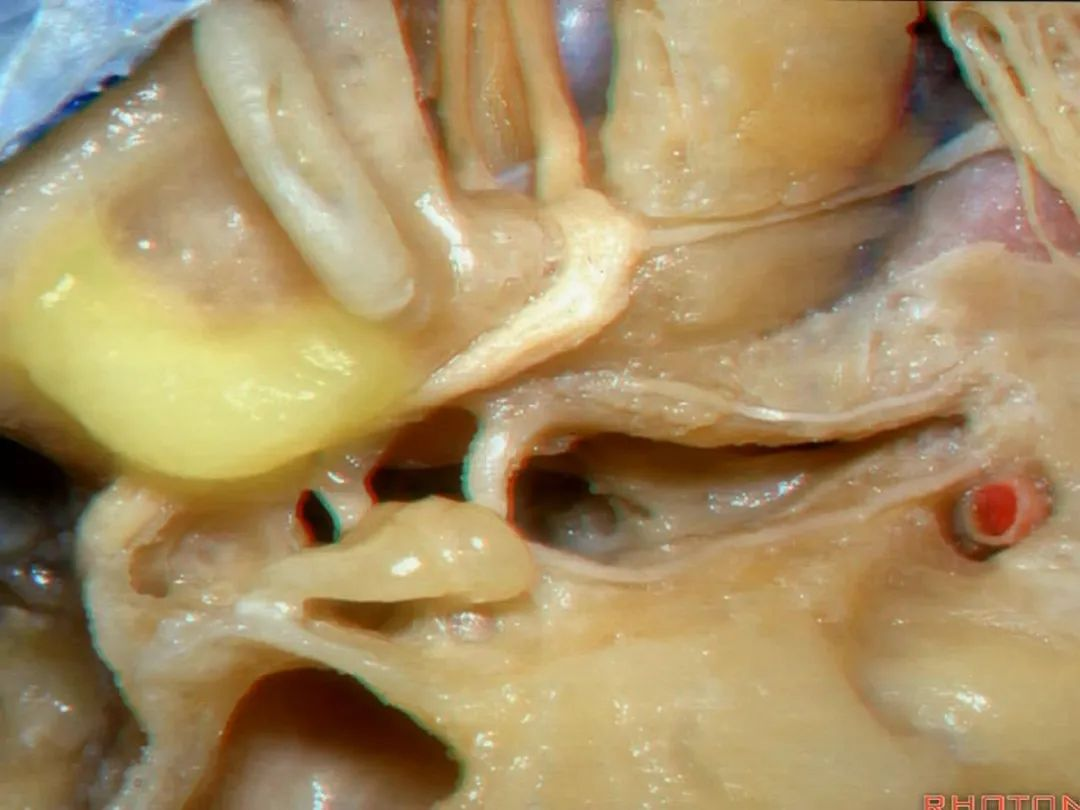
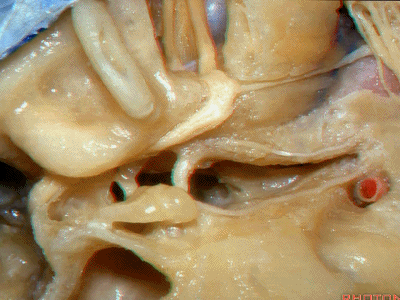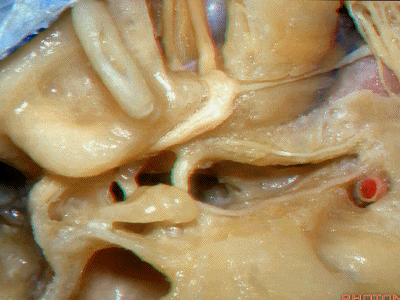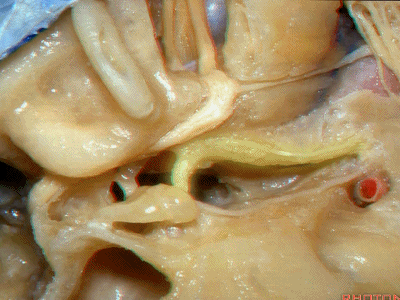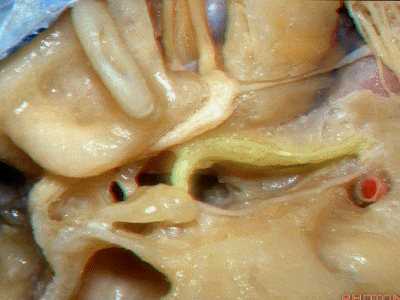
Kawase三角(Kawase's triangle 下图)

三叉神经压迹(trigeminal despanssion)

三叉神经突起(trigeminal prominence)
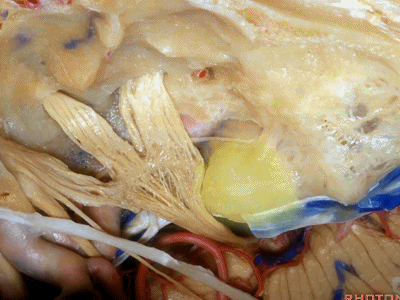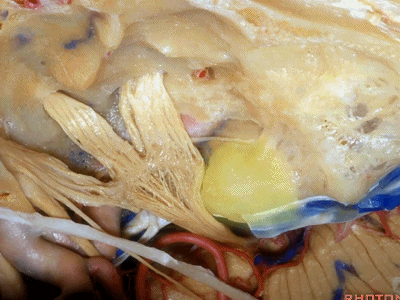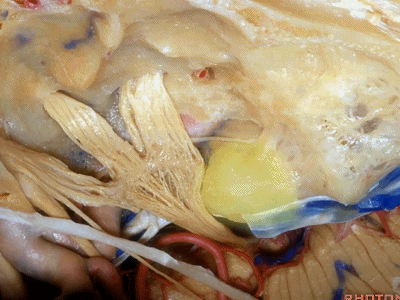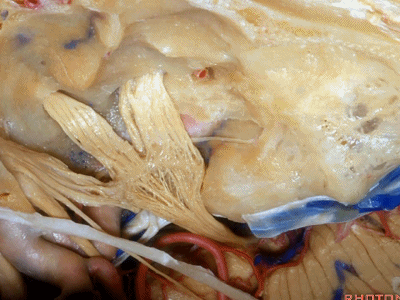
内听道压迹(meatal despanssion)

弓状隆起(arcuate eminence)
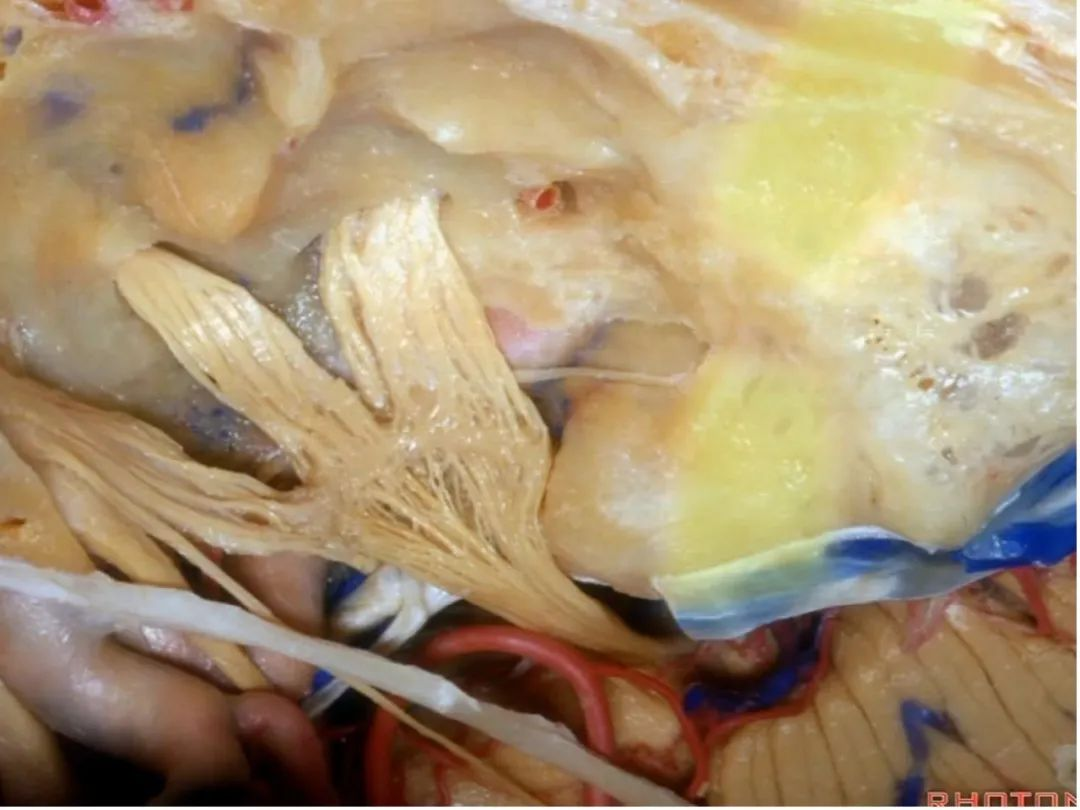
这是外耳道(external canal)

外耳道方向与内听道几乎成一直线。
But if you look at the external canal here,at side down it, that's gonna be almost directly in a line with the internal acoustic meatus.
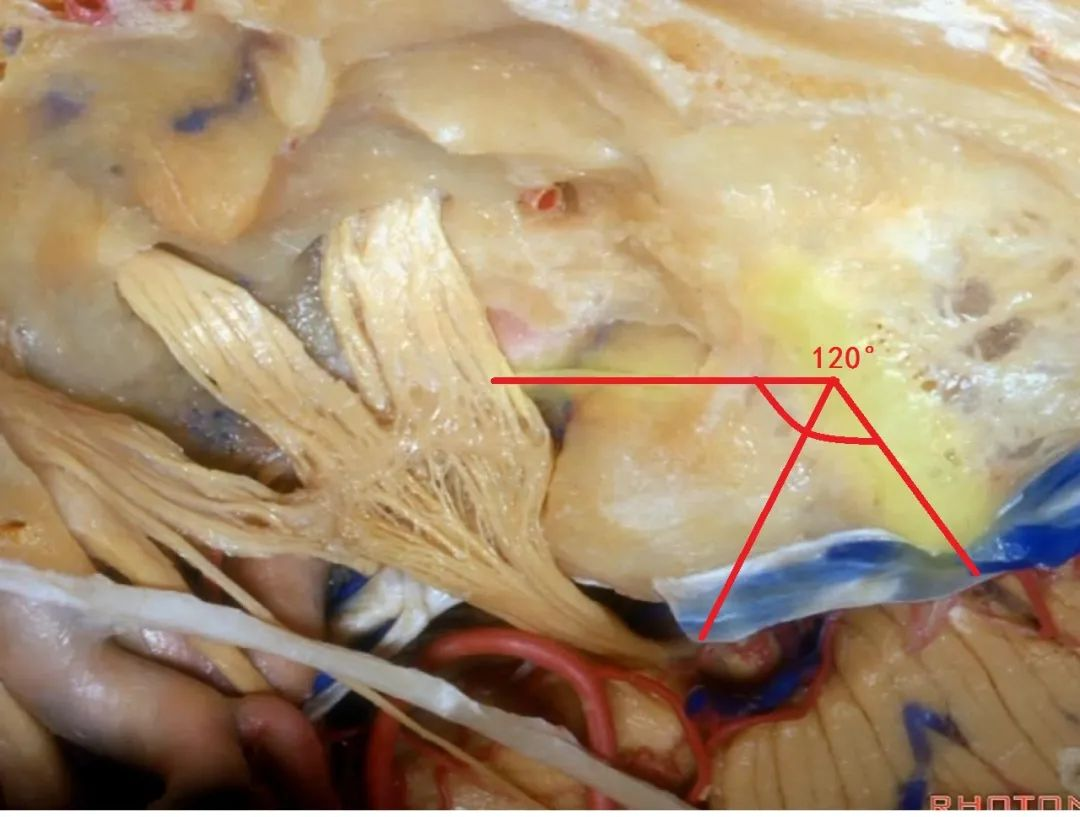
还有另一种方法来定位内听道,就是以岩浅大神经和弓状隆起之间作一夹角,这一夹角约120°,随后作一角平分线。
The other way of deciding how to drill out the internal acoustic meatus is to take and create an angle between the greater petrous and the... arcuate eminence.That angle is usually about 120 degrees.And then you bisect that angle,
随后,岩骨嵴与该平分线的交点,就是开始磨骨的部位。
and you lock the retractor on top of the petrous ridge, and you begin drilling here,
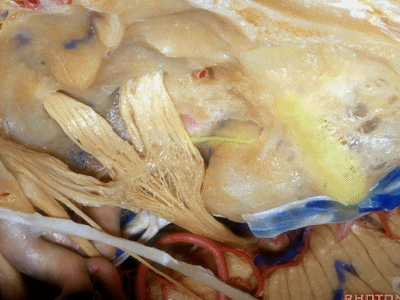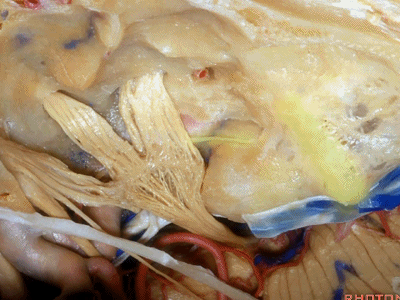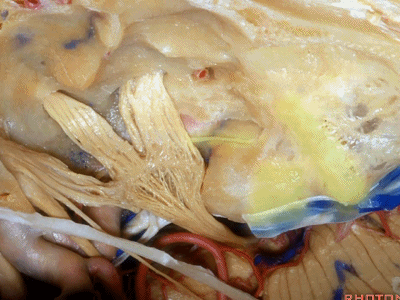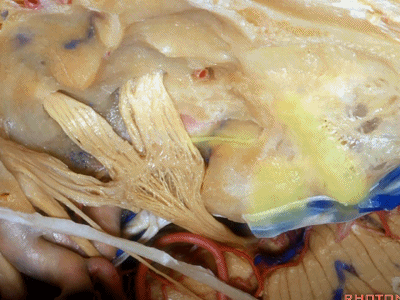
现在我们就从内听道口(porus ['pɒrəs])磨向底部(fundus ['fʌndəs]基底)。神经位于该处以下很深的地方,但周围管腔的空间也很大,而越靠近内听道底,神经越表浅,磨骨时也须万分谨慎。
So we drill now from porus to fundus. above the porus which is deep,but wide with lots of room around the nerves to the fundus where the nerve is going to be very superficial, but the drilling is going to be very tight.
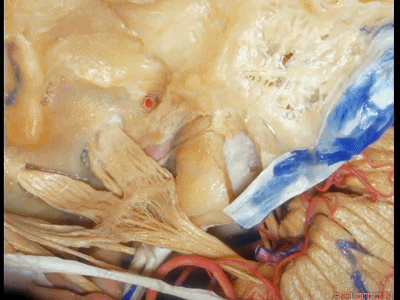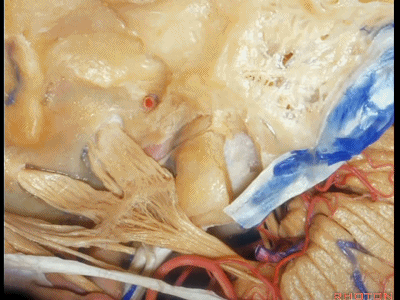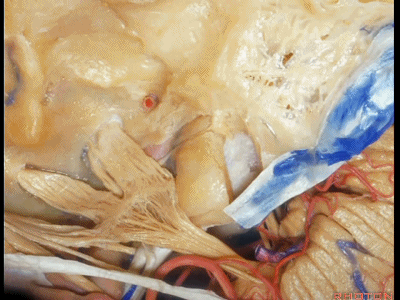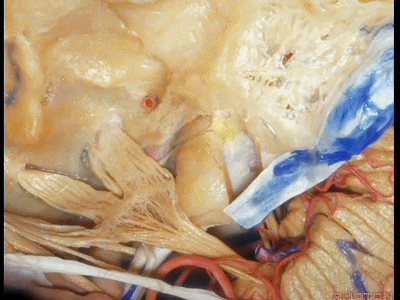
因此,经中颅窝的手术入路,一般可有三种选择:
一是经岩尖(岩前入路)
二是打开内听道
三是磨除迷路的扩大中颅窝入路
So as coming through the middle fossa, you can drill out three approaches. one through the petrous apex, one to the internal acoustic means,the other drill out the labyrinth and do an extended middle fossa approach.
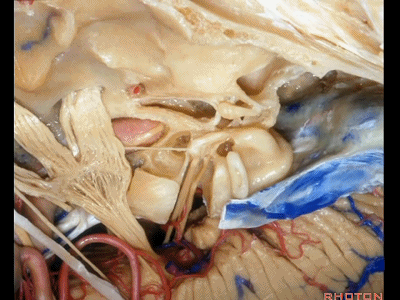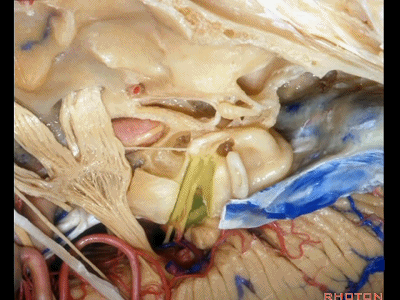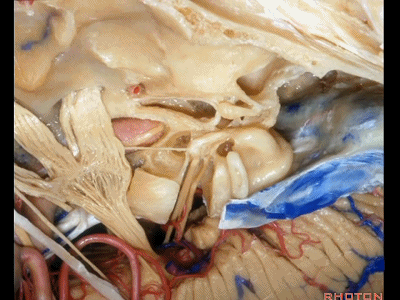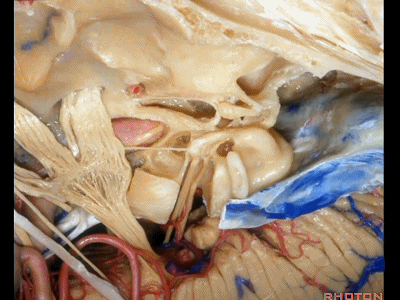
接下来我们看到的就是,在内听道内侧进行的前岩骨切除术(岩前入路,Kawase入路)(anterior petrosectomy approach)
So, here we've now drilled out medial to the meatus, the anterior petrosectomy approach

Kawase入路一直可暴露至斜坡和岩下窦。
down to the clivus and the inferior petrosal sinus.
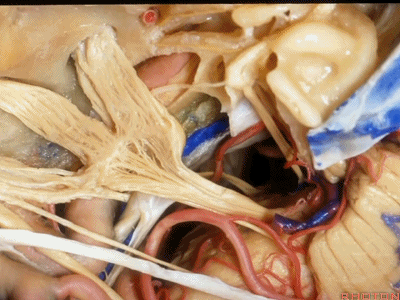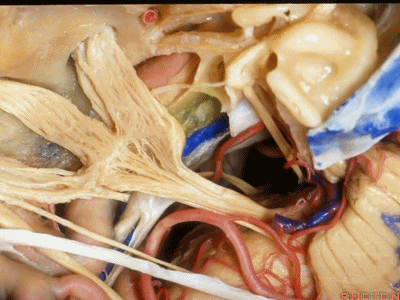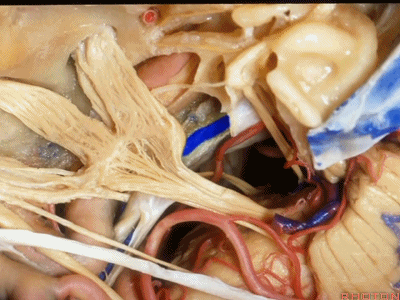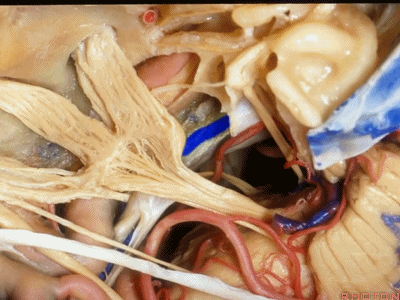
这里是小脑前下动脉(AICA)、内侧的外展神经,都可由此岩前入路暴露。
We see the AICA,the 6th nerve medially,in the anterior petrosectomy approach.
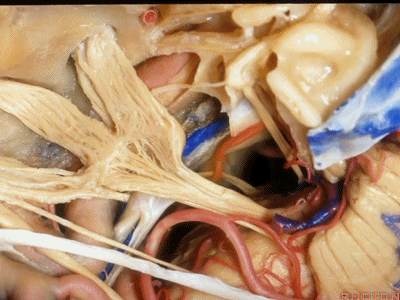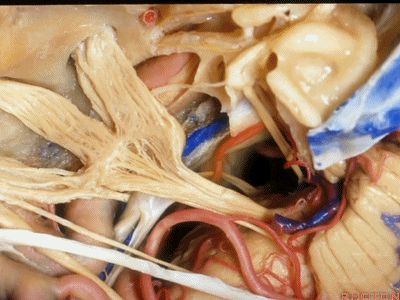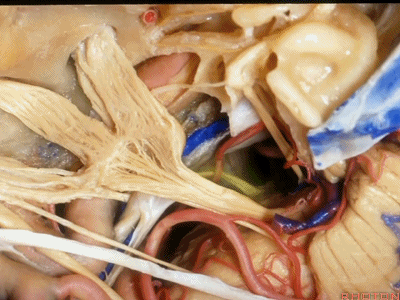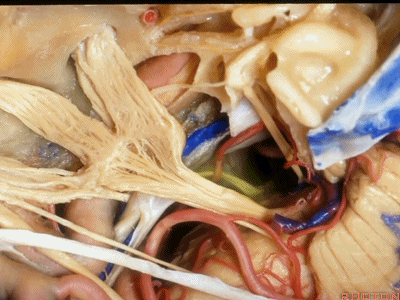
这根神经是外展神经(abducens nerve)[æb'dju:sənz]
This is what nerve...passes under Gruber's ligament? That's 6th
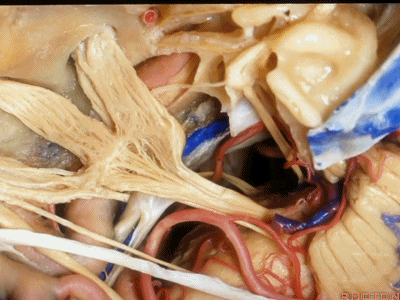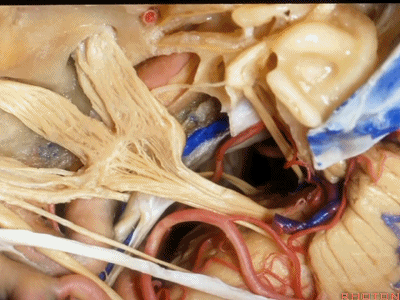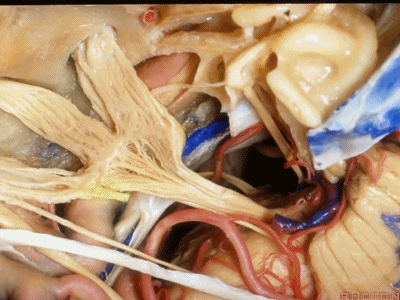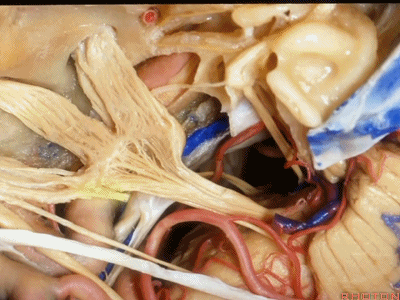
外展神经从Gruber韧带(蝶岩韧带)下方穿行。
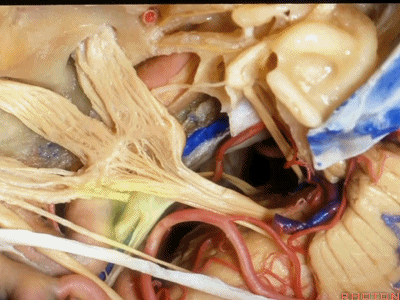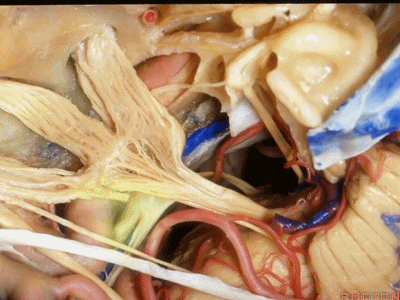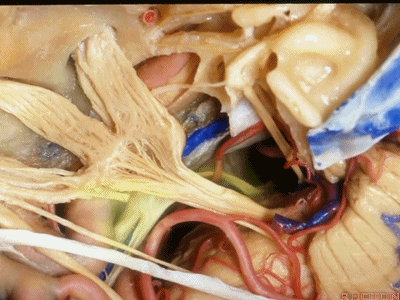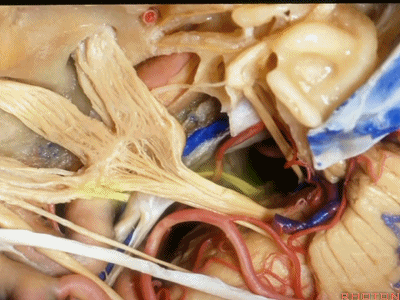
这是滑车神经( trochlear nerve) ['trɒklɪə]

动眼神经(oculomotor nerve) [ˌɒkjʊlə'moʊtə]

动眼神经上方是后交通动脉
running above it...PCom
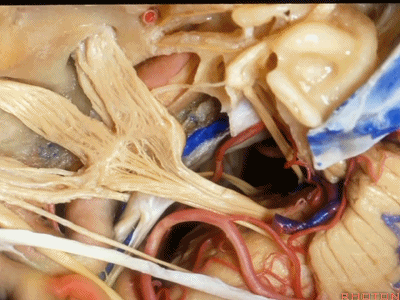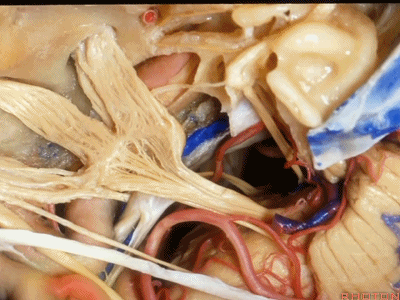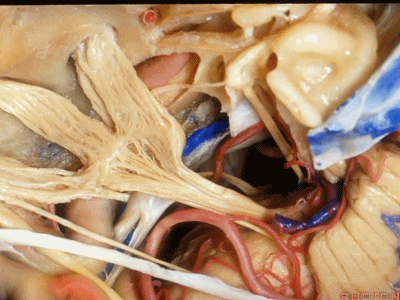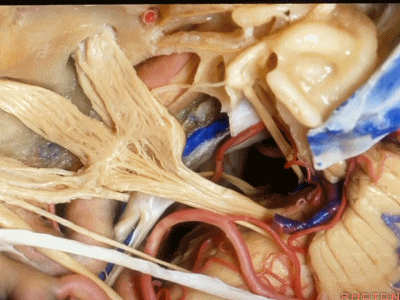
小脑上动脉(superior cerebellar artery)
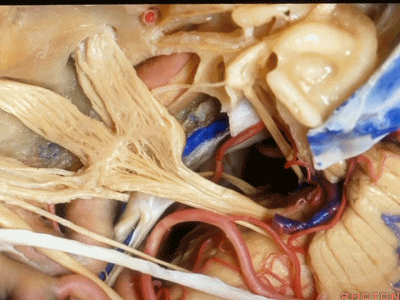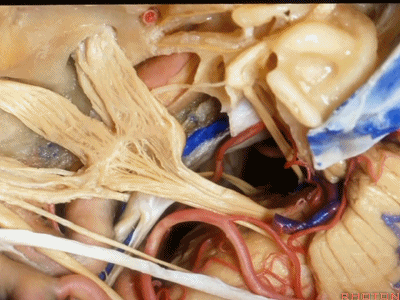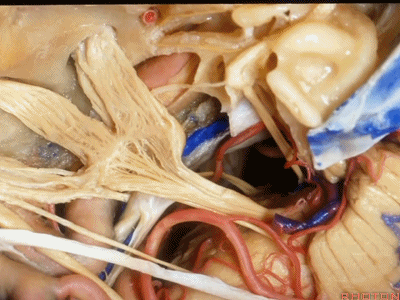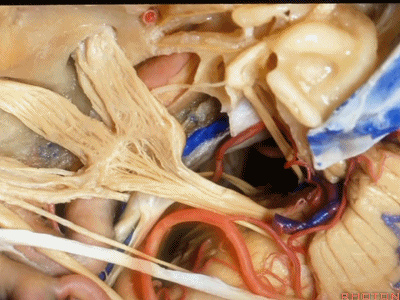
小脑前下动脉 AICA
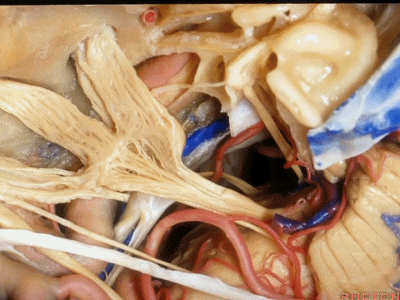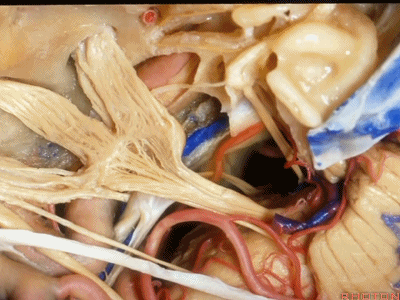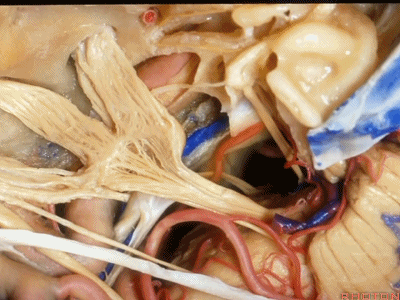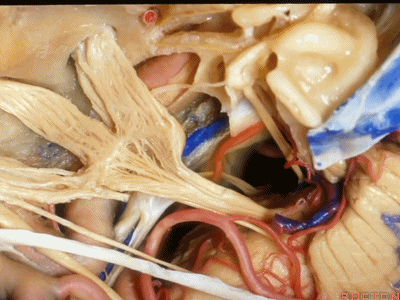
现在,我们可以经眶颧开颅、经中颅底 行 内听道入路,或者行岩前入路。
我们可做颞部开颅,以颧弓后根为中点。
Now, you can expose this area from middle fossa through an OZ for just going to the middle fossa approach to the meatus, or the anterior petrosectomy.
We can do a temporal craniotomy, centered above the posterior root of the zygoma.
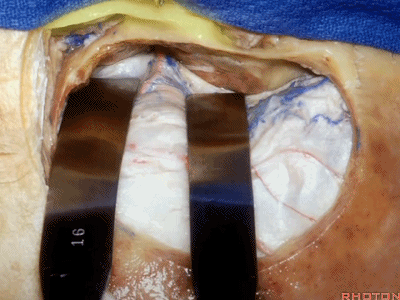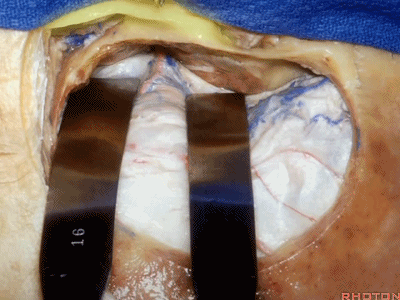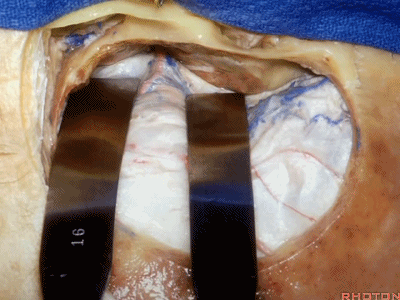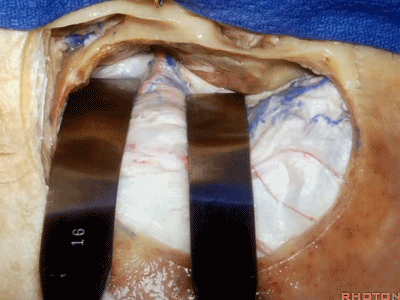
抬起硬膜后,我们可看到岩浅大神经。
We elevate the dura and here we see...greater petrosal.
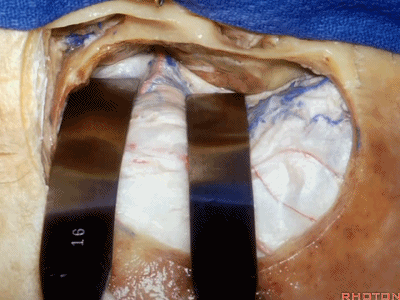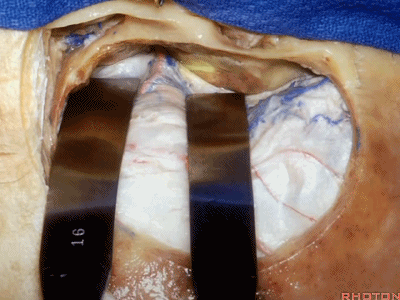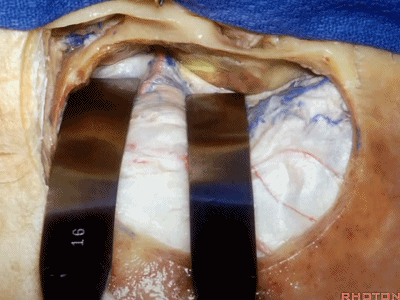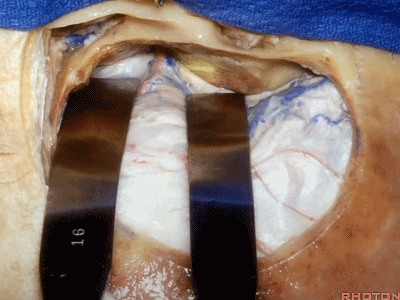
当进行海绵窦区解剖三角的暴露时,我们是将硬膜向后剥离的。但如果在显露岩浅大神经时也这么从前向后剥离硬膜,就容易进入下面而撕脱神经。
Now when we're exposing the triangles in the cavernous sinus, we peel this dura backwards.But if you're peeling from front to back to the greater petrosal, it's easy to get under the nerve and avulse it.
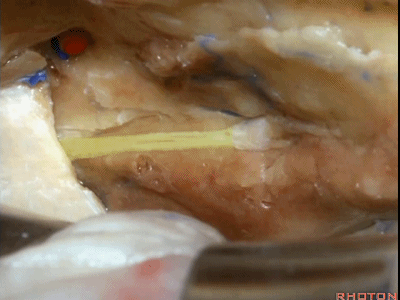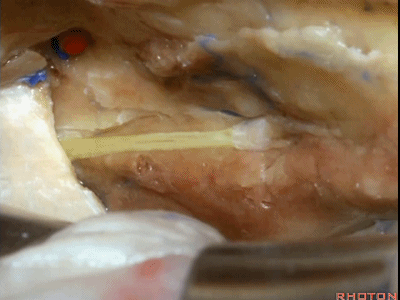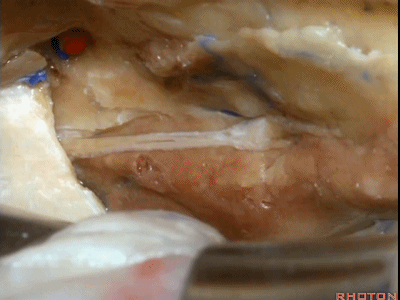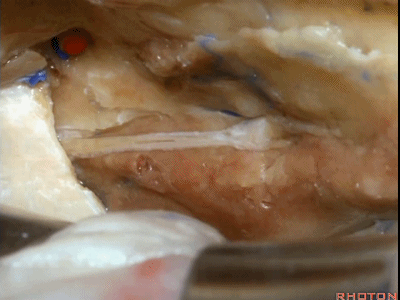
因此,在显露这一区域及岩浅大神经时,应该从后方开始,向前掀起硬膜。通常都能将硬膜从岩浅大神经剥离开。
So when we want to expose this area and the greater petrosal,we get in posteriorly.We elevate this dura forward,and usually that dura peels up off of the greater petrosal nerve.

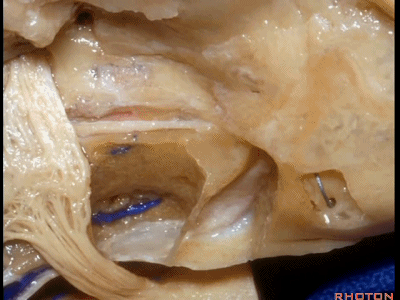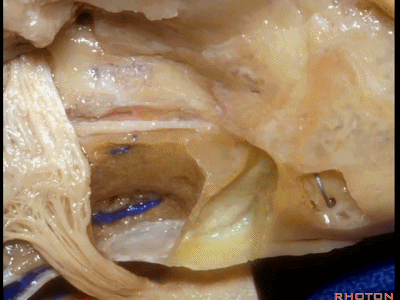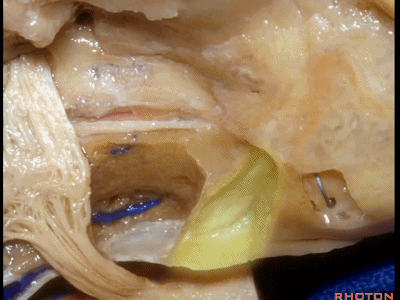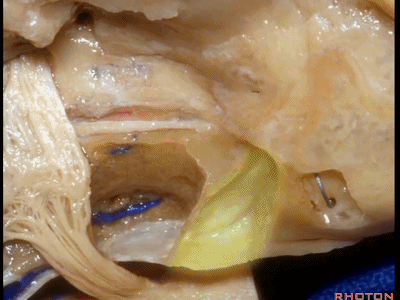
还有约16%的病例,在三叉神经侧方掀开硬膜即可发现膝状神经节(GG, geniculate ganglion)裸露在中颅底。
And in about 16 percent of cases,lateral to the trigeminal,we see the...geniculate ganglion exposed under the dura in the floor of middle fossa.
geniculate [dʒə'nɪkjʊlɪt] 膝状弯曲的

而且不仅仅是膝状神经节,有时可见部分面神经迷路段,鼓室段,也直接显露在硬膜下方,因此,这个区域的操作须非常小心。
下图示 面神经迷路段(labyrinthine segment)
And not only as the ganglion exposed but you see some of the...what segment? Labyrinthine [ˌlæbə'rɪnθɪn], and here...tympanic segment exposed under the dura.So you wanna be very careful in this area.
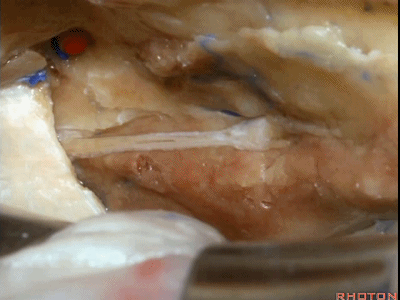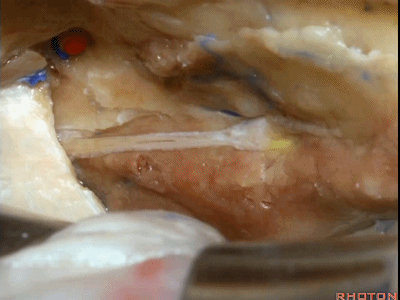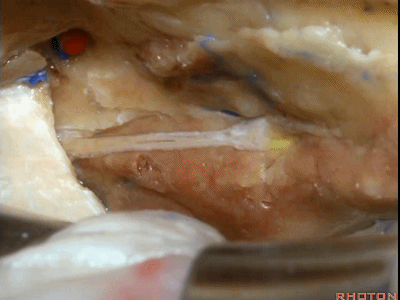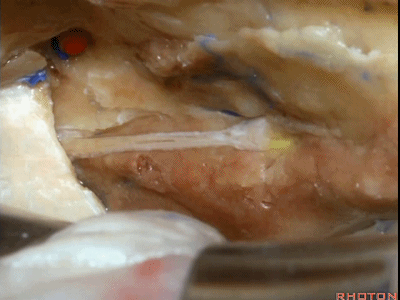
下图示 面神经鼓室段(tympanic segment) [tɪm'pænɪk]
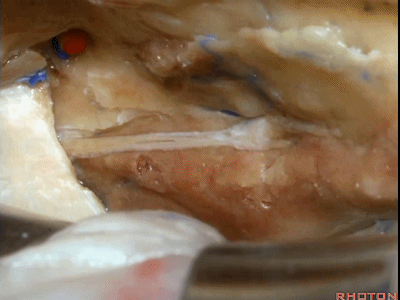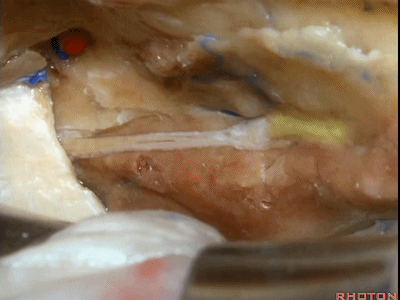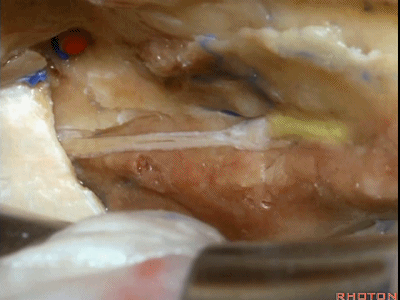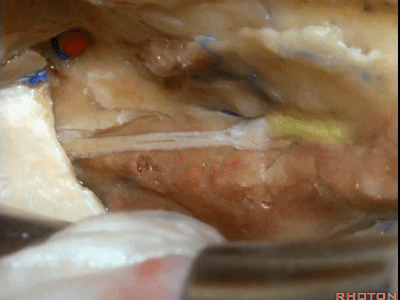
当我们仅需行内听道入路时,常可保留脑膜中动脉(下图),此动脉对面神经也有一定供血。如果需行岩前入路,这条动脉则常需牺牲掉。
If you're going to do just an approach to the internal acoustic meatus, we can often save the middle meningeal artery, which does sends some blood supply to the facial nerve. But for drilling out the anterior petrosectomy, we usually need to sacrifice the middle meningeal artery.
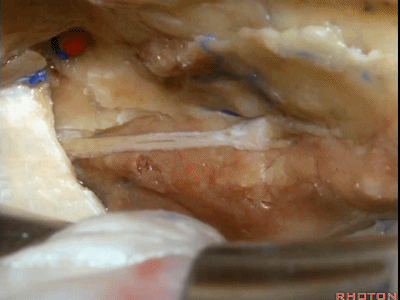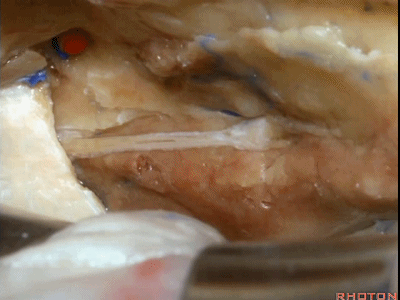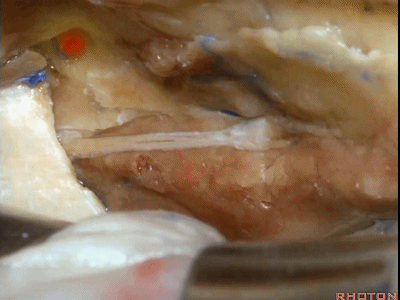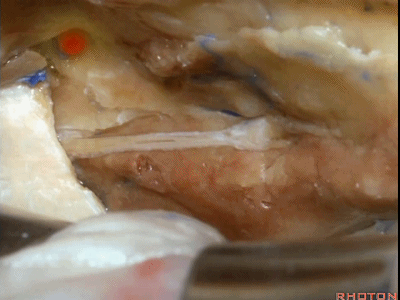
综上,该区域最常用的两种入路,一种是经中颅窝暴露内听道
The two most common approaches that we take to this area are either...the approach to the internal acoustic meatus,
内听道可根据岩浅大神经和弓状隆起夹角间的平分线进行定位。
bisecting this angel between the greater petrosal and arcuate eminence that overlies the superior canal.
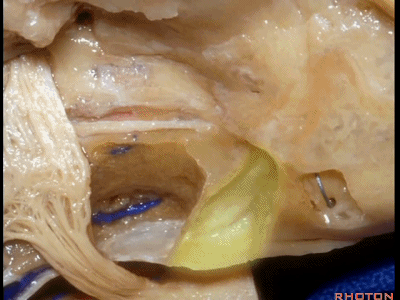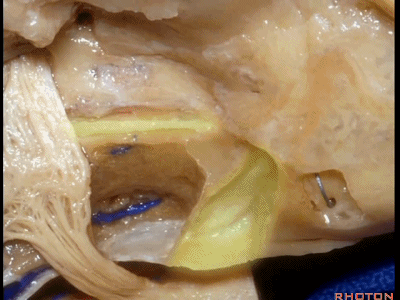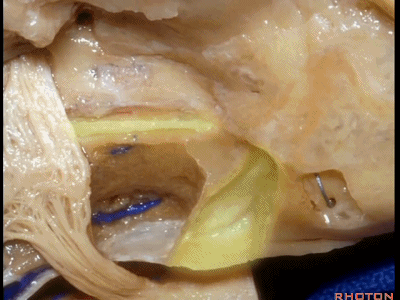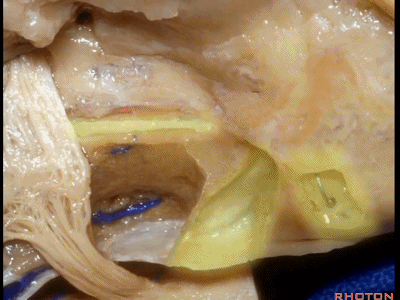
该入路从岩骨嵴的内听道口开始,向内听道底磨除内听道。
And we begin drilling at the petrous ridge and work toward the fundus.

另一种是岩前入路,在三叉神经内侧磨除岩尖,向下可至斜坡侧方。
For the anterior petrosectomy, we drill medially under the trigeminal nerve, down to the side of the clivus.
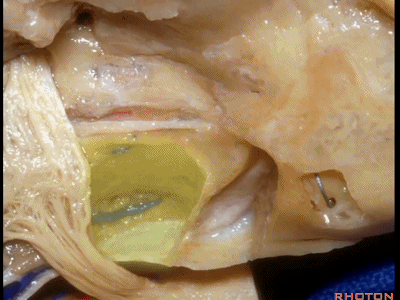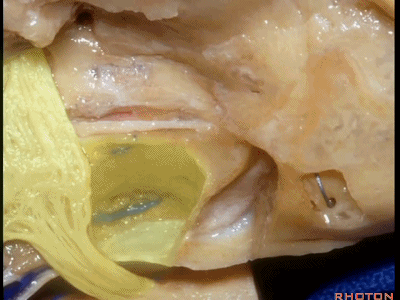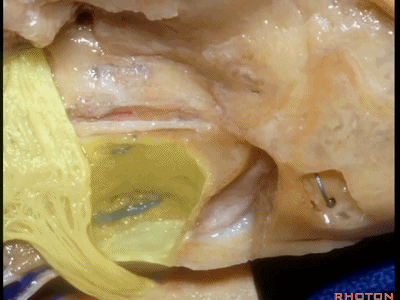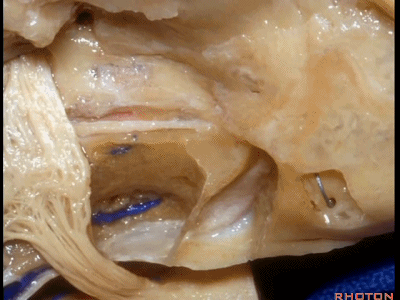
下图示斜坡侧方。
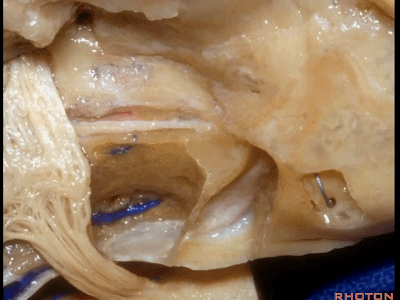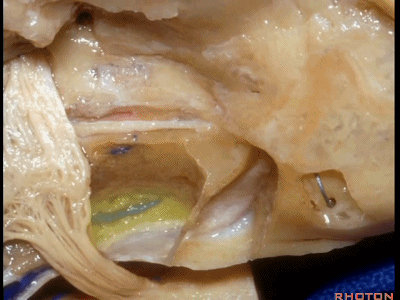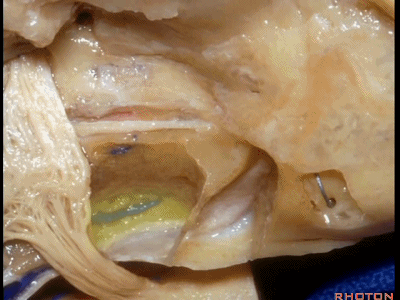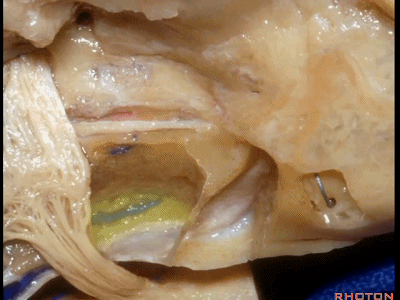
这里我们已经打开了内听道,顺序是从内听道开口至底部。
And here we've opened the meatus working from porus to fundus.
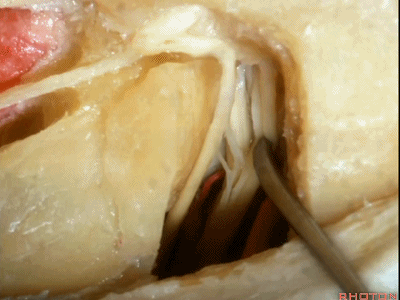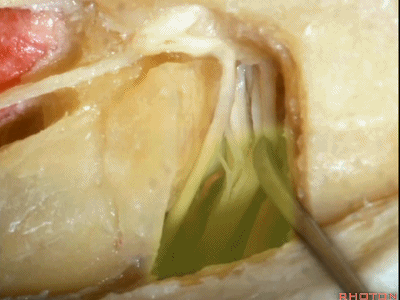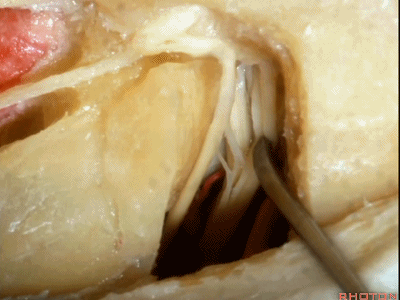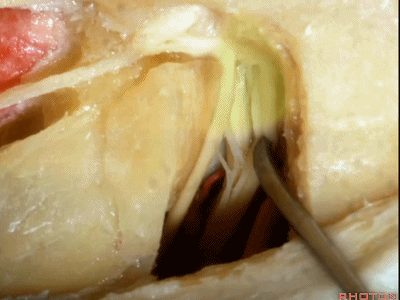
这是面神经(facial nerve)
And this is...what nerve?Facial,
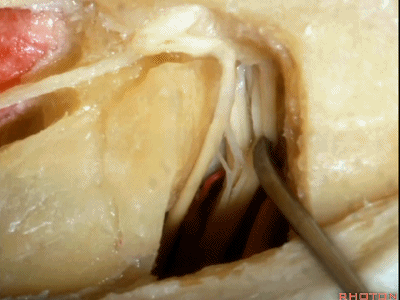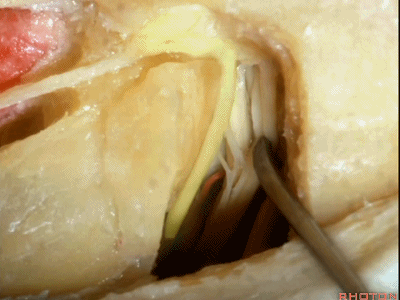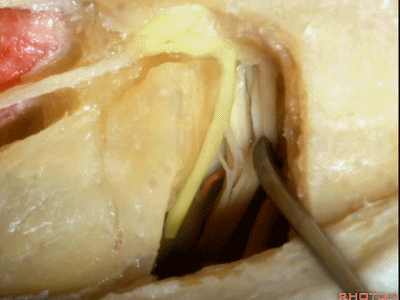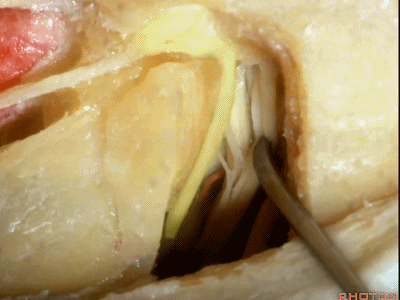
这是蜗神经(cochlear nerve)

这是中间神经(intermedius),可有多达四支神经束组成
intermedius that can be made up of as many as four bundles,
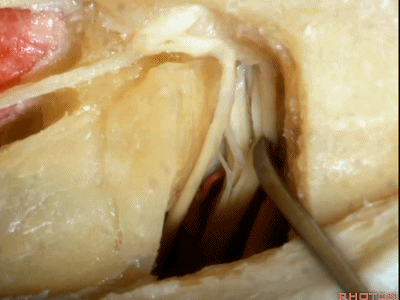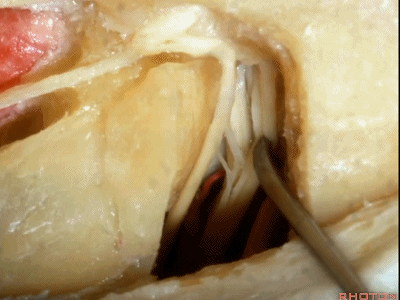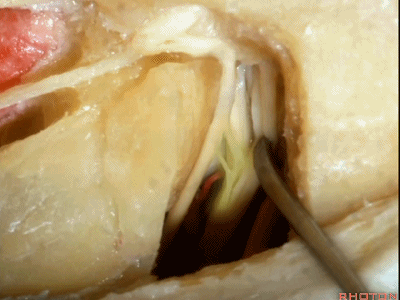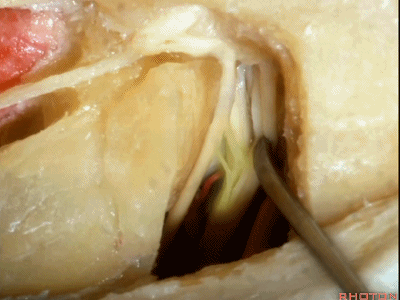
这是前庭上神经(superior vestibular nerve)
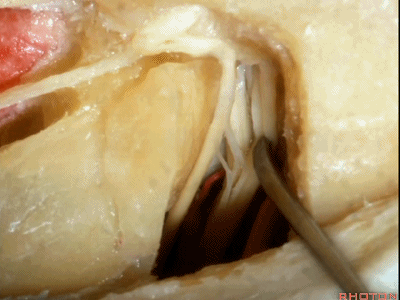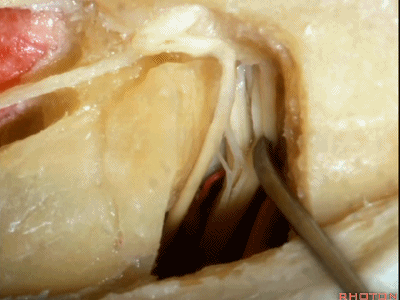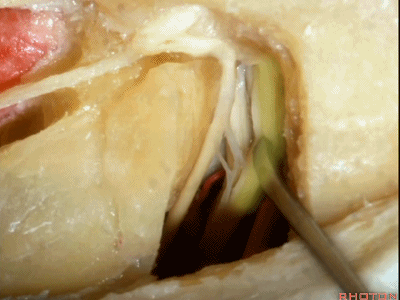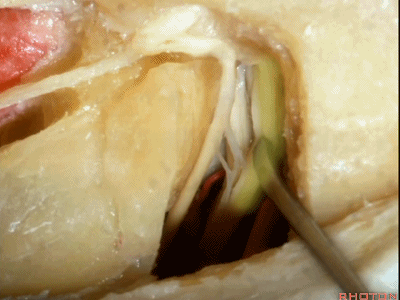
这是前庭下神经(inferior vestibular nerve)
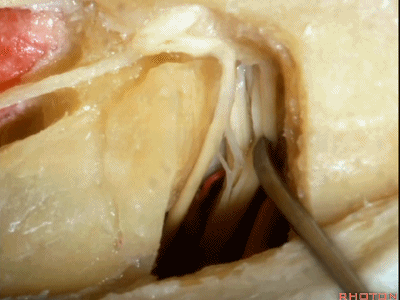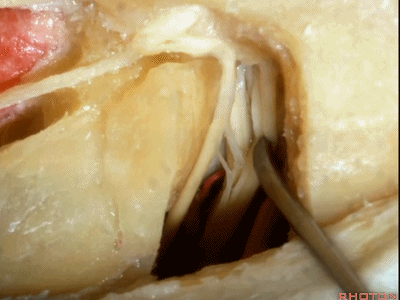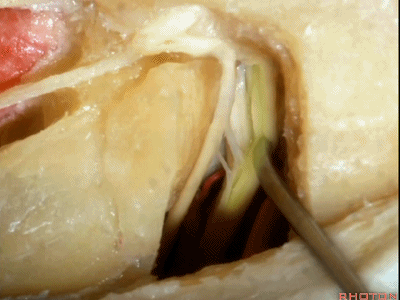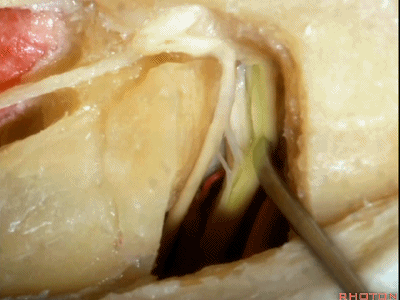
这里再看一下在内听道底,耳蜗与前庭贴得有多紧。下图示内听道底。
And this just shows you at the fundus how close the cochlea and the vestibule are.

下图示耳蜗(cochlea)
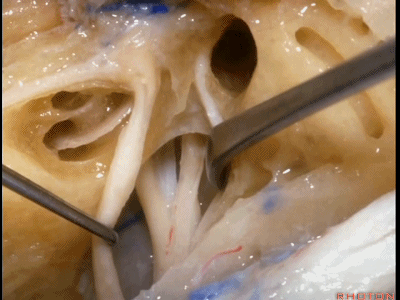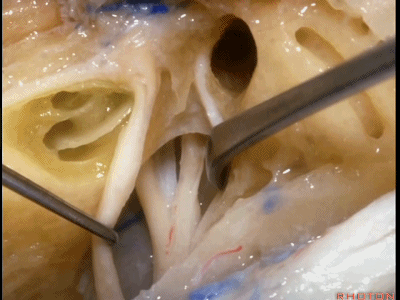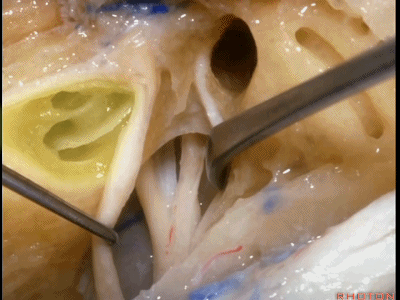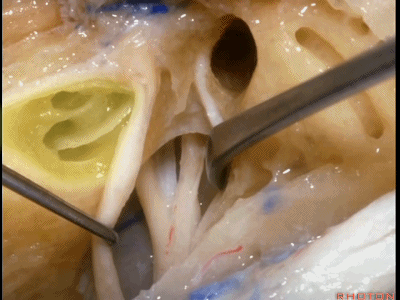
下图示 前庭(vestibule[ˈvestɪbju:l])
这是面神经、前庭上神经、蜗神经、前庭下神经
Facial nerve,superior vestibular,cochlear,inferior vestibular,

这是Bill棒(垂直嵴)
this is Bill's bar
这是 水平嵴(transverse crest)

再来看看岩前入路,在内听道口内侧、岩浅大神经后方磨除岩尖。磨除这片骨质后,可见颈内动脉就在岩浅大神经下方。
So the anterior petrosectomy approach,we drill medially to the porus,behind the greater petrosal nerve.The carotid, if you drill this bone, you find it just under the the greater petrous nerve.

我们从岩上窦、三叉神经下颌支下方,一直暴露到斜坡侧方、岩下窦。
You drill under the superior petrosal sinus,down under the third trigeminal division,to the side of the clivus,Along the inferior petrosal sinus.
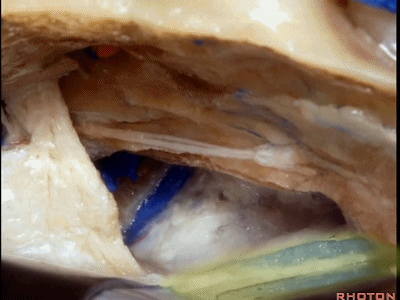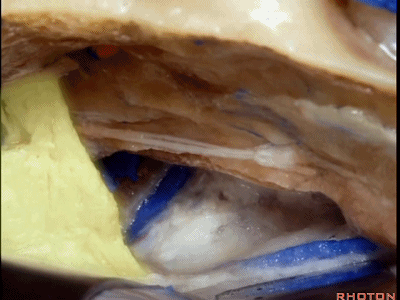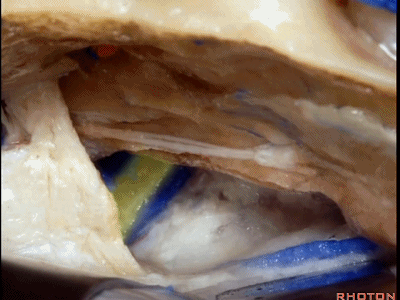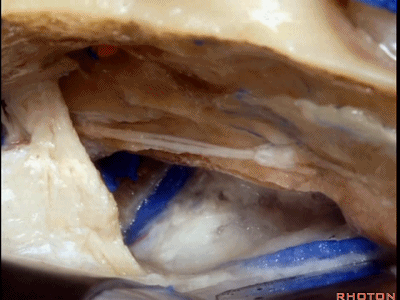
随后打开颞叶硬膜,切开岩上窦,从而切开并悬吊小脑幕。
And then you open the temporal dura,and divide the superior petrosal sinus,and then you divide the tent.

然后抬起颞叶,时刻注意保护Labbe静脉(下图)。
You open the temporal dura,and elevate the temporal lobe,always taking care to spanserve...Labbe

切开小脑幕时必须注意保护小脑幕游离缘处的滑车神经。
And then we divide the tent,taking care to spanserve...the 4th nerve at the medial edge.

该入路可暴露至脑干前外侧,并可显露三叉神经上方和下方的区域。
And it gives you this approach to the anterolateral brainstem. You have the exposure above and below the trigeminal nerve,

向下可显露基底动脉侧方。
and it delivers you down to the side of the basilar artery.

对于低位基底动脉分叉处的暴露,有些术者习惯利用床突三角和动眼神经三角作经海绵窦入路,有些术者则会通过这个岩前入路暴露脑桥和斜坡之间的区域来显露低位基底动脉分叉。
So some surgeons, if they are gonna go to a low basilar bifurcation,do transcavernous approach through the clinoidal and oculomotor triangle.And others do an anterior petrosectomy that opens up this area between the pons and the clivus to reach a low basilar bifurcation.
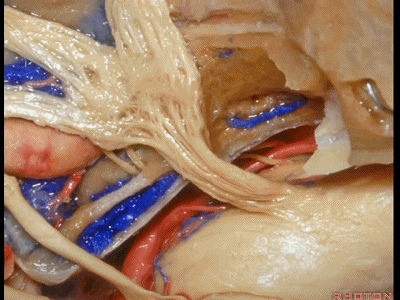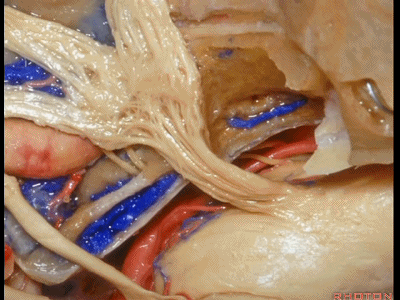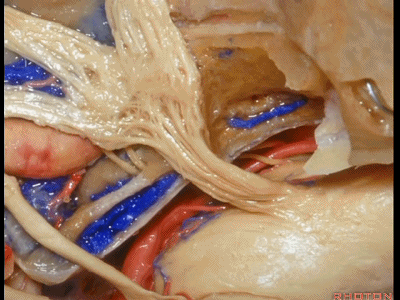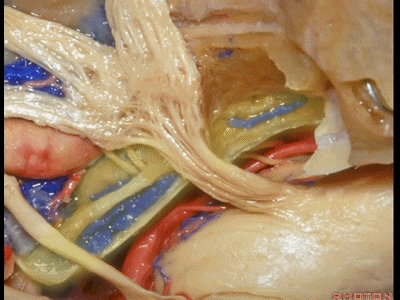
这是外展神经
And what nerve is this? 6th nerve
这是外展神经穿行于Gruber(蝶岩)韧带。
6th nerve passing below Gruber's ligament.
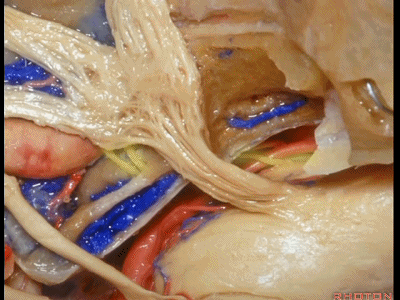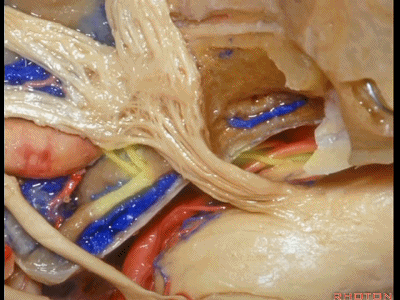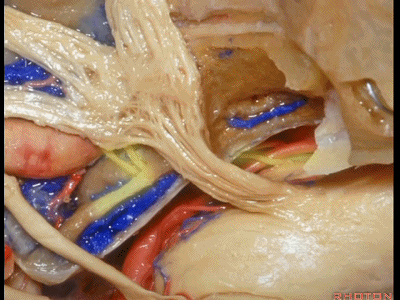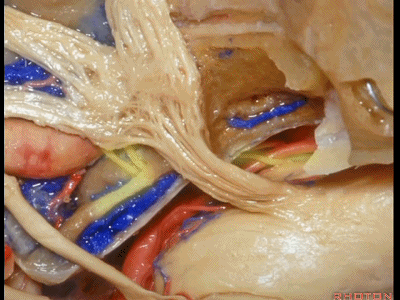
正如之前说的,经中颅窝的三个入路,一种是暴露内听道,其隐藏在上半规管前方(下图示上半规管,即弓状隆起位置)。
And, so that we can drill three approaches, one through the petrous apex,One goes to the internal acoustic meatus that's hidden here behind the superior canal.

第二种是磨除岩尖,在三叉神经下方,向下至岩下窦
The second comes through the petrous apex. under the trigeminal nerve,down to the side of the inferior petrosal sinus.
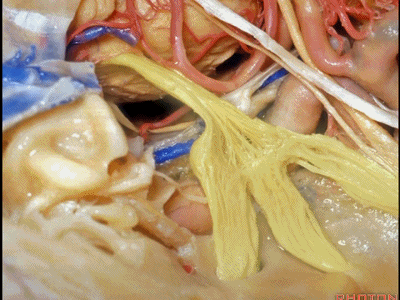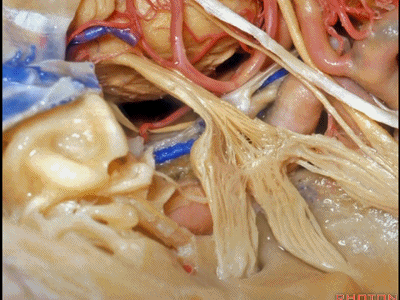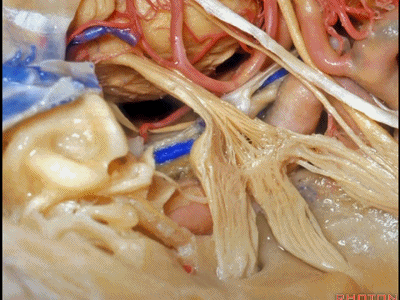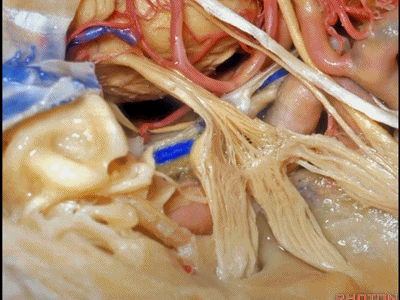
在外展神经进入Dorello管附近,需要注意的是,在磨岩尖内侧时,很容易对此处的外展神经造成热传导损伤。我见过不少外展神经一过性麻痹的患者,这是由于这样的热传导损伤造成的,尤其在行前岩骨切除术靠近内侧时。
Adjacent to where the 6th nerve passes through Dorello's canal. And,when you're drilling medially to the petrous apex,it's easy to have sspanad of heat to the 6th nerve.I've seen a number of transient 6th nerve palsies from sspanad of heat to that nerve at the medial part of the anterior petrosectomy.

第三种中颅窝入路,即为扩大中颅窝入路,通过磨除迷路(下图)以进入后颅窝。
The third approach you can take through the middle fossa is an extended middle fossa approach when you can expose and drill out the labyrinth to get into the posterior fossa.

下面我们进一步学习迷路(内耳)相关解剖。
这是面神经的脑池段,内听道段,迷路段。迷路段是从内听道底至膝状神经节的一段。
This is cisternal,meatal,and then from fundus to geniculate ganglion, what segment of facial nerve?Labyrinthine.

在其远端的是鼓室段。
And distal to that is...is tympanic segment.

当你磨骨时,若想从外侧经乳突至上前庭区、内听道底,你磨何处?是a点。下图示乳突区
Now where are you going to drill if you're coming through the mastoid from lateral to open the superior vestibular area, the fundus of the meatus?Where do you drill?At a.
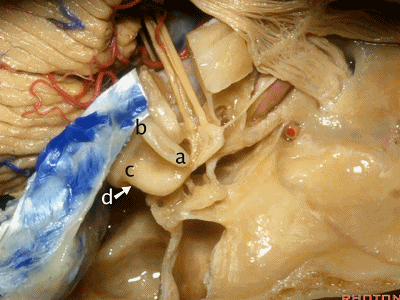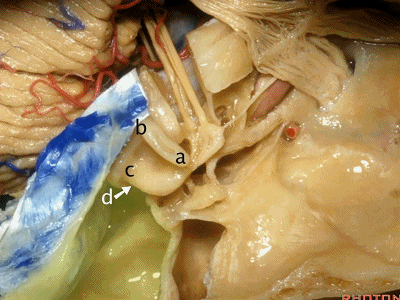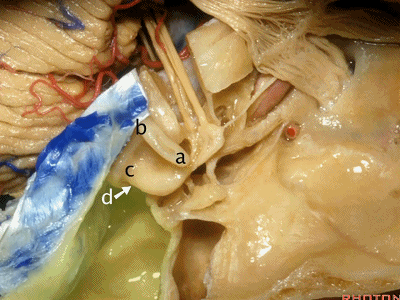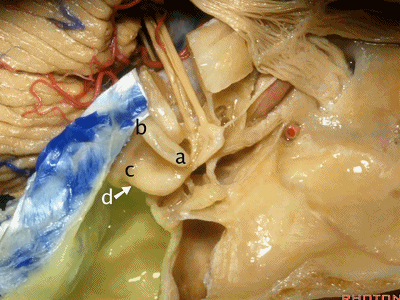
我们知道所有三个半规管均各有一条壶腹骨脚及一条细骨脚。
We said the all the canals of three had an ampullated and non-ampullated end,

其中上半规管和外侧半规管的壶腹骨脚位于前方。因此,当你磨除a点,你将暴露前庭上区。
And the ampullated end of the superior and lateral canal is anterior.So when you drill through this area,you'll expose superior vestibular area.

当你想暴露迷路和下前庭区时,你会磨位于下半规管下骨脚所在的d点,来暴露下前庭区。
When you're coming through the Labyrinth and inferior vestibular area,you're going to drill at the lower end of the posterior canal at d,to expose inferior vestibular area.

总骨脚位于b点,该处为上半规管的后脚与后半规管的上脚汇合处。
And the common crus is going to be located at b, here where the back end of the superior and the up end of the posterior canal join.

我们继续磨开中颅窝,即可见乳突(下图)
So, now we've drilled out the the middle fossa.We see the mastoid,

外耳道(the external canal)
鼓室(tympanic cavity)
内听道(internal acoustic meatus)

耳蜗位于b点
And is the cochlea going to sit at a or b?It's going to be at b.
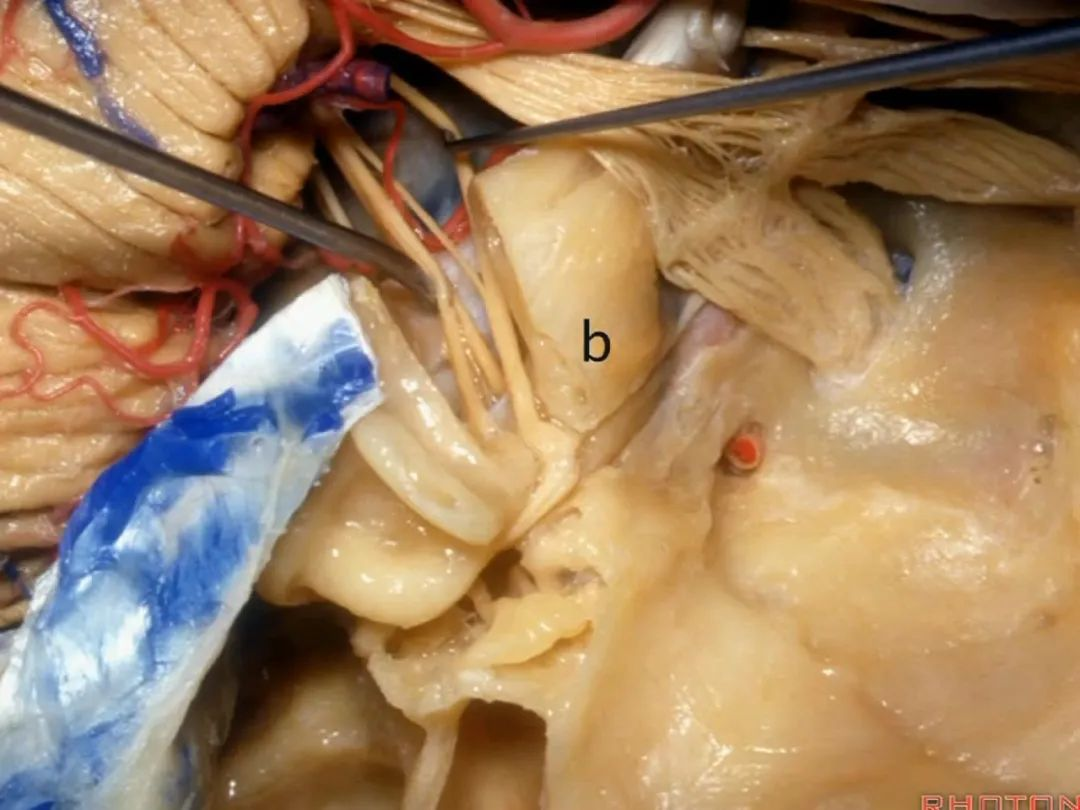
对于该处解剖的理解,有一个窍门,称之为“Y法则”:外耳道是“Y”的一条边,内听道是另一条边,咽鼓管(eustachian tube)是第三条边。[ju:sˈteiʃiən]
So, a way of thinking about this area is to think about it as what I call the "rule of Y": external canal is one limb,internal canal, the second limb,and eustachian tube is the third limb.
在这第三条边上,鼓膜张肌其位于咽鼓管顶壁,贴着颈内动脉,与后者之间仅一薄层骨质分隔, 三叉神经支配鼓膜张肌(tensor tympani['tɪmpənɪ]) 。
And along this anterior limb of the letter "Y"is this structure which is the...anyone?in the roof of the eustachian tube nestled up right against the carotid, separated from the carotid by a little thin shallow bone is the...tensor tympani, innervated by the...V. V innervates the tensor tympani.
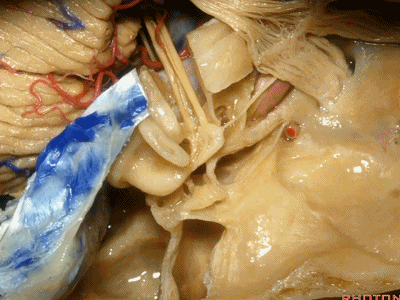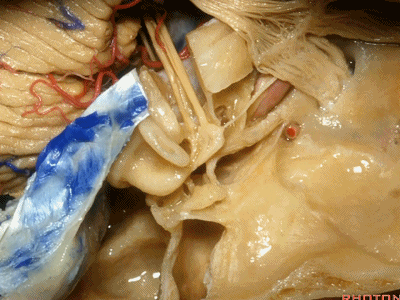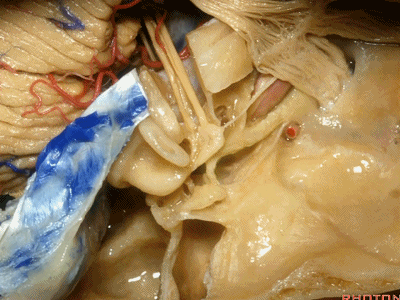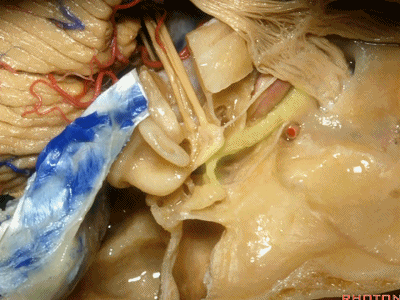
因此,鼓膜张肌、咽鼓管、岩浅大神经、以及颈内动脉,这些结构都位于“Y”的这一条边上。三条边汇合处的结构是鼓室。
So you have tensor tympani,eustachian tube,greater petrosal,and carotid,all oriented along that anterior limb of the letter "Y".Sitting at the junction of the three limbs is the tympanic cavity.

砧骨(incus)、锤骨(malleus)、镫骨(stapes),均位于鼓室内。
incus ['ɪŋkəs] ,malleus ['mælɪəs] ,stapes ['steɪpi:z] ,here in the tympanic cavity.
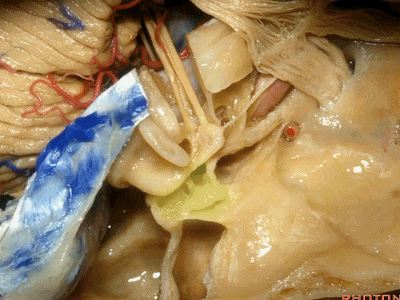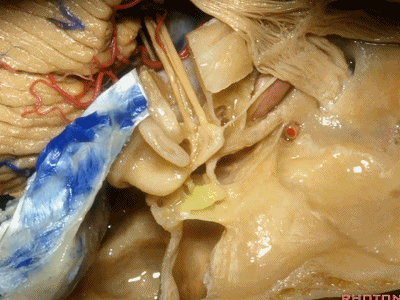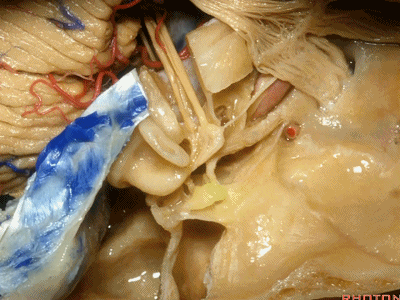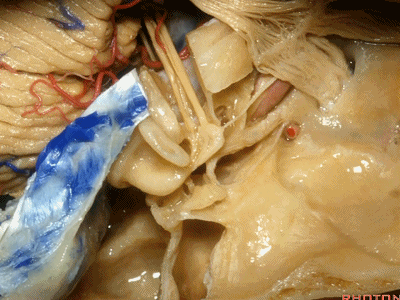
还有几个结构也夹在这三条边交界处,分别是耳蜗(下图)、前庭、以及半规管,其开口于前庭。
And then also wrapped around...the junction of the three limbs is the cochlea,and the vestibule into which the semicircular canals open at this junction.
下图示前庭、三个半规管

上半规管(superior canal)
外半规管(lateral canal)
后半规管(posterior canal)
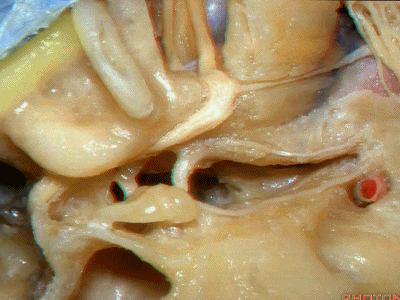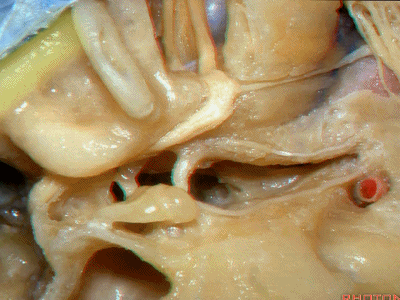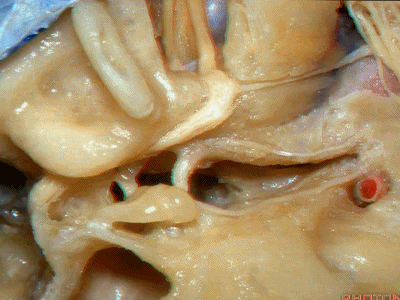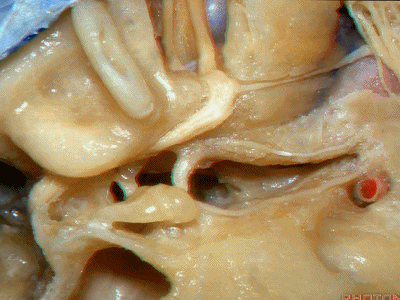
鼓室(tympanic cavity)
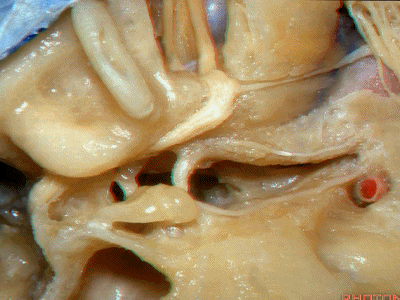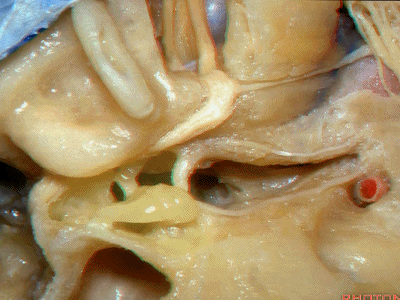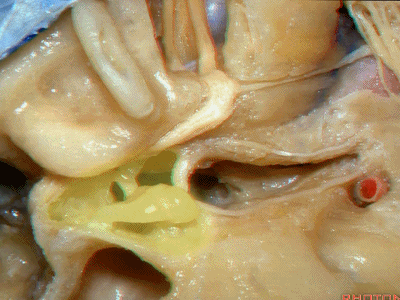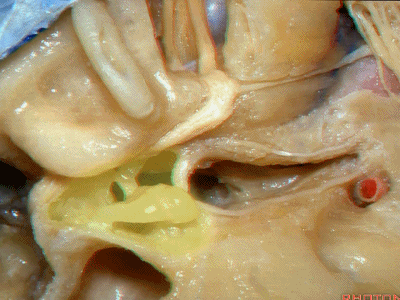
鼓膜张肌(tensor tympani)
耳蜗位于b点
Is cochlea going to be at a or b? It's gonna be at b

这是面神经
This is facial.

这是前庭上神经
This is superior vestibular

这是前庭下神经
inferior vestibular
再来看一下耳蜗。
And here we see the cochlea

耳蜗底周坐落于耳蜗三角内,
The basal turn sits in this cochlear angle,
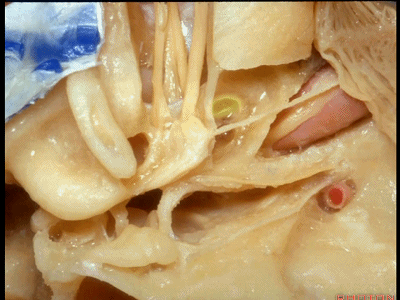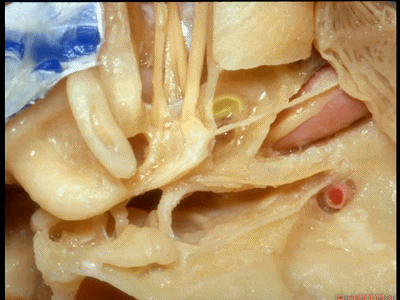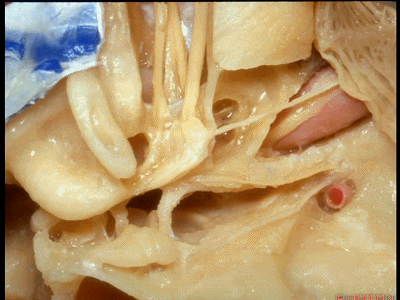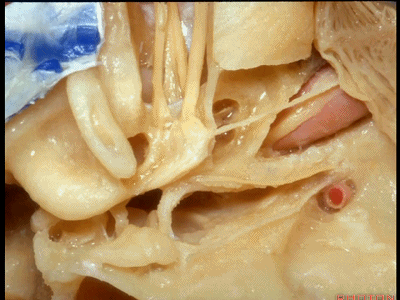
中周,顶周
the middle turn, the apical turn. apical ['æpɪkəl] 顶点的

顶周 位于岩浅大神经下方,从后方与鼓膜张肌相邻。
the apical turn comes forward under the greater petrosal nerve as nestled right against the back of the tensor tympani.

这是三个半规管及其开口所在的前庭。
The vestibule into which the three canals open.

在进行经中颅窝暴露内听道时,对于内听道底的磨除须非常谨慎。
And if you're going to the internal acoustic meatus through the middle fossa,the drilling is very tight at the fundus of the meatus.

一毫米的偏差,也许就会磨到面神经迷路段,也可能损伤耳蜗,或者前庭,导致听力丧失。而对于听力的保护,是这些入路的常规。
If you get a millimeter off target in drilling out over the labyrinthine segment,you get into the cochlea,or the vestibular,and hearing is lost.And usually in these approaches, they're designed to spanserve hearing.
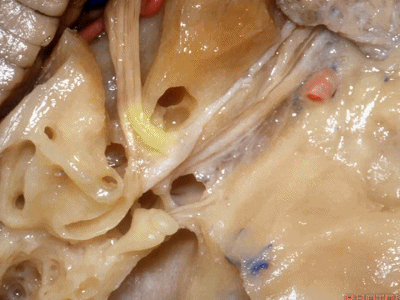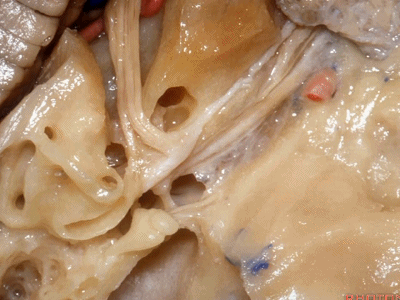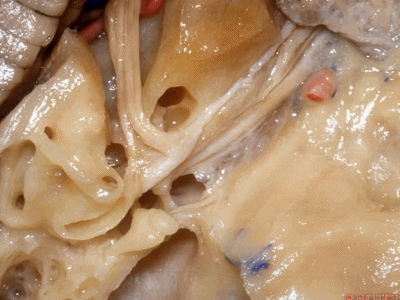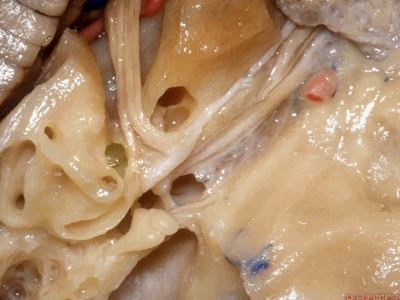
这里我们看到在面神经与前庭上神经之间的这个结构是垂直嵴,也称Bill棒,为了纪念Bill House在中颅窝入路研究中的贡献。
And here between the facial and superior vestibular is the Bill's bar, the vertical crest named for Bill House who introduced this middle fossa approach.
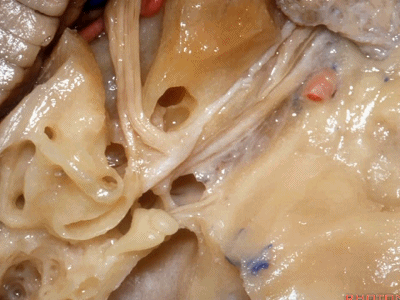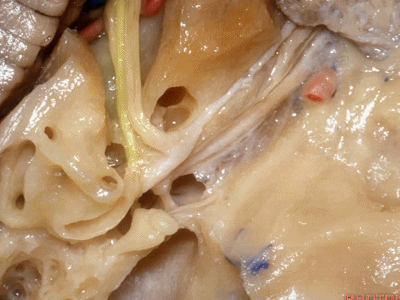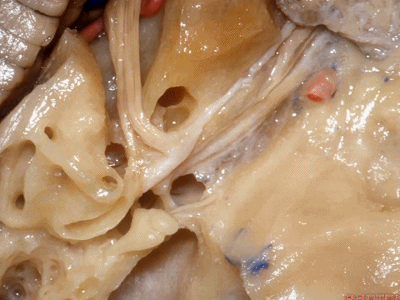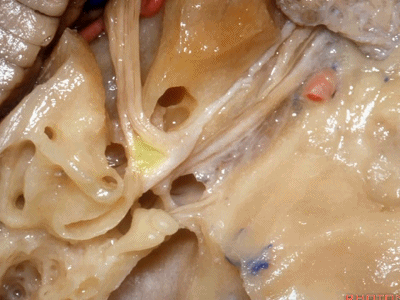
在内听道口,神经周围的管腔很大,而在内听道底则非常狭小。因此,在磨开内听道时,从内听道口磨向内听道底更为安全,毕竟神经周围的空间靠近岩骨嵴时更大。
Now if you look at the area of the porus of the meatus,there's lots of room over the nerves at the porus.It's very tight at the fundus.So that when we drill out the internal acoustic meatus,it's best to work from the porus to the fundus of the meatus that there's lots of room around the nerves back here below the petrous ridge.

但是,在内听道底,膝状神经节就在中颅窝薄层骨质的下方,有时甚至会暴露在中颅底。
But, here at the fundus, the geniculate ganglion is just below the floor of the middle fossa.Sometimes it's even exposed in the floor of middle fossa.
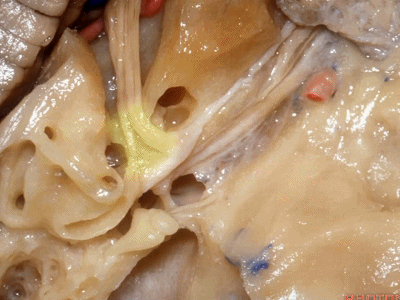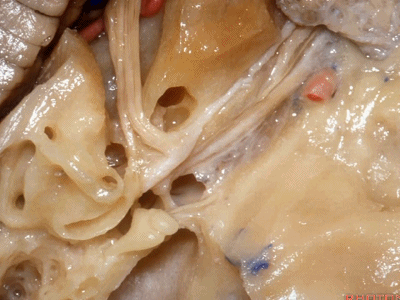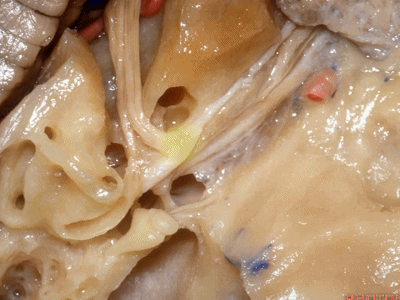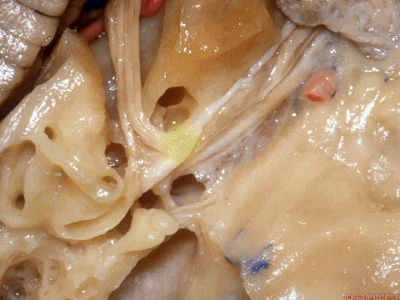
然而在内听道口,神经上方的岩骨嵴骨质相当厚。因此,起初磨除内听道口时,需磨除很厚的骨质才能显露内听道口下方的硬膜。随着逐步向内听道底暴露,骨质会越来越薄,面神经迷路段就在这层中颅窝骨质的深面。
But to get to the nerves in the porus,there's quite of thickness of bone below the petrous ridge. So that,when you begin drilling at the petrous ridge above the porus,you have to go through a lot of bone to get down to the dura around the nerves at the porus.But then as you work toward the fundus to expose the meatus,you're coming progressively more superficial and the labyrinthine segment is just below the floor of the middle fossa.