CTA检测到的阳性结果可信,阴性结果可信性差。因此CTA可以用来评估动脉瘤夹闭后是否残留,但CTA未见残留的却不一定可信。
————摘自文章章节
【Ref:Uricchio M,et al.Stroke. 2019;50:00-00. DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.023614.】
研究背景
颅内动脉瘤是一种潜在的危及生命的脑血管疾病。外科夹闭术是一种阻断动脉瘤腔内血流的手术方式。若夹闭术后动脉瘤未完全闭塞,仍有潜在的生长和破裂可能会危及患者生命。DSA是评价动脉瘤夹闭效果的金标准,CTA是一种较新侵袭性低的成像技术,也被用来评估动脉瘤闭塞效果;然而,与DSA相比,它的确切性仍存在争议。美国麻省波士顿MCPHS大学Matthew Uricchio教授等人对CTA与DSA评估外科夹闭动脉瘤术后效果的确切性进行了meta分析。结果发表在2019年2月的《Stroke》上。
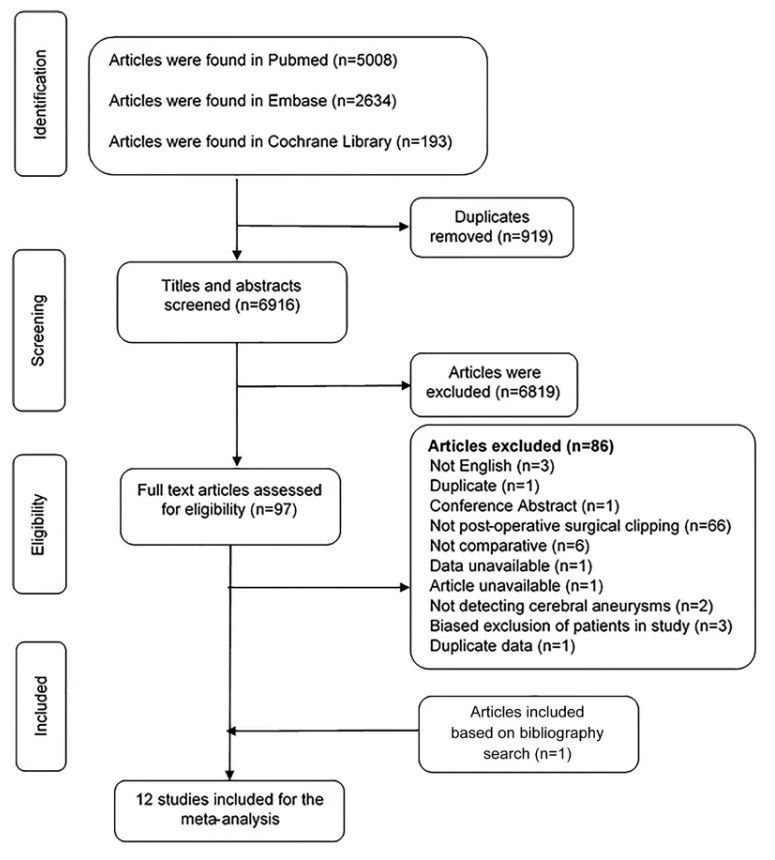
Figure 1. Flowchart, study selection process of the identified articles.
研究方法
检索Pubmed、EMBASE和Cochrane数据库,收集2017年11月6日之前文献相关病例,对数据进行Mata分析。评估夹闭动脉瘤的效果,CTA是否同DSA一样可信?应用双变量随机效应模型,计算得到敏感性、特异性、阳性似然比(LR+)和阴性似然比(LR-)数值。
Table 1. Characteristics of Studies Included in the Analysis of CTA Versus DSA for the Detection of Postoperative Aneurysmal Obliteration
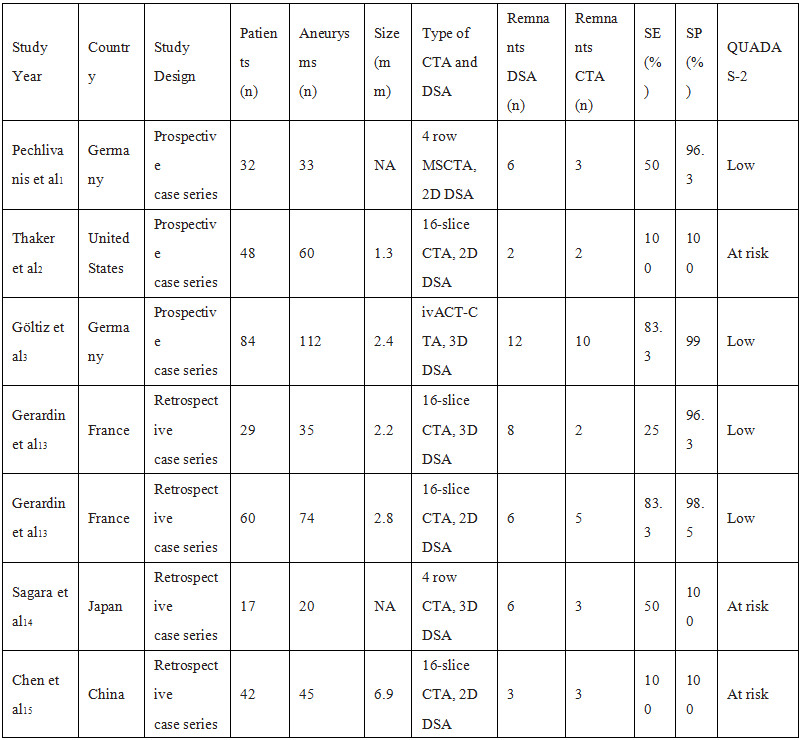
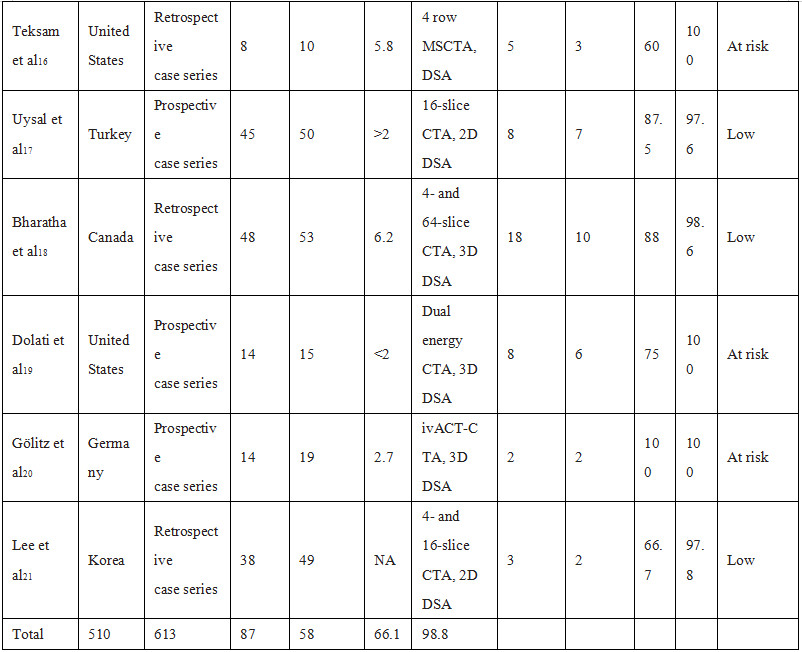
CTA indicates computed tomography angiography; DSA, digital subtraction angiography; ivACT, angiographic CT with intravenous contrast material injection; MSCTA,multisection CT angiography; QUADAS-2 Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies; SE, sensitivity; and SP, specificity.Downloaded from ht
研究结果
在6916项研究中,有13项符合纳入标准。共510例患者,613例动脉瘤包括在内。DSA检测到87例动脉瘤残余,而CTA检测到58例,CTA检测敏感度为69% (95% CI,54%-81%),特异性为99%(95% CI,97%-99%)。与之相应的LR+55.5(95% CI,23.6 - -130.9)和LR−0.31(95% CI,0.20 - -0.48)。在前瞻性单因素回归设计中显示,CAT检测的敏感性较差(P<0.05),而特异性较高,甚至在术后残留动脉瘤直径<2mm中仍较好(P<0.001)。
Table 2. Revised Tool for Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies 2 for Risk of Bias in Each Study
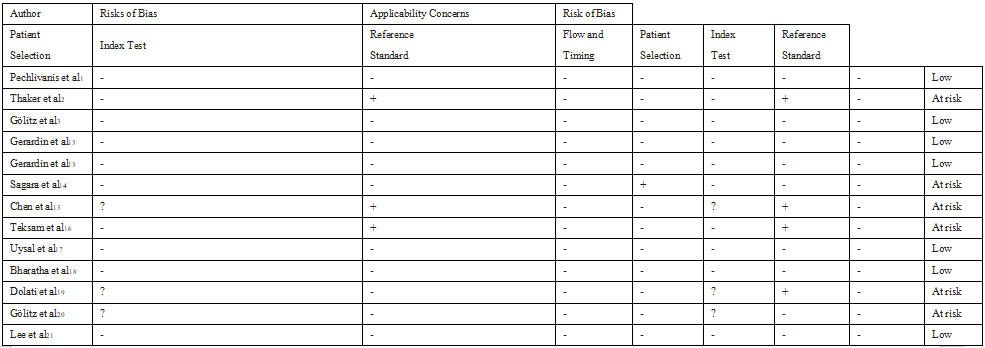
- indicates low risk; +, high risk; and ?, unclear
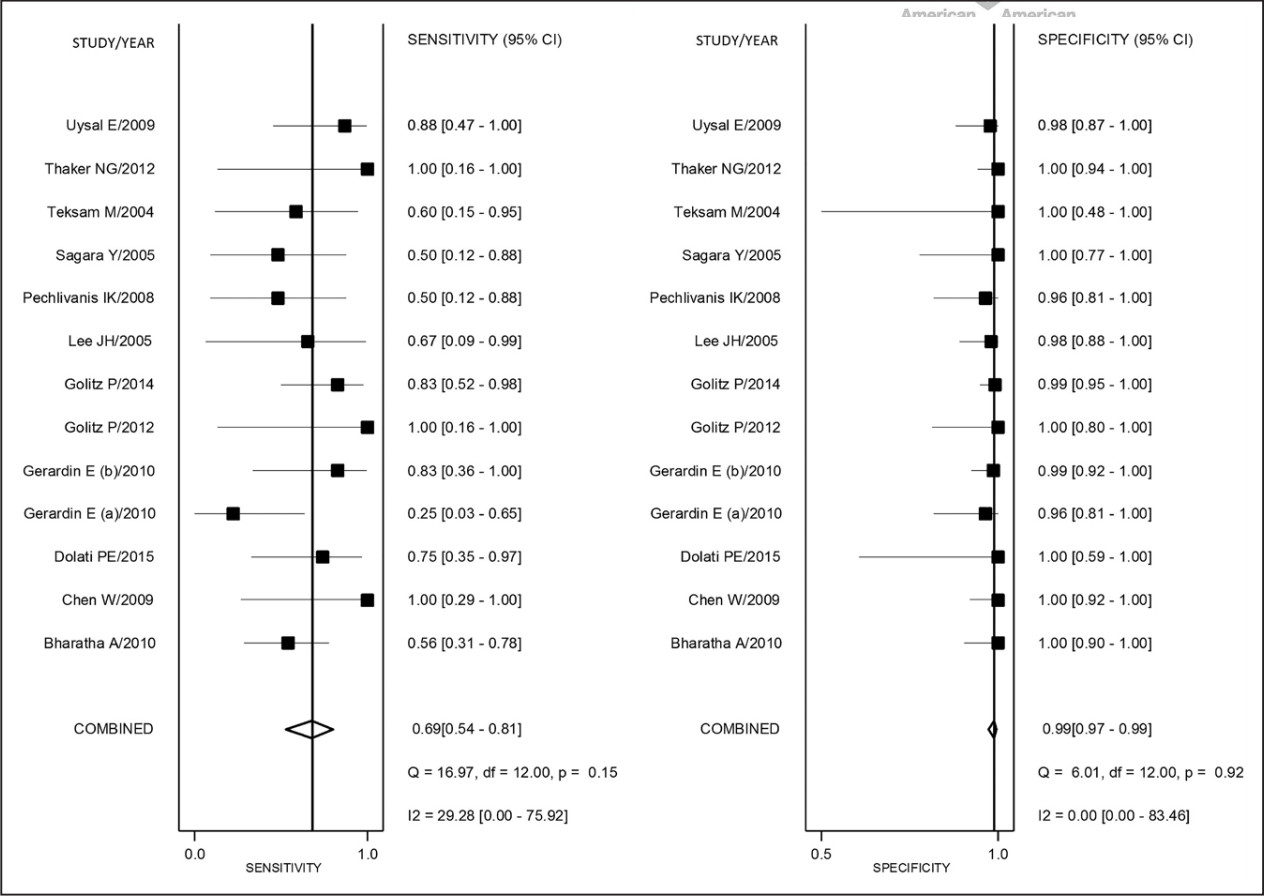
Figure 2. Coupled forest plots of pooled sensitivity and specificity with corresponding heterogeneity statistics. Numbers are pooled estimates with 95% CI in parentheses. Horizontal lines indicate 95% CI.
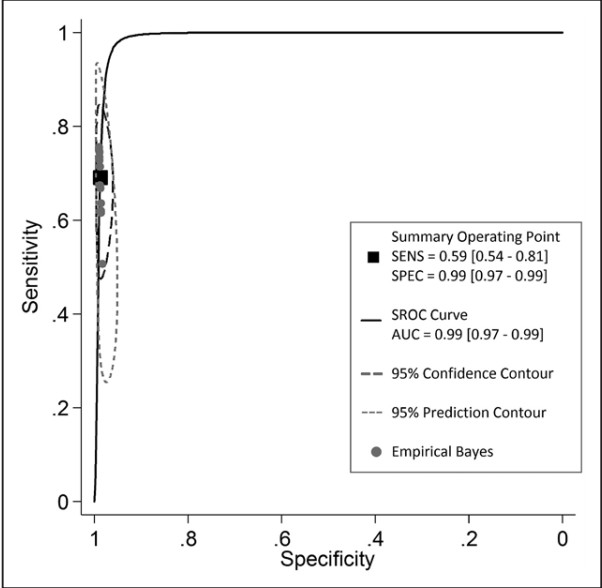
Figure 3. The receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) plot of computed tomography angiography (CTA) diagnostic test studies with confidence and prediction regions around mean operating sensitivity (SE) and specificity (SP) point (black square) is shown along with results from each study (gray circles).
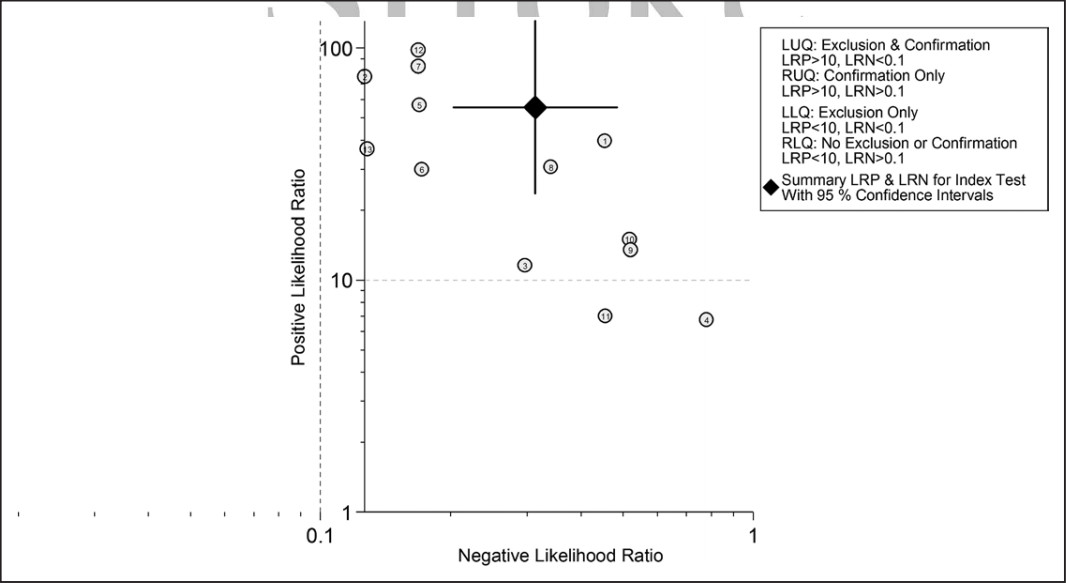
Figure 4. The likelihood ratio scattergram showing summary point of likelihood ratios obtained as functions of mean sensitivity and specificity. The likelihood ratio scatter graph or matrix defines quadrants of informativeness based on established evidence-based thresholds and is interpreted as such: Left lower quadrant, likelihood ratio positive<10, likelihood ratio negative<0.1, exclusion only, suggesting that the test is not useful for confirmation of presence of disease (when positive) but is for its exclusion (when negative). Right lower quadrant, likelihood ratio positive<10, likelihood ratio negative>0.1, no exclusion or confirmation, suggesting that the test is neither useful for confirmation of presence of disease (when positive) nor for its exclusion (when negative). Left upper quadrant, likelihood ratio positive>10, likelihood ratio negative<0.1, confirmation and exclusion, suggesting that the test is useful for confirmation of presence of disease (when positive) and for its exclusion (when negative). Right upper quadrant, likelihood ratio positive>10, likelihood ratio negative>0.1, confirmation only, suggesting that the test is useful for confirmation of presence of disease (when positive) and not for its exclusion (when negative).
结论
Mate分析显示,CTA检测到的阳性结果可信,阴性结果可信性差。因此CTA可以用来评估动脉瘤夹闭后是否残留,但CTA未见残留的却不一定可信。